Hybrid Dynamic Event-Triggered Interval Observer Design for Nonlinear Cyber–Physical Systems with Disturbance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
3. Main Results
3.1. Design of the HDETIO Frame
3.2. Stability Analysis of HDETIO
- Case 1:
- When , , which implies .
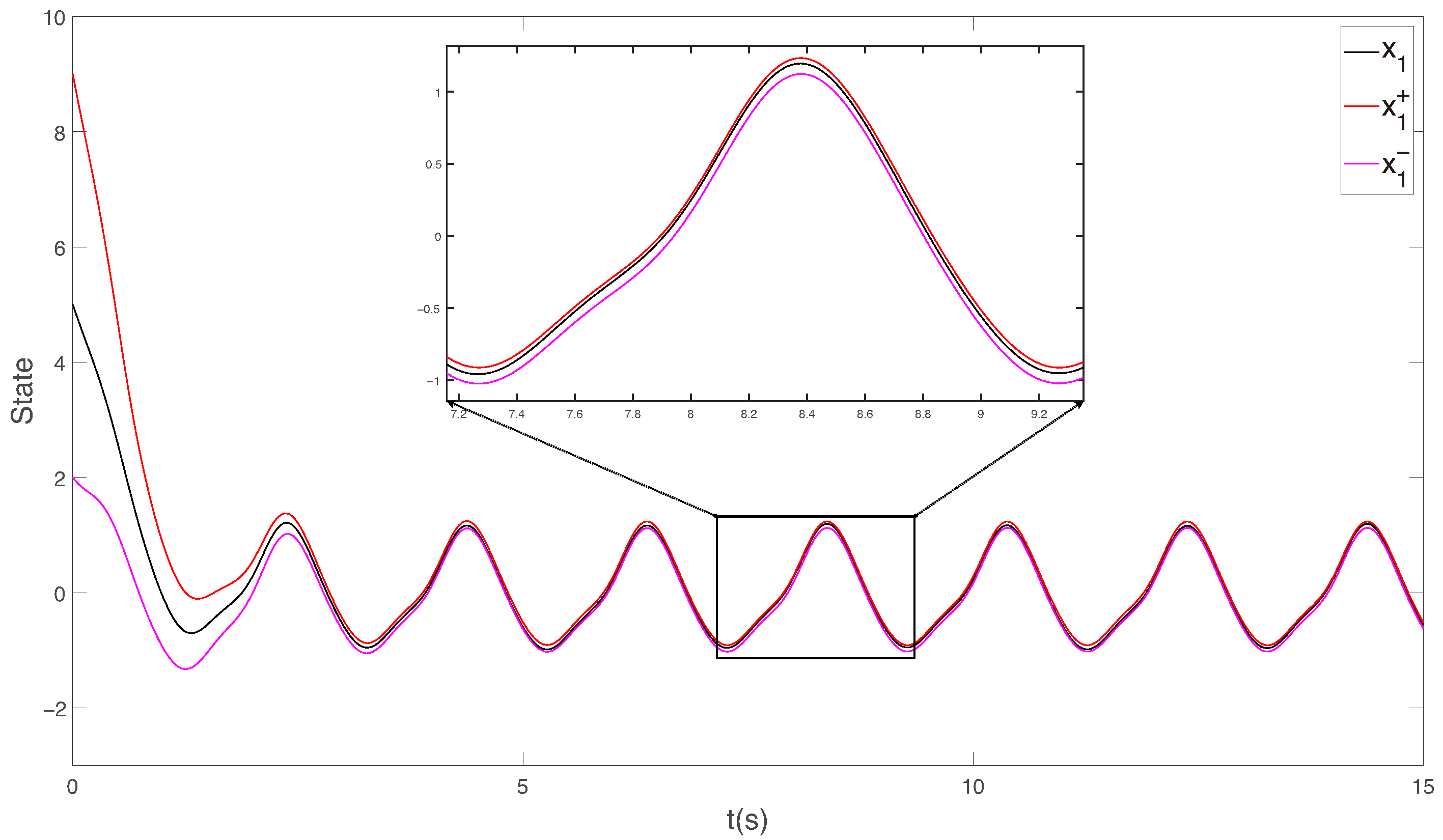
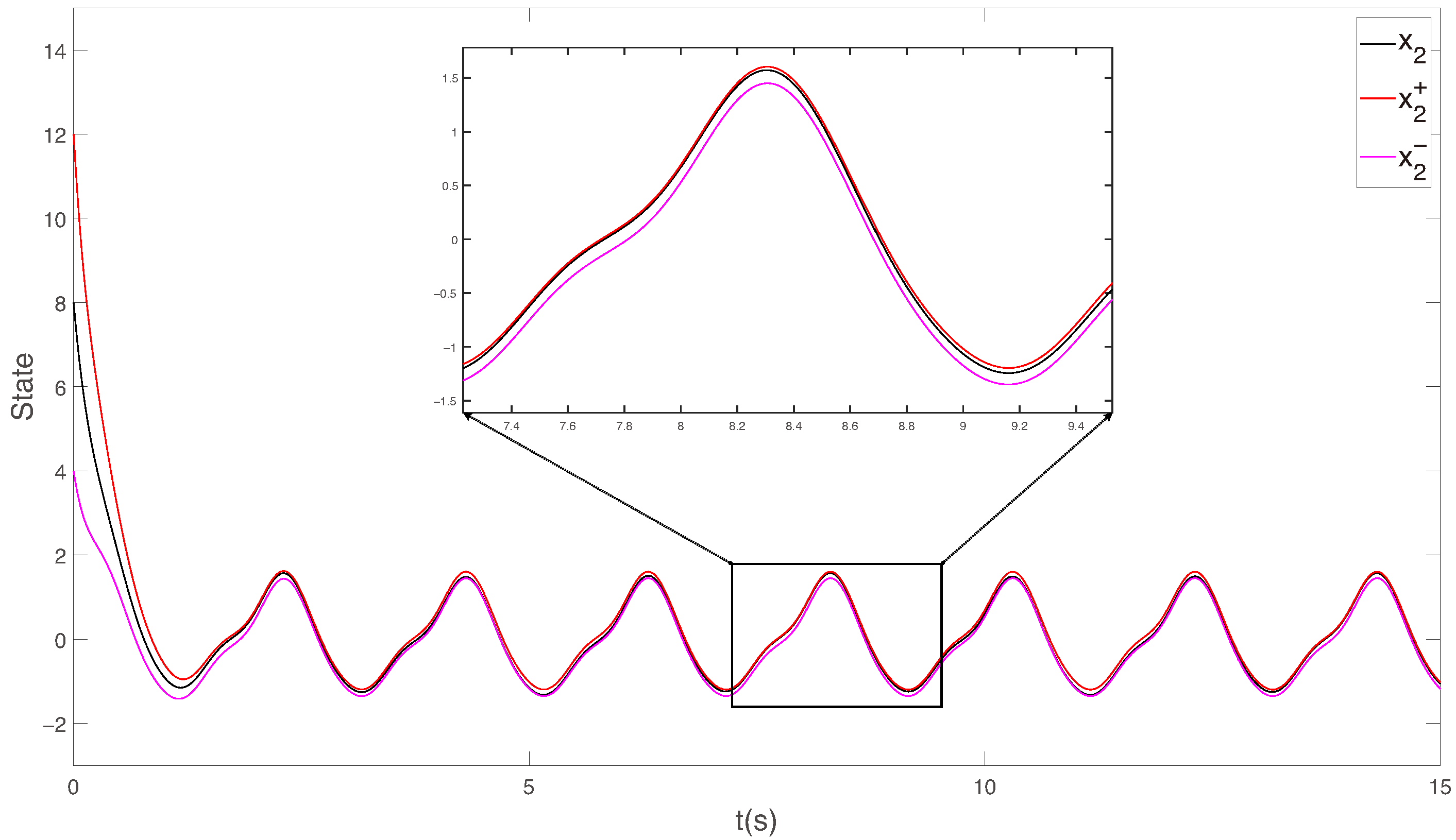
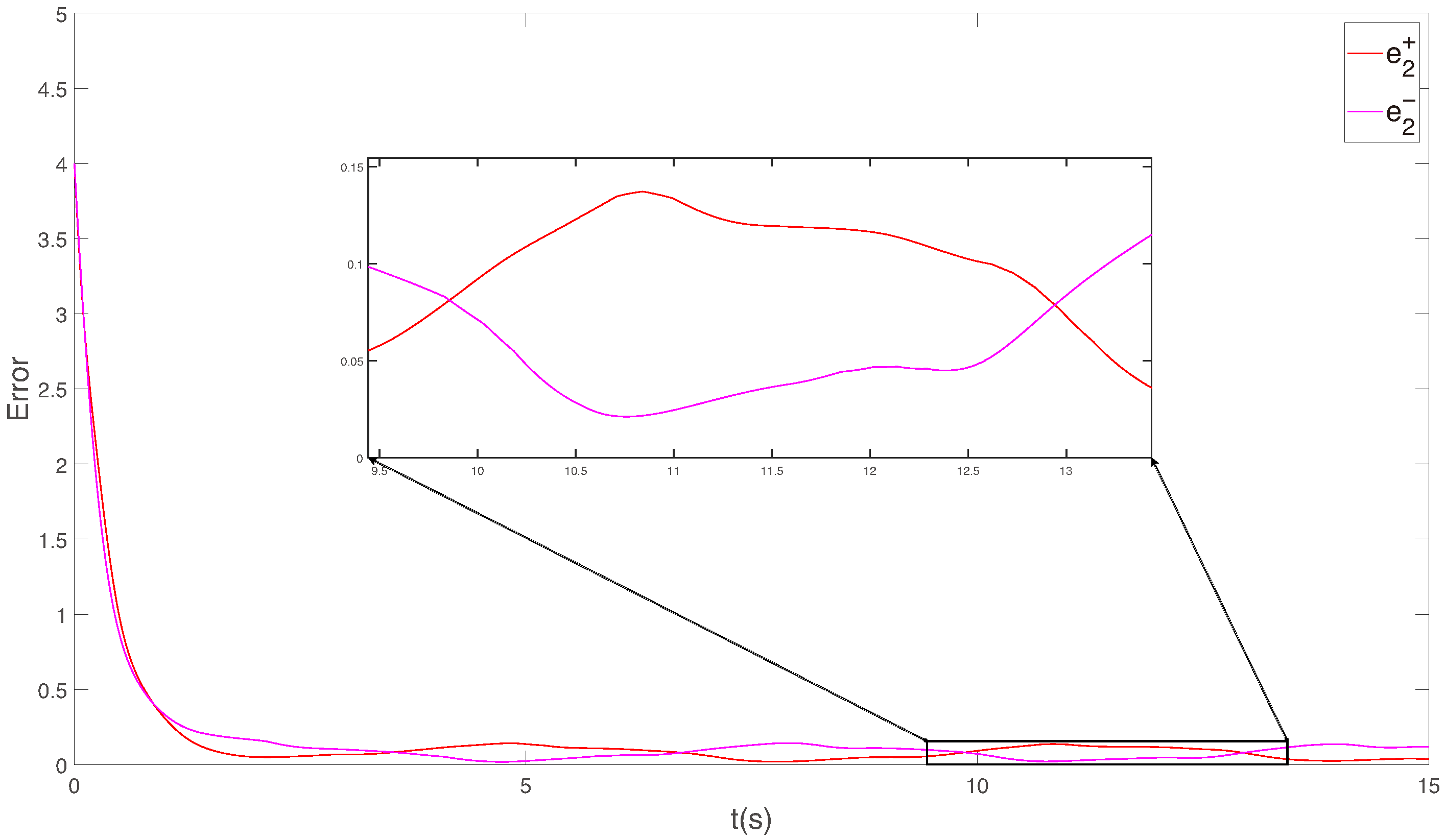
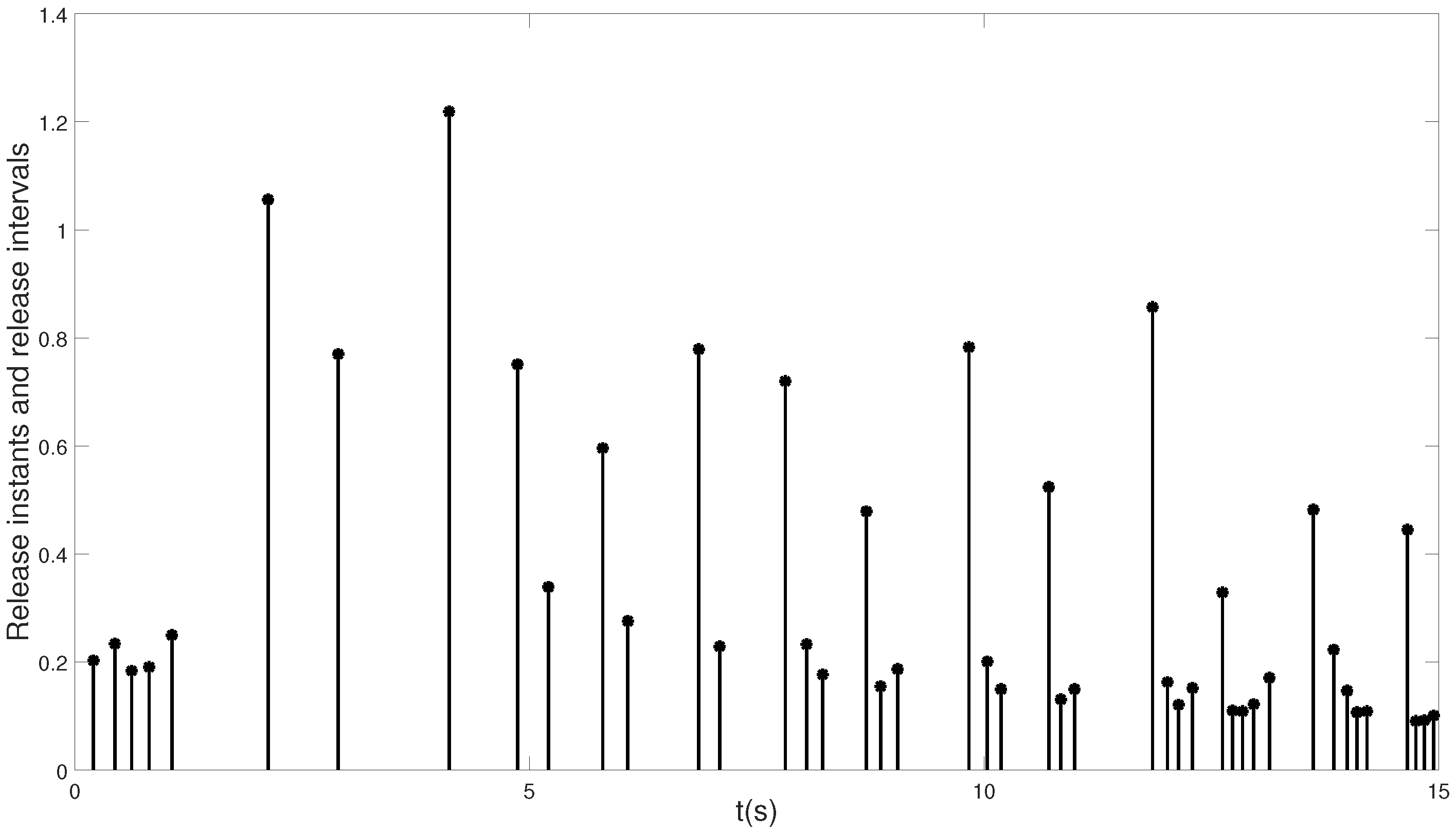
4. Numerical Simulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pasqualetti, F.; Dörfler, F.; Bullo, F. Attack detection and identification in cyber-physical systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2013, 58, 2715–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Xue, Y. Smart grids: A cyber-physical systems perspective. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampigethaya, K.; Poovendran, R. Aviation cyber–physical systems: Foundations for future aircraft and air transport. Proc. IEEE 2013, 101, 1834–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Lau, V.K.N. A stability analysis framework for multiantenna multisensor cyber-physical systems with rank-deficient measurement matrices. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2020, 7, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Guo, H.; Cao, D.; Wang, F.Y. Simultaneous observation of hybrid states for cyber-physical systems: A case study of electric vehicle powertrain. IEEE T. Cybern. 2018, 48, 2357–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wang, Z.; Han, Q.L.; Liu, X. State estimation under false data injection attacks: Security analysis and system protection. Automatica. 2018, 87, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, W.; Song, Y.; Wen, C.; Lai, J. Finite time attack detection and supervised secure state estimation for CPSs with malicious adversaries. Inf. Sci. 2018, 451–452, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouzé, J.; Rapaport, A.; Hadj-Sadok, M. Interval observers for uncertain biological systems. Ecol. Model. 2000, 133, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethabet, H.; Rabehi, D.; Efimov, D.; Raïssi, T. Interval estimation for continuous-time switched linear systems. Automatica 2018, 90, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouani, G.; Dinh, T.N.; Raïssi, T.; Wang, X.; Messaoud, H. Unknown input interval observers for discrete-time linear switched systems. Eur. J. Control 2021, 59, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, T.; Hosoe, Y.; Hagiwara, T. Robust H2 analysis of discrete-time linear systems characterized by random polytopes and time-varying parameters. IFAC-Pap. OnLine 2023, 56, 10402–10407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Raïssi, T.; Shen, Y. Ellipsoid-based interval estimation for Lipschitz nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 67, 6802–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Z. Interval-observer-based fault detection and isolation design for T-S fuzzy system based on zonotope analysis. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 30, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raissi, T.; Efimov, D.; Zolghadri, A. Interval state estimation for a class of nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2012, 57, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Che, H.; Raïssi, T.; Wang, Z. Functional interval observer for discrete-time switched descriptor systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 67, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Huang, J.; Zhao, X. Improved interval estimation method for cyber-physical systems under stealthy deception attacks. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Proc. Netw. 2022, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemels, W.P.M.H.; Donkers, M.C.F.; Teel, A.R. Periodic event-triggered control for linear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2013, 58, 847–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Chen, T.; Shi, L. Event-triggered maximum likely-hood state estimation. Automatica 2014, 50, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yan, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, M. H∞ control of singular system based on stochastic cyber-attacks and dynamic event-triggered mechanism. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 51, 7510–7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, B.; Xing, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, X. Model-based dynamic event-triggered control for cyber-physical systems subject to dynamic quantization and DoS attacks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 2406–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Han, Q.L.; Ge, X.; Zhang, X.M. An overview of recent advances in event-triggered consensus of multiagent systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 1110–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, D.C.; Huynh, V.T.; Trinh, H. Dynamic event-triggered state observers for a class of nonlinear systems with time delays and disturbances. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs. 2020, 67, 3457–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, S.A.; Kar, I. Event-triggered adaptive backstepping control of nonlinear uncertain systems with input delay. IFAC-Pap. OnLine 2022, 55, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, S.A.; Kar, I.N. Design and implementation of event-triggered adaptive controller for commercial mobile robots subject to input delays and limited communications. Control Eng. Pract. 2021, 114, 104865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Li, Z. Fully distributed event-triggered protocols for linear multiagent networks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2019, 64, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Lv, Y.; Li, Z. Distributed adaptive event-triggered consensus with discrete control updating. In Proceedings of the 2020 59th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 14–18 December 2020; pp. 2793–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Hua, C.; Guan, X. A hybrid event-triggered approach to consensus of multiagent systems with disturbances. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2020, 7, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, Y.; Fu, X. Hybrid event-triggered consensus tracking of multi-agent systems with discrete control update. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs. 2022, 69, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, J.; He, S. Fractional-order interval observer for multiagent nonlinear systems. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimov, D.; Raissi, T.; Zolghadri, A. Control of nonlinear and LPV systems: Interval observer-based framework. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2013, 58, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, A. Dynamic triggering mechanisms for event-triggered control. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2014, 60, 1992–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Dong, J. Robust adaptive event-triggered fault-tolerant consensus control of multiagent systems with a positive minimum interevent time. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2023, 53, 4003–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Park, J.H. State-based dynamic event-triggered observer for one-sided Lipschitz nonlinear systems with disturbances. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs. 2022, 69, 2326–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



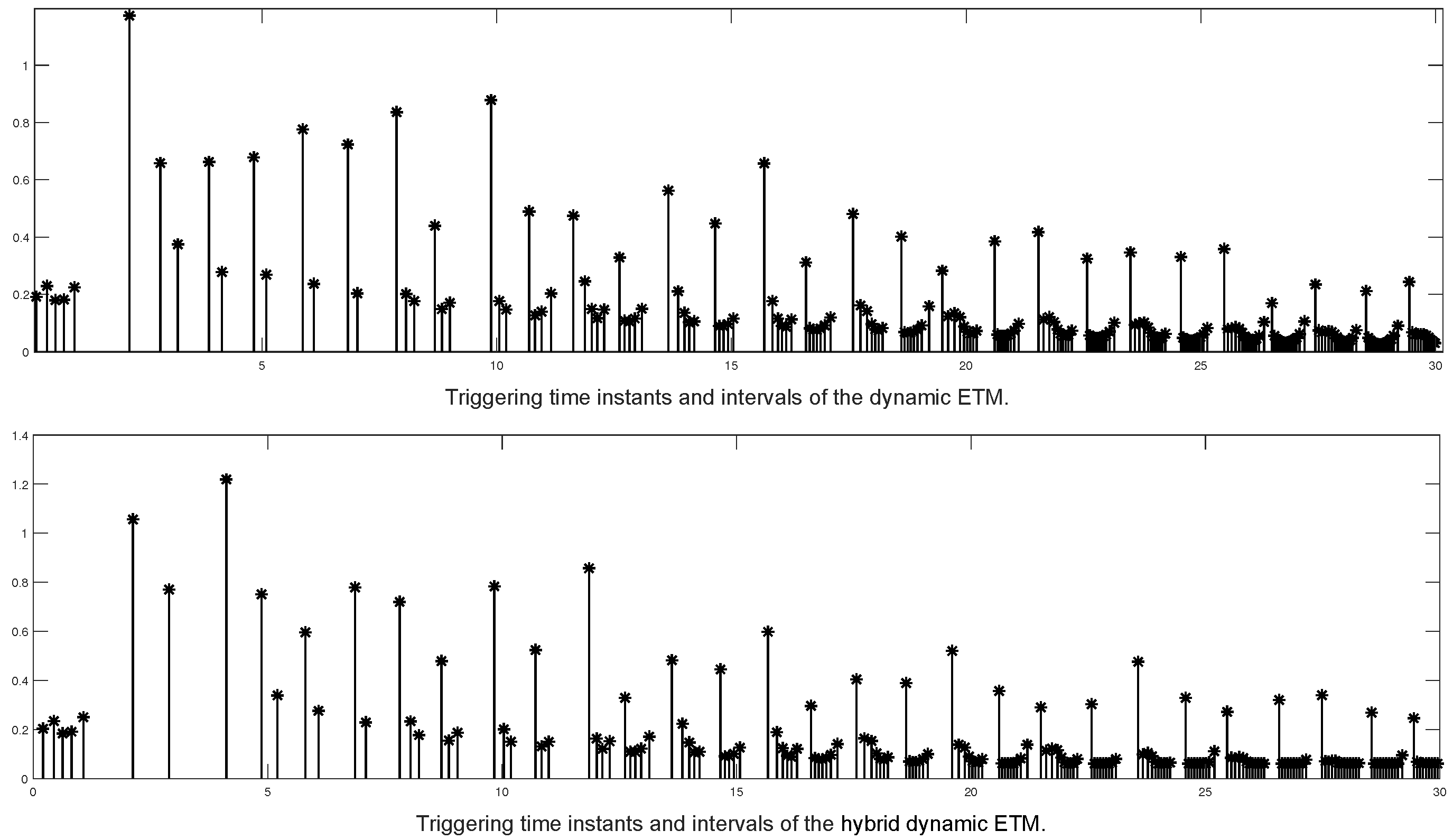
| 0.0504 | 0.0604 | 0.1346 | |
| Number of triggers (30 s) | 193 | 183 | 143 |
| The utilization rate of system resources | 0.643% | 0.610% | 0.477% |
| Different ETM | Hybrid Dynamic ETM of This Paper | Dynamic ETM of [33] |
|---|---|---|
| Number of triggers | 183 | 223 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, H.; Huang, J.; Qin, Y.; Sun, Y. Hybrid Dynamic Event-Triggered Interval Observer Design for Nonlinear Cyber–Physical Systems with Disturbance. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9020086
Wu H, Huang J, Qin Y, Sun Y. Hybrid Dynamic Event-Triggered Interval Observer Design for Nonlinear Cyber–Physical Systems with Disturbance. Fractal and Fractional. 2025; 9(2):86. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9020086
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Hongrun, Jun Huang, Yong Qin, and Yuan Sun. 2025. "Hybrid Dynamic Event-Triggered Interval Observer Design for Nonlinear Cyber–Physical Systems with Disturbance" Fractal and Fractional 9, no. 2: 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9020086
APA StyleWu, H., Huang, J., Qin, Y., & Sun, Y. (2025). Hybrid Dynamic Event-Triggered Interval Observer Design for Nonlinear Cyber–Physical Systems with Disturbance. Fractal and Fractional, 9(2), 86. https://doi.org/10.3390/fractalfract9020086







