Contraction Integral Equation for Three-Dimensional Electromagnetic Inverse Scattering Problems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The CIE-I is firstly implemented to tackle the computationally costly full 3-D ISPs, to address the highly nonlinear 3-D ISPs, and to accelerate the convergence of the inversions.
- A relaxed type of inversion scheme based on CIE-I is proposed, with different auxiliary parameters (the parameter in CIE-I to control the portion of MSE in estimating the contrast) in updating the contrast sources and in updating the contrast. This means to further accelerate the convergence of the inversions.
- Several numerical tests are provided with details, for the sake of further algorithmic studies.
2. Inversion with CIE-I
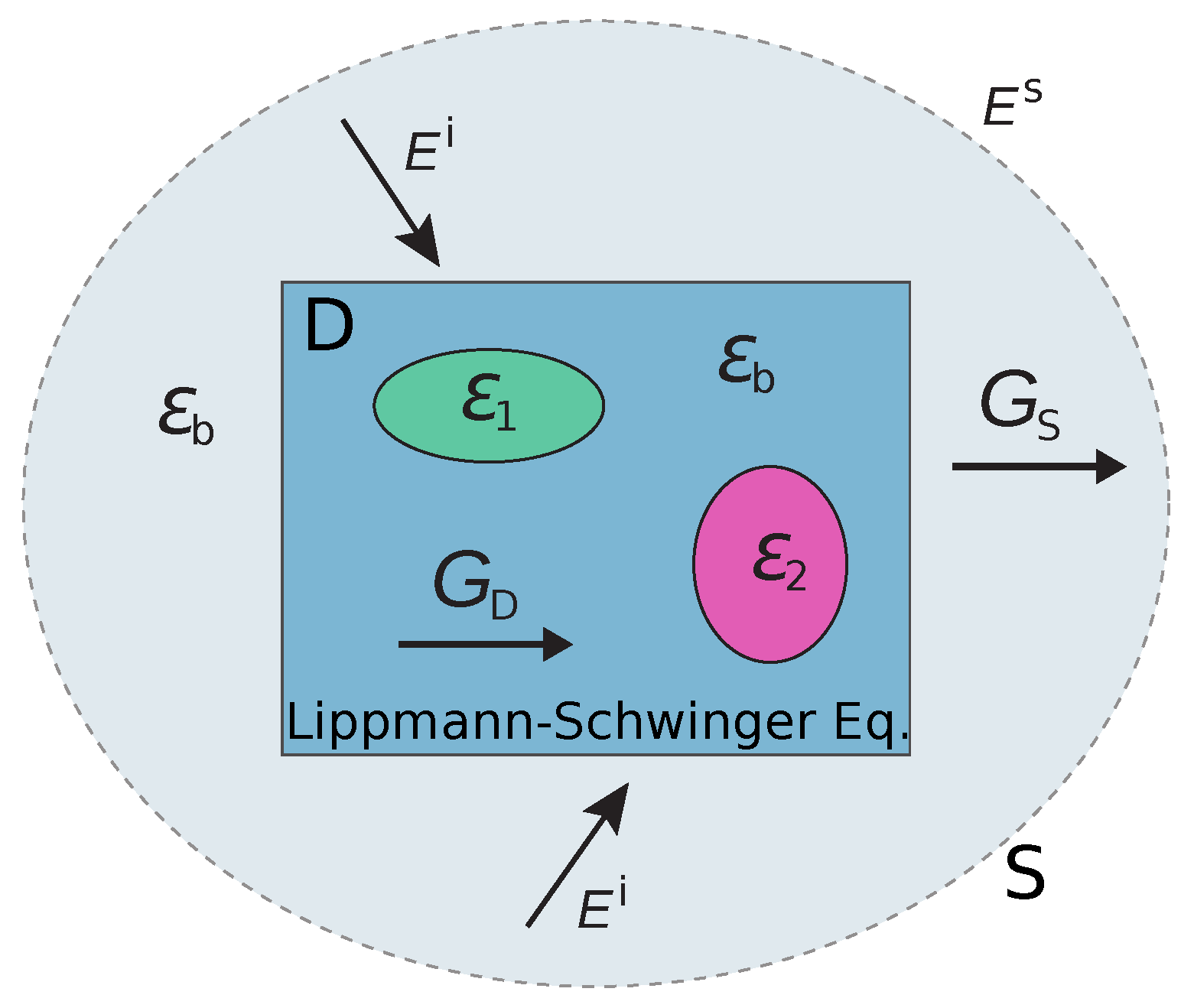
2.1. 3-D Modeling
2.2. Objective Function for Inversions
2.3. Sketch of the Inversion Method
- Set the background medium and null APCS as the initial guesses and choose an L value such that the corresponding first L singular values of are larger than the noise level (assuming that the noise is a white Gaussian one).
- Set proper values for in CIE-I modeling and proper value for to control the number of Fourier bases being used.
- Carry out the CG type optimization algorithm to alternatively update the two types of variables, where the APCS is updated with a one-step Polak–Ribière CG scheme and the contrast is updated with the least squares method.
- Stop the optimization if a termination condition is met, which can be a maximum number of iterations or a pre-defined relative change of APCS coefficients.
- If the maximum number of rounds of inversion is met, go to Step 6. Otherwise, the obtained contrast and APCS will be used as the initial guesses for the next round of optimization with smaller and larger in Step 3.
- Output the obtained contrast.
2.4. Updating Contrast and Contrast Sources with Different
3. Numerical Simulations
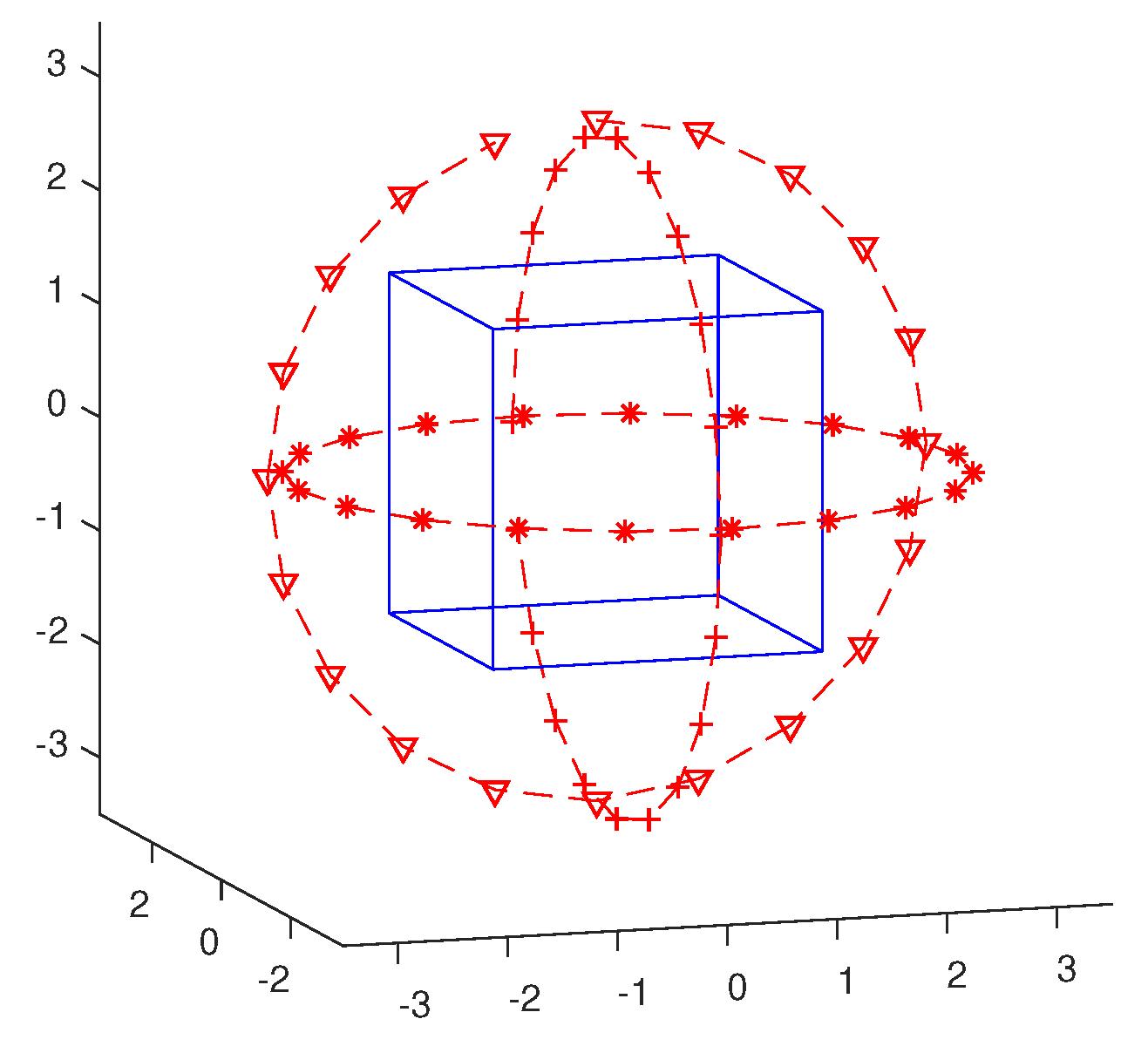
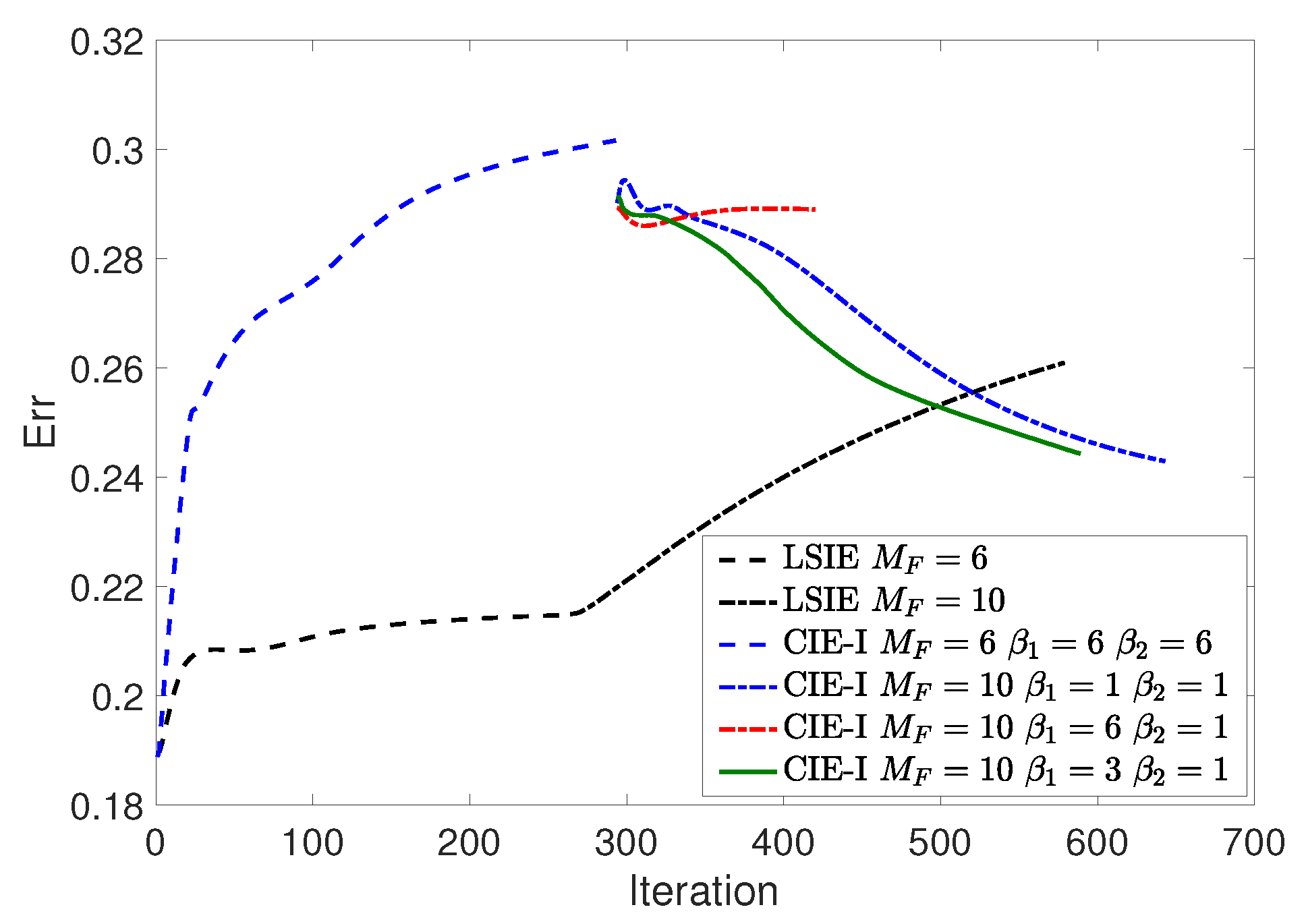
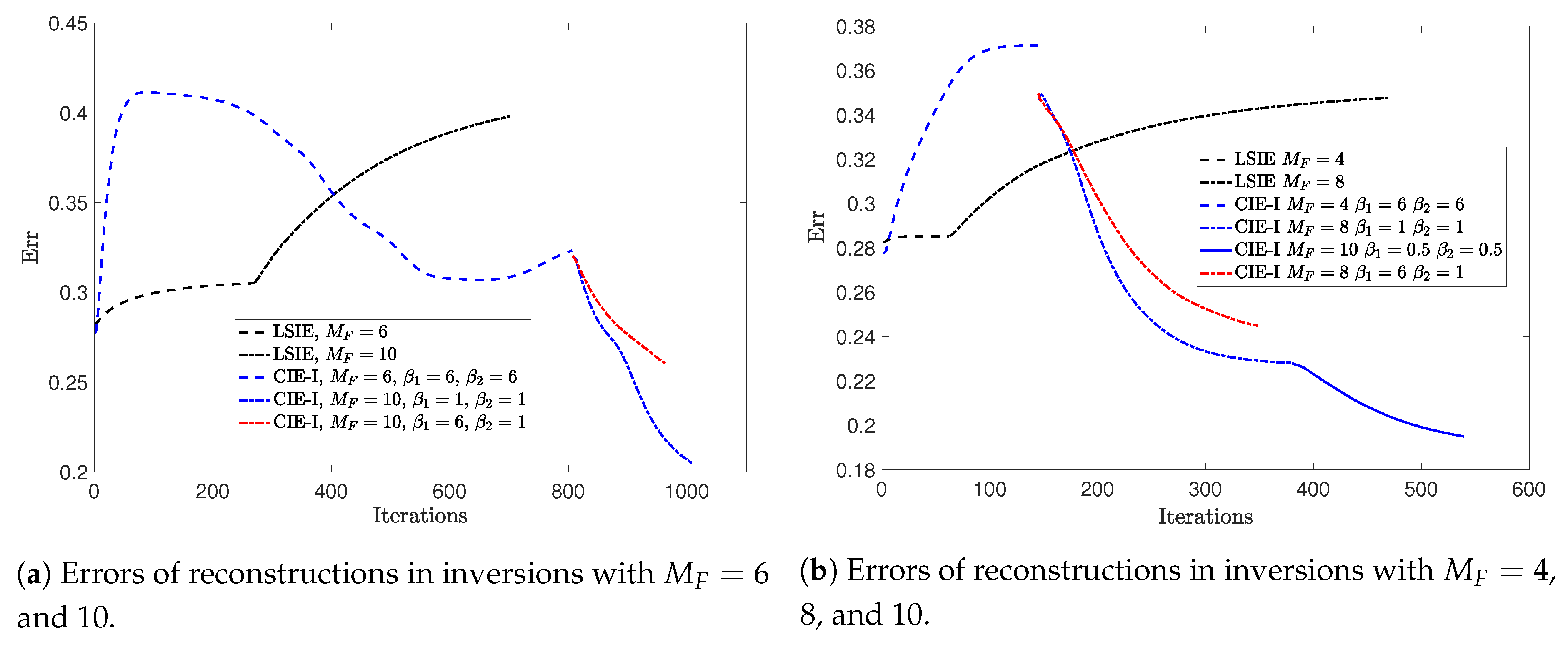
3.1. Example 1
3.2. Example 2
3.3. Example 3
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CIE-I | Contraction integral equation for inversion |
| LSIE | Lippmann–Schwinger integral equation |
| 3-D | Three-dimensional |
| CSI | Contrast source inversion |
| SOM | Subspace-based optimization method |
| FFT-TSOM | FFT type twofold subspace-based optimization method |
| APCS | Ambiguous part of the contrast source |
| DPCS | Deterministic part of the contrast source |
| DoI | Domain of interest |
| MSE | Multiple scattering effects |
References
- Colton, D.; Kress, R. Inverse Acoustic and Electromagnetic Scattering Theory; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abubakar, A.; van den Berg, P.M.; Mallorqui, J. Imaging of biomedical data using a multiplicative regularized contrast source inversion method. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2002, 50, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, A.; van den Berg, P.M. Three-dimensional inverse scattering applied to cross-well induction sensors. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2000, 38, 1669–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, A.; Boni, A.; Donelli, M. A classification approach based on SVM for electromagnetic subsurface sensing. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2005, 43, 2084–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatier, P.C. Past and future of inverse problems. J. Math. Phys. 2000, 41, 4082–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, A.; van den Berg, P.M. Iterative forward and inverse algorithms based on domain integral equations for three-dimensional electric and magnetic objects. J. Comput. Phys. 2004, 195, 236–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Chen, X.; Agarwal, K. An improved subspace-based optimization method and its implementation in solving three-dimensional inverse problems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 3763–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Chen, X. An FFT twofold subspace-based optimization method for solving electromagnetic inverse scattering problems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2011, 59, 914–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litman, A.; Lorenzo, C. Special section on testing inversion algorithms against experimental data: 3-D targets. Inverse Probl. 2009, 25, 020201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, P.M.; Kleinman, R.E. A contrast source inversion method. Inverse Probl. 1997, 13, 1607–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, P.M.; van Broekhoven, A.L.; Abubakar, A. Extended constrast source inversion. Inverse Probl. 1999, 15, 1325–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chew, W.C. An iterative solution of two-dimensional electromagnetic inverse scattering problem. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 1989, 1, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, W.C.; Wang, Y. Reconstruction of two-dimensional permittivity distribution using the distorted Born iterative method. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1990, 9, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorn, O.; Lesselier, D. Level set methods for inverse scattering. Inverse Probl. 2006, 22, R67–R131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, M.; Lesselier, D.; Lambert, M.; Massa, A. A multi-resolution technique based on shape optimization for the reconstruction of homogeneous dielectric objects. Inverse Probl. 2009, 25, 015009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Subspace-based optimization method for solving inverse scattering problems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Chen, X. Twofold subspace-based optimization method for solving inverse scattering problems. Inverse Probl. 2009, 25, 085003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, K.; Pan, L.; Chen, X. Subspace-based optimization method for reconstruction of two-dimensional complex anisotropic dielectric objects. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2009, 58, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorino, M. Stochastic optimization methods applied to microwave imaging: A review. IEEE Trans. Antenna Propag. 2007, 55, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca, P.; Benedetti, M.; Donelli, M.; Franceschini, D.; Massa, A. Evolutionary optimization as applied to inverse scattering problems. Inverse Probl. 2009, 25, 123003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zaeytijd, J.; Franchois, A.; Geffrin, J.M. A new value picking regularization strategy-Application to the 3-D electromagnetic inverse scattering problem. IEEE Trans. Antenna Propag. 2009, 57, 1133–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaumet, P.; Belkebir, K. Three-dimensional reconstruction from real data using a conjugate gradient-coupled dipole method. Inverse Probl. 2009, 25, 024003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yuan, M.; Liu, Q.H. Reconstruction of 3-D objects from multi-frequency experimental data with a fast DBIM-BCGS method. Inverse Probl. 2009, 25, 024007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donelli, M.; Franceschini, D.; Rocca, P.; Massa, A. Three-dimensional microwave imaging problems solved through an efficient multiscaling particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 1467–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, K.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Y. A multipole-expansion based linear sampling method for solving inverse scattering problems. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 6366–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bevacqua, M.T.; Isernia, T. Boundary Indicator for Aspect Limited Sensing of Hidden Dielectric Objects. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 838–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isernia, T.; Crocco, L.; D’Urso, M. New tools and series for forward and inverse scattering problems in lossy media. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2004, 1, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Urso, M.; Isernia, T.; Morabito, A.F. On the Solution of 2-D Inverse Scattering Problems via Source-Type Integral Equations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Lambert, M.; Lesselier, D.; Chen, X. A new integral equation method to solve highly nonlinear inverse scattering problems. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2016, 64, 1788–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankratov, O.V.; Avdeyev, D.B.; Kuvshinov, A.V. Electromagnetic field scattering in a heterogeneous earth: A solution to the forward problem. Phys. Solid Earth 1995, 31, 201–209. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, A.F.; Ray, S.L.; Mittra, R. Computational Methods for Electromagnetics; IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, G. A hybrid regularization technique for solving highly nonlinear inverse scattering problems. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 64, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, Y.; Xu, K. Contraction Integral Equation for Three-Dimensional Electromagnetic Inverse Scattering Problems. J. Imaging 2019, 5, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging5020027
Zhong Y, Xu K. Contraction Integral Equation for Three-Dimensional Electromagnetic Inverse Scattering Problems. Journal of Imaging. 2019; 5(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging5020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Yu, and Kuiwen Xu. 2019. "Contraction Integral Equation for Three-Dimensional Electromagnetic Inverse Scattering Problems" Journal of Imaging 5, no. 2: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging5020027
APA StyleZhong, Y., & Xu, K. (2019). Contraction Integral Equation for Three-Dimensional Electromagnetic Inverse Scattering Problems. Journal of Imaging, 5(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging5020027




