Nutrition Component Adjustment of Distilled Dried Grain with Solubles via Aspergillus niger and Its Change about Dynamic Physiological Metabolism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Microorganism and Substrate
2.1.1. Microorganism, Medium, and Culture
2.1.2. Substrate and Inoculum
2.2. Solid-State Fermentation
2.3. Nutrient Composition Analysis
2.3.1. Determination of Nutrient Content
2.3.2. Determination of Amino Acids Composition
2.3.3. Determination of Lignocellulose Composition
2.4. Metabolomics Experiments
2.5. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
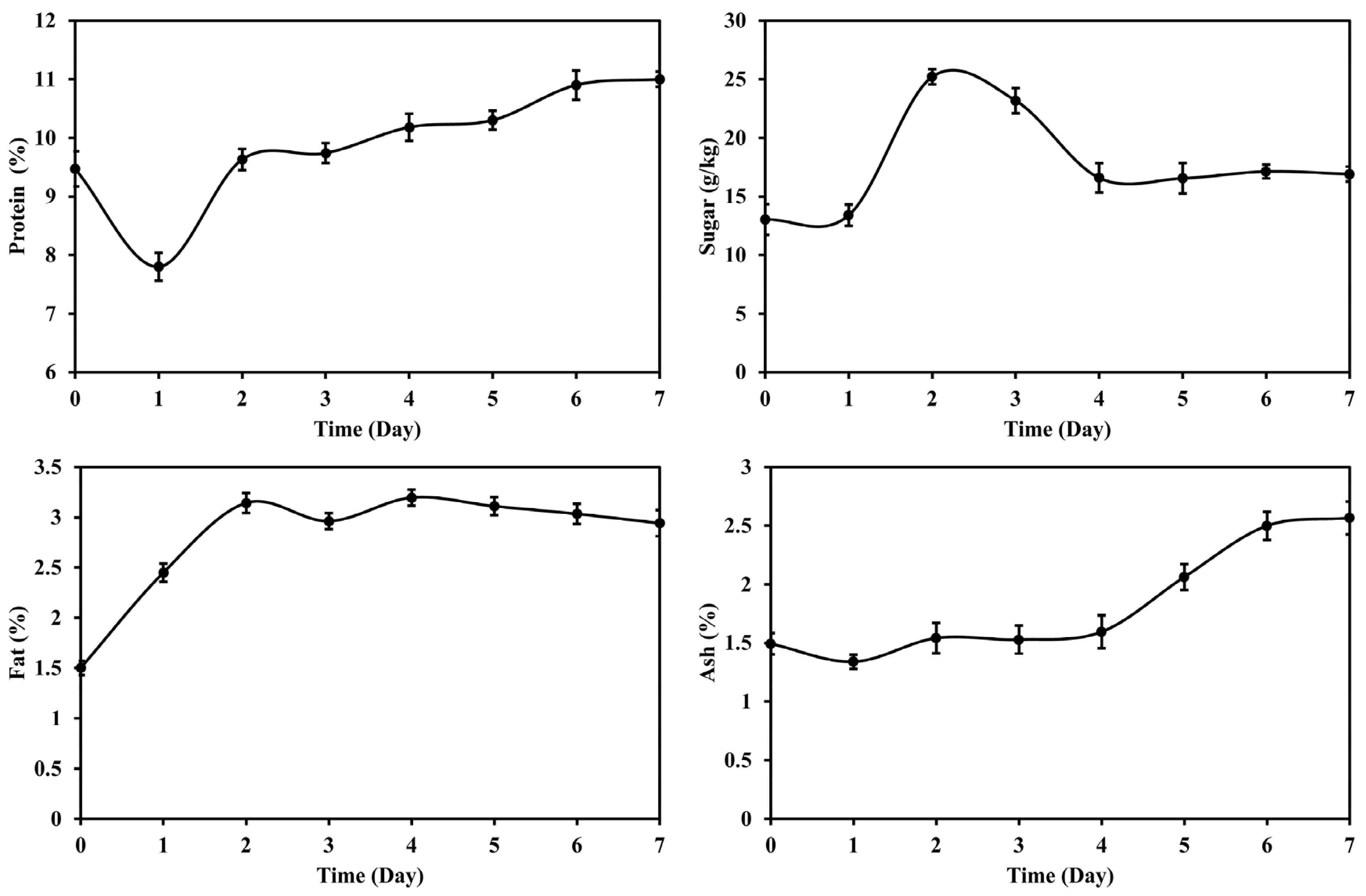
3.1. Changes in Main Nutrients of DDGS during Fermentation
3.2. Effects of A. niger on Degradation of Structural Carbohydrates in DDGS
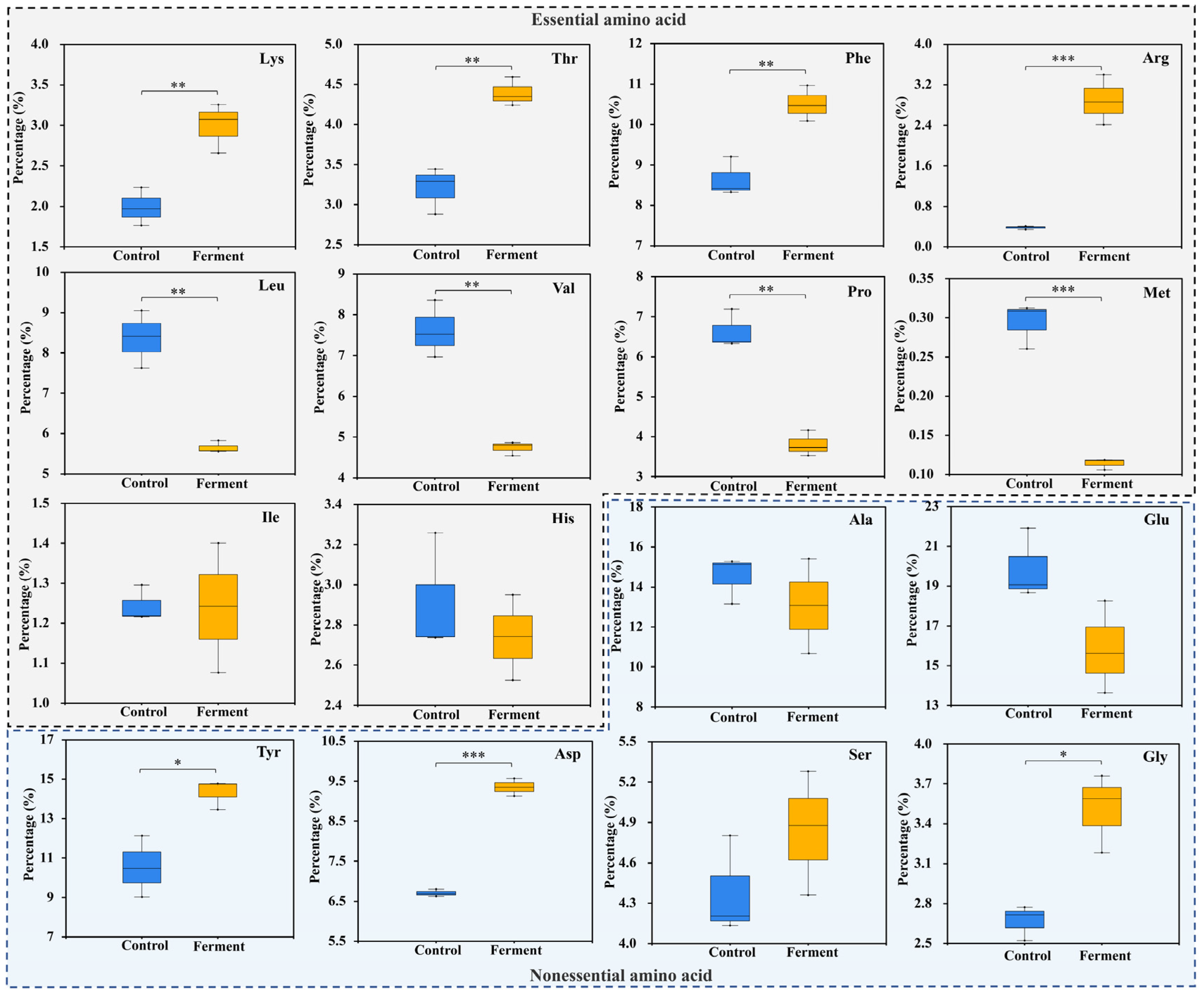
3.3. Effects of A. niger on Amino Acid Composition Proportion Adjustment
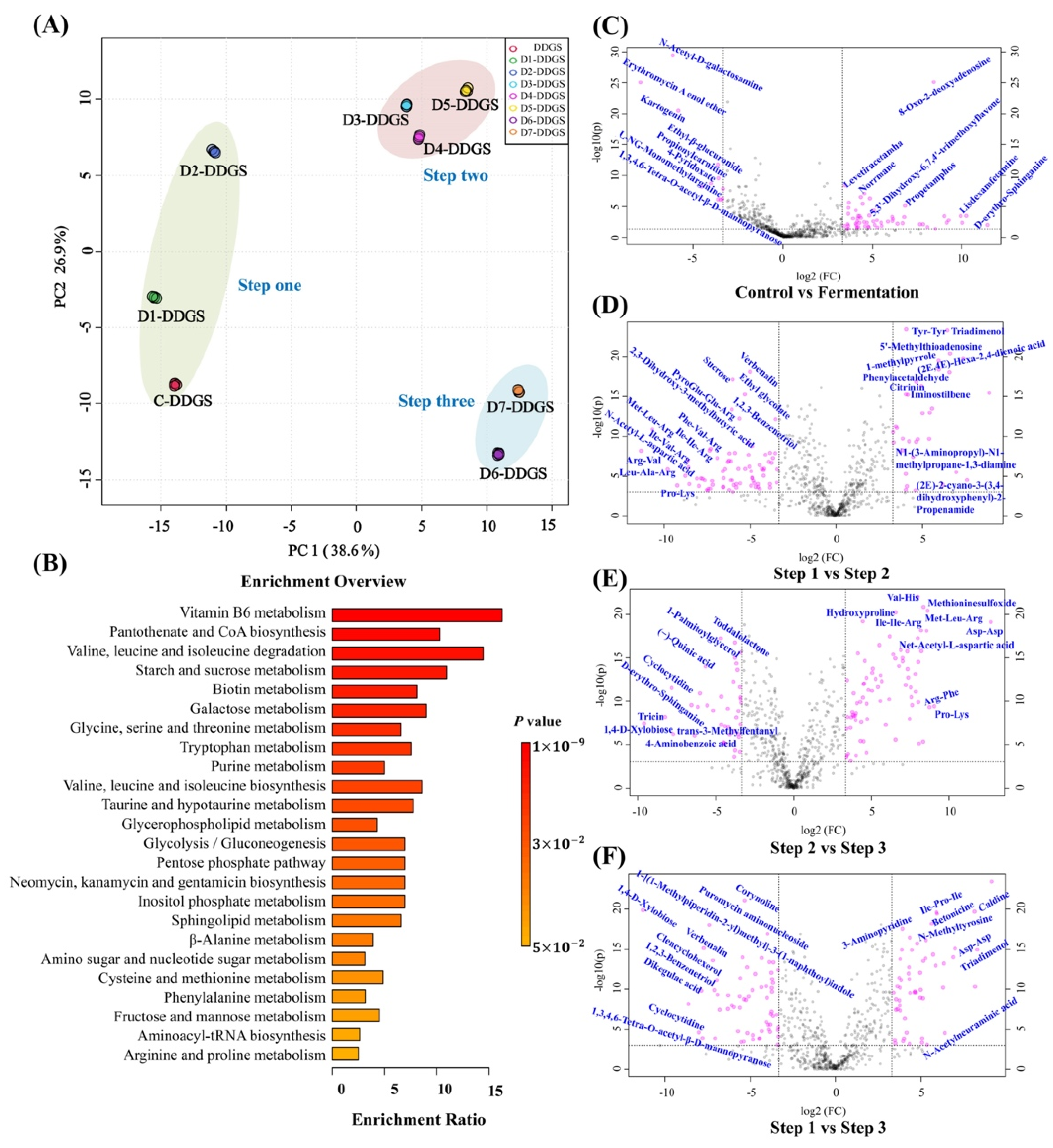
3.4. Analysis of Key Regulatory Pathways of A. niger for Adjusting DDGS Nutrition
3.5. Key regulatory Pathways Identified and Mapped
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- RFA. Ethanol Industry Outlook; Renewable Fuel Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Busic, A.; Mardetko, N.; Kundas, S.; Morzak, G.; Belskaya, H.; Santek, M.I.; Komes, D.; Novak, S.; Santek, B. Bioethanol production from renewable raw materials and its separation and purification: A review. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 56, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devries, J.W.; Camire, M.E.; Cho, S.; Craig, S.; Tungland, B.C. The definition of dietary fiber. Cereal Foods World 2001, 46, 112–129. [Google Scholar]
- Stein, H.H.; Shurson, G.C. Board-invited review: The use and application of distillers dried grains with solubles in swine diets. J. Anim. Sci. 2009, 87, 1292–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, H.H.; Gibson, M.L.; Pedersen, C.; Boersma, M.G. Amino acid and energy digestibility in ten samples of distillers dried grain with solubles fed to growing pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cromwell, G.L.; Herkelman, K.L.; Stahly, T.S. Physical, chemical, and nutritional characteristics of distillers dried grains with solubles for chicks and pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 1993, 71, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatzifragkou, A.; Kosik, O.; Prabhakumari, P.C.; Lovegrove, A.; Frazier, R.A.; Shewry, P.R.; Charalampopoulos, D. Biorefinery strategies for upgrading distillers’ dried grains with solubles (ddgs). Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 2194–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.W. Aspergillus niger as a secondary metabolite factory. Front. Chem. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iram, A.; Cekmecelioglu, D.; Demirci, A. Screening of bacterial and fungal strains for cellulase and xylanase production using distillers’ dried grains with solubles (ddgs) as the main feedstock. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 11, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Jun, S.C.; Han, K.H.; Hong, S.B.; Yu, J.H. Diversity, application, and synthetic biology of industrially important aspergillus fungi. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 100, 161–202. [Google Scholar]
- Houbraken, J.; de Vries, R.P.; Samson, R.A. Modern taxonomy of biotechnologically important aspergillus and penicillium species. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 86, 199–249. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, E.; Dunn-Coleman, N.; Frisvad, J.C.; van Dijck, P.W.M. On the safety of Aspergillus niger—A review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Yao, L.; Hou, Y.; Hou, Y.; Qian, L. Optimization of culture conditions during the solid-state fermentation of tea esidue using mixed strains. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 6667–6675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.O.; Alves, D.G.; Brito, D.E.; Vieira, P.; Marcelo, F. Effect of solid state fermentation on nutritional content and evaluation of degradability in cactus pear. Rev. Caatinga 2015, 28, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yalemtesfa, B.; Alemu, T.; Santhanam, A. Solid substrate fermentation and conversion of orange waste in to fungal biomass using Aspergillus niger ka-06 and chaetomium spp kc-06. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 1275–1281. [Google Scholar]
- Sukaryani, S.; Yakin, E.A.; Harinta, Y.W.; Vincēvia–Gaile, Z.; Purbajanti, E.D. Lignin and cellulose content of fermented rice straw with Aspergillus niger (van tieghem) and trichoderma mutan aa1. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 226, 00043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, K.; Huang, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhu, P.; Chi, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q. Signature of dissolved organic matter and microbial communities based on different oxygen levels response during distillers dried grains with solubles plus sugarcane pith co-fermentations. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 349, 126868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, K.K.; Punekar, N.S. Expression of lactate dehydrogenase in Aspergillus niger for l-lactic acid production. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Su, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, L.; Wang, F.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Solid-state fermentation of distilled dried grain with solubles with probiotics for degrading lignocellulose and upgrading nutrient utilization. AMB Express 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopandi, T.; Surtiningsih, T.; Wardah, A. Nutrient compositions of distillers dried grain from rice husks with co-culture fermentation of saccharomyces cerevisiae with candida tropicalis. Malays. J. Microbiol. 2019, 15, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjoun, K.; Kalscheur, K.F.; Garcia, A.D. Fermentation characteristics and aerobic stability of wet corn distillers grains with solubles ensiled in combination with whole plant corn. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaenovi, I.; Kind, T.; Sa, M.R.; Jian, J.; Fiehn, O. Structure annotation of all mass spectra in untargeted metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lio, J.Y.; Wang, T. Solid-state fermentation of soybean and corn processing coproducts for potential feed improvement. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 7702–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meini, M.R.; Cabezudo, I.; Galetto, C.S.; Romanini, D. Production of grape pomace extracts with enhanced antioxidant and prebiotic activities through solid-state fermentation by Aspergillus niger and aspergillus oryzae. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradstreet, R.B. Kjeldahl method for organic nitrogen. Anal. Chem. 1954, 26, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmia, A.R.; Srihardyastutie, A.; Prasetyawan, S.; Safitri, A. Submerged-fermentation of brassica oleracea l. Capitata using lactobacillus plantarum to reduce anti-nutrient compound. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 546, 062006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Park, S.K. Comparison of fat determination methods depending on fat definition in bakery products. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 972–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Kan, L.J.; Nie, S.P.; Chen, H.H.; Cui, S.W.; Phillips, A.O.; Phillips, G.O.; Li, Y.J.; Xie, M.Y. A comparison of chemical composition, bioactive components and antioxidant activity of natural and cultured cordyceps sinensis. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluiter, A.D.; Hames, B.; Ruiz, R.; Scarlata, C.; Sluiter, J.; Templeton, D.W.; Crocker, D. Determination of Structural Carbohydrates and Lignin in Biomass. Lab. Anal. Proced. 2008, 1617, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, J.; Wu, Q.X.; Battino, M.; Bai, W.B.; Tian, L.M. Using untargeted metabolomics to profile the changes in roselle (hibiscus sabdariffa l.) anthocyanins during wine fermentation. Food Chem. 2021, 364, 130425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Sinelnikov, I.V.; Han, B.; Wishart, D.S. Metaboanalyst 3.0—Making metabolomics more meaningful. Nuclc Acids Res. 2015, 43, W251–W257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Luo, L.N.; Heidari, F.; Tiffany, D.G.; Urriola, P.E.; Shurson, G.G.; Hu, B. Feeding value improvement by co-fermentation of corn-ethanol co-product and agro-industrial residues with rhizopus oryzae. Process Biochem. 2021, 111, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Rosentrater, K.A. Distillers Grains: Production, Properties, and Utilization; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Huntley, N.F.; Patience, J.F. Xylose metabolism in the pig. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Devi, N.D.; Urriola, P.E.; Tiffany, D.G.; Jang, J.C.; Shurson, G.G.; Hu, B. Feeding value improvement of corn-ethanol co-product and soybean hull by fungal fermentation: Fiber degradation and digestibility improvement. Food Bioprod. Processing 2021, 130, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.H. Comparative species utilization and toxicity of sulfur amino acids. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1670S–1675S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jha, R.; Fouhse, J.M.; Tiwari, U.P.; Li, L.G.; Willing, B.P. Dietary fiber and intestinal health of monogastric animals. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, G.N. Biosynthesis of amino acids derived from phosphoglyceric acid and pyruvic acid. In Microbial Biochemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 347–361. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, W.; Huang, X.; Liu, K.; Xu, Y.; Hu, B.; Chi, Z. Nutrition Component Adjustment of Distilled Dried Grain with Solubles via Aspergillus niger and Its Change about Dynamic Physiological Metabolism. Fermentation 2022, 8, 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8060264
Fan W, Huang X, Liu K, Xu Y, Hu B, Chi Z. Nutrition Component Adjustment of Distilled Dried Grain with Solubles via Aspergillus niger and Its Change about Dynamic Physiological Metabolism. Fermentation. 2022; 8(6):264. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8060264
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Weiwei, Xuhui Huang, Kehan Liu, Yongping Xu, Bo Hu, and Zhanyou Chi. 2022. "Nutrition Component Adjustment of Distilled Dried Grain with Solubles via Aspergillus niger and Its Change about Dynamic Physiological Metabolism" Fermentation 8, no. 6: 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8060264
APA StyleFan, W., Huang, X., Liu, K., Xu, Y., Hu, B., & Chi, Z. (2022). Nutrition Component Adjustment of Distilled Dried Grain with Solubles via Aspergillus niger and Its Change about Dynamic Physiological Metabolism. Fermentation, 8(6), 264. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8060264






