Fractional-Order Control of Fluid Composition Conductivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
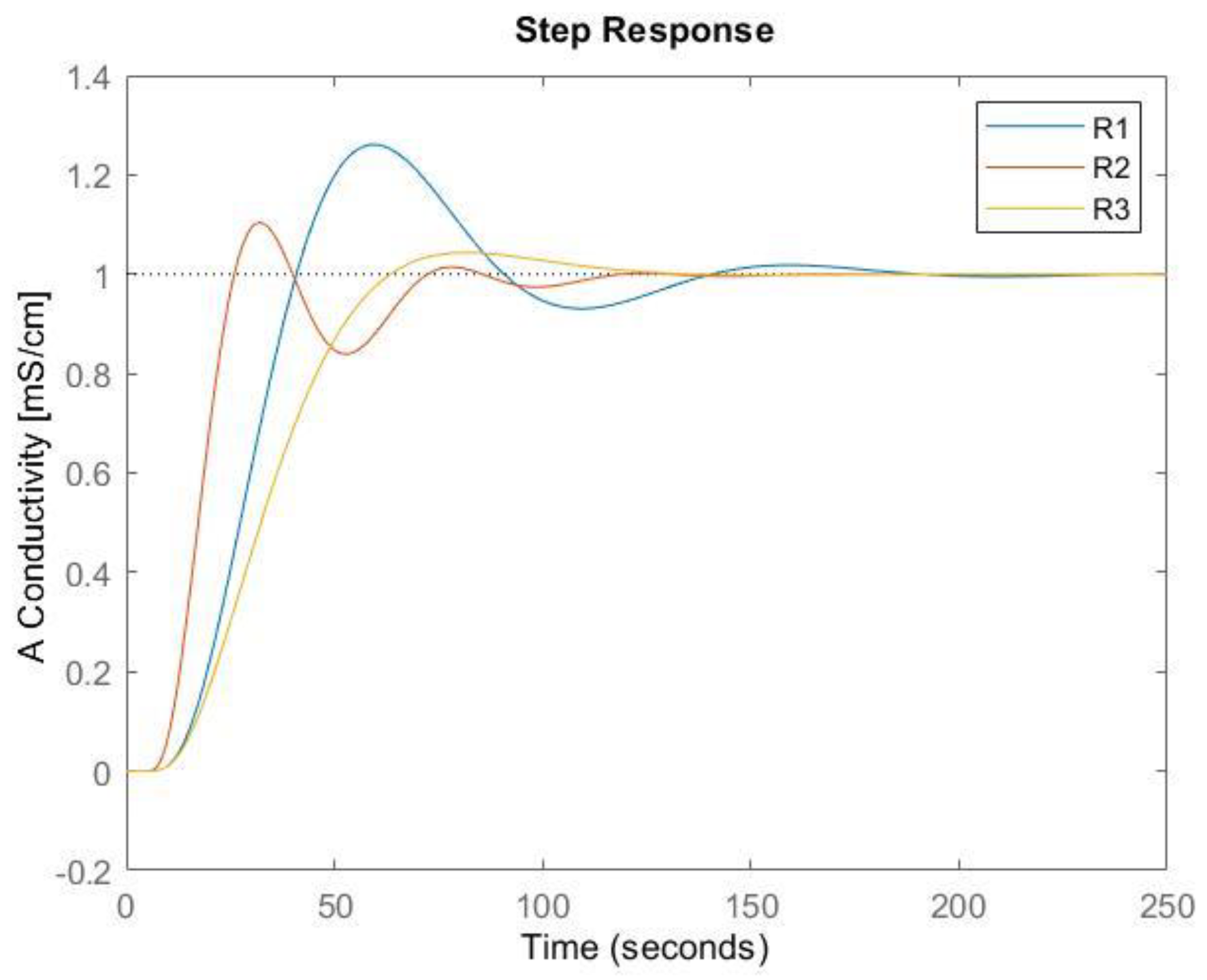
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Jafar, T.H.; Nitsch, D.; Neuen, B.L.; Perkovic, V. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2021, 398, 786–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnani, P.; Remuzzi, G.; Glassock, R.; Levin, A.; Jager, K.J.; Tonelli, M.; Massy, Z.; Wanner, C.; Anders, H.-J. Chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanholder, R. Future Directions for Dialysis. Kidney Dial. 2022, 2, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainol, M.F.; Farook, R.S.M.; Hassan, R.; Halim, A.H.A.; Rejab, M.R.A.; Husin, Z. A New IoT Patient Monitoring System for Hemodialysis Treatment. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Open Systems (ICOS), Pulau Pinang, Malaysia, 19–21 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.-Y.; Wu, X.-Q.; Wang, L.-H.; Li, L. Design of Real-time Detection System for Hemodialysis Machine Operating Parameters. J. Appl. Sci. Eng. Innov. 2018, 5, 113–116. [Google Scholar]
- Klespitz, J.; Takács, M.; Kovács, L. Application of Fuzzy Logic in Hemodialysis Equipment. In Proceedings of the IEEE 18th International Conference on Intelligent Engineering Systems INES 2014, Tihany, Hungary, 3–5 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bosetto, A.; Bene, B.; Petitclerc, T. Sodium management in dialysis by conductivity. Adv. Ren. Replace. Ther. 1999, 6, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, F.; Buoncristiani, U.; Canaud, B.; Köhler, H.; Petitclerc, T.; Zucchelli, P. Haemodialysis with on-line monitoring equipment: Tools or toys? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliger, A.S. Maintaining safety in the dialysis facility. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrology 2015, 10, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polaschegg, H.D. Red Blood Cell Damage from Extracorporeal Circulation in Hemodialysis. In Seminars in Dialysis; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2009; Volume 22, pp. 524–531. [Google Scholar]
- Hoenich, N.; Thijssen, S.; Kitzler, T.; Levin, R.; Ronco, C. Impact of water quality and dialysis fluid composition on dialysis practice. Blood Purif. 2008, 26, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canaud, B.; Granger, A.; Chenine-Khoualef, L.; Patrier, L.; Morena, M.; Leray-Moragués, H. On-Line Hemodialysis Monitoring: New Tools for Improving Safety, Tolerance and Efficacy. In Modeling and Control of Dialysis Systems. Studies in Computational Intelligence; Azar, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.A.; Valtuille, R.; Balzarini, M. Artificial Neural Networks Applications in Dialysis. In Modeling and Control of Dialysis Systems. Studies in Computational Intelligence; Azar, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, G.; Azar, A.T.; White, J.C. Renal System Dynamics Modeling. In Modeling and Control of Dialysis Systems. Studies in Computational Intelligence; Azar, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.C.; Brimble, K.S. Factors Affecting Peritoneal Dialysis Dose. In Modeling and Control of Dialysis Systems. Studies in Computational Intelligence; Azar, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, K.; Morimoto, K.; Washida, N.; Kusahana, E.; Nakayama, T.; Itoh, T.; Kasai, T.; Wakino, S.; Itoh, H. Effects of a remote patient monitoring system for patients on automated peritoneal dialysis: A randomized crossover controlled trial. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 54, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.T.; Blankestijn, P.J.; Dember, L.M.; Gallieni, M.; Harris, D.C.; Lok, C.E.; Mehrotra, R.; Stevens, P.E.; Wang, A.Y.M.; Cheung, M.; et al. Dialysis initiation, modality choice, access, and prescription: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azar, A.T. Modeling and Control of Dialysis Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Giove, S.; Azar, A.T.; Nordio, M. Fuzzy Logic Control for Dialysis Application. In Modeling and Control of Dialysis Systems. Studies in Computational Intelligence; Azar, A., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Cao, J. Bifurcations in a fractional-order BAM neural network with four different delays. Neural. Netw. 2021, 141, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Mu, D.; Liu, Z.; Pang, Y.; Liao, M.; Aouiti, C. New insight into bifurcation of fractional-order 4D neural networks incorporating two different time delays. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2023, 118, 107043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Gao, R.; Xu, C.; Shang, Y. New exploration on bifurcation in fractional-order genetic regulatory networks incorporating both type delays. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2022, 137, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oustaloup, A.; Sabatier, J.; Lanusse, P. From Fractional Robustness to CRONE Control. In Fractional Calculus and Applied Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; Volume 2, pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional-order systems and PIλDμ controllers. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1999, 44, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulf, E.H. Simplified fractional order controller design algorithm. Mathematics 2019, 7, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulf, E.H.; Dulf, F.V.; Muresan, C.I. Fractional model of the cryogenic (13C) isotope separation column. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2015, 202, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Ying, L. An analytical synthesis of fractional order PIλDμ controller design. ISA Trans. 2022, 131, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oziablo, P.; Mozyrska, D.; Wyrwas, M. Fractional-variable-order digital controller design tuned with the chaotic yellow saddle goatfish algorithm for the AVR system. ISA Trans. 2022, 125, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulf, E.H.; Șușcă, M.; Kovács, L. Novel Optimum Magnitude Based Fractional Order Controller Design Method. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegedus, E.T.; Birs, I.R.; Ghita, M.; Muresan, C.I. Fractional-Order Control Strategy for Anesthesia–Hemodynamic Stabilization in Patients Undergoing Surgical Procedures. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fällman, M. Model-Based Conductivity Control of Fluid Composition. MSc Thesis, Department of Automatic Control, Lund University, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Paducel, I.; Safirescu, C.O.; Dulf, E.H. Fractional Order Controller Design for Wind Turbines. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepljakov, A. FOMCON Toolbox for MATLAB. Available online: https://github.com/extall/fomcon-matlab/releases/tag/v1.50.3 (accessed on 19 October 2022).
- Oustaloup, A.; Levron, F.; Mathieu, B.; Nanot, F.M. Frequency-band complex noninteger differentiator: Characterization and synthesis. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Fundam. Theory Appl. 2020, 47, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

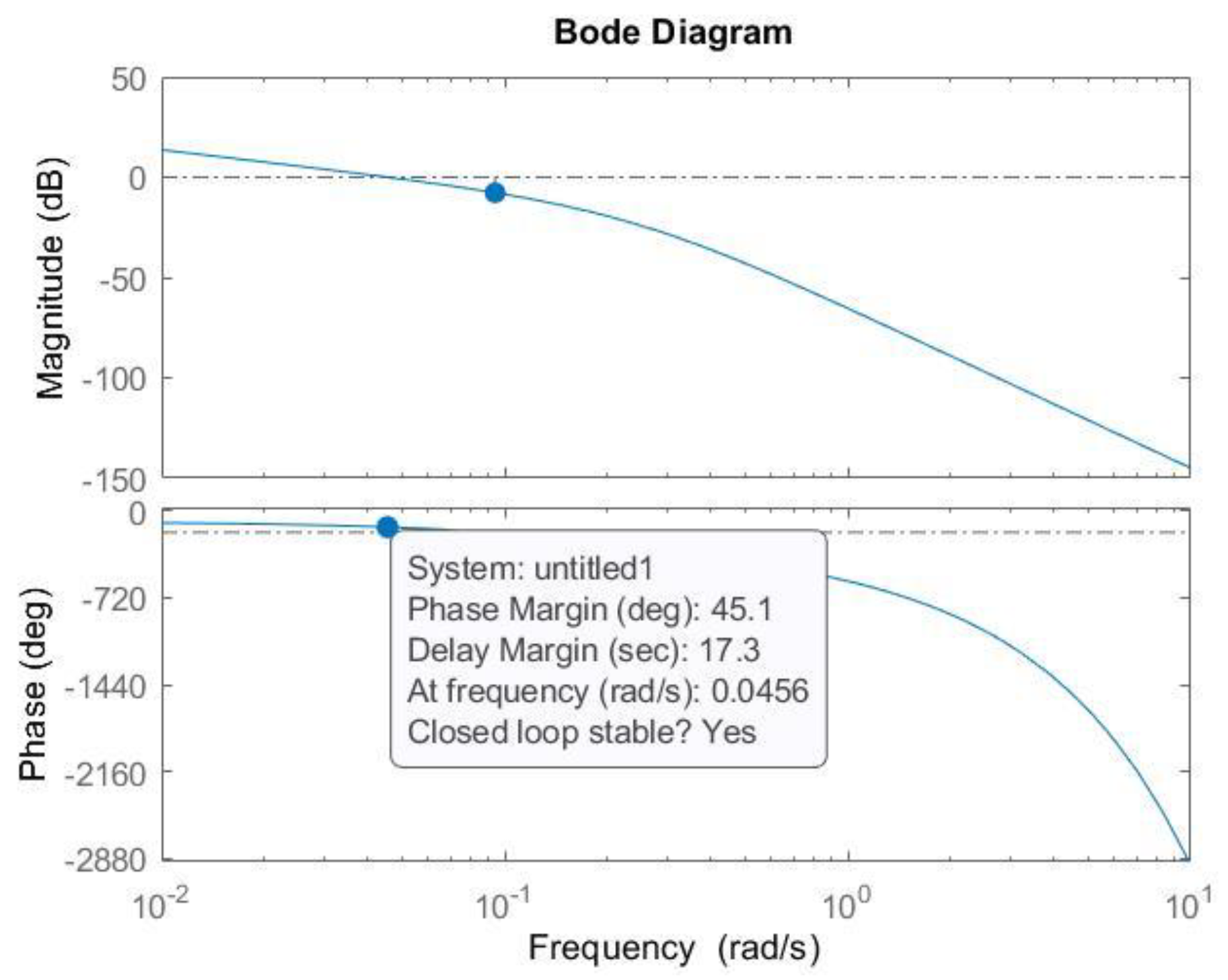



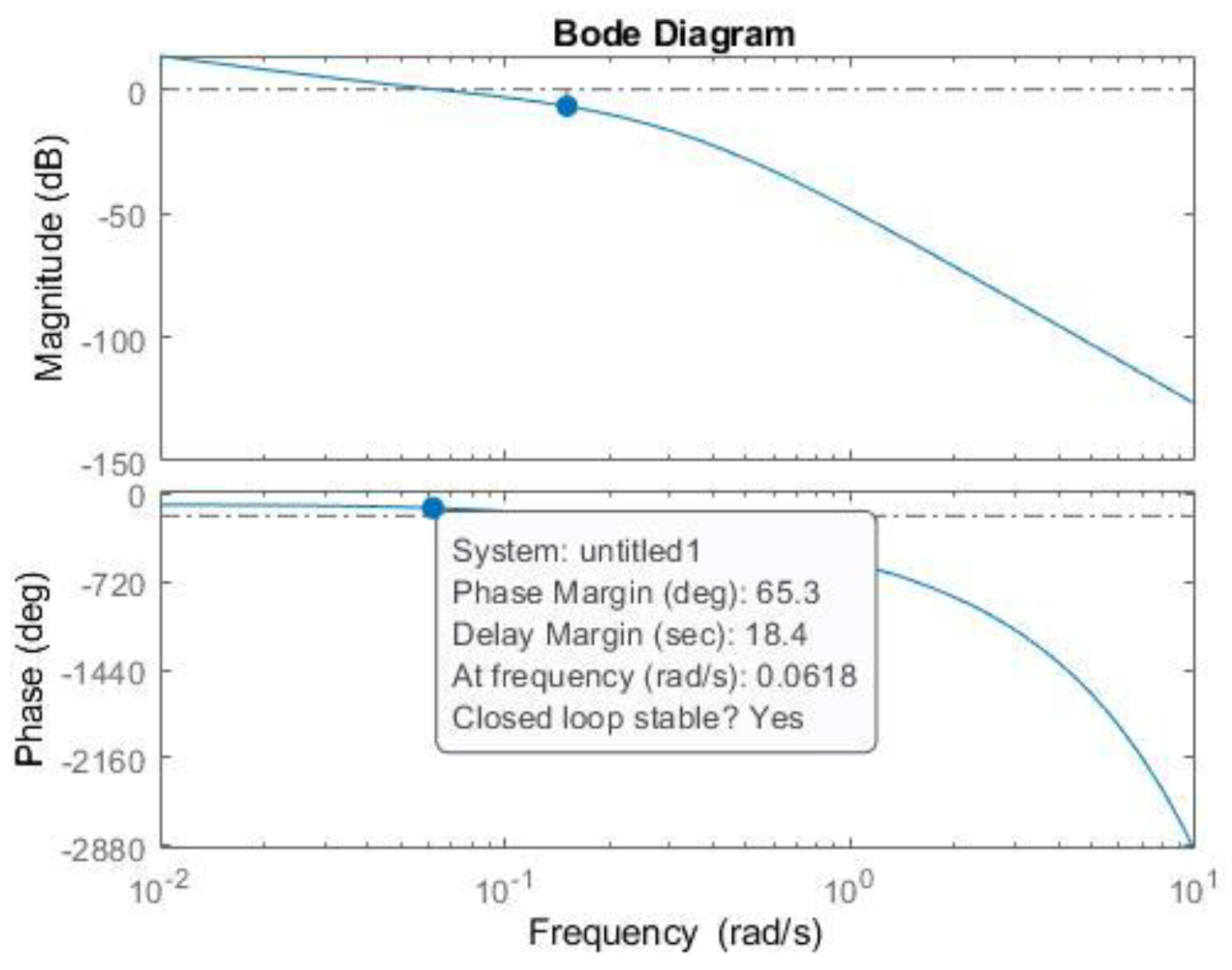
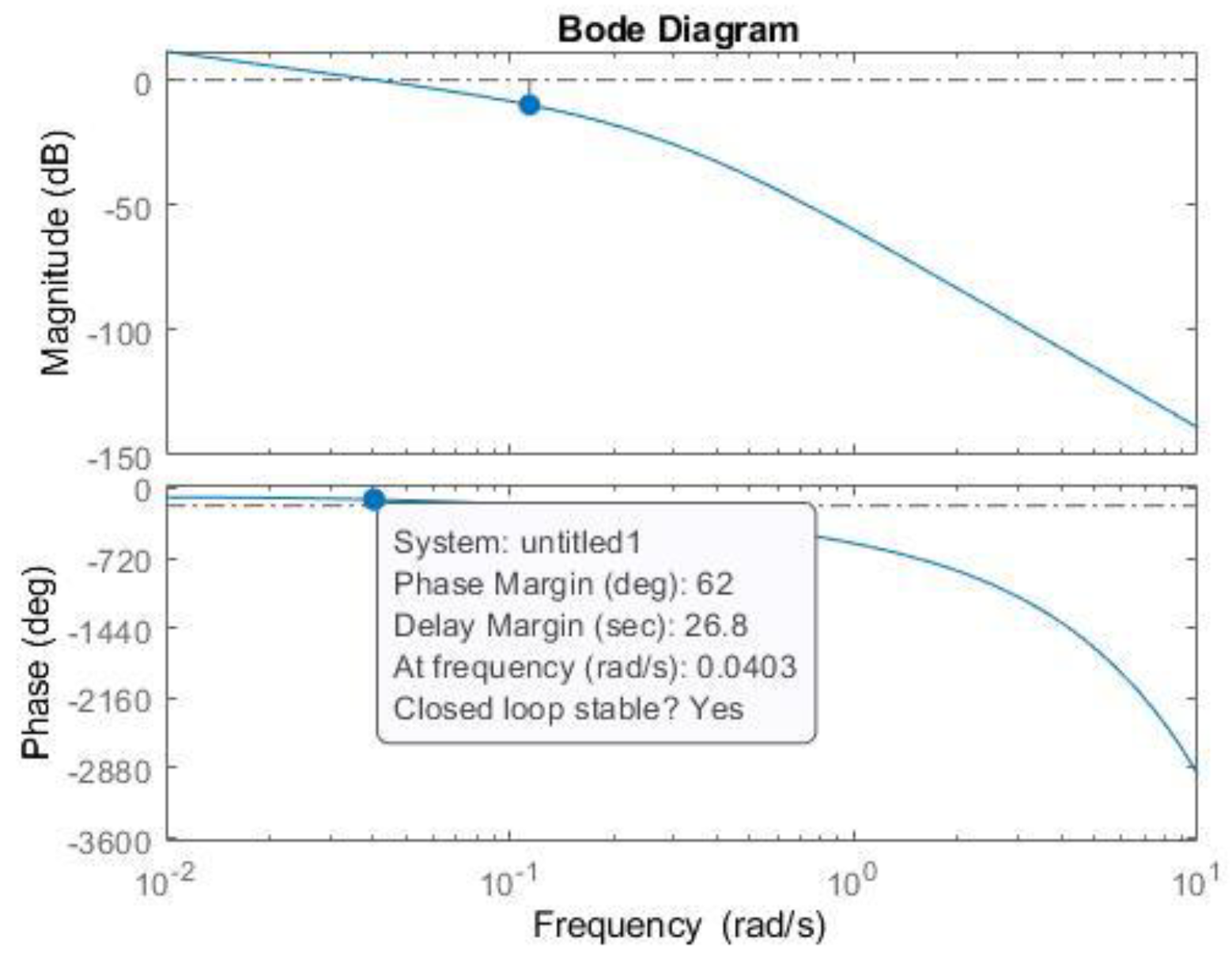
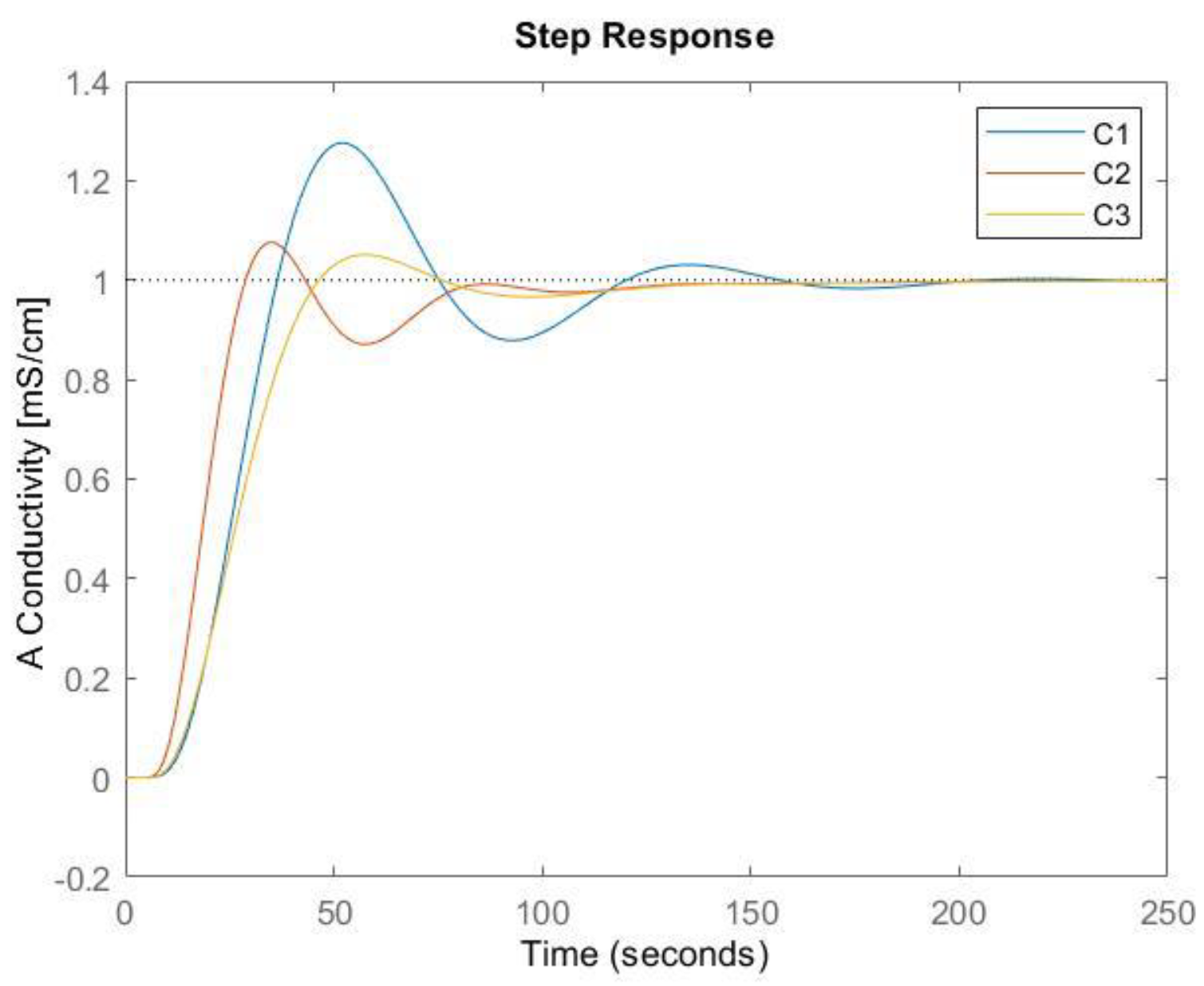
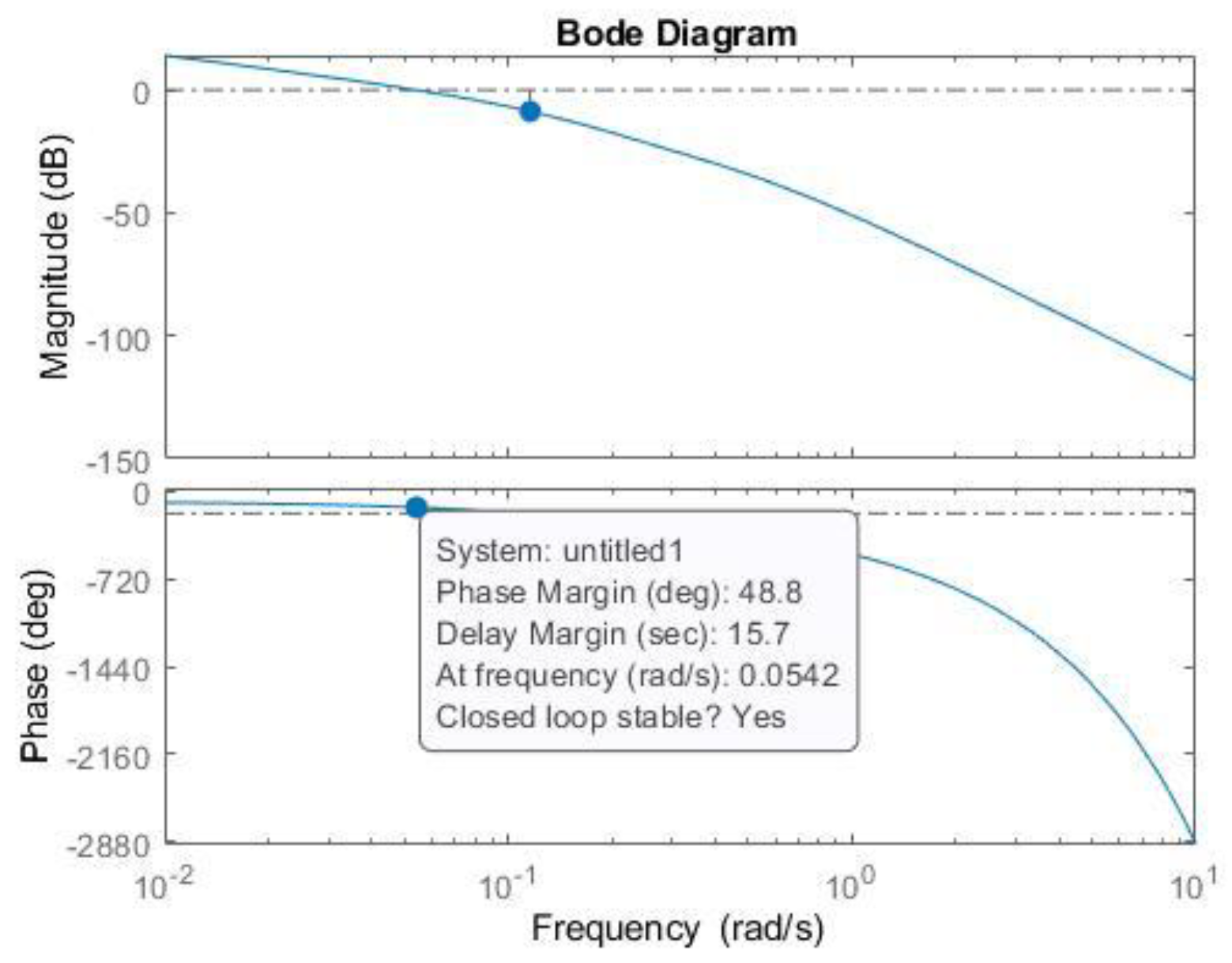
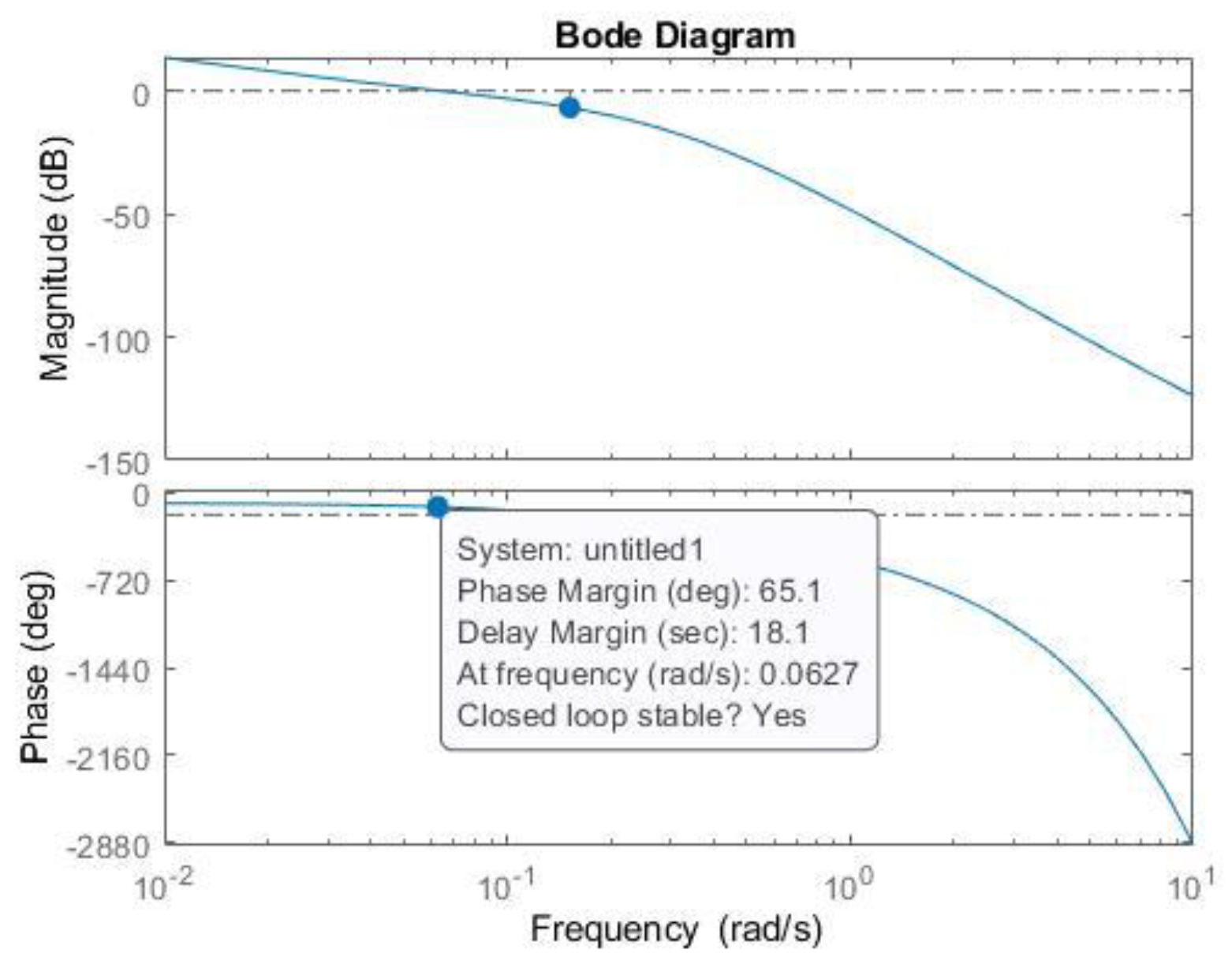
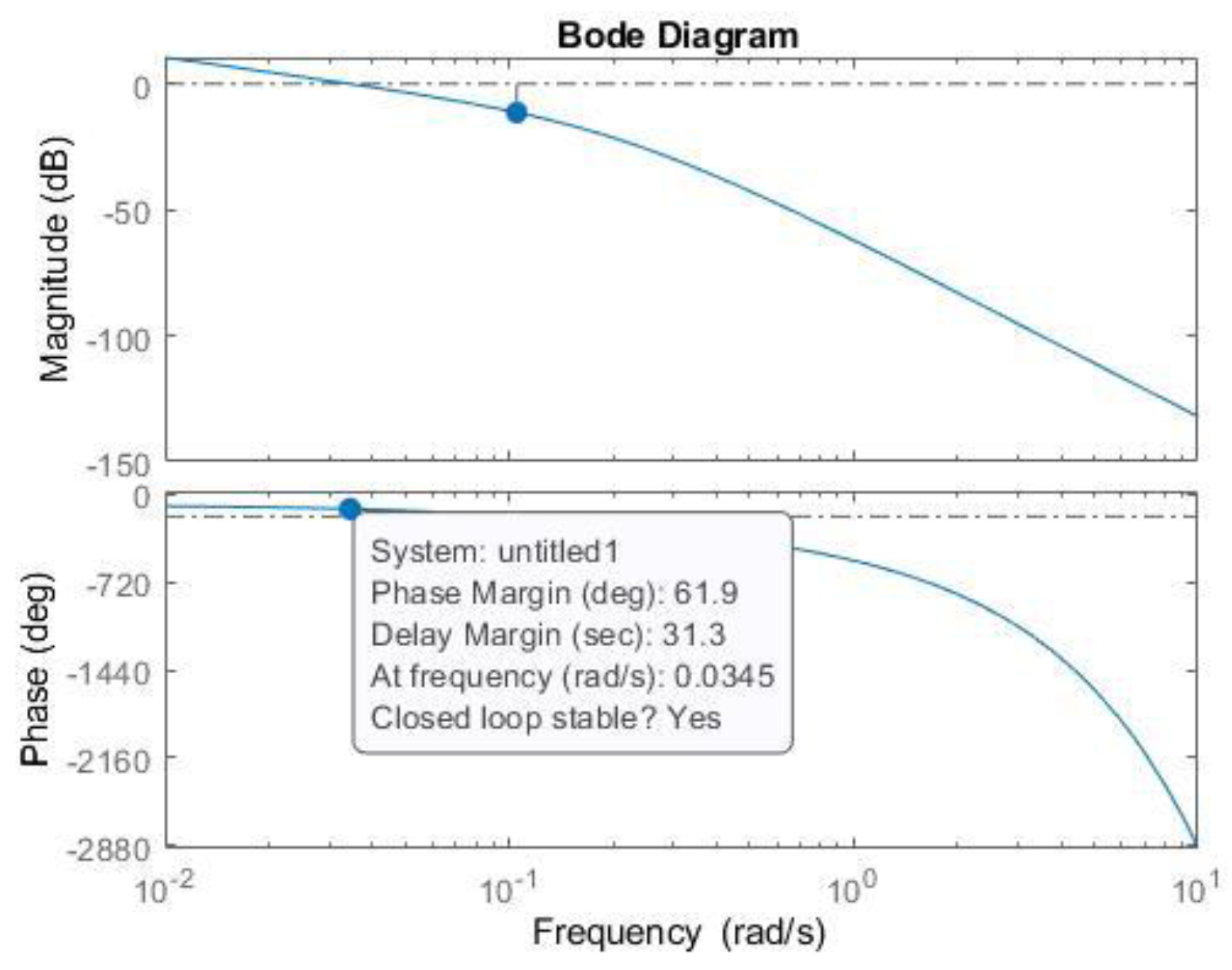

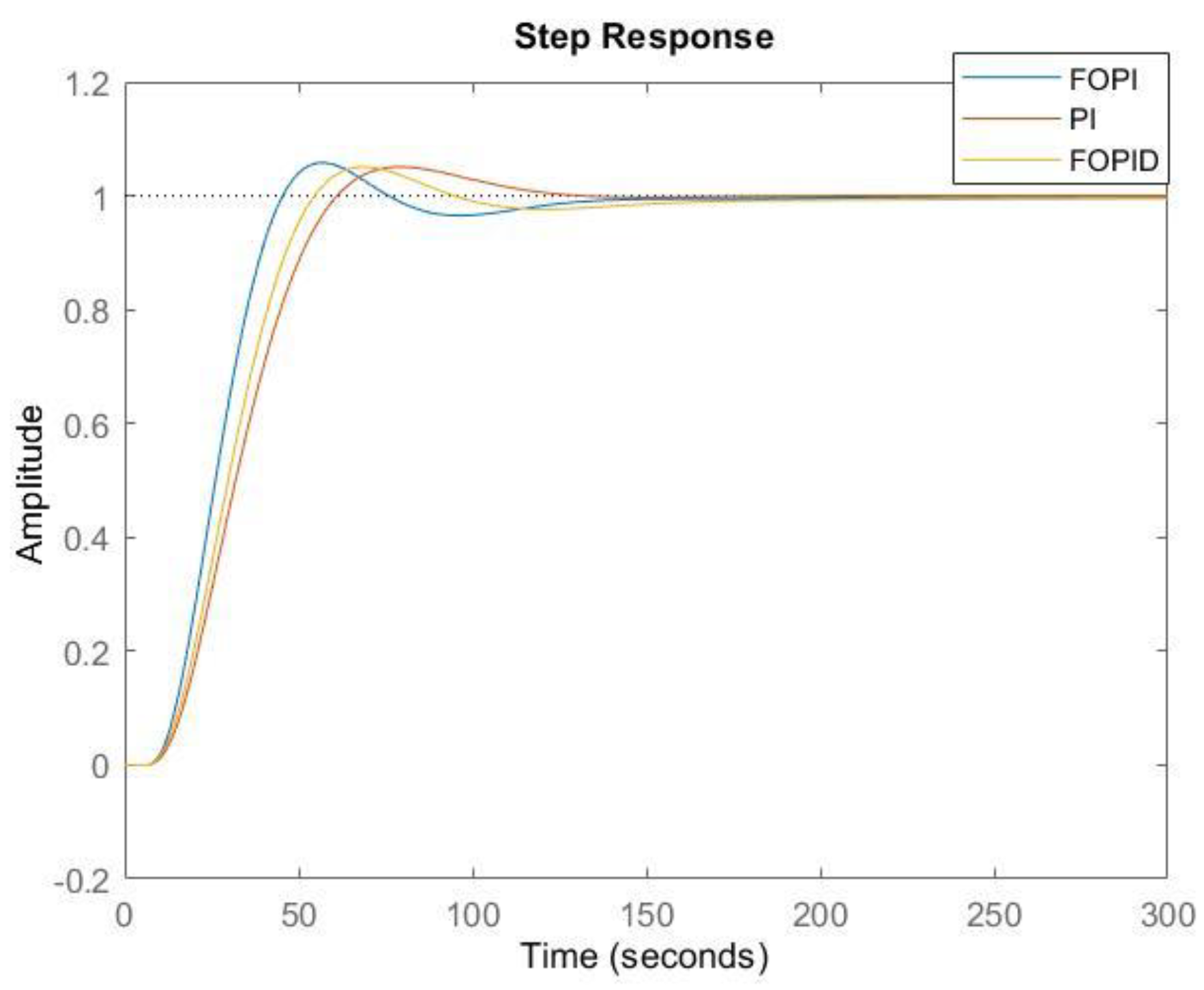


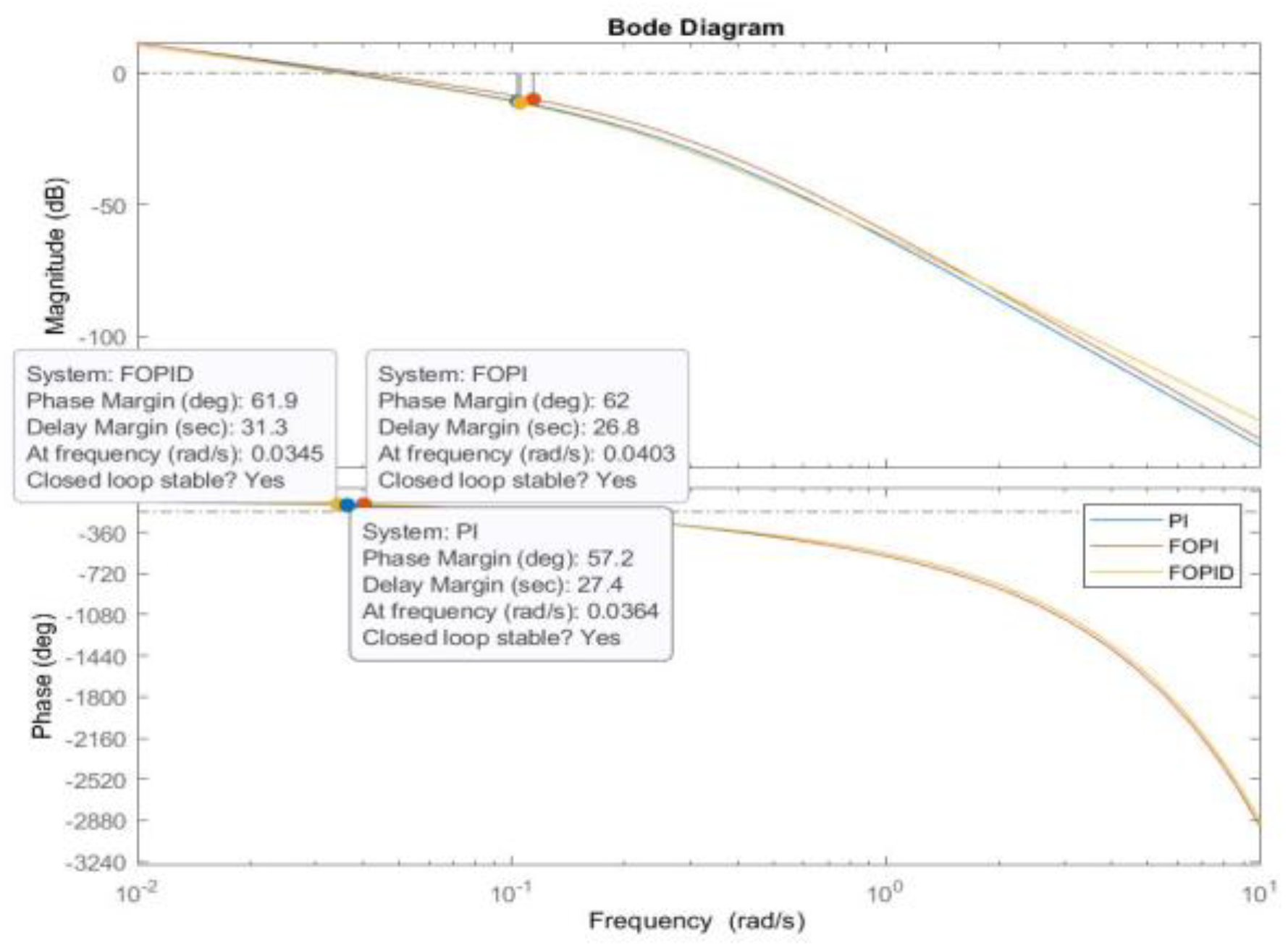
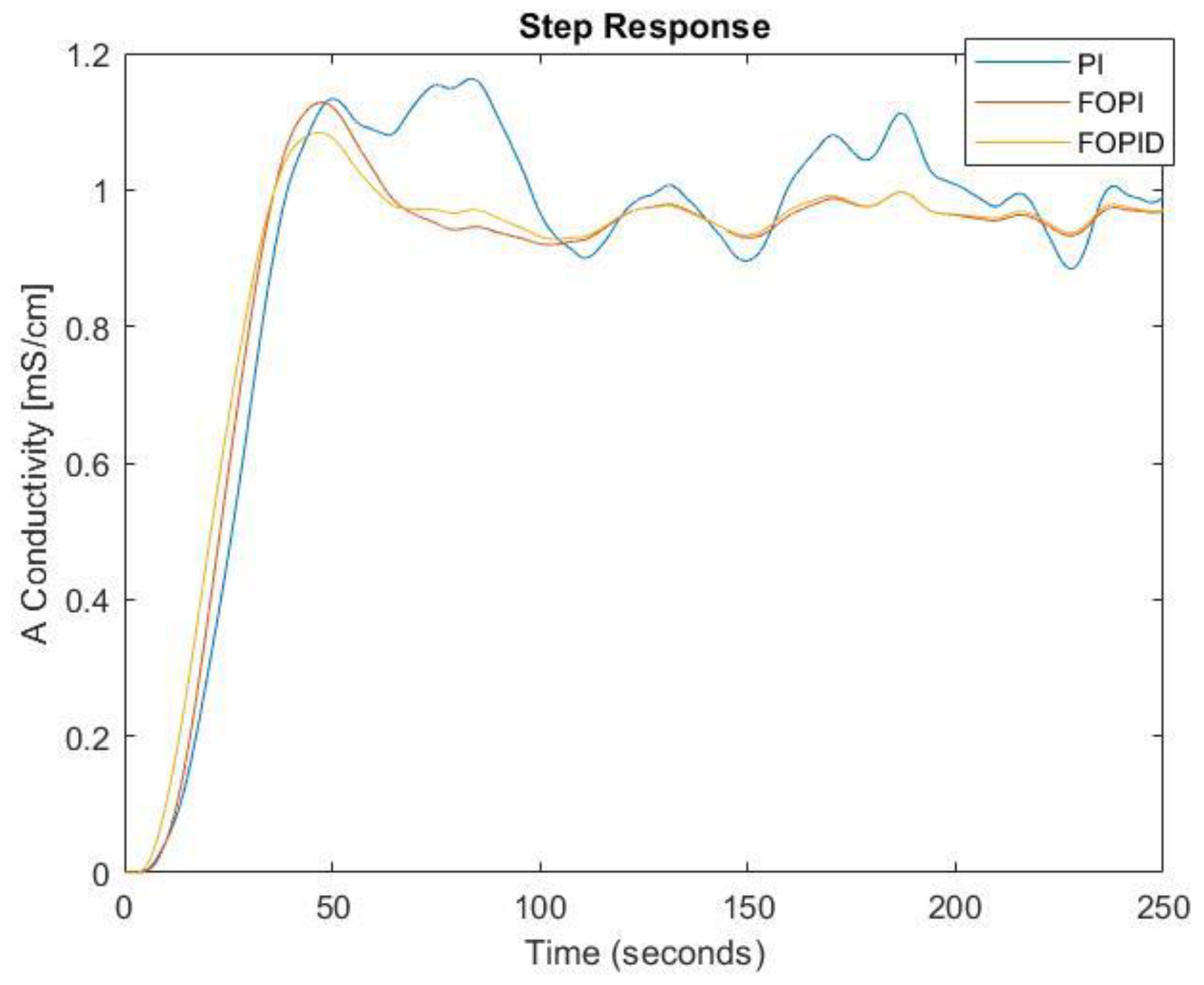

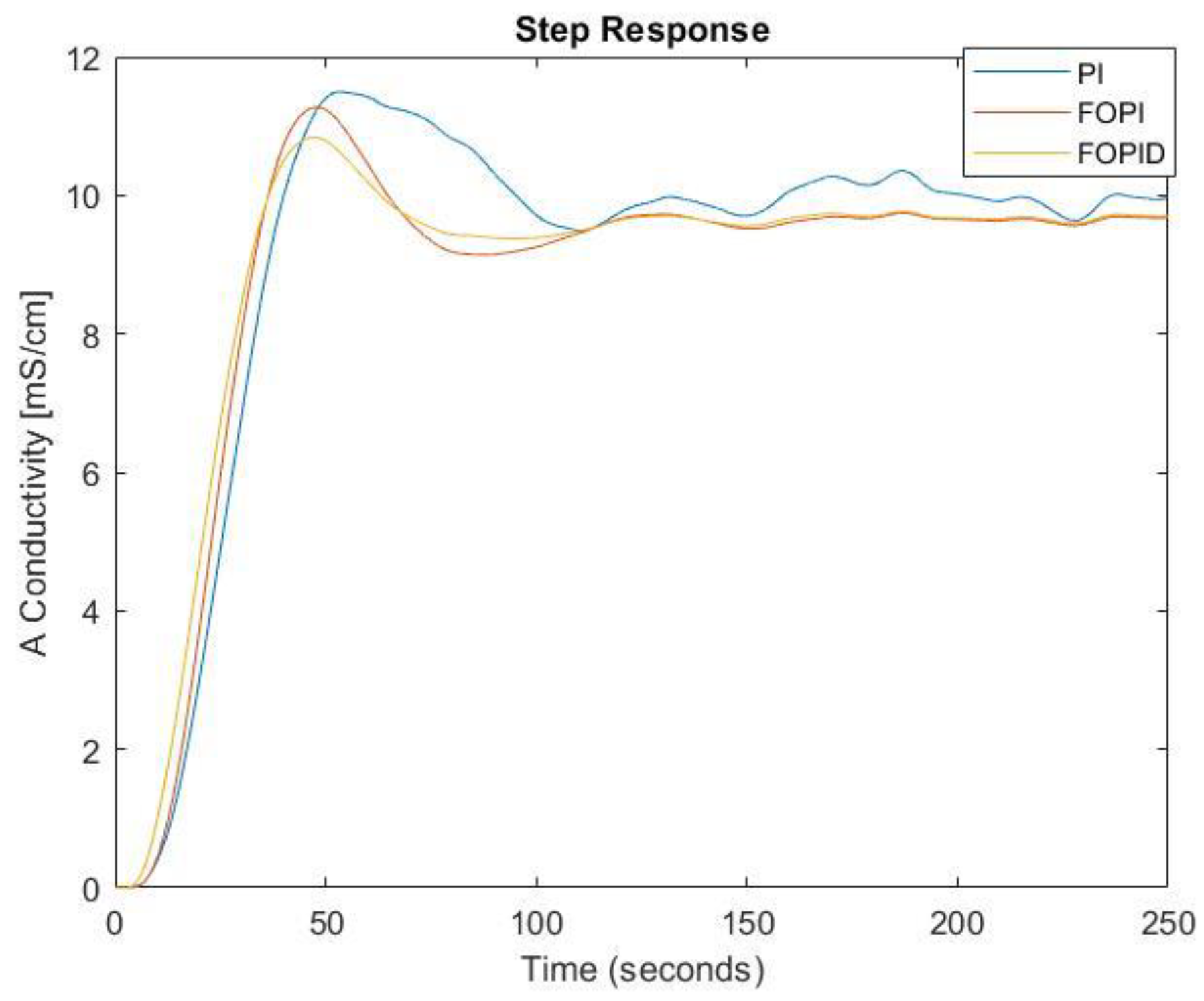
| Controller | PM [°] | [rad/s] | Kp | Ki |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 1.75 | |
| 65 | 0.06 | 1.012 | 16.86 | |
| 62 | 0.03 | 0.12 | 3.23 |
| Controller | PM [°] | [rad/s] | Kp | Ki | λ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 10.68 | 0.89 | |
| 65 | 0.06 | 0.79 | 13.52 | 0.93 | |
| 62 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 15.48 | 0.91 |
| Controller | PM [°] | [rad/s] | Kp | Ki | λ | Kd | μ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 45 | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.1 | 0.89 | 0.6 | 0.55 | |
| 65 | 0.06 | 0.79 | 0.075 | 0.93 | 0.09 | 0.9 | |
| 62 | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.95 | 0.1 | 0.58 |
| Controller | Results with Nominal Parameters | Performance Changes with +2% Parameter Changes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM [°] | [s] | σ [%] | PM [°] | [s] | σ [%] | |||
| PI | 62 | 0.03 | 136 | 4.5 | 1.8 | 0.0540 | 1 | 4.03 |
| FO-PI | 0 | 0.0103 | 0.5 | 0.70 | ||||
| FO-PID | 0.1 | 0.0045 | 0 | 0.57 | ||||
| Controller | Results with Nominal Parameters | Performance Changes with −2% Parameter Changes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM [°] | [s] | σ [%] | PM [°] | [s] | σ [%] | |||
| PI | 62 | 0.03 | 136 | 4.5 | 2.8 | 0.0640 | 6 | 2.80 |
| FO-PI | 0 | 0.0103 | 2 | 1.88 | ||||
| FO-PID | 0.1 | 0.0045 | 1 | 0.70 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giurgiu, R.; Dulf, E.-H.; Kovács, L. Fractional-Order Control of Fluid Composition Conductivity. Fractal Fract. 2023, 7, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7040305
Giurgiu R, Dulf E-H, Kovács L. Fractional-Order Control of Fluid Composition Conductivity. Fractal and Fractional. 2023; 7(4):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7040305
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiurgiu, Raluca, Eva-H. Dulf, and Levente Kovács. 2023. "Fractional-Order Control of Fluid Composition Conductivity" Fractal and Fractional 7, no. 4: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7040305
APA StyleGiurgiu, R., Dulf, E.-H., & Kovács, L. (2023). Fractional-Order Control of Fluid Composition Conductivity. Fractal and Fractional, 7(4), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract7040305











