A Bayesian Pipe Failure Prediction for Optimizing Pipe Renewal Time in Water Distribution Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Study Area and Data Sources
3.2. Counting Process
- N(t) ≥ 0.
- N(t) is an integer value.
- If s < t, then N(s) ≤ N(t).
- For s < t, [N(t)−N(s)] is the number of previous events in the interval (s, t).
3.3. Poisson Process
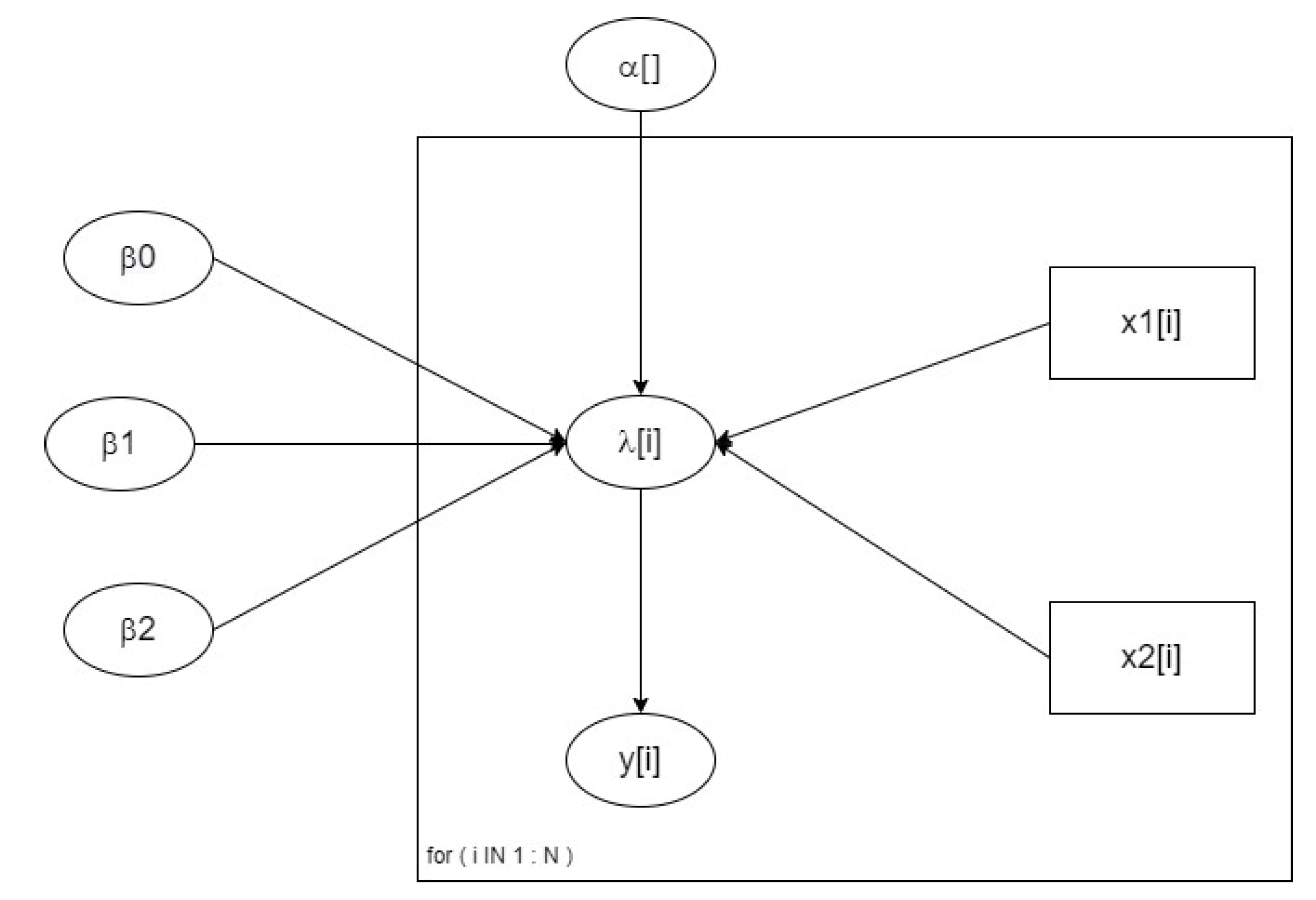
3.4. Bayesian Inference
3.5. Maximum Likelihood Estimation
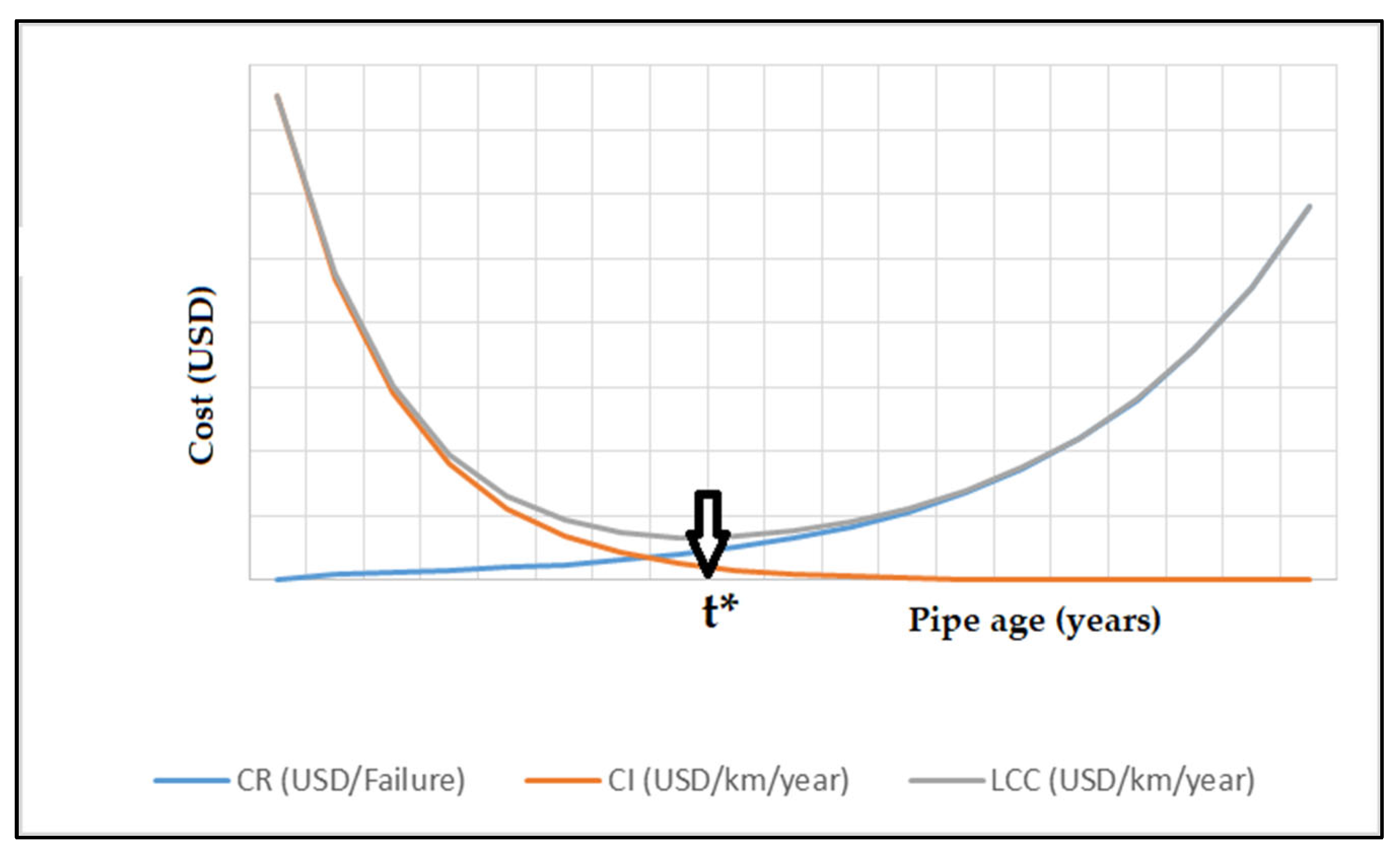
3.6. Life-Cycle Cost (LCC)
4. Results and Discussion
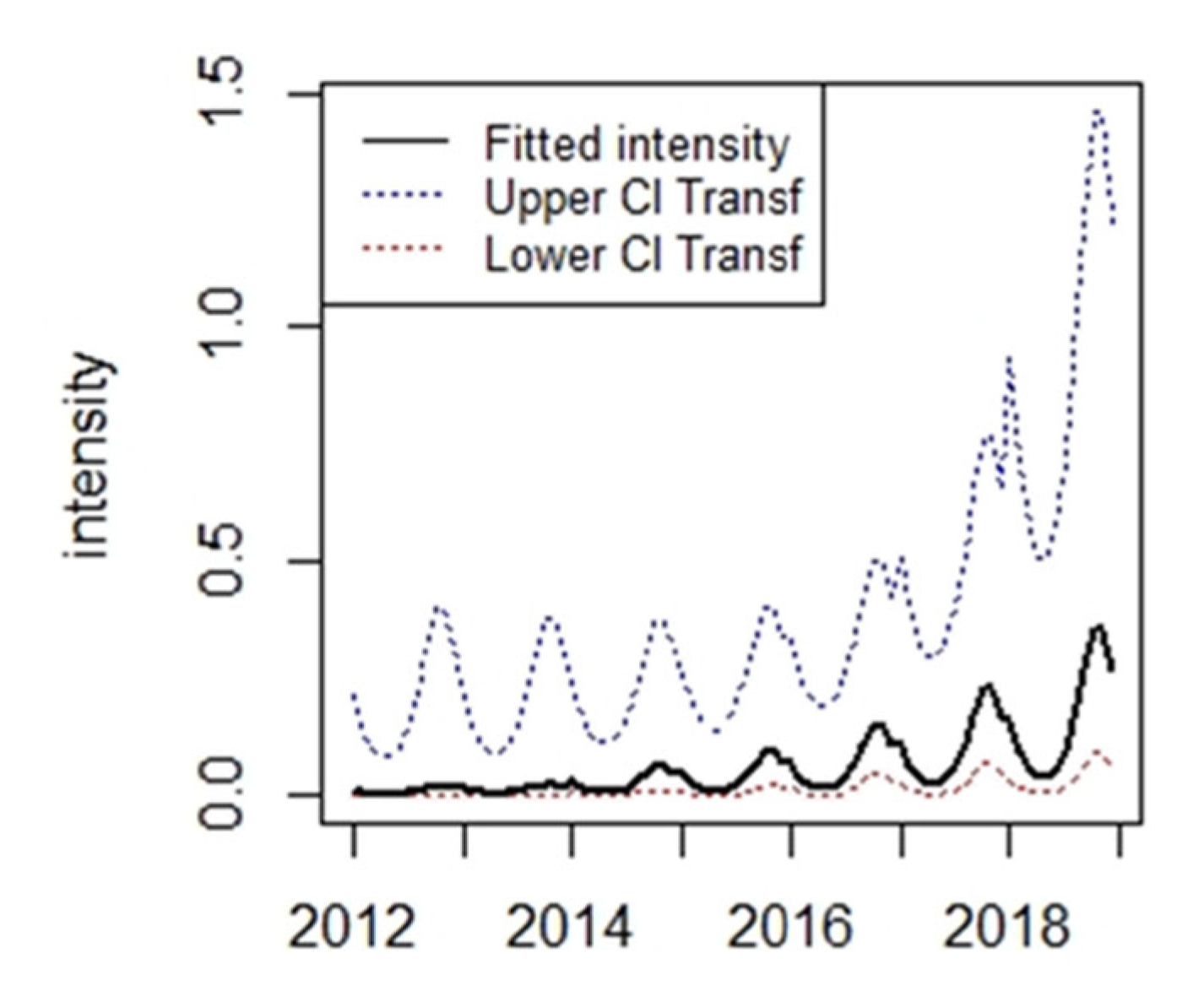
4.1. Pipe Failure Intensity
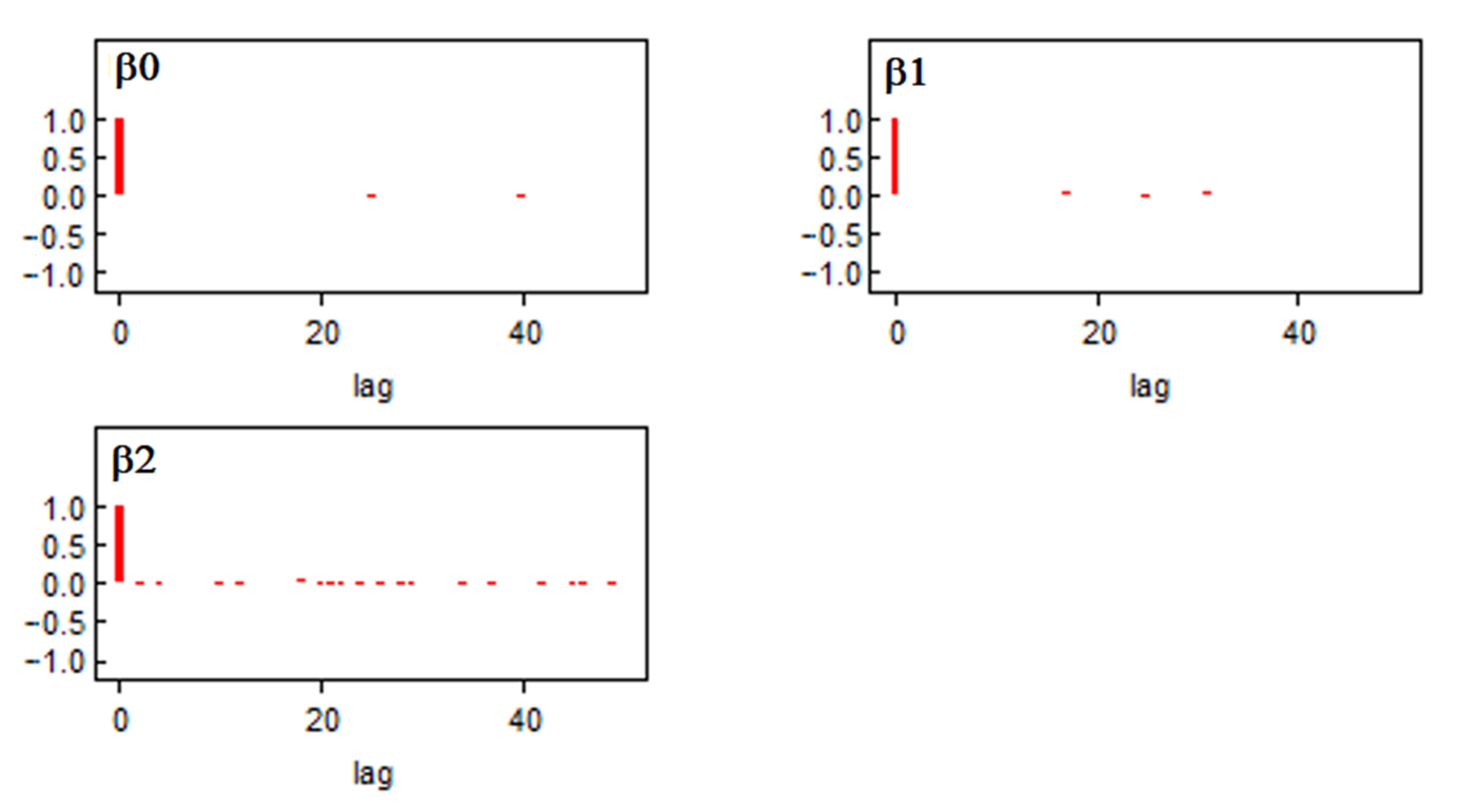
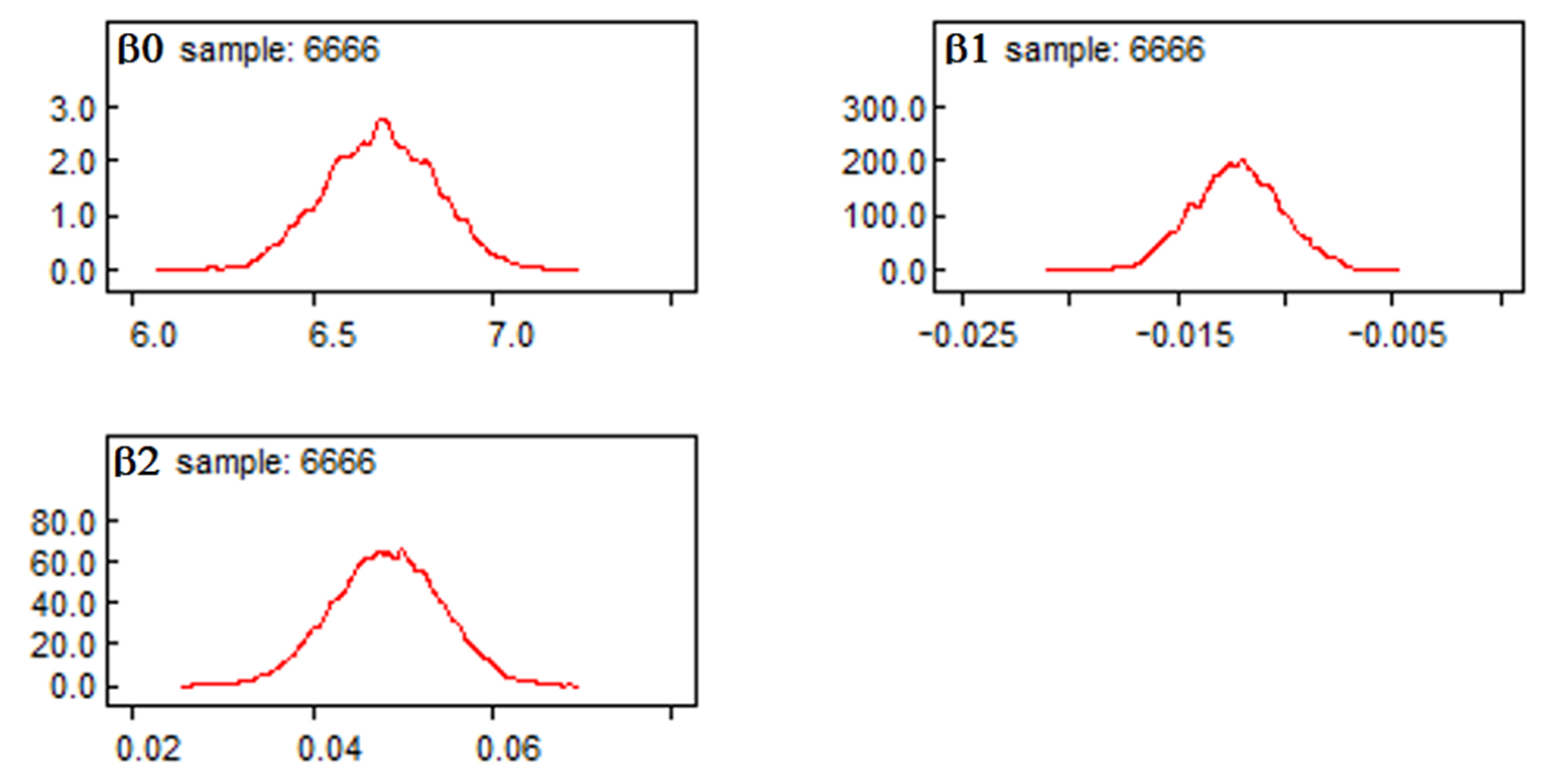
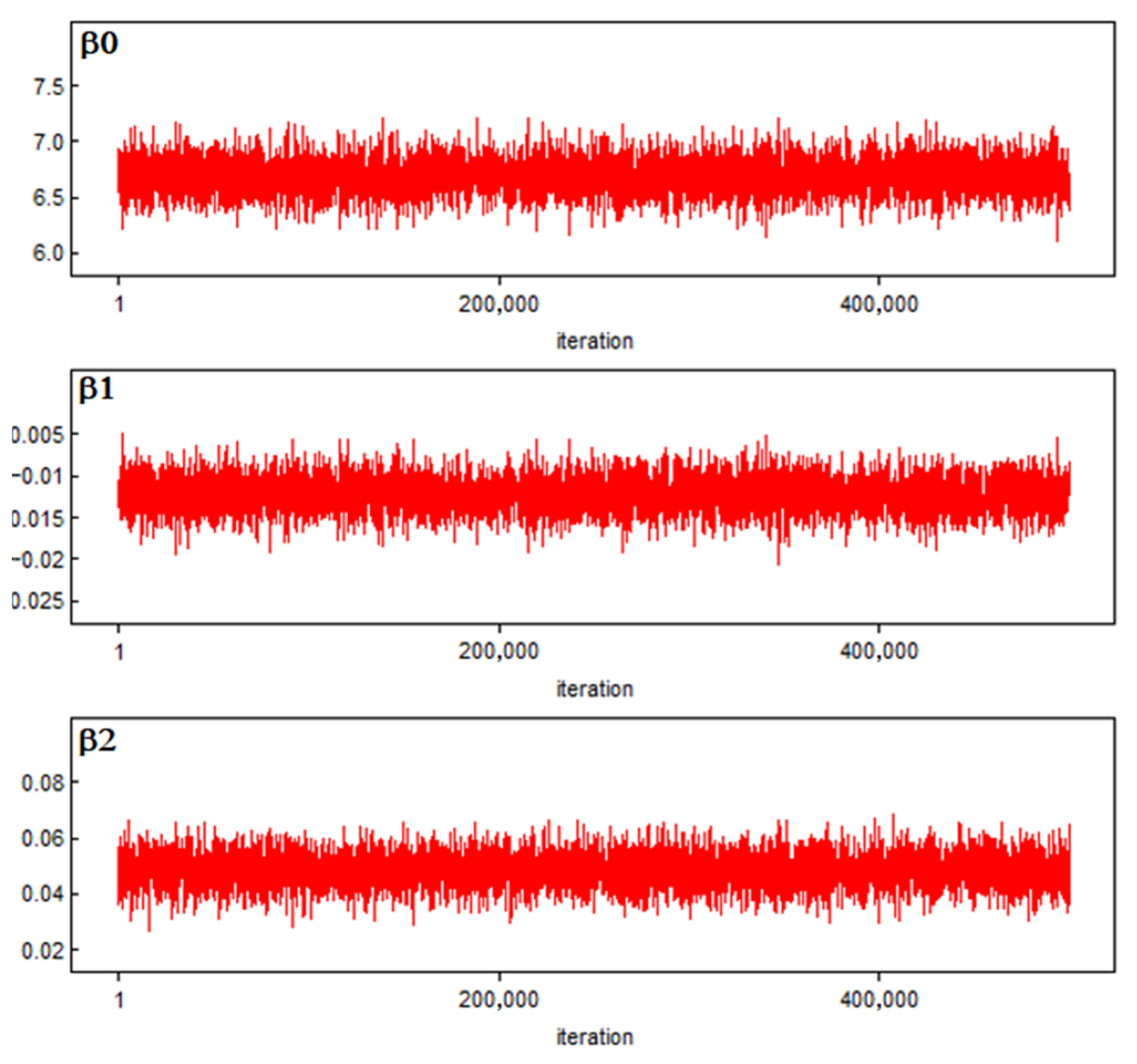
4.2. Parameter Estimation of Bayesian Inference
4.3. Parameter Estimation of Frequentist Inference
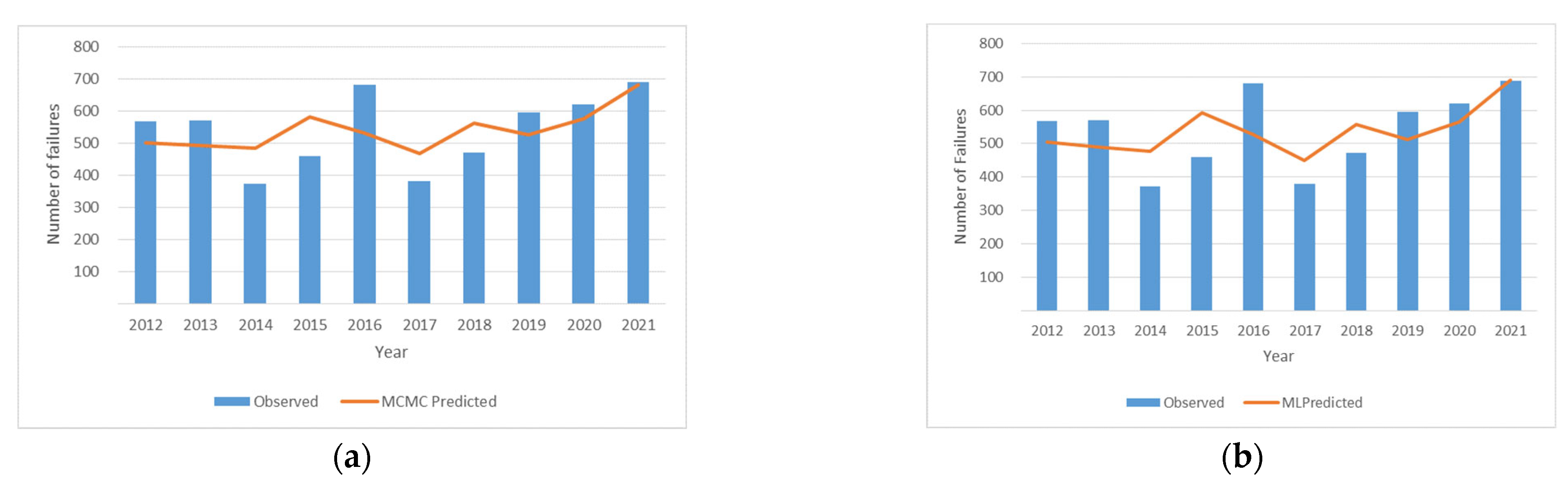
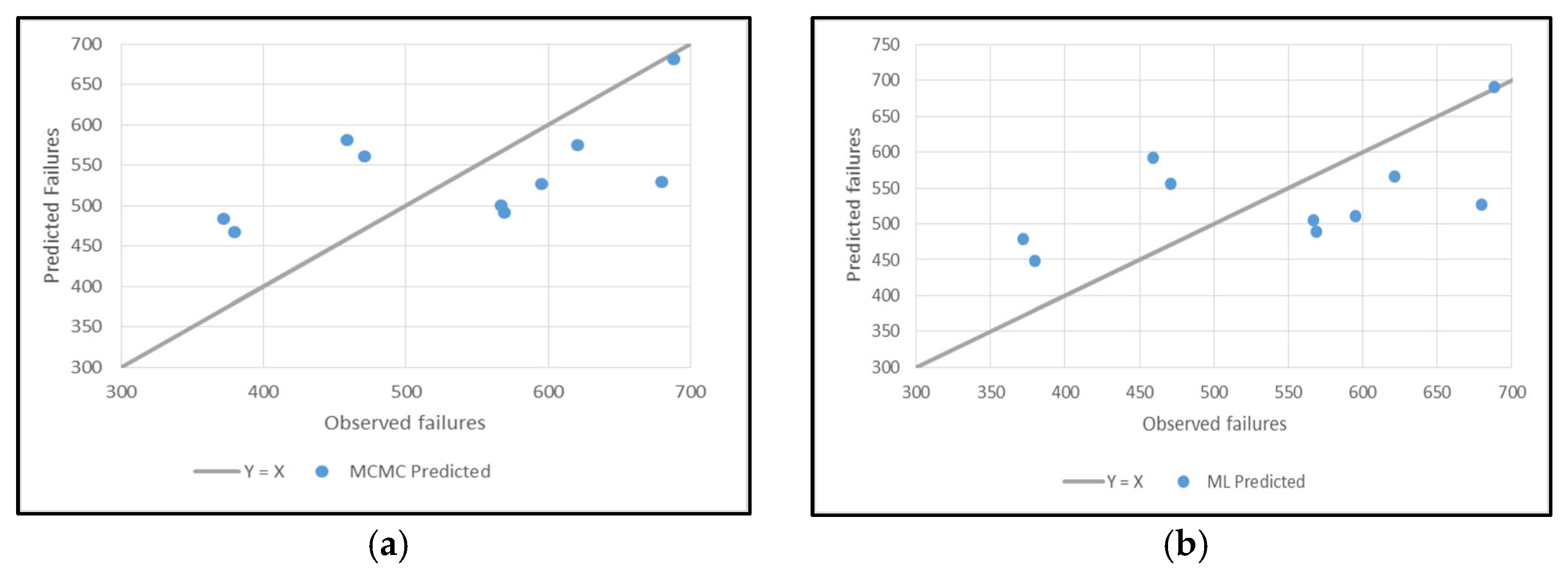
4.4. Pipe Failure Analysis
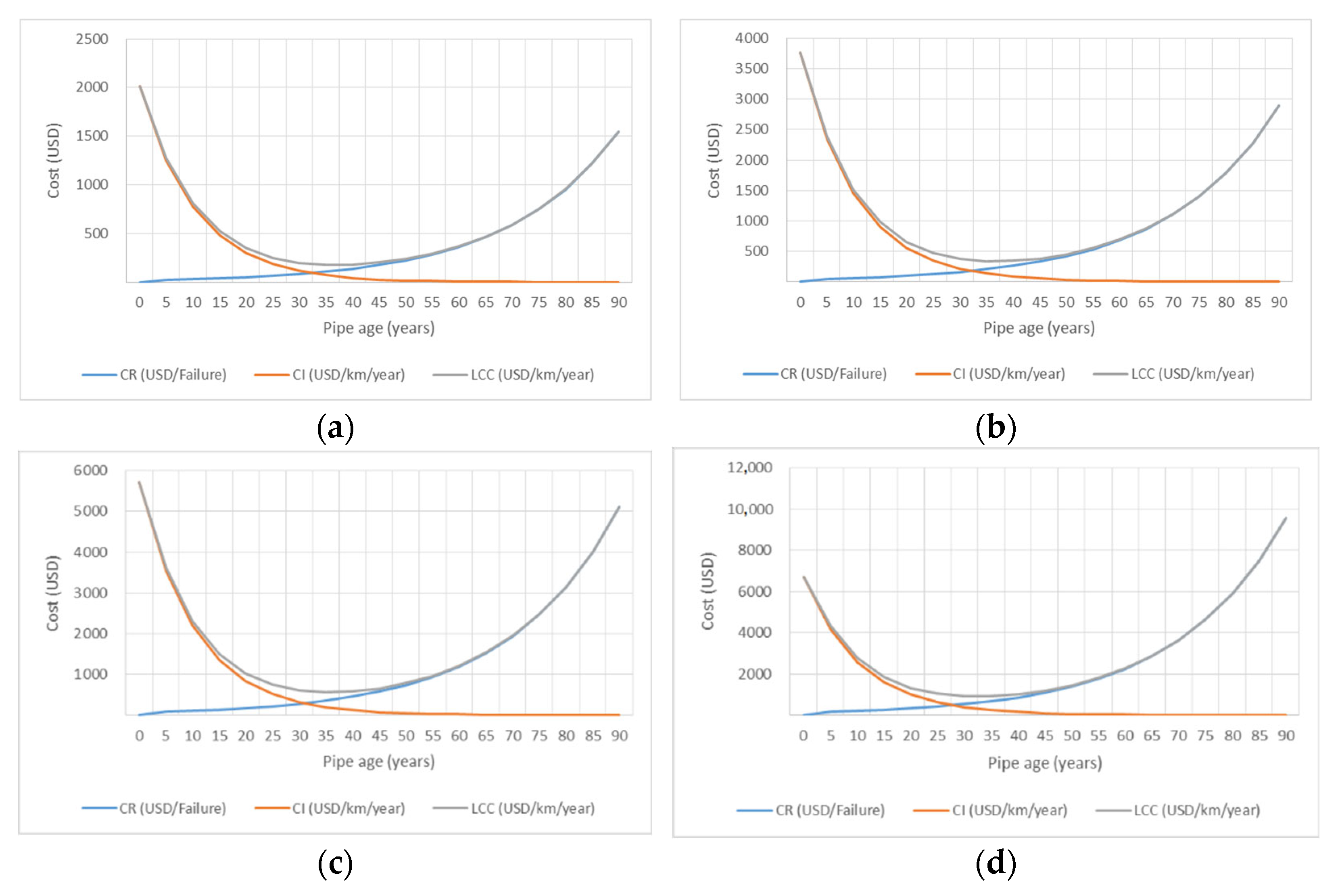
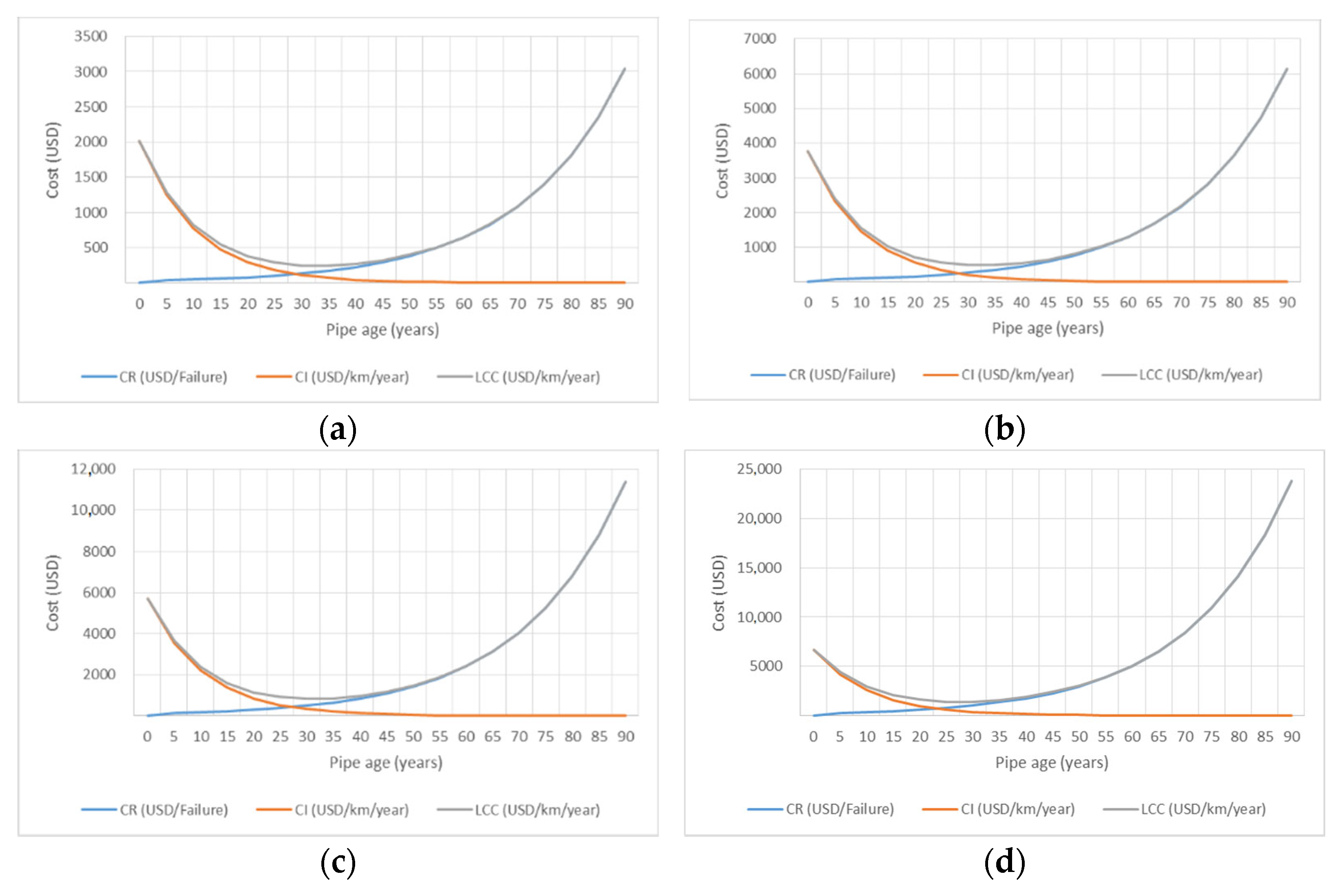
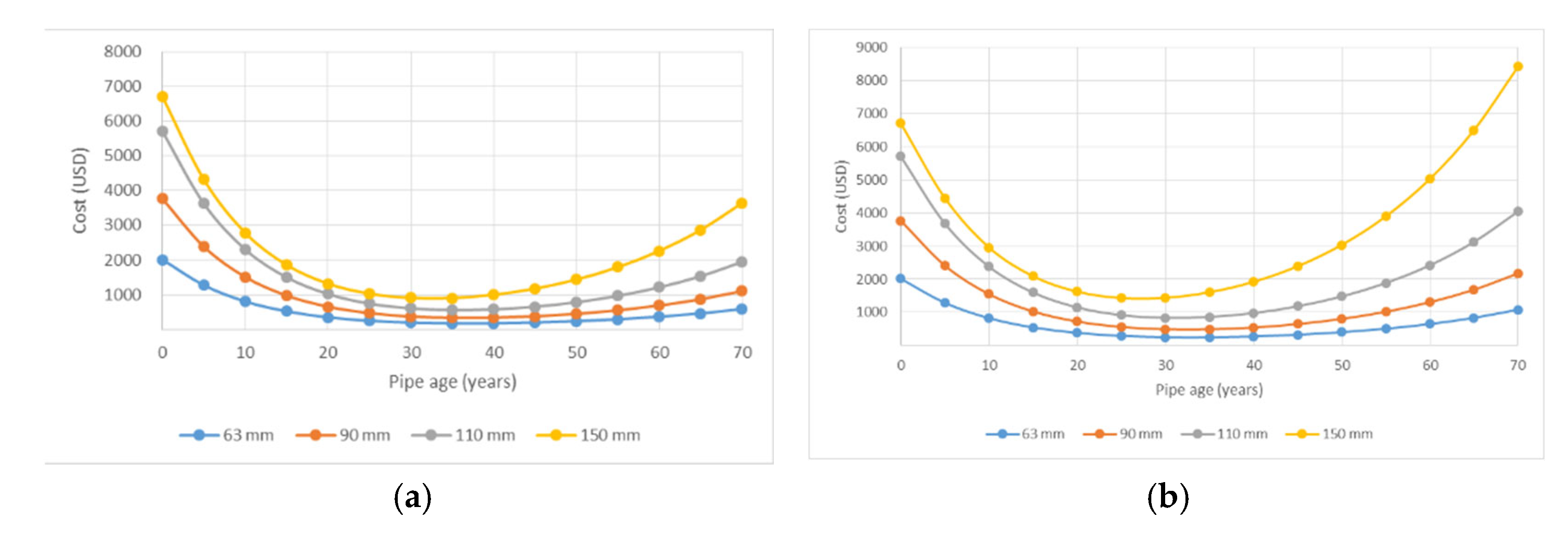
4.5. Life-Cycle Cost (LCC) Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mazumder, R.K.; Salman, A.M.; Li, Y.; Yu, X. Performance Evaluation of Water Distribution Systems and Asset Management. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2018, 24, 03118001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, Q. Serviceability Assessment for Cascading Failures in Water Distribution Network under Seismic Scenario. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1431457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathirana, A.; den Heijer, F.; Sayers, P.B. Water Infrastructure Asset Management Is Evolving. Infrastructures 2021, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, T.; Elwakil, E.; Mayol Novoa, H.; Fernando Gárate Delgado, J. Pressure data-driven model for failure prediction of PVC pipelines. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 116, 104769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, N.A.; Hallett, S.H.; Jude, S.R.; Tran, T.H. An evolution of statistical pipe failure models for drinking water networks: A targeted review. Water Supply 2022, 22, 3784–3813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldo-González, M.M.; Rodríguez, J.P. Comparison of Statistical and Machine Learning Models for Pipe Failure Modeling in Water Distribution Networks. Water 2020, 12, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, R.; Torres, D.; López-Jimenez, P.A.; Cobacho, R. A Front-Line and Cost-Effective Model for the Assessment of Service Life of Network Pipes. Water 2020, 12, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Koo, J.; Do, M. Estimating burst probability of water pipelines with competing hazard model. J. Hydroinform. 2016, 18, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, Y.; Nafi, A.; Rajani, B. Planning renewal of water mains while considering deterioration, economies of scale and adjacent infrastructure. Water Supply 2010, 10, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs-Hanusch, D.; Kornberger, B.; Friedl, F.; Scheucher, R.; Kainz, H. Whole of life cost calculations for water supply pipes. Water Asset Manag. Int. 2012, 8, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Scholten, L.; Scheidegger, A.; Reichert, P.; Mauer, M.; Lienert, J. Strategic rehabilitation planning of piped water networks using multi-criteria decision analysis. Water Res. 2014, 49, 124–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaitik, N.M.; Amaitik, S.M. Prediction of pipe failures in water mains using artificial neural network models. In Proceedings of the 11th International Arab Conference of information Technology (ACIT’2010), University of Garyounis, Benghazi, Libya, 14–15 December 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kabir, G. Planning Repair and Replacement Program for Water Mains: A Bayesian Framework. Ph.D. Thesis, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Motiee, H.; Ghasemnejad, S. Prediction of pipe failure rate in Tehran water distribution networks by applying regression models. Water Supply 2019, 19, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Nardo, A.; Di Natale, M.; Giudiciann, C.; Greco, R.; Santonastaso, G.F. Complex network and fractal theory for the assessment of water distribution network resilience to pipe failures. Water Supply 2018, 18, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutyłowska, M. Forecasting failure rate of water pipes. Water Supply 2019, 19, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gat, Y. Extending the Yule process to model recurrent pipe failures in water supply networks. Urban Water J. 2014, 11, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atique, F.; Attoh-Okine, N. Copula parameter estimation using Bayesian inference for pipe data analysis. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 45, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Yuan, X.-X. A two-time-scale point process model of water main breaks for infrastructure asset management. Water Res. 2019, 150, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailhot, A.; Poulin, A.; Villeneuve, J.-P. Optimal replacement of water pipes. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.P.; Allouche, E.N.; Trivedi, M. Optimal Scheduling of Replacement and Rehabilitation of Water Distribution Systems. J. Infrastruct. Syst. 2006, 12, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, H.T.; Nagarur, N.N. Optimal Maintenance Policy and Fund Allocation in Water Distribution Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2005, 131, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigg, N.S. Water Main Breaks: Risk Assessment and Investment Strategies. J. Pipeline Syst. Eng. Pract. 2013, 4, 4013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansey, K.E.; Basnet, C.; Mays, L.W.; Woodburn, J. Optimal Maintenance Scheduling for Water Distribution Systems. Civ. Eng. Syst. 1992, 9, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Mays, L.W. Optimal Rehabilitation Model for Water-Distribution Systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1994, 120, 674–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandy, G.C.; Engelhardt, M.O. Multi-Objective Trade-Offs between Cost and Reliability in the Replacement of Water Mains. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2006, 132, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamir, U.; Howard, C.D.D. An Analytic Approach to Scheduling Pipe Replacement. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1979, 71, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.S.; Estrada, H.; Baumert, M. Time-Dependent Reliability Analysis of FRP Rehabilitated Pipes. J. Compos. Constr. 2010, 14, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzouk, M.; Ahmed, O. Fuzzy-based methodology for integrated infrastructure asset management. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2017, 10, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshani, E.; Filion, Y. WDS leakage management through pressure control and pipes rehabilitation using an optimization approach. Procedia Eng. 2014, 89, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frangopol, D.M.; Soliman, M. Life-cycle of structural systems: Recent achievements and future directions. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2016, 12, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadi, F.; Jeong, G.; Kang, D. Water Pipe Replacement Scheduling Based on Life Cycle Cost Assessment and Optimization Algorithm. Water 2021, 13, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocco, D.; Giona, M. Generalized Counting Processes in a Stochastic Environment. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Tian, H.; Deng, F.; Dong, L.; Li, J. The Failure Intensity Estimation of Repairable Systems in Dynamic Working Conditions Considering Past Effects. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, E.; Rigdon, A.P.B. Statistical Methods for the Reliability of Repairable Systems, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 8–10. [Google Scholar]
- Rabarijoely, S. A Bayesian Approach in the Evaluation of Unit Weight of Mineral and Organic Soils Based on Dilatometer Tests (DMT). Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raveendran, N.; Sofronov, G. A Markov Chain Monte Carlo Algorithm for Spatial Segmentation. Information 2021, 12, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Xiao, W.; Yu, J. Maximum Likelihood Estimation for the Fractional Vasicek Model. Econometrics 2020, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, J. Financial Risk Forecasting: The Theory and Practice of Forecasting Market Risk with Implementation in R and Matlab, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chicester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Iriawan, N.; Yasmirullah, S.D.P. An Economic Growth Model Using Hierarchical Bayesian Method. In Bayesian Networks: Advances and Novel Applications; McNair, D., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 5–20. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Jun, H.; Agbenowosi, N.; Kim, B.J.; Lim, K. The Proportional Hazards Modeling of Water Main Failure Data Incorporating the Time-dependent Effects of Covariates. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 25, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre, H.; do Ceu Almeida, M. Strategic Asset Management of Water Supply and Wastewater Infrastructures, 1st ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2009; pp. 59–83. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, N.A.; Farewell, T.S.; Hallett, S.H.; Acland, T.F. Improving pipe failure predictions: Factors affecting pipe failure in drinking water networks. Water Res. 2019, 164, 114926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisque, A.; Tesfamariam, S.; Kabir, G.; Haider, H.; Reeder, A.; Sadiq, R. Water mains renewal planning framework for small to medium sized water utilities: A life cycle cost analysis approach. Urban Water J. 2016, 14, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Velasco, A.; Cortés, P.; Muñuzuri, J.; Onieva, L. Prediction of pipe failures in water supply networks using logistic regression and support vector classification. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2020, 196, 106754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, B.; McBean, E.A. Improving Urban Water Security through Pipe-Break Prediction Models: Machine Learning or Survival Analysis. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 4019129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, B.; McBean, E.A. Watermain breaks and data: The intricate relationship between data availability and accuracy of predictions. Urban Water J. 2020, 17, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Li, W. Application of genetic programming to modeling pipe failures in water distribution systems. J. Hydroinform. 2010, 13, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Røstum, J. Statistical Modelling of Pipe Failures in Water Networks. Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.; Robert, D.J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, D.; Kodikara, J. Probabilistic physical modelling of corroded cast iron pipes for lifetime prediction. Struct. Saf. 2017, 64, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, D.; Haltmeier, M.; Kleidorfer, M.; Rauch, W.; Tscheikner-Gratl, F. Pipe failure modelling for water distribution networks using boosted decision trees. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2018, 14, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidegger, A.; Leitão, J.P.; Scholten, L. Statistical failure models for water distribution pipes—A review from a unified perspective. Water Res. 2015, 83, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorenstein, A.; Kalech, M.; Hanusch, D.F.; Hassid, S. Pipe Fault Prediction for Water Transmission Mains. Water 2020, 12, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnaashari, A.; McBean, E.A.; Gharabaghi, B.; Tutt, D. Forecasting watermain failure using artificial neural network modelling. Can. Water Resour. J. 2013, 38, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, R.; McBean, E.A.; Gharabaghi, B. Predicting the Timing of Water Main Failure Using Artificial Neural Networks. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2014, 140, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Pipe Material | Length (km) | Year of Installation |
|---|---|---|
| AC | 25.42 | 1986 |
| GI | 5.04 | 1990 |
| PVC | 1241.87 | 2002 |
| HDPE | 1047.71 | 2012 |
| Period | Number of Pipe Failures | Average Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 567 | 82.30 |
| 2013 | 569 | 87.88 |
| 2014 | 372 | 92.96 |
| 2015 | 459 | 82.04 |
| 2016 | 680 | 93.47 |
| 2017 | 380 | 107.70 |
| 2018 | 471 | 96.77 |
| 2019 | 595 | 105.92 |
| 2020 | 621 | 102.62 |
| 2021 | 688 | 92.71 |
| Parameter | Mean | Standard Deviation | 2.5% | Median | 97.5% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β0 | 6.69 | 0.1561 | 6.387 | 6.691 | 6.99 |
| β1 | −0.001222 | 0.002068 | −0.01617 | −0.01221 | −0.008135 |
| β2 | 0.04833 | 0.006018 | 0.03645 | 0.04839 | 0.05966 |
| Parameter | Estimate | Standard Error (SE) |
|---|---|---|
| β0 | 6.88818 | 0.1557 |
| β1 | −0.01489 | 0.0021 |
| β2 | 0.051891 | 0.0059 |
| Period | Observed | MCMC Predicted | ML Predicted |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 567 | 501 | 505 |
| 2013 | 569 | 491 | 490 |
| 2014 | 372 | 484 | 478 |
| 2015 | 459 | 581 | 593 |
| 2016 | 680 | 530 | 527 |
| 2017 | 380 | 467 | 449 |
| 2018 | 471 | 561 | 556 |
| 2019 | 595 | 526 | 511 |
| 2020 | 621 | 575 | 566 |
| 2021 | 688 | 681 | 690 |
| Total | 5402 | 5396 | 5365 |
| Failure Quartile | Observed | Predicted | Margin (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Quartile | 1191 | 1441 | −20.93 |
| 2nd Quartile | 1059 | 1030 | 2.68 |
| 3rd Quartile | 1799 | 1665 | 7.43 |
| 4th Quartile | 1353 | 1260 | 6.87 |
| Total | 5402 | 5396 | 0.10 |
| Failure Quartile | Observed | Predicted | Margin (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Quartile | 1191 | 1414 | −18.71 |
| 2nd Quartile | 1059 | 1027 | 2.97 |
| 3rd Quartile | 1799 | 1648 | 8.40 |
| 4th Quartile | 1353 | 1276 | 5.67 |
| Total | 5402 | 5365 | 0.68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nugroho, W.; Utomo, C.; Iriawan, N. A Bayesian Pipe Failure Prediction for Optimizing Pipe Renewal Time in Water Distribution Networks. Infrastructures 2022, 7, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7100136
Nugroho W, Utomo C, Iriawan N. A Bayesian Pipe Failure Prediction for Optimizing Pipe Renewal Time in Water Distribution Networks. Infrastructures. 2022; 7(10):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7100136
Chicago/Turabian StyleNugroho, Widyo, Christiono Utomo, and Nur Iriawan. 2022. "A Bayesian Pipe Failure Prediction for Optimizing Pipe Renewal Time in Water Distribution Networks" Infrastructures 7, no. 10: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7100136
APA StyleNugroho, W., Utomo, C., & Iriawan, N. (2022). A Bayesian Pipe Failure Prediction for Optimizing Pipe Renewal Time in Water Distribution Networks. Infrastructures, 7(10), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/infrastructures7100136










