Abstract
The genus Trichoderma is widely recognized for its ability to secrete lignocellulosic enzymes, establishing it as a crucial technological resource for the bioconversion of agro-industrial waste biomass via fermentation. This review explores the potential of utilizing lignocellulosic waste from diverse industries as a sustainable nutrient source for producing Trichoderma spp. and various desirable metabolites via fermentation. Significant emphasis is placed on the enzymatic activities of Trichoderma species in two critical stages of second-generation biofuel production. Firstly, in the pre-treatment stage to break down complex polysaccharides of lignocellulosic biomass, thereby enhancing production efficiency and yield, and, secondly, during the hydrolysis process to produce fermentable sugars essential for biofuel production. Additionally, this review discusses other applications of Trichoderma fermentation, such as enhancing animal feedstock nutrition and employing its spores as biocontrol agents. Ongoing research efforts are directed at optimizing fermentation protocols, identifying suitable waste substrates, and genetic manipulation of strains to enhance the economic viability of Trichoderma’s biotechnological applications. This manuscript contributes to the field of circular biotechnology by offering a detailed review of recent progress on the integration of agro-industrial waste materials in Trichoderma-based bioconversion technologies, highlighting both current achievements and future research directions necessary to enhance the economic and environmental sustainability of waste biomass utilization.
1. Introduction
The genus Trichoderma encompasses a diverse group of rhizocompetent filamentous fungal strains found in various temperate and tropical ecosystems [1]. Trichoderma spp. are highly successful colonizers of diverse habitats, as demonstrated by their efficient utilization of many types of substrates, their high reproductive capacity, their rapid adaptation to environmental changes, and their production of a wide array of secondary metabolites (e.g., phytohormones, growth promoters, organic acids, and antibiotics) and extracellular enzymes (e.g., cellulases, amylase, chitinase, and β-glucanases) [1,2,3]. These characteristics, combined with the fact that Trichoderma spp. can be easily established and maintained under in vitro culture conditions and genetically manipulated [4,5], allow this genus and its secreted metabolites to be extensively exploited in the production of single-cell protein, food additives, recombinant proteins, biocontrol agents, and a wide spectrum of enzymes for the biofuel, textile, pulp, and paper industries [5,6,7,8,9,10]. Amongst the enzymes produced by the genus Trichoderma, those with cellulolytic (i.e., cellobiohydrolases (exogluconases), endoglucanase, and β-glucosidades) and lignocellulolytic (i.e., xylanase and β-xylosidase) potential are the most studied due to their pivotal role in lignocellulosic biofuel production [11].
This study aims to review the multifaceted roles of Trichoderma’s enzymatic toolbox in the bioconversion of lignocellulosic waste biomass through fermentation. While the main emphasis is on the use of agro-industrial waste as a sustainable and cost-effective feedstock for producing Trichoderma-derived lignocellulolytic enzymes for bioethanol production, alternative industrial-waste-based circular applications of the genus are also discussed. Overall, this review highlights recent advancements in Trichoderma-based bioconversion technologies, emphasizes current achievements, and outlines future research directions essential for enhancing the economic and environmental sustainability of integrating waste biomass utilization into biotechnological processes.
2. Structure and Composition of Lignocellulosic Biomass
Lignocellulosic biomass represents the most abundant renewable resource on Earth, offering immense potential for sustainable energy production. It serves as the primary supporting tissue in plant cell walls and is widely distributed among agricultural residues, comprising 30–50% of the total dry weight of plants [11]. Lignocellulosic biomass consists of a complex matrix predominantly composed of three main polymers: cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin [12]. These polymers are intricately intertwined within a matrix in which the composition varies depending on the plant species and the tissue type [13].
Cellulose stands out as the predominant polymer in lignocellulosic biomass, making up 35–50% of its dry weight. Composed of linear chains of β-1,4-linked glucose units, cellulose forms crystalline microfibrils that provide structural strength to plant cell walls and exhibit high resistance to enzymatic degradation [14]. In contrast, hemicellulose constitutes a heterogeneous group of polysaccharides, comprising 20–40% of lignocellulosic biomass. Hemicellulose contains various sugar monomers, such as xylose, mannose, galactose, and arabinose, often as branched or mixed-linkage polymers [15].
Lignin is a complex aromatic polymer comprising 15–25% of lignocellulosic biomass. It is highly cross-linked and hydrophobic, forming a recalcitrated physical barrier that protects cellulose and hemicellulose within the cell wall, thereby limiting the accessibility of cellulolytic and hemicellulolytic enzymes [13].
Therefore, the bottleneck in the bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass lies in efficiently hydrolyzing these complex polymers into simple fermentable sugars [16]. Lignocellulolytic enzymes play a pivotal role in this process, facilitating the breakdown of cellulose and hemicellulose to enable their conversion into biofuels and other valuable products.
3. Bioethanol Production
The increasing pressure to reduce reliance on non-renewable fossil fuels as an energy source has prompted scientists to explore sustainable alternatives, such as bioethanol production using microbe-driven processes with second-generation lignocellulosic biomass derived from agro-industrial waste [17]. Despite its potential as a technology for sustainable transportation fuels, the significant contribution of enzymes’ cost to the operating expenses of lignocellulosic biomass-based biorefineries remains a critical factor affecting the commercial viability of biofuel production [18]. Consequently, onsite enzyme production using low-value substrates has been explored to enhance the economic feasibility and environmental sustainability of bio-based facilities. Agricultural residues, such as husks, bagasse, seeds, leaves, straw, stalks, pulp, and peel derived from crops, grains, and horticulture, along with biomass from paper and textile streams, are regarded as cost-effective, renewable, and abundant sources of lignocellulosic biomass, offering viable alternatives to conventional feedstocks like corn and sugarcane used in first-generation biofuels [19].
Figure 1 illustrates the conversion process involved in ethanol production from lignocellulosic feedstocks, encompassing several critical steps: (1) pre-treatment, which can be biological, physical, and/or chemical, (2) cellulose hydrolysis (saccharification), (3) fermentation, and (4) product separation. Microbes, including bacteria, yeast, and/or fungi, play crucial roles throughout these stages, beginning with biological pre-treatment to soften biomass and release cellulose and hemicellulose from the complex lignin present in lignocellulosic materials [20]. Subsequently, during hydrolysis, cellulolytic and hemicellulolytic enzymes convert sugar polymers in pre-treated lignocellulosic biomass into fermentable monomeric sugars, either through direct microbial growth on feedstocks with accompanying enzyme secretion or through the addition of purified enzymes [21]. In the fermentation stage, microorganisms facilitate the conversion of sugars into ethanol [22]. Hydrolysis may occur simultaneously with or separate from the fermentation process. Within this framework, the primary role of Trichoderma spp. in bioethanol production is enzymatic hydrolysis, facilitated by the many cellulolytic enzymes that effectively convert cellulose into fermentable sugars. In addition to this central function, species within the genus Trichoderma also play a role in degrading hemicellulose during biomass pre-treatment and subsequent hydrolysis stages, and, to a lesser extent, in lignin degradation. Therefore, this section will primarily focus on Trichoderma’s role in cellulase production from agro-industrial waste biomass while also addressing its secondary roles in hemicellulose and lignin degradation.
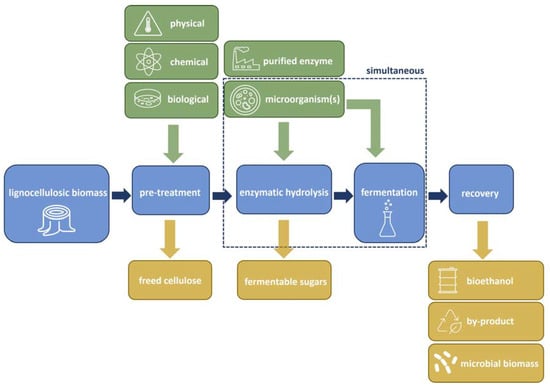
Figure 1.
Schematic flow for the bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol, which typically consists of three main steps: pre-treatment, enzymatic hydrolysis, and fermentation. Green arrows = inputs, orange arrows = outputs.
3.1. Trichoderma spp.’s Application in the Biological Pre-Treatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass
The cellulose–hemicellulose–lignin matrix is highly recalcitrant, thus hindering the accessibility of cellulose and hemicellulose for enzymatic hydrolysis into reducing sugars [23]. Therefore, pre-treatment of lignocellulosic biomass is required prior to enzymatic hydrolysis to break down or modify the structural barriers of lignocellulose, making it more accessible to hydrolytic enzymes and microorganisms in subsequent hydrolysis and fermentation processes [24]. In this context, biological pre-treatment relies on the natural ability of certain microbes to produce lignocellulolytic enzymes that can break down complex structures, such as lignin and hemicellulose [25]. Considering that most studies on Trichoderma’s application in biological pre-treatment focus on other biomass degradation purposes (e.g., pulp bleaching) [26,27,28], this section will briefly explore the potential impact of Trichoderma-driven pre-treatment in biofuel production.
While Trichoderma reesei is renowned for its robust cellulolytic activity, the lack of an effective lignin-degrading enzyme system hampers its efficiency in producing fermentable sugars and increases the costs associated with biomass pre-treatment for biofuel production [29]. However, successful efforts to heterologously express laccase [26,27,28,30,31] and versatile peroxidase [29] genes in T. reesei—enzymes crucial for lignin degradation—demonstrate the potential for engineering effective ligninolytic enzymes. Indeed, a genetically modified T. reesei strain engineered to produce heterologous laccase exhibited an enzyme mixture that significantly outperformed the host strain in converting corncob residues into fermentable sugars [30]. These findings suggest that the newly introduced enzyme enhanced cellulase efficiency by modifying the lignin surface to reduce non-productive binding of cellulases and/or partial degradation of the lignin structure, thereby improving cellulase’s access to cellulose. Likewise, the supernatant of T. reesei Rut-C30 expressing an exogenous versatile peroxidase gene (vp1) was employed in the simultaneous pre-treatment and hydrolysis of paddy straw, yielding 25.45 mg/mL of reducing sugar in comparison to 18.69 mg/mL by the parent T. reesei strain [29]. However, the treatments subjected to separate acid or alkali pre-treatment still exhibited the highest saccharification rates. This highlights the need for further research in this area, particularly considering that biological treatments, despite their environmental advantages, such as low energy input and minimal disposal costs, are hindered by low efficiency and a slow rate of lignin removal, which currently limit their scalability [32]. Future studies should prioritize optimizing enzyme expression levels, enhancing enzyme stability, and improving the compatibility of lignin-degrading enzymes to ensure that they can operate synergistically with cellulases and hemicellulases during enzymatic hydrolysis. For example, T. reesei Rut-C30 has been successfully engineered to co-express β-glycosidase and laccase for enhanced cellulase system and lignin degradation, respectively [31]. However, despite the anticipated improvement in hydrolysis from partial laccase-mediated lignin removal, the crude enzymes produced by the strain engineered to co-express both genes resulted in lower glucose levels during the degradation of acid-treated wheat straw compared to the strain expressing only β-glycosidase. Nonetheless, the glucose levels were still higher than those observed with the parent Rut-C30 strain. Further research should focus on purifying and utilizing the secreted laccase to determine the optimal levels necessary for significantly enhancing the hydrolysis process. These advancements offer a promising pathway to significantly improve overall biomass conversion efficiency through integrated pre-treatment and hydrolysis, thereby increasing yields of fermentable sugars and reducing production costs. Another approach could involve enhancing the efficiency of engineered lignin-degrading T. reesei strains through co-cultivation with other Trichoderma species with known lignin-degrading capabilities.
For instance, the recent discovery of novel laccases from other Trichoderma species, such as the copper-tolerant strain of Trichoderma asperellum Ts93 [33], creates potential for the use of complementary species consortia or for genetically engineering an enhanced array of laccase activity with improved tolerances into T. reesei. Additionally, other Trichoderma species, such as T. harzianum, T. atroviride, and T. viride, have also been recognized as laccase producers [34,35,36], offering further opportunities for synergistic effects in bioconversion processes.
In addition to laccase, T. viride has been shown to secrete other lignin-degrading enzymes, such as lignin peroxidase and manganese peroxidase, during the bio-delignification of rice straw [34]. The study showed that applying wet-milling and surfactant (Tween 80) in the delignification process, along with optimizing key parameters, such as glucose levels, the temperature, and the biomass-to-liquid ratio, resulted in enhanced biological lignin removal and subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis of pre-treated rice straw biomass. This underscores the extensive lignocellulolytic potential of T. viride and emphasizes the importance of integrating pre-treatment methods and optimizing protocols for improving the effectiveness and scalability of lignocellulosic biofuel production using Trichoderma species. The efficacy of T. viride in biological pre-treatment was also demonstrated in the lignocellulosic degradation of cocoa shell [37], where substrate treated with T. viride showed the lowest percentages of lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose content among five tested mold species, highlighting its potential in co-cultivation strategies with T. reesei. Moreover, the study by Ghorbani et al. [34] reported a 21% conversion of cellulose to reducing sugars during the pre-treatment stage of rice straw, further validating the potential for achieving higher saccharification efficiency through simultaneous pre-treatment and saccharification processes.
Within the scope of integrating Trichoderma species into microbial consortia, understanding the compatibility between different microbial species is crucial for optimizing co-culturing strategies that rely on microbial interactions. Multiple microbes need to synergistically enhance enzymatic processes without outcompeting each other. If species are found to be incompatible due to competition for resources or conflicting enzymatic activities, an alternative approach involves using a purified enzyme cocktails derived from these microbes. Although this method adds to production costs, it offers a practical solution by utilizing specific enzymatic activities essential for efficient biomass conversion. Despite the increased costs, focusing on the purification and formulation of these enzymes can tailor the enzyme cocktail to optimize performance in enzymatic hydrolysis processes. Additionally, tailoring genetic engineering strategies to specific biomass can further enhance this process, improving overall efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness in biofuel production.
3.2. Application of Trichoderma spp. in Hemicellulose Production
Hemicellulose-degrading enzymes play a key role in breaking down lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production. During pre-treatment, these enzymes modify and partially degrade hemicelluloses, facilitating subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis. In the enzymatic hydrolysis stage, where these enzymes are mainly employed, they further degrade hemicelluloses into fermentable sugars (e.g., xylose, arabinose, mannose), which are then converted into ethanol through fermentation [38].
Hemicelluloses primarily consist of xylan, a heteropolysaccharide composed of a β-1,4-linked D-xylose backbone, with a substitution of different side chains with L-arabinose, D-galactose, D-mannose, and glucuronic acid interconnected through glycosidic and ester bonds [39]. Due to its complex structure, the degradation of xylan requires a combination of several different hemicellulases, including key enzymes, such as endoxylanase and β-xylosidase [40]. Several review papers have discussed the status of xylanase in biofuel production, including the different microbial sources, types of lignocellulosic substrates, parameters affecting xylanase production, and different biotechnological approaches for enhanced xylanase biofuel conversion efficiency [38,39,40].
While T. reesei has long been recognized as a leading producer of cellulase and xylanase, other members of the Trichoderma genus, including T. atroviride, T. harzianum, Trichoderma asperellum, and Trichoderma longibrachiatum [41,42,43,44,45,46,47], have also been reported as xylanase producers utilizing a variety of lignocellulosic substrates, such as wheat bran, barley bran, rice bran, rice straw, saw dust, sugarcane bagasse, corn stover, and olive mill pomace [41,42,44,45,46,47]. In this context, strategies to enhance xylanase activity and reduce sugar yields using Trichoderma spp. include statistical modeling [41,44,47], different fermentation methods [42,44], optimization of culture parameters [41,44,47], substrate selection [44,45], particle size [42,44], nutrient supplementation [41,42], and genetic engineering [43,48,49].
Genomic and transcriptional analyses of T. reesei have shown the expression of diverse xylanolytic enzymes across multiple enzyme families, each with distinct cleavage specificities towards xylan [49]. These findings highlight T. reesei’s potential as an industrial-scale host for maximizing xylanases secretion for the bioethanol industry. However, transcriptome studies comparing T. reesei, T. harzianum, T. atroviride, and Trichoderma virens revealed that T. harzianum harbors the most comprehensive array of lignocellulosic-degrading enzyme-encoding genes, totaling 24 compared to 14 for T. reesei [50]. Notably, an endo-1,4-β-xylanase was the most highly expressed gene in T. harzianum when cultured in delignified sugarcane bagasse, highlighting its potential application during enzymatic co-hydrolysis. Moreover, T. harzianum demonstrated higher xylanase, endoglucanase (filter paperase (FPase), and carboxymethyl–cellulase (CMCase)) activity when grown on pre-treated sugarcane bagasse compared to media containing synthetic glucose, cellulose, or xylan [46]. These results suggest that biomass rich in complex polymers, such as sugarcane bagasse, can effectively support the simultaneous production of various enzyme groups by T. harzianum, thereby enhancing the efficiency of lignocellulosic biomass hydrolysis.
In a study using pre-treated corn stover as a substrate, the T. harzianum strain EM0925 secreted a diverse array of hemicellulases, including eight xylanases, one xylosidase, three arabinofuranosidases, seven galactosidases, eleven mannosidases, one mannanase, and eight carboxylesterases, demonstrating the complexity and diversity of the T. harzianum enzymatic toolbox [45]. Furthermore, an enzyme cocktail from T. harzianum outperformed commercial preparations by yielding higher enzymatic activity (FPase, β-glucosidase, and xylanase) and releasing 100% of glucose and xylose from pre-treated corn stover under the tested conditions [45].
Another promising candidate for co-hydrolysis strategies with T. reesei would be T. asperellum. The hemicellulase profile secreted by T. asperellum USM SD4 utilizing untreated oil palm fruit waste biomass was dominated by β-1,4-xylanase (activity = 186.30 U/mL) [47]. Accessory enzymes, such as β-xylosidase, α-arabinofuranosidase, acetyl xylan esterase, and β-glucosidase, were also present but exhibited low activity levels. Interestingly, the crude enzyme profile of this strain showed minimal FPase (0.04 U/mL) and endoglucanase (0.03 U/mL) activity. Subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis of alkaline-treated substrate using a commercial cellulase preparation in combination with T. asperellum’s hemicellulase crude filtrate achieved a notable 91.7% saccharification yield, which was significantly higher than the 77.9% yield without hemicellulase supplementation [47]. A Trichoderma strain that predominantly secretes xylanase could significantly enhance synergistic co-hydrolysis strategies by efficiently degrading hemicellulose into fermentable sugars (i.e., xylose), thereby increasing the overall yield of sugars available for ethanol fermentation. Moreover, employing an efficient xylanase-producing strain during biomass pre-treatment would not only ensure enhanced hemicellulose degradation, thus improving the accessibility of cellulose to subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis, but also reduce the formation of fermentation inhibitors and other by-products commonly generated during chemical pre-treatment methods.
Significantly higher hemicellulase and β-glucosidase enzyme activities compared to T. reesei Rut-C30 were also observed for T. asperellum S4F8 under solid-state fermentation (SSF) using sugarcane bagasse as a substrate [51]. A detailed analysis of the biological functions and glycoside hydrolase family representation within the secretomes revealed that T. asperellum S4F8 not only exhibited a greater diversity of hemicellulases and β-glucosidases but also had a greater abundance of these proteins compared to T. reesei Rut-C30 [51]. Despite T. reesei’s ability to produce a complete set of extracellular cellulase systems, β-glucosidase activity for the species is known to be weak, which poses a critical bottleneck in cellulase’s efficiency [52]. Therefore, integrating T. asperellum and T. reesei in a microbial consortium could potentially enhance the commercial feasibility of biomass-to-ethanol conversion processes by addressing both the low β-glucosidase activity and the limited repertoire of hemicellulases in T. reesei.
The significant impact of different induction conditions on Trichoderma’s secretome profile emphasizes the importance of understanding the regulatory mechanisms governing hemicellulase production in Trichoderma species. The integration of omics technologies, such as genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, can facilitate the identification of key regulatory genes, pathways, and metabolic networks to be targeted in novel biotechnological strategies and bioengineering approaches to further boost hemicellulase production and overall biomass conversion efficiency. Furthermore, investigating novel Trichoderma species and their distinct enzymatic capabilities across a range of lignocellulosic substrates holds promise for discovering untapped potential. This exploration could lead to the development of optimized, substrate-specific protocols aimed at enhancing the feasibility and broadening the scope of sustainable bioenergy solutions.
3.3. Application of Trichoderma spp. in Cellulose Production
Trichoderma reesei is renowned for its significant contribution to bioethanol production, primarily due to its ability to produce a robust extracellular cellulase enzyme system comprising endoglucanases, exoglucanases (cellobiohydrolases), and β-glucosidases [53]. Endoglucanases initiate cellulose degradation by cleaving internal glycosidic bonds within cellulose chains, generating shorter oligosaccharides [54]. Exoglucanases then act on the exposed ends of these oligosaccharides, releasing cellobiose units from the cellulose surface [23]. Finally, β-glucosidases hydrolyze cellobiose into glucose, which serves as the preferred substrate for ethanol fermentation by yeast, thereby making it a key intermediate in bioethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass [23]. In addition to cellulases, T. reesei produces a variety of accessory proteins, including lytic polysaccharide monooxygenases (LPMOs) and swollenins [55]. These proteins work synergistically with cellulases to disrupt the cellulose structure, increase substrate accessibility, and enhance enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency. Specifically, LPMOs facilitate the breakdown of crystalline cellulose by introducing oxidative cleavages in the polysaccharide chains, thus creating additional sites for cellulases to act upon and thereby accelerating the overall hydrolysis process [56]. Swollenins, on the other hand, target and modify the cellulose structure by inducing physical changes, such as swelling and disruption, which make the cellulose less resistant and more accessible to enzymatic attack [57].
Despite its strong cellulose-degrading properties, low β-glucosidase production is commonly reported for T. reesei [14]. Because an efficient cellulolytic system requires the coordinated action of all three classes of enzymes listed above [13], increased research efforts are devoted to the isolation or genetic manipulation of new Trichoderma strains with enhanced β-glucosidase activity, as well as the development of novel methods and optimized fermentation protocols for β-glucosidase secretion [15,16,17,18]. Such advancements are crucial for maximizing the bioconversion potential of Trichoderma-based enzymatic systems, ensuring sustainable bioethanol production from agricultural and industrial lignocellulosic residues. The following sub-sections will explore the research efforts aimed at harnessing the potential of the genus Trichoderma for bioconverting various lignocellulosic waste biomasses into cellulolytic enzymes and fermentable sugars required for bioethanol production. Table 1 provides an overview of the studies to be discussed, detailing the species used, the source of agro-industrial waste biomass, the fermentation methods, and the parameters assessed to evaluate the effectiveness of the protocols.

Table 1.
The use of agro-industrial waste biomass for the production of cellulase via Trichoderma spp. fermentation.
3.3.1. Grain-Derived Waste
Agricultural wastes derived from major production crops, such as corn, rice, wheat, and sugar cane, are considered a sustainable and cost-effective source of lignocellulosic biomass for biofuel production and are widely available as large quantities of biomass in the form of residual stalks, straw, leaves, roots, husks, sheaths, and bagasse [97,98]. Given that species from the genus Trichoderma have long been considered the most productive and powerful cellulase producers [99], these cellulolytic fungal strains have been widely explored for the bioconversion of crop-derived waste material to produce hydrolytic enzymes for lignocellulosic degradation required for the conversion of fermentable sugars into bioethanol [7]. A few examples of the use of Trichoderma spp. in the bioconversion of grain waste are discussed below.
Acid-treated, alkali-treated, and ball-milled rice straw were used as a substrate to investigate the effect of pre-treatment on cellulase production by T. reesei [58]. Compared with growth on commercial cellulose, ball-milled rice straw yielded the highest protein content, Fpase, and β-glucosidase activity, which increased by 1.8-, 1.3-, and 2.2-fold, respectively. The effect of different pre-treatments on the enzymatic activity (cellulase, CMCase, and β-glucosidase) of T. reesei was also reported when using canola meal as the fermentation substrate [100]. Soluble polysaccharides (SPSs) produced during rice straw saccharification on cellulase production substrates also showed a significant increase in FPase (1.5-fold) and β-glucosidase (2.3-fold) when compared to media without SPS [58]. Moreover, the use of the crude enzymes produced in cultures with SPS significantly increased the glucose yield in subsequent saccharification. The study indicated that rice-straw-derived SPS could play a key role in addressing the lack of β-glucosidase activity produced by T. reesei. The observed increase in β-glucosidase production could be improved even further through the use of mixed fungi cultures. For example, Dhillon et al. [59] found that bioconversion of rice straw using mixed culture containing T. reesei and Aspergillus niger resulted in higher FPase, β-glucosidase, CMCase, and xylanase activity when compared to SSF by T. reesei alone. The authors also demonstrated higher enzyme activity when rice straw was supplemented with wheat bran at a 3:2 ratio [59]. According to Muthuvelayudham et al. [60], maximum protein and enzyme production, including β-glucosidase, could also be achieved by combining a synthetic substrate (i.e., xylose or lactose) with the natural rice straw during batch fermentation with T. reesei. However, enhanced cellulase activity was seen when xylose or lactose were inoculated with sugarcane bagasse as opposed to rice straw [60]. Sugarcane bagasse and Trichoderma koningii were also considered the most suitable of all substrates and fungi species tested by Salomão et al. [61] in the production of cellulase by SSF. These studies, altogether, suggest that further research on protocol optimization for achieving optimum Trichoderma-derived β-glucosidase synthesis is still required. For example, the response surface methodology (RSM), which is a collection of statistical techniques for designing experiments, building models, evaluating the effects of factors, and searching for the optimum conditions, has been successfully employed by Rocky-Salimi and Hamidi-Esfahani [62] to assess the impact of the aeration rate, particle size, and harvesting time on FPase, avicelase and CMCase activities during SSF using T. reesei and rice bran as an alternative substrate. The same methodology could also be explored to maximize β-glucosidase production by Trichoderma spp.
Another possibility to improve cellulase production during biomass hydrolysis is to employ an enzyme mix containing enzymes derived from different fungi species. Crude cellulase and β-glucosidases were produced by SSF on wheat bran substrate using T. reesei and A. niger, respectively [63]. While the bioconversion of wheat bran by T. reesei resulted in significant levels of FPase and CMCase activity but lesser of β-glucosidases, bioconversion of the same substrate by A. niger yielded reduced levels of FPase and CMCase and a several-fold increase in β-glucosidase activity. The combined crude enzyme mix was tested for biomass saccharification of three waste types (i.e., rice straw, sugarcane bagasse and water hyacinth) and the hydrolysate generated from the most effective substrate (i.e., rice straw) was successfully used for ethanol production [63]. These results suggest that combining the enzymes produced by different fungal species could be an alternative for overcoming the low β-glucosidases yields usually observed for T. reesei. A similar mixed-enzyme approach including the same two fungi species has also been shown to improve enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency by 17.26% when using alkali pre-treated corn stover as the substrate [64]. Co-culturing two fungal species (i.e., T. reesei and Penicillium citrinum) on wheat bran substrate, as opposed to combining the purified enzymes afterwards, has also been evaluated as an alternative method to enhance cellulase complex production [65]. The same study also demonstrated that comparable hydrolysis efficiency can be achieved by using the whole fermented wheat bran biomass instead of purified cellulase extract, which means that the enzyme extraction step could be avoided, thus improving the economic feasibility of unit operations. Mixed co-culture of T. reesei and A. niger was also confirmed as an effective method to enhance cellulolytic enzyme production when using steam-exploded corn stover as the substrate [66]. Substrate pre-treatment methods [68], the type of plant waste hydrolysates [63,67], and the fungi species [67] were also shown to affect cellulase production with wheat bran substrate SSF. Other factors involved in wheat bran SSF fermentation by T. reesei, such as the temperature, pH, inoculum dosages, particle size, moisture percentage, and incubation period, have been effectively established by the Box–Behnken design (BBD), which is a reliable tool for finding the optimal conditions of process parameters used in cellulase production [67].
The concept of combining enzyme mixes produced by multiple fungi strains could also be extrapolated to enzyme mixes derived from a single species but from different lignocellulosic crop waste substrates. For example, liquid-state fermentation by T. viride induced maximum endoglucanase and exoglucanase activity when using corn stover substrate, while the highest β—glucosidase activity was achieved using oat hay [68]. However, the potential effect of combining both enzyme outputs on subsequent saccharification was not assessed by the authors.
Engineered strains of Trichoderma spp. have also been explored as an alternative strategy to enhance the titer and productivity of on-site waste-based cellulolytic enzyme production [69,70,101,102]. A T. reesei strain has been developed to overexpress the cbh2 gene encoding cellobiohydrolase II, an exoglucanase that cleaves primarily cellobiose units from the non-reducing end of cellulose and for which the expression levels are usually low in T. reesei [69]. Improved enzymatic activity by the modified strain was confirmed through fed-batch fermentation using alkali pre-treated corn stover as the substrate in combination with synthetic glucose–sophorose as a soluble inducer for cellulase production. Pre-treated corn cob [70] and corn cob powder [71] were also assessed and deemed the most efficient amongst the tested substrates when evaluating the effectiveness of similar engineered strains of T. asperellum and T. harzianum under SSF and shake flask fermentation, respectively.
Lignocellulosic waste residues derived from other grains, such as pea [72], barley [73], rye [74], soybean [75], and sorghum [77], have also been successfully investigated for cellulase bioconversion by Trichoderma spp.
3.3.2. Fruit Waste
Fruit waste, generated in large quantities by the agricultural sector and fruit processing industries, is a promising fermentation substrate due to its low cost, abundant availability, and high content of fermentable sugars [103].
An indigenous strain of T. viride was employed by Irshad et al. [78] to produce cellulose-degrading enzymes via SSF using various agricultural and paper industry waste as the substrate (i.e., wheat straw, sugarcane bagasse, apple pomace, banana stalk, orange peel, and municipal paper waste). Out of all of the tested substrate waste sources, orange peel elicited the highest yields of the three major enzymes that form the cellulase enzyme system: endoglucanase, exoglucanase and β-glucosidase. Apart from the substrate type, the fermentation time, temperature, pH, substrate concentration, and inoculum were other determinants of cellulase production efficiency. The effect of the same fermentation parameters on cellulase production was also seen by Omojasola and Jilani [79] when assessing the bioconversion of orange wastes (i.e., peel, pulp, and albedo) to produce cellulase using different fungi species (i.e., Trichoderma longibrachiatum, A. niger, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae). In this case, the type of orange waste and the microorganisms employed also influenced the cellulase activity, with optimum levels being achieved using orange pulp and T. longibrachiatum. Variable cellulase production according to fungi species and fruit waste type has also been reported under submerged fermentation conditions [80]. However, as opposed to what was seen by Omojasola and Jilani [79], the highest levels of cellulase were observed for A. niger rather than for the targeted Trichoderma species (i.e., T. viridae). The same study also showed that pineapple peel was more effective than orange and banana peel under submerged fermentation. These studies combined demonstrate the importance of protocol optimization to ensure optimum resource utilization. In this respect, the Plackett–Burman design (PBD), BBD, Genetic Algorithm (GA), and RSM have been successfully employed to assist the optimization of fermentation process variables and to maximize cellulase activity by T. reesei when using pineapple waste as the substrate [81,82].
Raw waste material derived from banana [83], grapes [84], olives [84], lychee [85], cocoa [104], apple, and strawberries [105] have also been assessed as useful feedstocks for Trichoderma-derived cellulase production.
3.3.3. Wood/Husk Waste
Horticulture waste in the form of wood chips was successfully utilized as a substrate to produce cellulase (i.e., FPase, CMCase, and β-glucosidase) and hemicellulase (xylanase and β-xylosidase) activity under SSF by T. reesei [86]. The resultant T.-reesei-derived crude enzyme mix hydrolyzed the lignocellulosic biomass of waste newspaper, wood chips, wood dust, and palm oil fiber to its constituent sugars (i.e., glucose) more effectively than a commercial enzyme cocktail. The results suggest that the fermentable sugars derived from the saccharification of various waste biomasses can be effectively utilized as substrates for ethanol production. Likewise, fermentable sugars produced by T. reesei during pre-treated palm wood hydrolysis were also effectively employed to produce ethanol via batch fermentation using Kluveromyces marxianus [87]. The use of copra waste from the coconut-pressing process for cellulase production by T. reesei SSF was also attempted in the presence and absence of wheat bran as the nitrogen source [88], demonstrating that wheat bran supplementation significantly increased fungal growth and the production of total cellulase, CMCase, and β-glucosidase activity. The observed results are consistent with what was found by Idris et al. [76], who showed that the addition of wheat bran into sorghum stover substrate increased both growth and CMCase activity in SSF by T. reesei. Coconut mesocarp has also been effectively utilized as a natural inducer of cellulase activity in T. reesei, presenting a viable alternative to pure cellulose in fed-batch fermentation processes. [89]. In this case, maximum cellulase expression was achieved through the optimization of most influencing fermentation parameters via RSM.
3.3.4. Other Plant Waste
Delignified bioprocessing of medicinal and aromatic plants, namely citronella (Cymbopogon winterianus) and marc of Artemisia (Artemisia annua), has been selected as a substrate to assess the ability of six different Trichoderma species to produce cellulase activity under submerged fermentation conditions [90]. The induction of specific enzymes of the cellulase system (i.e., FPase, CMCase, and β-glucosidase) was found to be species- and substrate-specific. The results also demonstrated the importance of screening for optimum substrates as, for example, T. virens was able to produce all three analyzed enzymes under the bioprocessing of marc of Artemisia but not when other substrates were used, including pure polymer cellulose. Floral waste, plant litter, and tea leaf waste, alongside mixed fruit pomace (pineapple, orange, and pomegranate), vegetable refuse, sugarcane bagasse, and sawdust, were also employed as substrates to assess the degradation potential of T. viride under SSF [91]. Similarly to what was seen by Chandra et al. [90], the fermentation efficiency was substrate-dependent. In this case, the plant wastes were found to be the ones resulting in the least biomass yield. The production of T. reesei cellulases using steam-pre-treated willow (SPW) as the carbon source via batch fermentation has also been investigated [92]. Surprisingly, the use of solid residues of enzymatically hydrolyzed SPW was found to be as effective as SPW, even though a 20% lower cellulose content was found in the hydrolyzed residue. This could be attributed to deactivated enzymes remaining adsorbed on the hydrolyzed residues, which reduces the adsorption of new enzymes and thereby increases cellulase activity in the solution. Additionally, using delignified SPW significantly reduced cellulase yields, indicating that the alkali pre-treatment used was not compatible with the substrate. The reduction in cellulase yields may result from the pre-treatment conditions being too harsh, leading to the degradation of cellulose fibers, a reduction in the overall cellulose content, and the formation of degradation products that inhibit enzyme activity. This underscores the importance of carefully optimizing treatment conditions to prevent negative effects on the cellulose structure and ensure effective enzymatic processes.
3.3.5. Paper Waste
The paper industry is considered one of the largest consumers of natural resources (e.g., wood and water) and energy (e.g., electricity and fossil fuels), and waste paper materials also represent a significant portion of annual organic waste disposal [96]. Consequently, there is a growing interest in finding sustainable methods to convert waste generated during paper production into value-added products [106]. The high lignocellulosic content in industrial paper residues positions them as promising and cost-effective raw materials for bioprocesses that aim to convert cellulosic materials into cellulase. Despite this potential, Trichoderma spp. have not been widely examined for the bioconversion of industrial waste paper, although the existing literature supports their use for cellulase production from lignocellulosic waste.
An evaluation of recent studies highlights several advancements and areas for further research. For instance, Damisa et al. [93] utilized submerged fermentation to assess the suitability of pre-treated waste paper as a substrate for cellulase production using a Trichoderma sp. isolated from the soil. Similarly, the enzymatic hydrolysate of waste paper has been evaluated as a soluble inducer of cellulase production in continuous cultures of T. reesei [94]. These studies demonstrate that waste paper hydrolysate can induce cellulase production with comparable efficacy to cellulose itself, producing a complete range of cellulase components, including FPase, CMCase, and β-glucosidase.
Further research into alternative substrates reveals the successful use of deinking paper sludge and meat-processing blood waste as carbon and nitrogen sources, respectively, for T. reesei cellulase production [95]. However, while animal-processing blood provides a more cost-effective alternative to traditional nitrogen sources, such as urea, deinking sludge—although not toxic to microorganisms—requires acid/base pre-treatment to improve its suitability as a substrate for growth and enzyme production by T. reesei. Filter paper, newspaper, and office paper have also been assessed for microbial fermentation to produce cellulase using monocultures and mixed cultures of Penicillium citrinum, Aspergillus oryzae, and T. viride [96]. Although the three strains showed good performance for the saccharification of all waste papers, the maximum cellulase activity, protein content, and total reducing sugars were obtained using a 2:2:2 mixed fungi culture ratio. A potential explanation for the observed results could be the synergistic utilization of combined metabolic pathways by all involved strains in a co-culture situation with shared metabolic burden [107]. This indicates a promising direction for future research in optimizing co-culture systems to enhance waste paper bioconversion processes.
Moreover, the potential of using various types of waste paper (e.g., office paper, corrugated board, magazine paper, and tissue paper) without pre-treatment for simultaneous cellulase and xylanase production by T. longiflorum has been validated [108]. The study highlighted that the structural features of different waste materials, such as raw wood sources and papermaking processes, affect fermentation capacity. Remarkably, enzyme activity improved by 56.86% when corrugated board was used in combination with wheat bran. The ability of T. longiflorum to utilize natural waste paper substrates directly, without expensive pre-treatment, could greatly contribute to reducing the cost of enzyme production and bioconversion using this species.
Overall, Trichoderma spp. play a pivotal role in bioethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass due to their diverse enzymatic toolbox. Moving forward, future research should prioritize enhancing overall biomass degradation efficiency by exploring synergistic interactions between cellulose-degrading enzymes and other lignocellulosic enzymes, such as hemicellulases and lignin-modifying enzymes. Investigating these interactions could lead to the development of more efficient enzyme cocktails tailored for specific biomass compositions and pre-treatment strategies. The integration of systems biology approaches, such as metabolomics and fluxomics, can provide a holistic understanding of metabolic pathways and enzyme kinetics involved in biomass degradation by Trichoderma species. Leveraging these omics tools may identify metabolic bottlenecks and optimize enzyme production and secretion pathways, thereby advancing the effectiveness and economic feasibility of biofuel production from lignocellulosic biomass. Furthermore, unravelling the regulatory networks governing enzyme production would deepen insights into the genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying enzyme expression and secretion in Trichoderma spp. Optimized cultivation conditions, enhanced enzyme yields, and tailored enzyme cocktails for specific lignocellulosic substrates and pre-treatment methods should result from the elucidation of these mechanisms. Continued exploration of genetic engineering strategies to manipulate key regulatory genes would also further boost enzyme production and overall biomass conversion efficiency.
However, ensuring the sustainability of Trichoderma-based processes requires a comprehensive assessment of their environmental impact, including substrate handling, enzyme production, and waste management, in order to develop mitigation strategies. Economic studies are equally crucial for evaluating the cost-effectiveness and feasibility of biomass utilization across its lifecycle stages, including improving enzymatic activity, optimizing protocols, and ensuring the practical scalability of developed technologies for commercial deployment. Evaluating expenses related to collecting, sorting, and transporting biomass considering certain factors, such as the distance to the processing facility, infrastructure requirements, and seasonal biomass availability, is essential to overcome limitations that could hinder the use of specific substrates. Additionally, assessing transport logistics and the economic impact of selected biomass conversion technologies, including capital investment, operational expenses, and maintenance requirements, is crucial for evaluating the economic feasibility of biofuel production technologies from lignocellulosic biomass.
4. Biocontrol Agent Production
The use of biological pesticides to control phytopathogens has been widely investigated as a more sustainable strategy than the excessive use of agrochemicals, which are not only costly but also toxic to the environment and consumers [109]. In this regard, the genus Trichoderma holds great potential as a biological control agent, particularly against pathogenic fungi that affect agriculture crops [110]. Reported mechanisms of action include antibiosis, mycoparasitism, the production of lytic enzymes, and competition for nutrients and space [111]. The use of agricultural waste as feedstocks to produce Trichoderma-derived biocontrol agents through fermentation has also been explored (Table 2).

Table 2.
The use of agro-industrial waste as an organic substrate for the production of Trichoderma spp. to be used as a biological control agent.
The production of T. viride as a biocontrol agent was successfully achieved using winery wastes [112]. Trichoderma viride produced by SSF using grape marc and wine lees as substrate not only yielded significant levels of extracellular enzymes important for pathogen inhibition (i.e., chitinase, β-glucanase, and pectinase) but also demonstrated a high level of antagonistic activity towards several genera of pathogenic plant fungi, including Cladosporium, Fusarium, Fulvia, Botrytis, Aspergillus, Penicillium, Mucor, and Rhizopus. A fermentation protocol for extracellular β-glucosidase secretion by T. harzianum using agro-industrial banana waste has also been developed and optimized [113]. The efficacy of the resultant β-glucosidase as a biocontrol agent against Macrophomina phaseoline, a fungal phytopathogen known to cause charcoal rot in plants, was confirmed using in vitro plate inhibition assays. Banana waste (i.e., banana pseudostem), as well as cassava peels, coconut shell, sugarcane bagasse, and pineapple peels, were also tested as substrates for the production of the biopesticide Trichoderma Brev T069 [114]. In this case, cassava peel was the optimal SSF substrate in terms of spore yields, which showed a 64.65% biocontrol efficiency on banana fusarium wilt when employed in a pot experiment. Significant differences in conidia yields were also observed during the evaluation of different agro-industrial residues (i.e., rice husk, apple pomace, whisky draff, soy fiber, rice fiber, wheat straw, beer draff, orange peel, and potato peel) as a substrate for T. harzianum production [115].
Solid-state fermentation using mango industrial waste as a carbon source and polyurethane foam as an inert support matrix was employed to achieve high production of T. asperellum spores [116]. Spores produced by mango waste fermentation survived storage at 4 °C for 7 days and were effectively tested in vitro as a biocontrol agent against the causative agent of anthracnose, Colletotrichum gloesporioides. Spore shelf life and viability have also been assessed for T. harzianum produced under SSF using several waste substrates: rice husk, rice straw, rice bran, wheat bran, broom sorghum grain, sawdust, cow dung, sugar beet pulp, soybean meal, peanut pod, barley grain, and water fern [117]. All substrates resulted in successful fungus colonization and conidiation, albeit at different levels. However, a further greenhouse experiment showed that the spores derived from these substrates all yielded the same biocontrol efficacy against rice sheath blight disease caused by Rhizoctonia solani.
Extracellular production of amylase through the co-cultivation of T. harzianum and the bacteria Pseudomonas fluorescens on maize waste was also investigated [118]. It was demonstrated that supplementing fermentation with copper (Cu)–chitosan nanoparticles, which enhance enzyme production by microorganisms through the biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles, resulted in higher amylase yields. Moreover, a subsequent field experiment showed that maize grains pre-treated with fermented maize waste media supplemented with Cu–chitosan were more effective at preventing diseases than both nanoparticle-free and fungicide treatments. That work reinforces previous findings with other yeast genera where higher enzyme production was achieved using co-cultured fermentation conditions with either a combination of multiple yeast species or yeast associated with bacteria as opposed to single cultures. The increased enzymatic activity observed with mixed consortia cultivation may stem from enhanced resource utilization through combined metabolic activities, resulting in a reduced metabolic burden on each individual species due to either antagonistic or symbiotic interactions [119]. Therefore, the production of biological agents through agricultural waste fermentation using Trichoderma spp. in consortia association with other microbes deserves to be further explored.
Apart from biological control, Trichoderma spp. has also been explored as a plant-growth promoter. For instance, stevia residue supplemented with amino acids hydrolyzed from animal carcasses was used for spore production from Trichoderma guizhouense by SSF, with resultant spores significantly increasing corn plant growth when combined with organic fertilizer [120]. Cellulose-rich by-products generated from paper production (i.e., paper sludge) have also been successfully explored as the sole carbon source used to obtain spores from the fungus T. asperellum via SSF [121]. Fermented paper sludge showed a positive effect on seedlings’ growth when applied to Capsicum anuum seeds.
While Trichoderma spp. demonstrate robust potential as biocontrol agents and growth promoters, ongoing research is crucial to optimize fermentation processes, assess substrate suitability, and further explore synergistic interactions with other microbes to enhance biocontrol efficacy and broaden the spectrum of targeted pathogens. Moreover, understanding the complex interactions between Trichoderma, the host plant, and the target pathogen under different environmental conditions is essential for predicting and enhancing biocontrol outcomes. For example, the possibility of inconsistent efficacy under different environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and soil characteristics, could limit the reliability of Trichoderma as a standalone solution for disease management. Integration of Trichoderma spp. may also be incompatible with existing agricultural practices, such as fertilization, irrigation, and pesticide application. Consequently, comprehensive knowledge of persistence and long-term efficacy across diverse agricultural settings and crop systems, including their impact on subsequent crop rotations, is essential. Assessing the potential ecological effects of Trichoderma on indigenous microorganisms, such as beneficial fungi, is also critical for integrated pest management strategies aimed at minimizing ecological disruption. Such advancements are pivotal for maximizing the sustainable benefits of Trichoderma-based biocontrol in agriculture while minimizing environmental impacts and ensuring food security.
5. Animal Nutrition
The use of agro-industrial waste as organic substrates for the production of single-cell protein (SCP) as an alternative to fish meal and plant-based protein in animal feeds has gained increasing attention [122,123]. Additionally, microbiological treatments aimed at enhancing the digestibility and nutritional profile of crop residues and low-quality roughages for livestock nutrition have been extensively investigated [124,125]. Although not traditionally considered for SCP production, the conversion of agricultural waste by Trichoderma spp. has been explored as a method to enrich and add value to animal diets (Table 3).

Table 3.
The use of agro-industrial waste as an organic substrate for the production of single-cell protein and as a means of enhancing and adding value to animal diets.
Siada et al. [126] used SSF by T. harzianum to evaluate the protein enrichment of different types of agro-industrial wastes (i.e., peels of mango, orange, apple, banana, and tomato) for animal nutrition. Increases in crude protein content varied significantly depending on the fermented substrate, with tomato proving to be the most effective feedstock for protein enrichment (61.11% increase) and banana the least effective (8.1% increase). These results show the importance of evaluating different waste sources when developing protocols for microbial-derived protein production. However, selection of suitable fungal strains is also required to ensure optimum fermentation outcomes. For example, when evaluating the efficacy of seven fungi species, including T. harzianum, T. reesei, and T. koningii, on the bioconversion of olive cake, Fadel and El-Ghonemy [127] found that A. oryzae produced the highest total protein yields and achieved the greatest reduction in fiber content through the production of lignocellulolytic enzymes. Differences in strain performance were also seen when evaluating the effect of Trichoderma sp. and Phanerochaete chrysosporium on corn stover fermentation [128]. In this case, Trichoderma sp. was the most effective candidate for improving the nutritional value of ruminant feed, as it significantly improved both crude protein content and fiber digestibility. The ability of Trichoderma spp. to enhance fodder quality over other fungal species was further highlighted by Helal [129]. Out of sixty-two fungal isolates, T. koningii exhibited the highest cellulolytic activity and crude protein production when cultivated on rice straw under controlled conditions.
Secondary metabolites produced by different fungi strains during the fermentation process may have a synergistic effect and, therefore, should be explored to improve SCP production outcomes. For example, a three-day fermentation process using T. harzianum, followed by subsequent seven-day fermentation with S. cerevisiae, has been shown to significantly improve the nutritional value of duckweed substrate in terms of increased crude protein content and lower crude fiber levels [130]. According to the authors, T. harzianum fermentation provided a nitrogen source for the growth of S. cerevisiae, which, in turn, was subsequently used as a raw material for the formation of amino acids. Trichoderma harzianum was also used to produce fungal biomass protein with rice polishing [131]. The results showed that the final fungal biomass not only contained all of the essential amino acids at significant levels but also allowed for partial replacement of soybean meal to up to 60% without affecting poultry growth.
Rice-processing waste has also been explored as a substrate to produce T. reesei SCP [132]. Solid-state fermentation using rice straw pulp combined with urea as a nitrogen source effectively reduced lignin levels from 7 to 0.63%, significantly improving the digestibility of the grain waste. The highest total crude protein content achieved was 25% with a substrate C/N ratio of 20:1. Similarly, a 48.1% increase in total protein content was obtained when urea was added to the SSF of cassava residue using T. pseudokoningii [133]. Given that external nitrogen sources like urea can impact production costs, a more affordable and sustainable alternative could be to further recycle agricultural waste and use composted manure as a nitrogen source. However, while manure is a nutrient-rich resource, its use in bioprocesses requires careful management to mitigate potential biosecurity risks. Implementing sterilization protocols can address these concerns but may impact the cost-effectiveness of using such a waste source. Therefore, exploring cleaner nitrogen-rich alternatives, such as animal-processing blood, which has been shown to support T. reesei growth [115], could be a viable option.
The effect of fermented T. reesei on animal nutrition has also been tested in vivo with Barki lambs [134]. A 50% substitution of a concentrated feed mix with sugar beet pulp treated with T. reesei, whether or not supplemented with urea, positively affected nutrient digestibility, nutritional content, and growth performance compared to a diet containing untreated sugar beet pulp at the same level. Omer et al. [139] also showed that corn stalks treated with T. reesei can completely replace clover hay in the food ration of growing Rahmani sheep. Sheep fed on diets containing biologically treated corn stalks exhibited improved digestibility of nutrients and cell wall constituents, as well as enhancements in final weight, total body weight gain, average daily gain, relative gain, and daily feed intake compared to those fed the control ration. Despite these promising findings, challenges remain. For instance, no significant differences in weight gain, feed intake, and feed conversion ratio were seen when 25% of grass hay was replaced by rice straw fermented with a strain of Trichoderma spp. and fed to Barbados sheep [135]. Nonetheless, higher nutritional value, increased digestibility, and lower lipid oxidation were seen in the biologically treated diet, indicating that fermented rice straw may still be used as a feed replacement with no deleterious effect on animals.
Trichoderma viride has also been found to be suitable for upgrading the nutritional value of animal feed through the fermentation of low-quality roughages. For example, SSF by T. viride significantly increased the total feed intake, crude protein content, and organic matter digestibility of rations containing either fermented rice straw or treated corn straw when compared to untreated feeds [136]. Trichoderma viride was also successfully employed to reduce organic matter and fiber content of peanut hull to be used as feed for ruminants [137]. According to the authors, sheep fed with T.-viride-treated peanut hull also showed increased digestibility, feed intake, and dry matter intake.
Apart from agricultural by-products, waste from the paper industry has also been used as a carbon source for T. reesei fermentation for animal nutrition [138]. However, in this case, the final goal was to produce feed additives (i.e., digestive enzymes) and not to increase the nutritional value of low-quality crop residues. The results showed that old corrugated cardboard served as an effective substrate for the production of cellulase and amylase activity. A further feeding trial showed that rabbits fed diets supplemented with T.-reesei-derived enzymes showed improved production traits, including enhanced nutrient digestibility, which consequently reduced mortality rates associated with digestive disorders during the early post-weaning period. Production of vitamin B12 has also been achieved through waste fermentation [140]. In this case, the resulting sugars obtained from hydrolysis of the cellulose fraction in tomato pomace using T. reesei were used in a subsequent fermentation with the bacteria Propionibacterium shermanii to produce vitamin B12. Although the final concentration of B12 produced in the medium (52.7 mg/kg of dried material) may not be economically feasible for human use, it compares very favorably with the typical concentration of vitamin B12 employed in animal feed (e.g., 0.25 mg/kg for commercial fish meal).
While using Trichoderma spp. to enhance the digestibility and nutritional profile of agricultural waste for livestock nutrition presents exciting possibilities, it also involves significant challenges and opportunities for future research. Scaling up Trichoderma spp. treatment from laboratory to industrial or farm-scale settings while maintaining efficacy, consistency, and cost-effectiveness is a substantial hurdle. For example, seasonal fluctuations in the supply of agricultural waste biomass can alter its composition and availability [141]. Variable factors, such as growth conditions, harvesting methods, and post-harvest handling practices, can further exacerbate the challenges associated with variations in biomass composition. These fluctuations not only create logistical challenges but also highlight the need to develop optimized and standardized protocols that ensure consistent feed formulations. Microbial interactions between Trichoderma spp. and substrate-specific microbiota could also significantly impact fermentation outcomes and may lead to the generation of unwanted microbial by-products, such as mycotoxins, which could pose a significant threat to animal and public health [142]. Exploring and assessing biomass sterilization during pre-treatment stages, and adopting best operating practices to circumvent contamination, are, therefore, highly desirable. Moreover, there is a crucial research gap regarding the long-term effects of Trichoderma-treated feed on animal health, growth performance, and product quality (e.g., milk, meat). Understanding these aspects is essential for assessing the overall benefits and potential adverse effects associated with using Trichoderma in animal nutrition over extended periods. Addressing regulatory requirements and safety assessments to ensure compliance with food safety regulations is also paramount. This becomes particularly critical when considering the use of genetically modified strains, which could face social acceptance challenges. In addition, assessment of the environmental sustainability and economic feasibility of integrating Trichoderma spp. into livestock feeding systems is required. Conducting comprehensive cost–benefit analyses and life cycle assessments will help promote adoption by farmers and stakeholders, demonstrating the economic viability and environmental benefits of incorporating this approach into existing feeding practices.
6. Engineering Strategies to Enhance Trichoderma’s Enzymatic Activity
Lignocellulose-based bioprocesses demand an enormous availability of cellulases and other lignocellulose-degrading enzymes with high activities but low costs. As previously mentioned, Trichoderma spp. can produce and secrete large quantities of cellulase-degrading enzymes when provided with an appropriate lignocellulosic substrate. Still, T. reesei cellulase production falls short of perfection for real-world applications, especially in terms of the resultant product composition. As a result, genetic strategies have been employed to develop superior Trichoderma strains for the production and secretion of native cellulases and, therefore, to enhance the bioconversion efficiency of lignocellulosic biomass [143]. These strategies include both targeted and untargeted modifications to the Trichoderma genome, including the use of alternate promoters, signal peptides, possible carrier proteins, the codon-optimized target gene, and alternate terminators [144,145]. Because Section 3.1 already covered genetic approaches to enhancing lignin-degrading enzyme activity in Trichoderma spp., and given the critical role of cellulases in the effective breakdown of lignocellulosic biomass into fermentable sugars, this section will primarily focus on engineering strategies aimed at improving cellulase activity.
Native production and secretion of cellobiohydrolase by T. reesei is controlled by the inducible CBH1 promoter and utilizes the CBH1 secretion peptide signal. The CBH1 promoter, in turn, is regulated by the transcription repressors CRE1 and ACE1 [146], as well as the positive activators XYR1 [147], ACE2 [148], and the HAP2/3/5 complex [149]. In this context, promoter modification has been used to increase cellulase production. For example, a recent study demonstrated that replacing binding sites for the negative regulator ACE1 with the positive regulators for ACE2 and XYR1 improved promoter transcription efficiency, resulting in increased expression of the target protein [145]. Upon engineering the CBH1 promoter, where the CRE1 binding site was substituted with the binding site of the transcriptional activator ACE2 and HAP2/3/5 complexes, the expression of green fluorescent protein in T. reesei was significantly enhanced by more than sevenfold under induction conditions. Also, cellulases produced by the T. reesei strain with the modified CBH1 promoter resulted in a 40% increase in overall FPase activity compared to the wild-type T. reesei Rut-C30 strain [150]. Moreover, restructuring the cis elements of XYR1 within the CBH1 promoter significantly increased the strength of the promoter by over sevenfold [151].
Modifying transcription factors has also proven to be an effective method for enhancing enzyme production in T. reesei. For example, eliminating CRE1, which is responsible for carbon metabolism repression, enhances cellulase production in T. reesei. Notably, CRE1–96 consistently binds to the upstream regulatory region of the key regulator XYR1 involved in cellulase regulation. Interestingly, T. reesei carrying CRE1–96 exhibits superior cellulase-induced production compared to strains lacking the ΔCRE1 gene [152]. The Trvib-1 gene, encoding a possible transcription factor, was also overexpressed in T. reesei Rut-C30. As a result, cellulase production and protein secretion in the T. reesei Vib-1 culture increased significantly by 200% and 219%, respectively, compared to the parent strain [153]. A 40% increase in glucose release from the pre-treated corn stover hydrolyzed was also observed when the crude enzyme generated by the modified strain was employed.
Apart from the natural regulators, there is an alternative option for controlling cellulase induction, which involves the expression of chimeric transcription factors. For instance, a synthetic transcription activator incorporating the CRE1 binding domain fused with the XYR1 regulator was engineered and consistently expressed in T. reesei Rut-C30. Notably, the strain with this chimeric regulator exhibited an increase in FPase activity, even in the presence of glucose as the carbon source, reaching a level 12.75 times higher than the wild-type Rut-C30 [102]. Innovative transcriptional activators, comprising the DBD-Ace2 and the VP16 effector domain, markedly enhanced cellulase production when glucose was the only carbon source. The FPase activity showed an improvement of over 25-fold compared to the original T. reesei Rut-C30 strain [154]. The synthetic zinc finger proteins AZFP-U5, AZFP-M2, and AZFP-U3, including the Cyc2-His2-type DNA binding domain, increased cellulase production in T. reesei Rut-C30 [155,156,157]. The artificial transcriptional activators, named DBDace2-VP16 and DBDcre1-VP16, were engineered by fusing DNA binding domains from ACEII or CREI with the potent transcriptional activation domain VP16 from the herpes simplex virus [158]. The minimal transcriptional activators DBDace2-VP16 and DBDcre1-VP16 have the ability to increase cellulase production [154]. Recently, a novel mutation (R434L) in xylanase regulator 1 (Xyr1) was identified, leading to the significantly improved production of cellulases and xylanases in T. reesei [159].
In another study, the T. reesei Rut-C30 strain underwent six genetic modifications engineered using clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR-Cas9) technology. These modifications included the overexpression of XYR1 activator, the addition of heterologous β-glucosidase CEL3A and invertase SUC1, as well as the deletion of native repressor ACE1 and secreted proteases PEP1 and SLP1 [160].
Each of the T. reesei strains currently used in the industrial production of cellulase enzymes originates from the one T. reesei strain, QM6a [161,162]. Since its discovery, QM6a has had improvements in its secretion capability through random mutagenesis. One of the most successful strains resulted from multiple random mutagenesis events, generating the T. reesei Rut-C30 strain [163]. The improvements in the organism’s ability to secrete both native and recombinant proteins impact the production and secretion of the natively produced cellulase. Further improvements in the cellulase production of T. reesei have been demonstrated to be influenced by the truncation of a single transcription factor, ACE3 [134]. An engineered T. reesei strain harboring the introduced truncated version of the ACE3 gene has been revealed as a hyper-producer for the major cellobiohydrolase enzyme when compared to a strain containing the full-length native ACE3 gene [134]. The truncated ACE3 gene demonstrated an increase in the transcription levels of both positive regulators ACE3 and XYR1, as well as the transcription levels of the CBH1 gene. Additionally, a subsequent study demonstrated an enhancement in cellulase production in T. reesei through the disruption of multiple protease genes identified through comparative secretomics. The identified genes include three proteases: tre81070, tre120998, and tre123234 [135].
Another example using genetic engineering to optimize the cellulase system involves T. reesei mutant SEU-7. This strain was developed from the Rut-C30 strain by introducing an additional copy of the native gene β-glucosidase (BGL1) through insertional mutagenesis facilitated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation (AMT). In contrast to Rut-C30, SEU-7 exhibits significantly improved cellulase and hemicellulase activities when cultured on either lactose or cellulose substrates [164]. Genetic engineering of the T. reesei QEB4 strain resulted in the enhanced expression of native β-glucosidase and endoglucanase, as well as the production of cellulase enzymes with significantly enhanced bioconversion of filter paper. This modification also increased saccharification efficiency, leading to a remarkable 94.2% conversion of cellulose [165].
The potential methyltransferase Lae1/LaeA, functioning as a global regulator in fungal secondary metabolite production, is essential for (hemi-)cellulase expression in T. reesei. Through molecular engineering of promoters and regulatory networks, T. reesei has been genetically modified to express diverse heterologous proteins, overcoming the natural cellulase repression induced by glucose in wild-type T. reesei [166]. A T. reesei chassis strain was optimized for enhanced secondary metabolite biosynthesis through the deletion of major (hemi-)cellulase genes and overexpression of the transcriptional factor XYR1A824V. Significant improvements in ophiobolin F production were observed, with yields reaching 1187.06 mg/L in shake flask fermentation and 3072.45 mg/L under fed-batch conditions, utilizing glucose, lactose, and corn steep as substrates [167]. A recent study investigated the impact of Trctf1 gene knockout on cellulase synthesis in T. reesei induced by different soluble inducers. Enhanced cellulase activity was observed when lactose was employed, providing insights into the regulation of cellulase synthesis by various inducers and facilitating the development of high-yield cellulase gene-engineered strains [168].
One study has shown that site-directed mutagenesis of the T. harzianum β-glucosidase enzyme improved enzyme glucose tolerance, further optimizing the efficiency of this enzyme to work under higher glucose concentrations and release glucose during saccharification [169]. This dual amino acid substitution in the β-glucosidase enzyme has the potential to increase enzymatic hydrolysis of plant biomass in an industrial setting, further freeing fermentable glucose for ethanol production. Another genetic engineering strategy employed to enhance bioconversion of agro-industrial waste by T. reesei involves the reduction of secretion pressure through deletion of the endogenous cbh1 gene—for example, to enhance the heterologous expression of laccase (LacA) from Trametes sp. AH28-2 in T. reesei [30].
In summary, the ongoing advancements in genetic engineering of Trichoderma species, particularly T. reesei, highlight a promising trajectory towards optimizing enzyme production for lignocellulose bioprocesses. The strategies explored, ranging from the modification of native and synthetic promoters to the engineering of transcription factors and the application of CRISPR-Cas9 technology, underscore the complexity and potential of tailoring Trichoderma’s enzymatic systems. These innovations pave the way for more cost-effective and efficient bioconversion processes, addressing the critical need for scalable cellulase production in industrial applications. Moving forward, investigating the synergistic effects of combining multiple genetic modifications could lead to even greater improvements in Trichoderma’s enzymatic capabilities and enzyme stability. Additionally, exploring the role of post-translational modifications and their impact on enzyme performance might reveal new avenues for optimization. Expanding the use of high-throughput screening techniques to identify novel regulatory elements or genetic variations that enhance enzyme production could accelerate the development of superior strains. Finally, integrating systems biology approaches to model and predict the impact of genetic changes on the overall metabolic network of Trichoderma could provide a more holistic understanding of the factors influencing cellulase production. These research directions hold the potential to drive significant advancements in the field, contributing to more sustainable and efficient lignocellulose bioprocessing solutions.
7. Conclusions
Waste lignocellulosic biomass from agricultural, forestry, and other industry sources are being explored for use as renewable, clean, and abundant raw materials for the sustainable production of value-added bioproducts through microbial fermentation. In this respect, the genus Trichoderma has been widely investigated as the catalyst to successfully achieve waste reduction and product development via the bioconversion of renewable waste sources. Enzymatic hydrolysis of biowaste to yield fermentable sugars for subsequent bioethanol production, biological pre-treatment of crop residues to enhance animal nutrition, and the production of biocontrol agents are amongst the most widely investigated applications of fermentation–bioconversion by Trichoderma species. However, effective biological degradation of cellulose and hemicellulose substrates requires an efficient extracellular enzyme-secretion system. This has led to extensive research efforts to improve the technological development of Trichoderma-derived enzymatic activity via the optimization of pre-treatment and fermentation protocols, the identification of alternative waste substrates and microbial strains, the application of different enzyme mixtures and additives, and the development of genetically enhanced fermentative and cellulolytic microorganisms. Although scientific research regarding Trichoderma bioprocesses has evolved rapidly, further progress in key areas is still required in order to achieve economic viability at full commercial scale. This includes understanding how the chemical and physical characteristics of different lignocellulosic substrates affect enzyme production, as well as the microbial metabolic pathways, secretome composition, and synergic interactions involved in the fermentation process. Comprehensive research on and development of the economic aspects of waste biomass microbial utilization, such as capital cost estimation, the implementation of operation process standards, operating cost estimation, and profitability assessment, are also necessary.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.C.L. and C.J.H.; data curation, P.C.L., E.J. and P.K.; writing (original draft preparation), P.C.L.; writing (original draft of Section 5), E.J. and P.K.; writing (review and editing), P.C.L. and C.J.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Tom Loan for reviewing and providing feedback on the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kubicek, C.P.; Steindorff, A.S.; Chenthamara, K.; Manganiello, G.; Henrissat, B.; Zhang, J.; Cai, F.; Kopchinskiy, A.G.; Kubicek, E.M.; Kuo, A.; et al. Evolution and Comparative Genomics of the Most Common Trichoderma Species. BMC Genomics 2019, 20, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorai, P.S.; Barman, S.; Gond, S.K.; Mandal, N.C. Trichoderma. In Beneficial Microbes in Agro-Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 571–591. [Google Scholar]
- Adnan, M.; Islam, W.; Shabbir, A.; Khan, K.A.; Ghramh, H.A.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Lu, G. Plant Defense against Fungal Pathogens by Antagonistic Fungi with Trichoderma in Focus. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 129, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druzhinina, I.S.; Kubicek, C.P. Genetic Engineering of Trichoderma reesei Cellulases and Their Production. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1485–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, A.; Schmoll, M. Biology and Biotechnology of Trichoderma. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J. Trichoderma as Biocontrol Agent against Pests: New Uses for a Mycoparasite. Biol. Control 2021, 159, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preczeski, K.P.; Czapela, F.; Dalastra, C.; Kubeneck, S.; Klanovicz, N.; Fongaro, G.; Treichel, H. Trichoderma Potential in Biofuel Production and Biorefinery. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 221–239. [Google Scholar]
- Puranen, T.; Alapuranen, M.; Vehmaanperä, J. Trichoderma Enzymes for Textile Industries. In Biotechnology and Biology of Trichoderma; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 351–362. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Singh, V.K.; Aamir, M.; Dubey, M.K.; Patel, J.S.; Upadhyay, R.S.; Gupta, V.K. Cellulase in Pulp and Paper Industry. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 152–162. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Wu, M.; Fan, A.; Su, H. Recombinant Protein Production in the Filamentous Fungus Trichoderma. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 30, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Bunterngsook, B.; Li, J.-X.; Zhao, X.-Q.; Champreda, V.; Liu, C.-G.; Bai, F.-W. Regulation and Production of Lignocellulolytic Enzymes from Trichoderma reesei for Biofuels Production. Adv. Bioenergys 2019, 4, 79–119. [Google Scholar]
- Mujtaba, M.; Fernandes Fraceto, L.; Fazeli, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Savassa, S.M.; Araujo de Medeiros, G.; do Espírito Santo Pereira, A.; Mancini, S.D.; Lipponen, J.; Vilaplana, F. Lignocellulosic Biomass from Agricultural Waste to the Circular Economy: A Review with Focus on Biofuels, Biocomposites and Bioplastics. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 402, 136815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankar, A.R.; Pandey, A.; Modak, A.; Pant, K.K. Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass: A Review on Recent Advances. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 334, 125235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasić, K.; Knez, Ž.; Leitgeb, M. Bioethanol Production by Enzymatic Hydrolysis from Different Lignocellulosic Sources. Molecules 2021, 26, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.C. Hemicellulose Bioconversion. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putro, J.N.; Soetaredjo, F.E.; Lin, S.-Y.; Ju, Y.-H.; Ismadji, S. Pretreatment and Conversion of Lignocellulose Biomass into Valuable Chemicals. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 46834–46852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshayeshan-Agdam, H.; Salehi-Lisar, S.Y.; Zarrini, G. Lignocellulosic Biofuel Production Technologies and Their Applications for Bioenergy Systems. In Biofuels Production—Sustainability and Advances in Microbial Bioresources. Biofuel and Biorefinery Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 287–306. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, A.; Shah, A.R. Integrated Lignocellulosic Biorefinery: Gateway for Production of Second Generation Ethanol and Value Added Products. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 108–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, N.; Ghosh, S.K.; Bannerjee, S.; Aikat, K. Bioethanol Production from Agricultural Wastes: An Overview. Renew. Energy 2012, 37, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Chang, X.; Chen, D.; Xue, Y.; Liu, P.; Lin, H.; Han, S. A Review on the Pretreatment of Lignocellulose for High-Value Chemicals. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 160, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanakumar, K.; Kathiresan, K. Bioconversion of Lignocellulosic Waste to Bioethanol by Trichoderma and Yeast Fermentation. 3 Biotech 2014, 4, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raud, M.; Kikas, T.; Sippula, O.; Shurpali, N.J. Potentials and Challenges in Lignocellulosic Biofuel Production Technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 111, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, S.J.; Vaaje-Kolstad, G.; Westereng, B.; Eijsink, V. Novel Enzymes for the Degradation of Cellulose. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2012, 5, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Sun, S.; Cao, X.; Sun, R. The Role of Pretreatment in Improving the Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lignocellulosic Materials. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbe, M.; Zacchi, G. Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Materials for Efficient Bioethanol Production. In Biofuels; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 41–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zeng, S.; Xia, Y.; Xia, L. Expression of a Thermotolerant Laccase from Pycnoporus sanguineus in Trichoderma reesei and Its Application in the Degradation of Bisphenol A. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 125, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hong, Y.; Li, K.; Sun, Y.; Yao, C.; Ling, J.; Zhong, Y. Enhancing the Production of a Heterologous Trametes Laccase (LacA) by Replacement of the Major Cellulase CBH1 in Trichoderma reesei. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 50, kuad002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiiskinen, L.-L.; Kruus, K.; Bailey, M.; Ylösmäki, E.; Siika-aho, M.; Saloheimo, M. Expression of Melanocarpus albomyces Laccase in Trichoderma reesei and Characterization of the Purified Enzyme. Microbiology 2004, 150, 3065–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, R.M.; Manavalan, T.; Ramesh, J.; Thangavelu, K.P.; Heese, K. Improvement of Saccharification and Delignification Efficiency of Trichoderma reesei Rut-C30 by Genetic Bioengineering. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qu, Y.; Xiao, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; He, F. Improved Biomass Saccharification by Trichoderma reesei through Heterologous Expression of LacA Gene from Trametes Sp. AH28-2. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2012, 113, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, J.; Zhang, G.; Chao, Y.; Li, Z.; Ye, Q.; Qian, S. Co-Expression of Beta-Glucosidase and Laccase in Trichoderma reesei by Random Insertion with Enhanced Filter Paper Activity. Mol. Biotechnol. 2017, 59, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, R.P.; Bura, R.; Mabee, W.E.; Berlin, A.; Pan, X.; Saddler, J.N. Substrate Pretreatment: The Key to Effective Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lignocellulosics? In Biofuels; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 67–93. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, K.; Fan, L.; Luo, X. Identification of Laccase Genes in Trichoderma Asperellum Ts93. Biotechnol Lett 2023, 45, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, F.; Karimi, M.; Biria, D.; Kariminia, H.R.; Jeihanipour, A. Enhancement of Fungal Delignification of Rice Straw by Trichoderma viride sp. to Improve Its Saccharification. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 101, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölker, U.; Dohse, J.; Höfer, M. Extracellular Laccases in Ascomycetes Trichoderma atroviride and Trichoderma harzianum. Folia Microbiol. 2002, 47, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.M.; Mahmoud, M.; Abdelraof, M.; Abdel Karim, G.S.A.; Elsayed, A.M. Enhancement of Laccase Production from a Newly Isolated Trichoderma harzianum S7113 Using Submerged Fermentation: Optimization of Production Medium via Central Composite Design and Its Application for Hydroquinone Degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djali, M.; Kayaputri, I.L.; Kurniati, D.; Sukarminah, E.; Mudjenan, I.M.H.; Utama, G.L. Degradation of Lignocelluloses cocoa Shell (Theobroma cacao L.) by Various Types of Mould Treatments. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, R.; Kuthiala, T.; Singh, G.; Rarotra, S.; Kaur, A.; Arya, S.K.; Kumar, P. Current Status of Xylanase for Biofuel Production: A Review on Classification and Characterization. Biomass. Convers. Biorefin. 2023, 13, 8773–8791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kumar, B.; Verma, P. A Detailed Overview of Xylanases: An Emerging Biomolecule for Current and Future Prospective. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2019, 6, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polizeli, M.L.T.M.; Rizzatti, A.C.S.; Monti, R.; Terenzi, H.F.; Jorge, J.A.; Amorim, D.S. Xylanases from Fungi: Properties and Industrial Applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 67, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaver, P.; Pletschke, B.; Sithole, B.; Govinden, R. Optimization, Purification, and Characterization of Xylanase Production by a Newly Isolated Trichoderma harzianum Strain by a Two-Step Statistical Experimental Design Strategy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alananbeh, K.M.; Alkfoof, R.; Muhaidat, R.; Massadeh, M. Production of Xylanase by Trichoderma Species Growing on Olive Mill Pomace and Barley Bran in a Packed-Bed Bioreactor. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Faria, F.P.; Te’O, V.S.J.; Bergquist, P.L.; Azevedo, M.O.; Nevalainen, K.M.H. Expression and Processing of a Major Xylanase (XYN2) from the Thermophilic Fungus Humicola grisea var. thermoidea in Trichoderma reesei. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 34, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, S.; Sona Gauri, S.; Das, A.; Jana, A.; Maity, C.; Mandal, A.; Das Mohapatra, P.K.; Pati, B.R.; Mondal, K.C. Process Optimization of Xylanase Production Using Cheap Solid Substrate by Trichoderma reesei SAF3 and Study on the Alteration of Behavioral Properties of Enzyme Obtained from SSF and SmF. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 36, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Luo, L.; Wang, E.; Wang, R.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Yuan, H. Low-Cost Cellulase-Hemicellulase Mixture Secreted by Trichoderma harzianum EM0925 with Complete Saccharification Efficacy of Lignocellulose. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Mendoza, D.P.; Junqueira, M.; do Vale, L.H.F.; Domont, G.B.; Ferreira Filho, E.X.; de Sousa, M.V.; Ricart, C.A.O. Secretomic Survey of Trichoderma harzianum Grown on Plant Biomass Substrates. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 1810–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajijolakewu, K.A.; Leh, C.P.; Lee, C.K.; Wan Nadiah, W.A. Characterization of Novel Trichoderma Hemicellulase and Its Use to Enhance Downstream Processing of Lignocellulosic Biomass to Simple Fermentable Sugars. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 11, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Xing, M.; Yu, S.; Liu, G. Achieving Efficient Protein Expression in Trichoderma reesei by Using Strong Constitutive Promoters. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.-W. Rational Engineering of Xylanase Hyper-Producing System in Trichoderma reesei for Efficient Biomass Degradation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira Filho, J.A.; Horta, M.A.C.; Beloti, L.L.; dos Santos, C.A.; de Souza, A.P. Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes in Trichoderma harzianum: A Bioinformatic Analysis Bioprospecting for Key Enzymes for the Biofuels Industry. BMC Genomics 2017, 18, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, I.J.; van Wyk, N.; Smit, S.; Jacobson, D.; Viljoen-Bloom, M.; Volschenk, H. Comparative Secretome Analysis of Trichoderma asperellum S4F8 and Trichoderma reesei Rut C30 during Solid-State Fermentation on Sugarcane Bagasse. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saloheimo, M.; Kuja-Panula, J.; Ylösmäki, E.; Ward, M.; Penttilä, M. Enzymatic Properties and Intracellular Localization of the Novel Trichoderma reesei β-Glucosidase BGLII (Cel1A). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4546–4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Steindorff, A.S.; de Paula, R.G.; Silva-Rocha, R.; Mach-Aigner, A.R.; Mach, R.L.; Silva, R.N. The Post-Genomic Era of Trichoderma reesei: What’s Next? Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 970–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandeep; Liu, H.; Shukla, P. Synthetic Biology and Biocomputational Approaches for Improving Microbial Endoglucanases toward Their Innovative Applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 6055–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, R.H.; Ramoni, J.; Seiboth, B. Cellulases and beyond: The First 70 Years of the Enzyme Producer Trichoderma reesei. Microb. Cell Fact. 2016, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani Singhania, R.; Dixit, P.; Kumar Patel, A.; Shekher Giri, B.; Kuo, C.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Di Dong, C. Role and Significance of Lytic Polysaccharide Monooxygenases (LPMOs) in Lignocellulose Deconstruction. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 335, 125261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloheimo, M.; Paloheimo, M.; Hakola, S.; Pere, J.; Swanson, B.; Nyyssönen, E.; Bhatia, A.; Ward, M.; Penttilä, M. Swollenin, a Trichoderma reesei Protein with Sequence Similarity to the Plant Expansins, Exhibits Disruption Activity on Cellulosic Materials. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 4202–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Chen, X.; Xue, Y.; Hu, J.; Gao, M.-T.; Tsang, Y.F. The Influence of Soluble Polysaccharides Derived from Rice Straw upon Cellulase Production by Trichoderma reesei. Process Biochem. 2017, 61, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, G.S.; Oberoi, H.S.; Kaur, S.; Bansal, S.; Brar, S.K. Value-Addition of Agricultural Wastes for Augmented Cellulase and Xylanase Production through Solid-State Tray Fermentation Employing Mixed-Culture of Fungi. Ind. Crops Prod. 2011, 34, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuvelayudham, R.; Deiveegan, S.; Viruthagiri, T. Triggering of Cellulase Protein Production Using Cellulose with Lactose by Trichoderma reesei. Asian J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci. 2006, 8, 249–251. [Google Scholar]
- Salomão, G.S.B.; Agnezi, J.C.; Paulino, L.B.; Hencker, L.B.; de Lira, T.S.; Tardioli, P.W.; Pinotti, L.M. Production of Cellulases by Solid State Fermentation Using Natural and Pretreated Sugarcane Bagasse with Different Fungi. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocky-Salimi, K.; Hamidi-Esfahani, Z. Evaluation of the Effect of Particle Size, Aeration Rate and Harvest Time on the Production of Cellulase by Trichoderma reesei QM9414 Using Response Surface Methodology. Food Bioprod. Process. 2010, 88, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, R.K.; Singhania, R.R.; Mathew, G.M.; Pandey, A. Cellulase Production Using Biomass Feed Stock and Its Application in Lignocellulose Saccharification for Bio-Ethanol Production. Renew. Energy 2009, 34, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Su, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Chen, H.; Yu, X.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G. Establishment of a Highly Efficient and Low Cost Mixed Cellulase System for Bioconversion of Corn Stover by Trichoderma reesei and Aspergillus niger. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 32, 101849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodha, A.; Pawar, S.; Rathod, V. Optimised Cellulase Production from Fungal Co-Culture of Trichoderma reesei NCIM 1186 and Penicillium citrinum NCIM 768 under Solid State Fermentation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Zhao, C.; Song, X.-Y. Optimization of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Steam-Exploded Corn Stover by Two Approaches: Response Surface Methodology or Using Cellulase from Mixed Cultures of Trichoderma reesei RUT-C30 and Aspergillus niger NL02. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 4111–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Kumar, V. Impact of Process Parameters and Plant Polysaccharide Hydrolysates in Cellulase Production by Trichoderma reesei and Neurospora crassa under Wheat Bran Based Solid State Fermentation. Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 25, e00416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshi, G.; Giridhar, S. Induction and Optimization of Cellulases Using Various Agro-Wastes by Trichoderma virdii: Effect of Alkali Pretreatment. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 3426–3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, L.; Mehmood, M.A.; Zhao, X.; Bai, F. On-Site Cellulase Production and Efficient Saccharification of Corn Stover Employing Cbh2 Overexpressing Trichoderma reesei with Novel Induction System. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghuwanshi, S.; Deswal, D.; Karp, M.; Kuhad, R.C. Bioprocessing of Enhanced Cellulase Production from a Mutant of Trichoderma asperellum RCK2011 and Its Application in Hydrolysis of Cellulose. Fuel 2014, 124, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhai, L.; Geng, A. Enhanced Cellulase and Reducing Sugar Production by a New Mutant Strain Trichoderma harzianum EUA20. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 129, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirohi, R.; Singh, A.; Tarafdar, A.; Shahi, N.C.; Verma, A.K.; Kushwaha, A. Cellulase Production from Pre-Treated Pea Hulls Using Trichoderma reesei Under Submerged Fermentation. Waste Biomass. Valoriz. 2019, 10, 2651–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, Y.M.; Heo, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, K.Y.; Kim, J.-J. Utilization of Agricultural Residues for Enhancement of Cellulolytic Enzyme Production and Enzymatic Saccharification by Trichoderma harzianum KUC1716. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smuga-Kogut, M.; Zgórska, K.; Kogut, T.; Kukiełka, K.; Wojdalski, J.; Kupczyk, A.; Dróżdż, B.; Wielewska, I. The Use of Ionic Liquid Pretreatment of Rye Straw for Bioethanol Production. Fuel 2017, 191, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libardi, N.; Soccol, C.R.; Góes-Neto, A.; de Oliveira, J.; Vandenberghe, L.P.d.S. Domestic Wastewater as Substrate for Cellulase Production by Trichoderma harzianum. Process Biochem. 2017, 57, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.S.O.; Pandey, A.; Rao, S.S.; Sukumaran, R.K. Cellulase Production through Solid-State Tray Fermentation, and Its Use for Bioethanol from Sorghum Stover. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 242, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwarasak, P.; Pajantagate, P.; Prasertlertrat, K. Use of Trichoderma reesei RT-P1 Crude Enzyme Powder for Ethanol Fermentation of Sweet Sorghum Fresh Stalks. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.; Anwar, Z.; But, H.I.; Afroz, A.; Ikram, N.; Rashid, U. The Industrial Applicability of Purified Cellulase Complex Indigenously Produced by Trichoderma viride through Solid-State Bio-Processing of Agro-Industrial and Municipal Paper Wastes. Bioresources 2013, 8, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omojasola, P.F.; Jilani, O.P. Cellulase Production by Trichoderma longi, Aspergillus niger and Saccharomyces cerevisae Cultured on Waste Materials from Orange. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 11, 2382–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannahi, M.; Elangeswari, S. Enhanced Production of Cellulase on Different Fruit Peel Under Submerged Fermentation. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2015, 32, 161–165. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, P.; Muthuvelayudham, R.; Viruthagiri, T. Enhanced Production of Cellulase from Pineapple Waste by Response Surface Methodology. J. Eng. 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, P.; Muthuvelayudham, R.; Rajesh Kannan, R.; Viruthagiri, T. Optimization of Cellulase Production Using Trichoderma reesei by RSM and Comparison with Genetic Algorithm. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2012, 6, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, S. Effect of Cellulase Production by Fungi Cultured on Banana Waste. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2016, 4, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordillo-Fuenzalida, F.; Echeverria-Vega, A.; Cuadros-Orellana, S.; Faundez, C.; Kähne, T.; Morales-Vera, R. Cellulases Production by a Trichoderma sp. Using Food Manufacturing Wastes. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, N.; Kumar, V.; Bansal, M.C. Utility of Luffa cylindrica and Litchi chinensis Peel, an Agricultural Waste Biomass in Cellulase Production by Trichoderma reesei under Solid State Cultivation. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, F.; Geng, A. Horticultural Waste as the Substrate for Cellulase and Hemicellulase Production by Trichoderma reesei Under Solid-State Fermentation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja Sathendra, E.; Baskar, G.; Praveenkumar, R.; Gnansounou, E. Bioethanol Production from Palm Wood Using Trichoderma reesei and Kluveromyces marxianus. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 271, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittanan, T.; Nareerat, L.; Sawwanit, K.; Teerin, C. Uses of Copra Waste and Wheat Bran for Cellulase Production by Trichoderma reesei in Solid State Fermentation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2018 8th International Conference on Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics—ICBBB 2018, Tokyo, Japan, 18–20 January 2018; ACM Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, P.; Singh, J.; Scaria, J.; Anand, A.P. Improved Production of Cellulase by Trichoderma reesei (MTCC 164) from Coconut Mesocarp-Based Lignocellulosic Wastes under Response Surface-Optimized Condition. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, M.; Kalra, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Sangwan, R.S. Cellulase Production by Six Trichoderma spp. Fermented on Medicinal Plant Processings. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, V.; Bhatt, A.K. Trichoderma Viride (MTCC 800): A Potential Candidate for Agri-Horti Waste Utilization by Solid State Fermentation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 15, 2679–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reczey, K.; Szengyel, Z.; Eklund, R.; Zacchi, G. Cellulase Production by Trichoderma reesei. Bioresour. Technol. 1996, 57, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damisa, D.; Sule, E.I.; Moneme, S. Cellulase Production from Waste Paper Using Trichoderma Species Isolated from Rhizospheric Soil. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 16342–16346. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, L.-K.; Afolabi, O.A. Wastepaper Hydrolysate as Soluble Inducing Substrate for Cellulase Production in Continuous Culture of Trichoderma reesei. Biotechnol. Prog. 1999, 15, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.; Eischer, A.; Tadic, T.; Gritsch, S.M.; Ortner, M.; Prall, K.; Neunteufel, E.; Putz, R.F.; Guebitz, G.M.; Nyanhongo, G.S. Valorisation of Slaughter House and Deinking Paper Waste Streams for the Production of Enzyme by Trichoderma reesei. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 122882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotkar, P. Bioconversion of Waste Paper into Bio-Ethanol by Co-Culture of Fungi Isolated from Lignocellulosic Waste. Int. J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2016, 4, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Dale, B.E. Global Potential Bioethanol Production from Wasted Crops and Crop Residues. Biomass. Bioenergy 2004, 26, 361–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.K.; Chatterjee, S.; Mazumder, P.B.; Gupta, S.K.; Sharma, S.; Vairale, M.G.; Datta, S.; Dwivedi, S.K.; Gupta, D.K. Bioethanol Production from Waste Lignocelluloses: A Review on Microbial Degradation Potential. Chemosphere 2019, 231, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusakov, A.V. Alternatives to Trichoderma reesei in Biofuel Production. Trends Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhomodi, A.F.; Gibbons, W.R.; Karki, B. Estimation of Cellulase Production by Aureobasidium pullulans, Neurospora crassa, and Trichoderma reesei during Solid and Submerged State Fermentation of Raw and Processed Canola Meal. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 18, 101063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarsaiya, S.; Awasthi, S.K.; Awasthi, M.K.; Awasthi, A.K.; Mishra, S.; Chen, J. The Dynamic of Cellulase Activity of Fungi Inhabiting Organic Municipal Solid Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 251, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Bai, F. Constitutive Cellulase Production from Glucose Using the Recombinant Trichoderma reesei Strain Overexpressing an Artificial Transcription Activator. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 223, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitranshi, R.; Kapoor, R. Utilization of Over-Ripened Fruit (Waste Fruit) for the Eco-Friendly Production of Ethanol. Vegetos 2021, 34, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktavianis, T.; Sofiyanita, S. Making Bioethanol From Cocoa Fruit Skin Waste By Hydrolysis Process Using Trichoderma viride Mold. Indones. J. Chem. Sci. Technol. IJCST 2020, 2, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska, U.; Kowalska, B.; Kowalczyk, W.; Szczech, M. The Use of Agro-Industrial Wastes as Carriers of Trichoderma Fungi in the Parsley Cultivation. Sci. Hortic. 2014, 179, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, A.; Gelebo, G.G.; Tesfaye, T.; Mengie, W.; Mebrate, M.A.; Abuhay, A.; Limeneh, D.Y. Pulp and Paper Mill Wastes: Utilizations and Prospects for High Value-Added Biomaterials. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, J.; Mast-Gerlach, E.; Popović, M.K.; Bajpai, R.; Stahl, U. Relevance of Microbial Coculture Fermentations in Biotechnology. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Wang, S.; Xu, F.; Xiao, G.; Bai, J. Efficient Utilization of Waste Paper as an Inductive Feedstock for Simultaneous Production of Cellulase and Xylanase by Trichoderma longiflorum. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 308, 127287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, A.; Barrena, R.; Artola, A.; Sánchez, A. Current Developments in the Production of Fungal Biological Control Agents by Solid-State Fermentation Using Organic Solid Waste. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 655–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zin, N.A.; Badaluddin, N.A. Biological Functions of Trichoderma spp. for Agriculture Applications. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2020, 65, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Kumar, D. Trichoderma: A Beneficial Antifungal Agent and Insights into Its Mechanism of Biocontrol Potential. Egypt J. Biol. Pest Control 2020, 30, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Jin, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Z. Utilization of Winery Wastes for Trichoderma viride Biocontrol Agent Production by Solid State Fermentation. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalili, E.; Huyop, F.; Myra Abd Manan, F.; Wahab, R.A. Optimization of Cultivation Conditions in Banana Wastes for Production of Extracellular β-Glucosidase by Trichoderma harzianum Rifai Efficient for in vitro Inhibition of Macrophomina phaseolina. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2017, 31, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ali Khan, R.A.; Wei, H.; Wang, R.; Hou, J.; Liu, T. Rapid and Mass Production of Biopesticide Trichoderma Brev T069 from Cassava Peels Using Newly Established Solid-State Fermentation Bioreactor System. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, A.; Vittone, S.; Barrena, R.; Sánchez, A.; Artola, A. Scanning Agro-Industrial Wastes as Substrates for Fungal Biopesticide Production: Use of Beauveria bassiana and Trichoderma harzianum in Solid-State Fermentation. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De los Santos-Villalobos, S.; Hernández-Rodríguez, L.E.; Villaseñor-Ortega, F.; Peña-Cabriales, J.J. Production of Trichoderma asperellum T8a Spores by a “Home-made” Solid-State Fermentation of Mango Industrial Wastes. Bioresources 2012, 7, 4938–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimi, S.; Khosravi, V.; Varga, A.; Vágvölgyi, C.; Kredics, L. Screening of Organic Substrates for Solid-State Fermentation, Viability and Bioefficacy of Trichoderma harzianum AS12-2, a Biocontrol Strain Against Rice Sheath Blight Disease. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalla, S.M.M.; Abdel-Kader, M.M.; El-Gamal, N.G.; El-Mougy, N.S. Using Maize Wastes, Fermented by Co-Cultures of Trichoderma harzianum and Pseudomonas fluorescens, as Grain Dressing against m Maize Diseases under Field Conditions. Egypt J. Biol. Pest Control 2020, 30, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, V.; Cheepurupalli, L.; Rathore, S.S.; Ramakrishnan, J. Co-Culture: A Promising Method In Enzyme Production. Int. J. Chemtech Res. 2017, 10, 720–726. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Duan, W.; Liu, C.; Meng, L.; Li, H.; Li, R.; Shen, Q. Spore Production in the Solid-State Fermentation of Stevia Residue by Trichoderma guizhouense and Its Effects on Corn Growth. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorta-Vásquez, R.; Valbuena, O.; Pavone-Maniscalco, D. Solid-State Fermentation of Paper Sludge to Obtain Spores of the Fungus Trichoderma asperellum. EuroBiotech J. 2019, 3, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Piwowarek, K.; Kot, A.M.; Pobiega, K. The Aspects of Microbial Biomass Use in the Utilization of Selected Waste from the Agro-Food Industry. Open Life Sci. 2020, 15, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.W.; Karpol, A.; Friedman, S.; Maru, B.T.; Tracy, B.P. Recent Advances in Single Cell Protein Use as a Feed Ingredient in Aquaculture. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2020, 61, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Aziz, N.A.; Salem, A.Z.M.; El-Adawy, M.M.; Camacho, L.M.; Kholif, A.E.; Elghandour, M.M.Y.; Borhami, B.E. Biological Treatments as a Mean to Improve Feed Utilization in Agriculture Animals—An Overview. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 534–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmare, B. Biological Treatment of Crop Residues as an Option for Feed Improvement in the Tropics: A Review. Anim. Husb. Dairy Vet. Sci. 2020, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siada, O.; Negm, M.; Basiouny, M.; Fouad, M.; Elagroudy, S. Protein Enrichment of Agro–Industrial Waste by Trichoderma harzianum EMCC 540 through Solid State Fermentation for Use as Animal Feed. J. Geogr. Environ. Earth Sci. Int. 2018, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, M.; El-Ghonemy, D.H. Biological Fungal Treatment of Olive Cake for Better Utilization in Ruminants Nutrition in Egypt. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2015, 4, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islamiyati, R.; Rasjid, S.; Natsir, A. Crude Protein and Fiber Fraction of Corn Stover Inoculated by Fungi Trichoderma sp. and Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Res. 2013, 2, 149–152. [Google Scholar]
- Helal, G.A. Bioconversion of Straw Into Improved Fodder: Mycoprotein Production and Cellulolytic Acivity of Rice Straw Decomposing Fungi. Mycobiology 2005, 33, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setiyatwan, H.; Harlia, E.; Rusmana, D.; Benito, T.; Adriani, L. Effect of Fermentation Using Trichoderma harzianum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on Crude Protein, Crude Fibre and Zinc Content of Duckweed. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2018, 17, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Mustafa, G.; Arshad, M.; Rajoka, M.I. Fungal Biomass Protein Production from Trichoderma harzianum Using Rice Polishing. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, M.; Said, S.D. Trichoderma reesei Single Cell Protein Production from Rice Straw Pulp in Solid State Fermentation. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 345, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayitse, R.; Hou, X.; Laryea, G.; Bjerre, A.-B. Protein Enrichment of Cassava Residue Using Trichoderma pseudokoningii (ATCC 26801). AMB Express 2015, 5, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okab, A.B.; Ayoub, M.A.; Samara, E.M.; Abdoun, K.A.; Al-Haidary, A.A.; Koriem, A.A.; Hassan, A.A. Improvement of Growth and Nitrogen Utilization in Sheep Using Sugar Beet Pulp Treated with Trichoderma reesei or Urea. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2012, 44, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.-G.; Lin, W.-C.; Lo, C.-T.; Chang, S.-C.; Yu, B.; Lee, T.-T. Effects of Substitution of Bermuda Grass Hay with Trichoderma Fermented Rice Straw on Growth, Blood, and Rumen Fluid Parameters in Barbados Sheep. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2018, 46, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Azim, S.; Ahmed, M.; Abo-Donia, F.; Soliman, H. Evaluation of Fungal Treatment of Some Agricultural Residues. Egypt. J. Sheep Goats Sci. 2011, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Abo-Donia, F.M.; Abdel-Azim, S.N.; Elghandour, M.M.Y.; Salem, A.Z.M.; Buendía, G.; Soliman, N.A.M. Feed Intake, Nutrient Digestibility and Ruminal Fermentation Activities in Sheep-Fed Peanut Hulls Treated with Trichoderma viride or Urea. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2014, 46, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szijártó, N.; Faigl, Z.; Réczey, K.; Mézes, M.; Bersényi, A. Cellulase Fermentation on a Novel Substrate (Waste Cardboard) and Subsequent Utilization of Home-Produced Cellulase and Commercial Amylase in a Rabbit Feeding Trial. Ind. Crops Prod. 2004, 20, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, H.A.A.; Ali, F.A.F.; Gad, S.M. Replacement of Clover Hay by Biologically Treated Corn Stalks in Growing Sheep Rations. J. Agric. Sci. 2012, 4, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadin, M.S.Y.; Abu-Reesh, I.M.; Haddadin, F.A.S.; Robinson, R.K. Utilisation of Tomato Pomace as a Substrate for the Production of Vitamin B12—A Preliminary Appraisal. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 78, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langsdorf, A.; Volkmar, M.; Holtmann, D.; Ulber, R. Material Utilization of Green Waste: A Review on Potential Valorization Methods. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, O.; Siri-Anusornsak, W.; Petchkongkaew, A.; Elliott, C. A Systematic Review of Global Occurrence of Emerging Mycotoxins in Crops and Animal Feeds, and Their Toxicity in Livestock. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, C. Biotechnological Advances and Trends in Engineering Trichoderma reesei towards Cellulase Hyperproducer. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2021, 26, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloheimo, M.; Haarmann, T.; Mäkinen, S.; Vehmaanperä, J. Production of Industrial Enzymes in Trichoderma reesei. In Gene Expression Systems in Fungi: Advancements and Applications. Fungal Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 23–57. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y.; Tu, T.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Luo, H.; Yao, B.; et al. Engineering the Cbh1 Promoter of Trichoderma reesei for Enhanced Protein Production by Replacing the Binding Sites of a Transcription Repressor ACE1 to Those of the Activators. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saloheimo, A.; Aro, N.; Ilmén, M.; Penttilä, M. Isolation of the Ace1 Gene Encoding a Cys2-His2 Transcription Factor Involved in Regulation of Activity of the Cellulase Promoter Cbh1of Trichoderma reesei. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 5817–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T.; Shida, Y.; Kitagami, N.; Mori, K.; Kato, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Okada, H.; Ogasawara, W.; Morikawa, Y. Identification of Specific Binding Sites for XYR1, a Transcriptional Activator of Cellulolytic and Xylanolytic Genes in Trichoderma reesei. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2009, 46, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aro, N.; Saloheimo, A.; Ilmén, M.; Penttilä, M. ACEII, a Novel Transcriptional Activator Involved in Regulation of Cellulase and Xylanase Genes of Trichoderma reesei. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 24309–24314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeilinger, S.; Ebner, A.; Marosits, T.; Mach, R.; Kubicek, C. The Hypocrea Jecorina HAP 2/3/5 Protein Complex Binds to the Inverted CCAAT-Box (ATTGG) within the Cbh2 (Cellobiohydrolase II-Gene) Activating Element. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2001, 266, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.; Shi, S.; Jiang, Y.; van den Brink, J.; de Vries, R.P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Z. Construction of a Cellulase Hyper-Expression System in Trichoderma reesei by Promoter and Enzyme Engineering. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesenhofer, D.P.; Mach, R.L.; Mach-Aigner, A.R. Influence of Cis Element Arrangement on Promoter Strength in Trichoderma reesei. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassinger, A.; Gacek-Matthews, A.; Strauss, J.; Mach, R.L.; Mach-Aigner, A.R. Truncation of the Transcriptional Repressor Protein Cre1 in Trichoderma reesei Rut-C30 Turns It into an Activator. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2018, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhao, X.; Bai, F. Improvement of Cellulase Production in Trichoderma reesei Rut-C30 by Overexpression of a Novel Regulatory Gene Trvib-1. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, W.; Wei, D. Enhanced Cellulase Production in Trichoderma reesei RUT C30 via Constitution of Minimal Transcriptional Activators. Microb. Cell Fact. 2018, 17, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Bai, F.; Zhao, X. Enhanced Cellulase Production from Trichoderma reesei Rut-C30 by Engineering with an Artificial Zinc Finger Protein Library. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 11, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhang, F.; Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Bai, F. Identification of a Novel Repressor Encoded by the Putative Gene Ctf1 for Cellulase Biosynthesis in Trichoderma reesei through Artificial Zinc Finger Engineering. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 1747–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Li, J.-X.; Champreda, V.; Liu, C.-G.; Bai, F.-W.; Zhao, X.-Q. Global Reprogramming of Gene Transcription in Trichoderma reesei by Overexpressing an Artificial Transcription Factor for Improved Cellulase Production and Identification of Ypr1 as an Associated Regulator. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadowski, I.; Ma, J.; Triezenberg, S.; Ptashne, M. GAL4-VP16 Is an Unusually Potent Transcriptional Activator. Nature 1988, 335, 563–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhang, W.; Meng, X.; Liu, W. Single Mutation in Transcriptional Activator Xyr1 Enhances Cellulase and Xylanase Production in Trichoderma Reesei on Glucose. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 11993–12003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.M.; Parreiras, L.S.; Murakami, M.T. Rational Engineering of the Trichoderma reesei RUT-C30 Strain into an Industrially Relevant Platform for Cellulase Production. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2020, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reese, E.T. History of the Cellulase Program at the U.S. Army Natick Development Center. Biotechnol. Bioeng. Symp. 1976, 6, 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mandels, M.; Reese, E.T. Induction of Cellulase in Trichoderma viride as Influenced by Carbon Sources and Metals. J. Bacteriol. 1957, 73, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eveleigh, D.E.; Montenecourt, B.S. Increasing Yields of Extracellular Enzymes. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 1979, 25, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lin, F.; Zhou, L.; Qin, L.; Li, B.; Zhou, Z.; Jin, M.; Chen, Z. Cellulase Hyper-Production by Trichoderma reesei Mutant SEU-7 on Lactose. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhong, L.; Gao, J.; Sun, N.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Qu, Y.; Zhong, Y. Production of Highly Efficient Cellulase Mixtures by Genetically Exploiting the Potentials of Trichoderma reesei Endogenous Cellulases for Hydrolysis of Corncob Residues. Microb. Cell Fact. 2017, 16, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiboth, B.; Karimi, R.A.; Phatale, P.A.; Linke, R.; Hartl, L.; Sauer, D.G.; Smith, K.M.; Baker, S.E.; Freitag, M.; Kubicek, C.P. The Putative Protein Methyltransferase LAE1 Controls Cellulase Gene Expression in Trichoderma reesei. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 84, 1150–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhu, Z.; Tian, E.; Yang, C.; Ma, E.; Zou, G.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Repurposing the Cellulase Workhorse Trichoderma reesei as a ROBUST Chassis for Efficient Terpene Production. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 7362–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Peng, N.; Ran, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, L.; Li, Y. The Influence of Trctf1 Gene Knockout by CRISPR–Cas9 on Cellulase Synthesis by Trichoderma reesei with Various Soluble Inducers. Fermentation 2023, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.A.; Morais, M.A.B.; Terrett, O.M.; Lyczakowski, J.J.; Zanphorlin, L.M.; Ferreira-Filho, J.A.; Tonoli, C.C.C.; Murakami, M.T.; Dupree, P.; Souza, A.P. An Engineered GH1 β-Glucosidase Displays Enhanced Glucose Tolerance and Increased Sugar Release from Lignocellulosic Materials. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).