Abstract
The European Union’s circular economy strategy aims to increase the recycling and re-use of products and waste materials. According to the strategy, the use of industry waste material should be more effective. A chemical precipitation method to simultaneously remove phosphorus and nitrogen from synthetic (NH4)2HPO4 solution and the liquid phase of anaerobic digestate using fly ash as a precipitant was tested. Fly ash is a waste material formed in the power plant process. It mainly contains calcium oxide (CaO) and magnesium oxide (MgO). Saturated precipitant solution was prepared from fly ash, which was added in small proportions to (NH4)2HPO4 solution during the experiment. Fly ash’s effectiveness as a precipitant was compared with that of commercial CaO and MgO salts, and it can be observed that fly ash removed as much ammonium and phosphate as commercial salts. Fly ash sufficiently removed ammonium nitrogen and phosphate from the liquid phase of anaerobic digestate, which led to the formation of ammonium magnesium hydrogen phosphate hydrate, struvite (NH4MgPO4·6H2O), and calcium hydroxide phosphate, monetite, CaPO3(OH). In this study, we have shown for the first time that fly ash can be used to manufacture recycled, slow-release fertilizers from anaerobic digestate.
1. Introduction
The European Union’s circular economy strategy aims to increase the recycling and re-use of products and waste materials [1]. The use of industry waste material and side flows should be more effective. The strategy is closely linked to the EU Waste Framework Directive (2008/98/EC) [2] that includes a five-step waste hierarchy in which different options for dealing with waste are described. The first goal of the waste hierarchy is to prevent the formation of waste streams. If this is not possible, the next step is to prepare waste for re-use, followed by recycling and other recovery (e.g., energy recovery). Finally, if none of the first four steps are feasible, waste should be disposed of without harming the environment. According to Sokka et al. [3], re-use and symbiosis products manufactured from side flows or waste materials in the local industry carry a small environmental load.
Phosphorus and nitrogen are the main nutrients in wastewater that promote the growth of organic matter and algae, which cause eutrophication in water bodies. Discharges of phosphorus and nitrogen are known to occur in, for example, agricultural and anaerobic digestion wastewaters. Agriculture is the largest branch of industry that uses and recycles phosphorus and nitrogen in Finland. The effective recycling of nutrients decreases the use of traditional inorganic fertilizers. Therefore, the side streams and waste material of the industry should be utilized as effectively as possible [4,5].
Anaerobic digestion is a widely used sustainable method for the management of organic solid wastes and digestate. Anaerobic digestion plants can use various biomass materials for renewable energy production. Agricultural waste such as straw and grass are suitable and important raw materials. Pig and cow slurry, fur animal manure, stomach and gut content, corn residuals, and potato processing waste (stems and peals) are also useful raw materials in biogas production [6]. The composition of anaerobic digestate can differ significantly because of the numerous raw materials used in the gasification process [7]. Anaerobic digestate, used for agriculture purposes, is specifically regulated by both European and Finnish national legislations [8], namely, Regulation (EU) No. 2003/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council related to fertilizers [9], Animal by-products Regulation (EU) No. 1069/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council [10], and the Act on Fertilizer Products 539/2006 [11], among others. Anaerobic digestate contains high concentrations of nutrients. Therefore, the sludge can be used as a fertilizer, but it should be converted into a more slow-release solid form to decrease transport costs.
Currently, phosphorus is removed by collateral precipitation using aluminum or iron precipitant before the biological process, which reduces the potential to use the precipitate, for example, as a fertilizer. There are also various methods for phosphate removal, such as adsorption [12,13], ion exchange [14], electro-coagulation (EC) [15,16], and electro-Fenton treatment [17]. Nitrogen is typically present in the form of ammonium. Ammonium ions are not easy to precipitate and are therefore removed in the biological process by nitrification and denitrification [18]. One challenge is the pH, as ammonium volatilizes easily as ammonia gas in alkaline conditions. Ammonium–ammonia equilibrium is strongly pH-dependent [19]. Further, traditional nitrogen fertilizers are produced mainly using the energy-intensive Haber–Bosch reaction, which results in large amounts of greenhouse gas emissions, as production consumes high amounts of natural gas [20].
In Finland alone, the economic potential of recycled fertilizers is approximated to be €0.5 billion annually [21]. One answer to the recycled fertilizer market would be to convert phosphate and ammonium nitrogen into a product that enhances nutrient value. Chemical precipitation as struvite from wastewater is one method of phosphorus and ammonium nitrogen recovery [22]. Struvite, that is, magnesium ammonium phosphate hexahydrate (MgNH4PO4·6H2O), is generated by phosphate, ammonium, magnesium, and hydroxide ions [23,24]. During struvite precipitation, the solution’s pH decreases as a consequence of hydrogen ion(s) release into the solution. Therefore, it is stated that the dominant form of phosphates is HPO42− or H2PO4− instead of PO43− during the reaction course [23,25,26]. The struvite formation equations can be written as Equations (1) and (2):
In struvite precipitation, pH values range from 8.5–9.0, and precipitation temperature varies between 25 °C and 60 °C. The theoretical molar ratio for struvite formation is 1:1:1 Mg:NH4:PO4, but it can vary depending on the source materials [27,28]. Struvite can be used as a slow-release fertilizer, reducing the nutrient supply to the waterways. Commonly used precipitants for struvite precipitation are MgCl2, MgSO4 MgO, and Mg(OH)2 [29,30], but due to the high price of these commercial salts, and since magnesium is listed in European Union’s critical raw material list, alternative magnesium containing side streams and industrial waste material should be preferred instead of magnesium salts [1,31]. Therefore, inexpensive magnesium sources such as magnesite [32], brucite [33], a by-product of marine salt manufacturing and by-product of the thermal treatment of meat waste, bone meal, etc. [34], MgO-saponification wastewater [35], seawater [36,37], and bottom ash collected from a small residential fireplace [38] to produce struvite have been tested in several papers. However, Ca- and Mg-rich fly ash from a full-scale power plant has not been previously tested for struvite precipitation. Precipitation by Ca-rich fly ash would also lead to the formation of a struvite-like Ca-mineral such as calcium ammonium phosphate CaNH4PO4, and hydroxyapatite Ca5(PO4)3(OH) [39]. Biomass-based fly ash is often used as a fertilizer because it contains all the nutrients that plants need, excluding, nitrogen, which is released to the atmosphere during combustion. By using fly ash as a precipitant for nitrogen and phosphorus uptake, a new recycled fertilizer product that contains all the main nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium or NPK) could be manufactured.
In this study, Ca- and Mg-rich fly ash resulting from wood and peat combustion was used as a chemical precipitant in the simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphorus from synthetic (NH4)2HPO4 solution and from liquid phase of anaerobic digestate. The effectiveness of fly ash as precipitant was compared with commercial CaO and MgO salts. The effects of temperature, pH, and the nutrient content of the formed precipitates were also studied.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Precipitants
Fly ash originated from a 20 MW thermal power plant located in Northern Finland (63°92′23.6″ N, 24°99′33.8″ E). The power plant uses a bubbling fluidized bed combustion technique. The fuels used at the plant are wood and peat. The fuel ratios (dry mass) were approximately 75% wood (50% wood chips, 10% bark, and 15% recycled wood) and 25% peat. The ash sample was collected directly from the ash silo. The main components of fly ash were analyzed on an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF) analyzer (XRF, S4 Pioneer, Bruker AXS, Billerica, MA, USA) and are presented in Table 1. The concentrations of harmful elements are compared with the maximum values given in the Finnish fertilizer decree (Table 2).

Table 1.
X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF) characterization of the main components of fly ash.

Table 2.
XRF characterization of harmful element contents and a comparison to the limit values of Finnish fertilizer decree [40].
Commercial chemicals (analytically pure) CaO and MgO (VWR Chemicals, Radnor, PA, USA) were used as comparative precipitants.
2.1.2. Digestate from an Anaerobic Digestion Plant
The anaerobic digestate (after hygienization at 70 °C) used in this research originated from an anaerobic digestion plant using slurry from the fodder and food industry, manure, fur waste from the leather industry, agricultural waste, and bio-waste as raw materials. The anaerobic digestion plant is located in Central Finland (63°41′46.0″ N, 22°60′57.2″ E). The effluent from the reactor (Table 3) has been analyzed in a commercial, accredited laboratory. Nutrients content is given in Table 3 and Table 4.

Table 3.
Essential nutrient content of the solid phase of the anaerobic digestate.

Table 4.
Essential nutrient content of the liquid phase of the anaerobic digestate.
2.2. Experimental Methods
Ammonium phosphate (NH4)2HPO4 solution (10 mmol) (360 mg/L NH4+ and PO43− 950 mg/L) was prepared from analytically pure diammonium hydrogen phosphate, slightly modified from the method described by Hao et al., 2008 [27]. Before each precipitation experiment, the temperature of the (NH4)2HPO4 solution was adjusted to a regulated temperature of 20 ± 2 °C, 40 ± 2 °C or 60 ± 2 °C. In the experiments, the (NH4)2HPO4 solution (500 mL) was stirred with a magnetic stirrer at a speed of 160 rpm, and a pH meter (Knick Portable, Berlin, Germany) was connected to the system.
Saturated precipitant solutions were prepared from fly ash, or commercial calcium and magnesium salts. Saturated solution was added at 1 min intervals in 1 mL (commercial salts) or in 3 mL (fly ash) portions at a time up to 30 mL or 90 mL. The experiment was continued by adding the precipitant at 1 min intervals 5 mL or 15 mL at a time until the total volume of the added precipitant was 50 mL (commercial salts) or 150 mL (fly ash). After each addition, the pH value was read. Water samples were taken after 5, 10, 15, 20, 30, 50 mL additions (commercial salts) or after 15, 30, 45, 60, 90, and 150 mL additions (fly ash). Thus, calcium and magnesium content was similar using both commercial salts and fly ash, making the procedures comparable. Total reaction time of the experiments was 40 min. The water samples were filtered through Whatman 4 filter paper (20–25 μm), and the precipitates were air-dried to prevent the volatilization of ammonium.
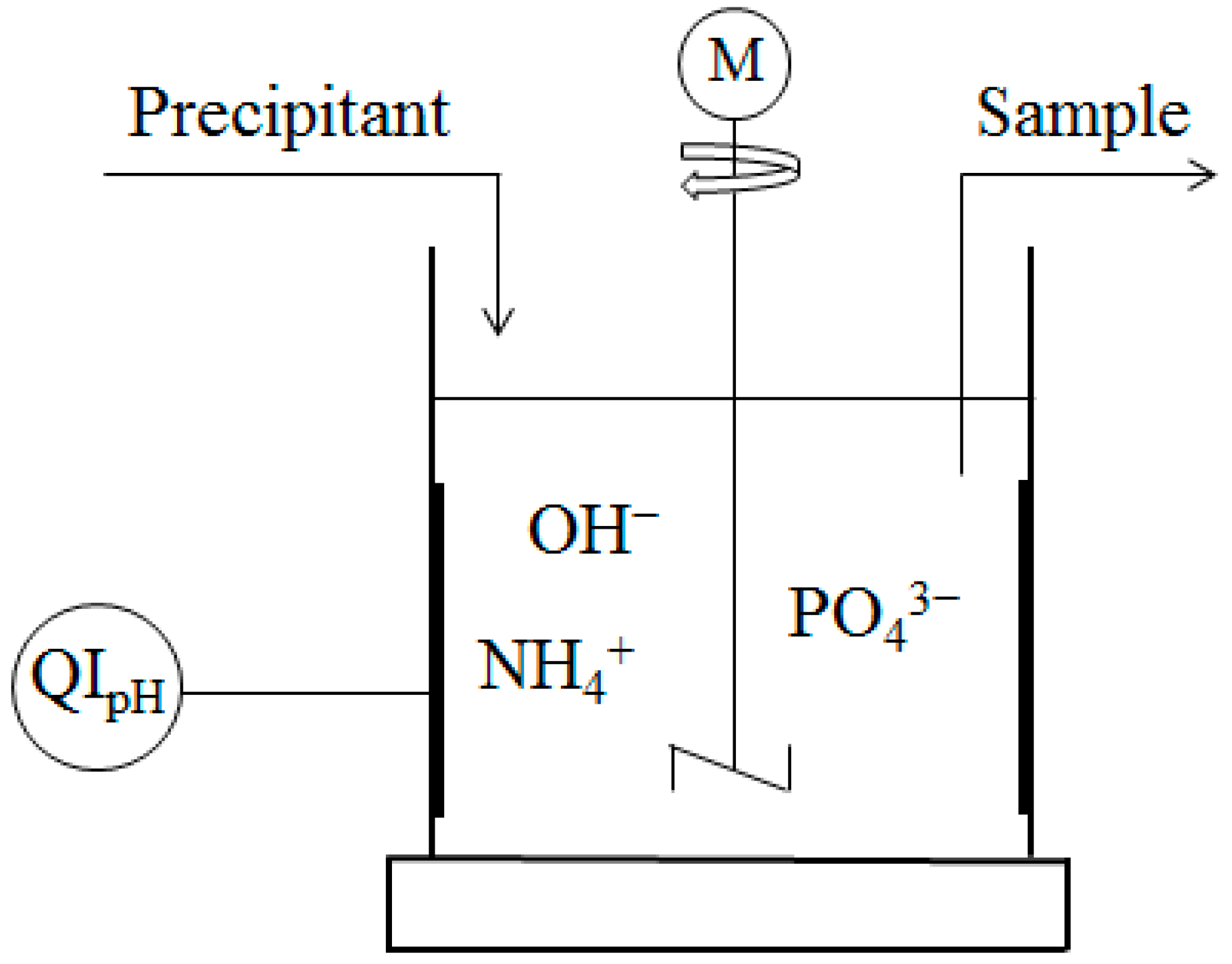
Experiments, using fly ash as a precipitant and the liquid phase of the anaerobic digestate as precipitable substance, were carried out at room temperature (20 ± 2 °C). In order to remove solid particles, the digestate was filtered, first through a coarse fabric and then a filter paper prior to the experiments. The optimal molar ratio Mg:N:P (1:1:1) for struvite precipitation was calculated, and therefore, KH2PO4 was added. In the experiment, 30 mL of the saturated precipitant suspension was added to 1600 mL of the anaerobic digestate filtrate while stirring the solution at a constant speed of 450 rpm for 1 min in order to mix up the two solutions properly. After that, the rotor speed was reduced to 50 rpm for the duration of the experiment (24 h), and the pH was adjusted to 9.0 and kept constant. Water samples were taken in the beginning, 30, 60, 90 120, 180 min and, the end of the experiments, 1440 min. They were filtered through 4−12 µm filter paper, and precipitates were air-dried before analyzing. The composition of the formed solid precipitates was characterized. The schematic description of the chemical precipitation system is shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Precipitation reactor consists of a curved blade connected to a motor (M); a 2 L decanter glass with stators attached to the wall of the glass; and a pH-meter (QIpH).
The removal efficiency (Reff) of ammonium nitrogen and phosphate from the aqueous solution was defined by Equation (3) as follows:
where C0 and Ct are concentrations at time o and time t, respectively.
Reff = [(C0 − Ct)/C0] · 100%
2.3. Description of Analytical Equipment
The ammonium concentration of the liquid samples was measured using a HACH HQ40d NH4-selective electrode (Model ISENH418101, Loveland, CO, USA). The phosphate concentration of the liquid samples was measured by ion chromatography (METROHM 761 Compact IC, Herisau, Switzerland). The concentrations of trace elements were analyzed using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES, Waltham, MA, USA) and atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS, Waltham, MA, USA). The composition of the formed precipitates was measured by x-ray diffractometer (XRD, Krakow, Poland). X-ray diffraction patterns were recorded by a PANalytical X’Pert Pro X-ray diffraction equipment using monochromatic CuKα1 radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å) at 45 kV and 40 mA. Diffractograms were collected in the 2θ range 10–80° at 0.017° intervals and with a scan step time of 100 s. The crystalline phases and structures were analyzed by HighScore Plus program (Version 4.0, PANalytical B. V., Almelo, The Netherlands). The composition of the formed precipitates was measured by scanning electron microscope (SEM). Fly ash was characterized using FESEM, and X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF, S4 Pioneer, Bruker AXS, Billerica, MA, USA). The microstructure shown in FESEM images were obtained using a Zeiss Sigma field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM, Zeiss Sigma, Rödermark, Germany) at the Centre of Microscopy and Nanotechnology in the University of Oulu operated at 5 kV. For XRF measurement, the sample powders were added 6% C-wax as binder and press into pellet specimen with diameter of 37 mm in a steel ring. The detectable element concentration is 5–10 ppm for XRF. The distribution of the particle size of fly ash was measured using a MALVERN Mastersizer 3000 (Malvern, UK). The particle size distribution measurements were based on laser diffraction technique. The analyzer utilizes static light scattering and Mie theory to calculate the particle size distribution. The specific surface area was measured using a Micromeritics ASAP 2020 (Norcross, GA, USA). The specific surface area was calculated from adsorption isotherms according to the BET method [40].
3. Results
3.1. Fly Ash
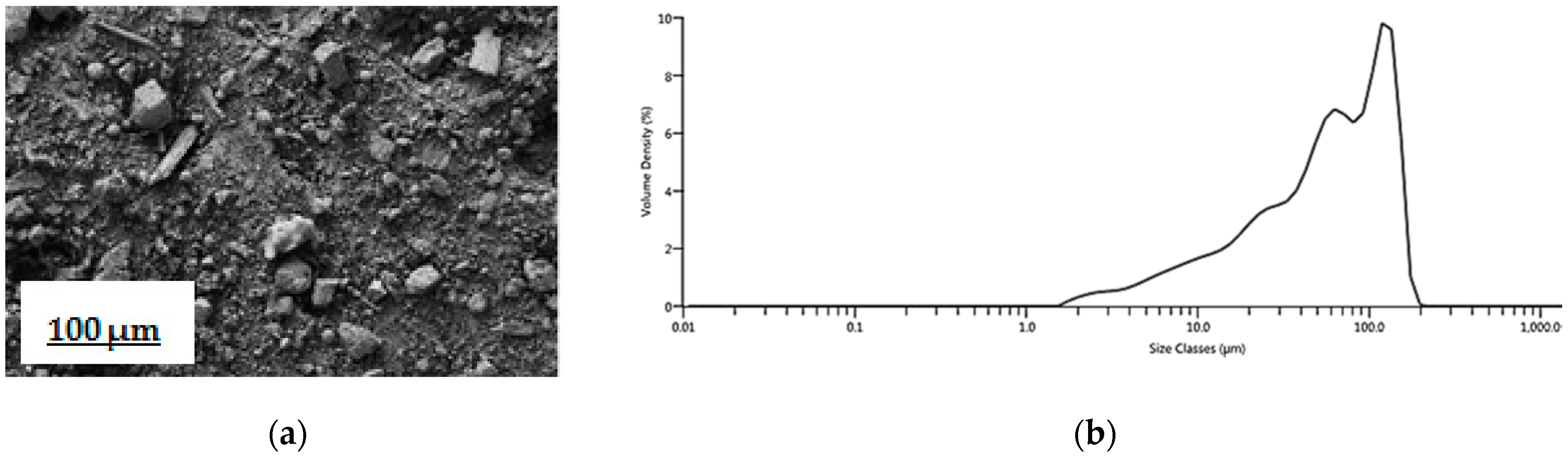
Fly ash contains mainly irregularly shaped particles and therefore has no clear morphology. This is verified by FESEM; an image of untreated fly ash presented in Figure 2a,b illustrates the distribution of particle size. All particles were smaller than 200 μm. The particle size distribution was the following: Dv (10) 10.4 μm (i.e., 10% of the particles are smaller than 10.4 μm), Dv (50) 60.1 μm (i.e., 50% of the particles are smaller than 60.1 μm), and Dv (90) 134 μm (i.e., 90% of the particles are smaller than 134 μm). The specific surface area of the fly ash was 8 m2/g.
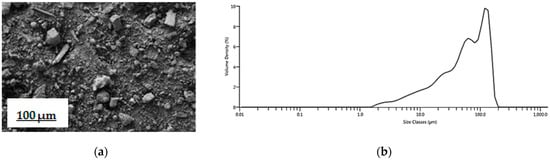
Figure 2.
(a) FESEM image of untreated fly ash, 250×, the bar indicates 100 μm length.; (b) particle size distribution of fly ash.
The main components of fly ash are given in Table 1. The amount of calcium oxide (CaO) is 34.6 wt% (wt = weight percent, dry basis) and the amount of magnesium oxide (MgO) is 14.7 wt%. Fly ash also contains other elements, such as potassium and phosphorus, which are the main nutrients for plants.
The harmful metal contents of fly ash together with the limit values of harmful elements listed in the Finnish Fertilizer Product Act (24/2011) are given in Table 2 [41]. The number of harmful elements in fly ash is relatively low, and therefore, it would be suitable for fertilizer use. Based on previous research [42,43,44,45], the leaching of heavy metals from wood and peat based ashes is typically very low, thus having no significant effect on the precipitation.
3.2. Solid Phase and Liquid Phase of the Anaerobic Digestate
The results from the analyses of the digestate is presented in Table 3 [46], as delivered from the anaerobic digestion plant. The main compounds are given in kg/m3 for the whole digestate and as g/kg for the results on a dry basis.
According to Table 3, ca. 10% of ammonium nitrogen and ca. 20% of phosphorus is in the liquid phase. According to Wäger-Baumann [47], 70–80% of ammonium nitrogen and 35–45% of phosphorus occur in the liquid phase. Comparing the observation of Wäger-Baumann [47], the proportions of ammonium nitrogen and phosphorus are lower. This may be due to the ammonium volatilization during storage and the raw material used in the present study. However, nutrient concentrations can vary widely, depending on the raw material [48].
Essential nutrient content was measured from the liquid phase of anaerobic digestate, and it is illustrated in Table 4.
3.3. Results of the Synthetic Solution Experiments
3.3.1. Ammonium Removal
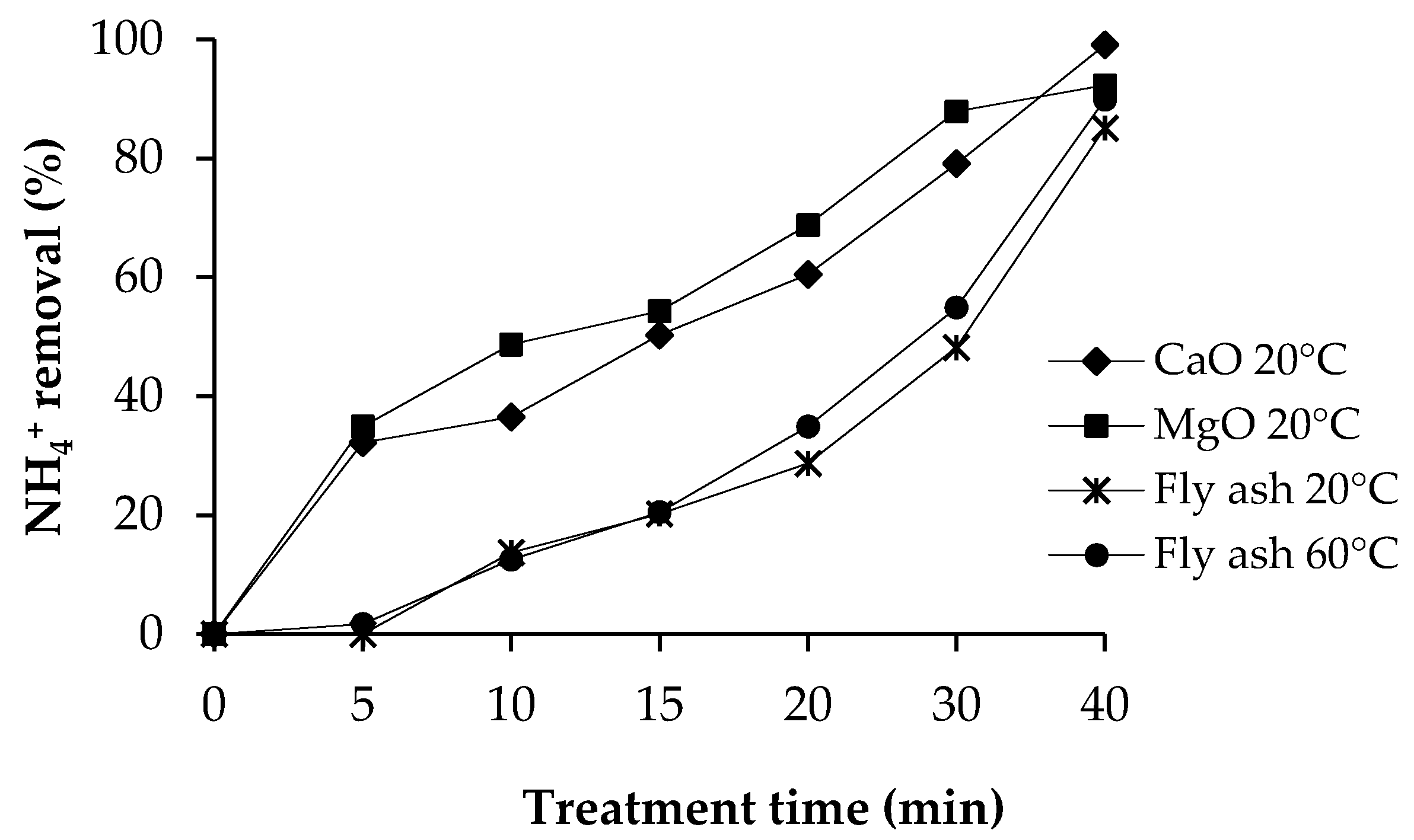
Ammonium removal percentages of different precipitants as a function of treatment time are presented in Figure 3. Commercial CaO removed 99.1% of ammonium nitrogen at 20 °C, 98.8% at 40 °C, and 99.0% at 60 °C. Commercial MgO removed 92.3% of ammonium nitrogen at 20 °C, 88.0% at 40 °C, and 90.5% at 60 °C from the synthetic (NH4)2HPO4 solution.
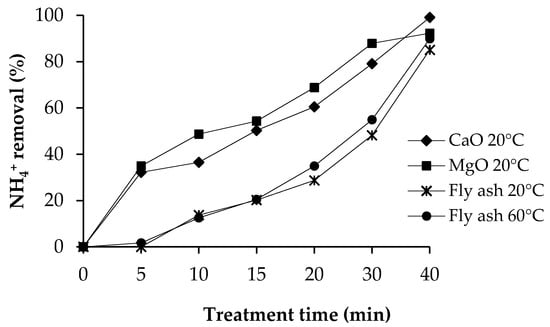
Figure 3.
Ammonium removal percentage of different precipitants, and temperature.
Fly ash sludge removed ammonium nitrogen 85.1% at 20 °C, 88.9% at 40 °C, and 89.9% at 60 °C. When comparing the effectiveness of fly ash sludge for ammonium removal with the effectiveness of commercial salts, it can be observed that fly ash sludge removed as much ammonium nitrogen as commercial salts. The change in temperature has no essential effect on the removal of ammonium using either fly ash sludge or commercial salts. During the experiments with fly ash and MgO, the pH value was between 8.0 and 10.3, which is the optimal pH range for struvite precipitation [22,28]. However, with CaO, the pH was up to 12.0 at the end of the precipitation. As ammonium is completely as ammonia gas at this pH, it is highly possible that at least some of the ammonium evaporated as ammonia gas.
3.3.2. Phosphate Removal
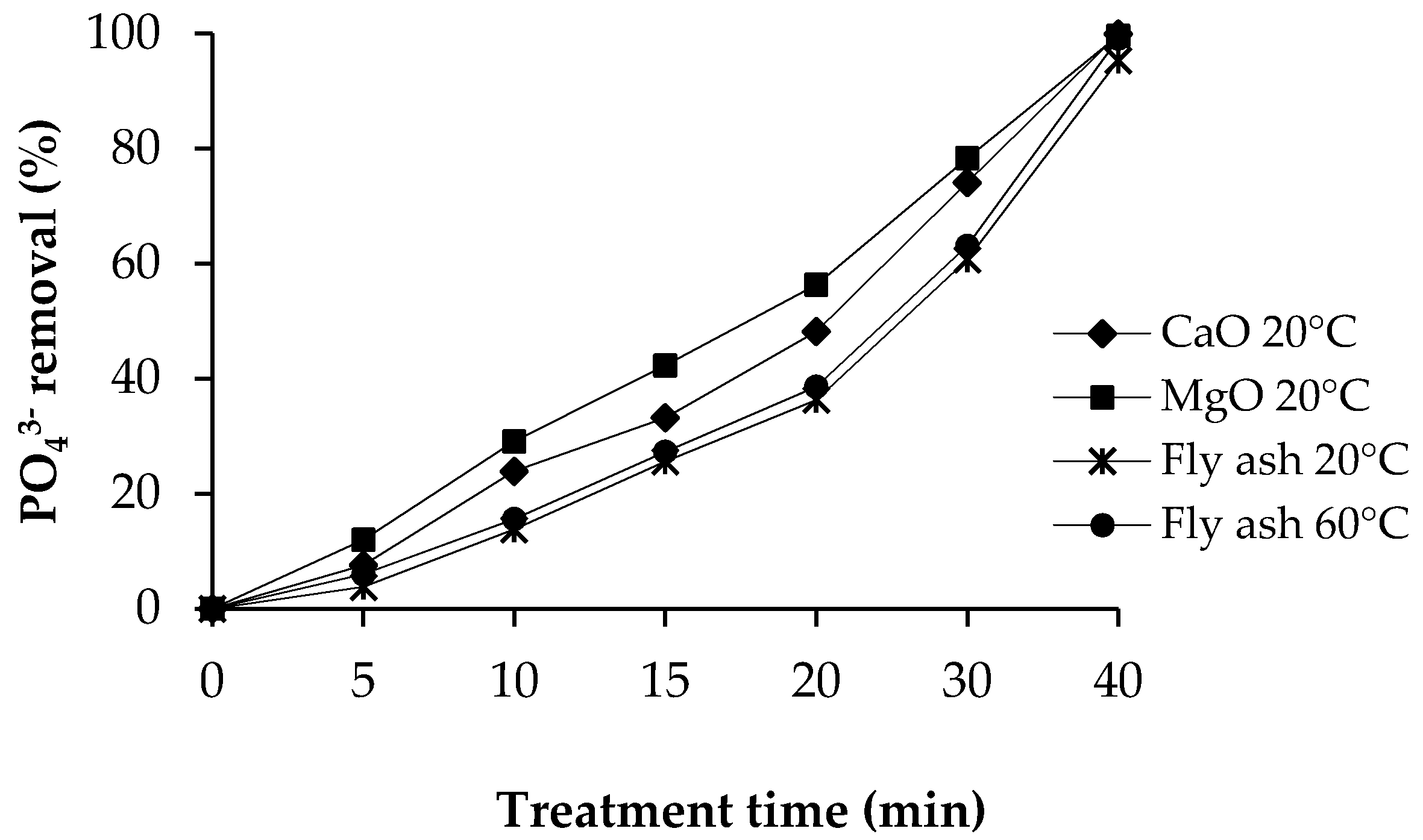
Phosphate removal percentages of different precipitants as a function of time are presented in Figure 4. Commercial calcium oxide removed 99.9% of phosphate at 20 °C, 100% at 40 °C, and 100% at 60 °C. Commercial magnesium oxide removed 99.6% of phosphate at 20 °C, 99.2% at 40 °C, and 99.1% at 60 °C.
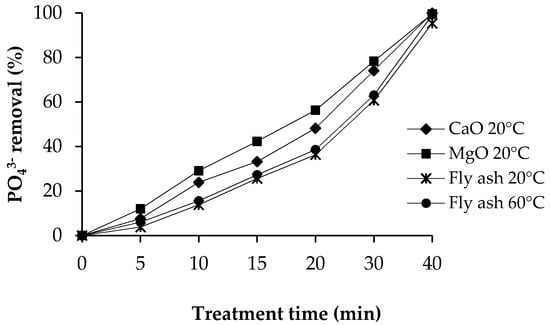
Figure 4.
Phosphate removal percentage of different precipitants, and temperature.
Fly ash sludge removed phosphate 95.3% at 20 °C, 98.2% at 40 °C, and 99.1% at 60 °C. When comparing the effectiveness of fly ash sludge in phosphate removal with the effectiveness of commercial salts, it can be observed that fly ash sludge removed as much phosphate as commercial salts. The change in temperature had no essential effect on the removal of phosphate using either fly ash sludge or commercial salts.
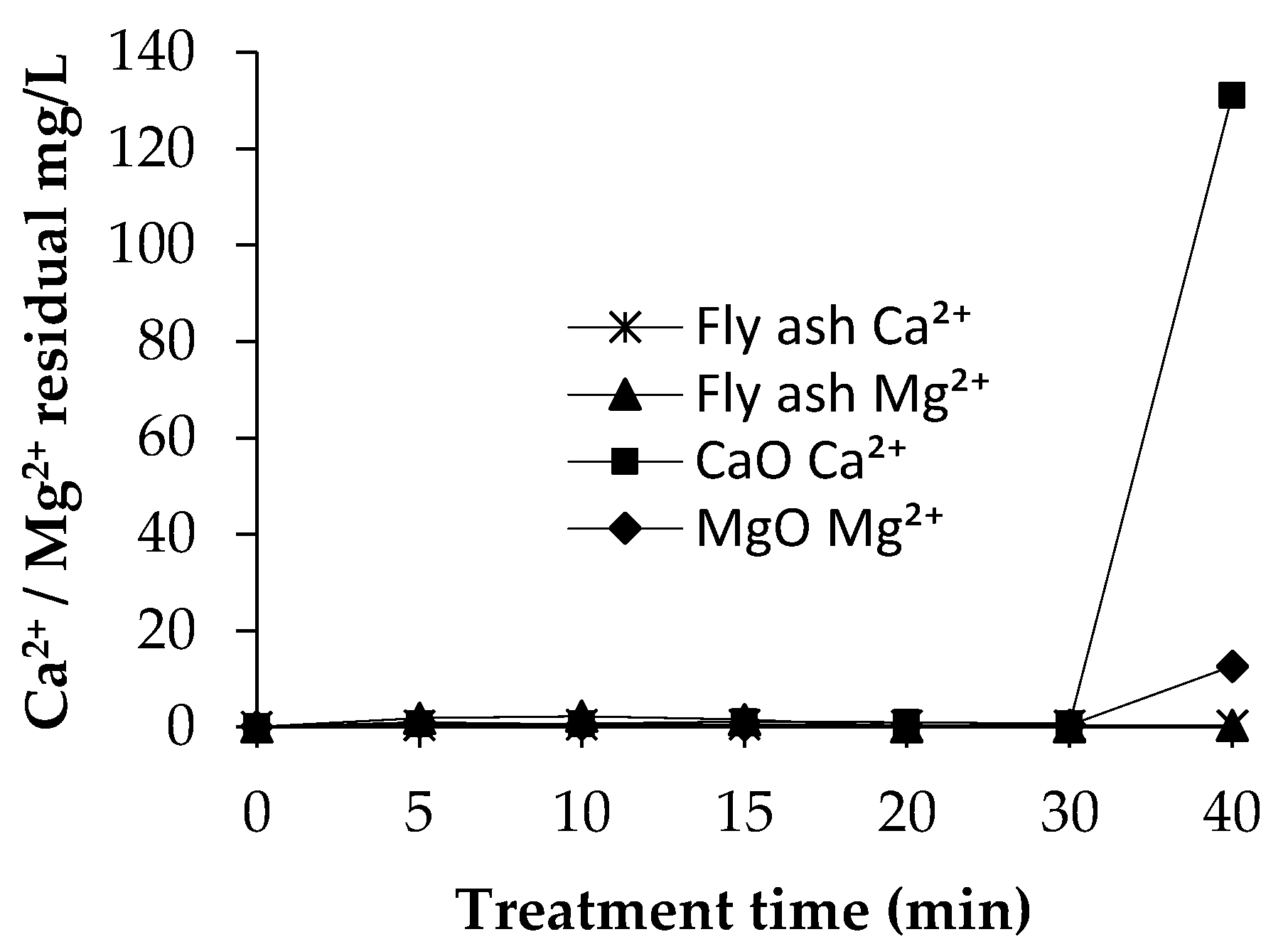
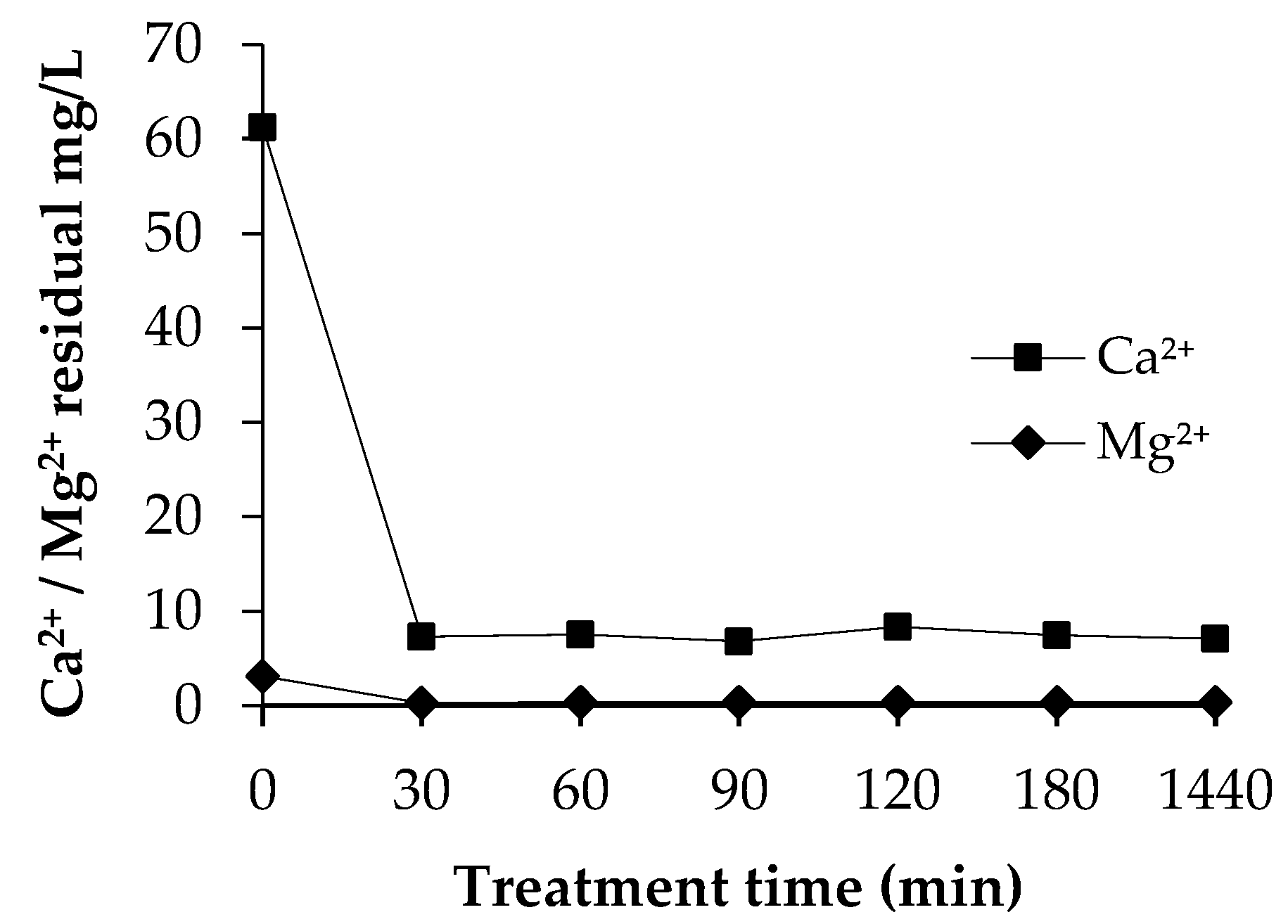
3.3.3. Residual Concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+
Figure 5 illustrates the residual concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ that remained in the synthetic solution. As shown in Table 4, the soluble Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions participate readily in the precipitation reaction as long as there are ammonium and phosphate ions available in the solution. Therefore, the concentration of Ca2+ and Mg2+ was at a very low level during the experiment. However, with CaO, the Ca2+ residual was up to 131 mg/L, and with MgO, the Mg residual was up to 12.6 mg/L at the end of the precipitation. Fly ash contains significantly lower amounts of calcium and magnesium than commercial salts. According to Table 4, it is obvious that the added Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions have almost quantitatively participated in the removal of ammonium and phosphate ions from the solution. However, in the precipitation experiments in which the commercial salts with significantly higher concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ were used, the residual concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ at the end of the experiments were notably higher. The results were at the similar level at all temperatures. Therefore, the temperature did not have any impact on the residual Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations.

Figure 5.
Atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) characterization of residual concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ during the fly ash, CaO, and MgO experiments, at 20 °C.
3.3.4. Characterization of Precipitates
The XRD diffraction patterns in the synthetic (NH4)2HPO4 solution precipitation are presented in Figure 5. The identified precipitation product from the CaO precipitation was calcium hydroxide phosphate (Ca10OH2(PO4)6). The identified precipitation products from the MgO precipitation were ammonium magnesium phosphate NH4Mg(PO3)3 and ammonium phosphate (NH4)4P4O12.
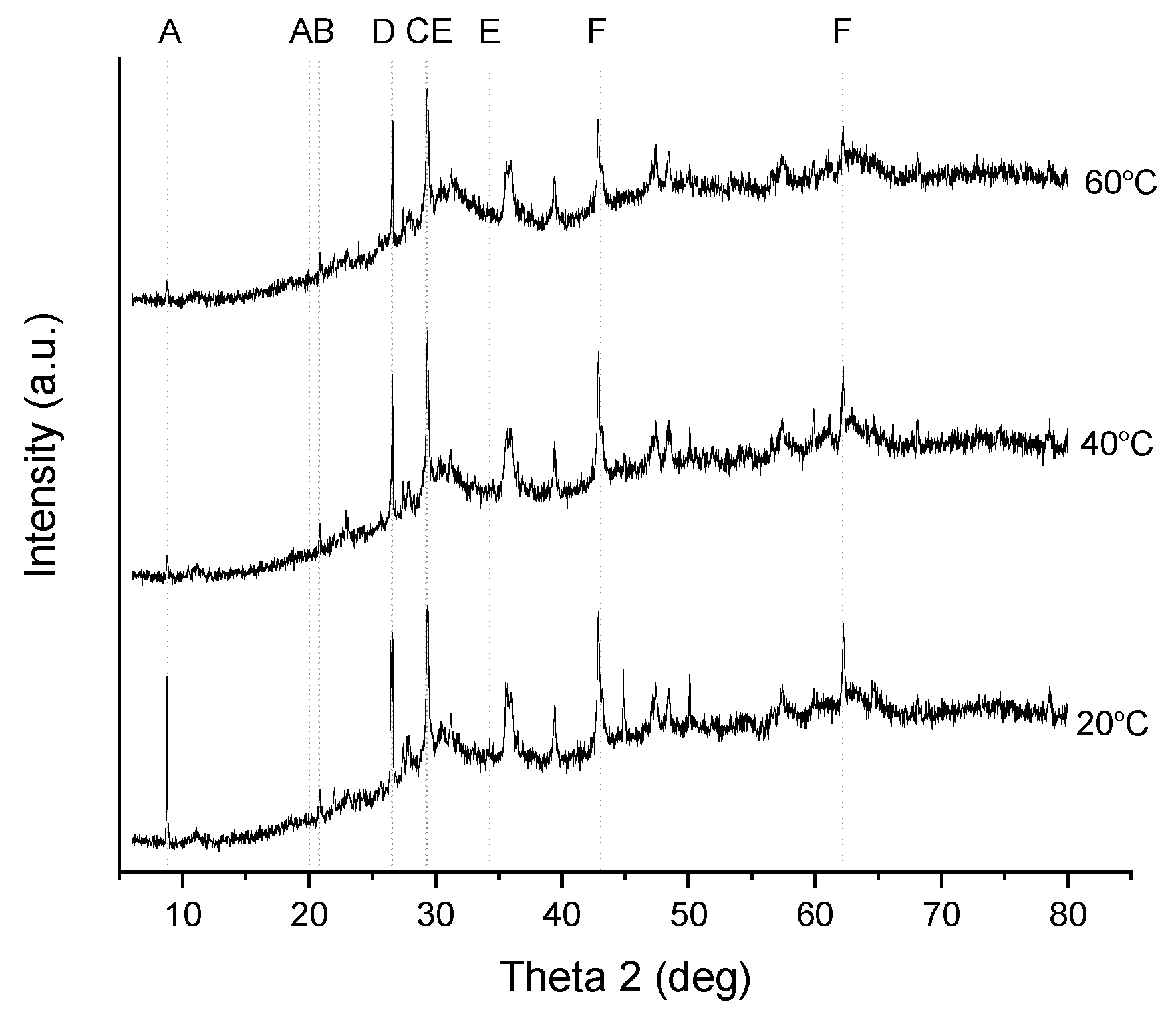
The XRD diffraction patterns in the synthetic solution experiments for fly ash sludge are presented in Figure 6. Peak A shows ammonium calcium hydrogen phosphate hydrate, NH4Ca2H3(P2O7)2·3H2O, peaking at 2θ = 8.8° and at 2θ = 20.1° at 20 °C. At the higher temperatures, 40 °C and 60 °C, the corresponding peak is at 2θ = 8.8°. Peak B shows ammonium magnesium hydrogen phosphate hydrate, that is, struvite, NH4MgPO4·6H2O, peaking at 2θ = 20.8°. Peak C shows CaO peaking at 2θ = 26.6°. Peak D shows magnesium phosphate, Mg3(PO4)2, peaking at 2θ = 29.3°. Peak E shows calcium phosphate hydrate, CaHPO4·2H2O, peaking at 2θ = 29.4° and at 2θ = 34.3°. Peak F shows MgO peaking at 2θ = 43.0° and at 2θ = 62.3°.
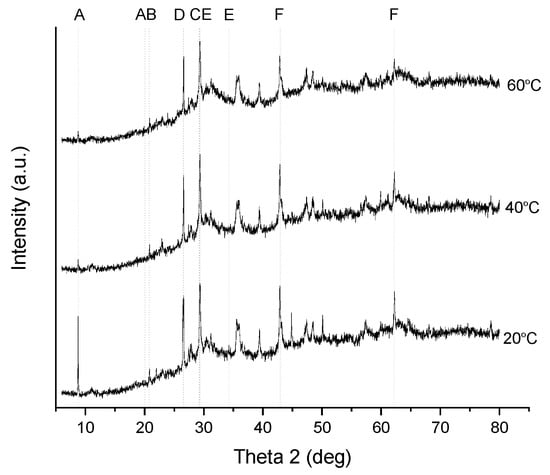
Figure 6.
X-ray diffraction patterns of the solid precipitates in the synthetic solution experiments at different temperatures. (A) NH4Ca2H3(P2O7)2·3H2O; (B) NH4MgPO4·6H2O; (C) CaO; (D) Mg3(PO4)2; (E) CaHPO4·2H2O; and (F) MgO.
3.4. Results of the Authentic Solution Experiments
3.4.1. Ammonium Nitrogen and Phosphate Removal
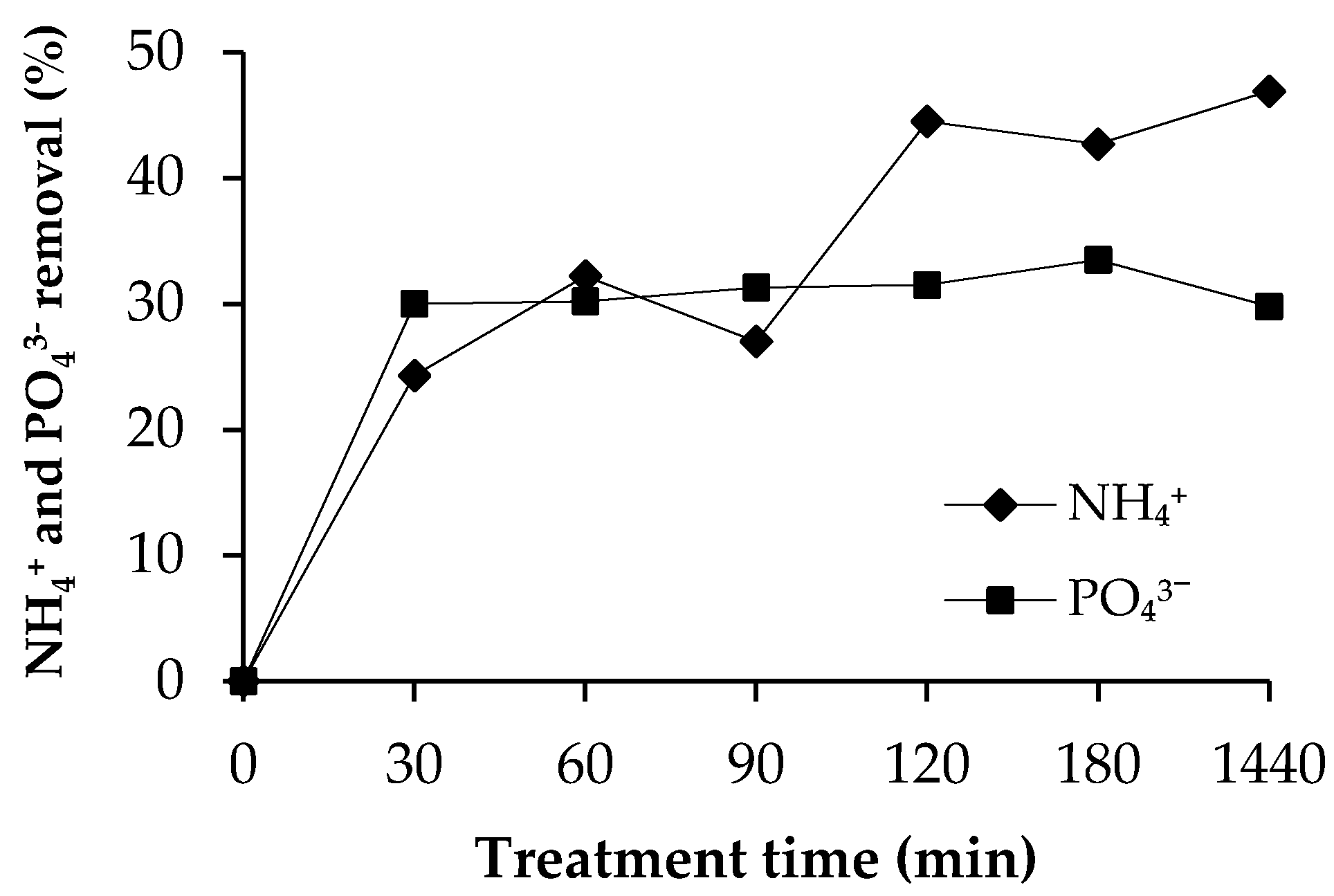
Ammonium nitrogen removal percentage and phosphate removal percentage as a function of treatment time are presented in Figure 7. Fly ash sludge removed 43% of ammonium nitrogen and 33.5% of phosphate from the liquid phase of anaerobic digestate after 180 min experiment. After that, removal efficiency did not improve essentially. When comparing the effectiveness of synthetic solution with the authentic solution, the removal efficiency in both cases was fairly satisfactory. However, it was sufficient for struvite and calcium phosphate formation, as shown in XRD diffraction patterns in Figure 8.
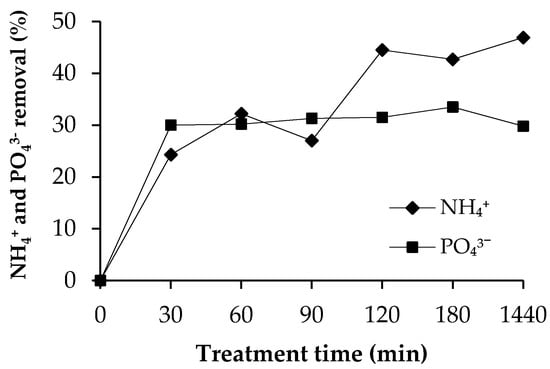
Figure 7.
Ammonium nitrogen and phosphate removal percentage using fly ash sludge as a precipitant, at 20 °C.
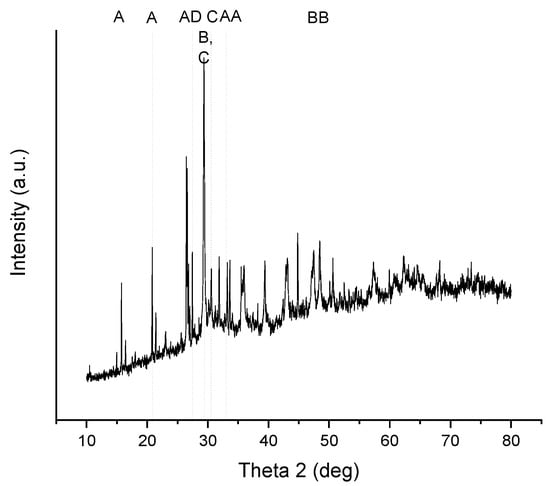
Figure 8.
X-ray diffraction patterns of the solid precipitates in the authentic solution experiments.
3.4.2. Residual Concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+
Figure 9 illustrates the residual concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ that remained in the authentic solution. The zero value illustrates the Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations of the authentic solution before the addition of fly ash as a precipitant. As shown in Figure 9, the soluble Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions have almost quantitatively participated in the removal of ammonium and phosphate ions from the solution. Therefore, the concentration of Ca2+ and Mg2+ was at a very low level during the experiment. The experiments were performed at 20 °C because, according to synthetic experiments, the results were at the similar level at all temperatures.
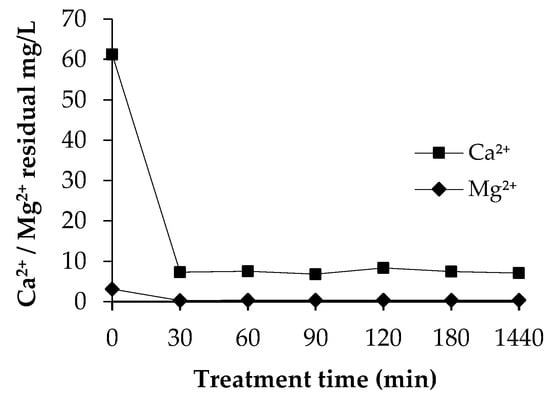
Figure 9.
Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) characterization of the residual concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ during the experiment, at 20 °C.
3.4.3. Characterization of Precipitates
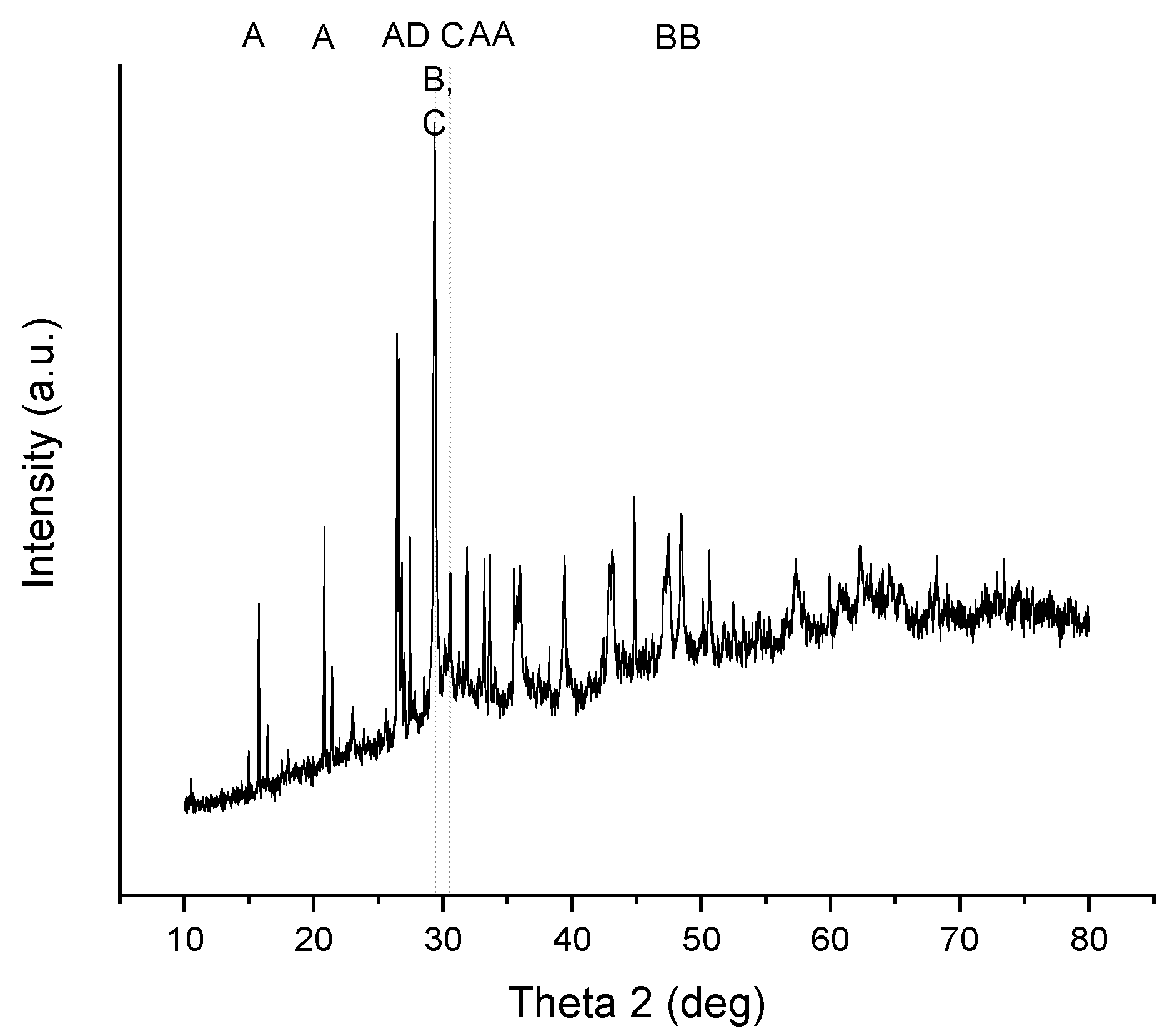
The XRD diffraction patterns in the authentic solution experiments for fly ash sludge are presented in Figure 8. Peak A shows ammonium magnesium hydrogen phosphate hydrate, that is, struvite, NH4MgPO4·6H2O, 51.4%, peaking at 2θ = 15.8°, 20.8°, 27.1°, 33.2°, and at 2θ = 33.6°. Peak B shows calcium carbonate, that is, calcite, CaCO3, 28.4%, peaking at 2θ = 29.4°, 47.5°, and at 2θ = 48.4° at 20 °C. Peak C shows calcium hydroxide phosphate, that is, monetite, CaPO3(OH),18.2%, peaking at 2θ = 28.5°, and at 2θ = 30.2°. Peak D shows phosphorus oxide nitride, PNO, 2.0%, peaking at 2θ = 27.5°.
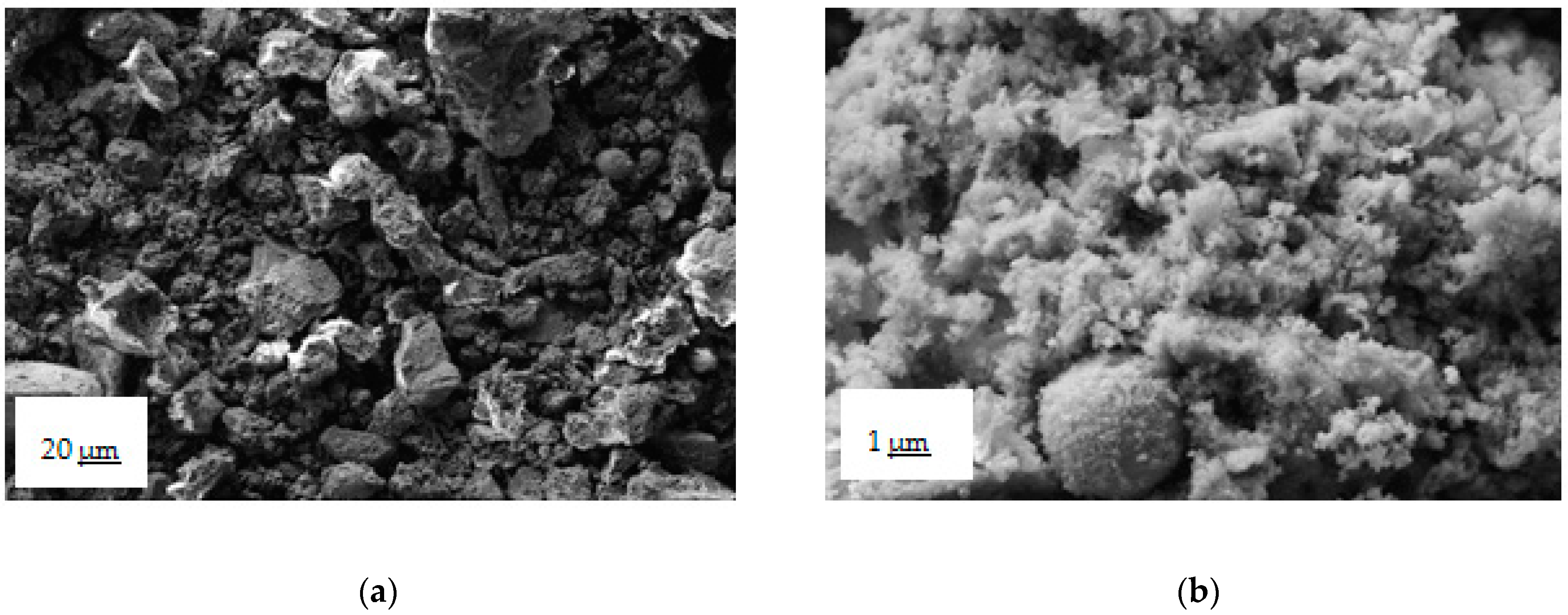
White struvite crystals are clearly visible among the particles in SEM images (Figure 10), Figure 10a illustrates the precipitate, zoom 500×, and Figure 10b illustrates the precipitate, zoom 20,000×.
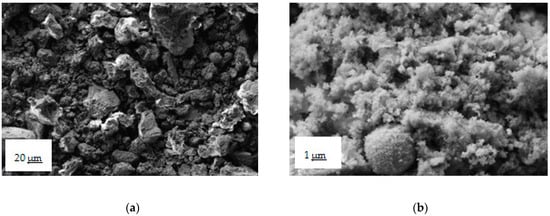
Figure 10.
(a) SEM image of the solid precipitates in the authentic solution experiment, where the bar indicates 20 μm length; (b) SEM image of the solid precipitates in the authentic solution experiment, where the bar indicates 1 μm length.
4. Discussion
The results of ammonium removal using fly ash are comparable with the results of other types of inexpensive magnesium sources, such as magnesium hydroxide based industrial by-product [49], hydrolysate from hydrothermal process [50], bone and meat waste [34], and MgO-saponification wastewater [35]. The other researchers obtained similar phosphate removal efficiencies with other types of ashes, such as fly ash [51], bottom ash [38], and waste bones ash [52].
However, when fly ash was used as a precipitant, the formed precipitates contain sustainable slow-release nutrients, such as NH4MgPO4·6H2O and CaPO3(OH). Others have obtained similar results with other types of side streams. Sakthivel et al. [38] found struvite when precipitating phosphorus and ammonium by bottom ash. Johansson [53] precipitated phosphate as hydroxyapatite, Ca10OH2(PO4)6, from wastewater with fly ash. Moriyama et al. [54] achieved 75–85% efficiency of hydroxyapatite formation using Ca-rich media in phosphorus removal. Chemical precipitation as struvite is the best known method of simultaneous phosphorus and ammonium nitrogen recovery from wastewater [22,23]. However, Ca-rich media can also be used in the simultaneous removal of nitrogen and phosphate, which leads to the formation of a struvite-like Ca-mineral [39], but it was not visible in our XRD diffraction patterns.
According to Urdalen [28], temperature also has an influence for struvite formation: When the temperature increases, the formation of crystals increases with increasing temperature until around 60 °C. The formation of crystals then decreases due to increased solubility of struvite. However, in our study, the change in temperature had no essential effect on the removal of phosphate using either fly ash sludge or commercial salts. Since this was the case also with ammonium, precipitation at room temperature would be the preferred option, because no heating is required.
However, a subject for further research would be to investigate solubility of recycled fertilizers and also make growth tests in greenhouses and fields, to confirm the suitability for fertilizer use. Previous research has indicated that the dissolution of heavy metal ions from fly ash takes place in chemically drastic conditions (i.e., when using concentrated hydrogen peroxide or mineral acids) [42,43,44,45]. The leaching of heavy metal ions to water and especially to alkaline solutions (as in struvite precipitation) is typically very low. Therefore, the leaching of heavy metals from the fly ash should not reduce the quality of struvite nor prevent the fertilizer use of struvite. However, this needs to be verified in the future research. The utilization of industrial waste material as secondary raw material is crucial for developing new sustainable removal methods from nutrient containing wastewaters.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, fly ash was used as a precipitant for ammonium and phosphate recovery from a synthetic (NH4)2HPO4 solution and the liquid phase of anaerobic digestate. The study results showed that Ca- and Mg-rich fly ash sludge removed 90% of ammonium nitrogen and almost 100% of phosphate from the synthetic solution working as effectively as precipitant as commercial salts. Fly ash sludge removed 43% of ammonium nitrogen and 33% of phosphate from the liquid phase of anaerobic digestate. The formed precipitates contain valuable crystals, such as struvite and calcium phosphate, and therefore can be used as slow-release recycled fertilizer.
Author Contributions
P.M., J.P., P.T., and H.R. have designed the experiments. P.M. implemented the experiments and wrote the manuscript draft. T.H. has characterized the materials with X-ray fluorescence, X-ray diffraction, and FESEM. All authors analyzed the data and contributed to the text.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank student Emilia Sauvola and laboratory assistant Jaakko Pulkkinen for their assistance with the laboratory work and analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- European Commission 2018: Circular Economy Strategy—Environment—European Commission. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/circular-economy/index_en.htm (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- European Commission 2018b: Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32008L0098 (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Sokka, L.; Pakarinen, S.; Melanen, M. Industrial symbiosis contributing to more sustainable energy use—An example from the forest industry in Kymenlaakso, Finland. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, S.; Manninen, K.; Leskinen, P. Combining biogas LCA reviews with stakeholder interviews to analyse life cycle impacts at a practical level. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 80, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marttinen, S.; Venelampi, O.; Iho, A.; Koikkalainen, K.; Lehtonen, E.; Luostarinen, S.; Rasa, K.; Sarvi, M.; Tampio, E.; Turtola, E.; et al. Kohti Ravinteiden Kierrätyksen Läpimurtoa; Luonnonvara- ja biotalouden tutkimus 45/2017; Luonnonvarakeskus: Helsinki, Finland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pan-in, S.; Sukasem, N. Methane production potential from anaerobic co-digestions of different animal dungs and sweet corn residuals. Energy Procedia 2017, 138, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latvala, M. Biokaasun Tuotanto Suomalaisessa Toimintaympäristössä; Suomen Ympäristö 24/2009; Suomen ympäristökeskus: Helsinki, Finland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, J.; Herbes, C.; Nelles, M. Biogas digestate marketing: Qualitative insights into the supply side. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2015, 104, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission 2003: Regulation (EU) No 2003/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council Relating to Fertilizers. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/FI/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32003R2003&from=FI (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- European Commission 2009: Animal by-products Regulation (EU) No 1069/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/FI/ALL/?uri=CELEX:32009R1069 (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Finnish Legislation 2006: The Act on Fertilizer Products 539/2006. Available online: https://www.finlex.fi/fi/laki/ajantasa/2006/20060539 (accessed on 11 April 2018).
- Bolan, N.S.; Wong, L.; Adriano, D.C. Nutrient removal from farm effluents. Bioresource Technol. 2004, 94, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, B.; Zang, Z.; Liu, S.; Lei, S.; Xiao, R. Simultaneous capture removal of phosphate, ammonium and organic substances by MgO impregnated biochar and its potential use in swine wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kong, M. Simultaneous removal of ammonium and phosphate from eutrophic waters using natural calcium-rich attapulgite-based versatile adsorbent. Desalination 2014, 351, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektaş, N.; Akbulut, H.; Inan, H.; Dimoglo, A. Removal of phosphate from aqueous solutions by electro-coagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 106, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, A.; Udert, K.M. Struvite precipitation from urine with electrochemical magnesium dosage. Water Res. 2013, 47, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos-Castillo, R.; Sillanpää, M.; Brillas, E.; Sirés, I. Removal of metals and phosphorus recovery from urban anaerobically digested sludge by electro-Fenton treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpimaa, S.; Runtti, H.; Kangas, T.; Lassi, U.; Kuokkanen, T. Physical activation of carbon residue from biomass gasification: Novel sorbent for the removal of phosphates and nitrates from aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 21, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Veznikova, K.; Tolonen, E.T.; Runtti, H.; Yliniemi, J.; Hu, T.; Kemppainen, K.; Lassi, U. Removal of ammonium from municipal wastewater with powdered and granulated metakaolin geopolymer. Environ. Technol. 2017, 39, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvers, B. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Aho, M.; Pursula, T.; Saario, M.; Miller, T.; Kumpulainen, A.; Päällysaho, M.; Autio, M.; Hillgren, A.; Descombes, L. Ravinteiden Kierron Taloudellinen Arvo ja Mahdollisuudet Suomelle; Sitra: Helsinki, Finland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kataki, S.; West, H.; Clarke, M.; Baruah, D.C. Phosphorus recovery as struvite: Recent concerns for use of seed, alternative Mg source, nitrogen conservation and fertilizer potential. Resour. Conserv. Recy. 2016, 49, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.S.; Mavinic, D.S.; Bhuiyan, M.I.H.; Koch, F.A. Exploring the determination of struvite solubility product from analytical results. Environ. Technol. 2006, 27, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, M.; Yao, M.; Tsuno, H.; Somiya, I. Removal and recovery of phosphate and ammonium as struvite from supernatant in anaerobic digestion. Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 48, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelen, I.; Türker, M. Recovery of Ammonia as Struvite from Anaerobic Digester Effluents. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabdaşlı, I.; Tünay, O. Nutrient recovery by struvite precipitation, ion exchange and adsorption from source-separated human urine—A review. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2018, 7, 106–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.D.; Wang, C.C.; Lan, L.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Struvite formation, analytical methods and effects of pH and Ca2+. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 58, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urdalen, I. Phosphorus Recovery from Municipal Wastewater; Norwegian University of Science and Technology: Trondheim, Norway, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Kumar, J.; Kwag, J.; Ra, C. Magnesium ammonium phosphate formation, recovery and its application as valuable resources: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymańska, M.; Szara, E.; Sosulski, T.; Wąs, A.; van Pruissen, G.W.P.; Cornelissen, R.L.; Borowik, M.; Konkol, M. A Bio-Refinery Concept for N and P Recovery—A Chance for Biogas Plant Development. Energies 2019, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CRM Alliance. Critical Raw Materials. Available online: www.criticalrawmaterials.org/critical-raw-materials.OK (accessed on 31 December 2018).
- Gunay, A.; Karadag, D.; Tosun, I.; Ozturk, M. Use of magnesit as a magnesium source for ammonium removal from leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.M.; Xiao, X.M.; Yang, L.P.; Yan, B. Removal of ammonium from rare-earth wastewater using natural brucite as a magnesium source of struvite precipitation. Water Sci. Technol. 2011, 63, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siciliano, A.; De Rosa, S. Recovery of ammonia in digestates of calf manure through a struvite precipitation process using unconventional reagents. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, L. Treatment of swine wastewater combined with MgO-saponification wastewater by struvite precipitation technology. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crutchik, D.; Sánchez, A.; Garrido, J.M. Simulation and experimental validation of multiple phosphate precipitates in a saline industrial wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Giannis, A.; Zhang, J.; Chang, V.W.; Wang, J. Characterization of induced struvite formation from source-separated urine using seawater and brine as magnesium sources. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 2738–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, S.R.; Tilley, E.; Udert, K.M. Wood ash as a magnesium source for phosphorus recovery from source-separated urine. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 419, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, A.W.; Lehr, J.R.; Smith, J.P. Calcium Ammonium Orthophosphates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1964, 12, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of gases in multimolecular layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry Decree on Fertilizer Products 24/2011; Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry: Helsinki, Finland, 2011.
- Pöykiö, R.; Nurmesniemi, H.; Perämäki, P.; Kuokkanen, T.; Välimäki, I. Leachability of metals in fly ash from a pulp and paper mill complex and environmental risk characterization for eco-efficient utilization of the fly ash as a fertilizer. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2005, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuokkanen, T.; Pöykiö, R.; Nurmesniemi, H.; Rämö, J. Sequential leaching of heavy metals and sulfur in bottom ash and fly ash from the co-combustion of wood and peat at a municipal district heating plant. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2006, 18, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesonen, J.; Yliniemi, J.; Illikainen, M.; Kuokkanen, T.; Lassi, U. Stabilization/solidification of fly ash from fluidized bed combustion of recovered fuel and biofuel using alkali activation and cement addition. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesonen, J.; Kuokkanen, T.; Rautio, P.; Lassi, U. Bioavailability of nutrients and harmful elements in ash fertilizers: Effect of granulation. Biomass Bioenerg. 2017, 100, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepua: Jepuan Biokaasu. Available online: https://jeppobiogas.fi/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/TUOTESELOSTE-2018.pdf (accessed on 29 November 2018).
- Wäger-Baumann, F. Physical and Biological Methods for the Treatment of the Liquid Fraction of Anaerobic Digester Effluent; University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences: Vienna, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nkoa, R. Agricultural benefits and environmental risks of soil fertilization with anaerobic digestates: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 473–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yunqin Lin, Y.; Wang, D.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Tan, S. Ammonium removal from digested effluent of swine wastewater by using solid residue from magnesium-hydroxide flue gas desulfurization process. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 58, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Lei, Z.; Yuan, T.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Shimizu, K.; Zhang, Z. Simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen recovery from anaerobically digested sludge using a hybrid system coupling hydrothermal pretreatment with MAP precipitation. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, M.Y.; Yildiz, E. Phosphate removal from water by fly ash: Factorial experimental design. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, B135, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, M.; Aris, A.; Puteh, M.H.; Jusoh, M.N.H.; Kadir, A.A. Waste bones ash as an alternative source of P for struvite preciptation. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L. Industrial by-products and natural substrata as phosphorus sorbents. Environ. Technol. 1999, 20, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, K.; Kojima, T.; Minawa, Y.; Matsumoto, S.; Nakamachi, K. Development of artificial seed crystal for crystallization of calcium phosphate. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).