Multilesion Segmentations in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Reliability of ICH, IVH and PHE Masks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
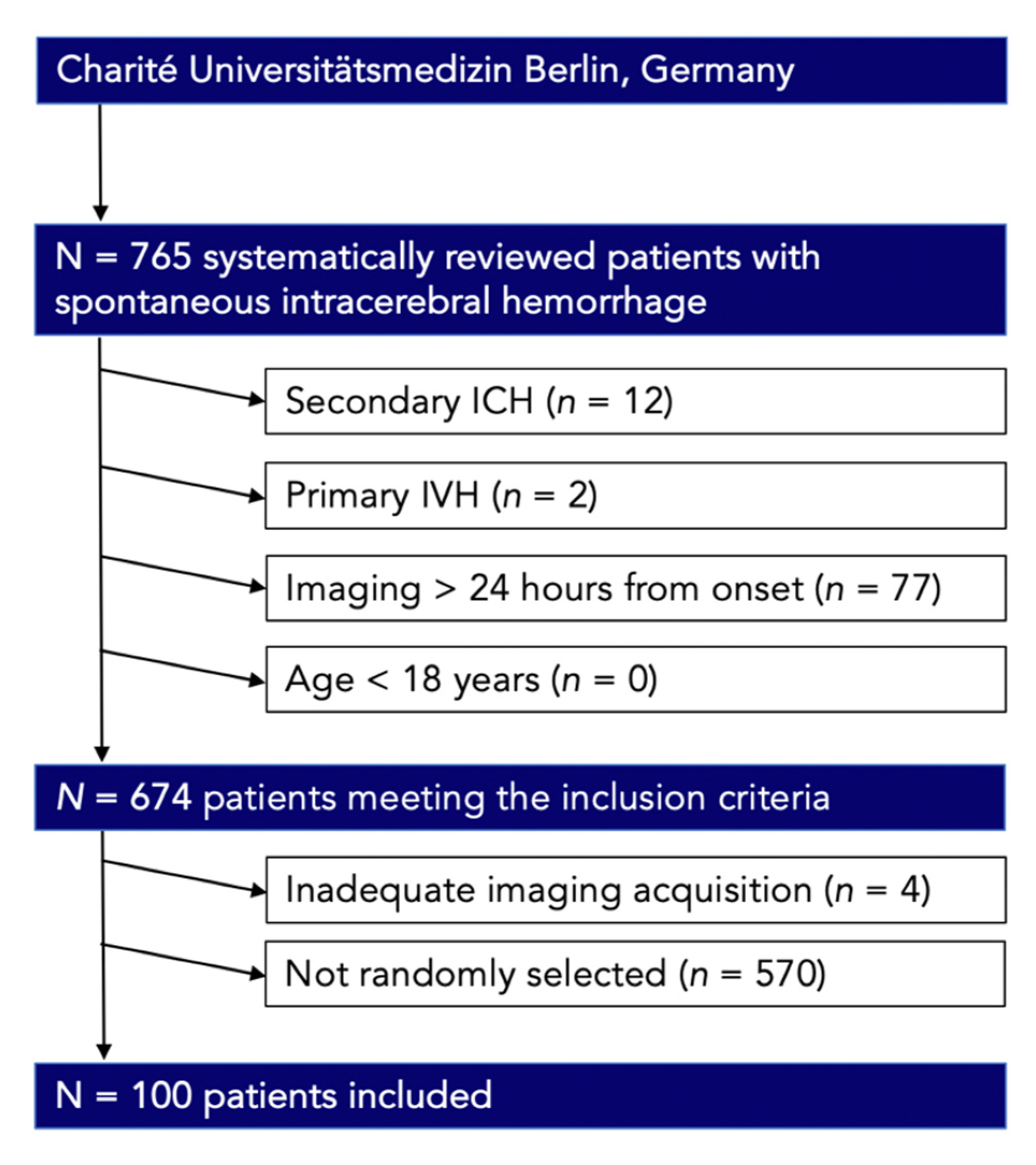
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Image Acquisition
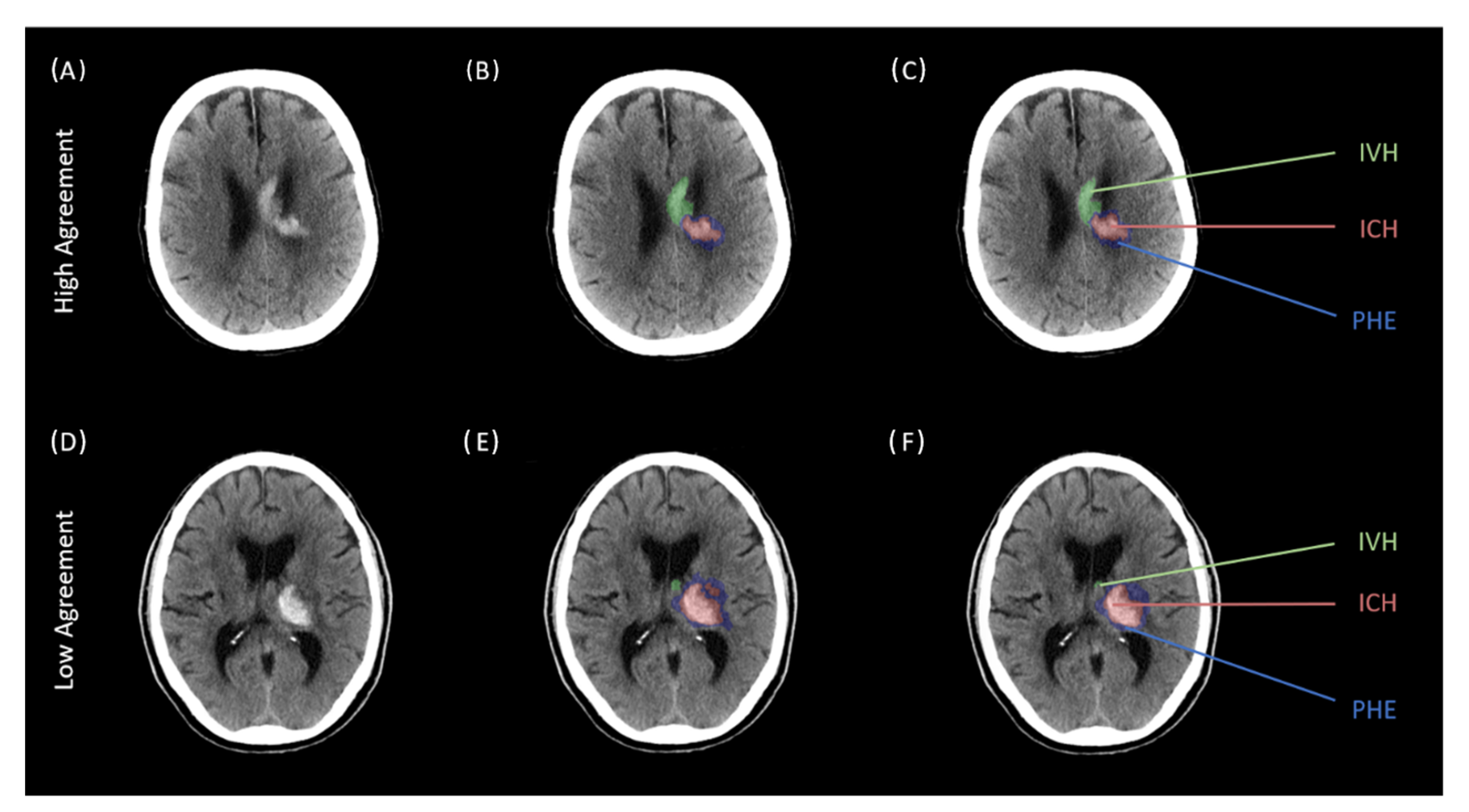
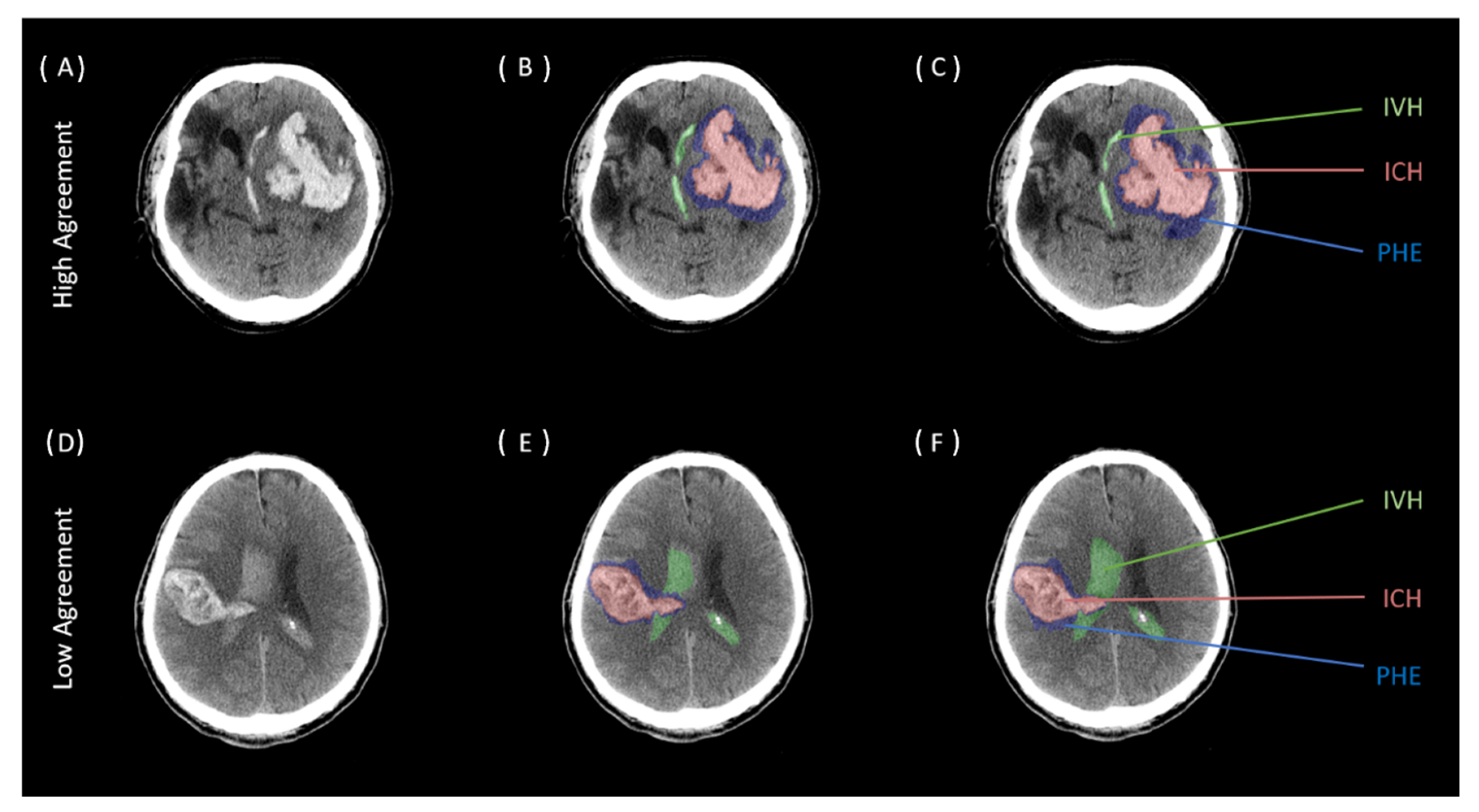
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drury, I.; Whisnant, J.P.; Garraway, W.M. Primary intracerebral hemorrhage: Impact of CT on incidence. Neurology 1984, 34, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubovic, R.; Aviv, R.I. Intracerebral hemorrhage: Toward physiological imaging of hemorrhage risk in acute and chronic bleeding. Front. Neurol. 2012, 3, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Broderick, J.P.; Brott, T.G.; Duldner, J.E.; Tomsick, T.; Huster, G. Volume of intracerebral hemorrhage. A powerful and easy-to-use predictor of 30-day mortality. Stroke 1993, 24, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.; Wang, D.; Li, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, J. Advances in computed tomography-based prognostic methods for intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 45, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, R.B.; Teeple, S.; Navathe, A.S. Addressing Bias in Artificial Intelligence in Health Care. JAMA 2019, 322, 2377–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ironside, N.; Chen, C.J.; Mutasa, S.; Sim, J.L.; Ding, D.; Marfatiah, S.; Roh, D.; Mukherjee, S.; Johnston, K.C.; Southerland, A.M.; et al. Fully Automated Segmentation Algorithm for Perihematomal Edema Volumetry After Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2020, 51, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, K.; Wu, G.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, X.; Lv, C.; Wu, S.; Chen, Y.; Xie, G.; Yao, Z. Deep learning shows good reliability for automatic segmentation and volume measurement of brain hemorrhage, intraventricular extension, and peripheral edema. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 5012–5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, R.; Falcone, G.J.; Chen, Y.; Hamzehloo, A.; Kirsch, E.P.; Noche, R.B.; Roth, K.; Acosta, J.; Ruiz, A.; Phuah, C.-L.; et al. Deep Learning for Automated Measurement of Hemorrhage and Perihematomal Edema in Supratentorial Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2020, 51, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, L.; Su, J.; Van Loon, D.; van Es, A.; van Doormaal, P.J.; Majoie, C.; van Zwam, W.; Dippel, D.; van der Lugt, A.; van Walsum, T. Inter-rater reliability for assessing intracranial collaterals in patients with acute ischemic stroke: Comparing 29 raters and an artificial intelligence-based software. Neuroradiology 2022, 64, 2277–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microsoft Support. INDEX Function. Available online: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/index-function-a5dcf0dd-996d-40a4-a822-b56b061328bd (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Falcone, G.J.; Biffi, A.; Brouwers, H.B.; Anderson, C.D.; Battey, T.W.; Ayres, A.M.; Vashkevich, A.; Schwab, K.; Rost, N.S.; Goldstein, J.N.; et al. Predictors of hematoma volume in deep and lobar supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Anderson, C.S.; Robinson, T.; Lavados, P.M.; Lindley, R.I.; Chalmers, J.; Delcourt, C.; INTERACT Investigators. Infratentorial Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2019, 50, 1257–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volbers, B.; Staykov, D.; Wagner, I.; Dorfler, A.; Saake, M.; Schwab, S.; Bardutzky, J. Semi-automatic volumetric assessment of perihemorrhagic edema with computed tomography. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011, 18, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urday, S.; Beslow, L.A.; Goldstein, D.W.; Vashkevich, A.; Ayres, A.M.; Battey, T.W.; Selim, M.H.; Kimberly, W.T.; Rosand, J.; Sheth, K.N. Measurement of perihematomal edema in intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2015, 46, 1116–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, M.; Shukla, P.; Bodhit, A.; Asaithambi, G.; Velez, A.; Rosado, C.; Mishra, M.; Saravanapavan, P.; Khan, S.; Reddy, V.; et al. Intracerebral Hematoma Volume Measurement Using ITK-SNAP Software: Initial Experience (P7.145). Neurology 2014, 82 (Suppl. 10), P7.145. [Google Scholar]
- Morotti, A.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Boulouis, G.; Al-Ajlan, F.; Demchuk, A.M.; Aviv, R.I.; Yu, L.; Schwab, K.; Romero, J.M.; Gurol, M.E.; et al. Predicting Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion with Noncontrast Computed Tomography: The BAT Score. Stroke 2018, 49, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morotti, A.; Boulouis, G.; Dowlatshahi, D.; Li, Q.; Barras, C.D.; Delcourt, C.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Z.; Aviv, R.I.; et al. Standards for Detecting, Interpreting, and Reporting Noncontrast Computed Tomographic Markers of Intracerebral Hemorrhage Expansion. Ann. Neurol. 2019, 86, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilms, L.M.; Radke, K.L.; Latz, D.; Thiel, T.A.; Frenken, M.; Kamp, B.; Filler, T.J.; Nagel, A.M.; Müller-Lutz, A.; Abrar, D.B.; et al. UTE-T2* versus conventional T2* mapping to assess posterior cruciate ligament ultrastructure and integrity—An in-situ study. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2022, 12, 4190–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, M.R.; Fillyaw, M.J.; Thompson, W.D. The use and interpretation of the Friedman test in the analysis of ordinal-scale data in repeated measures designs. Physiother. Res. Int. 1996, 1, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlunk, F.; Kuthe, J.; Harmel, P.; Audebert, H.; Hanning, U.; Bohner, G.; Scheel, M.; Kleine, J.; Nawabi, J. Volumetric accuracy of different imaging modalities in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. BMC Med. Imaging 2022, 22, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ironside, N.; Chen, C.J.; Ding, D.; Mayer, S.A.; Connolly, E.S., Jr. Perihematomal Edema After Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Stroke 2019, 50, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, K.H.; Warfield, S.K.; Bharatha, A.; Tempany, C.M.; Kaus, M.R.; Haker, S.J.; Wells, W.M.; Jolesz, F.A.; Kikinis, R. Statistical validation of image segmentation quality based on a spatial overlap index. Acad. Radiol. 2004, 11, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ironside, N.; Patrie, J.; Ng, S.; Ding, D.; Rizvi, T.; Kumar, J.S.; Mastorakos, P.; Hussein, M.Z.; Naamani, K.E.; Abbas, R.; et al. Quantification of hematoma and perihematomal edema volumes in intracerebral hemorrhage study: Design considerations in an artificial intelligence validation (QUANTUM) study. Clin. Trials 2022, 19, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montemurro, N.; Murrone, D.; Romanelli, B.; Ierardi, A. Postoperative Textiloma Mimicking Intracranial Rebleeding in a Patient with Spontaneous Hemorrhage: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Neurol. 2020, 12, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpinar, A.; Ucler, N.; Ozdemir, C.O. Textiloma (gossypiboma) mimicking recurrent intracranial abscess. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nawabi, J.; Hanning, U.; Broocks, G.; Schon, G.; Schneider, T.; Fiehler, J.; Thaler, C.; Gellissen, S. Neoplastic and Non-Neoplastic Causes of Acute Intracerebral Hemorrhage on CT: The Diagnostic Value of Perihematomal Edema. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2020, 30, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Baseline Clinical and Imaging Characteristics | All = 100 |
|---|---|
| Clinical characteristics | |
| Age median, (IQR) | 75.5 (65–78) |
| Male, n (%) | 83 (83%) |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 68 (68%) |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 12 (12%) |
| Initial GCS, median (IQR) | 11 (10–14) |
| RRsys, median (IQR) | 155.5 (0–189.25) |
| Anticoagulation, n (%) | 34 (34%) |
| Antiplatelet Treatment, n (%) | 16 (16%) |
| Imaging characteristics | |
| Bleeding location, n (%) | |
| lobar | 92 (92%) |
| basal ganglia | 8 (8%) |
| thalamus | 0 |
| brainstem/Pons | 0 |
| cerebellar | 0 |
| Black hole sign, n (%) | 13 (13%) |
| Blend sign, n (%) | 6 (6%) |
| Hypodensities, n (%) | 13 (13%) |
| Island sign, n (%) | 12 (12%) |
| Spot sign, n (%) | 8 (8%) |
| Surgical Treatment, n (%) | |
| Supratentoriell craniectomy | 26 (26%) |
| Infratentoriell craniectomy | 3 (3%) |
| EDV | 13 (13%) |
| Minimally invasive surgery | 4 (4%) |
| Clinical Outcome | |
| mRS > 3, n (%) | 45 (45%) |
| mRS < 3, n (%) | 55 (55%) |
| Radiological Features | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rating 1 (Rater 1, First Rating) | Rating 2 (Rater 1, Second Rating) | Rating 3 (Rater 2) | p-Value * | |
| ICH volume [mL], median (IQR) | 17.325 (7.57–40.38) | 18.33 (7.665–41.808) | 19.825 (8.17–42.84) | <0.001 |
| PHE volume [mL], median (IQR) | 12.6 (5.12–23.39) | 11.81 (5.42–24.64) | 16.55 (7.84–28.76) | <0.001 |
| IVH volume [mL], median (IQR) | 6.34 (2.33–13.15) | 6.5 (1.96–12.02) | 6.11 (2.26–12.31) | 0.005 |
| Intraclass Correlation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | ICC * | 95% Lower CI | 95% Upper CI | p-Value |
| ICH (n = 100) | 0.997 | 0.996 | 0.998 | <0.001 |
| PHE (n = 100) | 0.980 | 0.971 | 0.987 | <0.001 |
| IVH (n = 100) | 0.995 | 0.992 | 0.996 | <0.001 |
| Interclass Correlation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | ICC * | 95% Lower CI | 95% Upper CI | p-Value |
| ICH (n = 100) | 0.998 | 0.993 | 0.997 | <0.001 |
| PHE (n = 100) | 0.886 | 0.760 | 0.938 | <0.001 |
| IVH (n = 100) | 0.979 | 0.984 | 0.993 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vogt, E.; Vu, L.H.; Cao, H.; Speth, A.; Desser, D.; Schlunk, F.; Dell’Orco, A.; Nawabi, J. Multilesion Segmentations in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Reliability of ICH, IVH and PHE Masks. Tomography 2023, 9, 89-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010008
Vogt E, Vu LH, Cao H, Speth A, Desser D, Schlunk F, Dell’Orco A, Nawabi J. Multilesion Segmentations in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Reliability of ICH, IVH and PHE Masks. Tomography. 2023; 9(1):89-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010008
Chicago/Turabian StyleVogt, Estelle, Ly Huong Vu, Haoyin Cao, Anna Speth, Dmitriy Desser, Frieder Schlunk, Andrea Dell’Orco, and Jawed Nawabi. 2023. "Multilesion Segmentations in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Reliability of ICH, IVH and PHE Masks" Tomography 9, no. 1: 89-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010008
APA StyleVogt, E., Vu, L. H., Cao, H., Speth, A., Desser, D., Schlunk, F., Dell’Orco, A., & Nawabi, J. (2023). Multilesion Segmentations in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Reliability of ICH, IVH and PHE Masks. Tomography, 9(1), 89-97. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010008






