Abstract
Availability of feedstock is one of the uncertainties impeding cellulosic biofuel production, and conservation of whole crop biomass as silage is a promising method to ensure year-round feedstock availability for biofuel production. This study investigated lignocellulose degradation and subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis of a 90-d sorghum silage incorporated with soybean and inoculated with Lactobacillus plantarum A1 in a three (0, 25, and 50%; soybean inclusions) by two (uninoculated and inoculated) factorial experiment. The results revealed that L. plantarum A1 inoculated silages had improved fermentation characteristics. The silages’ total N and non-fiber carbohydrate increased with L. plantarum A1 and soybean inclusion (p < 0.05). Inoculation also increased the residual water-soluble carbohydrate by 33.9% (p < 0.05). Inoculation and soybean inclusion significantly hydrolyzed the biomass’ lignocellulose, altered its morphology and microstructural matrix, increased production of ferulic acid and reduced the biomass crystallinity by 15.60% (p < 0.05). L. plantarum A1 inoculation × soybean inclusion improved glucose yield and cellulose conversion during enzymatic saccharification compared to uninoculated treatments. Therefore, incorporating soybean into sorghum silage with L. plantarum A1 inoculation enhanced fermentation quality, lignocellulose degradation and enzymatic saccharification which could serve as a sure way for sustainable year-round feedstock supply for enhanced biofuel production.
1. Introduction
Lignocellulosic biofuel production provides a sustainable renewable energy that could ameliorate the global energy crisis. The process mainly utilizes carbon from structural carbohydrates in a three-step process: pretreatment, saccharification and final fermentation [1]. Year-round feedstock availability is among the uncertainties impeding cellulosic biofuel production [2,3]. Conservation of whole crop biomass as silage is a promising method to ensure year-round feedstock availability [4]. Additionally, the proposed decentralization of biofuel production through small-scale farm production [5] to provide cleaner, renewable and environment friendly energy for the farming activities could be achieved through the use of ensiled feedstocks from forage crops. Ensilage conserves the biomass quality through anaerobic microbial fermentation. Dry matter (DM) is well preserved and recovered when excellent fermentation is achieved. Pretreatment in biofuel production process is essential for biomass delignification and decrystallization to facilitate subsequent enzymatic or acid hydrolysis. Ensilage alone is considered biomass pretreatment, however, additives such as mineral acids [6], enzymes and biological inoculants [7,8,9], organic acids [10], or tannins are used to achieve desirable silage fermentation. Biological inoculants have recently gained much attention. Several studies have reported the efficacy of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) for improved silage fermentation [11,12,13,14].
Sorghum is a high yielding forage crop that is drought tolerant with high water use efficiency. It performs well in different climatic regions with limited and variable rainfall condition, which made it an excellent alternative silage crop and increased its acceptance as a maize replacement in such areas [15,16]. Several sorghum varieties have been developed and broadly categorized into grain and forage sorghum. F10 Sorghum bicolor variety is forage variety used in the present study for its high dry matter yield and resistance to drought and soil salinity. However, one of the limitations of sorghum silage is high fiber concentration [15]. The bonds linking the cell wall phenolic acids with lignin and hemicellulose prevent the degradation of the fiber components by microbial enzymes during ensilage. Lignin is a major fiber component that acts as a barrier for the enzymatic degradation of cellulose [17,18]. Studies showed that feruloyl-esterase could dismantle these bonds in-between lignin and structural polysaccharides, thereby enhancing fiber degradation [19,20,21]. Interestingly, evidence confirmed that inoculation with Lactobacillus plantarum A1 releases feruloyl-esterase, which enhanced the fiber degradation and silage fermentation quality [14,22]. Therefore, pretreating sorghum biomass with L. plantarum A1 before ensiling could improve the fermentation quality and hydrolyze the fiber bonds during fermentation, and subsequently enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of the cellulose. Biomass’ post-ensiling morphological metamorphosis resulting from fiber degradation activity of L. plantarum A1 has not been visualized in any study. Thus, this study employed scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) to visualize the morphological changes and determine the crystallinity index of the biomass.
Anzola-Rojas [23], reported from a liquid medium experiment that low concentration of N during fermentation inhibits the activity of the microbial enzymes. Thus, complementary incorporation of leguminous crops into the sorghum silage to provide adequate N for improved fermentation quality is required [24,25]. The sorghum could provide the DM and water-soluble carbohydrate (WSC) required for excellent fermentation thereby preventing severe proteolytic degradation of the legume’s N [24,25,26]. Soybean is an annual legume grown worldwide and has been integrated into different cropping systems in Australia [27], Europe [28], Brazil [13] USA [29], and various places in China, including the present study’s location [30,31]. Soybean silage is rich in N with relatively higher fiber degradability [13], but the crop has poor fermentation quality when ensiled alone [24,26]. These attributes informed our choice of the crop for complementary incorporation into sorghum silage in this study.
The efficiency of L. plantarum A1 in improving the fermentation quality and lignocellulose degradation, as well as ferulic acid production of different biomass have previously been reported [12,14,22,32]. However, despite the higher cellulosic content of sorghum, and its ensiling potential as well as its potential for biofuel production, there is no report from any study on inoculating whole crop sorghum biomass with any feruloyl-esterase producing lactobacillus during ensiling. Hence, this study hypothesizes that inoculating the whole crop sorghum biomass with L. plantarum A1 during ensiling could equally improve the fermentation quality, and enhance lignocellulose degradation and subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis of the sorghum silage. Additionally, incorporating soybean into the silage could complementarily improve the N content and fermentation quality, thereby enhancing subsequent enzymatic hydrolysis for biofuel production. Therefore, this study’s objective is to determine the fermentation quality, N dynamics, biomass degradation, ferulic acid production and enzymatic hydrolysis of soybean incorporated sorghum silage inoculated with L. plantarum A1.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Forages, Inoculant and Ensiling
Forages of F10 S. bicolor variety (sorghum) and Guxia 7 Glycine max variety (soybean) were harvested at late dough and flowering stage, respectively, on 20 October 2019 at Lanzhou University research station in Qingyang city (40°54′ N, 107°09′ E; 1035 m above sea level), Gansu, China. The sorghum and soybean forages were separately wilted to about 63.5% moisture content and chopped to approximately 2 cm. The chopped forages were combined according to the soybean inclusion treatments (DM basis): 0% Soybean (sorghum only), 25% Soybean (75% sorghum + 25% soybean) and 50% Soybean (50% sorghum + 50% soybean) and apportioned into 36 piles of 400 g each (12 for each soybean inclusion treatment). Four piles from each treatment were frozen (−20 °C) immediately for subsequent laboratory analyses.
The preparation of L. plantarum A1 has been earlier reported by Li et al. [14]. A Mini sprayer was used to spray the inoculant at the rate of 5 × 106 CFU/g fresh weight to 12 piles of the forages; 4 piles from each of the soybean inclusion treatments (inoculated treatments). The sprayed piles were thoroughly mixed in plastic container that was pre-disinfected with 75% ethanol. An equivalent amount of sterile distilled water was also applied to the remaining 12 piles of the different soybean inclusion treatments (uninoculated treatments). The 24 piles (3 soybean inclusions × 2 inoculations × 4 replicates) were vacuum sealed individually in a laboratory silo (300 mm × 350 mm; polyethylene plastic bags) using a vacuum sealing machine (Xh860 Vacuum Packaging Machine, Zhejiang Jiangnan Co., Ltd., Wenzhou, China) and stored in an air-conditioned room with a temperature of 25 ± 0.2 °C.
2.2. Silage Opening and Chemical Analyses
Silos were opened after 90 d and the opening weight of the silages were recorded. The contents of the silos were mixed thoroughly, and a fresh sample (20 g) was collected from each bag and homogenized with 180 mL distilled water in a juice extractor at high speed for 30 s. Four-layer medical gauze was used to filter the silage extract, and the filtrate was subsequently apportioned into two aliquots. The remaining silage was sealed and frozen (−20 °C) for subsequent analysis.
After measuring the pH, 7.14 M H2SO4 was added to the first portion of the filtrate and further filtered with 0.22 μm dialyzer. This portion was used to determine the lactic acid (LA), acetic acid (AA) and propionic acid (PA) according to the method of Li et al. [22], using HPLC (Shodex KC-811 column; Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan; oven temperature: 50 °C; flow rate: 1 mL/min; SPD-10Avp, Shimadzu: 210 nm). In the second portion of the filtered silage extract, trichloroacetic acid [250 g/L (w/w)] was added at a ratio of 1:4 (acid to sample) and allowed to stand at 4 °C overnight for the precipitation of protein. After the precipitation of protein, the samples were centrifuged at 4 °C for 15 min (18,000× g) and the supernatant was analyzed for ammonia-N (NH3-N) and amino acid N (AAN) [33] as well as water-soluble carbohydrates (WSC) [34]. The non-protein N (NPN) was also determined from the protein precipitated samples, using the method of Licitra et al. [35]. The measurement of buffering capacity was conducted according to McDonald and Henderson [36], where 1 g sample was homogenized with100 mL of distilled water and shaken at 150 rpm for 30 min. The homogenized liquid was filtered and the pH was adjusted to 6 using 0.1 M NaOH and then titrated from pH 6 to pH 4 with 0.1 M LA.
Samples from the fresh forages and silages were oven-dried at 65 °C for 72 h in a forced-air oven. The oven-dried samples were ground with a 1-mm screen fitted mill and used to determine the Kjeldahl N [37]. ANKOM fiber bag technology was used for the determination of neutral detergent fiber (NDF), acid detergent fiber (ADF) and acid detergent lignin (ADL) [38]. Hemicellulose and cellulose were computed as the difference between NDF and ADF as well as ADF and ADL, respectively. The non-fiber carbohydrate (NFC) content was calculated using the Cornell Net Carbohydrate and Protein System (CNCPS) equation [39]. The contents of glucose, fructose, and sucrose were measured according to Desta et al. [40]. The extraction and measurement of ferulic acid was conducted following a modified procedure of Zhao et al. [41].
2.3. SEM and FTIR Analysis
Samples of the ensiled biomass were freeze dried (to avoid surface tension) and ground using hammer mill. To ensure conductivity, the samples used for SEM were first sputter coated with platinum and subsequently scanned at an acceleration voltage of 15 kV and magnification range between 15,000–20,000 using SEM machine (Thermo Scientific Apreo S, Waltham, MA, USA). Pure KBr (to obtain the FTIR background) and combination of KBr and freeze-dried samples (1:100; sample to KBr) were pressed into slices for FTIR spectrometry at a range from 4000 to 500 cm−1 with a resolution of 4 cm-1 using FTIR spectrometer (Nexus 670, Nicolet, Madison, WI, USA). The cellulose crystallinity was determined according to the Nelson crystallinity index (A1375/A2900) [42].
2.4. Enzymatic Saccharification
Enzymatic conversion of the soybean incorporated sorghum silage was conducted following the standard protocols of the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) [43]. Biomass (0.3 g) of DM basis was mixed with 5 mL of 0.1 M citrate-phosphate buffer (pH 4.8) and 2%(w/w) of Acremonium cellulase (100 FPU/g; Meiji Seika Pharma Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) on the basis of cellulose content. To prevent microbial contamination 300 μL of 0.2% sodium azide was added to the biomass slurry and the total volume of each vial was made to 10.0 mL using distilled water. An enzyme blank reaction was prepared using the same quantity of reagents and biomass. The prepared vials were put in an incubator (50 °C) equipped with a shaker (160 rpm) to keep the solids in constant suspension for 72 h. The incubated samples were centrifuged (10,000× g) for 10 min, and the supernatants were filtered through 0.22 μm dialyzer for analysis of glucose yield (GY) according to the method of Desta et al. [40]. Cellulose conversion (CC) was computed as [19].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All the statistics were conducted in R studio of R statistical package [44]. Linear model was used to analyze the data of the fresh forages to test the effect of incremental soybean inclusion, subsequently, all data from the ensiled forages were analyzed using GLM procedure following the 3 × 2 factorial experiment model:
where Yijk represents the fermentation profile, N fractions, carbohydrate components, ferulic acid content and glucose yield of the ensiled forages; μ is the overall mean; αi is the effect of soybean inclusion i (i = 0%, 25%, or 50%), βj is the effect of inoculation j (j = uninoculated or inoculated), (α × β)ij is the effect of interaction between soybean inclusion and inoculation; and eijk is the error term.
Yijk = µ + αi + βj + (α × β)ij + eijk,
Orthogonal polynomial contrast was used to examine the linear and quadratic effects of the equidistant levels of soybean inclusion. Means were considered significantly different at p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition of Soybean Incorporated Sorghum Forage before Ensiling
The chemical characteristics of the fresh forages are presented in Table 1. The increase in the proportion of soybean had a significant linear effect on TN. Similarly, the NFC linearly increased with increasing soybean inclusion from 0% to 50%, while WSC conversely decreased (p < 0.05). These fulfilled the N enrichment by soybean inclusion and the complementary provision of sufficient substrates (WSC) from the sorghum forages for a better subsequent fermentation process during ensiling. A significant linear effect was observed on all the fiber fractions of the forages (with significant quadratic effect on ADL and holocellulose), where they decreased with increasing soybean inclusion from 0% to 50%. ADL decreased from 0% to 25% and slightly increased at 50% soybean inclusion. Soybean inclusion had significant linear and quadratic effect on the BC of the silages, which increases from 0% to 50% soybean inclusion. Leguminous forages are known to have higher BC [36,45] as observed with the inclusion of soybean forages.

Table 1.
Chemical characteristics of soybean incorporated sorghum forage before ensiling (g kg−1 DM).
3.2. Fermentation Profile of Soybean Incorporated Sorghum Silage Inoculated with or without L. Plantarum A1
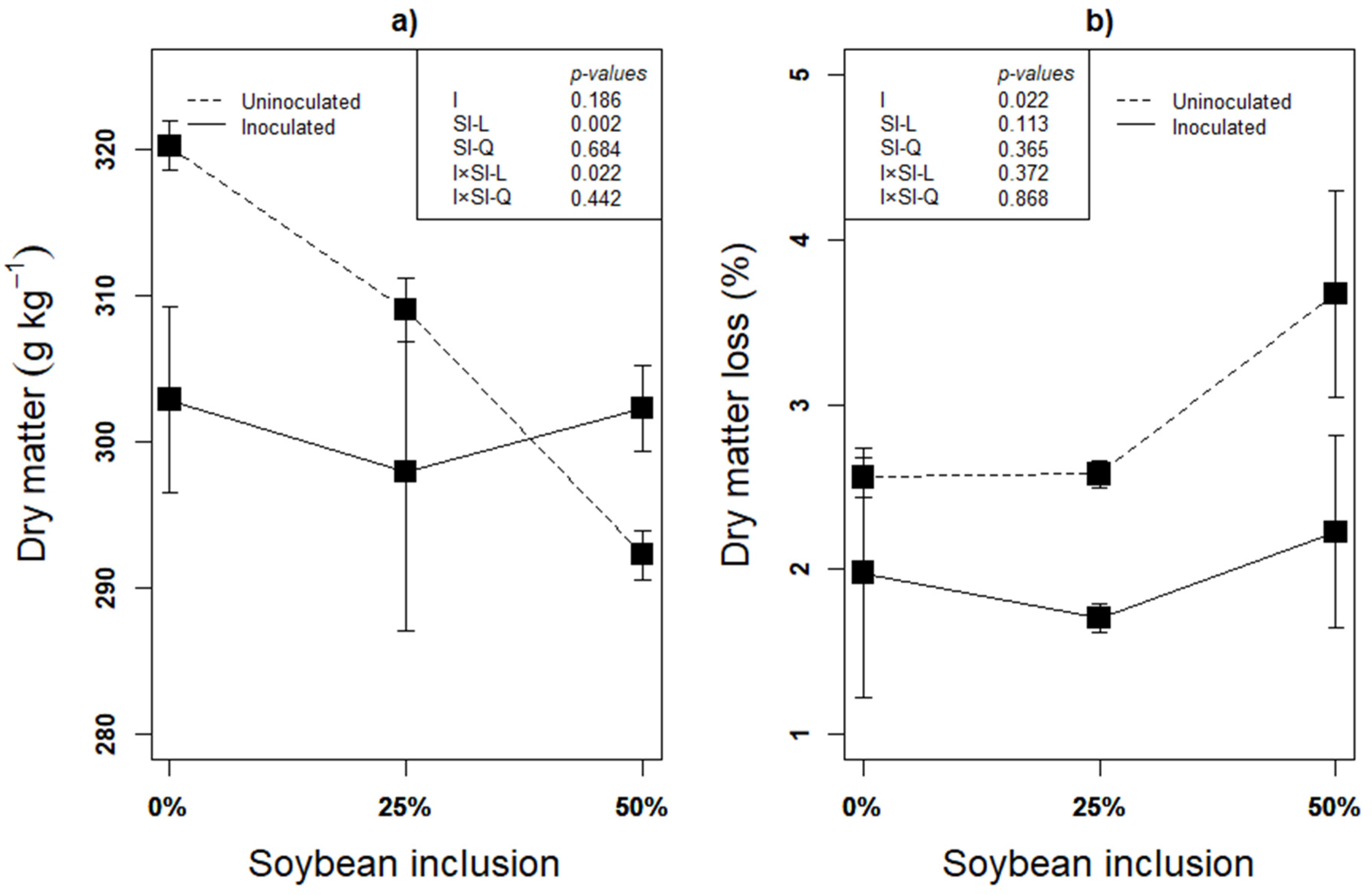
Recovery of as much DM as possible is the first indication of successful ensilage, and it is inversely related to the DM loss. Subsequently, fermentation characteristics such as pH and organic acids could be used to assess the fermentation quality [46]. Linear effect of inoculation × soybean inclusion was observed on the silages’ DM after 90 d of ensilage (Figure 1a). The DM decreased linearly from 0% to 50% soybean inclusion (p < 0.05) in the uninoculated silages, but inoculated silages had a relatively stable DM across the soybean inclusion treatments. The percentage of DM lost in the uninoculated silages in the present study is 12.71% (0% Soybean), 20.56% (25% Soybean) and 24.41% (50% Soybean) higher, compared to inoculated silages, implying more DM recovery in L. plantarum A1 inoculated silages (Figure 1b). DM loss during fermentation is determined by availability of fermentable substrates and dominant microbial species. Glucose fermentation by homolactic bacteria (L. plantarum A1 in this study) mainly produce lactate with no any DM loss while epiphytic microorganisms are responsible for the fermentation process of forages ensiled without LAB inoculation [47].
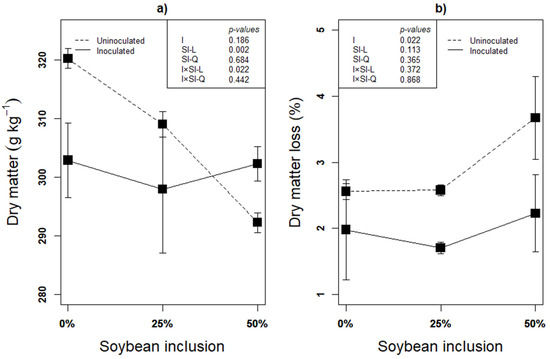
Figure 1.
(a,b): Influence of soybean inclusion and L. plantarum A1 inoculation on dry matter and dry matter loss of sorghum silage.
Table 2 shows that the pH of the silages decreased with increasing soybean inclusion in both uninoculated and inoculated silages, with more acidic values (3.80–3.97) in the inoculated silages (p < 0.05). The LA concentration was 29.0 and 84.8 g kg−1 (0% soybean inclusion) and 85.2 and 97.6 g kg−1 (25% soybean inclusion) as well as 86.4 and 175 g kg−1 (50% soybean inclusion) in uninoculated and inoculated silages, respectively. Conversely, AA was significantly higher in uninoculated silages, with a liner increment trend across the soybean inclusion treatments (p < 0.05). In uninoculated silages, the AA linearly increased from 25.4 g kg−1 in 0% soybean inclusion to 43.5 g kg−1. Whereas the increment was from 13.0 g kg−1 (0% soybean inclusion) to 39.0 g kg−1 (50% soybean inclusion) in inoculated silages. However, the ratio of LA/AA in inoculated silages was at least twice higher, compared to uninoculated silages in all the soybean inclusion treatments (p < 0.05). LA is the primary driver for the decline in silage pH due to its strength (3.86 pKa), which is about 12 times stronger than AA (4.75 pKa) and PA (4.87 pKa) [46]. Several studies have reported higher LA concentration in silages inoculated with L. plantarum [14,16,22,32,48]. The AA concentration in this study was within the range (3–4%) said to be often found in L. buchneri inoculated silages [46]. The ratio of LA to AA is low in uninoculated silage treatments. This is because silage fermentation by epiphytic bacteria is mainly heterofermentative as in uninoculated treatments, while inoculation with L. plantarum A1 (a homolactic LAB) results in homofermentation. Muck and Kung [49] reported that treating silage with homolactic LAB could result in higher LA/AA ratio as observed in the L. plantarum A1 inoculated silages in this study.

Table 2.
Influence of soybean inclusion and L. plantarum A1 inoculation on fermentation profile of sorghum silage.
3.3. Nitrogen Fractions of Soybean Incorporated Sorghum Silage Inoculated with or without L. plantarum A1
Enzymatic machinery of carbohydrate metabolism is more adequate and efficient with sufficient assimilation of N [50]. The microbiomes require adequate N for optimal activity during fermentation and subsequent enzymatic activities, thereby the need for efficient conservation of the biomass N content. The N fractions of the silages are presented in Table 3. Linear effect of Soybean inclusion × inoculation interaction increased the TN contents of the silages (p < 0.05). In uninoculated silages, the TN increased by 11.55% and 17.79% with inclusion of 25% and 50% soybean, respectively. However, the increase of TN with inclusion of 25% and 50% soybean was 11.70% and 21.08%, respectively, in inoculated silages. Improvement in the TN found in this study agreed with the report by Lima et al. [24] that soybean inclusion improved the CP (reported as N × 6.25) content of silages made from two different sorghum varieties. Similarly, the significant increase of the silage TN content by L. plantarum A1 inoculation corroborates the findings of Ni et al. [51], where an increased CP content was found with the addition of an inoculant containing L. plantarum in a molasses treated soybean silage. Notably, an adequate fermentable substrate is required for the efficient preservation of N from the soybean forage. Otherwise, it will take a relatively long time to produce sufficient LA that could lower the silage pH, during which enzymatic proteolysis could degrade the N content of the ensiled forage. Proteolysis occurs rapidly in a freshly ensiled forage but declined with a decrease in silage pH. In this study, sorghum provided the required fermentable substrate (WSC) for immediate conversion into LA, thereby enhanced rapid fermentation and simultaneously prevented the N compound of the ensiled forages from severe proteolytic degradation. Therefore, inoculation with L. plantarum A1 improved the N contents of the ensiled forages by accelerating the LA production and lowering the silage pH, halting the proteolytic activities [46,49]. In addition, the decline of pH and the increase in LA with increasing soybean inclusion in both uninoculated and inoculated silage treatments could be partly attributed to the enhanced microbial and enzymatic activities due to sufficient N provided by the soybean forage [23], and also the ease of degradability of soybean compared to sorghum [13,52]. Hence, the degradation of soybean forage by microbial and enzymatic activities during fermentation added fermentable substrates into the soybean incorporated treatments, resulting in higher LA production, which ultimately declined the silages’ pH.

Table 3.
Influence of soybean inclusion and L. plantarum A1 inoculation on N fractions of sorghum silage.
Protein degradation during silage fermentation leads to the metamorphosis of nitrogen-based compounds [46]. There is both linear and quadratic effect of soybean inclusion × inoculation on NPN concentration of the silages. The concentration of NPN initially increased from 0 to 25% soybean inclusion level and declined at 50% soybean inclusion. NH3-N was only affected by inoculation (p < 0.05) and uninoculated silages had the highest concentration of the NH3-N in all the soybean inclusion treatments. The significant decrease in the NPN and NH3-N concentration of the silages confirmed that L. plantarum A1 enhanced the fermentation process and preserved the silage quality. The significantly high concentration of LA in 50% soybean inclusion that prevented proteolysis was the reason for the decline of NPN in this treatment.
3.4. Non-Fiber Carbohydrates and Fiber Fractions of Soybean Incorporated Sorghum Silage Inoculated with or without L. plantarum A1
Table 4 presents the residual NFC, WSC, glucose, fructose and sucrose of soybean incorporated sorghum silage inoculated with or without L. plantarum A1. There was a significant linear effect of soybean inclusion × inoculation on all the carbohydrate components (only main effects on WSC) (p < 0.05). NFC content of both uninoculated and inoculated silages increased from (412.63 and 401.78 g kg−1) 0% soybean inclusion to 435.74 and 452.58 g kg−1, respectively, in 25% soybean inclusion. However, in 50% soybean inclusion treatment, the NFC further increased to 467.01 g kg−1 in uninoculated treatment, but declined to 448.85 g kg−1 in inoculated treatment (p < 0.05). This implies that other fiber components, substantially from easy-degradable soybean forage, must have been degraded to provide the fermentation substrates for organic acid production [53,54,55], resulting in low fibrous components and high concentration of LA in soybean-containing silages. Inoculation with L. plantarum A1 increased the residual WSC concentration by an average of 33.9% after ensiling (p < 0.05). WSC consists mainly of glucose, fructose and sucrose [56]. Its high concentration in the inoculated treatments implies that L. plantarum A1 preserved the original WSC of the ensiled forages and degraded other fiber components to replace the WSC converted to LA [32]. The main monosaccharides existing in most plant species are glucose and fructose, while sucrose as a disaccharide exists in a relatively higher concentration than the monomers [57]. Both linear and quadratic effects of soybean inclusion × inoculation were significant on the glucose, sucrose and fructose content of the silages under study (p < 0.05). Regardless of inoculation, the nonstructural carbohydrates decreased with increasing proportion of soybean in the silages. However, inoculated silages had higher glucose concentration as well as lower sucrose and fructose in all the soybean inclusion treatments except in 50% soybean where sucrose was significantly higher in inoculated silages (p < 0.05).

Table 4.
Influence of soybean inclusion and L. plantarum A1 inoculation on NFC, WSC, glucose, sucrose and fructose in g kg−1 DM of sorghum silage.
About 250 to over 10,000 glucose chains bound by β—14 glycosidic bonds made up the cellulose [55,58]. Whereas, hemicellulose is made up of glucose, mannose, or xylose chains bound by β—1, 4—bonds [55,59]. Lignin on the other hand, is a heterogenous biopolymer in lignocellulose that is made up of radical-mediated oxidative coupling of phenyl-propane unit bound together by several kinds of ether and carbon-carbon bonds [55,60]. All the fiber components had a similar trend of linear decrease with increasing soybean inclusion in both inoculated and uninoculated silages (p < 0.05; Table 5), except that ADL slightly increased from 38.18 g kg−1 DM (25% soybean inclusion) to 39.66 g kg−1 DM (50% soybean inclusion) in inoculated silages. At the initial stage of ensiling, the cell wall components are hydrolyzed by the help of the enzymes produced from microbial activity until the silage pH declines to inhibit enzymatic activity. When the silage becomes acidic, acidolysis is responsible for the preceding hydrolysis of structural carbohydrates in the ensiled forage [22,32]. Although L. plantarum A1inoculation did not influence the NDF content, but the concentrations of the other fiber fractions were significantly affected (p < 0.005). The ADF, ADL and cellulose fractions of the inoculated silages were reduced significantly, while hemicellulose and holocellulose were increased (p < 0.05). The decrease in ADL and cellulose as well as the increase in hemicellulose had confirmed the disintegration of the lignocellulose (undigestible) fractions of the silages into relatively more digestible component (hemicellulose). Evidence has shown a pronounced fiber degradation in L. plantarum A1 pretreated corn stalk silage [22] and when L. plantarum A1 was fortified with cellulase [32] or Acremonium cellulase [14]. Inoculation with L. plantarum A1 also increased the potential biodegradability of the silages by 13.54, 16.56 and 4.04% in 0%, 25% and 50% soybean inclusion treatments, respectively. In addition, since L. plantarum A1 produces ferulic acid esterase; an enzyme that help in the breakdown of the links between the structural carbohydrates through the production of ferulic acid [14,22,32], we posited that the activity of this enzyme had weakened the bonds between the silages’ fibrous components, thereby facilitating subsequent degradation of the fiber during the main fermentation for biofuel production. To substantiate our proposition, we further quantify the ferulic acid content in the silages and evaluate the effect of the L. plantarum A1 inoculation on GY and cellulose conversion CC of the soybean incorporated sorghum silage during enzymatic saccharification.

Table 5.
Influence of soybean inclusion and L. plantarum A1 inoculation structural carbohydrates (g kg−1 DM) and potential biodegradability of sorghum silage.
3.5. Ferulic Acid Concentration of Soybean Incorporated Sorghum Silage Inoculated with or without L. plantarum A1
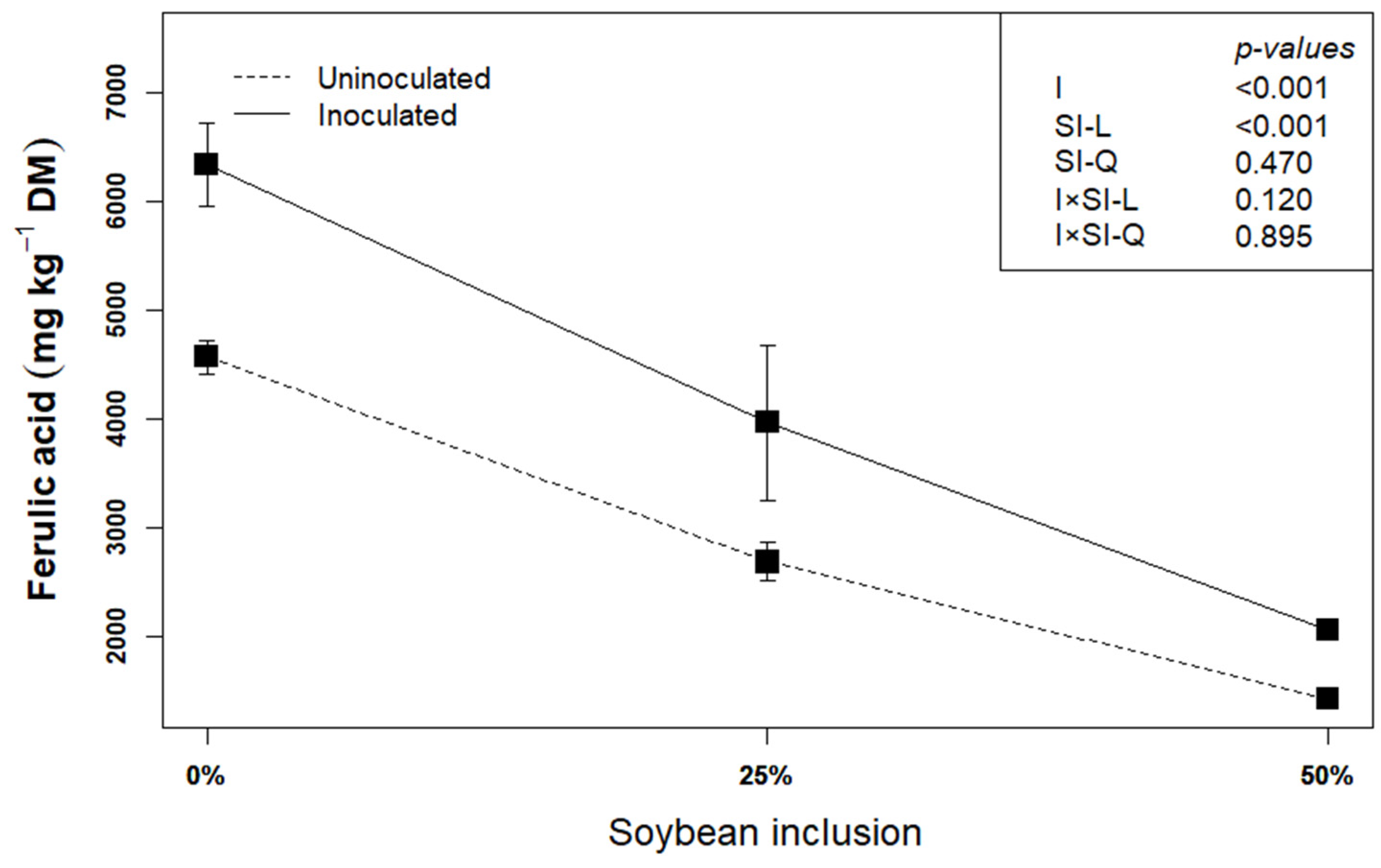
Ferulic acid could be used as an indicator of lignocellulose degradation [22]. This is because ferulic acid is covalently esterified or etherified to cell wall polysaccharide and lignin, and the production of feruloyl-esterase by L. plantarum A1 which helps in hydrolyzing the cell wall components by dismantling the ester and ether bonds, leads to the release of the ferulic acid. In the present study, inoculating the biomass with L. plantarum A1 before ensiling increased the concentration of ferulic acid by an average of 17.48% (p < 0.05), compared to uninoculated silages (Figure 2). This corroborates earlier findings that L. plantarum A1increased the release of ferulic acid [14,22,32], thereby confirming the degradation of the structural components of the biomass.
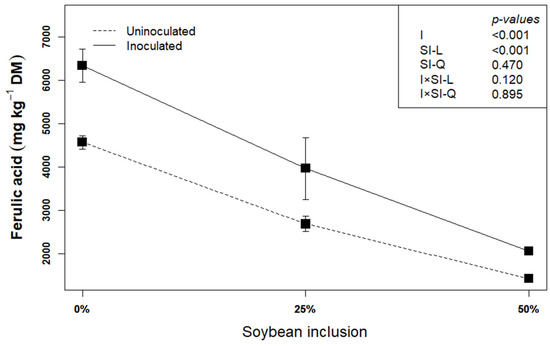
Figure 2.
Influence of soybean inclusion and L. plantarum A1 inoculation on the concentration ferulic acid of sorghum silage.
3.6. Structural and Morphological Changes of Soybean Incorporated Sorghum Silage Inoculated with or without L. plantarum A1
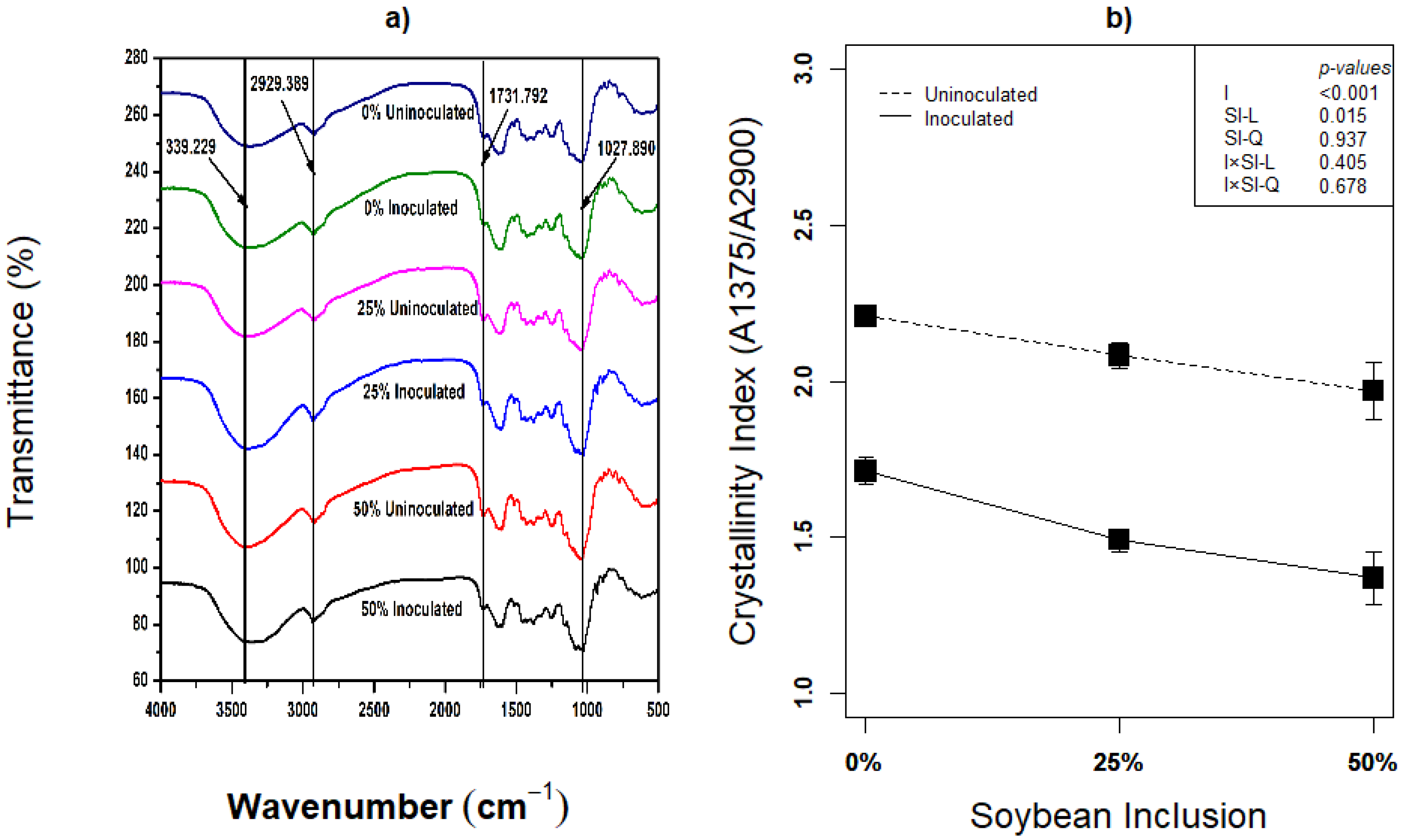
Compositional analysis is not sufficient in investigating pretreatment’s effect on lignocellulose biomass, because delamination of cell wall and re-localization of lignin could equally be important in enhancing the hydrolysis of lignocellulose biomass [61]. The biomass’ post-ensiling morphological metamorphosis resulting from fiber degradation activity of L. plantarum A1 has not been visualized in any study. This study therefore, employed scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) to visualize the morphological changes and determine the crystallinity index of the biomass. Structural transformation of the silages using FTIR analysis revealed that both uninoculated and inoculated silages had little or no difference in FTIR features (Figure 3a). Ren et al. [62] also reported the absence of obvious microstructural changes among silages pretreated with different doses of rumen fluid and varied storage period, presented FTIR features almost similar to what was obtained in the present study. The bands obtained at different wavenumber represents the H–bond (–OH group), C–H, C=O and C–O–C as they affect the lignocellulose structure [62]. The stretching vibrations of H–bonded–OH group is represented by the band obtained around 3396 cm–1 and the band around 2929 cm–1 represents the C–H stretching [62]. The peak observed around 1731 cm–1 corresponds the C=O bond stretching vibration, which is the typical functional group of orthosubstituted arylskeleton related to the stretching of lignin structure [63]. The transmittance reduction around 1731 cm–1 implied the partial removal or dissolution of lignin [62]. The intensity around 1027 cm–1 is assigned to C–O–C stretching of hemicelluloses, and the band dynamics implies hemicelluloses degradation [62,64].
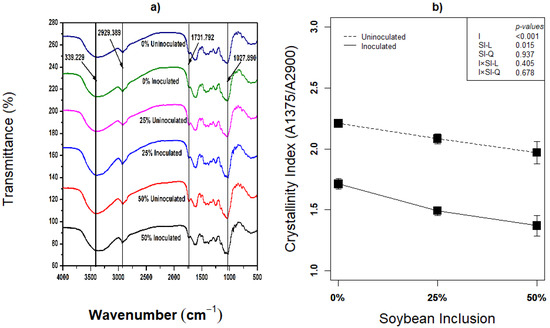
Figure 3.
(a,b): Influence of soybean inclusion and L. plantarum A1 inoculation on FITR and crystallinity index of sorghum silage.
The crystallinity index was significantly influenced by inoculation and linear effect of soybean inclusion (p < 0.05). Inoculation with L. plantarum A1 generally decreased the crystallinity index by an average of 15.60%, and the crystallinity index decreased linearly with increasing soybean inclusion from 2.21 and 1.71 (inoculated and uninoculated) in 0% soybeans inclusion to 1.97 and 1.37 (inoculated and uninoculated) in 50% soybeans inclusion, respectively. These results correspond with the various compositional analysis and other biochemical indicators that suggest fiber degradation in this study. Similar trend of reduction in crystallinity index has been reported by Ren et al. [62], although crystallinity index is higher in the present study which is obviously due to the difference in the sorghum species.
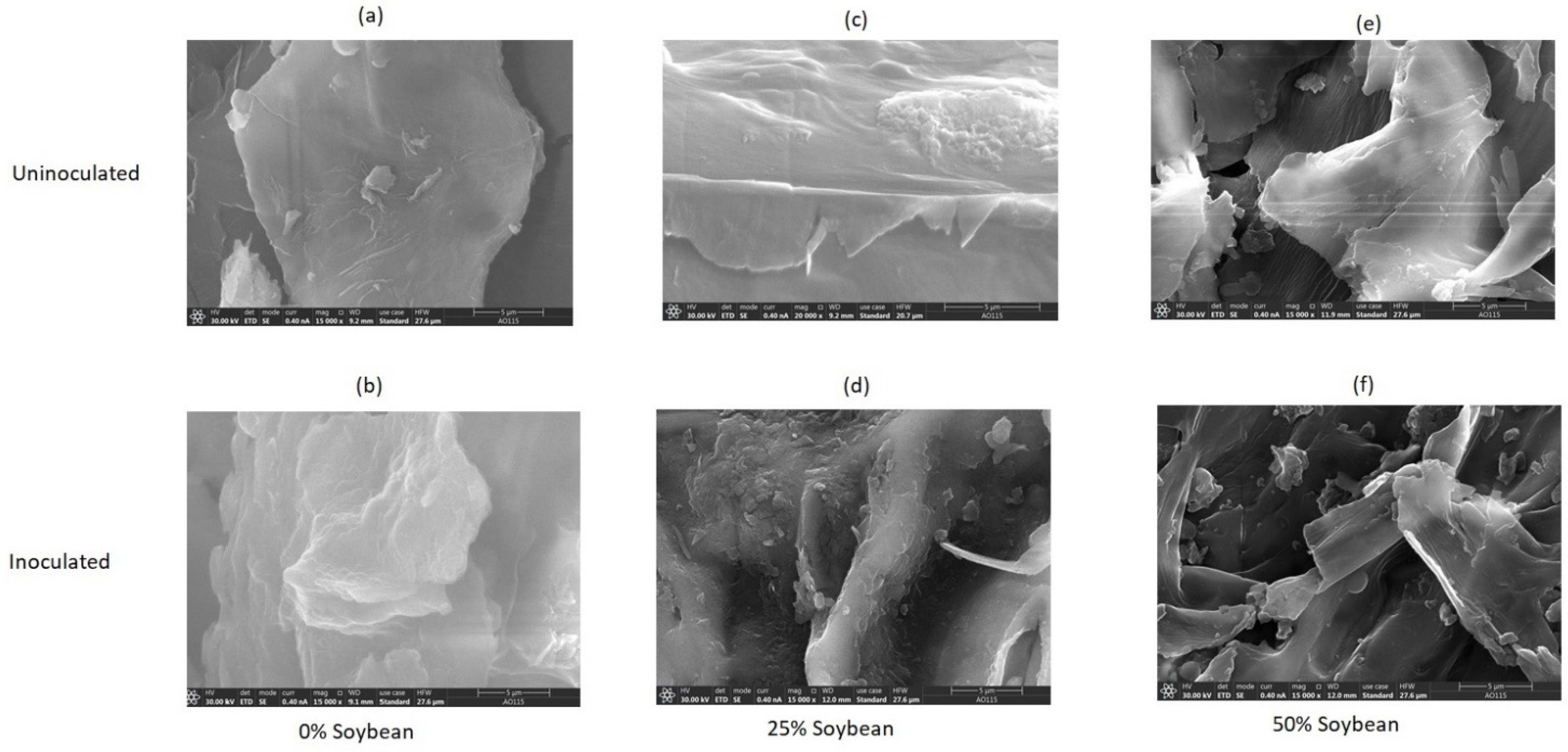
Surface morphology as revealed by the images obtained from SEM analysis (Figure 4a–f) suggest metamorphosis of microstructural matrix of the biomass in inoculated silages of 0% soybean inclusion (compared to uninoculated) and the changes were more intense in inoculated silages of 25% soybean inclusion with some deposits on the outer surface [61]. Ren et al. [62] have described the surface deposition as either carbohydrates, fragments of lignin or ashes. These generally suggest that the improvement in the fermentation characteristics, biochemical composition and the reduction in crystallinity index of the inoculated 0% and 25% soybean inclusion treatments was basically due to the lignin re-localization and degradation. In 50% soybean inclusion treatment, there was more obvious fiber splitting which is more excessive in the L. plantarum A1 inoculate silages.
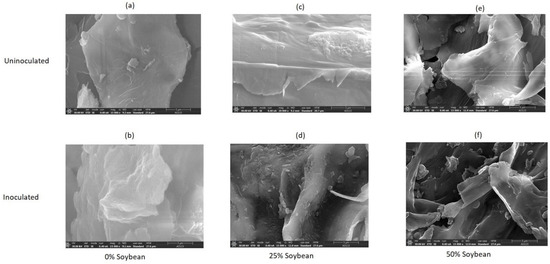
Figure 4.
(a–f): SEM images showing the influence of soybean inclusion and L. plantarum A1 inoculation on surface morphology of sorghum silage.
3.7. Enzymatic Saccharification of Soybean Incorporated Sorghum Silage Inoculated with or without L. plantarum A1
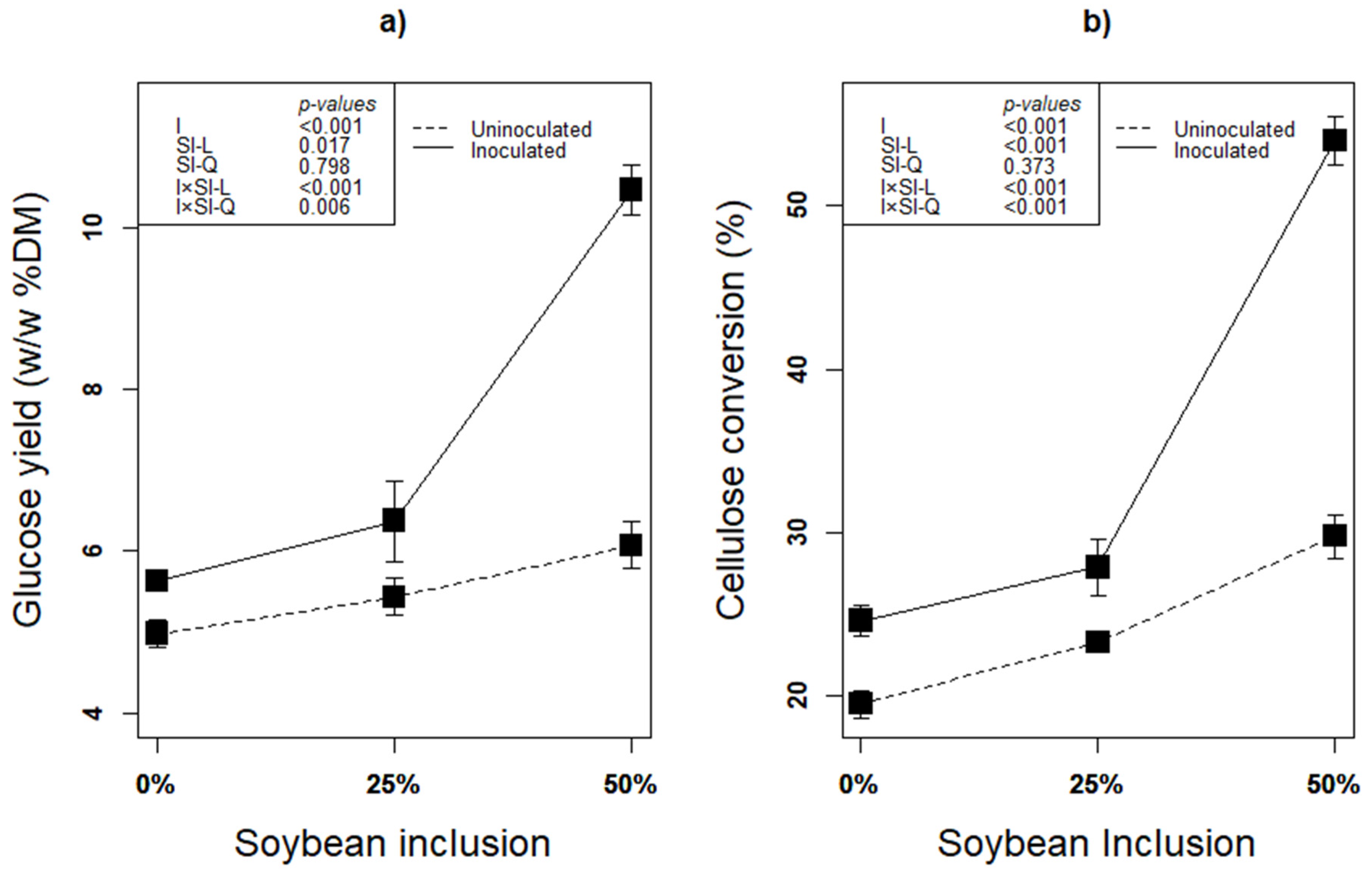
The second step of lignocellulose biofuel production after pretreatment is saccharification [1] Due to minimized loss of sugars and less byproducts of enzymatic saccharification, it has been recognized as an efficient way of lignocellulose hydrolysis without negative effect on the environment [22,65]. Regardless of inoculation with any additive, ensiling biomass is considered an effective pretreatment to enhance accessibility to the biomass’ polysaccharides thereby enhancing subsequent enzymatic digestibility of the lignocellulosic biomass [22]. In addition, inoculation especially with an inoculum that has fiber degradation ability such as L. plantarum A1 further improve the process. In this study, linear effect of soybean inclusion × inoculation significantly improved both glucose yield and cellulose conversion of the silages (p < 0.05; Figure 5a,b). The higher glucose yield and cellulose conversion in these treatments were obviously due to enhanced fermentation and fiber degradation activity of L. plantarum A1 during ensilage [12,14,22,32]. The higher degradability of soybean fiber is the reason for the linear increase in GY and CC with increasing soybean inclusion during enzymatic saccharification. Higher LA concentration, lower structural carbohydrates with corresponding higher content of residual glucose, as well as higher ferulic acid produced from treatments with higher soybean proportion are the evidence that initially confirms the readiness in the degradability soybean fiber.
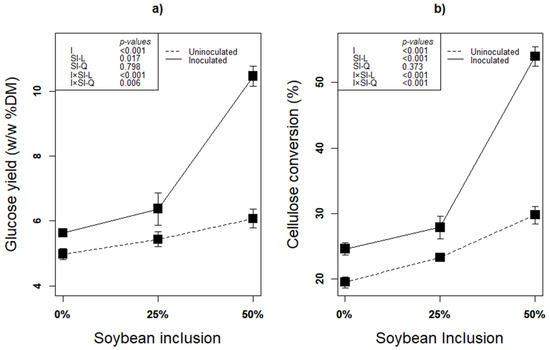
Figure 5.
(a,b): Influence of soybean inclusion and L. plantarum A1 inoculation on glucose yield and cellulose conversion of sorghum silage.
4. Conclusions
Fermentation quality was enhanced by L. plantarum A1 and soybean improved the CP content of the silages. Inoculation and soybean inclusion promoted lignocellulose degradation, alter the surface morphology and microstructural matrix of the biomass, increased the release of ferulic acid, and reduced the biomass crystallinity by 15.60%. L. plantarum A1 inoculation and soybean inclusion also improved the GY and CC during enzymatic saccharification. Thus, pretreating soybean incorporated sorghum silage with L. plantarum A1 is a sure way of enhancing fermentation quality, lignocellulose degradation, and enzymatic hydrolysis of the biomass. Simultaneously, ensiling could ensure sustainable year-round feedstock supply for on the farm biofuel production.
Author Contributions
S.U.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing—original draft. F.L.: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Visualization. D.A.: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization. N.S.: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization. J.D.: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization. Y.Z.: Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization. X.G.: Investigation, Data curation, Validation, Writing—review & editing. Y.S.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing—review & editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by of China Agricultural Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-34) and NSFC (72033009).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, T.; Lü, X. Overcome Saccharification Barrier. In Advances in 2nd Generation of Bioethanol Production; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 137–159. [Google Scholar]
- Tyner, W.E. Biofuel Economics and Policy. In Bioenergy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 511–521. [Google Scholar]
- Tyner, W.E. Policy Update: Cellulosic Biofuels Market Uncertainties and Government Policy. Biofuels 2010, 1, 389–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, M.; Rusanowska, P.; Zielinska, M.; Dudek, M.; Nowicka, A.; Purwin, C.; Fijałkowska, M.; De bowski, M. Influence of Preparation of Sida Hermaphrodita Silages on Its to Methane. Renew. Energy 2021, 163, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamoto, H.K.; Horita, M.; Cai, Y.; Shinozaki, Y.; Sakaki, K. Silage Produces Biofuel for Local Consumption. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2011, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagel, S.A.; Broderick, G.A. Effect of Formic Acid or Formaldehyde Treatment of Alfalfa Silage on Nutrient Utilization by Dairy Cows 1. J. Dairy Sci. 1992, 75, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addah, W.; Baah, J.; Mcallister, T.A. Effects of an Exogenous Enzyme-Containing Inoculant on Fermentation Characteristics of Barley Silage and on Growth Performance of Feedlot Steers. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 96, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.G.; Ham, J.S.; Li, Y.W.; Park, H.S.; Huh, C.; Park, B. Development of a New Lactic Acid Bacterial Inoculant for Fresh Rice Straw Silage. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Sun, Z.; Gao, R.; Yu, Z. Lactic Acid Bacterial Inoculant Effects on the Vitamin Content of Alfalfa and Chinese Leymus Silage. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.C.; Ding, W.R.; Xu, D.M.; Ding, L.M.; Zhang, P.; Li, F.D.; Guo, X.S. Effects of Addition of Malic or Citric Acids on Fermentation Quality and Chemical Characteristics of Alfalfa Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 8958–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oliveira, J.S.; Santos, E.M.; dos Santos, A.P.M. Intake and Digestibility of Silages. In Advances in Silage Production and Utilization; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; pp. 101–121. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.H.; Ding, Z.T.; Chen, X.Z.; Zhang, Y.X.; Ke, W.C.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.Q.; Usman, S.; Guo, X.S. The Effects of Lactobacillus Plantarum with Feruloyl Esterase-Producing Ability or High Antioxidant Activity on the Fermentation, Chemical Composition, and Antioxidant Status of Alfalfa Silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 273, 114835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandra, J.R.; Takiya, C.S.; del Valle, T.A.; Oliveira, E.R.; de Goes, R.H.T.B.; Gandra, E.R.S.; Batista, J.D.O.; Araki, H.M.C. Soybean Whole-Plant Ensiled with Chitosan and Lactic Acid Bacteria: Microorganism Counts, Fermentative Profile, and Total Losses. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 7871–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ke, W.; Ding, Z.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D. Pretreatment of Pennisetum Sinese Silages with Ferulic Acid Esterase-Producing Lactic Acid Bacteria and Cellulase at Two Dry Matter Contents: Fermentation Characteristics, Carbohydrates Composition and Enzymatic Saccharification. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 295, 122261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolsen, K.K.; Moore, K.J.; Coblentz, W.K.; Siefers, M.K.; White, J.S. Sorghum Silage. In Silage Science and Technology; Buxton, D.R., Muck, R.E., Harrison, J.H., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy, Inc. Crop Science Society of America, Inc. Soil Science Society of America, Inc.: South Segoe Road, Madison, WI, USA, 2003; pp. 609–632. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, T.; Paula, E.M.; Sultana, H.; Ferraretto, L.F. Short Communication: Influence of Sorghum Cultivar, Ensiling Storage Length, and Microbial Inoculation on Fermentation Profile, N Fractions, Ruminal in Situ Starch Disappearance and Aerobic Stability of Whole-Plant Sorghum Silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2020, 266, 114535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, C.; Yong, Q. Understanding the Effects of Different Residual Lignin Fractions in Acid-Pretreated Bamboo Residues on Its Enzymatic Digestibility. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Lin, W.; Lai, C.; Li, X.; Jin, Y.; Yong, Q. Coupling the Post-Extraction Process to Remove Residual Lignin and Alter the Recalcitrant Structures for Improving the Enzymatic Digestibility of Acid-Pretreated Bamboo Residues. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 285, 121355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nsereko, V.L.; Smiley, B.K.; Rutherford, W.M.; Spielbauer, A.; Forrester, K.J.; Hettinger, G.H.; Harman, E.K.; Harman, B.R. Influence of Inoculating Forage with Lactic Acid Bacterial Strains That Produce Ferulate Esterase on Ensilage and Ruminal Degradation of Fiber. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 145, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, N.A.; Adesogan, A.T.; Staples, C.R.; Krueger, W.K.; Dean, D.B.; Littell, R.C. The Potential to Increase Digestibility of Tropical Grasses with a Fungal, Ferulic Acid Esterase Enzyme Preparation. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 145, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addah, W.; Baah, J.; Okine, E.K.; Mcallister, T.A. A Third-Generation Esterase Inoculant Alters Fermentation Pattern and Improves Aerobic Stability of Barley Silage and the Effi Ciency of Body Weight Gain of Growing Feedlot Cattle 1. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ding, Z.; Ke, W.; Xu, D.; Zhang, P.; Bai, J.; Mudassar, S.; Muhammad, I.; Guo, X. Ferulic Acid Esterase-Producing Lactic Acid Bacteria and Cellulase Pretreatments of Corn Stalk Silage at Two Different Temperatures: Ensiling Characteristics, Carbohydrates Composition and Enzymatic Saccharification. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pilar Anzola-Rojas, M.; da Fonseca, S.G.; da Silva, C.C.; de Oliveira, V.M.; Zaiat, M. The Use of the Carbon/Nitrogen Ratio and Specific Organic Loading Rate as Tools for Improving Biohydrogen Production in Fixed-Bed Reactors. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 5, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, R.; Lourenc, M.; Díaz, R.F.; Castro, A.; Fievez, V. Effect of Combined Ensiling of Sorghum and Soybean with or without Molasses and Lactobacilli on Silage Quality and In Vitro Rumen Fermentation. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2010, 155, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbers, L.H.; Bolsen, K.K.; Hartadi, H. Evaluation of Interseeded Grain Sorghum and Soybeans as a Silage Crop. Kansas Agric. Exp. Stn. Res. Rep. 1992, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, B.; Su, R.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, G.; Tao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J. Assessing the Fermentation Quality and Microbial Community of the Mixed Silage of Forage Soybean with Crop Corn or Sorghum. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.W.; Moore, A.D. Integrated Crop-Livestock Systems in Australian Agriculture: Trends, Drivers and Implications. Agric. Syst. 2012, 111, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawęda, D.; Nowak, A.; Haliniarz, M.; Woźniak, A. Yield and Economic Effectiveness of Soybean Grown Under Different Cropping Systems. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2020, 14, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sulc, R.M.; Tracy, B.F. Integrated Crop-Livestock Systems in the U.S. Corn Belt. Agron. J. 2007, 99, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, N.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, K.; Li, F.; Malhi, S.S. Effects of Planting Soybean in Summer Fallow on Wheat Grain Yield, Total N and Zn in Grain and Available N and Zn in Soil on the Loess Plateau of China. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 58, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Bell, L.W.; Shen, Y.; Whish, J.P.M. Indices of Forage Nutritional Yield and Water Use Efficiency amongst Spring-Sown Annual Forage Crops in North-West China. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 93, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ding, Z.; Bai, J.; Ke, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Guo, X. Evaluation of the Effect of Feruloyl Esterase-Producing Lactobacillus Plantarum and Cellulase Pretreatments on Lignocellulosic Degradation and Cellulose Conversion of Co-Ensiled Corn Stalk and Potato Pulp. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 310, 123476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated Simultaneous Determination of Ammonia and Total Amino Acids in Ruminal Fluid and In Vitro Media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.A. An Automated Procedure for the Determination of Soluble Carbohydrates in Herbage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1977, 28, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G.; Hernandez, T.M.; van Soest, P.J. Standardization of Procedures for Nitrogen Fractionation of Ruminant Feeds. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1996, 57, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, P.; Henderson, R. Buffering Capacity of Harbage Samples as a Factor in Ensilage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1962, 13, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of the Official Analytical Chemists, 17th ed.; Horwitz, W., Ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, R.J.; Chase, L.E.; Ross, D.A.; van Amburgh, M.E. Updating the Cornell Net Carbohydrate and Protein System Feed Library and Analyzing Model Sensitivity to Feed Inputs. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 6340–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, S.T.; Yuan, X.J.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Ensiling Characteristics, Structural and Nonstructural Carbohydrate Composition and Enzymatic Digestibility of Napier Grass Ensiled with Additives. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 221, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Yao, S.; Ou, S.; Lin, J.; Wang, Y.; Peng, X.; Li, A.; Yu, B. Preparation of Ferulic Acid from Corn Bran: Its Improved Extraction and Purification by Membrane Separation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2014, 92, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, M.L. Relation of Certain Infrared Bands to Cellulose Crystallinity and Crystal Lattice Type. Part 11. A New Infrared Ratio for Estimation of Crystallinity in Celluloses I and 11. J. Appl. Plym. Sci. 1964, 8, 1325–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resch, M.G.; Baker, J.O.; Decker, S.R. Low Solids Enzymatic Saccharification of Lignocellulosic Biomass: Laboratory Analytical Procedure (LAP); National Renewable Energy Laboratory: Golden, CO, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Gao, R.; Franco, M.; Hannaway, D.B.; Ke, W.; Ding, Z.; Yu, Z.; Guo, X. Effect of Mixing Alfalfa with Whole-Plant Corn in Different Proportions on Fermentation Characteristics and Bacterial Community of Silage. Agriculture 2021, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.J.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage Review: Interpretation of Chemical, Microbial, and Organoleptic Components of Silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borreani, G.; Tabacco, E.; Schmidt, R.J.; Holmes, B.J.; Muck, R.E. Silage Review: Factors Affecting Dry Matter and Quality Losses in Silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3952–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, D.; Ding, W.; Ke, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, P.; Guo, X. Modulation of Metabolome and Bacterial Community in Whole Crop Corn Silage by Inoculating Homofermentative Lactobacillus Plantarumand Heterofermentative Lactobacillus Buchneri. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muck, R.E.; Kung, L.J. Effects of Silage Additives on Ensiling. In Silage: Field to Feedbunk. Proceedings of the North American Conference, Hershey, PA, USA, 11–13 February 1997; NRAES Series; Northeast Regional Agricultural Engineering Service, Cooperative Extension: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, N.L.; dos Santos, L.F.; Soccol, C.R.; Suguimoto, H.H. Dynamics of Ethanol Production from Deproteinized Whey by Kluyveromyces Marxianus: An Analysis about Buffering Capacity, Thermal and Nitrogen Tolerance. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2015, 58, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, K.; Wang, F.; Zhu, B.; Yang, J.; Zhou, G.; Pan, Y.; Tao, Y.; Zhong, J. Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria and Molasses Additives on the Microbial Community and Fermentation Quality of Soybean Silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandra, J.R.; del Valle, T.A.; Takiya, C.S.; Oliveira, E.R.; Goes, R.H.T.B.; Batista, J.D.O.; Acosta, A.P.; Noia, I.Z.; Antônio, G.; Urio, G.S.; et al. Soybean Silage in Dairy Heifers’ Diets: Ruminal Fermentation, Intake and Digestibility of Nutrients. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielenz, J.R.; Bardsley, J.S.; Wyman, C.E. Fermentation of Soybean Hulls to Ethanol While Preserving Protein Value. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3532–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, J.; Alavi, S.; Vadlani, P.; Amanor-Boadu, V. Thermo-Mechanical Extrusion Pretreatment for Conversion of Soybean Hulls to Fermentable Sugars. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7583–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.M.; Li, H.Y. Application and Conversion of Soybean Hulls. In Soybean—The Basis of Yield, Biomass and Productivity; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2017; pp. 111–132. [Google Scholar]
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.E.; Driehuis, F.; Elferink, S.J.W.H.O.; Spoelstra, S.F.; Buxton, D.R.; Harrison, J.H. Microbiology of Ensiling. In Silage Science and Technology; Agronomy Monographs; Buxton, D.R., Muck, R.E., Holmes, H.J., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy, Inc. Publishers: Madison, WI, USA, 2003; Volume 42, pp. 31–93. [Google Scholar]
- Mcdonald, P.; Henderson, A.R.; Heron, S.J.E. The Biochemistry of Silage, 2nd ed.; Chalcombe: Marlow, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Mohnen, D. Pectin Structure and Biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, F.; Peng, P.; Xu, F.; Sun, R.C. Fractional Purification and Bioconversion of Hemicelluloses. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholme, R.; Morreel, K.; Ralph, J.; Boerjan, W. Lignin Engineering. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, K.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A Critical Review of Analytical Methods in Pretreatment of Lignocelluloses: Composition, Imaging, and Crystallinity. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, H.; Sun, W.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, B.; Zheng, Y.; Li, J. Bioaugmentation of Sweet Sorghum Ensiling with Rumen Fluid: Fermentation Characteristics, Chemical Composition, Microbial Community, and Enzymatic Digestibility of Silages. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 294, 126308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhipei, Y.; Jihong, L.; Sandra, C.; Ting, C.; Yan, J.; Menghui, Y.; Lei, Z.; Gang, Z.; Panlun, Q.; Shizhong, L. Lignin Relocation Contributed to the Alkaline Pretreatment Efficiency of Sweet Sorghum Bagasse. Fuel 2015, 158, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Tan, T. The Effects of Four Different Pretreatments on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Sweet Sorghum Bagasse. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4585–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinozaki, Y.; Kitamoto, H.K. Ethanol Production from Ensiled Rice Straw and Whole-Crop Silage by the Simultaneous Enzymatic Saccharification and Fermentation Process. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).