Abstract
Combining multivariable statistics and geostatistics with landscape metrics, we attempted to quantify the spatial pattern of urbanization in the city of Niamey, Niger. Landscape metrics provided local quantification of both landscape composition and physiognomy while the Principal Component Analysis (PCA) yielded a multivariable summary of the main source of landscape metrics variation across the city. We used the variogram (geostatistics) to analyze the spatial pattern of the PCA outcomes and to characterize the associated spatial scales of variation. In Niamey, the main urban structure corresponded to a gradient ranging from highly diversified, fragmented, and both wooded and built-up areas in the city center and along the Niger River, to less green zones gathering steel-roofed houses whose density diminished towards the periphery. This concentric structure centered on the Niger River clearly reflected the history of Niamey. PCA and geostatistics provided appealing quantitative estimates of spatial patterns, scales, anisotropy and intensity of urban structures. Although these different tools are known in landscape ecology, they are rarely used together. The present paper illustrates how they allow characterizing the marked spatial variation of the urban landscape of the fast-growing African city of Niamey (Niger). Such a quantification of the urban landscapes may be extremely useful for future correlative investigations in various fields of research and planning.
1. Introduction
While 54% of the world’s population was urban in 2014, this figure is expected to reach more than 66% by 2050. It is recognized that urban areas are currently expending faster than urban populations and this raises acute environmental concerns. Land-cover change associated with urbanization is a dramatic form of land transformation that strongly impacts various facets of biological systems and the evolution of living organisms. Among these features, urban ecosystems are characterized by altered local and regional climates through the urban heat island effect [1] or drastically modified water run-off and floods patterns. This sometimes leads to uncomfortable or unhealthy conditions for city dwellers. Growing cities have increasing demands for natural resources (e.g., water, food and energy demands [2,3]) and greatly contribute to pollution (e.g., increased vehicles use, concentration of industries, solid and liquid waste accumulation and treatment, non-electric domestic sources of energy and indoor contamination, etc.) [4], thereby raising the issue of urban sustainability that has recently attracted considerable attention.
The environmental impact of cities is largely dependent on population density and repartition (e.g., formal vs. informal settlements in the cities of many developing countries) and the citywide distribution of infrastructures, basic services, medical facilities, or public amenities, as well as connected areas (e.g., transports and transport networks). It is also modulated by the urban form per se, i.e., urban morphology [5] and ecological context (e.g., rivers, relief, sea front, flooding areas, etc). As a result, the spatial pattern of cities strongly affects ecological and socio-economic processes within and beyond city limits. One of the goals of urban ecology is to understand how city structure and dynamics impact ecological processes and sustainability. Another facet of urban ecology is related to human population health and its citywide spatial variability. This point is of particular concern in fast-growing cities often characterized by unplanned areas of dense and impoverished slums with inadequate infrastructures. In this context, urban landscape pattern have been recognized as a pertinent factor to human spatial epidemiology and health inequalities. The “one health” concept is based on the idea that human health should be understood and addressed as the result of multiple interactions between various actors, such as clinicians, researchers, local authorities, and/or citizens. Obviously, the pattern of urban and peri-urban landscapes is one of the factors that should be considered in such a multidisciplinary approach to the human and animal health issues.
Linking urban forms to ecological or epidemiological processes requires a quantification of the spatial patterns at hand. Landscape metrics of multi-class land cover or land use, originally developed in the field of landscape ecology, offer an efficient way to depict the complexity of cities in terms of landscape composition and physiognomy. In that context, the spatial variation of the landscape metrics across a city or along a transition between urban and rural environments [6,7] provide insights into how and at which scale(s) the pattern of urbanization changes in space. Characterizing the spatial variation of urban landscape composition and structure has useful operational consequences, as it offers a convenient way to arrange study plots in function of the gradient or patches [8] or to optimize citywide sampling design. Converting multi-class land cover maps into quantitative indices (i.e., landscape metrics) [9] also provides potentially meaningful covariates that can be used to feed correlative models to explore the links between urban patterns and ecological processes or epidemiological variables.
Africa displays the highest urban growth rate in the world (3.4% per year) [10], and it is expected to reach up to 5% in the next fifteen years, while the world average should be 2% [11]. The present study was carried out in Niamey, the capital city of Niger, the poorest country in the world (IDH 2017 of 0.354, rank 221/221). Niamey was created ex nihilo by French colonizers at the very end of the nineteenth century. The city is a typical example of the rapid urban population growth of colonial African cities with a population increasing from <20,000 in the early 1950s, to more than 1,300,000 inhabitants today. This recent explosive increase of the number of urban dwellers in Niamey was largely driven by a massive rural exodus following successive droughts (e.g., from 90,000 to 500,000 inhabitants from 1960 to 1980). Niamey currently displays one of the largest average annual growths of West African cities (2010–2020: 7.86%, 3rd rank after Ouagadougou and Yamoussoukro). Such a rapid population expansion translated into a marked urban sprawl associated with the development of informal settlements and poverty.
The purpose of our study was to explore how landscape metrics combined with multivariable and ad hoc spatial statistics can be used to characterize the urban form of an African urban area representative of the fastest growing cities of the continent. More specifically, we aimed to (i) explore how the analysis of landscape metrics by principal component analysis emphasizes the main urban features, (ii) map the corresponding patterns, (iii) examine how geostatistics allow to identify the main scales of the spatial variation and the presence of spatial anisotropy in the urban context, and (iv) discuss the value of the former approaches to set up sampling plans and experimental designs and derive synthetic urban landscape descriptors that can serve as explanatory variables in correlative models.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study City: Niamey
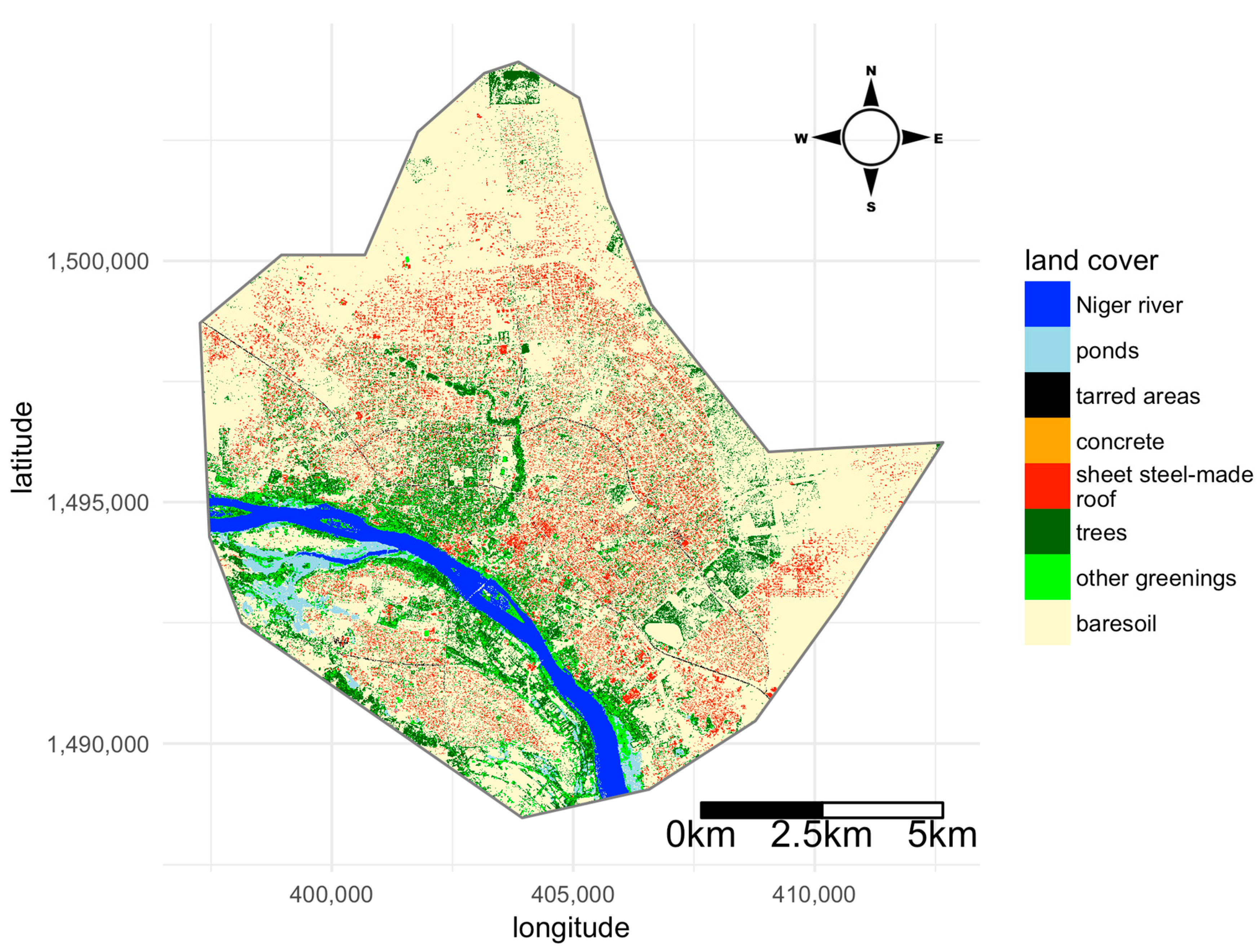
The city of Niamey (capital of Niger) lies on both sides of the Niger River. The climate is typical of a semi-arid Sahelian region, with low rainfalls (ca. 540 mm per year) and high temperatures (monthly average temperatures range between 22 °C and 36 °C). A single rainy season usually occurs between May and September. Niamey was created ca. 120 years ago and has experienced a continuous demographic growth that recently accelerated. This population growth has been accompanied by a spectacular spatial expansion associated with the development of many informal settlements and a marked variation of the socio-economic status across the city. In the present survey, we used a Geographic Information System (GIS) of Niamey implemented from a SPOT satellite image (scene reference number 506 132 308 121 010 151 32 T; CNES 2008, resolution of 2 m). Eight land-cover categories have been distinguished: Niger river, ponds, bare soils, tarred areas, concrete areas, trees, other greenings, and sheet steel-made roofs (Figure 1). The analyses were carried out on the basis of a raster map of 2 m by 2 m resolution derived from the satellite image. The projected coordinate system is WGS 84 / UTM zone 31N (EPSG: 32631, http://spatialreference.org). In Niamey, people sometimes use unfired ground as a building material (referred to as “banco”). This traditional material is associated with a spectral signature very close to that of bare soil; thus, some settlements were mistaken for bare soil. Today, the “banco”-made roofs are increasingly replaced by sheet steels and mostly occur in two old and underprivileged districts named Gamkallé and Karadjé (Figure S1, Supplementary Material).
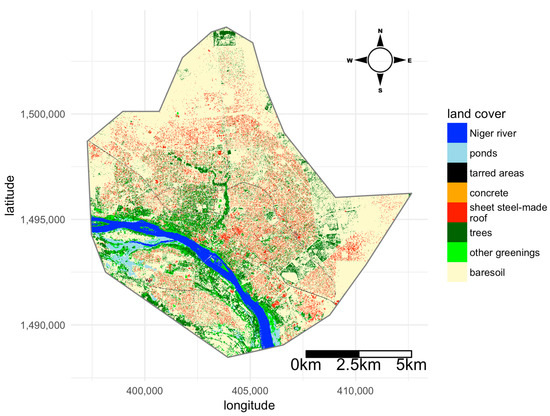
Figure 1.
Map of the city of Niamey (Niger) showing the 8 land-cover classes used in the study. The projected coordinate system is WGS 84/UTM zone 31N (EPSG: 32631, http://spatialreference.org/ref/epsg/32631/).
2.2. Landscape Metrics
Landscape metrics are mathematical indices developed to quantify various aspects of a landscape from the categorical map describing that landscape. The aim is to capture some of the synoptic features of landscapes, such as composition and physiognomy. A number of landscape metrics have been proposed [9] for that purpose. Class metrics focus on one land-cover class (e.g., bare soil, trees, etc.), while landscape metrics consider all classes simultaneously to provide synthetic indices of diversity and complexity among other features (Table 1). The percentage of landscape (PLAND) metric quantifies the proportion of the landscape covered by a given land-cover. Largest patch index (LPI) reflects the proportion of the landscape covered by the largest patch of a given land-cover. Both reflect the composition of the landscape. In the present study, we also computed the patch density and the edge density (PD and ED), which correspond to the number of patches and the amount of edge associated with them. Edge effects are recognized as having a key role in many ecological processes. This is the reason why we also considered, at the scale of the whole landscape, the ED metric, which quantifies the total edge length (i.e., for all land-covers). In addition, we used 3 measures of richness or diversity: patch richness density (PRD) measures the richness in a landscape as the number of different land-covers, the modified Simpson’s diversity index (MSIDI) measures landscape diversity, and the modified Simpson’s evenness index (MSIEI) quantifies how close the proportion of the surface occupied by the different land-covers is.

Table 1.
Landscape metrics used to describe the urban landscape in the city of Niamey (adapted from McGarigal et al. 2012).
The landscape metrics were computed from a local urban landscape corresponding to circular buffers positioned on 53,239 points located on a square grid of 50 m mesh size and covering the whole region under study (Figure 1). Each buffer led to a “local landscape” for which we computed all metrics. The computations were done for different values of buffer diameter (20 m, 40 m, 60 m, 80 m, and 100 m) in order to capture landscape features at different spatial scales. All landscape metrics were computed using the software FRAGSTATS [12].
2.3. Multivariate Analysis Using the Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
Landscape metrics computation yielded a dataset with 53,239 rows (the sampling points) for 4 × 8 = 32 class metrics and 4 landscape metrics. Multivariate analyses, such as the Principal Component Analysis (PCA), are well suited to extract the main multivariate patterns from such big datasets and to provide a typology of the sampling points in the form of their scores upon the principal components.
The PCA consists in the eigenanalysis of a dispersion matrix (here, the correlation matrix) and yields a set of principal axes that are a linear combination of the variables. Since they are orthogonal, the principal components reflect independent facets of the dataset. The PCA gives very good results when it is used to analyze highly correlated variables [13], which is precisely the case of landscape metrics. It also provides information about the relationship between landscape metrics and the contribution of each of them to the construction of the principal axes (correlation circle). As such, it is very helpful to hierarchize the sources of landscape variability. The scores of the sampling points can be analyzed using different methods, such as geostatistics (see below) to explore the spatial continuity and the scales at which multivariate landscape features vary across the city.
2.4. Variograms
The spatial variability of the principal components was analyzed using the variogram, an important tool in geostatistics, a branch of spatial statistics originally developed in earth sciences [14] and now widely used in life sciences.
The semi-variance quantifies the dissimilarity between the values of a variable z (here the score of sampling points upon the principal axes of the PCA) measured at points a distance h apart. It is:
where i denotes the sampling points and h the separating distance. The variogram is the plot of against h and represents the average rate of change of z with h. It provides clues to the pattern of spatial variation in terms of its general form, scales, and magnitude. If a spatial structure is present, increases with h and often reaches a plateau for a distance referred to as the range. Points separated by a distance larger than the range are considered statistically independent, and below that range, points are more similar than expected by chance. Flat variograms reveal the absence of spatial dependence. The spatial structure at hand can be conveniently characterized by fitting a mathematical function to the empirical variogram. Typically, model parameters characterize the range (the distance below which a spatial dependence is present), the sill (the semi-variance corresponding to the plateau), and the nugget variance, i.e., the semi-variance for h = 0, which accounts for measurement errors and variation occurring at a distance shorter than the minimum inter-sample distance. Complex spatial structures can be modeled using nested models.
The spatial variability may be directionally dependent; in other words, the variogram may reveal changes in the range or the sill when computed in different directions [14,15]. The first step of the analysis of directional anisotropies consists in finding the main anisotropy axes. This process can be conveniently undertaken by computing the variogram map (also referred to as the variogram surface). The semi-variance is computed at different lag distances (h) and represented as grid cells along multiple azimuths originating from a common point. A grid cell in the variogram map shows the semi-variance calculated for a group of paired data points that are aligned along a given azimuth and separated by given distance (Figure 5). The resulting map shows the semi-variance in all directions and for all lag distances. A transect in any single direction thus corresponds to the variogram computed for that direction. We computed the variogram map the points coordinates upon the first two PCA axes (PC1 and PC2) using a lag distance of 200 m.
All analyzes were performed using the R language [16]. The PCA was computed using the R package ade4 [17]. Variograms were computed and analyzed using the R package gstat [18].
3. Results
The 53,239 sampling points will be hereafter referred to as the pixels. The first and second axes of the PCA will be hereafter referred to as PC1 and PC2, respectively.
3.1. PCA Eigenvalues According to Buffer Sizes
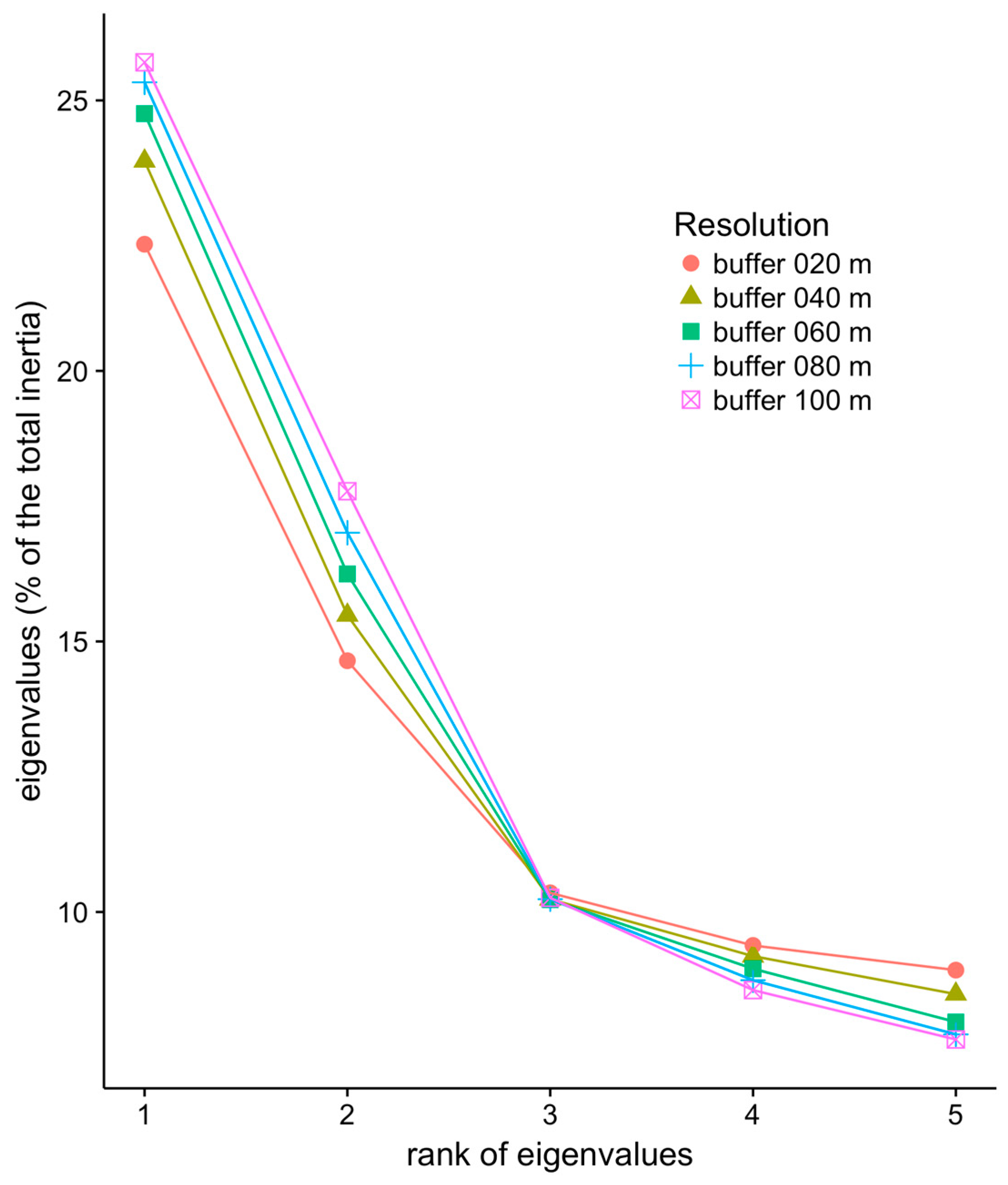
We performed PCA to analyze the landscape metrics computed at each investigated buffer size. The inertia associated with each of the first five eigenvalues is shown in Figure 2. Interestingly, smaller buffer sizes corresponded to a lower amount of inertia associated with the first two axes, while that amount became larger for axes of a rank >3. Larger buffer sizes led to a better concentration of the information along the first PCA components. In other words, larger “local landscapes” led to metric values that better segregated the pixels along the two first PCA axes. For that reason, we focused on the results of the PCA obtained for the largest resolution explored in the present study (i.e., 100 m resolution).
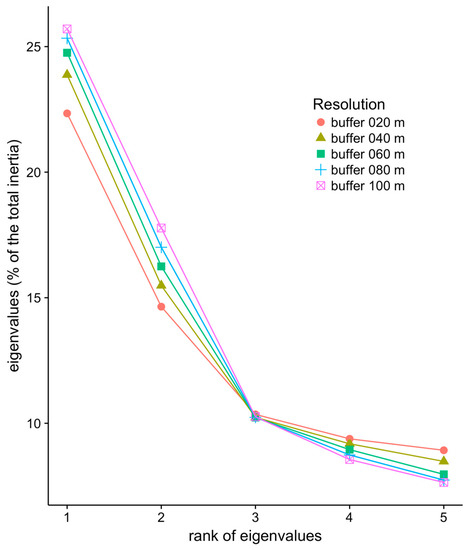
Figure 2.
First five eigenvalues of the principal component analysis (PCA) of the landscape metrics computed in Niamey for different buffer sizes, i.e., at different spatial resolutions. Eigenvalues are expressed as a proportion (%) of the total inertia of the dataset.
3.2. Citywide Variation of Landscape Features
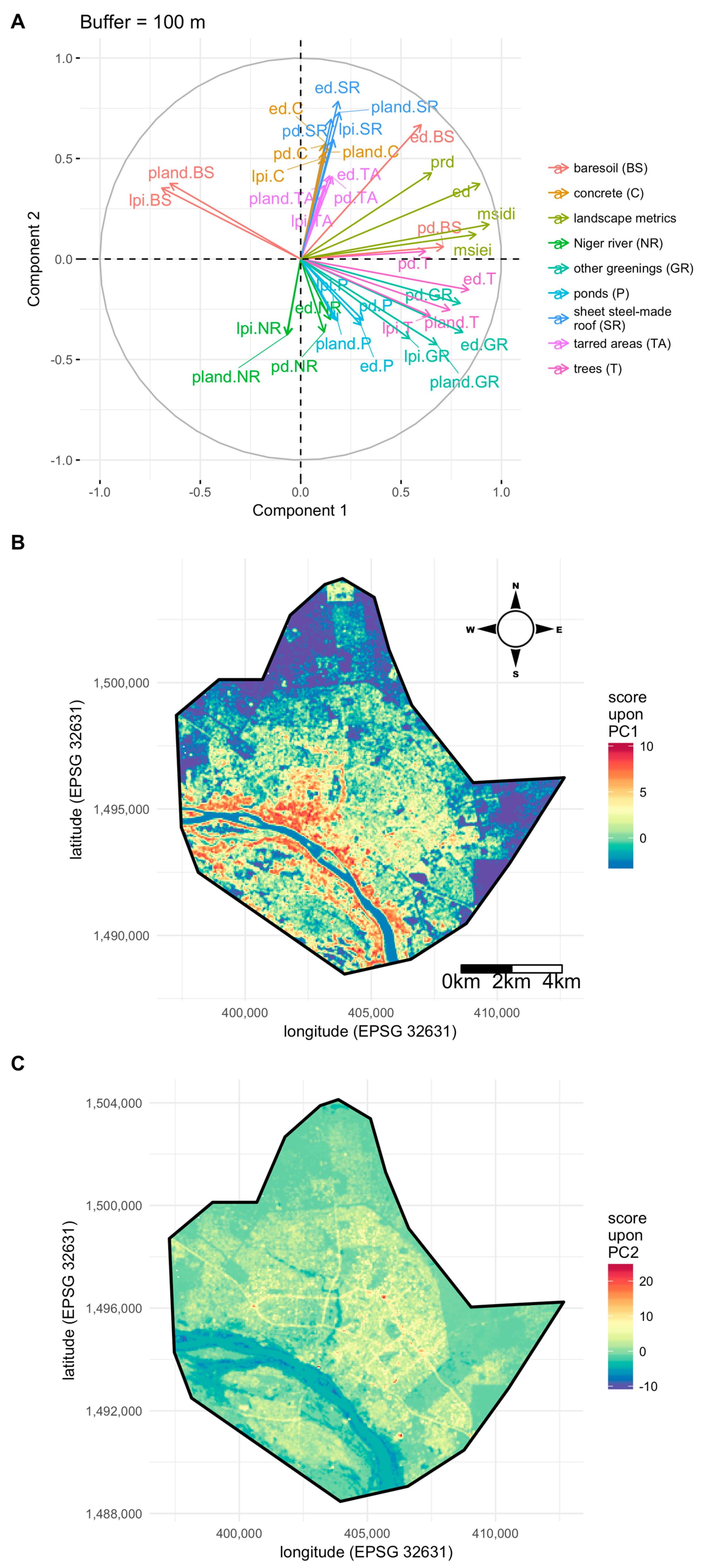
Figure 3A shows the correlation circle obtained with the PCA of the landscape data derived from a buffer size of 100 m. The first axis segregates pixels associated with high values of the diversity and equitability indices (MSIDI and MSIEI), patch richness density (PRD), as well as edge density (ED) (right-hand side of the PC1 axis) from pixels associated with high values of the metrics PLAND and LPI for bare soil (left-hand side of the PC1 axis). The tree and other greenings also contribute to the first component and higher vegetation cover is associated with areas of higher diversity and lower amount of bare soil (right-hand side of the PC1 axis i.e., positive scores). Mapping the pixel scores upon PC1 (Figure 3B) reveals that positive scores are spatially aggregated along the Niger River and in the city center. Conversely, lower scores are associated with pixels located in the periphery of Niamey, leading to a gradient from city center and Niger River (in red in Figure 3B) to city outskirts (in blue in Figure 3B).
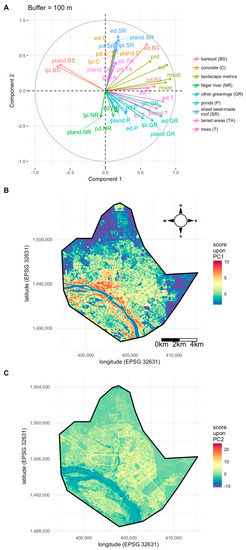
Figure 3.
PCA of landscape metrics describing the urban landscape of the city of Niamey (Niger): (A) correlation circle; (B) map of the first PCA axis; (C) map of the second PCA axis.
The PC2 axis (Figure 3A) segregates pixels characterized by high coverage of a sheet-steel-made roof (SR) and concrete (C) (top of vertical axis) to pixels with high coverage of ponds (P), greenings (GR), trees (T), and Niger River (NR) (bottom of vertical axis). The map of the pixel scores (Figure 3C) shows that PC2 depicts a gradient from areas located close to the Niger River or characterized by high tree or greening coverage of highly urbanized areas with very low (if any) greenings. Intermediate scores (yellow in Figure 3C) also reflect streets where pixel coverage of tarred areas (TR) is higher. Some very localized spots in red correspond to very high scores and materialize larger tarred areas (road circles, industrial sites, etc.).
3.3. Variography of PCA First Components
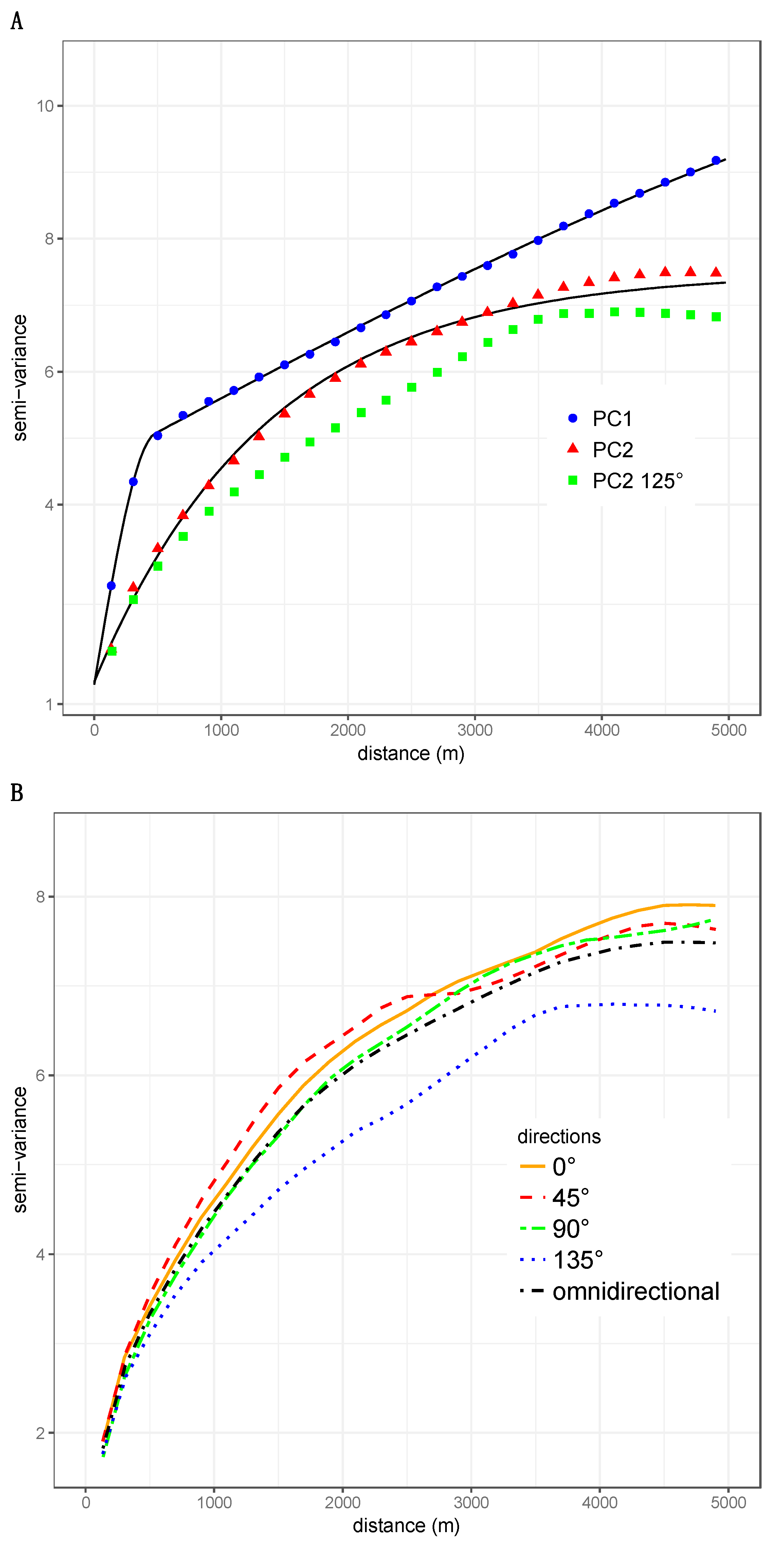
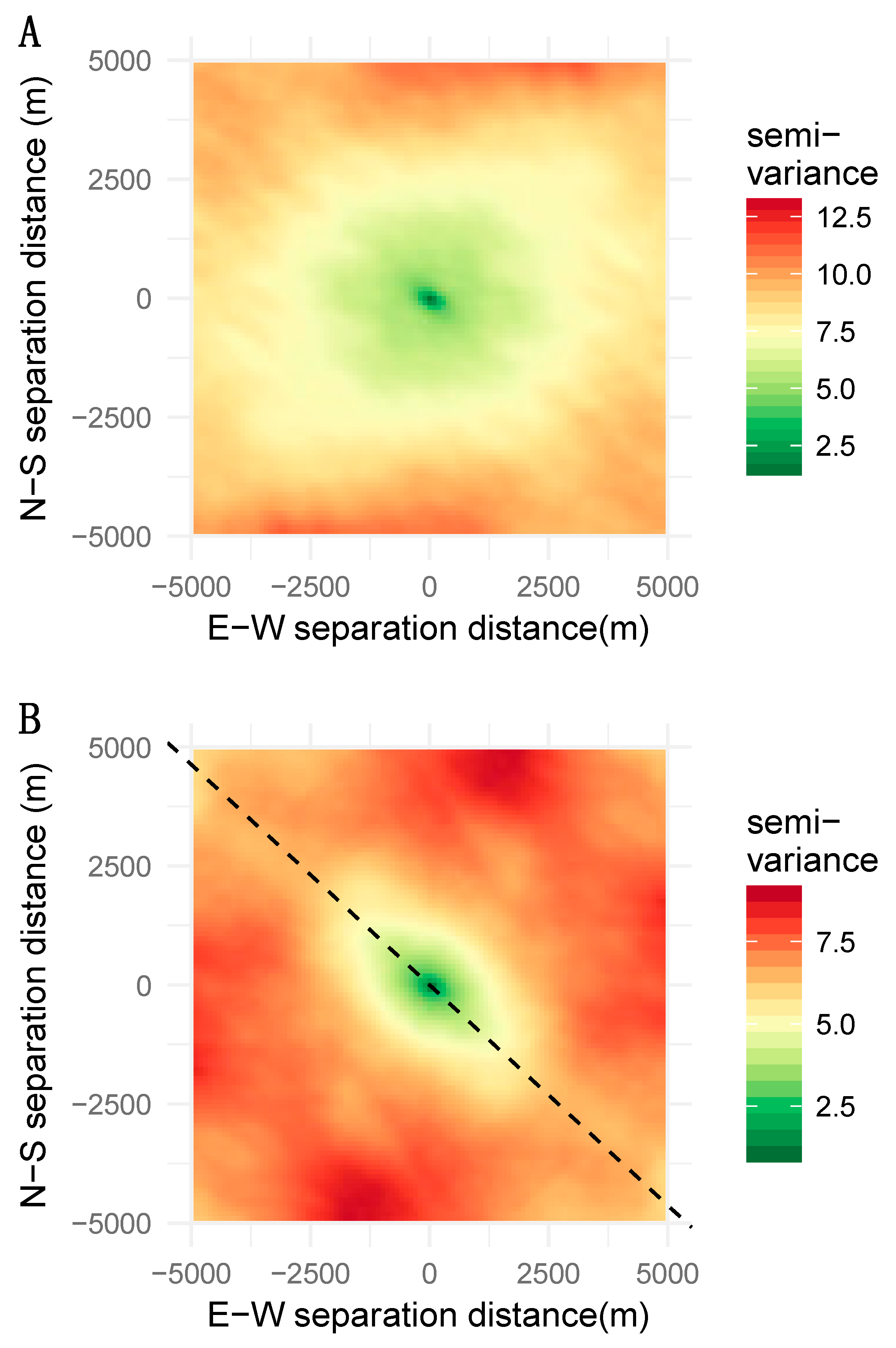
The scores of the 53,239 pixels upon PC1 and PC2 were used to compute omni-directional variograms. Data couples were grouped into 25 distance classes ranging from 0 to 5000 m. The spatial lag was 200 m and the average distance separating data points in the first distance class was 134 m. The number of data pairs in semi-variance estimation ranged from 1,257,853 to 33,759,596. Both variograms exhibited a very clear spatial structure (Figure 4A). The variogram of PC1 exhibited a nested structure with one component corresponding to short-scale spatial dependence (< 500m) and a long-range structure. Variogram modeling offers the advantage of allowing one to separate such superimposed sources of spatial autocorrelation. Figure 4A shows the empirical variogram for PC1 (points) and a nested model fitted from the observed semi-variance values (solid line) [19]. The nested model comprises two spherical models with very different ranges (477 m and 9440 m) that quantify the spatial scales at which PC1 varies. The variogram model of PC2 (Figure 4A) is exponential, with a range of 1356 m. Thus, contrary to PC1 that resembles a gradient, PC2 depicts a bounded structure.
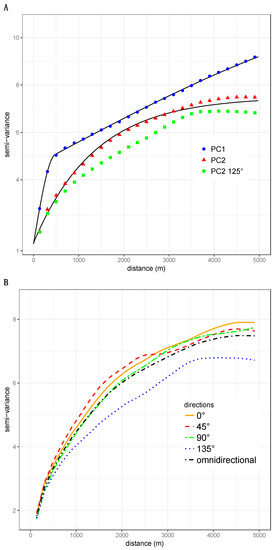
Figure 4.
Structural analysis of the first two axes of the PCA of landscape metrics describing the urban structure of the city of Niamey: (A) omni-directional variograms of the PCA axes 1 and 2 and directional variogram for the direction of 125° of axis 2; (B) directional (0°, 45°, 90°, and 135°) and omni-directional variograms for the axis 2 of the PCA.
We examined the possible presence of directional spatial dependences using the variogram maps shown in Figure 5. For PC1, the semi-variance increased regularly with separating distance, irrespective of the direction examined, which indicated an omnidirectional spatial structure. On the contrary, the variogram map for PC2 exhibited a clear anisotropy along the direction of 135° (Figure 5B). The map shows that the semi-variance increases more slowly along the 135° direction than it does in other directions, and that it reaches lower values. Having identified a direction of anisotropic variation using the variogram map, we computed the directional variograms in four different directions (0°, 45°, 90°, 125°, and 135°; Figure 4A,B). The directional variograms for 125° and 135° clearly indicated that PC2 varied differently in these directions. The semi-variance is lower (the pixels are more similar) and reached a plateau for a smaller range than that of other directions. The specific pattern along the direction of 135° may be explained by the spatial position of the Niger River and the associated ponds that strongly impact the construction of PC2.
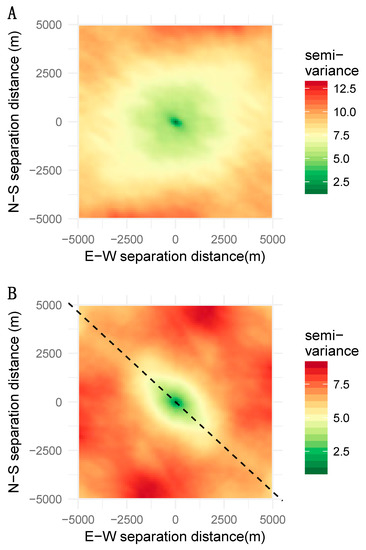
Figure 5.
Variogram maps for the first two axes of the PCA of landscape metrics describing the urban structure of the city of Niamey: (A) variogram map for axis 1 revealing an isotropic variation; (B) variogram map for axis 2 showing the presence of anisotropy in the direction of 135°.
4. Discussion
4.1. Niamey
In this study, we showed how landscape metrics computed from urban land-covers could capture and characterize the spatial structure of the city of Niamey, an emblematic example of fast-growing West African cities. Since the seminal work of Herold et al. [20] and Luck and Wu [6], the value of landscape metrics to depict urban landscape composition and physiognomy has been largely recognized, although surveys of cities from low and middle income countries are still too scarce. Interestingly, landscape metrics provided a clear picture of the city structure on the basis of very simple information consisting in only eight land-cover classes. Other data, such as land-uses, would have probably yielded different and complementary pictures of the city structure, but eight basic land-covers combined with landscape metrics proved to be sufficient to depict the trend of urbanization that globally radiates from the historical city center to the outskirts.
The main urban structure identified through the PCA corresponded to a gradient ranging from highly diversified, fragmented, and both wooded and built-up areas in the city center and along the Niger River, to less green zones, gathering steel-roofed houses whose density diminishes towards the periphery. The most external belt is made of bare soil that characterizes the non-urban peripheral areas. Such a concentric pattern is particularly marked on the northern half of the city (Figure 3). This rather simple concentric structure appears to be centered on the Niger River and clearly reflects the history of Niamey. Indeed, the first colonial settlement lied on the Niger River bank in an area that is now very central to the town and still shelters many political and public infrastructures. This administrative and residential center was close to a commercial area (e.g., the “Petit Marché” that was first created in 1936) that rapidly became saturated, thus driving the development of other markets that stood slightly further away (e.g., “Grand Marché”, built in the early 1960s). From the 1980s, the increase of density in this part of Niamey led to a rapid and constant centripetal expansion of the city [21], with the explosive, and still ongoing, development of the northern belt of the town. South of the Niger River, the city has developed only since the mid-1970s, after the construction of the first bridge and the University. There too, settlements have been growing fast, but spaces are still dedicated to urban agriculture [21], as clearly depicted by our GIS-based analysis (Figure 3).
The main source of land cover variation identified in our analysis opposes the city center on the outskirts. The quantification of this pattern allows ones to compare it to various other features in a clearly formalized analytical context. For instance, as part as the One Health concept, it could be interesting to investigate the relationship between the urban gradient retrieved here and the spatial heterogeneity of population health, access to health cares, etc. It is expected that the spatial patterning of urban land-cover covaries with demographic, social, and economic factors on one hand, and a wide spectrum of environmental factors on the other. For example, urban landscape most probably directly impacts the vector, reservoir, and pathogen distributions and lifecycles. Accordingly, various surveys have recently been conducted in Niamey to characterize the spatial variation of several small mammal-borne zoonotic agents. As such, a clear association between urban market gardening and leptospiral risk was retrieved, while highly built-up areas of the city appeared at very low risk, despite the abundance of potential rodent reservoirs of the pathogen [19]. In the same manner, a relationship between rodent-borne Trypanosoma lewisi and T. lewisi-like prevalence and land cover was recently identified [22]. These two cases studies illustrate how the approach detailed in the present work could greatly help in deciphering health drivers in the context of the urban landscape in African cities. We believe that this would be particularly useful with social uses (and not only land-uses) included in the analytical framework, something that is allowed by the methods used in our survey.
4.2. Multivariate Analysis
Landscape metrics are one of the most common tools used to quantify landscape structures both in natural ecosystems and in urbanized areas. Landscape metrics provide targeted quantitative information on specific aspects of urban landscape composition and structure [6,12] that can be directly interpreted or analyzed using different statistics. Overall, landscape metrics are known to be partially redundant and often highly correlated or collinear. Since redundancy may constitute a problem in certain statistical analyses [23], the use of multivariate analyses to summarize the datasets and extract the main sources of variation is an appealing strategy for analyzing urban landscapes.
The present study exemplifies how the PCA can pick up the main multivariate patterns of Niamey city through the principal components. As a linear combination of the initial landscape metrics, these principal factors could, themselves, be treated as a random variable leading to the straightforward maps shown in Figure 3B,C. Such graphical displays allow a quick and easy interpretation of city structures, as well as subsequent statistical analyses (discussed below). One interest of PCA and other multivariable analyses is that factors (or principal axes) are independent and can be ranked in terms of the amount of inertia they account for. This property allows one to hierarchize the sources of variability that drive the spatial variability of the landscape under study. In the case of Niamey, the patterns were rather simple and could be encapsulated in the first two principal axes. Beyond our study case, the PCA could efficiently decipher more complex correlation structures and situations, where very large geospatial datasets are to be analyzed.
The PCA and, more generally, multivariate analyses provide an assessment of the relationships between landscape metrics (correlation circle, Figure 3B) as well as a direct measure of the contribution of each metric to the principal axes. Identifying landscape metrics of importance could be the goal of an exploratory survey, as well as a prerequisite in correlative studies, where one or several metrics reflecting important landscape features are involved in statistical analysis or modeling, to identify a relationship with other variables.
Landscape metrics are sensitive to both spatial and thematic map resolutions that directly affect the amount of detail available to compute landscape metrics. This has been shown in urban systems [24,25], as well as in less anthropized environments. In the case of Niamey, we explored various buffer sizes with which we computed the landscape metrics. The PCA showed that the outputs differed in terms of inertia associated with PCA axes, the geospatial information being more concentrated on the first principal axes when larger buffers were used. Such effects may depend on the landscape at hand and could change according to the statistical analysis employed. In certain cases, the effect of buffer resolution was shown to be idiosyncratic [23], which suggests that such effects are complex, case-specific, and, as such, difficult to generalize.
In the present study, we analyzed one landscape at a specific date, but there is a wealth of literature dealing with space–time data, e.g., focused on land-use/land-cover change, in order to characterize landscape dynamics. If a city is described using landscape metrics computed at different dates, the analysis of the resulting time series could be achieved using a variant of the PCA called Partial Triadic Analysis (PTA). PTA belongs to the STATIS group of methods. Put simply, the PTA allows one to isolate the spatial structure common to different dates and to understand how the urban pattern quantified at each date differs from the common model. This approach, combined with the characterization of urban patterns by landscape metrics, deserves to be further explored in the context of urban ecology and planning.
4.3. Structural Analysis
In a spatially explicit approach, the scores of the sampling sites upon the principal axes can easily be visualized and analyzed to examine spatial dependence (or autocorrelation see [26]). Various methods can be used to do so. In the present study, we employed the geostatistics as a convenient way to determine whether a spatial structure is present or not, and to infer the scales at which it occurs. The variogram has proven to be a valuable tool to reveal not only the presence of spatial structures but also their range. For example, the variogram of the first PCA axis revealed a spatial structure made of two superimposed structures one rather local (<500 m) and one rather large (up to 9000m). Such features are very well known and currently used in various fields of life sciences [27] and their usefulness in landscape pattern analysis has been emphasized [28,29] but their dissemination in urban landscape analysis is yet to occur.
Again, these approaches could also be used to process space–time data, thus allowing a proper assessment of spatio-temporal dynamics in situations where diachronic data are available. In the case of Niamey, it is very likely that the range of the second model of the nested variogram for PC1 will increase in the future, as the city will expand (sprawl). However, not much is known about the presence of nested structures in urban environments.
Another input of geostatistics is the search for, and the characterization of, anisotropic variations of urban landscapes. In the case of Niamey, anisotropy was observed for the second component of the PCA (Figure 5). It was not a very marked feature of the Niamey landscape, but the situation could be very different in other cities where growth is not so obviously concentric. We showed how the variogram map could be used to search for the directions of the main anisotropic variation, and how the directional variograms could then finely quantify both direction and magnitude. Again, the ability of geostatistics (amongst other spatial statistics) has been emphasized by different authors [14,27,30], although its effective use in urban pattern analysis remains scarce. The variogram map, in particular, is not very popular, even in the fields of soil science and ecology where geostatistics are widely used. Our study case illustrates the efficiency of the method and its power when used to analyze the outputs of a PCA.
4.4. Feeding Models, Refining Sampling Strategies and Setting Up Experimental Designs
Landscape metrics are frequently used in inferential statistics in order to test and identify relationships between environment and biological datasets, such as species abundance or distribution or epidemiological data. As linear combinations of landscape metrics, the PCA axes are good candidates to include in correlative analyses and statistical models. One obvious advantage is that axes are independent from each other and have stronger explanatory power than any of the landscape metrics taken individually. Using PCA axes is, therefore, a potentially elegant way to tackle the problem of landscape metric redundancy. Landscape metrics, PCA and geostatistics offer a powerful tool to characterize the spatial pattern of the multivariate variability of urban environments. As shown in this study, PCA axes reveal different levels of spatial variation of geostatistics provide a quantitative assessment of scales and directions of variation. Such information could be utilized to improve sampling strategies either for ecological or socio-economical sciences. de Gruijter [31] emphasized how the a priori knowledge of spatial autocorrelation (dependence) could help in designing efficient sampling schemes for model-based inferences. Using Niamey as an example, the PC1 could be used to design a sampling scheme accounting for the city growth pattern and choose sampling points as a function of the values of the PC1. The sampling strategy could also be optimized to properly account for anisotropic variation. Conversely, a priori knowledge of major sources of spatial heterogeneities could be used to design experimental settings and/or analyze their output data. For example, maps of PCA components could be useful to identify the position of experimental sites while ensuring they meet similar urban conditions. Another option would be to use this a priori knowledge to design sampling along fine-scale urban gradients or along tracks of known isotropic or anisotropic variation gradient.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2413-8851/3/2/63/s1, Figure S1: Map of the city of Niamey showing the surveyed districts. The map was created using the R package Leaflet (Cheng et al. 2017) (data copyright OpenStreetMap contributors). Reference: Joe Cheng, Bhaskar Karambelkar and Yihui Xie (2017). leaflet: Create Interactive Web Maps with the JavaScript Leaflet Library. R package version 1.1.0. https://CRAN.R-project. org/package=leaflet.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-P.R. and G.D.; methodology, J.-P.R.; formal analysis, J.-P.R.; writing—original draft preparation, J.-P.R. and G.D.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ibrahima Kadaouré (Centre Régional Agrhymet, USAid/Fews-Net, Niamey, Niger) for helping in the implementation of Niamey GIS in the framework of earlier studies on rodent-borne pathogens conducted by G. Dobigny and M. Garba (Direction Générale de la Protection des Végétaux). The satellite image of Niamey is part of a Spot Image (CNES 2008, scene number 506 132 308 121 010 151 32 T) that was obtained under license through the ISIS program (file number 553). Our researches were conducted in the framework of the scientific partnership agreement (number 301027/00) between IRD and the Republic of Niger. The experiments presented in the manuscript comply with the current laws of the Niger. We are indebted to two anonymous referees for their comments and suggestions for this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mohajerani, A.; Bakaric, J.; Jeffrey-Bailey, T. The urban heat island effect, its causes, and mitigation, with reference to the thermal properties of asphalt concrete. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.-C.; Fan, C.; Huang, T.; Wang, C.-F.; Chen, Y.-H. Urban Metabolic Analysis of a Food-Water-Energy System for Sustainable Resources Management. Int. J. Enviorn. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keairns, D.L.; Darton, R.C.; Irabien, A. The energy-water-food nexus. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2016, 7, 239–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidja, L.; Ali-Khodja, H.; Khardi, S. Sources and levels of particulate matter in North African and Sub-Saharan cities: A literature review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12303–12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauleit, S.; Breuste, J.H. Land use and surface cover as urban ecological indicators. In Urban Ecology. Pattern, Processes, and Applications; Niemelä, J., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 19–30. [Google Scholar]
- Luck, M.; Wu, J. A gradient analysis of urban landscape pattern: A case study from the Phoenix metropolitan region, Arizona, USA. Landsc. Ecol. 2002, 17, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M. Quantifying Spatiotemporal Patterns of Urban Land-use Change in Four Cities of China with Time Series Landscape Metrics. Landsc. Ecol. 2005, 20, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, M.J.; Hahs, A.K. The use of gradient analysis studies in advancing our understanding of the ecology of urbanizing landscapes: Current status and future directions. Landsc. Ecol. 2008, 23, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.G.; Gardner, R.H.; O’Neill, R.V. Landscape Ecology in Theory and Practice; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, P.M.L.; Okereke, C.; Rudd, A.; Parnell, S. Regional Assessment of Africa. In Urbanization, Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services: Challenges and Opportunities; Elmqvist, T., Fragkias, M., Goodness, J., Güneralp, B., Marcotullio, P.J., McDonald, R.I., Parnell, S., Schewenius, M., Sendstad, M., Seto, K.C., et al., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision: Highlights; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McGarigal, K.; Cushman, S.A.; Ene, E. FRAGSTATS v4: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Categorical and Continuous Maps. Computer Software Program Produced by the Authors at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst. 2012. Available online: http://www.umass.edu/landeco/research/fragstats/fragstats.html (accessed on 12 June 2019).
- Manly, B.F.J.; Alberto, J.A.N. Multivariate Statistical Methods: A Primer; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics for Natural Resources Evaluation; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Isaaks, E.H.; Srivastava, R.M. Applied Geostatistics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 12 June 2019).
- Dray, S.; Dufour, A.-B. The ade4 Package: Implementing the Duality Diagram for Ecologists. J. Stat. Softw 2007, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pebesma, E.; Heuvelink, G. Spatio-temporal interpolation using gstat. RFID J. 2016, 8, 204–218. [Google Scholar]
- Dobigny, G.; Garba, M.; Tatard, C.; Loiseau, A.; Galan, M.; Kadaouré, I.; Rossi, J.-P.; Picardeau, M.; Bertherat, E. Urban Market Gardening and Rodent-Borne Pathogenic Leptospira in Arid Zones: A Case Study in Niamey, Niger. PLoS Negl. Trop Dis. 2015, 9, e0004097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, M.; Scepan, J.; Clarke, K.C. The use of remote sensing and landscape metrics to describe structures and changes in urban land uses. Environ. Plan. A 2002, 34, 1443–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamane, M. Croissance urbaine et politique de peuplement au Niger. In Proceedings of the Colloque de l’AIDELF, Rabat, Morroco, 15–17 May 1990; pp. 379–388. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, J.-P.; Kadaouré, I.; Godefroid, M.; Dobigny, G. Landscape epidemiology in urban environments: The example of rodent-borne Trypanosoma in Niamey, Niger. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 63, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, J.P.; van Halder, I. Towards indicators of butterfly biodiversity based on a multiscale landscape description. Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyantuyev, A.; Wu, J. Effects of thematic resolution on landscape pattern analysis. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyantuyev, A.; Wu, J.; Gries, C. Multiscale analysis of the urbanization pattern of the Phoenix metropolitan landscape of USA: Time, space and thematic resolution. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2010, 94, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P.; Sonnet, P.; Navarre, A. Factorial kriging analysis of springwater contents in the Dyle river basin, Belgium. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Reynolds, J.F. On definition and quantification of heterogeneity. Oikos 1995, 73, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, J. Landscape pattern analysis: Key issues and challenges. In Key Topics in Landscape Ecology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Buyantuyev, A.; Jenerette, G.D.; Litteral, J.; Neil, K.; Shen, W. Quantifying spatiotemporal patterns and ecological effects of urbanization: A multiscale landscape approach. In Applied Urban Ecology: A Global Framework; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 33–53. [Google Scholar]
- De Gruijter, J.; Brus, D.J.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Knotters, M. Sampling for Natural Resource Monitoring; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).