Minimal Wave Speed for a Nonlocal Viral Infection Dynamical Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- , , , J is compactly supported and for all .
2. Traveling Wave Solutions
2.1. The Existence of Traveling Fronts for
- If , the equation admits two positive roots and satisfying , for , for , and
- If , then , and for all
- If , then for all
2.2. The Existence of a Traveling Front with Wave Speed
2.3. The Nonexistence of Traveling Fronts for
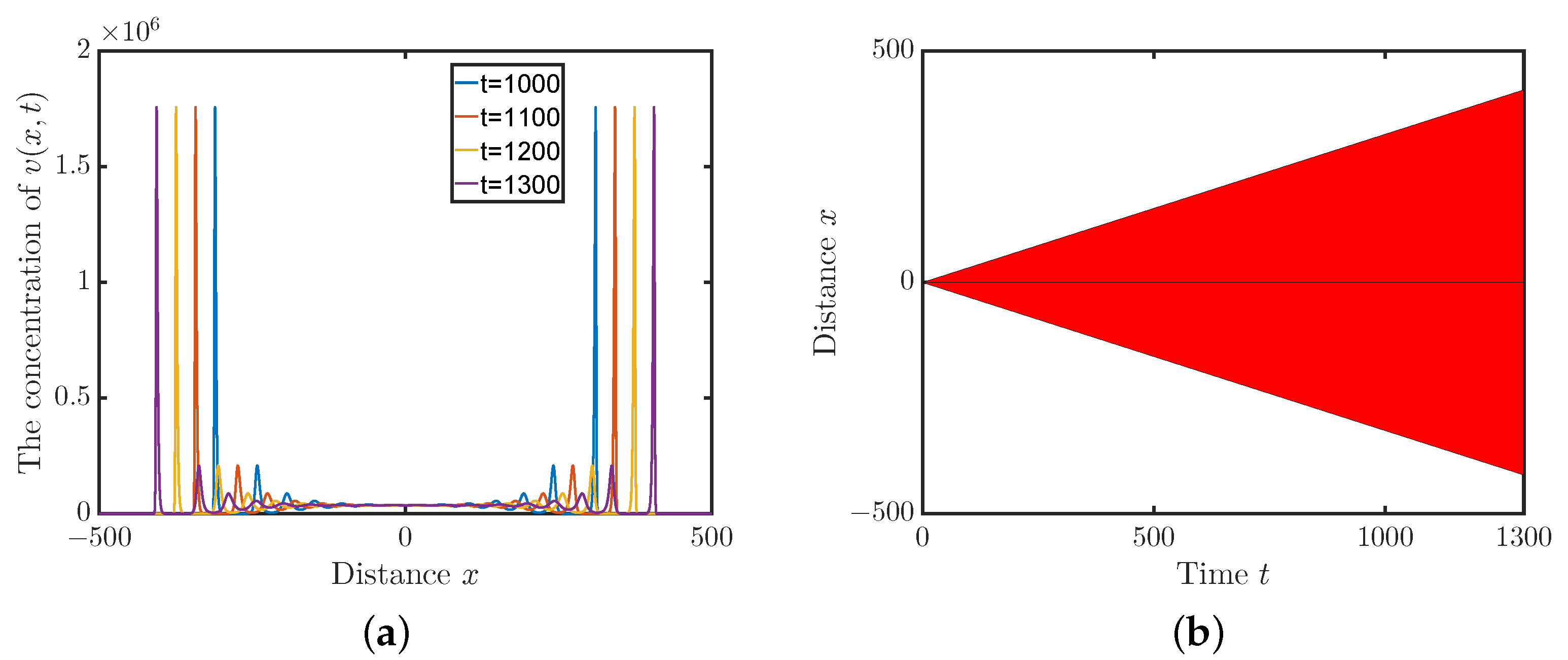
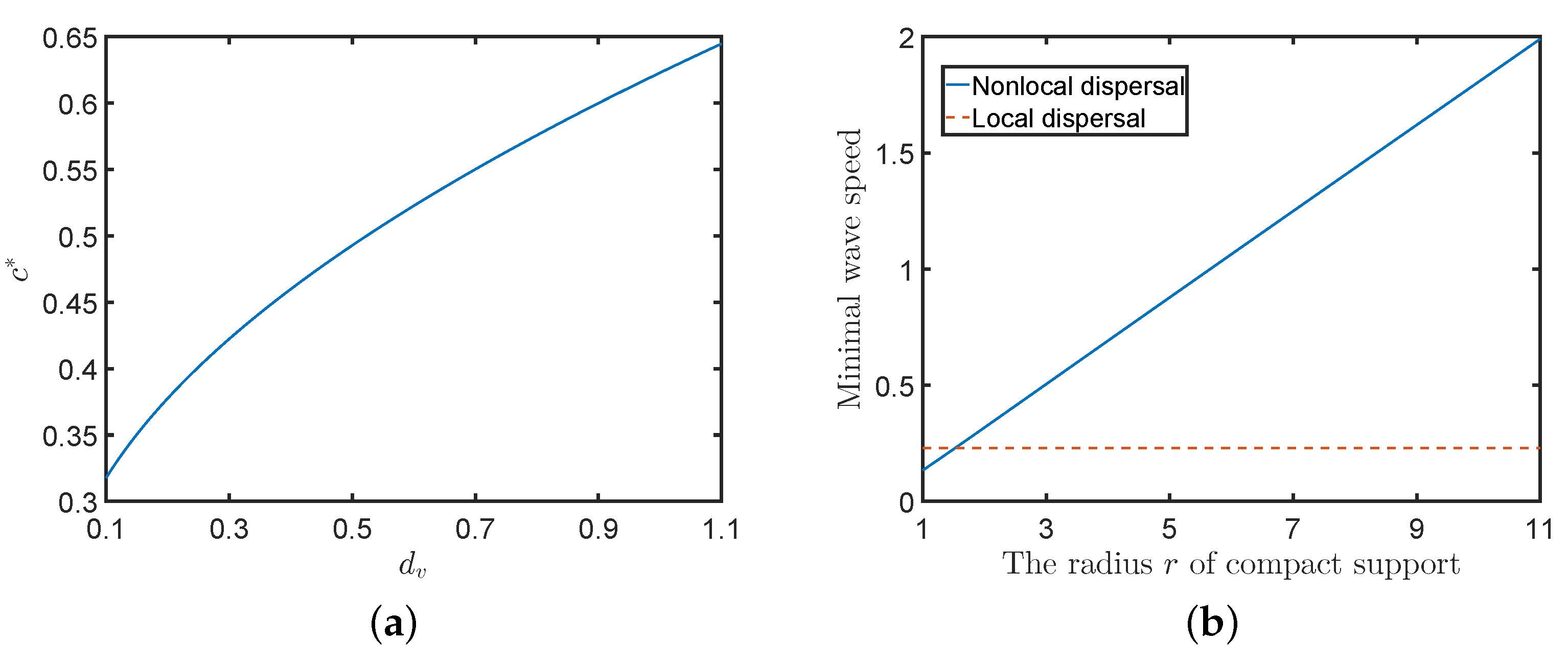
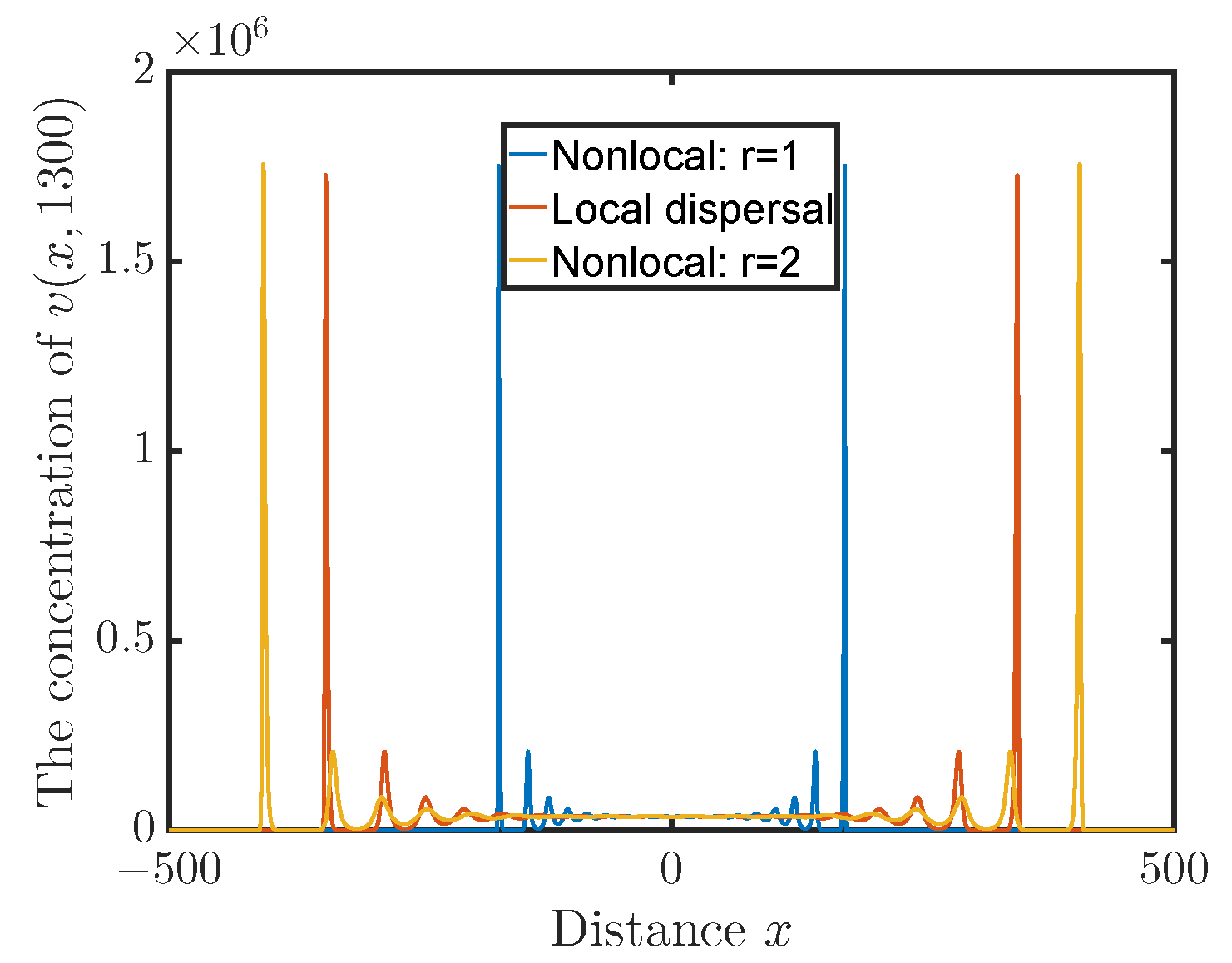
3. Discussion of Results
- Choose an appropriate spatial domain and then discretize it. We take the domain to be . The discretization step size is , which results in 5001 ordinary differential equations. Under our specified parameters and initial values, the viruses are always away from the boundaries of the domain during our simulation.
- Let be the time step. We use the ode45 function in Matlab to solve the ordinary differential equations for numerical simulation.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. World health Statistics 2017: Monitoring health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Jonit United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS). Miles to Go: Closing Gaps, Breaking Barriers, Righting Injustices; UNAIDS: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Perelson, A.; Neumann, A.; Markowitz, M.; Leonard, J.; Ho, D. HIV-1 dynamics in vivo: Virion clearance rate, infected cell life-span, and viral generation time. Science 1996, 271, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelson, A.S.; Nelson, P.W. Mathematical analysis of HIV-1 dynamics in vivo. SIAM Rev. 1999, 41, 3–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.A.; May, R.M. Virus Dynamics: Mathematical Principles of Immunology and Virology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Korobeinikov, A. Global properties of basic virus dynamics models. Bull. Math. Biol. 2004, 66, 879–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, K.; Chakrabarty, S.P. Chronic hepatitis B infection and HBV DNA-containing capsids: Modeling and analysis. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2015, 22, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, H.; Wang, L.; Watmough, J. Sustained and transient oscillations and chaos induced by delayed antiviral immune response in an immunosuppressive infection model. J. Math. Biol. 2014, 68, 477–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Neumann, A.U. Global stability and periodic solution of the viral dynamics. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2007, 329, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Ma, Z. An HBV model with diffusion and time delay. J. Theor. Biol. 2009, 257, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murooka, T.T.; Deruaz, M.; Marangoni, F.; Vrbanac, V.D.; Seung, E.; von Andrian, U.H.; Tager, A.M.; Luster, A.D.; Mempel, T.R. HIV-infected T cells are migratory vehicles for viral dissemination. Nature 2012, 490, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fackler, O.T.; Murooka, T.T.; Imle, A.; Mempel, T.R. Adding new dimensions: Towards an integrative understanding of HIV-1 spread. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strain, M.C.; Richman, D.D.; Wong, J.K.; Levine, H. Spatiotemporal dynamics of HIV propagation. J. Theor. Biol. 2002, 218, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wang, W. Propagation of HBV with spatial dependence. Math. Biosci. 2007, 210, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.; Zou, X. Repulsion effect on superinfecting virions by infected cells. Bull. Math. Biol. 2014, 76, 2806–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.D. Mathematical biology: Spatial models and biomedical applications II. In Interdisciplinary Applied Mathematics, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.B.; Li, W.T.; Sun, J.W. Global dynamics and spreading speeds for a partially degenerate system with non-local dispersal in periodic habitats. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. 2018, 148, 849–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Ruan, S. Spatial and temporal dynamics of a nonlocal viral infection model. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 2018, 78, 1954–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharov, G.; Meyerhans, A.; Bessonov, N.; Trofimchuk, S.; Volpert, V. Spatiotemporal dynamics of virus infection spreading in tissues. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Tian, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, X. A reaction-diffusion within-host HIV model with cell-to-cell transmission. J. Math. Biol. 2018, 76, 1831–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, W.; Lai, X. Repulsion effect on superinfecting virions by infected cells for virus infection dynamic model with absorption effect and chemotaxis. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2017, 33, 253–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ma, W. Travelling wave solutions for a nonlocal dispersal HIV infection dynamical model. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2018, 457, 868–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hsu, C.H.; Zou, L.; Zhou, J. A note on the propagation dynamics in a nonlocal dispersal HIV infection model. Proc. Am. Math. Soc. 2022, 150, 4867–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, W.T.; Wang, Z.C. Traveling waves in a nonlocal dispersal Kermack-McKendrick epidemic model. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. B 2013, 18, 1969–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.C.; Li, W.T.; Yang, F.Y. Traveling waves in a nonlocal dispersal SIRH model with relapse. Comput. Math. Appl. 2017, 73, 1707–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducrot, A.; Magal, P. Travelling wave solutions for an infection-age structured epidemic model with external supplies. Nonlinearity 2011, 24, 2891–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, W.T.; Yang, F.Y. Traveling waves for a nonlocal dispersal SIR model with delay and external supplies. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 247, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Tian, Y.; Xu, Z. Epidemic waves of a spatial SIR model in combination with random dispersal and non-local dispersal. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 313, 122–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, S. Traveling waves for SVIR epidemic model with nonlocal dispersal. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2019, 16, 1654–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, W.T.; Wu, S.L. Multi-type entire solutions in a nonlocal dispersal epidemic model. J. Dynam. Differ. Equations 2016, 28, 189–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zou, X. Traveling wave fronts of reaction-diffusion systems with delay. J. Dynam. Differ. Equations 2001, 13, 651–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Xu, W.B. The traveling wave solutions in a mixed-diffusion epidemic model. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elia, M.; Gunzburger, M. The fractional Laplacian operator on bounded domains as a special case of the nonlocal diffusion operator. Comput. Math. Appl. 2013, 66, 1245–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defterli, O.; D’Elia, M.; Du, Q.; Gunzburger, M.; Lehoucq, R.; Meerschaert, M.M. Fractional diffusion on bounded domains. Fract. Calc. Appl. Anal. 2015, 18, 342–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubert, M.G.; Parker, I.M. Projecting rates of spread for invasive species. Risk Anal. 2004, 24, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahari, H.; Lo, A.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Perelson, A.S. Modeling hepatitis C virus dynamics: Liver regeneration and critical drug efficacy. J. Theor. Biol. 2007, 247, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X. Minimal Wave Speed for a Nonlocal Viral Infection Dynamical Model. Fractal Fract. 2024, 8, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8030135
Ren X, Liu L, Zhang T, Liu X. Minimal Wave Speed for a Nonlocal Viral Infection Dynamical Model. Fractal and Fractional. 2024; 8(3):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8030135
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Xinzhi, Lili Liu, Tianran Zhang, and Xianning Liu. 2024. "Minimal Wave Speed for a Nonlocal Viral Infection Dynamical Model" Fractal and Fractional 8, no. 3: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8030135
APA StyleRen, X., Liu, L., Zhang, T., & Liu, X. (2024). Minimal Wave Speed for a Nonlocal Viral Infection Dynamical Model. Fractal and Fractional, 8(3), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract8030135





