Urban Aquatic Scene Expansion for Semantic Segmentation in Cityscapes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Efficient and resource-saving methodology: Our fusion model efficiently labels images with mixed urban and aquatic environments using the pretrained models Panoptic DeepLab and WaSR. This approach eliminates the need for retraining new networks, conserving significant time and computational resources.
- Versatile application across various environments: The model’s adaptability extends its application beyond the Cityscapes dataset, enhancing semantic segmentation performance in diverse fields such as environmental monitoring and underwater exploration.
- Comprehensive analysis of complex urban ecosystems: By integrating urban and aquatic segmentation, the model offers a more nuanced understanding of urban landscapes, particularly beneficial in coastal or riverine cities where water bodies are integral.
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
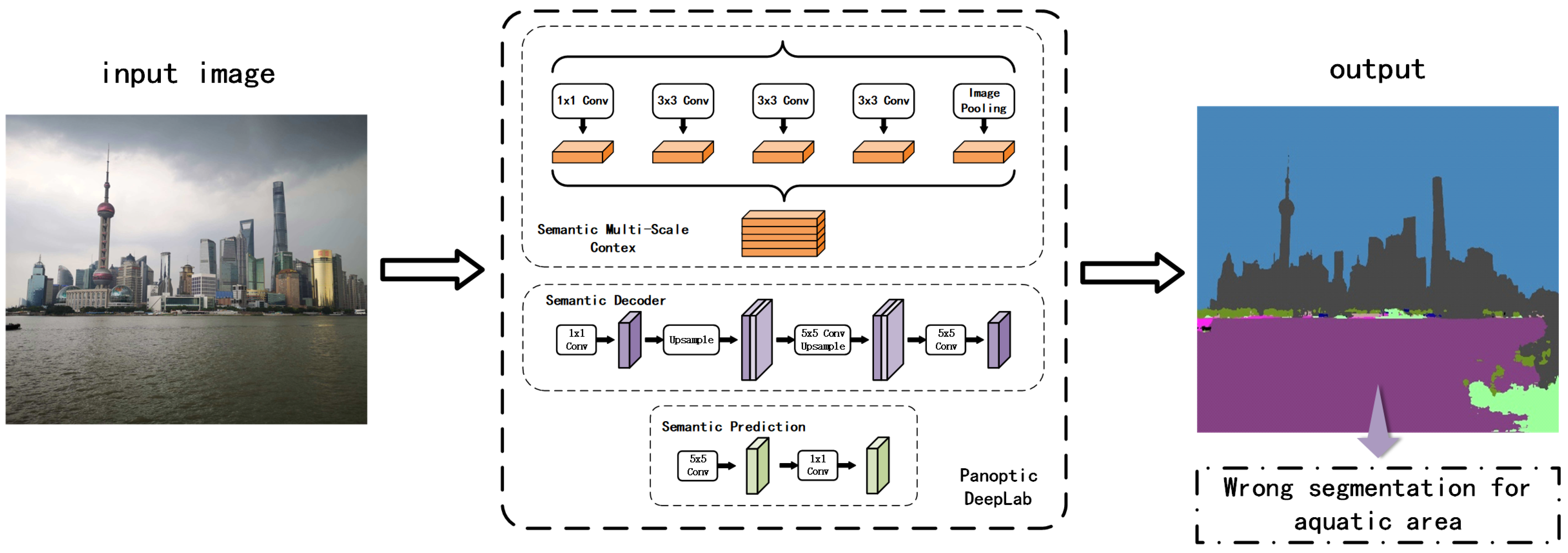
3.1. Panoptic DeepLab Trained on Cityscapes
- The dual-ASPP and dual-decoder modules enable the network to handle the intricacies of both semantic segmentation (categorizing areas into broad classes) and instance segmentation (identifying individual object instances).
- The shared backbone allows for feature extraction that is beneficial for both segmentation tasks, maximizing the use of learned features.
- The instance center regression facilitates the bottom-up approach for instance segmentation, identifying individual objects without needing region proposals.
- The efficient merging operation combines the outputs of both segmentation tasks to create a cohesive panoptic segmentation map, integrating both “thing” (individual objects) and “stuff” (amorphous regions like grass or sky) categories.
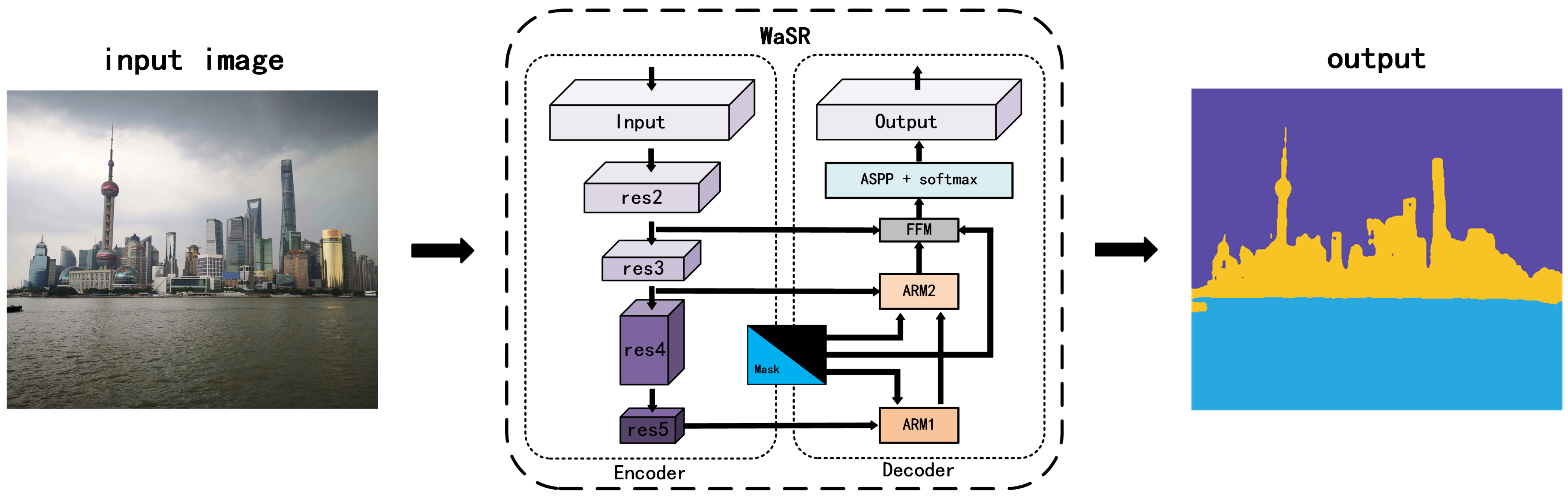
3.2. WaSR
- 1.
- Encoder–decoder architecture:
- (a)
- Encoder: Based on ResNet101 with atrous convolutions for extracting rich visual features.
- (b)
- Decoder: Integrates features from the encoder, upsampling them to construct the segmentation map. Includes multiple fusion modules for handling various water appearances.
- 2.
- Fusion modules:
- Essential for combining visual features with inertial measurements, addressing maritime challenges such as reflections and wakes.
- 3.
- Inertial measurement unit (IMU) integration:
- Incorporates IMU data to determine the horizon line and camera orientation, enhancing accuracy in ambiguous conditions.
- 4.
- IMU feature channel encoding:
- (a)
- Encoding methods: Drawing a horizon line, encoding a signed distance to the horizon, and creating a binary mask below the horizon.
- (b)
- These encoded channels are fused into the decoder for improved segmentation accuracy.
3.3. Model Fusion
4. Evaluation
4.1. Panoptic DeepLab Trained on Cityscapes
4.2. WaSR
4.3. Fusion Model
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, K.; Abe, H.; Otsuka, N.; Yasufuku, K.; Takahashi, A. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Walkability in the Main Urban Area of Xi’an. Urban Sci. 2022, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, D.; Jana, A.; Ramamritham, K. Quantifying Urban Surroundings Using Deep Learning Techniques: A New Proposal. Urban Sci. 2018, 2, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, V.; de Vries, W.T. Machine Learning Algorithms for Urban Land Use Planning: A Review. Urban Sci. 2021, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leya, R.S.; Jodder, P.K.; Rahaman, K.R.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Parida, D.; Islam, M.S. Spatial Variations of Urban Heat Island Development in Khulna City, Bangladesh: Implications for Urban Planning and Development. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 6, 865–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballouch, Z.; Hajji, R.; Poux, F.; Kharroubi, A.; Billen, R. A Prior Level Fusion Approach for the Semantic Segmentation of 3D Point Clouds Using Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Diao, W.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Chen, K.; Fu, K.; Gao, X. Npaloss: Neighboring Pixel Affinity Loss for Semantic Segmentation in High-Resolution Aerial Imagery. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 2, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, J.D.; Corstanje, R.; Harris, J.A. Bundling ecosystem services at a high resolution in the UK: Trade-offs and synergies in urban landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 1817–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The Cityscapes Dataset for Semantic Urban Scene Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 3213–3223. [Google Scholar]
- Vergaño-Salazar, J.G.; Meyer, J.F.; Córdova-Lepe, F.; Marín, E.D. Distribution model of toxic agents and runoff phenomenon in flat aquatic regions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1514, 012004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritikin, B.; Prochaska, J.X. AI based Out-Of-Distribution Analysis of Sea Surface Height Data. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.06072. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.A.; Ernstson, H. Contesting the Coast: Socioecological Cleavages and Coastal Planning in the Mississippi River Delta. Available online: https://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:su:diva-119412 (accessed on 7 December 2023).
- Vaishnav, M.; Cadene, R.; Alamia, A.; Linsley, D.; VanRullen, R.; Serre, T. Understanding the Computational Demands Underlying Visual Reasoning. Neural Comput. 2021, 34, 1075–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, R.; Sankur, O.; Jéron, T.; Markey, N.; Mentré, D. Repairing Real-Time Requirements. In Proceedings of the Automated Technology for Verification and Analysis, Virtual Event, 25–28 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C.Y.; Sham, C.W. Energy Efficient Fixed-point Inference System of Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 63rd International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Springfield, MA, USA, 9–12 August 2020; pp. 403–406. [Google Scholar]
- Tenorio, R.H.V.; Sham, C.W.; Vargas, D.V. Preliminary Study of Applied Binary Neural Networks for Neural Cryptography. In Proceedings of the 2020 Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference Companion. Association for Computing Machinery, Cancún, Mexico, 8–12 July 2020; pp. 291–292. [Google Scholar]
- Valencia, R.; Sham, C.W.; Sinnen, O. Evolved Binary Neural Networks Through Harnessing FPGA Capabilities. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Field-Programmable Technology (ICFPT), Tianjin, China, 9–13 December 2019; pp. 395–398. [Google Scholar]
- Valencia, R.; Sham, C.W.; Sinnen, O. Using Neuroevolved Binary Neural Networks to solve reinforcement learning environments. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems (APCCAS), Bangkok, Thailand, 11–14 November 2019; pp. 301–304. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C.Y.; Lau, F.C.M.; Sham, C.W. Fixed-Point Implementation of Convolutional Neural Networks for Image Classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Communications (ATC), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 18–20 October 2018; pp. 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, B.; Collins, M.D.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Huang, T.S.; Adam, H.; Chen, L.C. Panoptic-DeepLab: A Simple, Strong, and Fast Baseline for Bottom-Up Panoptic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 12472–12482. [Google Scholar]
- Bovcon, B.; Kristan, M. WaSR—A Water Segmentation and Refinement Maritime Obstacle Detection Network. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2021, 52, 12661–12674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Z.; Sham, C.W.; Lo, C.Y.; Cheung, W.; Yiu, C.Y. Sea View Extension for Semantic Segmentation in Cityscapes. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Conference on Applied System Innovation (ICASI), Chiba, Japan, 21–25 April 2023; pp. 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, X. A Multi-Task Model for Sea-Sky Scene Perception with Information Intersection. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Computing and Artificial Intelligence, Tianjin, China, 18–21 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, S.; Duan, J.; Aikaterini, M. A Superpixel-based Water Scene Segmentation Method by Sea-sky-line and Shoreline Detection. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Security, Pattern Analysis, and Cybernetics (SPAC), Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2021; pp. 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Seyedhosseini, M.; Tasdizen, T. Semantic Image Segmentation with Contextual Hierarchical Models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.J.; Hu, M.; Yang, H.; Tanaka, K. Design of low impact development in the urban context considering hydrological performance and life-cycle cost. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2020, 13, e12625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovcon, B.; Muhovič, J.; Pers, J.; Kristan, M. The MaSTr1325 dataset for training deep USV obstacle detection models. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Macau, China, 3–8 November 2019; pp. 3431–3438. [Google Scholar]
- Bovcon, B.; Muhovič, J.; Vranac, D.; Mozetic, D.; Pers, J.; Kristan, M. MODS—A USV-Oriented Object Detection and Obstacle Segmentation Benchmark. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 13403–13418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Shang, Y.; Wang, K.P. A Real-Time Sea-Sky-Line Detection Method under Complicated Sea-Sky Background. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 182–183, 1826–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Ren, H.; Song, Y.; Chang, S.; Zhao, Z.G. A Sea–Sky Line Detection Method Based on the RANSAC Algorithm in the Background of Infrared Sea–Land–Sky Images. J. Russ. Laser Res. 2021, 42, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Xiao, C.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yuan, H.; Xiu, S.; Zou, X.; Xie, C.H.; Li, Q. Adaptive Semantic Segmentation for Unmanned Surface Vehicle Navigation. Electronics 2020, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Bao, Y.; Wang, J.; Chu, H.; Zhao, N.; He, Y.; Liu, Y. Crop Row Segmentation and Detection in Paddy Fields Based on Treble-Classification Otsu and Double-Dimensional Clustering Method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Das, A. Modelling urban cooling island impact of green space and water bodies on surface urban heat island in a continuously developing urban area. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Qi, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Jia, J. Fully Convolutional Networks for Panoptic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Said, K.A.M.; Jambek, A.B. DNA Microarray Image Segmentation Using Markov Random Field Algorithm. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 2071, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Kuen, J.; Lin, Z.; Mordohai, P.; Chen, S. PRN: Panoptic Refinement Network. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–7 January 2023; pp. 3952–3962. [Google Scholar]
- Schachtschneider, J.; Brenner, C. Creating Multi-Temporal Maps of Urban Environments for Improved Localization of Autonomous Vehicles. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2020, XLIII-B2-2020, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Qi, X.; Chen, Y.; Qi, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Jia, J. Fully Convolutional Networks for Panoptic Segmentation With Point-Based Supervision. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 45, 4552–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ji, X.; Peng, K.; Wang, W.; Wang, S. PVONet: Point-voxel-based semi-supervision monocular three-dimensional object detection using LiDAR camera systems. J. Electron. Imaging 2023, 32, 053015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasperini, S.; Mahani, M.A.N.; Marcos-Ramiro, A.; Navab, N.; Tombari, F. Panoster: End-to-End Panoptic Segmentation of LiDAR Point Clouds. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 6, 3216–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodano, M.; Magistri, F.; Guadagnino, T.; Behley, J.; Stachniss, C. Robust Double-Encoder Network for RGB-D Panoptic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 4953–4959. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, P.Y.; Zhang, R.; Chen, T.; Hung, Y.P. Absolute Camera Pose Regression Using an RGB-D Dual-Stream Network and Handcrafted Base Poses. Sensors 2022, 22, 6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Qiao, Y.; Qu, Z.; Huang, Y. CASPPNet: A chained atrous spatial pyramid pooling network for steel defect detection. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 085403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanasutives, P.; Fukui, K.-I.; Numao, M.; Kijsirikul, B. Encoder-Decoder Based Convolutional Neural Networks with Multi-Scale-Aware Modules for Crowd Counting. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2020; pp. 2382–2389. [Google Scholar]
- Sholomov, D.L. Application of shared backbone DNNs in ADAS perception systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Vision, Online, 25–27 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Eicken, H.; Danielsen, F.; Sam, J.M.; Fidel, M.; Johnson, N.; Poulsen, M.K.; Lee, O.; Spellman, K.V.; Iversen, L.; Pulsifer, P.L.; et al. Connecting Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approaches in Environmental Observing. Bioscience 2021, 71, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, U.; Mishra, S.; Dash, K. An IoT and Semi-Supervised Learning-Based Sensorless Technique for Panel Level Solar Photovoltaic Array Fault Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Jung, S.; Yun, H.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, S.; Choo, J. RobustNet: Improving Domain Generalization in Urban-Scene Segmentation via Instance Selective Whitening. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual, 29–25 June 2021; pp. 11575–11585. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, M.; Li, A.Q. Efficient LiDAR-based In-water Obstacle Detection and Segmentation by Autonomous Surface Vehicles in Aquatic Environments. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 5387–5394. [Google Scholar]
- Barman, R.; Ehrmann, M.; Clematide, S.; Oliveira, S.A.; Kaplan, F. Combining Visual and Textual Features for Semantic Segmentation of Historical Newspapers. arXiv 2020, arXiv:abs/2002.06144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, F.M.; Akyildiz, Z.; Pino-Ortega, J.; Rico-González, M. Validity and Reliability of the Inertial Measurement Unit for Barbell Velocity Assessments: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coviello, G.; Avitabile, G. Multiple Synchronized Inertial Measurement Unit Sensor Boards Platform for Activity Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 8771–8777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neagoe, I.C.; Coca, M.; Vaduva, C.; Datcu, M. Cross-Bands Information Transfer to Offset Ambiguities and Atmospheric Phenomena for Multispectral Data Visualization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 11297–11310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Chung, D.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, A.; Yoon, H.K. In-water visual ship hull inspection using a hover-capable underwater vehicle with stereo vision. J. Field Robot. 2018, 36, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prunier, J.G.; Poésy, C.; Dubut, V.; Veyssière, C.; Loot, G.; Poulet, N.; Blanchet, S. Quantifying the individual impact of artificial barriers in freshwaters: A standardized and absolute genetic index of fragmentation. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 2566–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.X.; Phang, S.K. Classification and Detection of Obstacles for Rover Navigation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2523, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Liu, D.; Du, J.H.; zheng Li, Y. Research on Visual Perception for Coordinated Air–Sea through a Cooperative USV-UAV System. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzki, G.; Nielsen, I.E.; Golińska-Dawson, P.; Bocewicz, G.; Banaszak, Z.A. Reactive UAV Fleet’s Mission Planning in Highly Dynamic and Unpredictable Environments. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Humne, A.; Bucknall, R.W.G.; Englot, B.; Liu, Y. A Fully-Autonomous Framework of Unmanned Surface Vehicles in Maritime Environments Using Gaussian Process Motion Planning. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 48, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, S.; Kalogeraki, E.M.; Papastergiou, S.; Douligeris, C. Detecting Sophisticated Attacks in Maritime Environments using Hybrid Situational Awareness. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Disaster Management (ICT-DM), Paris, France, 18–20 December 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Caro, M.C.; Huang, H.Y.; Cerezo, M.; Sharma, K.; Sornborger, A.T.; Cincio, L.; Coles, P.J. Generalization in quantum machine learning from few training data. Nat. Commun. 2021, 13, 4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmes, A.; Alemohammad, S.H.; Avery, R.; Caylor, K.K.; Eastman, J.R.; Fishgold, L.; Friedl, M.A.; Jain, M.; Kohli, D.; Bayas, J.C.L.; et al. Accounting for Training Data Error in Machine Learning Applied to Earth Observations. Remote. Sens. 2019, 12, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Fu, C.; Xie, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Sham, C.W. Uncertainty-aware deep co-training for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 149, 106051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Fu, C.; Xie, H.; Zheng, X.; Geng, R.; Sham, C.W. Uncertainty teacher with dense focal loss for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 149, 106034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M. Identification of Night Time Poor Visibility Areas in Urban Streets; CSIR-NIScPR: New Delhi, India, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gudwani, H.; Singh, V.J.; Mahajan, S.; Mittal, D.; Das, A. Identification of poor visibility conditions in urban settings. In Proceedings of the 2017 8th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Delhi, India, 3–5 July 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Malygin, I.G.; Tarantsev, A.A. On ensuring the safe movement of emergency service vehicles under hazardous driving conditions. Pozharovzryvobezopasnost/Fire Explos. Saf. 2022, 30, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicco, D.; Jurman, G. The advantages of the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) over F1 score and accuracy in binary classification evaluation. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.Y.; Ma, L.; Sham, C.W. CNN Accelerator with Non-Blocking Network Design. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 10th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Kyoto, Japan, 12–15 October 2021; pp. 813–815. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, C.Y.; Sham, C.W.; Fu, C. Novel CNN Accelerator Design With Dual Benes Network Architecture. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 59524–59529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| ID | Name | RGB Value | Color Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | unlabeled | 0, 0, 0 | Black |
| 1 | ego vehicle | 0, 0, 0 | Black |
| 2 | rectification border | 0, 0, 0 | Black |
| 3 | out of roi | 0, 0, 0 | Black |
| 4 | static | 0, 0, 0 | Black |
| 5 | dynamic | 111, 74, 0 | Dark brown |
| 6 | ground | 81, 0, 81 | Purple |
| 7 | road | 128, 64, 128 | Medium purple |
| 8 | sidewalk | 244, 35, 232 | Bright pink |
| 9 | parking | 250, 170, 160 | Light salmon |
| 10 | rail track | 230, 150, 140 | Light taupe |
| 11 | building | 70, 70, 70 | Dim gray |
| 12 | wall | 102, 102, 156 | Slate gray |
| 13 | fence | 190, 153, 153 | Dusty rose |
| 14 | guard rail | 180, 165, 180 | Grayish-pink |
| 15 | bridge | 150, 100, 100 | Sienna |
| 16 | tunnel | 150, 120, 90 | Olive |
| 17 | pole | 153, 153, 153 | Gray |
| 18 | polegroup | 153, 153, 153 | Gray |
| 19 | traffic light | 250, 170, 30 | Yellow |
| 20 | traffic sign | 220, 220, 0 | Electric yellow |
| 21 | vegetation | 107, 142, 35 | Olive green |
| 22 | terrain | 152, 251, 152 | Pale green |
| 23 | sky | 70, 130, 180 | Steel blue |
| 24 | person | 220, 20, 60 | Crimson |
| 25 | rider | 255, 0, 0 | Red |
| 26 | car | 0, 0, 142 | Deep Blue |
| 27 | truck | 0, 0, 70 | Navy Blue |
| 28 | bus | 0, 60, 100 | Dark cerulean |
| 29 | caravan | 0, 0, 90 | Dark blue |
| 30 | trailer | 0, 0, 110 | Dark midnight blue |
| 31 | train | 0, 80, 100 | Dark teal |
| 32 | motorcycle | 0, 0, 230 | Blue |
| 33 | bicycle | 119, 11, 32 | Maroon |
| 34 | license plate | 0, 0, 142 | Deep blue |
| ID | Name | RGB Value | Color Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Obstacle | 247, 195, 37 | Goldenrod |
| 1 | Water | 41, 167, 224 | Dodger blue |
| 2 | Sky | 90, 75, 164 | Dark purple |
| Method | PQ | AP | MIoUorigin | MIoUwater |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panoptic DeepLab | 63.0% | 35.3% | 80.5% | 76.47% |
| Method | Pr | Re | F1 | MIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WaSR | 94.60% | 96.50% | 95.50% | 99.80% |
| Method | MIoU | Dataset |
|---|---|---|
| WaSR | 99.80% | MaSTr1325 |
| Panoptic DeepLab | 76.47% | Cityscapes |
| Fusion Model (Ours) | 81.46% | Cityscapes |
| ID | Name | RGB Value | Color Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | unlabeled | 0, 0, 0 | Black |
| 1 | ego vehicle | 0, 0, 0 | Black |
| 2 | rectification border | 0, 0, 0 | Black |
| 3 | out of roi | 0, 0, 0 | Black |
| 4 | static | 0, 0, 0 | Black |
| 5 | dynamic | 111, 74, 0 | Dark brown |
| 6 | ground | 81, 0, 81 | Purple |
| 7 | road | 128, 64, 128 | Medium purple |
| 8 | sidewalk | 244, 35, 232 | Bright pink |
| 9 | parking | 250, 170, 160 | Light salmon |
| 10 | rail track | 230, 150, 140 | Light taupe |
| 11 | building | 70, 70, 70 | Dim gray |
| 12 | wall | 102, 102, 156 | Slate gray |
| 13 | fence | 190, 153, 153 | Dusty rose |
| 14 | guard rail | 180, 165, 180 | Grayish-pink |
| 15 | bridge | 150, 100, 100 | Sienna |
| 16 | tunnel | 150, 120, 90 | Olive |
| 17 | pole | 153, 153, 153 | Gray |
| 18 | polegroup | 153, 153, 153 | Gray |
| 19 | traffic light | 250, 170, 30 | Yellow |
| 20 | traffic sign | 220, 220, 0 | Electric yellow |
| 21 | vegetation | 107, 142, 35 | Olive green |
| 22 | terrain | 152, 251, 152 | Pale green |
| 23 | sky | 70, 130, 180 | Steel blue |
| 24 | person | 220, 20, 60 | Crimson |
| 25 | rider | 255, 0, 0 | Red |
| 26 | car | 0, 0, 142 | Deep blue |
| 27 | truck | 0, 0, 70 | Navy blue |
| 28 | bus | 0, 60, 100 | Dark cerulean |
| 29 | caravan | 0, 0, 90 | Dark blue |
| 30 | trailer | 0, 0, 110 | Dark midnight blue |
| 31 | train | 0, 80, 100 | Dark teal |
| 32 | motorcycle | 0, 0, 230 | Blue |
| 33 | bicycle | 119, 11, 32 | Maroon |
| 34 | license plate | 0, 0, 142 | Deep blue |
| 35 | water | 41, 167, 224 | Dodger blue |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, Z.; Lo, C.-Y.; Wu, R.; Ma, L.; Sham, C.-W. Urban Aquatic Scene Expansion for Semantic Segmentation in Cityscapes. Urban Sci. 2024, 8, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8020023
Yue Z, Lo C-Y, Wu R, Ma L, Sham C-W. Urban Aquatic Scene Expansion for Semantic Segmentation in Cityscapes. Urban Science. 2024; 8(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Zongcheng, Chun-Yan Lo, Ran Wu, Longyu Ma, and Chiu-Wing Sham. 2024. "Urban Aquatic Scene Expansion for Semantic Segmentation in Cityscapes" Urban Science 8, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8020023
APA StyleYue, Z., Lo, C.-Y., Wu, R., Ma, L., & Sham, C.-W. (2024). Urban Aquatic Scene Expansion for Semantic Segmentation in Cityscapes. Urban Science, 8(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/urbansci8020023






