Recovering Zinc and Iron from Waste Tire-Derived Pyrolysis Carbon Black to Prepare Layered Metal Hydroxide Composites for Efficient Adsorption of Dye Methyl Orange
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Determination of Leaching Conditions and Material Characterization
2.2. Adsorption Performance of LDO and FeLDO
2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
2.4. Adsorption Thermodynamics
2.5. Recovery Properties of Adsorbents and the Adsorption Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
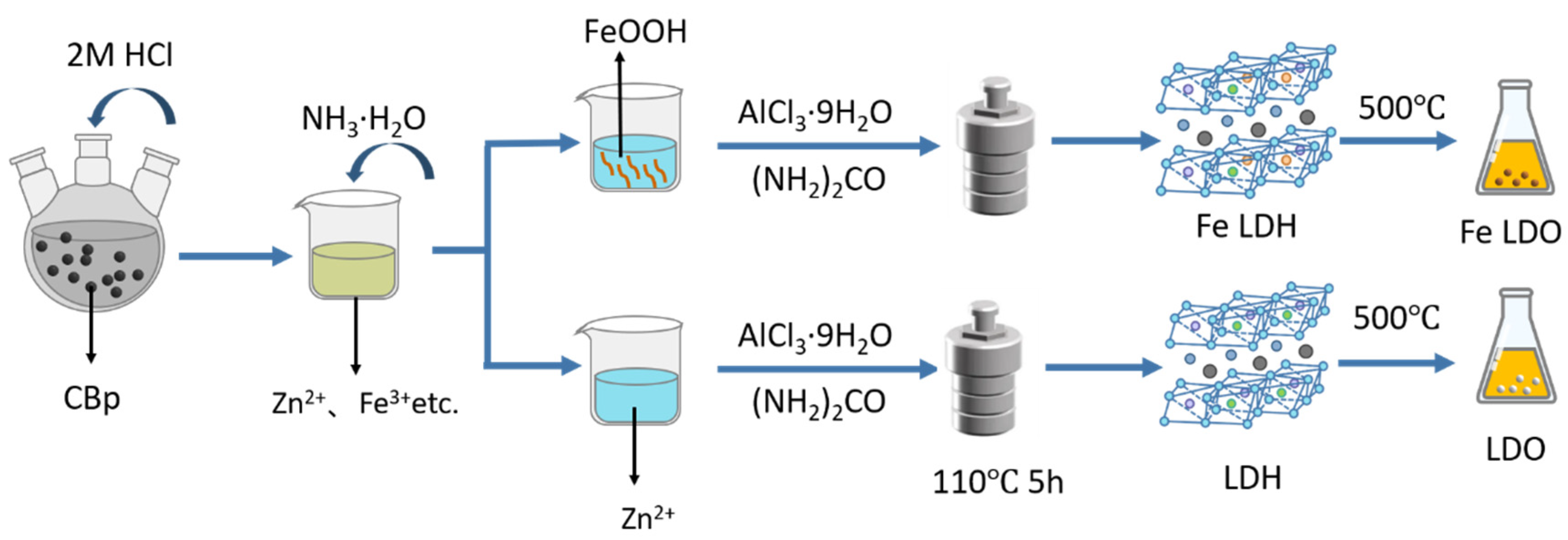
3.2. Preparation of LDH/FeLDH and LDO/FeLDO
3.3. Adsorption Experiments
3.4. The Regeneration of LDO and FeLDO
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Czarna-Juszkiewicz, D.; Kunecki, P.; Cader, J.; Wdowin, M. Review in Waste Tire Management—Potential Applications in Mitigating Environmental Pollution. Materials 2023, 16, 5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiskumar, C.; Karthikeyan, S. Recycling of Waste Tires and Its Energy Storage Application of By-Products—A Review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2019, 22, e00125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, P.; Choi, H.S.; Park, H.C.; Hwang, J.G.; Yoo, H.S.; Lee, B.-K.; Upadhyay, M. Influence of Process Conditions on Product Yield of Waste Tyre Pyrolysis-A Review. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 2268–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijo, B.; Soares Dias, A.P.; Wojnicki, Ł. Catalyzed Pyrolysis of Scrap Tires Rubber. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, R.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yang, H.; Yan, K.; Han, M.; Li, W.; Zhong, H.; Tan, X.; Xia, L.; et al. Simulation and Techno-Economical Analysis on the Pyrolysis Process of Waste Tire. Energy 2022, 260, 125039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabiourrutia, M.; Lopez, G.; Artetxe, M.; Alvarez, J.; Bilbao, J.; Olazar, M. Waste Tyre Valorization by Catalytic Pyrolysis—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 129, 109932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavukwana, A.; Stacey, N.; Fox, J.A.; Sempuga, B.C. Thermodynamic Comparison of Pyrolysis and Gasification of Waste Tyres. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Huang, C.; Li, D.; Huo, P.; Wang, M.; Han, L.; Chen, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Derived Oil Production by Catalytic Pyrolysis of Scrap Tires. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czajczyńska, D.; Krzyżyńska, R.; Jouhara, H.; Spencer, N. Use of Pyrolytic Gas from Waste Tire as a Fuel: A Review. Energy 2017, 134, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyeka Okoye, C.; Zhu, M.; Jones, I.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. An Investigation into the Preparation of Carbon Black by Partial Oxidation of Spent Tyre Pyrolysis Oil. Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Influence of a Novel Coupling Agent on the Performance of Recovered Carbon Black Filled Natural Rubber. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 255, 110614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimpe, K.M.; Ngila, J.C.; Nomngongo, P.N. Application of Waste Tyre-Based Activated Carbon for the Removal of Heavy Metals in Wastewater. Cogent Eng. 2017, 4, 1330912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, K.; Devi, N.; Alsanie, W.F.; Siwal, S.S.; Thakur, V.K. An Aniline-Complexed Bismuth Tungstate Nanocomposite Anchored on Carbon Black as an Electrode Material for Supercapacitor Applications. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202301878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikmann, E.; Mäeorg, U.; Liiv, J. Recycling of Low-Quality Carbon Black Produced by Tire Pyrolysis. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Wang, S.; Shan, R.; Gu, J.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y. Characteristics and Chemical Treatment of Carbon Black from Waste Tires Pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2024, 178, 106419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, C.; Manjare, S.; Rajan, S.K. Recycling of Waste Tire by Pyrolysis to Recover Carbon Black: Alternative & Environment-Friendly Reinforcing Filler for Natural Rubber Compounds. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 200, 108346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Dong, H.; Yang, H.; Yao, H.; Hu, S.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, S.; Sun, C. Application of Plasma Modified Pyrolytic Carbon Black in Improving Mechanical Properties of Natural Rubber Composite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e54061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Pan, J.; Deng, W.; Sun, Y.; Guo, J.; Che, K.; Yang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Sun, Y.; Huang, C.; et al. Recovery of High Pure Pyrolytic Carbon Black from Waste Tires by Dual Acid Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 133893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, V.; Grandón, H.; Segura, C.; Flores, M. Demineralization Strategies of Carbon Black Derived from Pyrolysis of Waste Tires. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2025, 27, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tran, T.Q.; Li, Q.; Ji, B.; Brand, A.S.; Zhang, W. Zn Leaching Recovery and Mechanisms from End-of-Life Tire Rubber. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 194, 107004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Peng, J.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Curing and Reinforcement Effect of Recovered Carbon Black from Waste Tires on Brominated Butyl Rubber. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 258, 110879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciğeroğlu, Z.; El Messaoudi, N.; Miyah, Y.; Georgin, J.; Franco, D.S.P.; Benjelloun, M.; Şenol, Z.M.; Kazan-Kaya, E.S.; Temur Ergan, B. Recent Advances in the Removal of Sunset Yellow Dye from Wastewater: A Review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2024, 42, e01187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, T.; Cen, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, Z. A Review on Modified Red Mud-Based Materials in Removing Organic Dyes from Wastewater: Application, Mechanisms and Perspectives. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 407, 125171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Gao, H.; Chen, H.; Xiao, X.; Zhao, C.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y. Insights and Perspectives of Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for the Removal of Heavy Metals and Dyes from Wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 292, 139280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Sun, S.-Y.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, H. Microplastics Affect the Removal of Dye in Textile Wastewater: Adsorption Capacity and Its Effect on Coagulation Behavior. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Si, T.; Shang, J.; Cai, S.; Gao, X.; Peng, L.; Zhang, H. The Top-down Construction of Cornstalk-Based Columns as Self-Adaptive Bio-Adsorbents for Selective Dye Adsorption from Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Recent Advances for Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs) Materials as Catalysts Applied in Green Aqueous Media. Catal. Today 2015, 247, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Jayababu, N.; Kim, D. Rational Design of Cobalt-Iron Bimetal Layered Hydroxide on Conductive Fabric as a Flexible Battery-Type Electrode for Enhancing the Performance of Hybrid Supercapacitor. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 904, 164082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jing, C.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, D.; Liu, X.; Dong, B.; Feng, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Acid-Salt Treated CoAl Layered Double Hydroxide Nanosheets with Enhanced Adsorption Capacity of Methyl Orange Dye. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 548, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-Y.; Kim, B.-K.; Hirata, S.; Inada, M.; Oh, J.-M. Particle Size Effect of Layered Double Hydroxide on the Porosity of Calcined Metal Oxide. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 195, 105701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Lan, Y.; Kong, Q. Preparation of CaMgAl-Calcined Layered Double Hydroxides and Application on the Removal of Phosphates. Water Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yang, S.; Yu, J.; Shu, Z. Novel Hollow Microspheres of Hierarchical Zinc–Aluminum Layered Double Hydroxides and Their Enhanced Adsorption Capacity for Phosphate in Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Z.-M.; Xia, S.-J.; Wang, L.-G.; Xing, F.-F.; Pan, G.-X. Treatment of Methyl Orange by Calcined Layered Double Hydroxides in Aqueous Solution: Adsorption Property and Kinetic Studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 316, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hassani, K.; Beakou, B.H.; Kalnina, D.; Oukani, E.; Anouar, A. Effect of Morphological Properties of Layered Double Hydroxides on Adsorption of Azo Dye Methyl Orange: A Comparative Study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 140, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrazek, K.; Frini Srasra, N.; Srasra, E. Synthesis and Characterization of [Zn-Al] Layered Double Hydroxides: Effect of the Operating Parameters. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2017, 64, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Xu, Z.; Nie, F.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z. Application of Mg-Fe Layered Double Hydroxides/Biochar Composite for the Removal of La (III) from Aqueous Solutions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybka, K.; Matusik, J.; Marzec, M. Mg/Al and Mg/Fe Layered Double Hydroxides Derived from Magnesite and Chemicals: The Effect of Adsorbent Features and Anions Chemistry on Their Removal Efficiency. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 332, 130084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciulescu, D.; Carja, G.; Lutic, D. Fabrication of Zinc-Iron-Aluminum Layered Double Hydroxides with Controlled Micromorphology in a Tailored Aqueous—Organic Synthesis Medium. Rev. Chim. 2020, 71, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, A.; Tian, H.; Wang, D. Controlled Release of Nitrate and Molybdate Intercalated in Zn-Al-Layered Double Hydroxide Nanocontainers towards Marine Anticorrosion Applications. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2018, 24, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jin, H.; Li, R.; Hua, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, R. Magnetic Fe3O4@SiO2 Study on Adsorption of Methyl Orange on Nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Tang, B.; Zhou, X. Effect of Preparation Methods on the Adsorption of Glyphosate by Calcined Ca–Al Hydrotalcite. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 15742–15749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahlahi-Attalhaoui, A.; Cuadra, J.G.; Porcar, S.; Fraga, D.; Nebot-Diaz, I.; Ribeiro, R.A.P.; Paulo, J.G.; Carda, J.B. A High-Speed Method to Obtain Ni-Zn Ferrite Nanoparticles by Microwave Hydrotalcite Decomposition for Magnetic Applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1004, 175846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ma, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, X.; Lv, Z.; Fang, M.; Tan, X.; Wang, X. Insight into the Performance and Mechanism of Low-Cost Phytic Acid Modified Zn-Al-Ti LMO for U(VI) Removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 402, 125510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Ren, H.; Jiang, S.; Bi, Y.; Li, C.; Fang, R. Comparative Investigation on the Adsorption Behavior of Bromate in Aqueous Solutions Using Zn/Ni/Al-LDH and Ni/Al-LDH: Optimization, Equilibrium Analysis, and Mechanistic Insights. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2025, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Su, M.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Tang, J.; Chang, X.; Chen, D. Superior Adsorption of Methyl Orange by H-MoS2 Microspheres: Isotherm, Kinetics, and Thermodynamic Studies. Dye. Pigment. 2019, 170, 107591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Najam, T.; Jabeen, S.; Wattoo, M.A.; Bashir, M.S.; Shah, S.S.A.; Rehman, A.U. Facile Synthesis of Tri-Metallic Layered Double Hydroxides (NiZnAl-LDHs): Adsorption of Rhodamine-B and Methyl Orange from Water. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 145, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Xu, J.; Mei, Y.; Tan, Q. Chloride Adsorption on Aminobenzoate Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxides: Kinetic, Thermodynamic and Equilibrium Studies. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 187, 105495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Song, H.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, H.; Zhang, L. Preparation of Composites Derived from Modified Loess/Chitosan and Its Adsorption Performance for Methyl Orange. Molecules 2024, 29, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Bi, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, M. Isotherm, Thermodynamics, and Kinetics of Methyl Orange Adsorption onto Magnetic Resin of Chitosan Microspheres. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yönten, V.; Sanyürek, N.K.; Kivanç, M.R. A Thermodynamic and Kinetic Approach to Adsorption of Methyl Orange from Aqueous Solution Using a Low Cost Activated Carbon Prepared from Vitis vinifera L. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 20, 100529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, N.S.M.; Ahmed, A.S.A.; Abdallah, M.H.; Gouda, G.A. ZnO@Activated Carbon Derived from Wood Sawdust as Adsorbent for Removal of Methyl Red and Methyl Orange from Aqueous Solutions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Odayni, A.-B.; Alsubaie, F.S.; Saeed, W.S. Nitrogen-Rich Polyaniline-Based Activated Carbon for Water Treatment: Adsorption Kinetics of Anionic Dye Methyl Orange. Polymers 2023, 15, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Shi, Z.; Peng, X.; Zhou, S. Magnetic Calcinated Cobalt Ferrite/Magnesium Aluminum Hydrotalcite Composite for Enhanced Adsorption of Methyl Orange. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 688, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyasi, H.; Mackey, H.; McKay, G. Adsorption of Methyl Orange from Water Using Chitosan Bead-like Materials. Molecules 2023, 28, 6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, Z.; Nasar, A. Polypyrrole-Decorated Bentonite Magnetic Nanocomposite: A Green Approach for Adsorption of Anionic Methyl Orange and Cationic Crystal Violet Dyes from Contaminated Water. Environ. Res. 2024, 247, 118193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Qu, R. Preparation of Metal Organic Framework by Strategy of Ligand Premodification Coupling with Dual Ligands and Adsorption Behaviors for Organic Dyes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 693, 134103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, J.; Li, Z.; He, X. Adding ZnO and SiO2 to Scatter the Agglomeration of Mechanochemically Prepared Zn-Al LDH Precursor and Promote Its Adsorption toward Methyl Orange. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 763, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Hill, J.M. Impact of Pore Size on Fenton Oxidation of Methyl Orange Adsorbed on Magnetic Carbon Materials: Trade-Off between Capacity and Regenerability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 4567–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaghouane-Boudiaf, H.; Boutahala, M.; Arab, L. Removal of Methyl Orange from Aqueous Solution by Uncalcined and Calcined MgNiAl Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs). Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 187, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanhaei, B.; Ayati, A.; Lahtinen, M.; Sillanpää, M. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Chitosan/Al2O3/Magnetite Nanoparticles Composite Adsorbent for Kinetic, Thermodynamic and Isotherm Studies of Methyl Orange Adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Chen, C. Hierarchical MWCNTs/Fe3O4/PANI Magnetic Composite as Adsorbent for Methyl Orange Removal. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 450, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, T.; Fang, L.; Lu, Y.; Wu, F.; Ling, F.; Gao, J.; Hu, B.; Meng, F.; Jin, X. A Facile Approach to Synthesize 3D Flower-like Hierarchical NiCo Layered Double Hydroxide Microspheres and Their Enhanced Adsorption Capability. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 529, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.H.; Chen, J.; Jiang, D.Y.; Guo, X.L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.X. Merging of Memory Effect and Anion Intercalation: MnOx-Decorated MgAl-LDO as a High-Performance Nano-Adsorbent for the Removal of Methyl Orange. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 10530–10538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.S.; Dasgupta, S. Effect of Time, pH, and Temperature on Kinetics for Adsorption of Methyl Orange Dye into the Modified Nitrate Intercalated MgAl LDH Adsorbent. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 137, 109203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taktak, F.; Gökçe, S. Ultrasound-Assisted Synthesis of Biodegradable Graphene Oxide-Based Hydrogel Nanocomposites for Highly Efficient and Cost-Effective Removal of Methyl Orange from Aqueous Media. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qian, A.; Pan, X.; Liu, F.; Li, R. Enhanced Adsorption of Methyl Orange from Aqueous Phase Using Chitosan–Palmer Amaranth Biochar Composite Microspheres. Molecules 2024, 29, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; He, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Qi, G.; Cai, X.; Li, P.; Zhang, J. Activated Carbon Based on Recycled Epoxy Boards and Their Adsorption toward Methyl Orange. Polymers 2024, 16, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wu, Z.; Bi, J.; Zhang, H.; Shahab, A. Calcined MgFe Layered Double Hydroxides for Magnetic Separation and Enhanced Adsorption Performance of Methyl Orange: Mechanism Based on the Memory Effect. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 63, 105418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
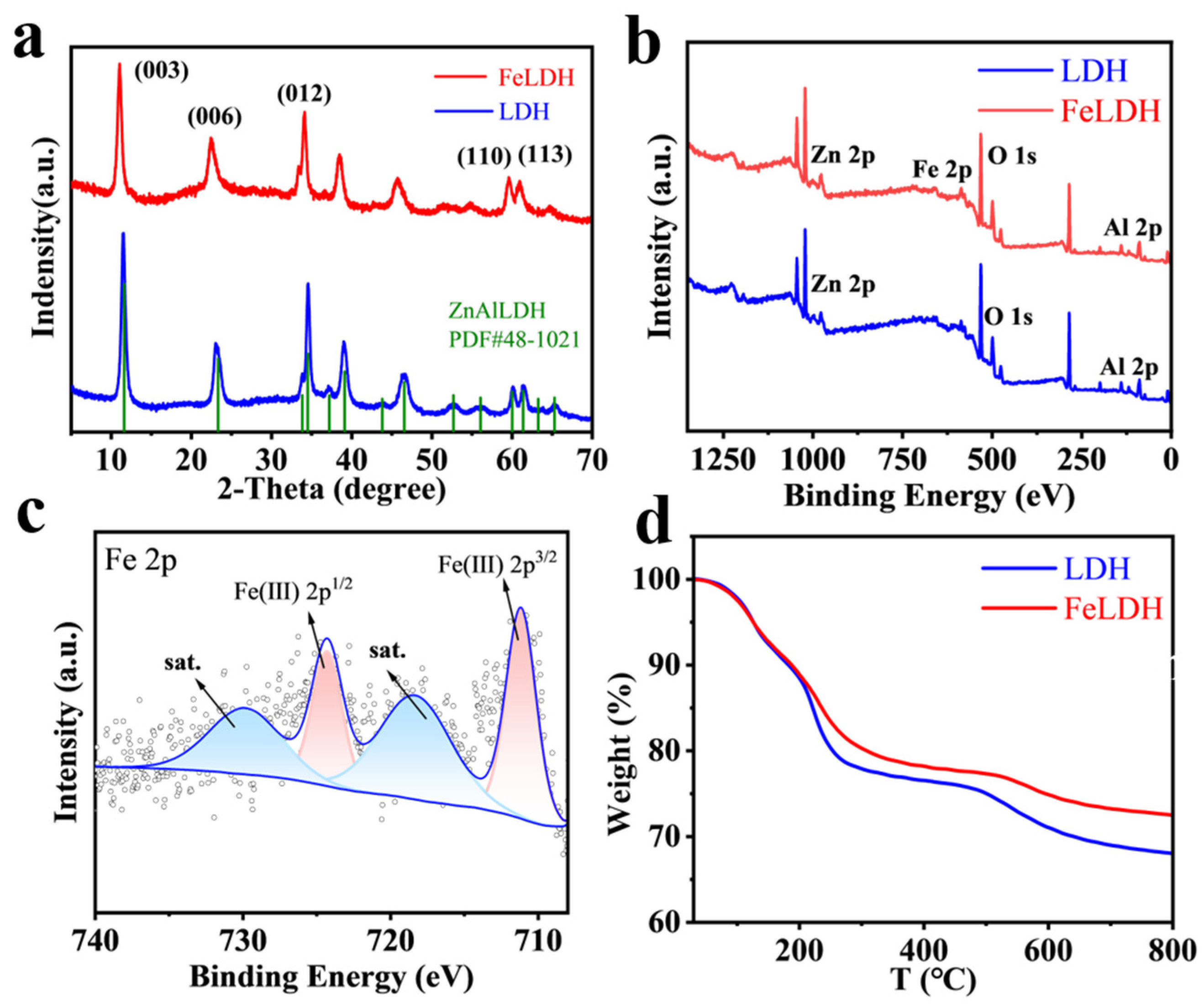

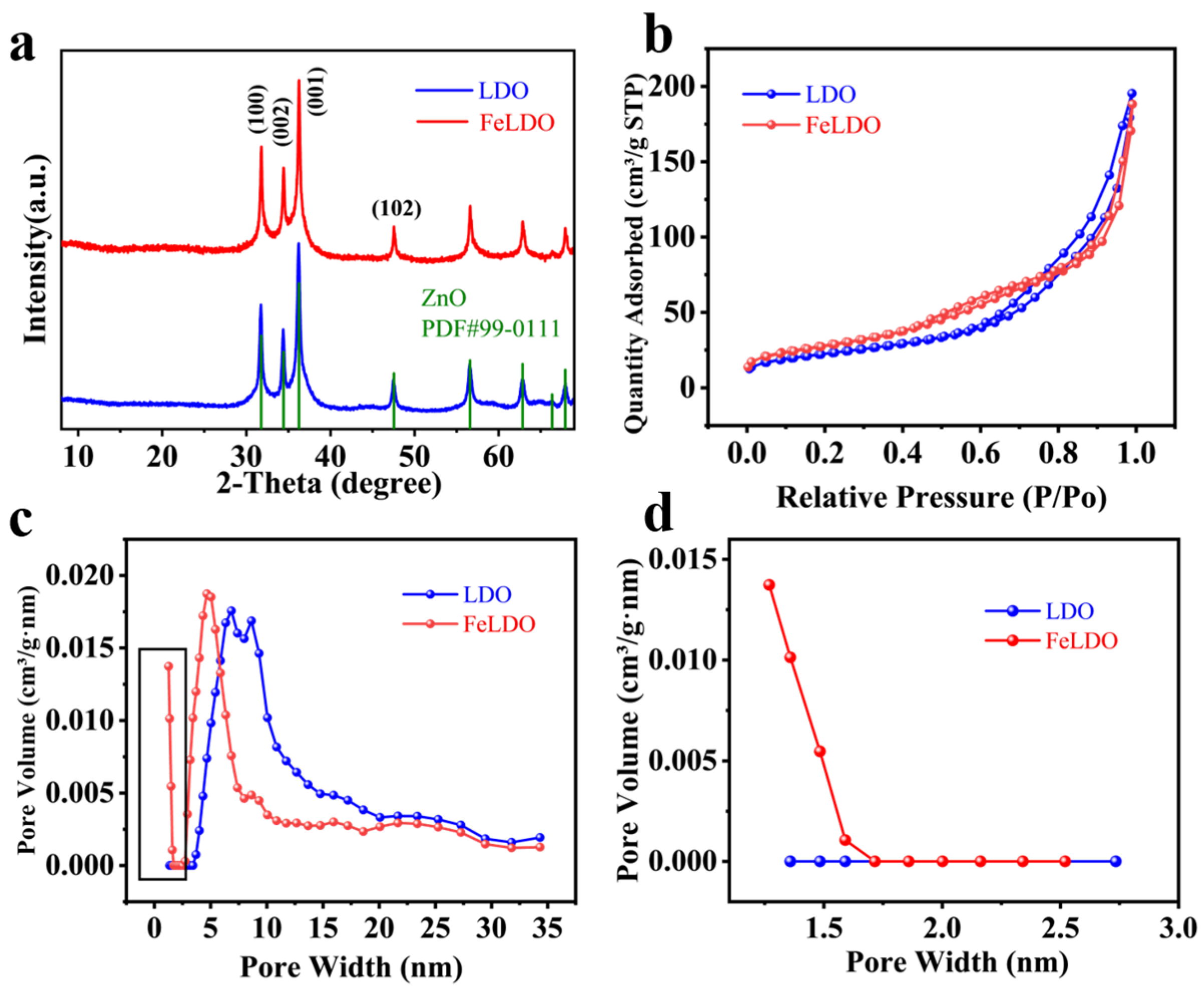
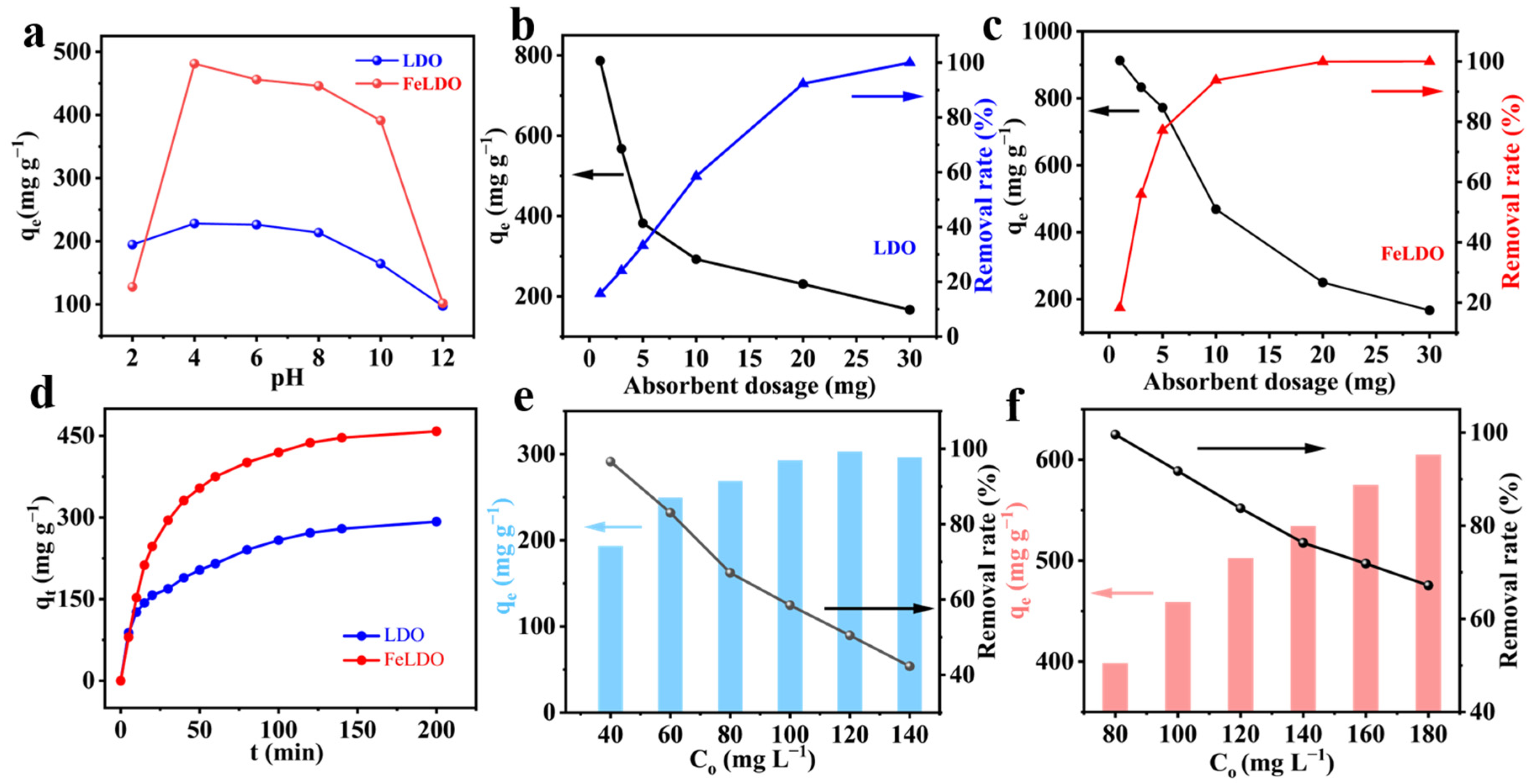

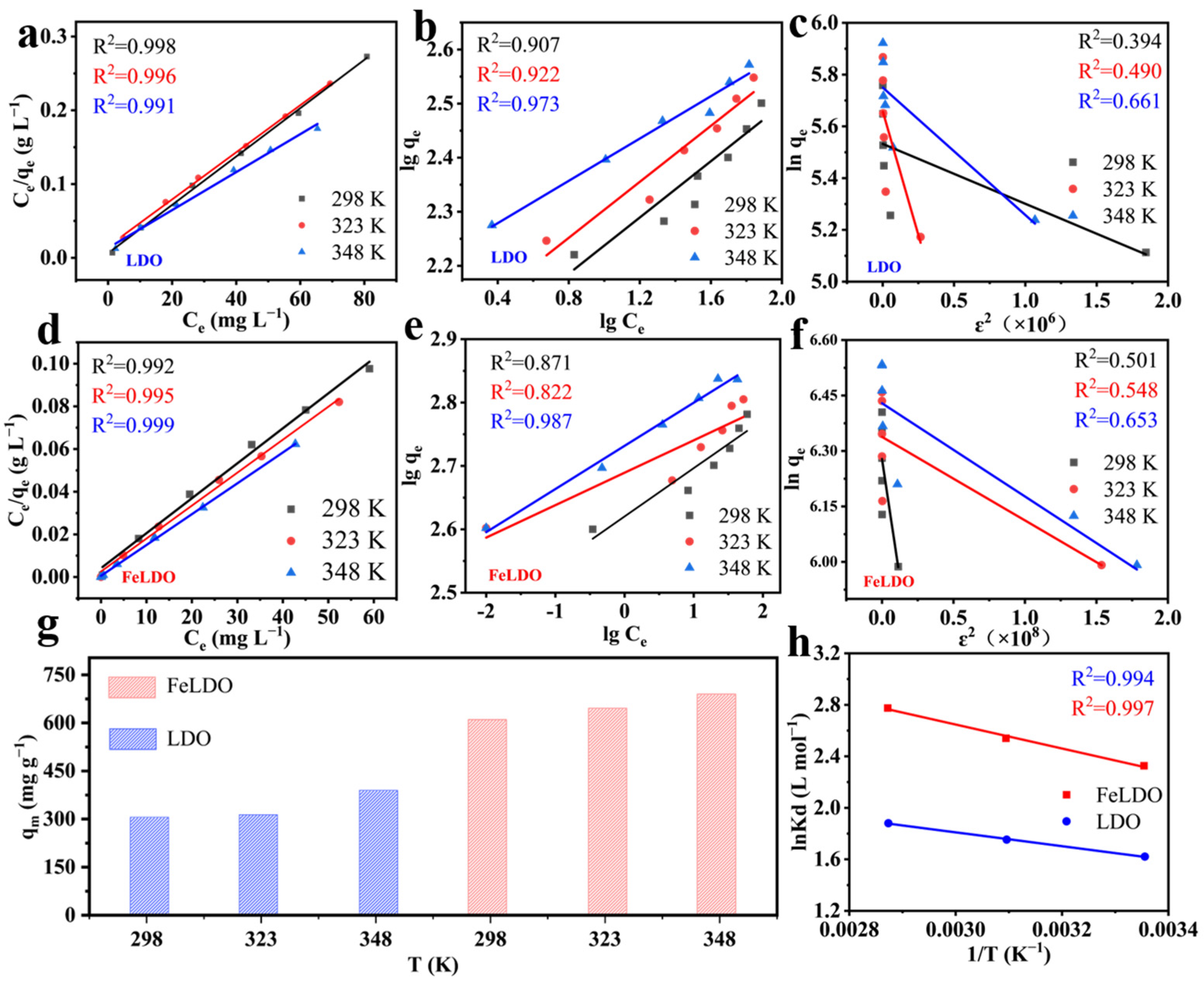
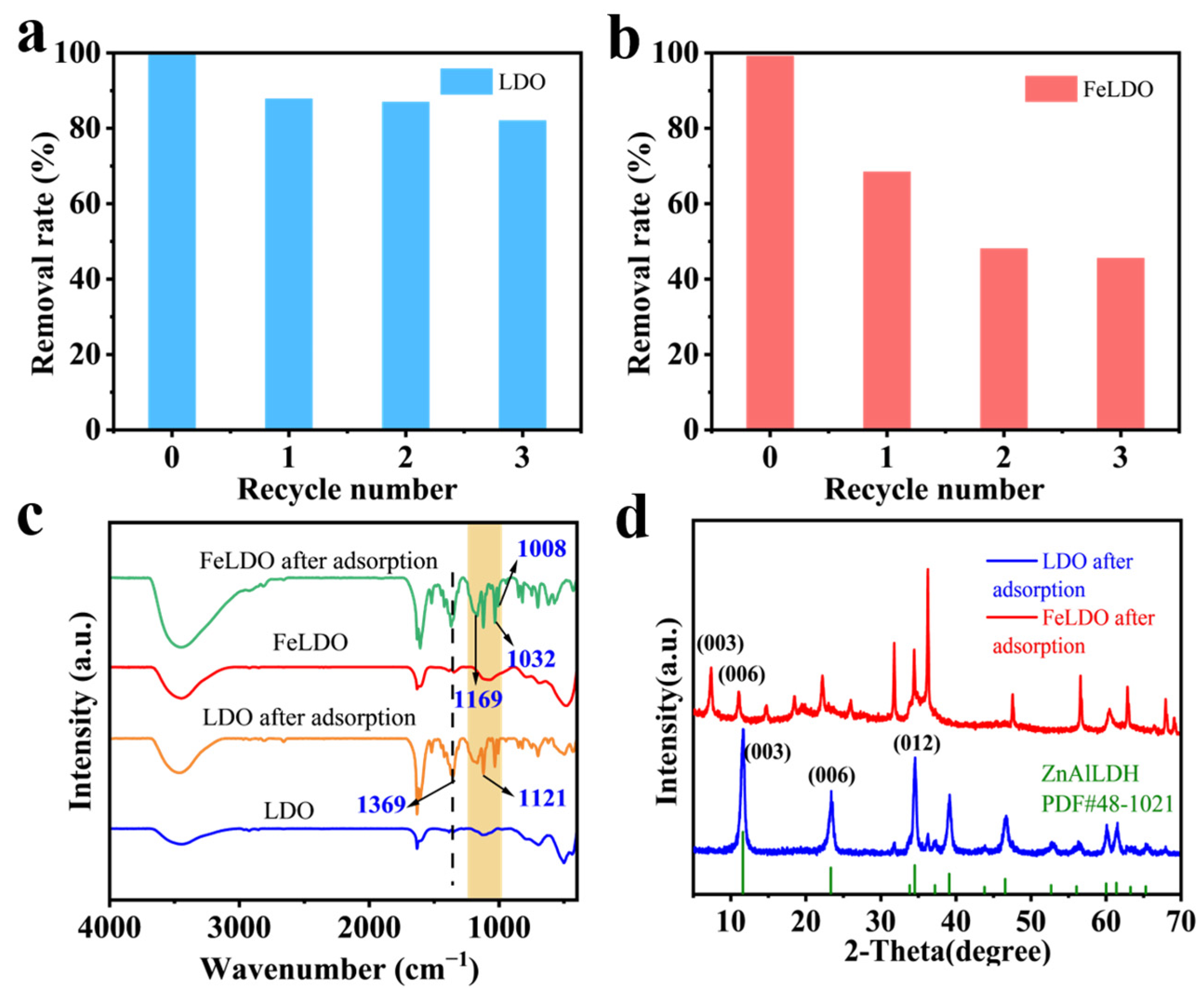

| Sample | 2θ003 | 2θ110 | d003 (Å) | d110 (Å) | c (Å) | a (Å) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDH | 11.54 | 60.13 | 7.701 | 1.536 | 23.10 | 3.07 |
| FeLDH | 11.02 | 59.59 | 8.029 | 1.550 | 24.09 | 3.10 |
| Samples | T(K) | Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | Dubinin–Radushkevich Isotherm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm (mg g−1) | b (L mg−1) | R2 | Kf (mg g−1) | n | R2 | qDR (mg g−1) | E (J mol−1) | R2 | ||
| LDO | 298 | 304.88 | 0.53 | 0.998 | 94.93 | 3.85 | 0.907 | 252.77 | 146.93 | 0.394 |
| 323 | 313.48 | 0.21 | 0.999 | 110.85 | 3.86 | 0.922 | 286.82 | 511.64 | 0.490 | |
| 348 | 389.11 | 0.19 | 0.991 | 158.72 | 5.11 | 0.973 | 314.22 | 100.76 | 0.661 | |
| FeLDO | 298 | 609.76 | 0.40 | 0.991 | 417.14 | 13.13 | 0.871 | 532.84 | 440.21 | 0.501 |
| 323 | 645.16 | 0.61 | 0.995 | 489.00 | 19.54 | 0.822 | 565.75 | 149.17 | 0.548 | |
| 348 | 689.66 | 2.70 | 0.999 | 539.11 | 14.69 | 0.987 | 619.62 | 141.26 | 0.633 | |
| Adsorbents | pH | qm (mg g−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZnAl-LDO | 6.0 | 181.9 | [33] |
| ZnAlLDH/ZnO | / | 276.6 | [57] |
| Fe2O3/AC | 3.0 | 362.0 | [58] |
| Calcined MgNiAl-LDH | 8.0 | 375.4 | [59] |
| Chitosan/Al2O3/magnetite composite | 6.0 | 416.0 | [60] |
| MWCNTs/Fe3O4/polyaniline | 4.5 | 446.3 | [61] |
| NiCoLDH | / | 497.0 | [62] |
| NiAlLDH | 3.0 | 500.6 | [34] |
| MnOx@MgAlLDO | / | 557.2 | [63] |
| LDO | 4.0 | 304.9 | This study |
| FeLDO | 4.0 | 609.8 | This study |
| Samples | T (K) | ΔG (kJ mol−1) | ΔH (kJ mol−1) | ΔS (J (mol K)−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDO | 298 | −4.02 | 4.47 | 28.44 |
| 323 | −4.71 | |||
| 348 | −5.44 | |||
| FeLDO | 298 | −5.64 | 8.59 | 47.62 |
| 323 | −6.71 | |||
| 348 | −8.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, P.; Liu, W.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Pan, J. Recovering Zinc and Iron from Waste Tire-Derived Pyrolysis Carbon Black to Prepare Layered Metal Hydroxide Composites for Efficient Adsorption of Dye Methyl Orange. Recycling 2025, 10, 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling10020076
Chen P, Liu W, Sun Y, Chen Y, Pan J. Recovering Zinc and Iron from Waste Tire-Derived Pyrolysis Carbon Black to Prepare Layered Metal Hydroxide Composites for Efficient Adsorption of Dye Methyl Orange. Recycling. 2025; 10(2):76. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling10020076
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Pei, Wenli Liu, Yanzhi Sun, Yongmei Chen, and Junqing Pan. 2025. "Recovering Zinc and Iron from Waste Tire-Derived Pyrolysis Carbon Black to Prepare Layered Metal Hydroxide Composites for Efficient Adsorption of Dye Methyl Orange" Recycling 10, no. 2: 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling10020076
APA StyleChen, P., Liu, W., Sun, Y., Chen, Y., & Pan, J. (2025). Recovering Zinc and Iron from Waste Tire-Derived Pyrolysis Carbon Black to Prepare Layered Metal Hydroxide Composites for Efficient Adsorption of Dye Methyl Orange. Recycling, 10(2), 76. https://doi.org/10.3390/recycling10020076







