Optimizing Selenium Application for Enhanced Quality and Nutritional Value of Spring Tea (Camellia sinensis)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Materials
2.2. Experimental Design and Sampling
2.3. Measurement of Plant Samples
2.4. Measurement of Soil Samples
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
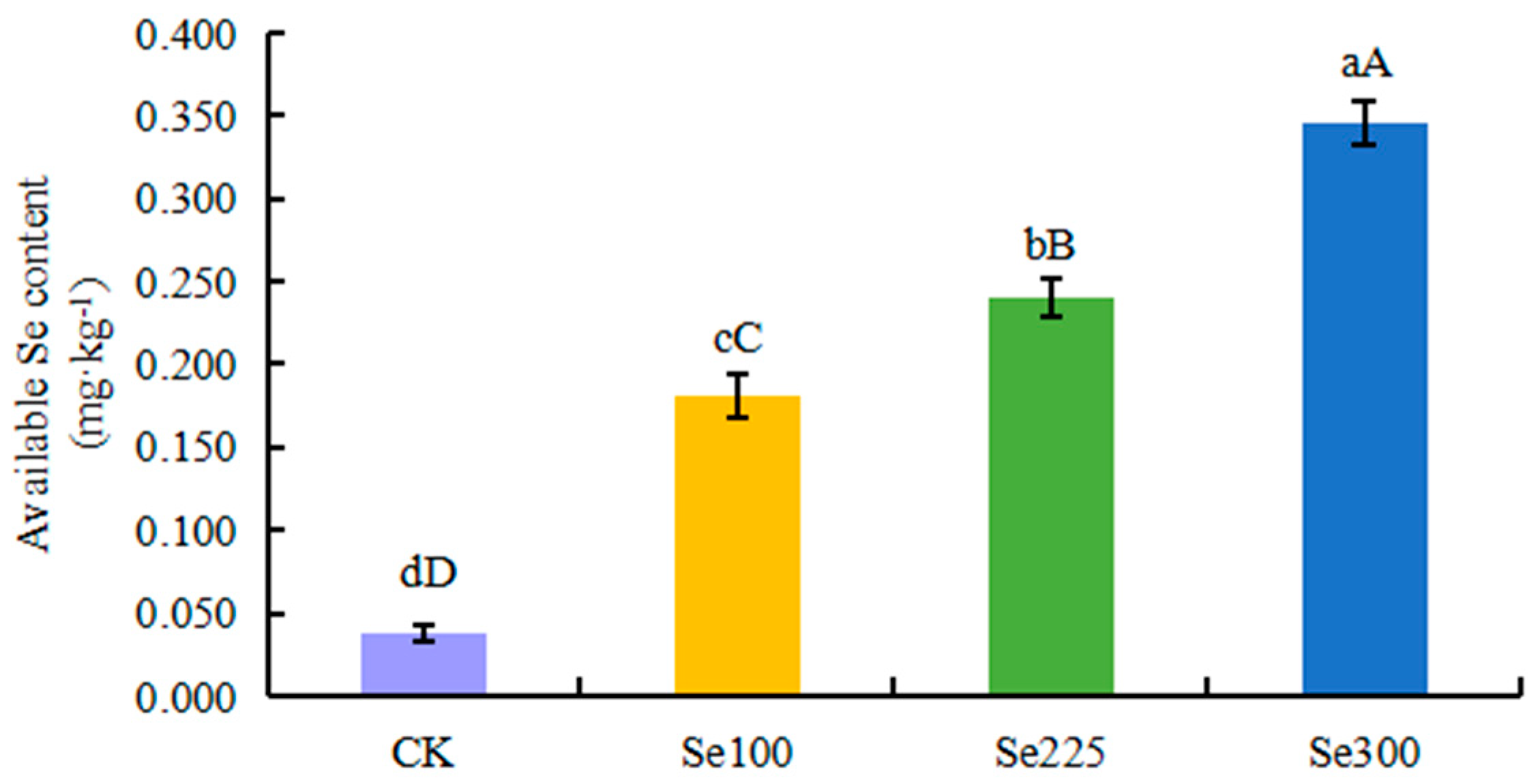
3.1. Selenium Application Enhances the Available Selenium in Soil
3.2. Selenium Application Exerts Diverse Effects on Soil Enzyme Activity
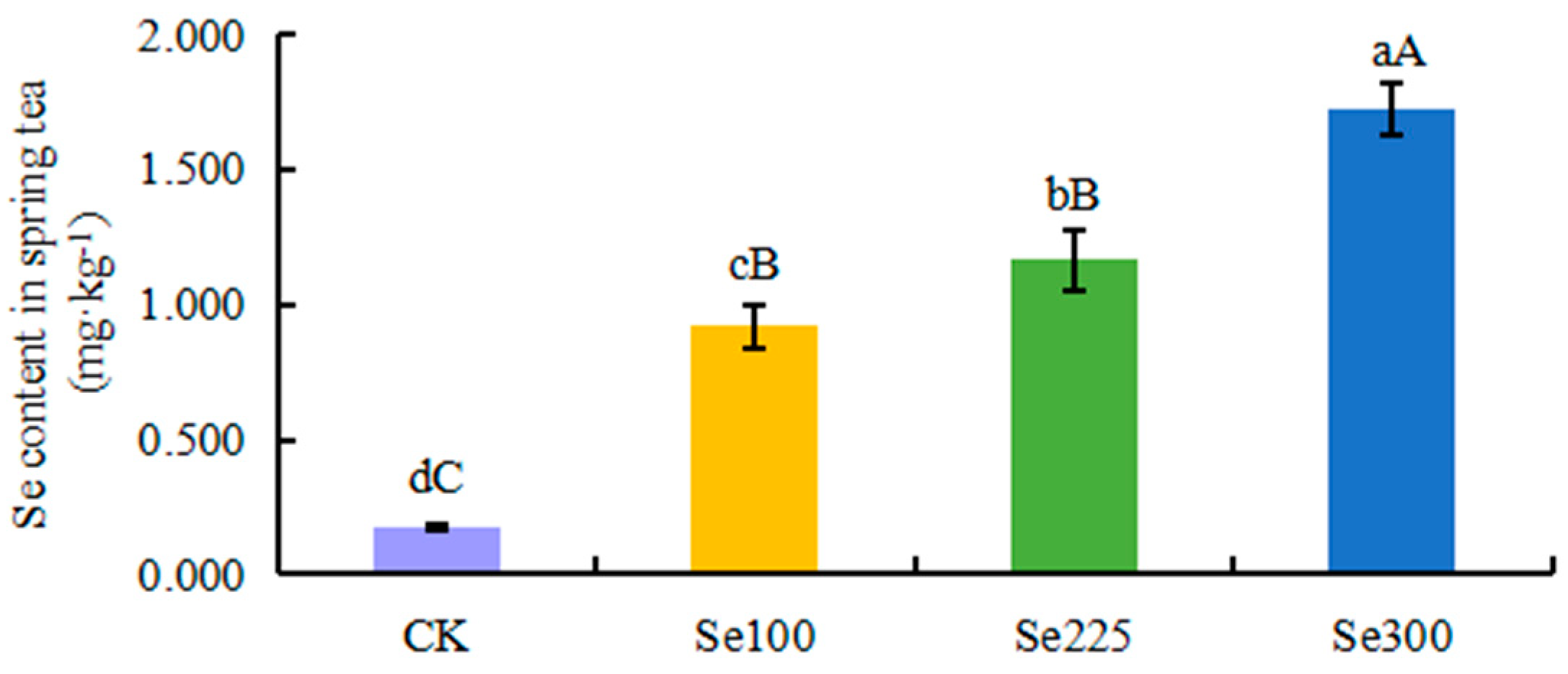
3.3. Selenium Application Increases the Selenium Content in Spring Tea
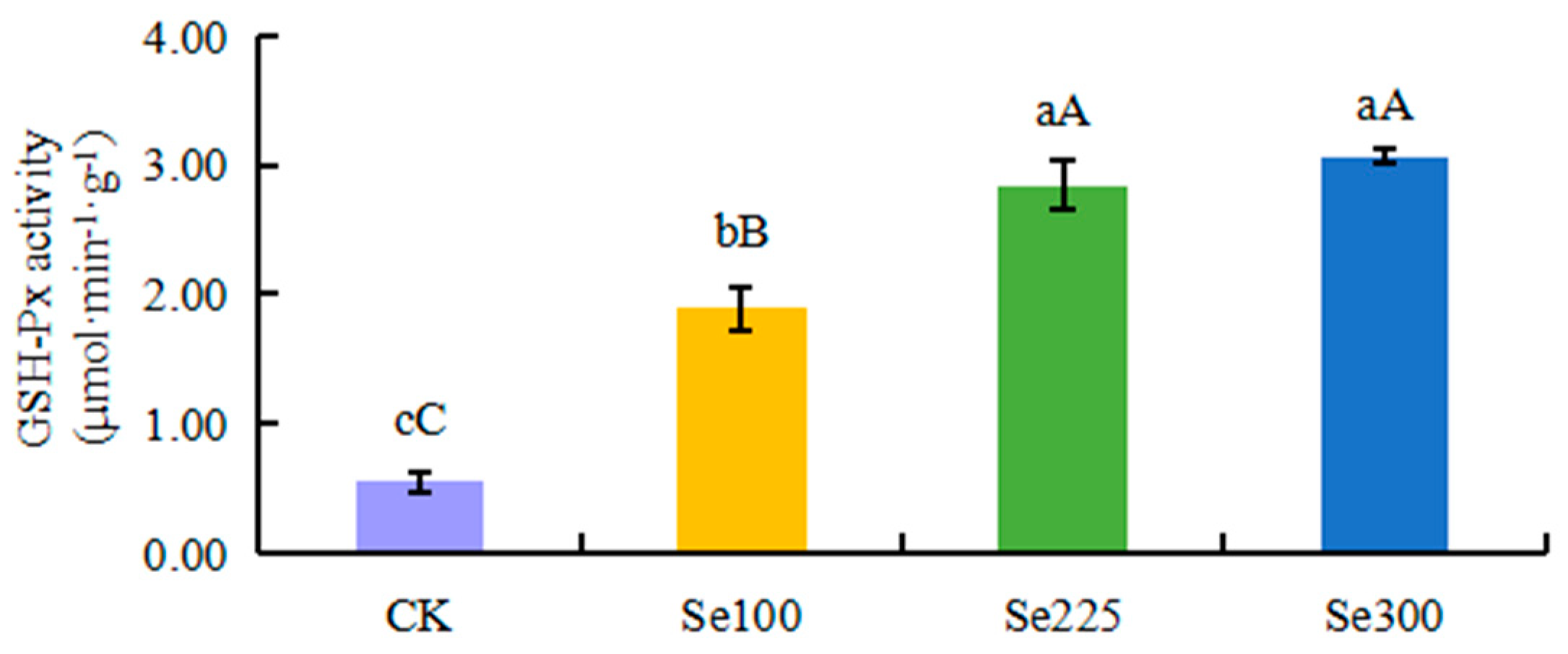
3.4. Selenium Application Enhances GSH-Px Activity in Spring Tea
3.5. Selenium Application Increases Chlorophyll Content in Spring Tea
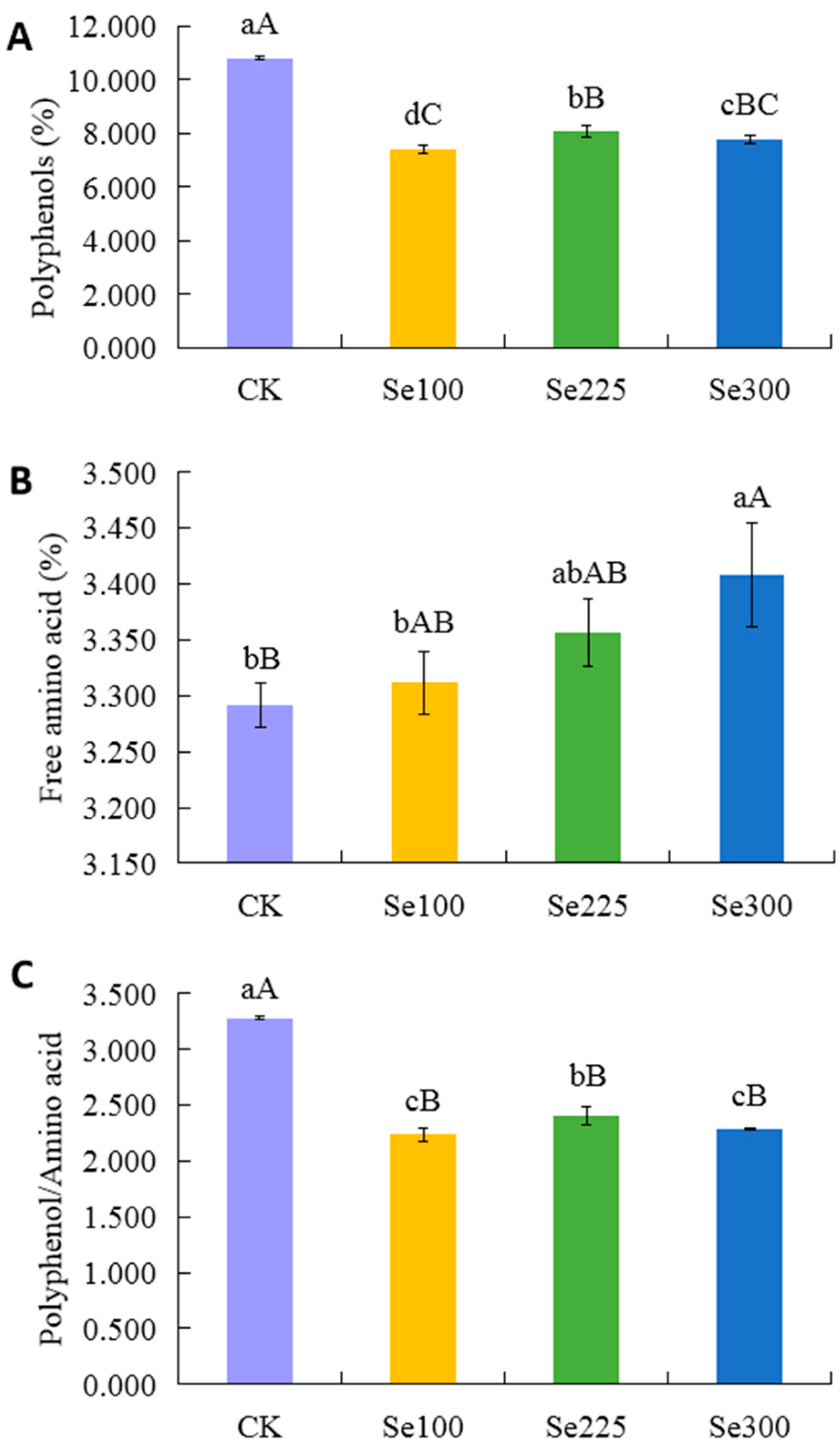
3.6. Selenium Application Reduces Polyphenol Content, Increases Free Amino Acid Content, and Lowers Phenol-to-Amino Acid Ratio in Spring Tea
3.7. Selenium Application Improves Polysaccharide Content in Spring Tea
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabrera, C.; Artacho, R.; Giménez, R. Beneficial Effects of Green Tea—A Review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2006, 25, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Mukhtar, H. Tea Polyphenols in Promotion of Human Health. Nutrients 2018, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.Q.; Li, Q.S.; Xiang, L.P.; Liang, Y.R. Recent Advances in Volatiles of Teas. Molecules 2016, 21, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.G.; Pilonsmits, E.A.H.; Zhao, F.J.; Williams, P.N.; Meharg, A.A. Selenium in Higher Plants: Understanding Mechanisms for Biofortification and Phytoremediation. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel, L.H.E.; Johnson, C.A.; Lenz, M.; Grundl, T.; Leupin, O.X.; Amini, M.; Charlet, L. Environmental Selenium Research: From Microscopic Processes to Global Understanding. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotuck, J.T.; Poope, A.L.; Ganther, H.E.; Swanson, A.B.; Hoekstra, D.G.H.G. Selenium: Biochemical Role as A Component of Glutathione Peroxidase. Science 1973, 179, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P. Selenium and Human Health. Lancet 2012, 379, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, M.G.D.B.; Reis, A.R.D. Roles of Selenium in Mineral Plant Nutrition: ROS Scavenging Responses Against Abiotic Stresses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 164, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto Irish, K.; Harvey, M.A.; Harris, H.H.; Aarts, M.G.M.; Chan, C.X.; Erskine, P.D.; van der Ent, A. Micro-analytical and Molecular Approaches for Understanding the Distribution, Biochemistry, and Molecular Biology of Selenium in (Hyperaccumulator) Plants. Planta 2022, 257, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Chung, D.S.; Bai, S.C.C.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, Y.B. Effects of Soil Selenium Supplementation Level on Selenium Contents of Green tea Leaves and Milk Vetch. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 12, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, H.P.G.; de Queiroz Barcelos, J.P.; Silva, V.M.; Santos, E.F.; Tavanti, R.F.R.; Putti, F.F.; Young, S.D.; Broadley, M.R.; White, P.J.; Dos Reis, A.R. Agronomic Biofortification with Selenium Impacts Storage Proteins in Grains of Upland Rice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 1990–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Xu, J.; Pang, G. Effect of Selenium on the Yield and Quality of Green Tea Leaves Harvested in Early Spring. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 3379–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.W.; Wei, C.Y.; Tu, S.X. The Roles of Selenium in Protecting Plants Against Abiotic Stresses-Science Direct. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 87, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhang, N.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Zhu, S.; Cong, X.; Cheng, S.; Barba, F.J.; Zhu, Z. Polysaccharides in Selenium-Enriched Tea: Extraction Performance under Innovative Technologies and Antioxidant Activities. Foods 2022, 11, 2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Li, F.; Zhu, J.; Sun, C.; Wang, Y. Selenium-Enriched and Ordinary Black Teas Regulate the Metabolism of Glucose and Lipid and Intestinal Flora of Hyperglycemic Mice. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2023, 78, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Gupta, S. An Overview of Selenium Uptake, Metabolism, and Toxicity in Plants. Front Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.J. Selenium Accumulation by Plants. Ann. Bot. 2016, 117, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soil Taxonomy Group; Nanjing Institute of Soil Research; Chinese Academy of Sciences. Chinese Soil Taxonomic Classification; University of Science and Technology of China Press: Hefei, China, 2001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xi, X.D.; Ji, L.J.; Li, H.D. Effect of selenium fertilizer on quality and selenium content of three staple herb-medicines in Gansu province. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2015, 31, 136–140. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Chen, H.X.; Yan, H.B.; Shang, X.H.; Zeng, W.D.; Lu, L.Y.; Xiao, L. Effect of adding bio-organic fertilizer on selenium absorption and utilization efficiency of edible cassava. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2021, 2, 116–122. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.X.; Liu, H.Z.; Bao, J.Q.; Chen, H.Z.; Sun, Y.Y.; Sun, C. Direct Micro Determination of Glutathione Peroxidase Activity in Mice Blood. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 1994, 21, 362–366. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qu, J.G.; Xu, B.X.; Gong, S.C. Sequential Extraction Techniques for Determination of Selenium Speciation in Soils and Sediments. Environ. Chem. 1997, 16, 277–283. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Q.; Li, A.-M.; Xing, Y.; Liang, P.-X.; Jiang, Z.-P.; Liu, Y.-X.; Huang, D.-L. Selenobacteria-mediated Se transformation and uptake involving the unique genetic code. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1392355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, F.; Cheng, N.; Chen, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhai, H.; Qi, M.; Liu, N.; Liu, Y.; Meng, L.; et al. Soil and foliar selenium application: Impact on accumulation, speciation, and bioaccessibility of selenium in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 988627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izydorczyk, G.; Ligas, B.; Mikula, K.; Witek-Krowiak, A.; Moustakas, K.; Chojnacka, K. Biofortification of edible plants with selenium and iodine—A systematic literature review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 141983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, G.H.; Van Rotterdam, A.M.D.; Bussink, D.W.; Bindraban, P.S. Selenium fertilization strategies for bio-fortification of food: An agro-ecosystem approach. Plant Soil 2016, 404, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Nutrition Society. Dietary Nutrient Reference Intakes for Chinese Residents 2023 Edition; People’s Health Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2023; pp. 628–639. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.Y.; Cao, K.; Hao, J.M. Effect of Na2SeO3 Application on Selenium Status in Dark Brown Forest Soils and Selenium Accumulation in Several Forest Vegetables. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2007, 44, 1111–1118. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Q.; Lin, Q.; Yan, M.J.; Chen, Z.C.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Y.S. Effects of Selenium Application on Selenium Accumulation of Astragalus Sinicus and Selenium Status in Soils. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2017, 38, 24–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Yin, D.; Zhou, M.; Yan, X.C.; Guo, C.; Huang, D.L.; Wang, Z.H. Biofortification and Residual Effects of Selenate Fertilizer on Wheat. J. Triticeae Crops 2022, 42, 605–613. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Xing, Y.; Li, A.-M.; Liang, P.-X.; Jiang, Z.-P.; Liu, Y.-X.; Huang, D.-L. Enhancing Selenium Biofortifcation: Strategies for Improving Soil-to-Plant Transfer. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Tang, J.C.; Li, J.L.; Zhao, C.Y. Effect of Selenium-rich, Yields and Quality by Applying Selenium Fertilizer on Yinghong 9 Tea Trees. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2012, 20, 2–54. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Sun, L.; Tan, C. Effect of Root Application of Selenium Fertilizer on Selenium Content and Quality Components of Tea. Shaanxi J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 65, 31–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.L.; Xu, B.Y.; Liu, J.H.; Jia, C.H.; Zhang, J.B.; Wang, J.S.; Jin, Z.Q. Isolation and Expression Analysis of a cDNA Encoding Glutathione Peroxidase from Banana. Acta Hortic. Sin. 2012, 39, 1471–1481. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.W.; Ma, L.J. Changes of Glutathione Peroxidase Activity and Malondialdehyde Content in Two Types of Wheat Male Sterile Lines at Fertility Sensitive Stage. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2013, 41, 60–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.T.; Yan, J.; Yang, R.Z.; Zhang, C.X.; Xu, R.H.; Ren, M.J.; Cheng, J.P. Effect of Sodium Selenate on Glutathione Peroxidase Activity of Different Wheat Varieties. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 89–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, Y.X.; Zhao, L.N.; Yuan, J.J.; Cheng, J.P.; Zhao, G.; Yan, J. Effect of Sodium Selenate on Glutathione Peroxidase Activity of Different Triticeae Crops. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 30, 1511–1515. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Sun, D.X.; Pang, L.X.; Zhang, A.J. Effects of Exogenous Selenium on Glutathione Peroxidase Activity and Quality in Millet. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 59–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y. Effects of Exogenous Selenium on Tea Plant Growth and Tea Quality; Shanghai Institute of Technology: Shanghai, China, 2022; p. 29, (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.L.; Yang, S.S. Study on the Mechanism of Sodium Selenite-induced Glutathione Peroxidase Biosynthesis of Wheat Seedlings. J. Southwest Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2003, 25, 518–521. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.L.; Yang, S.S. Effects of Sodium Selenite on Glutathione Peroxidase and Glutathione S-transferase Activities and Glutathione Content in Wheat Seedlings. Plant Physiol. Commun. 2004, 40, 178–180. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.J.; Fang, Y.P.; Meng, Z.T.; Lin, J.H. Analysis of Polyphenols and Polysaccharide Content in Fenggang Organic Tea and Meitan Cui Buds. J. Hebei North Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2012, 28, 17–20. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.J.; Luo, L.; Huang, C.H. Review on Antioxidative Activities of L-theanine. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 69–75. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Gao, X.Y.; He, Y.Q.; Gao, X.; Xiao, C.; Wu, G.X.; Zhou, H.J.; Yuan, W.X. Effect of Several Trace Elements on the Tea Plant Physiological and Tea Quality. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2010, 37, 162–165. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.Y.; Ni, D.J.; Xie, B.J. Effect of Tea Cultivars and Tenderness on Tea Polysaccharide. J. Huazhong Agric. Univ. 2005, 24, 406–409. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Rao, S.; Chen, Q.W.; Zhang, W.W.; Cheng, S.Y.; Cong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Xu, F. Research Progress on the Effects of Selenium on the Growth and Quality of Tea Plants. Plants 2022, 11, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xia, J.G.; Gong, F.Y.; Li, T.X.; Zhang, X.Z.; Yang, L.Y. Effect of Selenium Application on Selenium Content and Chemical Quality of Tea. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 19, 104–106+126. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; Liao, R.J.; Zhang, M.X.; Li, G.C.; Peng, Z.; Sheng, R.; Wang, K.B. Foliar Spraying Selenium Before Budding Period of Tea Plant Enhances the Abundance of Bacteria Genes Related to Quality and Stress Resistance in Tea Leaves. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2024, 30, 2380–2391. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Wu, C.S.; Mou, J.M.; Jiang, Y.; Guo, J.X. Effects of Maize Stubble Remaining in Field on Dynamics of Soil Microbial Biomass C and Soil Enzyme Activities. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2002, 13, 303–306. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.K.; Wang, S.L.; Feng, Z.W.; Huang, Y. Active Soil Organic Matter and Its Relationship with Soil Quality. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2005, 25, 513–519. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.B.; Xu, Z.; Sheng, Z.L.; Wu, X.H.; Deng, M. Effects of Selenium on Soil Enzyme Activity and Selenium Content of Tea Varieties. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2017, 26, 1872–1877. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, R.; Hu, H.Q.; Ye, X.J.; Xia, P.L.; Deng, J.Q. Effect of Exogenous Selenium with Different Valences on Se Forms, Enzyme Activities and Microbia Quantity of Soil. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 29, 137–171. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, H.; Hong, Y.C.; Shi, Y.T.; Zheng, S.L. Effects of Tea Varieties on Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil and Soil Enzyme Activities in Tea Plantations. J. Tea Commun. 2019, 46, 291–297. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.P.; Wu, T.X.; Fu, D.D.; Duan, M.L.; Wei, W.; Liang, D.L. Effects of Selenate and Selenite Pollution on Soil Enzymes Activity. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 29, 1526–1533. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, K.F.; Xu, X.Q.; Jin, X.; Xiang, Y.L. Eco-toxicology Effects of Soil Selenium Pollution on Soil Enzyme. China Environ. Sci. 2005, 25, 94–97. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, Z.L.; Niu, Y.B.; Zhang, C.L.; Lü, J.H. Effect of Selenium Application on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Quality of Chrysanthemum morifolium cv Hangbai. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2020, 57, 1449–1457. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Total Nitrogen | Total Phosphorus | Total Potassium | Available Nitrogen | Available Phosphorus | Available Potassium | pH Value | Organic Matter | Total Selenium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.21 g·kg−1 | 1.46 g·kg−1 | 7.30 g·kg−1 | 357.0 mg·kg−1 | 535.1 mg·kg−1 | 427.0 mg·kg−1 | 5.90 | 71.6 g·kg−1 | 0.82 mg·kg−1 |
| Treatments | SOL-Se | EX-Se | FMO-Se | OM-Se | RES-Se |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0.21 ± 0.03 dC | 4.59 ± 0.36 cC | 5.11 ± 0.16 aA | 64.26 ± 0.83 bB | 25.84 ± 0.99 aA |
| Se100 | 1.11 ± 0.10 cB | 11.34 ± 0.46 bB | 3.71 ± 0.11 bB | 65.70 ± 1.76 bAB | 18.14 ± 1.28 bBC |
| Se225 | 1.28 ± 0.08 bB | 12.65 ± 0.41 aA | 2.05 ± 0.21 cC | 64.74 ± 1.81 bAB | 19.29± 1.24 bB |
| Se300 | 1.64 ± 0.01 aA | 12.81 ± 0.13 aA | 1.14 ± 0.20 dD | 69.61 ± 1.03 aA | 14.80 ± 0.84 cC |
| Treatments | Sucrase (mg·g−1·d−1) | Urease (µg·g−1·d−1) | Acid Phosphatase (nmol·g−1·d−1) | Catalase (mmol·g−1·d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 59.93 ± 1.76 cC | 1823.96 ± 153.95 aA | 44,397.19 ± 493.14 a | 91.13 ± 1.65 a |
| Se100 | 78.55 ± 0.60 aA | 1742.31 ± 63.55 aA | 43,313.44 ± 1102.04 a | 92.74 ± 3.02 a |
| Se225 | 71.12 ± 3.36 bB | 1368.20 ± 55.96 bB | 42,606.21 ± 3269.90 a | 94.57 ± 3.77 a |
| Se300 | 62.55 ± 1.57 cC | 1183.33 ± 67.09 bB | 41,744.65 ± 1108.99 a | 93.16 ± 4.69 a |
| Treatments | Chlorophyll Content (mg·g−1) | Chlorophyll a/ Chlorophyll b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll a | Chlorophyll b | Total Content of Chlorophyll | ||
| CK | 0.684 ± 0.005 dC | 0.274 ± 0.009 cC | 0.958 ± 0.014 dD | 2.498 ± 0.067 aA |
| Se100 | 0.722 ± 0.008 bB | 0.306 ± 0.012 bB | 1.028 ± 0.020 bB | 2.364 ± 0.068 aA |
| Se225 | 0.746 ± 0.007 aA | 0.351 ± 0.005 aA | 1.097 ± 0.006 aA | 2.123 ± 0.044 bB |
| Se300 | 0.708 ± 0.010 cB | 0.286 ± 0.004 cBC | 0.994 ± 0.006 cC | 2.476 ± 0.070 aA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Q.; Liang, P.-X.; Xing, Y.; Yao, Z.-F.; Chen, J.-P.; Pan, L.-P.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Liu, Y.-X.; Huang, D.-L. Optimizing Selenium Application for Enhanced Quality and Nutritional Value of Spring Tea (Camellia sinensis). Horticulturae 2025, 11, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040423
Liao Q, Liang P-X, Xing Y, Yao Z-F, Chen J-P, Pan L-P, Deng Y-Q, Liu Y-X, Huang D-L. Optimizing Selenium Application for Enhanced Quality and Nutritional Value of Spring Tea (Camellia sinensis). Horticulturae. 2025; 11(4):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040423
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Qing, Pan-Xia Liang, Ying Xing, Zhuo-Fan Yao, Jin-Ping Chen, Li-Ping Pan, Yao-Qiu Deng, Yong-Xian Liu, and Dong-Liang Huang. 2025. "Optimizing Selenium Application for Enhanced Quality and Nutritional Value of Spring Tea (Camellia sinensis)" Horticulturae 11, no. 4: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040423
APA StyleLiao, Q., Liang, P.-X., Xing, Y., Yao, Z.-F., Chen, J.-P., Pan, L.-P., Deng, Y.-Q., Liu, Y.-X., & Huang, D.-L. (2025). Optimizing Selenium Application for Enhanced Quality and Nutritional Value of Spring Tea (Camellia sinensis). Horticulturae, 11(4), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae11040423






