Synthesis and CO2 Capture of Porous Hydrogel Particles Consisting of Hyperbranched Poly(amidoamine)s
Abstract
:1. Introduction
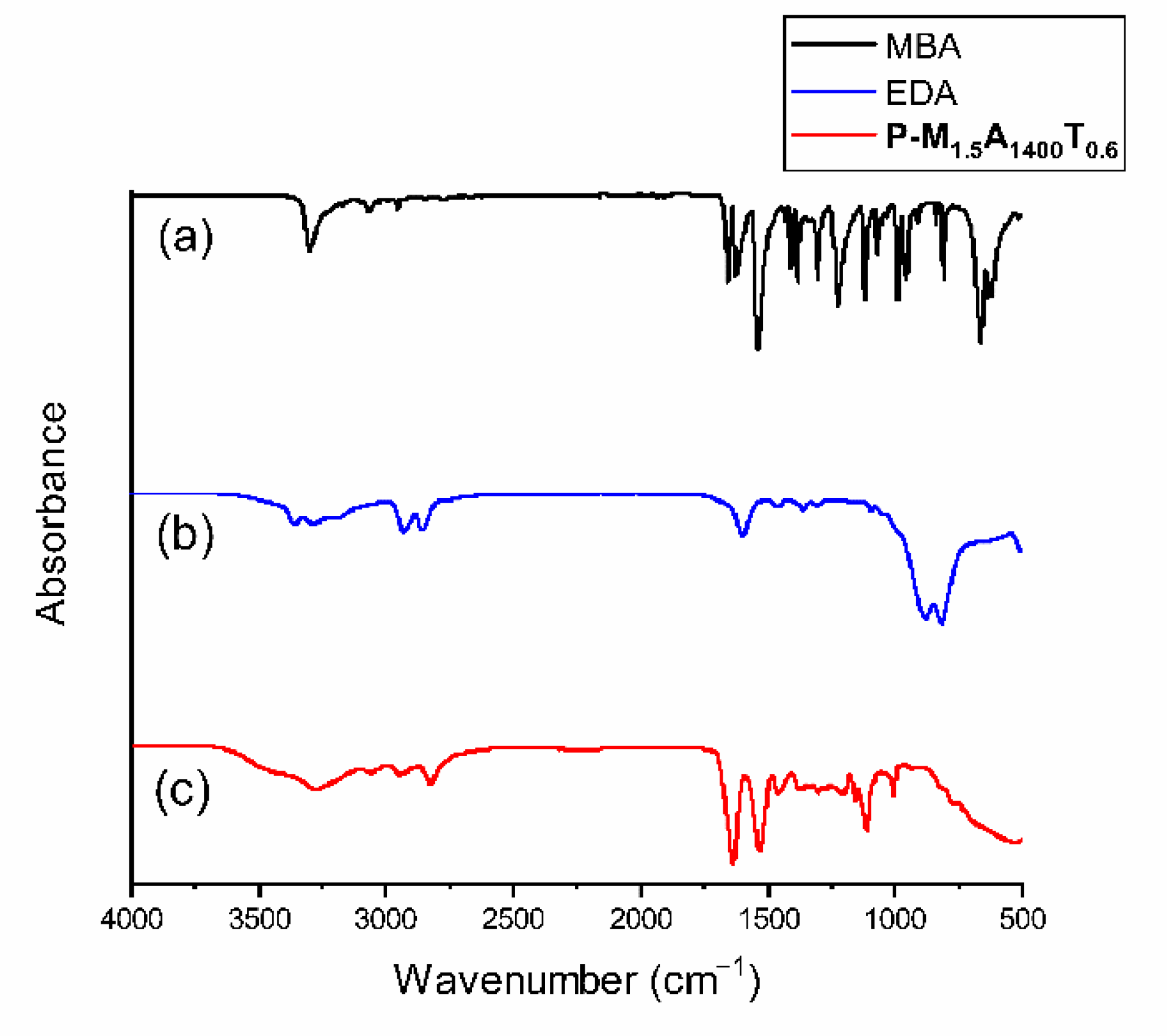
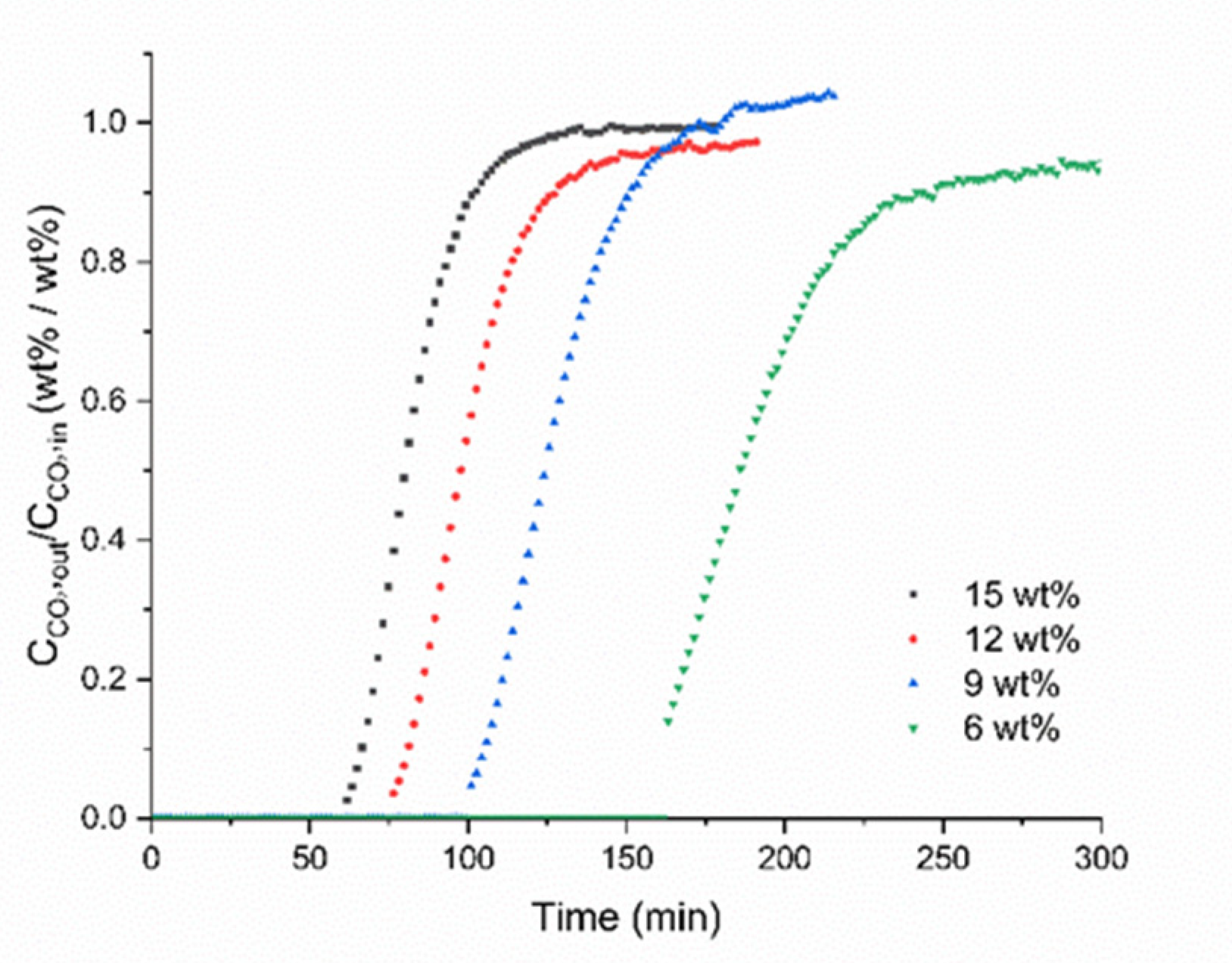
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Information
4.2. Various Agitation Speeds of Aqueous Phase
4.3. Scale up Process
4.4. CO2 Absorption Test
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carapellucci, R.; Milazzo, A. Membrane systems for CO2 capture and their integration with gas turbine plants. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A J. Power Energy 2003, 217, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Xu, Z.; Fan, M.; Gupta, R.; Slimane, R.B.; Bland, A.E.; Wright, I. Progress in carbon dioxide separation and capture: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemke, J.R.; Cooper, O.R. Tropospheric Ozone, in “State of the Climate in 2017”. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, S56–S59. [Google Scholar]
- Carbon Dioxide Now More than 50% Higher than Pre-Industrial Levels. Available online: https://www.noaa.gov/news-release/carbon-dioxide-now-more-than-50-higher-than-pre-industrial-levels (accessed on 25 June 2022).
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Energy Technology Systems Analysis Program (IEA-ETSAP) Technology Roadmap; International Energy Agency (IEA): Paris, France, 2013; Volume 59.
- Li, J.-R.; Ma, Y.; McCarthy, M.C.; Sculley, J.; Yu, J.; Jeong, H.-K.; Balbuena, P.B.; Zhou, H.-C. Carbon dioxide capture-related gas adsorption and separation in metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1791–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenarsari, S.D.; Yang, D.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Russell, A.G.; Wei, Q.; Fan, M. Review of recent advances in carbon dioxide separation and capture. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 22739–22773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochelle, G.T. Amine Scrubbing for CO2 Capture. Science 2009, 325, 1652–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchi, R.S.; Harlick, P.J.E.; Sayari, A. Applications of Pore-Expanded Mesoporous Silica. 2. Development of a High-Capacity, Water-Tolerant Adsorbent for CO2. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 8007–8013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, D.M.; Smit, B.; Long, J.R. Carbon Dioxide Capture: Prospects for New Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6058–6082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourhakkak, P.; Taghizadeh, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Ghaedi, M. Adsorption: Fundamental Processes and Applications, 1st ed.; Ghaedi, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 33, pp. 71–210. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, C.; Gonzalez, J.; Pérez-Mendoza, M.; Wright, P.A.; Seaton, N.A. Design of Hybrid Organic/Inorganic Adsorbents Based on Periodic Mesoporous Silica. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 5586–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Plaza, M.; Rubiera, F.; Pevida, C. Sustainable biomass-based carbon adsorbents for post-combustion CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 230, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouini, I.; Ledoux, A.; Estel, L.; Mary, S. Étude du captage du CO2 dans des gaz de combustion d’un incinérateur de déchets à l’aide d’un pilote utilisant un solvant à base de MEA. Oil Gas Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtch, N.C.; Jasuja, H.; Walton, K.S. Water Stability and Adsorption in Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10575–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCoste, J.B.; Peterson, G.W.; Schindler, B.J.; Killops, K.L.; Browe, M.A.; Mahle, J.J. The effect of water adsorption on the structure of the carboxylate containing metal-organic frameworks Cu-BTC, Mg-MOF-74, and UiO-66. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11922–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yao, M.; Hu, X.; Hu, G.; Lu, J.; Luo, M.; Fan, M. Amine-modified ordered mesoporous silica: The effect of pore size on CO2 capture performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 324, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, R.; Ghoshal, A.K. Amine-Modified Mesoporous Silica for CO2 Adsorption: The Role of Structural Parameters. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 6078–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Wei, L.; Mingyue, W.; Guansheng, Q. Application of amine-modified porous materials for CO2 adsorption in mine confined spaces. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 629, 127483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarrasa-Garcia, E.; Moya, E.O.; Cecilia, J.; Cavalcante, C.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Azevedo, D.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E. CO2 adsorption on amine modified mesoporous silicas: Effect of the progressive disorder of the honeycomb arrangement. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 209, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyanwu, J.-T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R.T. Amine-Grafted Silica Gels for CO2 Capture Including Direct Air Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 7072–7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garip, M.; Gizli, N. Ionic liquid containing amine-based silica aerogels for CO2 capture by fixed bed adsorption. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 310, 113227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayaz, M.; Sayari, A. Long-Term Effect of Steam Exposure on CO2 Capture Performance of Amine-Grafted Silica. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 43747–43754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, M.; Mazaj, M.; Garcia, S.; Xuan, J.; Maroto-Valer, M.; Logar, N.Z. Novel Amine-impregnated Mesostructured Silica Materials for CO2 Capture. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 2252–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Zhuang, L.; Ma, B.; Chen, S.; He, H.; Yin, F. Silanol-rich platelet silica modified with branched amine for efficient CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2018, 181, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demessence, A.; D’Alessandro, D.M.; Foo, M.L.; Long, J.R. Strong CO2 Binding in a Water-Stable, Triazolate-Bridged Metal-Organic Framework Functionalized with Ethylenediamine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8784–8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Chen, K.; Xing, H.; Yang, Q.; Krishna, R.; Bao, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhou, W.; Dong, X.; Han, Y.; et al. Pore chemistry and size control in hybrid porous materials for acetylene capture from ethylene. Science 2016, 353, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, F.; Sanz, R.; Orcajo, G.; Briones, D.; Yángüez, V. Amino-impregnated MOF materials for CO2 capture at post-combustion conditions. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 142, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wei, G.; Liu, Z.; Oliver, S.R.J.; Fei, H. A Robust Sulfonate-Based Metal-Organic Framework with Permanent Porosity for Efficient CO2 Capture and Conversion. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 6276–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalei, B.; Sakurai, K.; Kinoshita, Y.; Wakimoto, K.; Isfahani, A.P.; Song, Q.; Doitomi, K.; Furukawa, S.; Hirao, H.; Kusuda, H.; et al. Enhanced selectivity in mixed matrix membranes for CO2 capture through efficient dispersion of amine-functionalized MOF nanoparticles. Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavi, H.; Eskandari, A.; Shojaei, A.; Mousavi, S.A. Enhancing CO2/N2 adsorption selectivity via post-synthetic modification of NH2-UiO-66(Zr). Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 257, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.; Choi, W.; Kim, C.; Choi, M. Rational Design of the Polymeric Amines in Solid Adsorbents for Postcombustion Carbon Dioxide Capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 23825–23833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.; Choi, W.; Kim, C.; Choi, M. Oxidation-stable amine-containing adsorbents for carbon dioxide capture. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.; Won, Y.-J.; Kim, C.; Choi, M.; Jung, W.; Lee, K.S.; Na, J.-G.; Cho, S.-H.; Lee, S.Y.; et al. Epoxide-Functionalized, Poly(ethylenimine)-Confined Silica/Polymer Module Affording Sustainable CO2 Capture in Rapid Thermal Swing Adsorption. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 13923–13931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Choi, K.; Yu, H.J.; Won, Y.-J.; Kim, C.; Choi, M.; Cho, S.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.S. Thermal Stability Enhanced Tetraethylenepentamine/Silica Adsorbents for High Performance CO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 4632–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Park, J.; Kim, C.; Choi, M. Structural effects of amine polymers on stability and energy efficiency of adsorbents in post-combustion CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 408, 127289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujan, A.R.; Pang, S.H.; Zhu, G.; Jones, C.W.; Lively, R.P. Direct CO2 Capture from Air using Poly(ethylenimine)-Loaded Polymer/Silica Fiber Sorbents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 5264–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, P.; Hao, L.; Xu, Y. Amine-modified SBA-15(P): A promising adsorbent for CO2 capture. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 24, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduzco-Navarro, I.P.; Mendizábal, E.; Mayorga, J.A.R.; Rentería-Urquiza, M.; Gonzalez-Alvarez, A.; Rios-Donato, N. Arsenate Removal from Aqueous Media Using Chitosan-Magnetite Hydrogel by Batch and Fixed-Bed Columns. Gels 2022, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Su, K.; Yang, H.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Ang, S.; Zhang, K.; Wu, P. Novel Natural Glycyrrhetinic Acid-Derived Super Metal Gel and Its Highly Selective Dyes Removal. Gels 2022, 8, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kim, T.; Kim, S.Y. Poly (Amidehydrazide) Hydrogel Particles for Removal of Cu2+ and Cd2+ Ions from Water. Gels 2021, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Eom, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.Y. Copper Ions Removal from Water using A2B3 Type Hyperbranched Poly(amidoamine) Hydrogel Particles. Molecules 2019, 24, 3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Heath, C.; Pejcic, B.; Wood, C.D. CO2 capture by amine infused hydrogels (AIHs). J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 4829–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pejcic, B.; Heath, C.; Wood, C.D. Carbon capture with polyethylenimine hydrogel beads (PEI HBs). J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 21468–21474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.W.; Lee, W.; Ahn, Y.-H. Superabsorbent polymer for improved CO2 hydrate formation under a quiescent system. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 61, 102005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.-T.; Song, F.-P.; Zhang, G.-D.; Li, J.-Z.; Wang, F. Polymeric superabsorbent hydrogel-based kinetic promotion for gas hydrate formation. Fuel 2021, 288, 119676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, I.; Kinugasa, K.; Toyoda, M.; Minezaki, K. Effect of amine structure on CO2 capture by polymeric membranes. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2017, 18, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Eom, Y.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.Y. Micro-hydrogel Particles Consisting of Hyperbranched Polyamidoamine for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions from Water. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, A. Fabrication of magnetic porous microspheres via (O1/W)/O2 double emulsion for fast removal of Cu2+ and Pb2+. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 67, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sanguramath, R.A.; Israel, S.; Silverstein, M.S. Emulsion Templating: Porous Polymers and Beyond. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 5445–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, J.-L.; Jacoby, J.; Kim, S.; Stébé, M.-J.; Canilho, N.; Pasc, A. A meso-macro compartmentalized bioreactor obtained through silicalization of “green” double emulsions: W/O/W and W/SLNs/W. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 11871–11874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, W.-C.; Choi, M.; Lim, C.H.; Yang, S.-M. Microfluidic synthesis of atto-liter scale double emulsions toward ultrafine hollow silica spheres with hierarchical pore networks. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 5262–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao, W.; Jaramillo, L.Y.; López, D.; Romero-Sáez, M.; Buitrago-Sierra, W.A.H. Insights into the CO2 capture over amine-functionalized mesoporous silica adsorbents derived from rice husk ash. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, A.M.; Karanikolos, G.N. CO2 capture adsorbents functionalized by amine-bearing polymers: A review. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2020, 96, 103005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfong, W.C.; Kail, B.W.; Jones, C.W.; Pacheco, C.; Gray, M.L. Spectroscopic Investigation of the Mechanisms Responsible for the Superior Stability of Hybrid Class 1/Class 2 CO2 Sorbents: A New Class 4 Category. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12780–12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishor, R.; Ghoshal, A.K. N1-(3-Trimethoxysilylpropyl)diethylenetriamine grafted KIT-6 for CO2/N2 selective separation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 898–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, H.; Lee, S.; Jeong, S.; Hong, Y.K.; Kim, S.Y. Synthesis and CO2 Capture of Porous Hydrogel Particles Consisting of Hyperbranched Poly(amidoamine)s. Gels 2022, 8, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080500
Choi H, Lee S, Jeong S, Hong YK, Kim SY. Synthesis and CO2 Capture of Porous Hydrogel Particles Consisting of Hyperbranched Poly(amidoamine)s. Gels. 2022; 8(8):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080500
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Hojung, Sanghwa Lee, SeongUk Jeong, Yeon Ki Hong, and Sang Youl Kim. 2022. "Synthesis and CO2 Capture of Porous Hydrogel Particles Consisting of Hyperbranched Poly(amidoamine)s" Gels 8, no. 8: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080500
APA StyleChoi, H., Lee, S., Jeong, S., Hong, Y. K., & Kim, S. Y. (2022). Synthesis and CO2 Capture of Porous Hydrogel Particles Consisting of Hyperbranched Poly(amidoamine)s. Gels, 8(8), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8080500




