The Use of Earth Observation Data for Railway Infrastructure Monitoring—A Review
Abstract
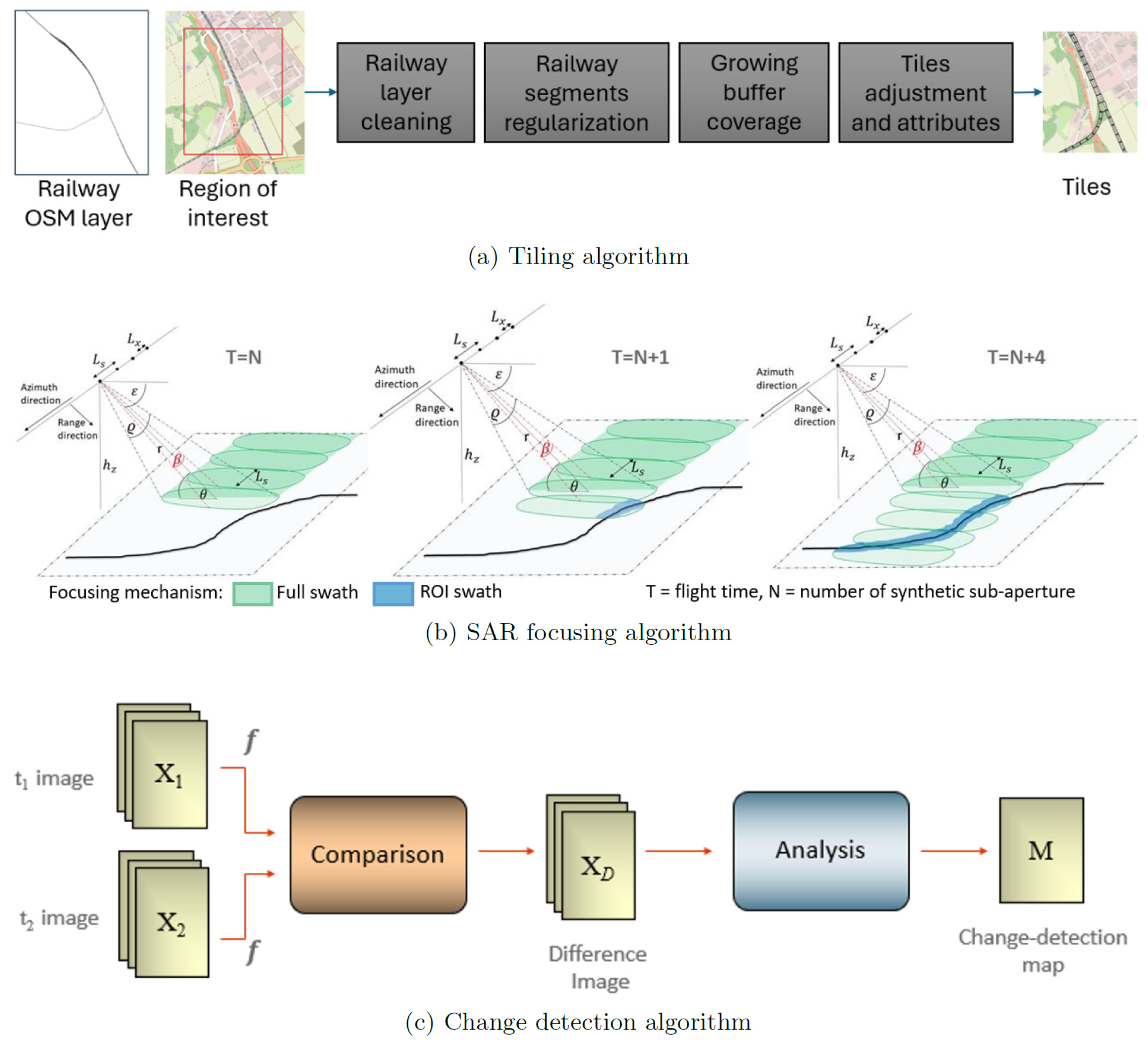
:1. Introduction
2. Railway Infrastructure Monitoring Use Cases and Satellite Data Potential
2.1. Monitoring of Rail Track Deformations (TD)
2.2. Monitoring of Ground Deformation (GD)
2.3. Monitoring of Railway Transition Zones (TZ)
2.4. Monitoring of Railway Bridges (B)
2.5. Monitoring of Vegetation Around the Rail Track (VG)
2.6. Monitoring of Water Level Around the Rail Track (WL)
3. EO-Based Railway Infrastructure Monitoring: Literature Review
3.1. Comparative Analysis of EO Data Use in Railway Infrastructure Monitoring
3.2. Limitations in the Existing EO-Based Methodologies, Datasets, and Technologies
3.3. Comparing Methods in Terms of Accuracy, Efficiency (Cost) and Scalability
3.4. Innovations: Proposals for Improvement in EO-Based Monitoring
4. Discussion and Outlook
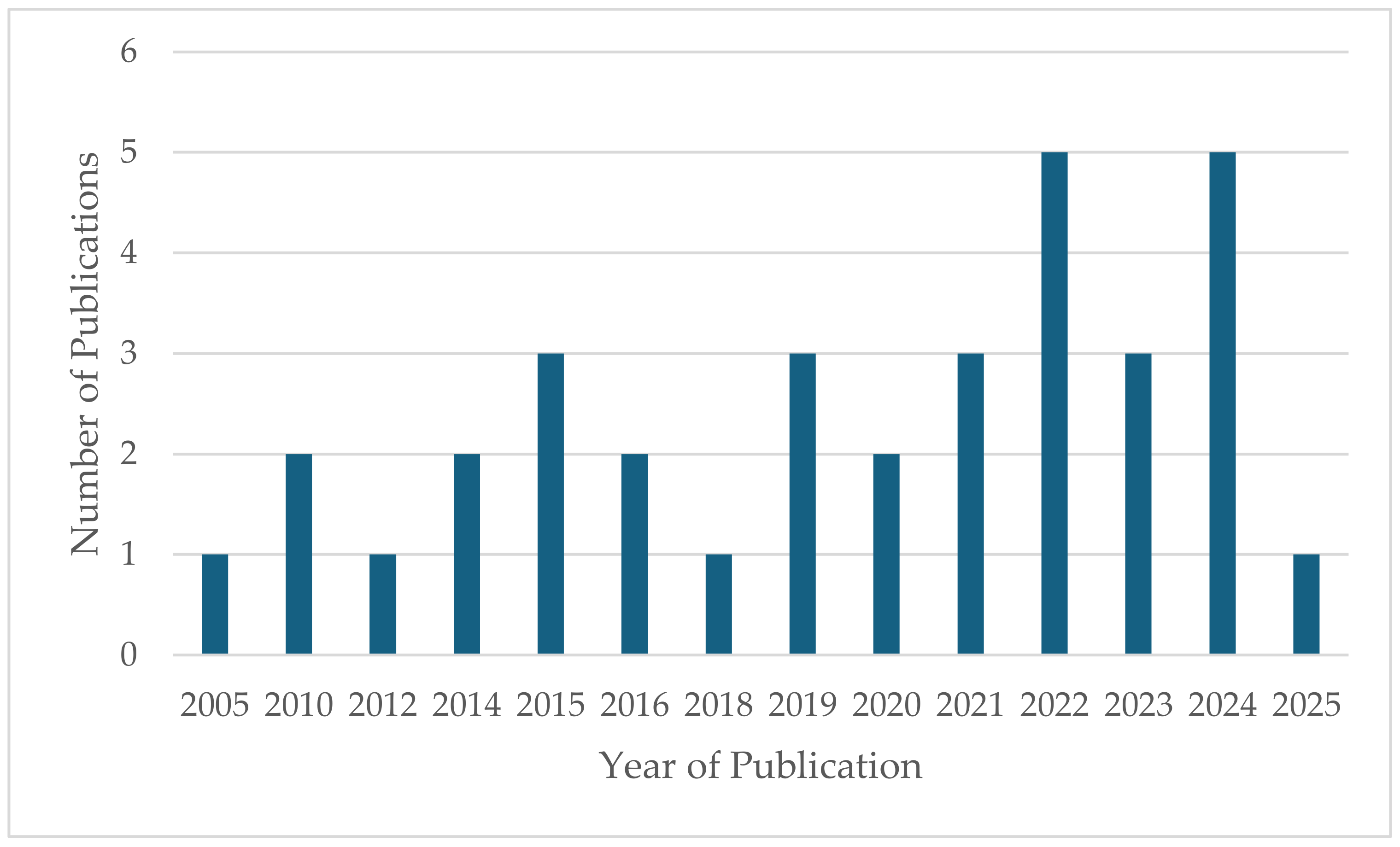
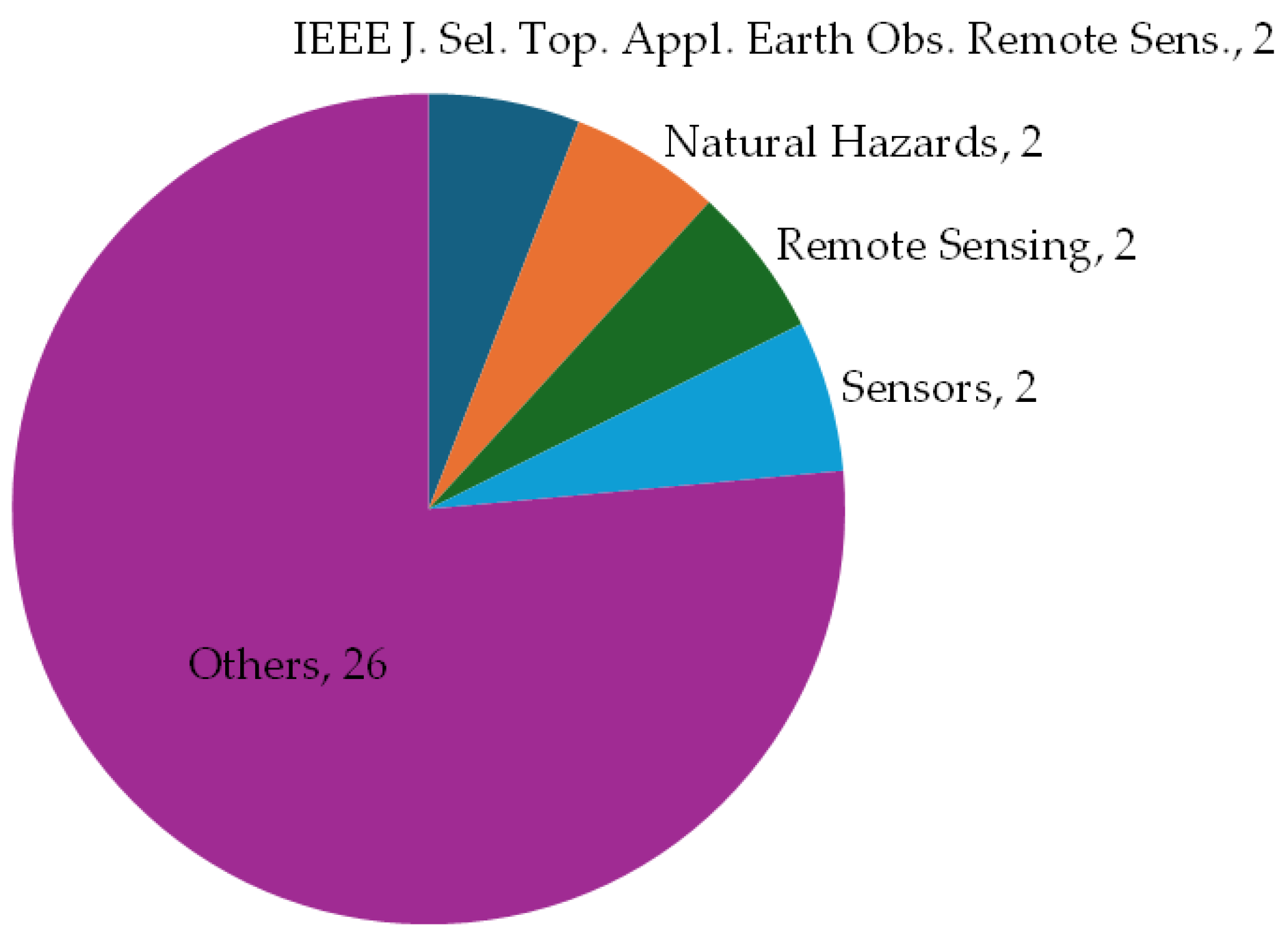
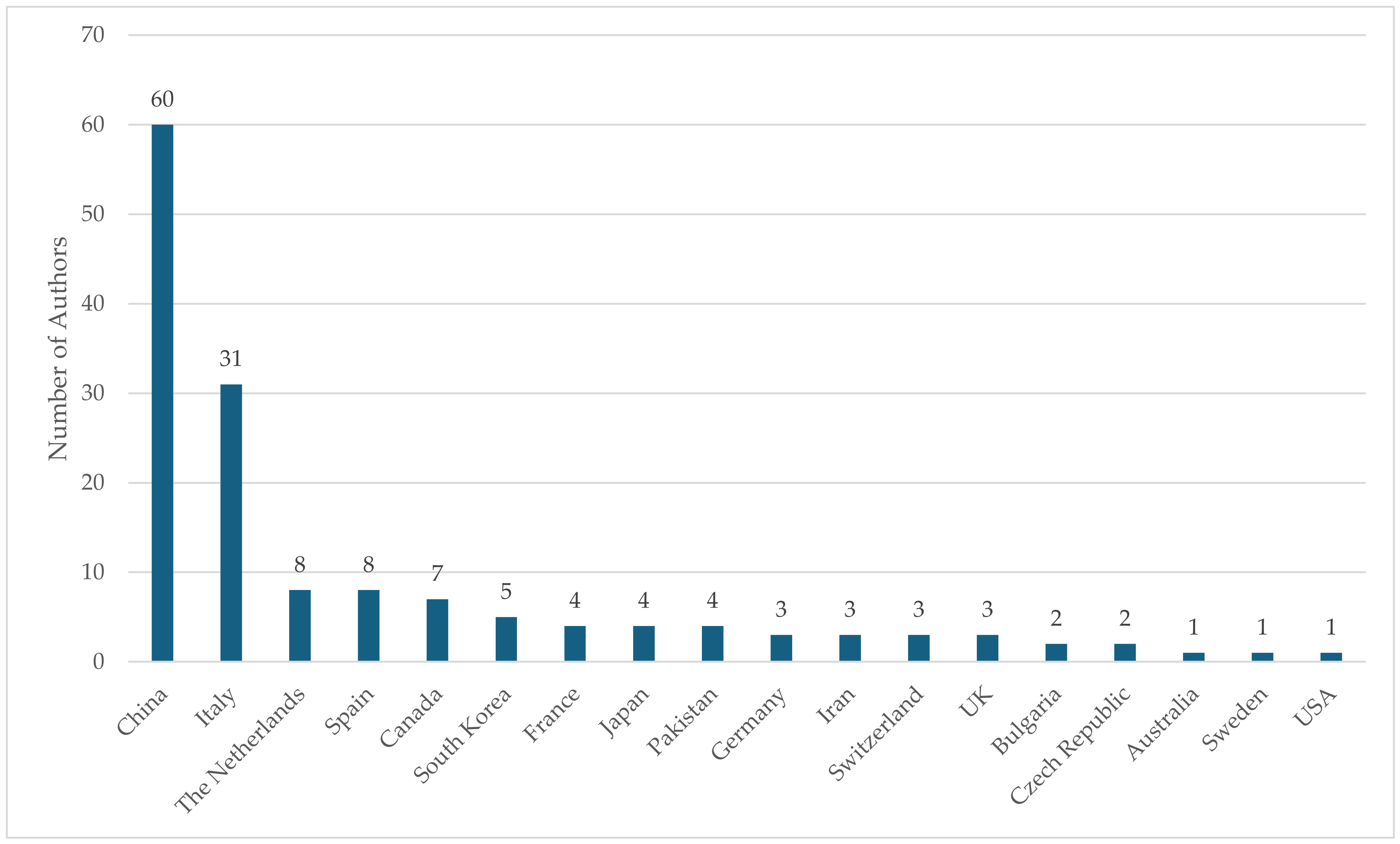
4.1. Meta-Analysis of Publications
4.2. Current Trends and Challenges in Satellite Data Utilization for Railway Monitoring
4.3. Future Directions
4.4. Technological Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ALOS | Advanced Land Observing Satellite |
| ASAR | Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| COTS | Commercial Off-The-Shelf |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| DInSAR | Differential Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| EO | Earth Observation |
| ESA | European Space Agency |
| GNSS | Global Navigation Satellite System |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| InSAR | Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| LiDAR | Light Detection and Ranging |
| LOS | Line of Sight |
| LST | Land Surface Temperature |
| MODIS | Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer |
| MSG | Meteosat Second Generation |
| MT-InSAR | Multi-Temporal Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| NDMI | Normalized Difference Moisture Index |
| NDVI | Normalized Difference Vegetation Index |
| PS-InSAR | Persistent Scatterer Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| PSI | Persistent Scatterer Interferometry |
| RCM | Radarsat Constellation Mission |
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| TZ | Transition Zones |
| UAS | Unmanned Aerial System |
| VTIR | Vegetation Threat Index for Railways |
References
- Kljaić, Z.; Pavković, D.; Cipek, M.; Trstenjak, M.; Mlinarić, T.J.; Nikšić, M. An overview of current challenges and emerging technologies to facilitate increased energy efficiency, safety, and sustainability of railway transport. Future Internet 2023, 15, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Summa, M.; Griseta, M.E.; Mosca, N.; Patruno, C.; Nitti, M.; Renò, V.; Stella, E. A review on deep learning techniques for railway infrastructure monitoring. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 114638–114661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezsias, L.; Brautigam, A.; Szurke, S.K.; Szalai, S.; Fischer, S. Sustainability in railways—A review. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2023, 107, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, G.; Fanelli, C.; Freddi, F.; Giuliani, F.; La Placa, A. Systematic review railway infrastructure monitoring: From classic techniques to predictive maintenance. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2025, 17, 16878132241285631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, A.; Ribeiro, D.; Malekjafarian, A.; Martínez-Rodrigo, M.D. Advances in Condition Monitoring of Railway Infrastructure. Sensors 2024, 24, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, G.; Goya, J.; Fernandez, N.; Arrizabalaga, S.; Mendizabal, J.; Adin, I. Map-Aided Software Enhancement for Autonomous GNSS Complementary Positioning System for Railway. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 11611–11620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marais, J.; Beugin, J.; Berbineau, M. A Survey of GNSS-Based Research and Developments for the European Railway Signaling. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transport. Syst. 2017, 18, 2602–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzan, M.; Ciszewski, T.; Nowakowski, W. Selected applications of satellite technologies in rail transport. AoT 2024, 71, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Project STARS: Satellite Technology for Advanced Rail Signalling. Available online: https://www.stars-rail.eu/wp-content/uploads/2016/04/STARS-leaflet_Final_WEB.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- EO & GNSS Market Report. Available online: https://www.euspa.europa.eu/publications-multimedia/publications/eo-gnss-market-report (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Piter, A.; Haghshenas Haghighi, M.; Motagh, M. Challenges and Opportunities of Sentinel-1 InSAR for Transport Infrastructure Monitoring. PFG 2024, 92, 609–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Killough, B.; Johnston, N. Insights from Earth Observation Data Can Optimise Rail Operation. Available online: https://www.ey.com/en_au/insights/space-tech/how-insights-from-earth-observation-data-can-optimise-rail-operations (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- Song, Y.; Wu, P. Earth Observation for Sustainable Infrastructure: A Review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, V.; Tosti, F.; Bianchini Ciampoli, L.; Battagliere, M.L.; D’Amato, L.; Alani, A.M.; Benedetto, A. Satellite Remote Sensing and Non-Destructive Testing Methods for Transport Infrastructure Monitoring: Advances, Challenges and Perspectives. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmi, W.; Bridgelall, R.; Askarzadeh, T. Remote Sensing and Machine Learning for Safer Railways: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo-Mora, J.; Kalacska, M.; Roghani, A.; Lucanus, O. Assessment of UAS Photogrammetry and Planet Imagery for Monitoring Water Levels around Railway Tracks. Drones 2023, 7, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roghani, A.; Mammeri, A.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Abdulrazagh, P.H.; Hendry, M.T.; Pulisci, R.M.; Canadian Rail Research, L. Using emerging technologies for monitoring surface water near railway tracks. In Proceedings of the Canadian & Cold Regions Rail Research Conference 2021 (CCRC 2021), Online, 9–10 November 2021; pp. 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Chang, L.; Markine, V. Structural Health Monitoring of Railway Transition Zones Using Satellite Radar Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusson, D.; Rossi, C.; Ozkan, I.F. Early warning system for the detection of unexpected bridge displacements from radar satellite data. J. Civ. Struct. Health Monit. 2021, 11, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasova-Zlatareva, M.; Nikolov, H. Establishing Surface Displacements along a Railway Route near Mirovo Salt Deposit, NE Bulgaria. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Geographical Information Systems Theory, Applications and Management, Online, 26–28 April 2022; pp. 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Bernhard, P.; Haener, D.; Frey, O. Detection of Railway Track Anomalies Using Interferometric Time Series of TerraSAR-X Satellite Radar Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 11750–11760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Dollevoet, R.; Hanssen, R.F. Railway Infrastructure Monitoring using Satellite Radar Data. Int. J. Railw. Technol. 2014, 3, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artagan, S.S.; Bianchini Ciampoli, L.; D’Amico, F.; Calvi, A.; Tosti, F. Non-destructive assessment and health monitoring of railway infrastructures. Surv. Geophys. 2020, 41, 447–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasi, D.; Philip, S.; David, R.; Swathi, J. A review on structural health monitoring of railroad track structures using fiber optic sensors. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, L.; Argentino, A.; Bernardini, L.; Radicioni, L.; Bono, F.M.; Somaschini, C.; Cazzulani, G.; Belloli, M. A three-year project on Structural Health Monitoring of railway bridges: Main results and lessons learnt. e-J. Nondestruct. Test. 2024, 29, 29796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Dollevoet, R.P.B.J.; Hanssen, R.F. Nationwide Railway Monitoring Using Satellite SAR Interferometry. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Sakpal, N.P.; Elberink, S.O.; Wang, H. Railway Infrastructure Classification and Instability Identification Using Sentinel-1 SAR and Laser Scanning Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machan, G.; Bennett, V.G. Use of inclinometers for geotechnical instrumentation on transportation projects: State of the practice. Transp. Res. Circ. 2008, E-C129, 01112776. [Google Scholar]
- Buzaboon, Y.; Aouad, M.; Mohamed, H. Structural Settlement Monitoring Using GPS and Conventional Terrestrial Surveying Methods. Appl. Math. 2024, 18, 909–914. [Google Scholar]
- Palic, S.S.; Stipanovic, I.; Gavin, K. D1.1: Report on Global Safety KPIs. Available online: https://projects.shift2rail.org/s2r_ipcc_n.aspx?p=GOSAFE_RAIL (accessed on 28 February 2025).
- Rizzo, P.; Enshaeian, A. Challenges in bridge health monitoring: A review. Sensors 2021, 21, 4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, C.; Shi, A.; Chen, Y. Deformation monitoring of long-span railway bridges based on SBAS-InSAR technology. Geod. Geodyn. 2024, 15, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinard, S.A.; Riant, J.-P.; Michelin, J.-C.; Costa D’Aguiar, S. Fast Weakly Supervised Detection of Railway-Related Infrastructures in Lidar Acquisitions. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 2, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kučera, M.; Dobesova, Z. Analysis of the Degree of Threat to Railway Infrastructure by Falling Tree Vegetation. IJGI 2021, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onody, A.-S.; Bah, F.; Boum, M.-A.; Duval, G. Use of satellite imagery to categorize vegetation on the French railway network (SNCF Réseau). Transp. Res. Procedia 2023, 72, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruvo, P.; De Ruvo, G.; Distante, A.; Nitti, M.; Stella, E.; Marino, F. A visual inspection system for rail detection &; tracking in real time railway maintenance. Open Cybern. Syst. J. 2008, 2, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Transportation Association. Rail Transit Track Inspection and Maintenance; APTA: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Gong, H.; Chen, Y.; Lei, K.; Zhou, C.; Si, Y.; Li, X.; Pan, Y.; Gao, M. Investigating land subsidence and its causes along Beijing high-speed railway using multi-platform InSAR and a maximum entropy model. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 96, 102284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, A.; Hostert, P.; Schiefer, S. Investigating urban railway corridors with geometric high resolution satellite data. Urban Remote Sens. 2005, 5. Available online: https://www.ugpti.org/smartse/research/citations/downloads/Damm-Urban_Railway_Monitoring-2005.pdf (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Hu, F.; Leijen, F.J.V.; Chang, L.; Wu, J.; Hanssen, R.F. Monitoring Deformation along Railway Systems Combining Multi-Temporal InSAR and LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galve, J.P.; Castañeda, C.; Gutiérrez, F. Railway deformation detected by DInSAR over active sinkholes in the Ebro Valley evaporite karst, Spain. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 2439–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geshi, S. Disaster Damage Detection and Its Recovery Support System of Road and Railroad Using Satellite Images. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, XXXVIII, 314–319. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.-K.; Kim, W.; Lee, C.; Yoo, M.; Lee, I. Validating Railway Infrastructure Deformation Monitoring: A Comparative Analysis of Field Data and TerraSAR-X PS-InSAR Results. KSCE J. Civ. Civil Eng. 2024, 28, 1777–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pigorini, A.; Ricci, M.; Sciotti, A.; Giannico, C.; Tamburini, A. Satellite remote-sensing PSInSAR™ technique applied to design and construction of railway infrastructures. IF 2010, 65, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Polcari, M. Anthropogenic subsidence along railway and road infrastructures in Northern Italy highlighted by Cosmo-SkyMed satellite data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2019, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Chou, X.; Xiao, X. Analysis of Railway Subgrade Settlement Deformation in Permafrost Regions Based on Satellite Interferometry. Sens. Transducers 2014, 168, 260–267. [Google Scholar]
- Javed, A.; Qazi, K.A.; Maqsood, M.; Shah, K.A. Efficient algorithm for railway tracks detection using satellite imagery. Int. J. Image Graph. Signal Process. 2012, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeli, E.; Iacobini, F.; Mungiello, I.; Cadavero, G.; D’Avino, D.; Tavano, F.; Agostino, I.; Meuti, S. Supervision of Railway Areas by Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the IRSC 2022 International Railway Safety Council, Sevilla, Spain, 16–21 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, L.; Hanssen, R.F. Detection of permafrost sensitivity of the Qinghai–Tibet railway using satellite radar interferometry. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Liu, B.; Xie, B.; Xiao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Shi, F. Study on InSAR deformation information extraction and stress state assessment in a railway tunnel in a plateau area. Front. Earth Sci. 2024, 12, 1367978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Liu, H.; Miao, C.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Safety assessment of the Qinghai–Tibet railway: Monitoring, analysis, and prediction. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2025, 231, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Hong, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, P.; Jin, Y.; Xie, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Feng, T. Detection of geometric change in railway curves caused by earthquakes, using high-resolution stereo satellite images. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 409–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini Ciampoli, L.; Gagliardi, V.; Clementini, C.; Latini, D.; Del Frate, F.; Benedetto, A. Transport infrastructure monitoring by InSAR and GPR data fusion. Surv. Geophys. 2020, 41, 371–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Yan, K.; Zhang, F.; Yang, S.; Yang, J. Monitoring environment transformation along the BTIC railway based on remote sensing by utilizing the R_RSEI. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2022, 88, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wei, B.; Ma, J.; Qin, J.; Luo, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, C. Monitoring and analysis of side-slope deformation along Changgan high-speed railway based on time-series InSAR and BDS techniques. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 13469–13491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosti, F.; Gagliardi, V.; D’Amico, F.; Alani, A.M. Transport infrastructure monitoring by data fusion of GPR and SAR imagery information. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 45, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassie, Y.; Gao, Q.; Monserrat, O.; Barra, A.; Crippa, B.; Crosetto, M. Differential SAR interferometry for the monitoring of land subsidence along railway infrastructures. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 43, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shami, S.; Azar, M.K.; Nilfouroushan, F.; Salimi, M.; Reshadi, M.A.M. Assessments of ground subsidence along the railway in the Kashan plain, Iran, using Sentinel-1 data and NSBAS algorithm. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poreh, D.; Iodice, A.; Riccio, D.; Ruello, G. Railways’ stability observed in Campania (Italy) by InSAR data. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 49, 417–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dindar, S.; Kaewunruen, S.; Osman, M.H. Review on Feasibility of using satellite imaging for risk management of derailment related turnout component failures. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 245, 042025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashov, S.I.; Tataraidze, A.B.; Razevig, V.V.; Smirnova, E.S. Railway transport infrastructure monitoring by UAVs and satellites. J. Transp. Technol. 2019, 9, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Project SPATRA. Available online: https://spatra-project.eu/ (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- Cheng, G.; Han, J.; Lu, X. Remote sensing image scene classification: Benchmark and state of the art. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 1865–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Qian, Y.; Zhong, X.; Chen, L.; Yang, G. Research on super-resolution reconstruction of remote sensing images: A comprehensive review. Opt. Eng. 2021, 60, 100901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alosaimi, N.; Alhichri, H.; Bazi, Y.; Ben Youssef, B.; Alajlan, N. Self-supervised learning for remote sensing scene classification under the few shot scenario. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumuni, A.; Mumuni, F.; Kobina Gerrar, N. A survey of synthetic data augmentation methods in computer vision. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.10075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vina, A. Active Learning Speeds Up Computer Vision Development. Available online: https://www.ultralytics.com/blog/active-learning-speeds-up-computer-vision-development?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Xu, A.; Vasileva, M.I.; Dave, A.; Seshadri, A. HandsOff: Labeled Dataset Generation With No Additional Human Annotations. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.12645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Ma, X.; Qu, F.; Wang, J.; Liang, T.; Chen, D. Research on SAR image denoising method based on feature extraction. Electron. Lett. 2024, 60, e13180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, M.; Palm, S.; Bovolo, F. Instantaneous infrastructure monitoring by Earth observation: SAR-based railway obstacle detection. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXX, Edinburgh, UK, 16–19 September 2024; p. 38. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Jeong, J. Speckle Noise Reduction Technique for SAR Images Using Statistical Characteristics of Speckle Noise and Discrete Wavelet Transform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, Z.; Ma, X.; Yang, Z. SAR Image Despeckling Based on Block-Matching and Noise-Referenced Deep Learning Method. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Albrecht, C.M.; Braham, N.A.A.; Mou, L.; Zhu, X.X. Self-supervised learning in remote sensing: A review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2022, 10, 213–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Peng, Q.; Liu, R.; Liu, L.; Bai, L. Track grid health index for grid-based, data-driven railway track health evaluation. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1687814019889768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Ma, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, L. Self-Supervised Representation Learning for Remote Sensing Image Change Detection Based on Temporal Prediction. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarzadeh, A.; Soleimani, H. Self-supervised in-domain representation learning for remote sensing image scene classification. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chen, L.; Deng, Z.; Xu, P.; Yan, Q.; Choi, K.-S.; Wang, S. Deep image feature learning with fuzzy rules. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.10575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbado, A.; Corcho, Ó.; Benjamins, R. Rule extraction in unsupervised anomaly detection for model explainability: Application to OneClass SVM. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 189, 116100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, C.; Bianchini Ciampoli, L.; Benedetto, A.; Alani, A.M.; Tosti, F. Non-destructive technologies for sustainable assessment and monitoring of railway infrastructure: A focus on GPR and InSAR methods. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, S.; Hudak, A.; Uebler, E.; Falkowski, M.; Megown, K. A comparison of accuracy and cost of LiDAR versus stand exam data for landscape management on the Malheur National Forest. J. For. 2011, 109, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.-Y. Segment anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 4015–4026. [Google Scholar]
- LiveEO. Available online: https://www.live-eo.com/ (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- Project IIMEO. Available online: https://ohb-theo.de/iimeo-project/ (accessed on 2 February 2025).
- Fischer, S.; Harangozó, D.; Németh, D.; Kocsis, B.; Sysyn, M.; Kurhan, D.; Brautigam, A. Investigation of Heat-Affected Zones of Thermite Rail Weldings. FU Mech. Eng. 2024, 22, 689–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristic-Durrant, D.; Klapper, A.; Kuhn, D.; Banić, M.; Madić, M.; Simonović, M.; Trifunović, M.; Trajković, A. Novel use of EO satellite data and AI in railways: A concept for rail buckling risk estimation in the SPATRA Project. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on “Artificial Intelligence for RAILwayS” co-located with EDCC 2025, Lisbon, Portugal, 8 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Fiore, N.; Bruno, S.; Del Serrone, G.; Iacobini, F.; Giorgi, G.; Rinaldi, A.; Moretti, L.; Duranti, G.M.; Peluso, P.; Vita, L.; et al. Experimental Analysis of Hot-Mix Asphalt (HMA) Mixtures with Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP) in Railway Sub-Ballast. Materials 2023, 16, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Serrone, G.; Riccio, G.; Moretti, L. Cradle-to-cradle life cycle assessment of railway prestressed concrete sleepers: A state-of-the-art review and strategies for reducing environmental impacts. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 214, 108020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Serrone, G.; Loprencipe, G.; Riccio, G.; Moretti, L. Analisi “dalla culla al cancello con opzioni” di traverse ferroviarie in calcestruzzo. IF 2024, 79, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantisani, G.; Del Serrone, G.; Mauro, R.; Peluso, P.; Pompigna, A. From Radar Sensor to Floating Car Data: Evaluating Speed Distribution Heterogeneity on Rural Road Segments Using Non-Parametric Similarity Measures. Sci 2024, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ézsiás, L.; Tompa, R.; Fischer, S. Investigation of the Possible Correlations between Specific Characteristics of Crushed Stone Aggregates. Spec. Mech. Eng. Oper. Res. 2024, 1, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S. Investigation of the Settlement Behavior of Ballasted Railway Tracks Due to Dynamic Loading. Spec. Mech. Eng. Oper. Res. 2025, 2, 24–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.; Kocsis Szürke, S. Detection Process of Energy Loss in Electric Railway Vehicles. FU Mech. Eng. 2023, 21, 081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
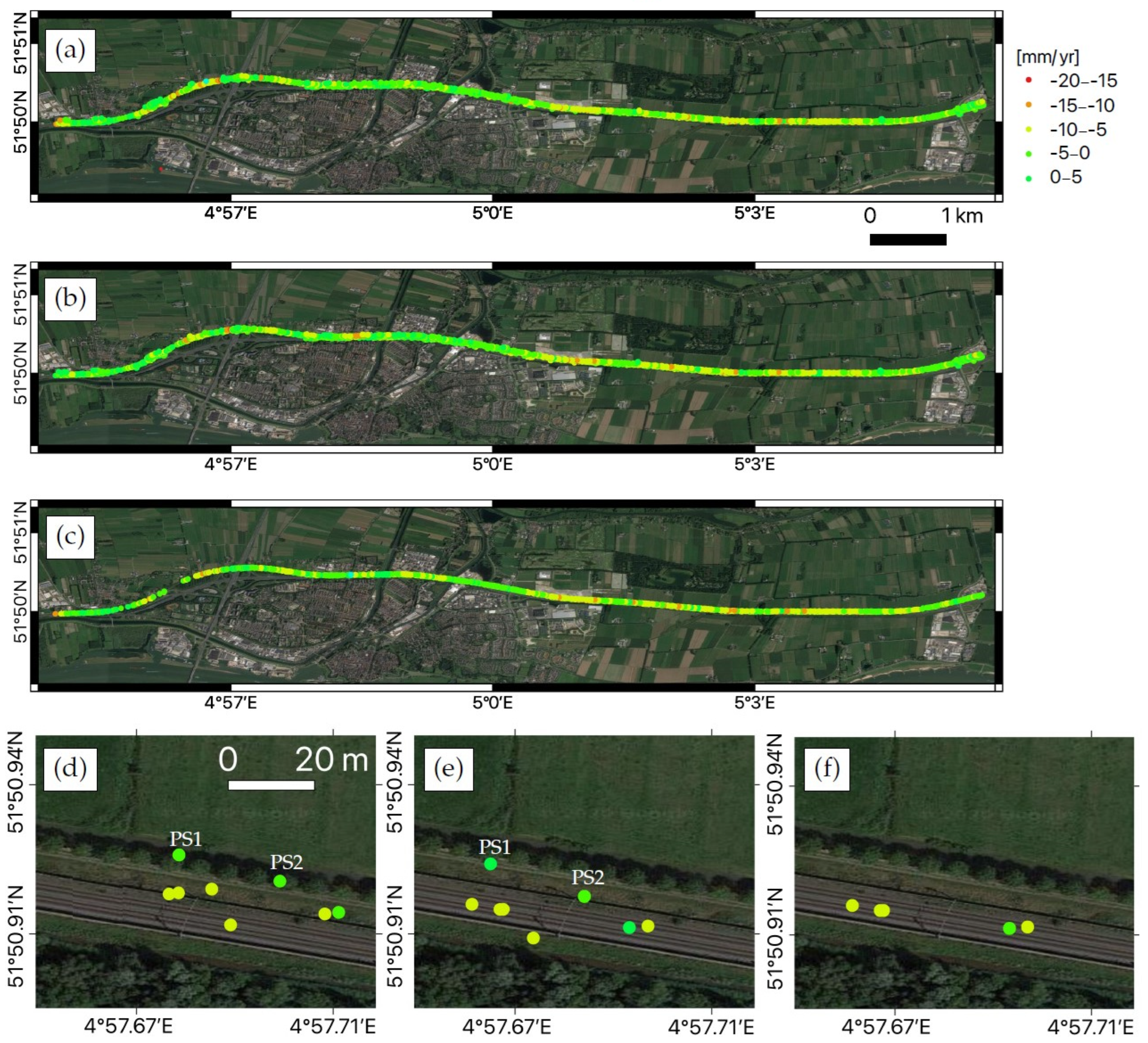


| Paper | Application | Used Satellite Data SAR/ Optical (O) | Used Satellites | Evaluation/Validation Tests | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Evaluation (E)/Testing (T)/Validation (V) | Comments | ||||
| [16] | WL | O | PlanetScope Dove | E | Railway line between the cities of Ottawa and Brockville, ON, Canada |
| [20] | GD | SAR | Sentinel-1 | E and T | Railway line passing through Provadia town, Bulgaria |
| [21] | GD | SAR | TerraSAR-X | E, T, and V | Approximately 50 km of railway tracks of the Swiss Federal Railways network in Northern Switzerland |
| [22] | TD TZ | SAR | TerraSAR-X | E, T, and V | Part of the Betuweroute (double-track freight railway) close to Rotterdam, the Netherlands |
| [26] | TD | SAR | Radarsat-2 | E | Entire railway network of the Netherlands |
| [27] | TD | SAR | Sentinel-1 | E and T | Betuwe freight train track, the Netherlands |
| [38] | GD | SAR | ENVISAT/ASAR, TerraSAR-X | E and T | Beijing–Tianjin High-Speed Railway, China |
| [19] | B | SAR | Radarsat-2/Sentinel-1 | E, T, andV | Bridges that link the cities of Montreal and Longueuil and the cities of Montreal and Saint-Lambert, QC, Canada |
| [39] | VG | O | QuickBird | E and T | Railway area in the Southeast of Berlin, Germany |
| [40] | TD GD | SAR | Radarsat-2 | E | Zaltbommel, the Netherlands |
| [41] | GD | SAR | ENVISAT/ALOS SAR missions | E | Castejón–Zaragoza conventional railway line, Spain |
| [42] | GD | O | SPOT | E | Ojiya city, Nagaoka city, Kawaguchi town, Horinouchi town, and Yamakoshi village, Japan |
| [43] | TD | SAR | TerraSAR-X | E, T, and V | South Korea |
| [34] | VG | O | Sentinel-2, LANDSAT-7 | E | Liberec Region, Czech Republic |
| [35] | VG | O | Pleiades | E and T | Different railway lines in France |
| [44] | GD | SAR | RADARSAT-1, ESA ERS-1, ESA ERS-2 | E and T | The Cassia–Monte Mario tunnel in Rome, the High-Speed/High-Capacity Bologna Node tunnel, the Scianina–Tracoccia tunnel, the preliminary design of the new Venice–Trieste railway line, Italy |
| [45] | GD | SAR | Cosmo-SkyMed | E and T | Several railways in Lombardia region, in the proximity of Milano city and between Lecco and Como cities, Northern Italy |
| [46] | GD B | SAR | ENVISAT/ASAR | E | Beiluhe test site of the Qinghai–Tibet railway, China |
| [18] | TZ | SAR | TerraSAR-X | E and T | Moerdijk, the Netherlands |
| [47] | TD | O | Google Maps | E | - |
| [48] | VG GD WL | SAR O | Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, LANDSAT-8, COSMO-SkyMed, PlanetScope | E | - |
| [49] | GD | SAR | ENVISAT SAR | E and T | Qinghai–Tibet railway, China |
| [50] | TZ | SAR | Sentinel-1 | E and T | Dongelu tunnel of the China–Tibet railway |
| [51] | TD | SAR | Sentinel-1 | E and T | Qinghai–Tibet railway, China |
| [52] | TD GD | O | IKONOS | E and T | pre- and post-seismic railway curves in Dujiangyan City, China |
| [32] | B | SAR | Sentinel-1A | E and T | Ganjiang Super Bridge, China |
| [14] | B | SAR | COSMO-SkyMed | E and T | Rochester Bridge, UK |
| [53] | GD | SAR | Sentinel-1A, COSMO-SkyMed | E and T | Foggia, Italy |
| [54] | VG | O | LANDSAT-7, LANDSAT-8 | E and T | Beijing–Tianjin intercity high-speed railway, China |
| [55] | TZ GD | SAR | Sentinel-1A | E and T | Changgan high-speed railway, China |
| [56] | GD | SAR | Sentinel-1A, COSMO-SkyMed | E and T | Puglia, Italy |
| [57] | GD | SAR | Sentinel-1 | E and T | Railway segment in Barcelona, Spain |
| [58] | GD | SAR | Sentinel-1 | E, T, and V | Qom–Kashan railway, Iran |
| [59] | B | SAR | Cosmo-SkyMed | E and T | Railway bridge over the Volturno river at Triflisco (Campania, Italy) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Banic, M.; Ristic-Durrant, D.; Madic, M.; Klapper, A.; Trifunovic, M.; Simonovic, M.; Fischer, S. The Use of Earth Observation Data for Railway Infrastructure Monitoring—A Review. Infrastructures 2025, 10, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10030066
Banic M, Ristic-Durrant D, Madic M, Klapper A, Trifunovic M, Simonovic M, Fischer S. The Use of Earth Observation Data for Railway Infrastructure Monitoring—A Review. Infrastructures. 2025; 10(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleBanic, Milan, Danijela Ristic-Durrant, Milos Madic, Alina Klapper, Milan Trifunovic, Milos Simonovic, and Szabolcs Fischer. 2025. "The Use of Earth Observation Data for Railway Infrastructure Monitoring—A Review" Infrastructures 10, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10030066
APA StyleBanic, M., Ristic-Durrant, D., Madic, M., Klapper, A., Trifunovic, M., Simonovic, M., & Fischer, S. (2025). The Use of Earth Observation Data for Railway Infrastructure Monitoring—A Review. Infrastructures, 10(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures10030066










