Dental X-ray Identification System Based on Association Rules Extracted by k-Symbol Fractional Haar Functions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
3. Mathematical Design by k-Symbol FHF
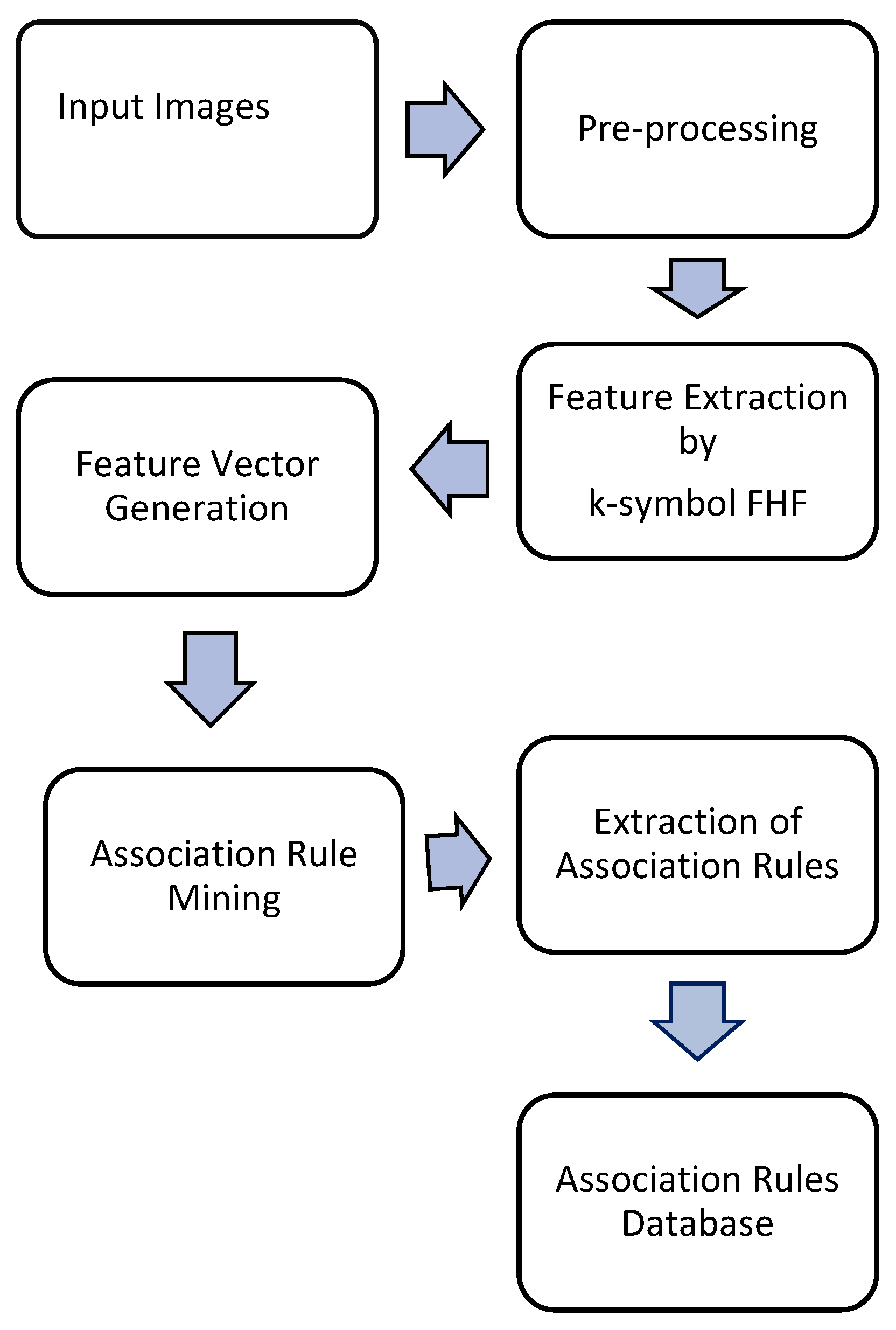
4. Proposed DIS
- Step1: Use image cropping and contrast enhancement as part of the pre-processing of the input images to define the area of interest (ROI) for the image extraction step.
- Step 2: extraction of features from teeth images.
- Step 3: create image vector.
- Step 4: employ AR mining utilizing the Apriori algorithm.
- Step 5: extraction of ARs.
4.1. Data Pre-Processing
- 1-
- Convert the input dental image into a grayscale image.
- 2-
- Calculate the frequency of the pixel value occurrence for the input dental image.
- 3-
- Find the cumulative occurrence of the pixel value occurrence.
4.2. Feature Extraction
- Read the dental image and convert it to a grayscale image.
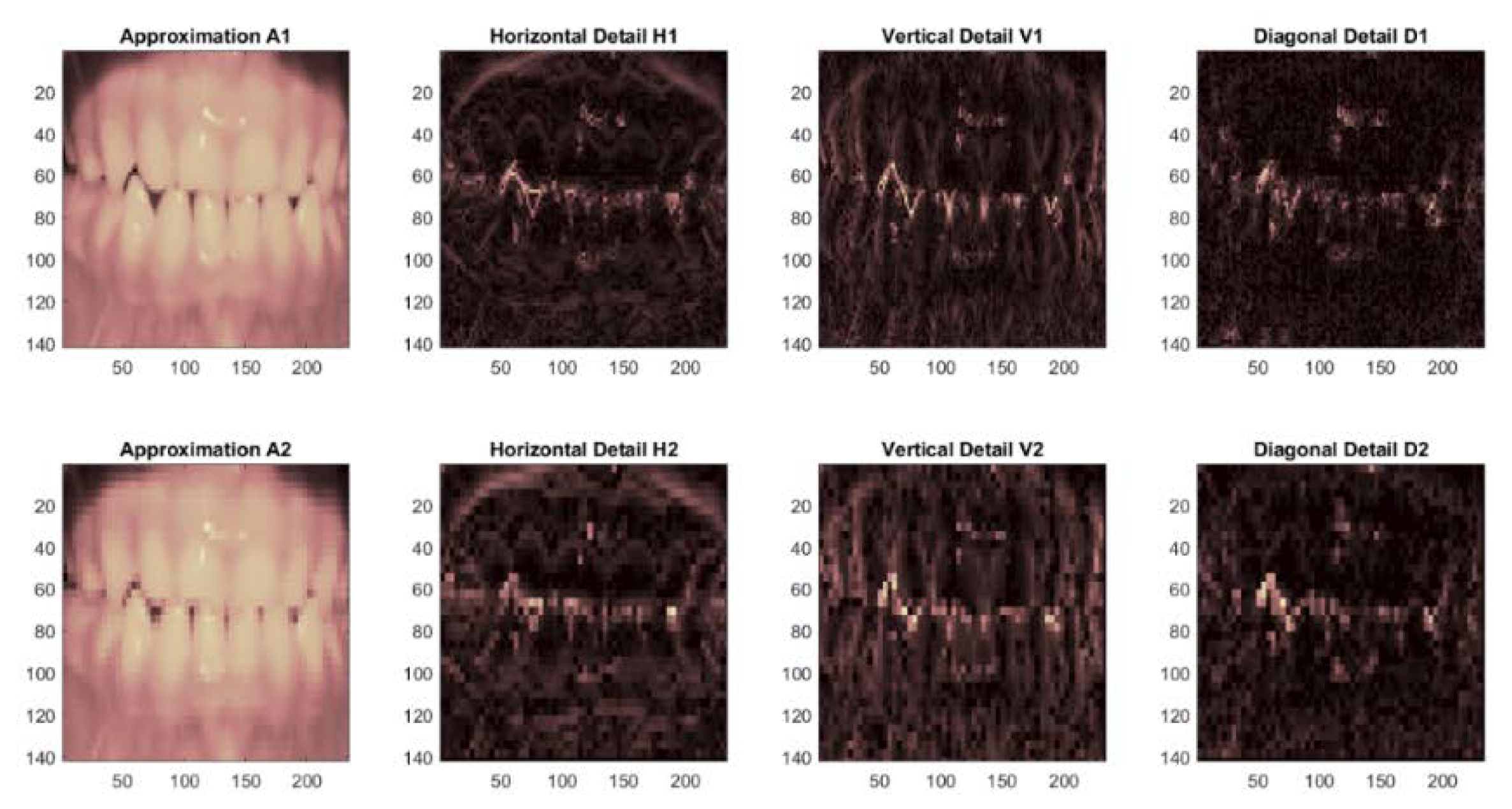
- Using the 2D wavelet decomposition-type k-symbol FHF wavelet and then calculating the “approximation coefficients” matrix cA with the horizontal (cH), vertical (cV), and diagonal (cD) “detail coefficient” matrixes. These are obtained from the wavelet decomposition of the input image.
- Store the cA matrix as an array in a feature vector. In the experiments, 12 features are extracted for every contribution image, which are signified by the estimate coefficients matrix cA at level 2 of the k-symbol FHF wavelet.
- Save the extracted images in a preparation database.
- Repeat the stages from 1 to 3 for all input dental images.
- End.
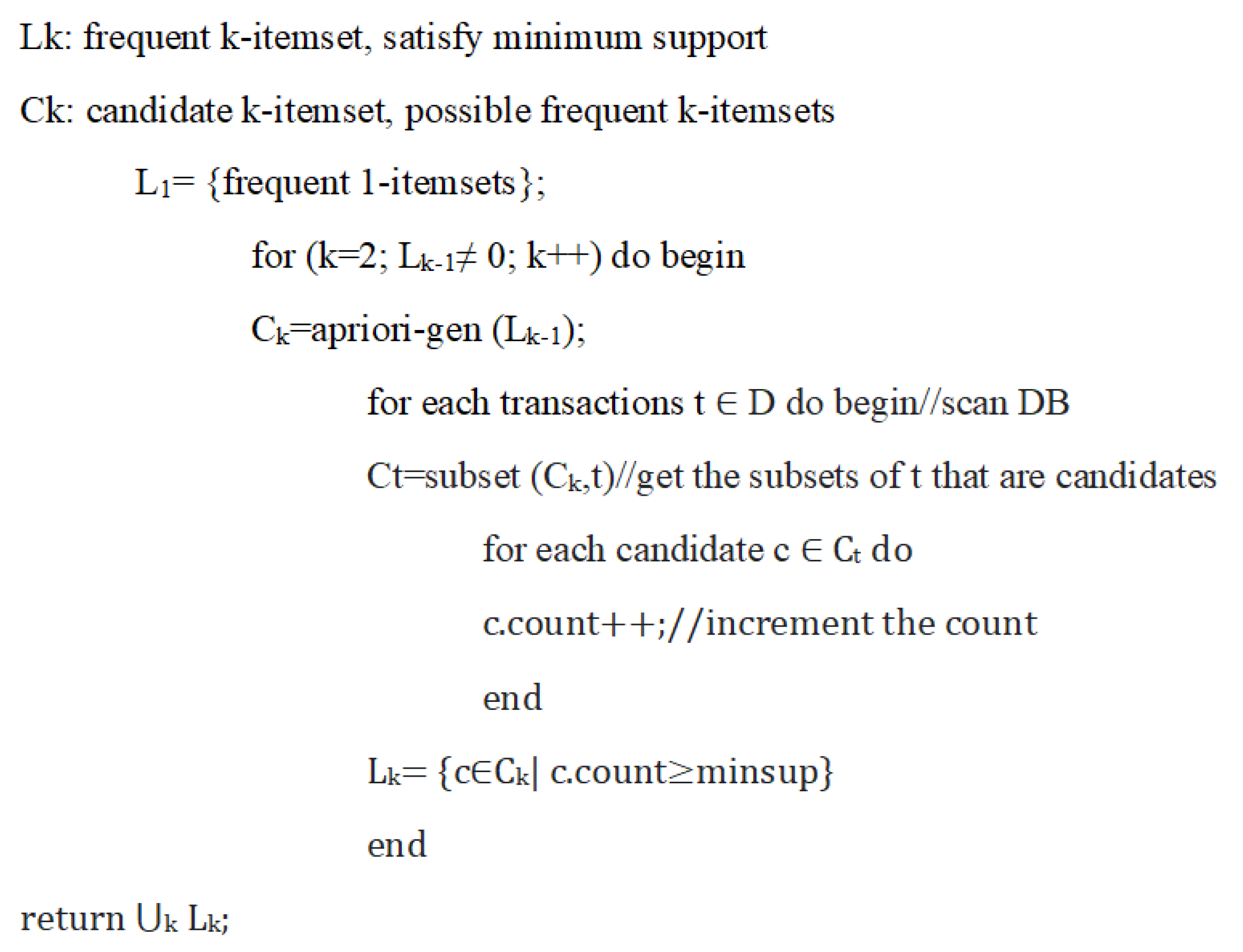
4.3. Association Rule Mining
- 1-
- Finding all frequent item sets, X, such that support (X) ≥ the support threshold.
- Determine the dental image database item set’s level of support and then determine the minimal level of support and confidence.
- Pick every higher support value available in the image database.
- Find every rule with a higher confidence value.
- Arrange the rules in descending priority.
- 1-
- If the image satisfies all of the rules, then the values of the image feature match the values of the instructions in the training set.
- 2-
- The types of stages that will be developed depend on how well the image feature values meet the guidelines.
- 3-
- If the image features do not fulfill any part of the instructions, the values of the image feature do not match the procedures [42].
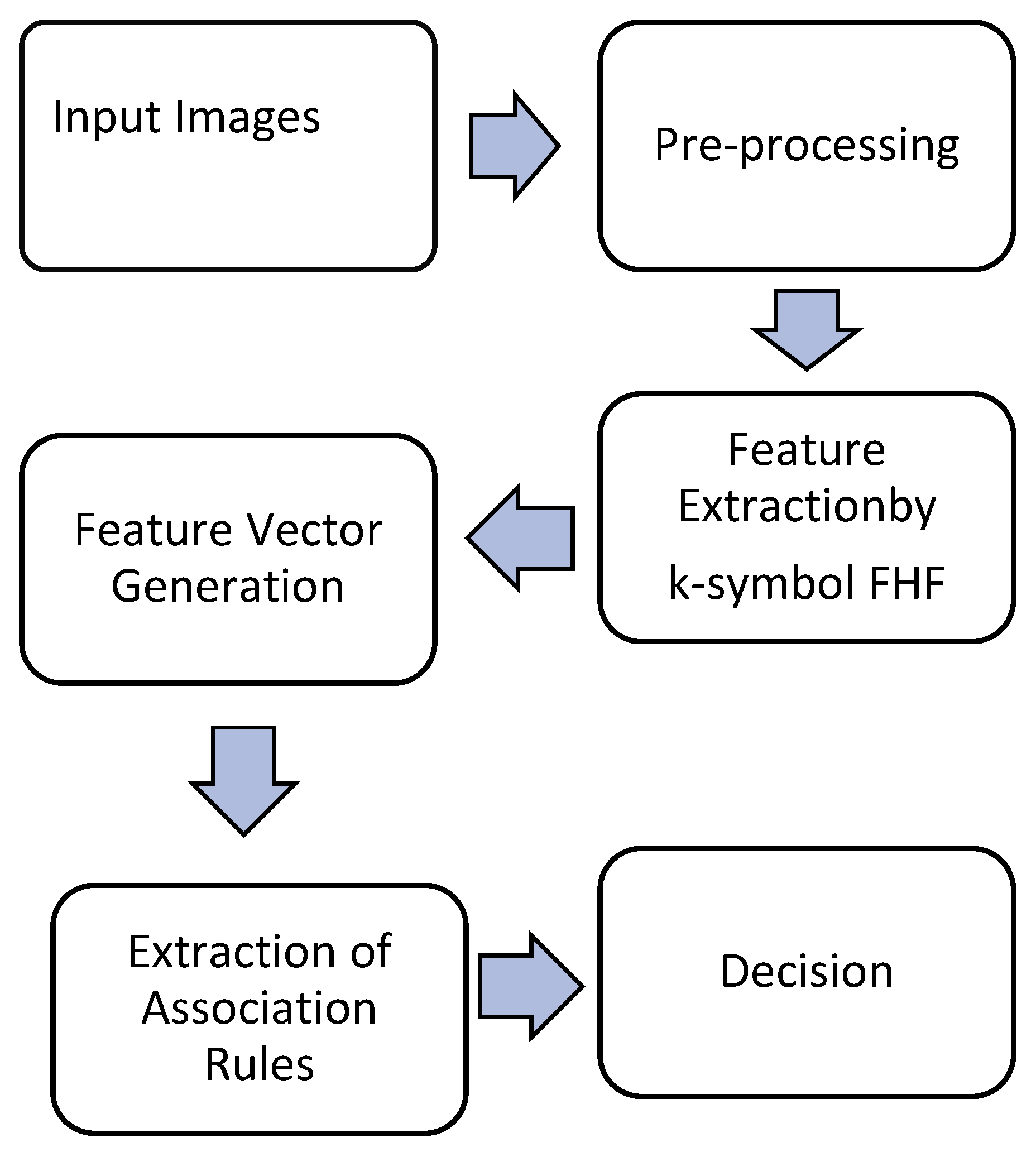
4.4. Testing Phase
4.5. Inquiry Stages
- Dental image acquisition;
- Dental image pre-processing;
- Dental image feature extraction;
- Association rules extraction.
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Assessment Standards
5.2. The Results
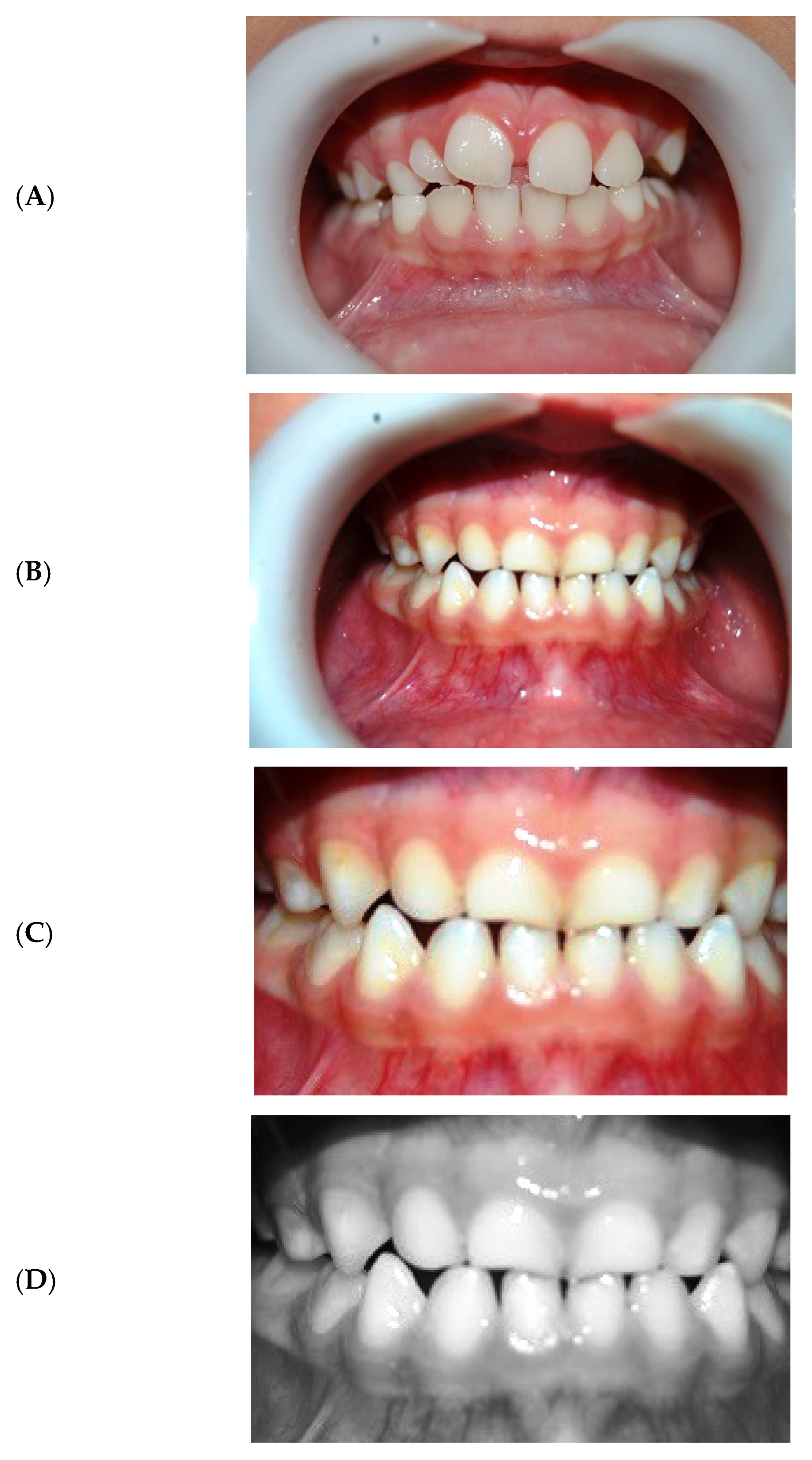
5.2.1. Result of Pre-Processing
5.2.2. Result of Image Extraction Phase
5.2.3. Result of Association Rules Step
5.2.4. Result of Testing Phase
- 1-
- The images utilized to assess the applicability of this study came from a single source and were obtained by several technologies.
- 2-
- The small dataset that was employed had an impact on the proposed identification model’s accuracy. The vast dataset, on the other hand, will help to construct a more robust dental identification model.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teng, X.; Gong, Y. Research on application of machine learning in data mining. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 392, 062202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, I.; Dssouli, R.; Serhani, M.A. Big Data Pre-Processing: A Quality Framework. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Congress on Big Data, New York, NY, USA, 27 June–2 July 2015; pp. 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, P.-Y.; Li, S.-H. Content-Based image retrieval using association rule mining with soft relevance feedback. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2006, 17, 1108–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veroneze, R.; Cruz Tfaile Corbi, S.; Roque da Silva, B.; Rocha, C.d.; Maurer-Morelli, C.V.; Perez Orrico, S.R.; Cirelli, J.A.; Von Zuben, F.J.; Mantuaneli Scarel-Caminaga, R. Using association rule mining to jointly detect clinical features and differentially expressed genes related to chronic inflammatory diseases. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, J.; Bhosle, U. Image mining using association rule for medical image dataset. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 85, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, N.; Xiao, H. Inferring implications in semantic maps via the Apriori algorithm. Lingua 2020, 239, 102808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, J.; Imam, T.; Tickle, K.S.; Chen, Y.-P.P. Association rule mining to detect factors which contribute to heart disease in males and females. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 1086–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, R.; Ramírez, J.; Górriz, J.; Puntonet, C.G.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Association rule-based feature selection method for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. Expert Syst. Appl. 2012, 39, 11766–11774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.J.; Liu, Y.-H.; Tsai, H.-M.; Lin, H.-H.; Wu, H.-W. Mining frequent patterns in image databases with 9D-SPA representation. J. Syst. Softw. 2009, 82, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.J.; Hong, R.-W.; Ko, W.-M.; Tsao, W.-K.; Lin, H.-H. Mining spatial association rules in image databases. Inf. Sci. 2007, 177, 1593–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, G.; Nassar, D.; Haj-Said, E.; Chen, H.; Nomir, O.; Zhou, J.; Howell, R.; Ammar, H.H.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M.; Jain, A.K. Towards An Automated Dental Identification System (ADIS). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biometric Authentication, Hong Kong, China, 15–17 July 2004; pp. 789–796. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, R.W.; Yahya, H.; Mohammed, A.J.; Al-Saidi, N.M.; Baleanu, D. Mathematical Design Enhancing Medical Images Formulated by a Fractal Flame Operator. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2022, 32, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Q.; Liu, M.; Ning, B.; Zhao, F.; Dong, L.; Kong, L.; Hui, M.; Zhao, Y. Image Dehazing Based on Local and Non-Local Features. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Yang, F.; Yang, Q. A Study of Adaptive Fractional-Order Total Variational Medical Image Denoising. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dai, L. Image Enhancement Based on Rough Set and Fractional Order Differentiator. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Y. A Novel Adaptive Fractional Differential Active Contour Image Segmentation Method. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saidi, N.M.; Al-Bundi, S.S.; Al-Jawari, N.J. A hybrid of fractal image coding and fractal dimension for an efficient retrieval method. Comput. Appl. Math. 2018, 37, 996–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, M.; Shrivastava, M.; Rizvi, M. Image Mining: A New Approach for Data Mining Based on Texture. In Proceedings of the 2012 Third International Conference on Computer and Communication Technology, Allahabad, India, 23–25 November 2012; pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rajendran, P.; Madheswaran, M. An improved image mining technique for brain tumour classification using efficient classifier. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1001.1988. [Google Scholar]
- Khodaskar, A.; Ladhake, S. Image Mining: An Overview of Current Research. In Proceedings of the 2014 Fourth International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies, Bhopal, India, 7–9 April 2014; pp. 433–438. [Google Scholar]
- Gajjar, T.; Chauhan, N. A review on image mining frameworks and techniques. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2012, 3, 4064–4066. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, N.; KarÁ¢a, W.B.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Banerjee, S.; Salem, M.A.; Azar, A.T. Image mining framework and techniques: A review. Int. J. Image Min. 2015, 1, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hsu, W.; Lee, M.L. Image Mining: Issues, Frameworks and Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGKDD International Workshop on Multimedia Data Mining (MDM/KDD’01), San Francisco, CA, USA, 26 August 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, S.; Singh, O.; Nagaria, D. Analysis and comparison of wavelet transforms for denoising MRI image. Biomed. Pharmacol. J. 2017, 10, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.; Lee, M.L.; Zhang, J. Image mining: Trends and developments. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2002, 19, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Zhanhuai, L.; Yong, W.; Longbo, Z. Joining Associative Classifier for Medical Images. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Hybrid Intelligent Systems (HIS’05), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 6–9 November 2005; p. 6. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, V.S.; Wang, M.-H.; Su, J.-H. A New Method for Image Classification by Using Multilevel Association Rules. In Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW’05), Tokyo, Japan, 3–4 April 2005; p. 1180. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, M.X.; Traina, A.J.; Traina, C.; Azevedo-Marques, P.M. An association rule-based method to support medical image diagnosis with efficiency. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2008, 10, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.X.; Bugatti, P.H.; Traina, C., Jr.; Marques, P.M.; Rosa, N.A.; Traina, A.J. Supporting content-based image retrieval and computer-aided diagnosis systems with association rule-based techniques. Data Knowl. Eng. 2009, 68, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, P.; Madheswaran, M. Hybrid medical image classification using association rule mining with decision tree algorithm. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1001.3503. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva, S.F.; Ribeiro, M.X.; Neto, J.d.E.B.; Traina, C., Jr.; Traina, A.J. Improving the ranking quality of medical image retrieval using a genetic feature selection method. Decis. Support Syst. 2011, 51, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.J.; Giveki, D. Automatic detection of erythemato-squamous diseases using PSO–SVM based on association rules. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangat, V.; Vig, R. Dynamic PSO-based associative classifier for medical datasets. IETE Tech. Rev. 2014, 31, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, I.; Amin, R. Numerical solution of a class of delay differential and delay partial differential equations via Haar wavelet. Appl. Math. Model. 2016, 40, 10286–10299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattani, C. Haar wavelet fractional derivative. Proc. Est. Acad. Sci. 2022, 71, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.; Pariguan, E. On hypergeometric functions and Pochhammer k-symbol. arXiv 2004, arXiv:math/0405596. [Google Scholar]
- Mubeen, S.; Habibullah, G. k-Fractional integrals and application. Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sci. 2012, 7, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Girija, O.; Elayidom, M.S. Overview of Image Retrieval Techniques. Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, R.E.; Eddins, S.L.; Gonzalez, R.C. Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB; Pearson: Noida, India, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ordonez, C. Association rule discovery with the train and test approach for heart disease prediction. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2006, 10, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, R.; KUMAR, L.; Tiwary, U. Exploring spatial ARM (Spatial Association Rule Mining) for geo-decision support system. J. Comput. Sci. 2007, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Padmapriya, A.; Maragatham, K. Priority Based Apriori Algorithm for Cancer Prediction Using Fuzzy Classification. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2013, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
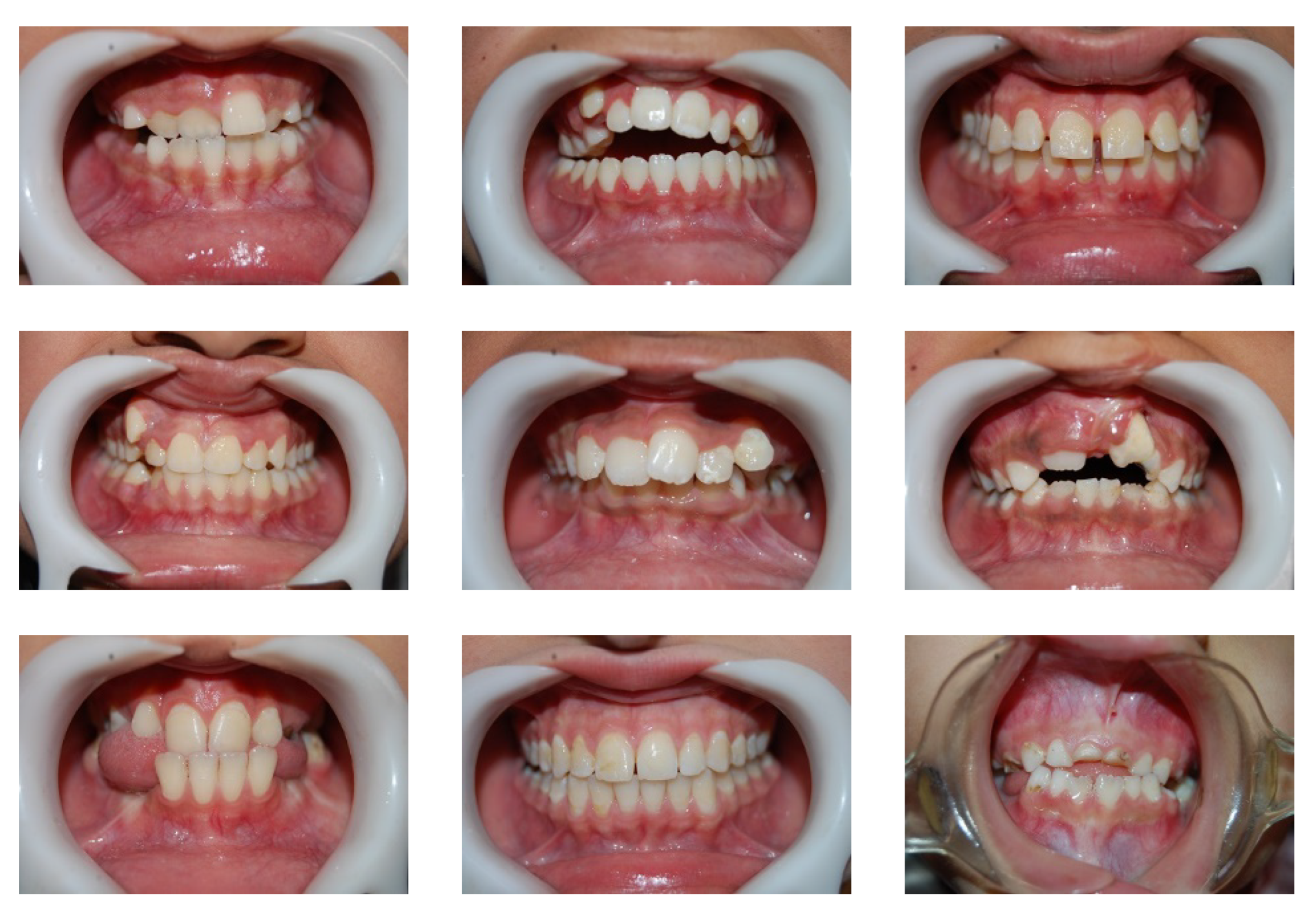


| Images | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 | F10 | F11 | F12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 111 | 113 | 117 | 87 | 116 | 126 | 123 | 94 | 84 | 98 | 95 | 89 |
| 2 | 127 | 171 | 136 | 49 | 109 | 146 | 123 | 109 | 113 | 122 | 104 | 117 |
| 3 | 135 | 155 | 142 | 51 | 142 | 151 | 138 | 97 | 88 | 96 | 93 | 92 |
| 4 | 124 | 160 | 148 | 77 | 125 | 137 | 129 | 92 | 91 | 128 | 108 | 96 |
| 5 | 114 | 150 | 113 | 83 | 114 | 147 | 126 | 104 | 120 | 132 | 106 | 119 |
| 6 | 120 | 129 | 96 | 92 | 140 | 123 | 118 | 76 | 119 | 119 | 109 | 110 |
| 7 | 94 | 140 | 116 | 58 | 121 | 145 | 151 | 105 | 117 | 136 | 133 | 94 |
| 8 | 117 | 170 | 163 | 85 | 109 | 114 | 117 | 107 | 101 | 112 | 110 | 98 |
| 9 | 135 | 170 | 163 | 95 | 138 | 152 | 146 | 97 | 106 | 82 | 95 | 77 |
| 10 | 99 | 149 | 141 | 81 | 111 | 141 | 140 | 104 | 96 | 124 | 107 | 102 |
| 77, 91, 92, 124, 125, 129, 137, 148, → 160, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 77, 91, 92, 124, 125, 129, 137, 160, → 148, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 77, 91, 92, 124, 125, 129, 148, 160, → 137, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 77, 91, 92, 124, 125, 137, 148, 160, → 129, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 77, 91, 92, 124, 129, 137, 148, 160, → 125, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 77, 91, 92, 125, 129, 137, 148, 160, → 124, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 77, 91, 124, 125, 129, 137, 148, 160, → 92, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 77, 92, 124, 125, 129, 137, 148, 160, → 91, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 91, 92, 124, 125, 129, 137, 148, 160, → 77, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 84, 87, 94, 111, 113, 116, 117, 123, → 126, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 84, 87, 94, 111, 113, 116, 117, 126, → 123, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 84, 87, 94, 111, 113, 116, 123, 126, → 117, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 84, 87, 94, 111, 113, 117, 123, 126, → 116, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 84, 87, 94, 111, 116, 117, 123, 126, → 113, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 84, 87, 94, 113, 116, 117, 123, 126, → 111, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 84, 87, 111, 113, 116, 117, 123, 126, → 94, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 84, 94, 111, 113, 116, 117, 123, 126, → 87, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| 87, 94, 111, 113, 116, 117, 123, 126, → 84, support: 2.500000 × 10−1, confidence: 1 |
| Images | No. of Rules Input in Image | No. of Rules Input in Image | Count Rule % | Similarity Matching % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | 23 | 6 | 5 | 5/6 = 83.33 |
| Second | 44 | 8 | 7 | 6/8 = 75.0 |
| Third | 26 | 6 | 5 | 7/8 = 87.5 |
| Fourth | 32 | 7 | 6 | 6/7 = 85.71 |
| Fifth | 48 | 8 | 7 | 7/8 = 87.5 |
| Average | 83.808% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlSheikh, M.H.; Al-Saidi, N.M.G.; Ibrahim, R.W. Dental X-ray Identification System Based on Association Rules Extracted by k-Symbol Fractional Haar Functions. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6110669
AlSheikh MH, Al-Saidi NMG, Ibrahim RW. Dental X-ray Identification System Based on Association Rules Extracted by k-Symbol Fractional Haar Functions. Fractal and Fractional. 2022; 6(11):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6110669
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlSheikh, Mona Hmoud, Nadia M. G. Al-Saidi, and Rabha W. Ibrahim. 2022. "Dental X-ray Identification System Based on Association Rules Extracted by k-Symbol Fractional Haar Functions" Fractal and Fractional 6, no. 11: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6110669
APA StyleAlSheikh, M. H., Al-Saidi, N. M. G., & Ibrahim, R. W. (2022). Dental X-ray Identification System Based on Association Rules Extracted by k-Symbol Fractional Haar Functions. Fractal and Fractional, 6(11), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract6110669









