Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of NF-Y Transcription Factors in Sweet Potato under Salt Stress
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Identification and Analysis of Sweet Potato NF-Y Family Members
2.2. Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis of IbNF-Y Proteins
2.3. Gene Structures, Conserved Motif, and Domain Analysis
2.4. Chromosomal Distribution and Gene Duplication of IbNF-Y Genes
2.5. miRNA Target Site Prediction
2.6. Cis-Acting Element Analysis for IbNF-Ys Promoters
2.7. Plant Growth Conditions and Treatments
2.8. RNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.9. Transcriptome Analysis
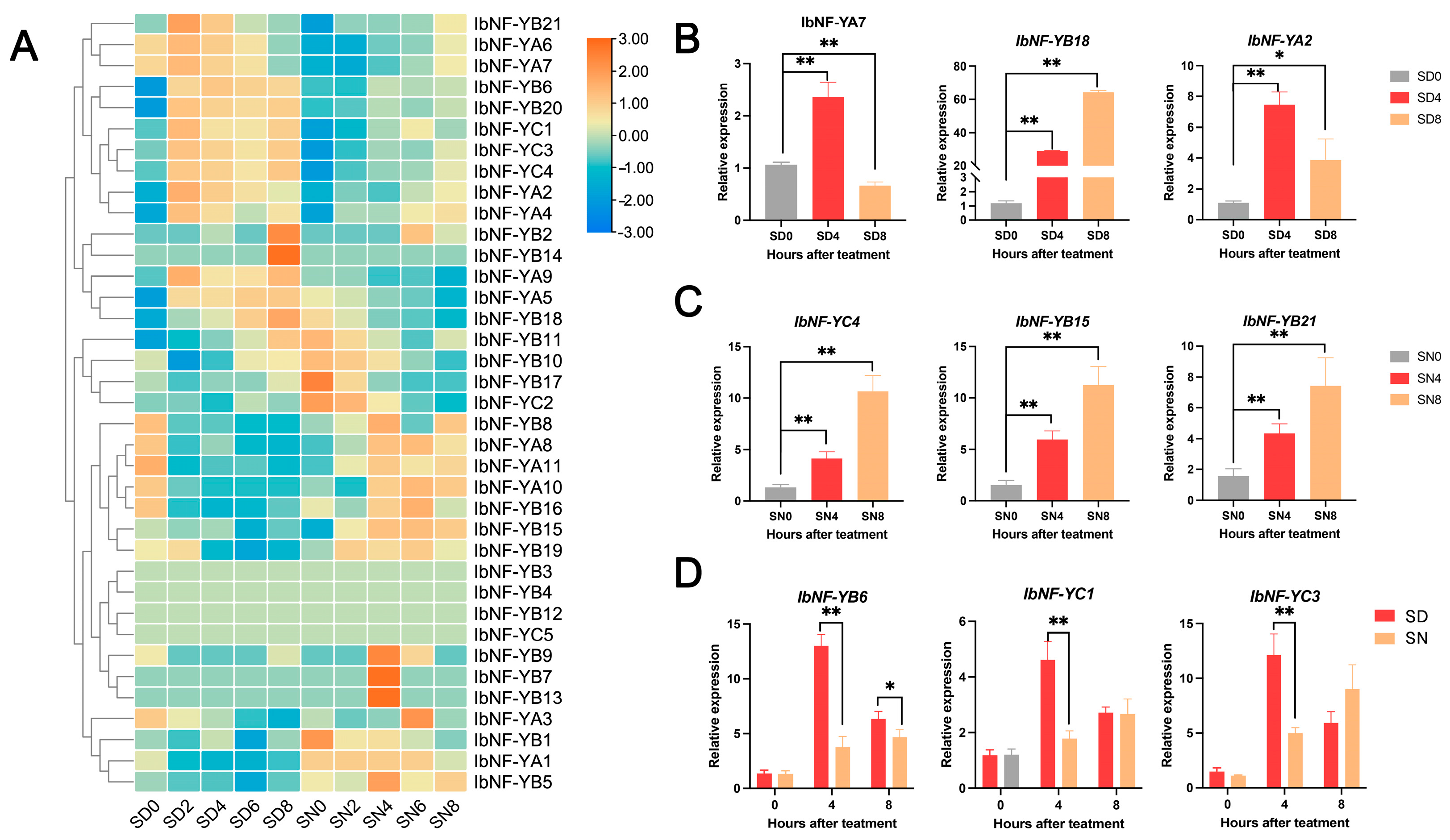
2.10. Expression Analysis by qRT-PCR
3. Results
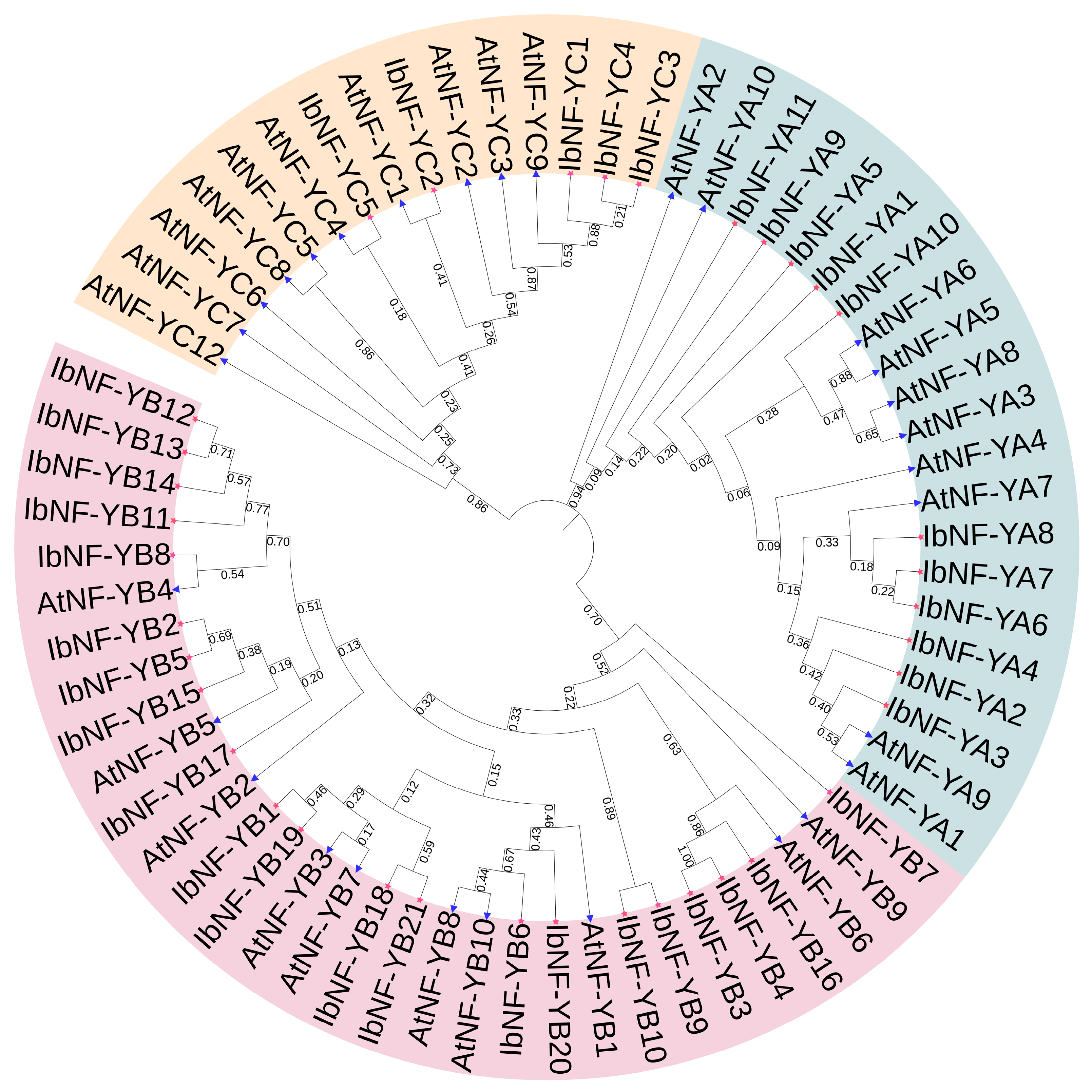
3.1. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of NF-Y Genes in I. batatas
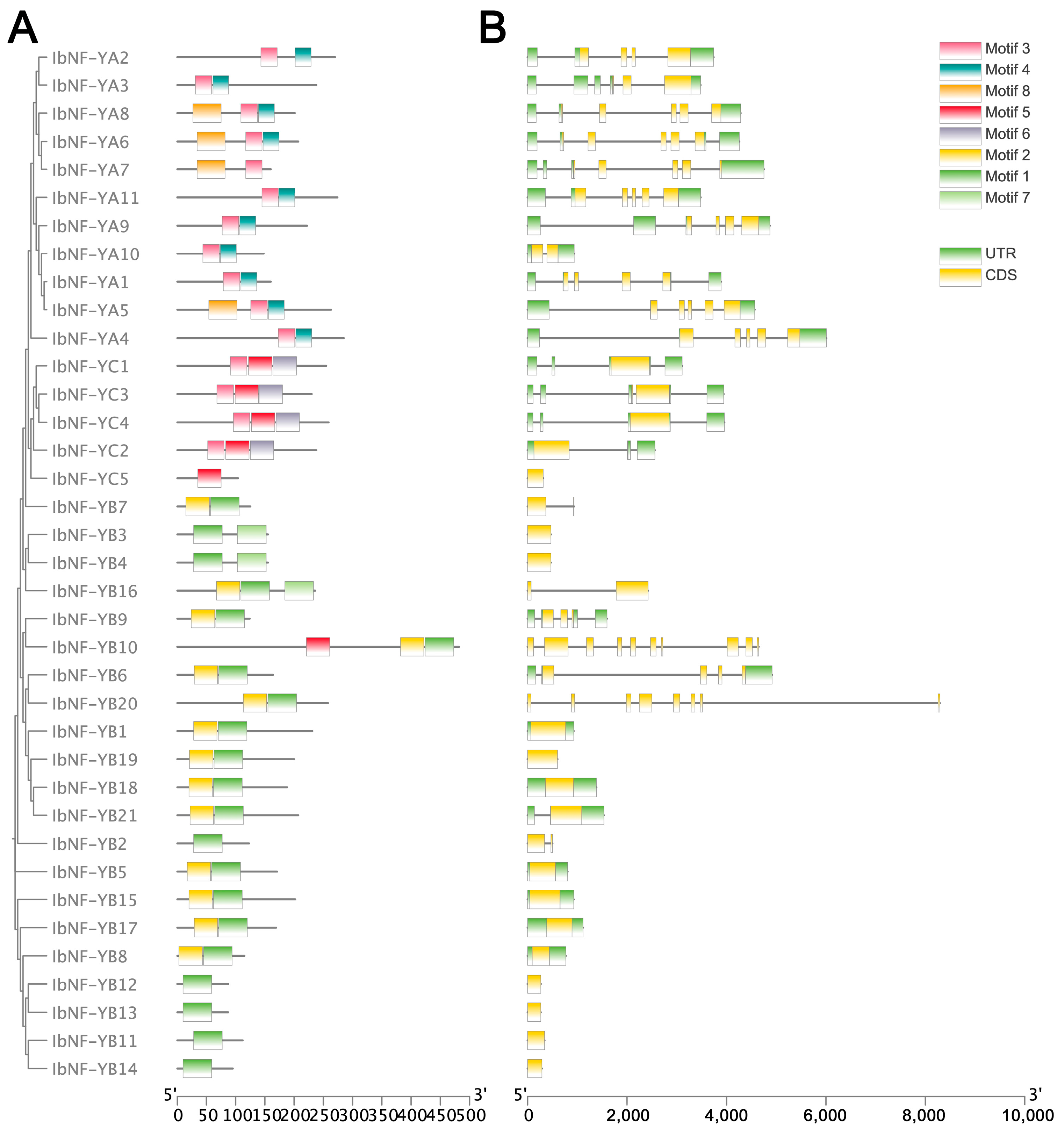
3.2. Conserved Motif and Gene Structure Analysis
3.3. Prediction of miRNA Target Site of IbNF-Y Genes
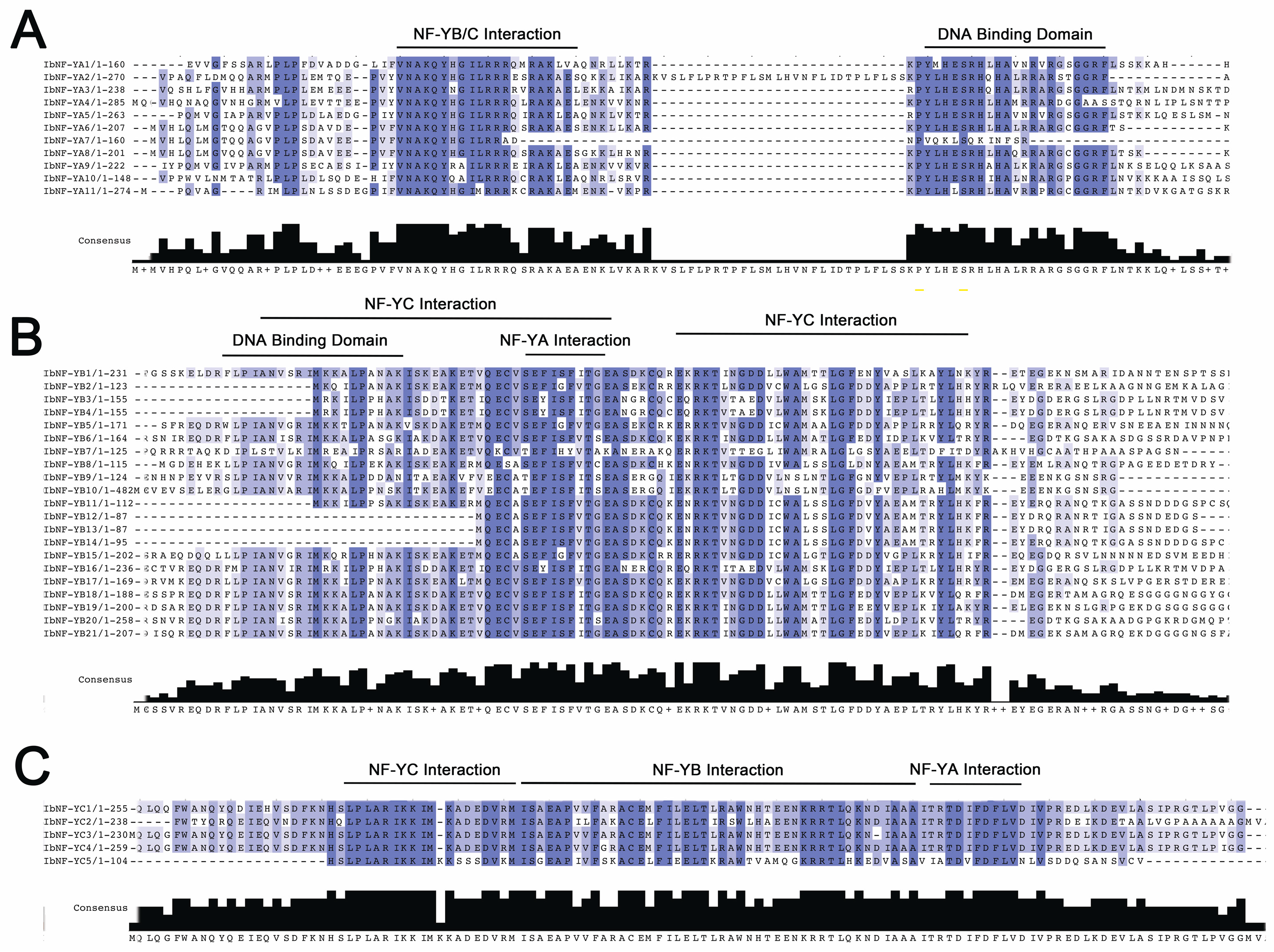
3.4. Conserved Regions of IbNF-Ys
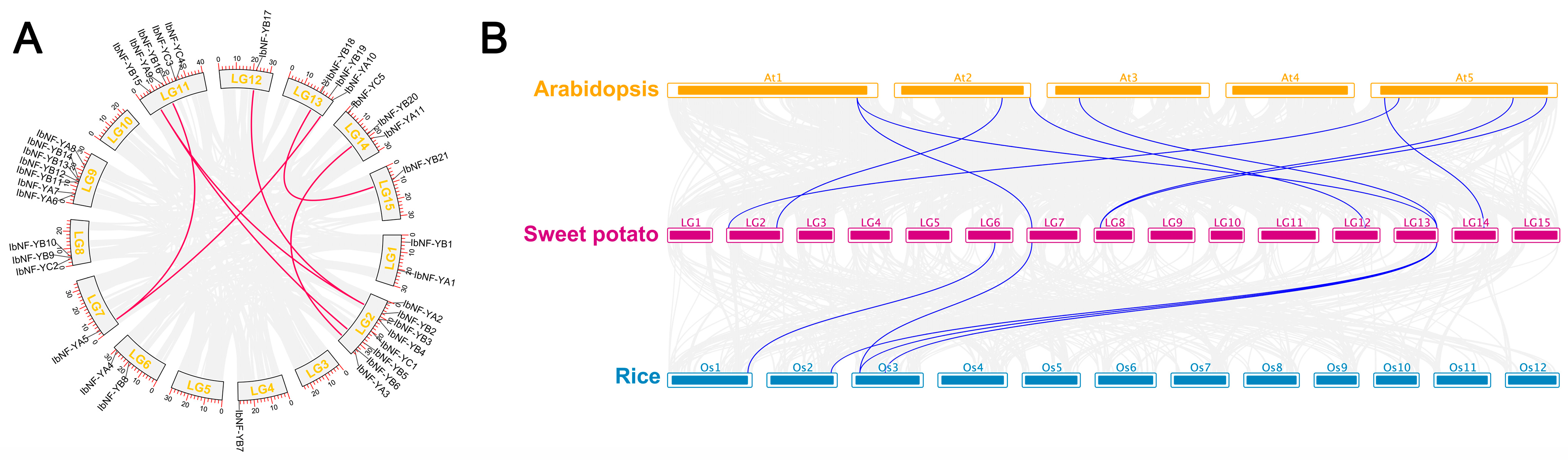
3.5. Chromosomal Location, Gene Duplication, and Synteny Analysis of IbNF-Ys
3.6. Cis-Acting Elements Analysis of IbNF-Y Genes
3.7. Three-Dimensional Structures of IbNF-Y Proteins
3.8. Expression Profiles of IbNF-Y Genes under Salt Stress
4. Discussion
4.1. Expansions of IbNF-Y Gene Family in Sweet Potato
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Evolution of IbNF-Ys
4.3. IbNF-Y Genes under Salt Stress
5. Conclusions
6. Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mantovani, R. The molecular biology of the CCAAT-binding factor NF-Y. Gene 1999, 239, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves-Sanjuan, A.; Gnesutta, N.; Gobbini, A.; Martignago, D.; Bernardini, A.; Fornara, F.; Mantovani, R.; Nardini, M. Structural determinants for NF-Y subunit organization and NF-Y/DNA association in plants. Plant J. 2021, 105, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.-J.; Zhang, X.-F.; Xue, H.-W. Rice aleurone layer specific OsNF-YB1 regulates grain filling and endosperm development by interacting with an ERF transcription factor. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, erw409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Heard, J.; Martin, G.; Reuber, L.; Jiang, C.-Z.; Keddie, J.; Adam, L.; Pineda, O.; Ratcliffe, O.; Samaha, R. Arabidopsis transcription factors: Genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 2000, 290, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, K.; Ju, Z.; Cao, D.; Fu, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, B.; Luo, Y. Genome-wide analysis of tomato NF-Y factors and their role in fruit ripening. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Lu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Yao, J. Genome-wide identification and co-expression network analysis of the OsNF-Y gene family in rice. Crop J. 2017, 5, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, X.; Ma, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Si, H. Genome-wide analysis of NF-Y genes in potato and functional identification of StNF-YC9 in drought tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 749688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, G.; Liu, W.; Dong, X.; Zhang, A. Genome-wide analysis of the NF-Y gene family in peach (Prunus persica L.). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, M.; Liu, H.L.; Gao, Y.M.; Chen, J.; Yan, H.W.; Xiang, Y. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NF-Y transcription factor family in Populus. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 171, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zhai, H.; He, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, N. IbNF-YA1 is a key factor in the storage root development of sweet potato. Plant J. 2024, 118, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, L. Genome-wide analysis of poplar NF-YB gene family and identified PtNF-YB1 important in regulate flowering timing in transgenic plants. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potsenkovskaia, E.; Tvorogova, V.; Lutova, L. NF-Y genes in the somatic embryogenesis. In Proceedings of the Bioinformatics of Genome Regulation and Structure/Systems Biology (BGRS/SB-2022), Novosibirsk, Russia, 4–8 July 2022; p. 661. [Google Scholar]
- Potsenkovskaia, E.; Tvorogova, V.; Yakovleva, D.; Zlydneva, N.; Lutova, L. Novel NF-Y genes expressed during somatic embryogenesis in Medicago truncatula. Plant Gene 2022, 31, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotan, T.; Ohto, M.-a.; Yee, K.M.; West, M.A.; Lo, R.; Kwong, R.W.; Yamagishi, K.; Fischer, R.L.; Goldberg, R.B.; Harada, J.J. Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON1 is sufficient to induce embryo development in vegetative cells. Cell 1998, 93, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, R.W.; Bui, A.Q.; Lee, H.; Kwong, L.W.; Fischer, R.L.; Goldberg, R.B.; Harada, J.J. LEAFY COTYLEDON1-LIKE defines a class of regulators essential for embryo development. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.-X.; Oono, Y.; Zhu, J.; He, X.-J.; Wu, J.-M.; Iida, K.; Lu, X.-Y.; Cui, X.; Jin, H.; Zhu, J.-K. The Arabidopsis NFYA5 transcription factor is regulated transcriptionally and posttranscriptionally to promote drought resistance. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 2238–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekanayake, I.J.; Collins, W. Effect of irrigation on sweet potato root carbohydrates and nitrogenous compounds. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2004, 2, 243–248. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.-P.; Kuo, Y.-W.; Lin, J.-S. Defense responses in sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas L.) against biotic stress. Plant Sci. 2023, 337, 111893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Yu, M.; Sun, L.; Qin, N.; Wei, L. Physiological responses of sweet potato seedlings under drought-stress conditions with selenium applications. J. Agric. Crop Res. 2020, 8, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Bo, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhai, H. Research Progress in the Mechanisms of Resistance to Biotic Stress in Sweet Potato. Genes 2023, 14, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Hou, F.; Li, A.; Dong, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. Transcriptome-wide identification of WRKY transcription factor and their expression profiles under salt stress in sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas L.). Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2020, 14, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.; Wang, L.; Ji, Z.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, K.; Qiao, Y. Comparative analysis of the MYB gene family in seven Ipomoea species. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1155018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, K.; Guo, H. Genome-wide comparative analysis of the r2r3-myb gene family in six ipomoea species and the identification of anthocyanin-related members in sweet potatoes. Plants 2023, 12, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, T.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, Z.; Li, A.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Hou, F.; Zhang, L. Genome-wide identification of the C2H2 zinc finger gene family and expression analysis under salt stress in sweetpotato. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1301848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Hao, X.; He, S.; Hao, X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of AP2/ERF transcription factors family in sweet potato. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G. Genome reannotation of the sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) using extensive Nanopore and Illumina-based RNA-seq datasets. Trop. Plants 2024, 3, e008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.; Tosatto, S.C.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, B.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.J.; Hu, S.; Chen, W.-H. Evolview v3: A webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W270–W275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Procter, J.; Martin, D.A.; Barton, G.J. Jalview: Visualization and analysis of molecular sequences, alignments, and structures. BMC Bioinform. 2005, 6, P28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W39–W49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; DeBarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.-h.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaka, S.; Zimin, A.V.; Pertea, G.M.; Razaghi, R.; Salzberg, S.L.; Pertea, M. Transcriptome assembly from long-read RNA-seq alignments with StringTie2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.; Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential analysis of count data–the DESeq2 package. Genome Biol 2014, 15, 10–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.-C.; Kim, Y.-H.; Ji, C.Y.; Park, S.; Jeong, J.C.; Lee, H.-S.; Kwak, S.-S. Stable internal reference genes for the normalization of real-time PCR in different sweetpotato cultivars subjected to abiotic stress conditions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, M.; Yin, X.; Lin, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhao, G. Identification and characterization of NF-Y transcription factor families in Canola (Brassica napus L.). Planta 2014, 239, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, T.N.; Nguyen, H.T.; Valliyodan, B.; Joshi, T.; Xu, D.; Nguyen, H.T. Genome-wide expression analysis of soybean NF-Y genes reveals potential function in development and drought response. Mol. Genet. Genom. MGG 2015, 290, 1095–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, R.; Li, X.Y.; Pessara, U.; Hooft van Huisjduijnen, R.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Dominant negative analogs of NF-YA. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 20340–20346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Fikes, J.D.; Guarente, L. Mutations in yeast HAP2/HAP3 define a hybrid CCAAT box binding domain. EMBO J. 1993, 12, 4647–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Zhang, S.; Olesen, J.T.; Rich, A.; Guarente, L. Subunit interaction in the CCAAT-binding heteromeric complex is mediated by a very short alpha-helix in HAP2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3009–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackenberg, D.; Wu, Y.; Voigt, A.; Adams, R.; Schramm, P.; Grimm, B. Studies on differential nuclear translocation mechanism and assembly of the three subunits of the Arabidopsis thaliana transcription factor NF-Y. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenkel, S.; Turck, F.; Singer, K.; Gissot, L.; Le Gourrierec, J.; Samach, A.; Coupland, G. CONSTANS and the CCAAT box binding complex share a functionally important domain and interact to regulate flowering of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 2971–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolfini, D.; Gatta, R.; Mantovani, R. NF-Y and the transcriptional activation of CCAAT promoters. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 29–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Kim, I.S.; Sohn, K.Y.; de Crombrugghe, B.; Maity, S.N. Three classes of mutations in the A subunit of the CCAAT-binding factor CBF delineate functional domains involved in the three-step assembly of the CBF-DNA complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romier, C.; Cocchiarella, F.; Mantovani, R.; Moras, D. The NF-YB/NF-YC structure gives insight into DNA binding and transcription regulation by CCAAT factor NF-Y. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 1336–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, D.; Kong, F.; Lin, K.; Zhang, H.; Li, G. The Arabidopsis thaliana nuclear factor Y transcription factors. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swain, S.; Myers, Z.A.; Siriwardana, C.L.; Holt, B.F., III. The multifaceted roles of NUCLEAR FACTOR-Y in Arabidopsis thaliana development and stress responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2017, 1860, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Zeng, X.; Hu, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, C.; Wu, Z. Structural insights into the multivalent binding of the Arabidopsis FLOWERING LOCUS T promoter by the CO–NF–Y master transcription factor complex. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 1182–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton-Rauh, A. Evolutionary dynamics of duplicated genes in plants. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2003, 29, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvenzani, V.; Testoni, B.; Gusmaroli, G.; Lorenzo, M.; Gnesutta, N.; Petroni, K.; Mantovani, R.; Tonelli, C. Interactions and CCAAT-binding of Arabidopsis thaliana NF-Y subunits. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siefers, N.; Dang, K.K.; Kumimoto, R.W.; Bynum IV, W.E.; Tayrose, G.; Holt III, B.F. Tissue-specific expression patterns of Arabidopsis NF-Y transcription factors suggest potential for extensive combinatorial complexity. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fornari, M.; Calvenzani, V.; Masiero, S.; Tonelli, C.; Petroni, K. The Arabidopsis NF-YA3 and NF-YA8 genes are functionally redundant and are required in early embryogenesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bararyenya, A.; Olukolu, B.A.; Tukamuhabwa, P.; Grüneberg, W.J.; Ekaya, W.; Low, J.; Ochwo-Ssemakula, M.; Odong, T.L.; Talwana, H.; Badji, A. Genome-wide association study identified candidate genes controlling continuous storage root formation and bulking in hexaploid sweetpotato. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rípodas, C.; Castaingts, M.; Clúa, J.; Blanco, F.; Zanetti, M.E. Annotation, phylogeny and expression analysis of the nuclear factor Y gene families in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 5, 120388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Pan, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Liu, C.; Hu, J.; Liu, T. Transcriptome-wide characterization, evolutionary analysis, and expression pattern analysis of the NF-Y transcription factor gene family and salt stress response in Panax ginseng. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, X.; An, Y.; Lin, S.; Shen, C.; Wen, J.; Liu, C.; Yin, W. Root-specific NF-Y family transcription factor, PdNF-YB21, positively regulates root growth and drought resistance by abscisic acid-mediated indoylacetic acid transport in Populus. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 407–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.F.; Liu, Y.; Fu, J.D.; Ma, J.; Fang, Z.W.; Chen, J.; Zheng, L.; Lu, Z.W.; Zhou, Y.B.; Chen, M. The NF-Y-PYR module integrates the abscisic acid signal pathway to regulate plant stress tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2589–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Jiao, J.; Zhai, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, W. Expression of the Malus sieversii NF-YB21 encoded gene confers tolerance to osmotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, K.; Hou, X. Arabidopsis NF-YCs mediate the light-controlled hypocotyl elongation via modulating histone acetylation. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeber, V.M.; Bajaj, I.; Rohde, M.; Schmülling, T.; Cortleven, A. Light acts as a stressor and influences abiotic and biotic stress responses in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 645–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
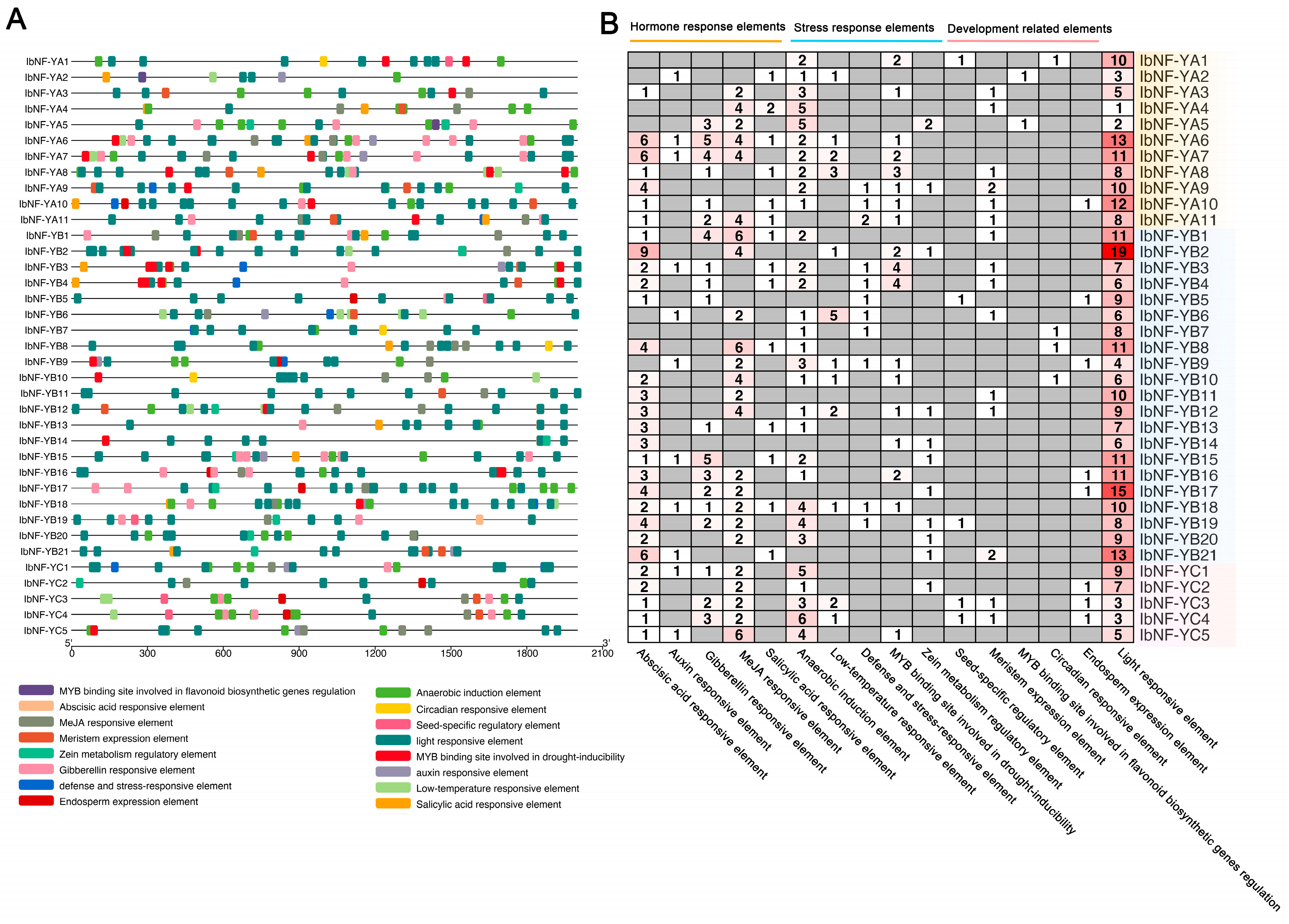

| Name | Gene ID | Chromosome Localization | CDS Length | Length (AA) | pI | Mw (kDa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IbNF-YA1 | IB01G23380 | LG1:20498162-20502055 | 480 | 160 | 9.83 | 17.69 |
| IbNF-YA2 | IB02G01210 | LG2:1281865-1285826 | 810 | 270 | 10.04 | 30.16 |
| IbNF-YA3 | IB02G30080 | LG2:34597820-34601301 | 714 | 238 | 9.62 | 26.47 |
| IbNF-YA4 | IB06G22910 | LG6:29233049-29239060 | 855 | 285 | 7.77 | 31.53 |
| IbNF-YA5 | IB07G05030 | LG7:3274382-3278981 | 789 | 263 | 9.97 | 28.43 |
| IbNF-YA6 | IB09G08540 | LG9:5842172-5846486 | 621 | 207 | 7.22 | 23.01 |
| IbNF-YA7 | IB09G08760 | LG9:6055325-6060077 | 480 | 160 | 6.1 | 17.80 |
| IbNF-YA8 | IB09G19400 | LG9:22621903-22626188 | 603 | 201 | 8.33 | 22.35 |
| IbNF-YA9 | IB11G20750 | LG11:16549446-16554321 | 666 | 222 | 9.43 | 24.58 |
| IbNF-YA10 | IB13G25510 | LG13:28536035-28536971 | 444 | 148 | 10.95 | 16.45 |
| IbNF-YA11 | IB14G15960 | LG14:21325438-21328917 | 822 | 274 | 9.25 | 30.21 |
| IbNF-YB1 | IB01G06700 | LG1:4056767-4057693 | 693 | 231 | 7.82 | 24.63 |
| IbNF-YB2 | IB02G10480 | LG2:8282844-8283342 | 369 | 123 | 5.53 | 13.82 |
| IbNF-YB3 | IB02G14110 | LG2:11787981-11788448 | 465 | 155 | 5.42 | 17.50 |
| IbNF-YB4 | IB02G14160 | LG2:11869246-11869713 | 465 | 155 | 5.42 | 17.50 |
| IbNF-YB5 | IB02G23820 | LG2:28008273-28009078 | 513 | 171 | 5.1 | 19.53 |
| IbNF-YB6 | IB02G28490 | LG2:33521179-33526727 | 492 | 164 | 6.83 | 17.87 |
| IbNF-YB7 | IB04G23730 | LG4:28702197-28703130 | 375 | 125 | 9.46 | 13.65 |
| IbNF-YB8 | IB06G12770 | LG6:19446997-19447766 | 345 | 115 | 5.44 | 13.24 |
| IbNF-YB9 | IB08G07290 | LG8:4619920-4621514 | 372 | 124 | 5.22 | 13.47 |
| IbNF-YB10 | IB08G07300 | LG8:4623964-4628612 | 1446 | 482 | 6.22 | 53.84 |
| IbNF-YB11 | IB09G14960 | LG9:13143008-13143346 | 336 | 112 | 5.86 | 12.60 |
| IbNF-YB12 | IB09G14970 | LG9:13159332-13159595 | 261 | 87 | 5.04 | 9.84 |
| IbNF-YB13 | IB09G15230 | LG9:13614901-13615164 | 261 | 87 | 5.04 | 9.84 |
| IbNF-YB14 | IB09G15240 | LG9:13625088-13625375 | 285 | 95 | 4.75 | 10.59 |
| IbNF-YB15 | IB11G09690 | LG11:7696191-7697120 | 606 | 202 | 8.94 | 23.06 |
| IbNF-YB16 | IB11G21910 | LG11:18055289-18057712 | 708 | 236 | 5.84 | 26.25 |
| IbNF-YB17 | IB12G15700 | LG12:21558874-21559987 | 507 | 169 | 5.09 | 19.16 |
| IbNF-YB18 | IB13G13850 | LG13:20788001-20789385 | 564 | 188 | 5.83 | 19.97 |
| IbNF-YB19 | IB13G21250 | LG13:25991816-25992418 | 600 | 200 | 6.21 | 20.77 |
| IbNF-YB20 | IB14G13160 | LG14:18527336-18536111 | 774 | 258 | 9.03 | 28.02 |
| IbNF-YB21 | IB15G12080 | LG15:8887698-8889231 | 621 | 207 | 6.3 | 21.67 |
| IbNF-YC1 | IB02G18000 | LG2:19872475-19875594 | 765 | 255 | 5.49 | 28.24 |
| IbNF-YC2 | IB08G06600 | LG8:4214030-4216591 | 714 | 238 | 5.21 | 25.97 |
| IbNF-YC3 | IB11G25670 | LG11:23699582-23703630 | 690 | 230 | 5.88 | 26.01 |
| IbNF-YC4 | IB11G25780 | LG11:23836415-23840480 | 777 | 259 | 5.65 | 28.80 |
| IbNF-YC5 | IB14G01500 | LG14:1605470-1605784 | 312 | 104 | 9.03 | 11.25 |
| miRNA | Target | Expectation | miRNA Length | Target_start | Target_end | Inhibition | Multiplicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ib-miRN6 | IbNF-YA2 | 4.5 | 21 | 962 | 982 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miR399i | IbNF-YA4 | 4.5 | 21 | 456 | 476 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miR2111 | IbNF-YA4 | 5 | 21 | 1037 | 1057 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miR403b | IbNF-YA4 | 5 | 21 | 1101 | 1121 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miR319d | IbNF-YA9 | 4 | 20 | 1447 | 1465 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miR164a | IbNF-YA9 | 5 | 21 | 34 | 53 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miR159b | IbNF-YA11 | 5 | 21 | 719 | 739 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miR1515 | IbNF-YB6 | 3.5 | 22 | 755 | 776 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miR396a/b/c | IbNF-YB10 | 4.5 | 21 | 418 | 438 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miRN10 | IbNF-YB10 | 5 | 21 | 1359 | 1379 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miRN13 | IbNF-YB16 | 5 | 21 | 123 | 143 | Translation | 1 |
| Ib-miRN15 | IbNF-YB17 | 5 | 21 | 74 | 94 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miR399i | IbNF-YB21 | 5 | 21 | 931 | 951 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miRN15 | IbNF-YB21 | 5 | 21 | 952 | 972 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miR530a/b | IbNF-YC2 | 5 | 21 | 234 | 254 | Translation | 1 |
| Ib-miR827a/b | IbNF-YC3 | 5 | 21 | 494 | 514 | Cleavage | 1 |
| Ib-miR827a/b | IbNF-YC4 | 5 | 21 | 513 | 533 | Cleavage | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, B.; Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B.; Gao, F.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G. Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of NF-Y Transcription Factors in Sweet Potato under Salt Stress. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10080798
Liang B, Wu J, Chen Y, Wang B, Gao F, Li Y, Zhu G. Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of NF-Y Transcription Factors in Sweet Potato under Salt Stress. Horticulturae. 2024; 10(8):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10080798
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Bei, Jiayun Wu, Ye Chen, Bei Wang, Feiyan Gao, Yongping Li, and Guopeng Zhu. 2024. "Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of NF-Y Transcription Factors in Sweet Potato under Salt Stress" Horticulturae 10, no. 8: 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10080798
APA StyleLiang, B., Wu, J., Chen, Y., Wang, B., Gao, F., Li, Y., & Zhu, G. (2024). Genome and Transcriptome Analysis of NF-Y Transcription Factors in Sweet Potato under Salt Stress. Horticulturae, 10(8), 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae10080798





