The Use of Waste Polymers in Asphalt Mixtures: Bibliometric Analysis and Systematic Review
Abstract
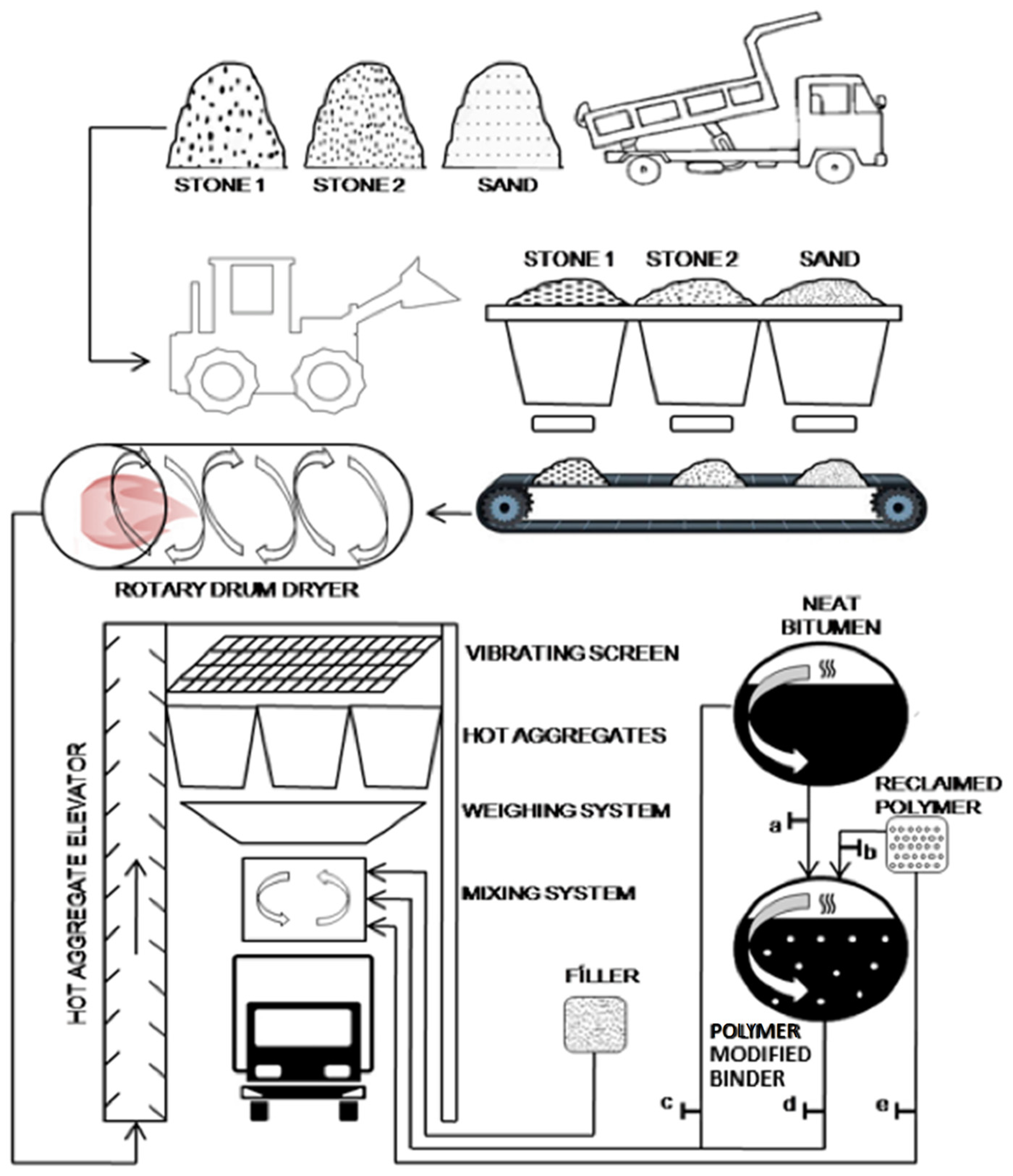
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Polymer Modification
3.1.1. PTP- and PET-Modified Asphalt
3.1.2. PE-Modified Asphalt
3.1.3. PU-Modified Asphalt
3.1.4. SBS-, SBR-, and EVA-Modified Asphalt
3.1.5. PVC-Modified Asphalt
3.1.6. CSR-Modified Asphalt
3.2. Hybrid Modification
3.3. Moisture Susceptibility
3.4. Aging, Rejuvenation, RAP
3.5. Benefits and Drawbacks
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
- As a modifier: Regardless of the type, waste polymers yield significant improvements in the resulting asphalt properties. These benefits include enhanced permanent deformation resistance, cracking at intermediate and low temperatures, and fatigue and rutting resistance. Waste polymer content and type influence the characteristics of modified asphalt, typically ranging between 1 and 15 wt.% of the asphalt binder.
- Hybrid modification: Incorporating polymer waste in asphalt may have adverse effects on pavement quality and performance. One approach to mitigate the drawbacks of polymer waste in asphalt is to incorporate other waste materials into the mixture. Crumb rubber, sulfur, and waste oils, for example, can improve the temperature performance, flexibility, and resilience of the asphalt.
- Moisture susceptibility: Incorporating waste polymers in asphalt mixtures enhances their moisture damage resistance. Acting as a barrier, the polymers reduce water penetration into the binder, thereby preserving strength and cohesion.
- RAP, rejuvenator, and aging: Adding waste polymers to RAP enhances the durability of asphalt. The polymers modify the properties of the asphalt binder, rendering it more resistant to aging, cracking, and deformation, resulting in longer lasting and more durable road surfaces. Waste polymers contribute to the performance characteristics of aged asphalt by improving its resistance to rutting and cracking, extending its lifespan.
- Advantages and disadvantages: Reclaimed polyethylene, such as LDPE and HDPE, provides superior performance among various waste polymers due to its favorable performance in the wet process.
- Create compatibilizer agents to improve the storage stability of polymeric-waste-modified asphalt.
- Analyze the effects of ultraviolet aging on the mechanical and rheological characteristics of polymer asphalt.
- Conduct field research to assess the long- and short-term performance of pavement through the use of various processes and investigate the practical implementation of waste polymer–asphalt mixtures in real-world construction projects.
- Determine the optimal polymer content that strikes a balance between performance enhancement and cost-effectiveness.
- Enhance the understanding of the mechanisms through which waste polymers modify the characteristics of asphalt. This knowledge will aid in the development of more effective polymer-modified asphalt.
- Contribute to the development of standardized testing protocols and guidelines for incorporating waste polymers into asphalt mixtures, ensuring consistent quality control and facilitating the widespread adoption of these technologies in the asphalt industry.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, P.; Chen, L.; Shao, L.; Zhang, H.; Lü, F. Municipal Solid Waste (MSW) Landfill: A Source of Microplastics? Evidence of Microplastics in Landfill Leachate. Water Res. 2019, 159, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, D.; Han, S.; Choi, J.; Hong, J. An Assessment of the Toxicity of Polypropylene Microplastics in Human Derived Cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameli, A.; Maher, J.; Mosavi, A.; Nabipour, N.; Babagoli, R.; Norouzi, N. Performance Evaluation of Binders and Stone Matrix Asphalt (SMA) Mixtures Modified by Ground Tire Rubber (GTR), Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Anti Stripping Agents (ASAs). Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 118932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvan, B.; Hassan, Z. Evaluation of Rutting Performance of Stone Matrix Asphalt Mixtures Containing Warm Mix Additives. J. Cent. South. Univ. 2017, 24, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Jiang, X.; Leng, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Zhong, J. Dual Responsive Microwave Heating-Healing System in Asphalt Concrete Incorporating Coal Gangue and Functional Aggregate. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 422, 138648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaro, N.S.A.; Sutanto, M.H.; Habib, N.Z.; Napiah, M.; Usman, A.; Jagaba, A.H.; Al-Sabaeei, A.M. Modeling and Optimization of Asphalt Content, Waste Palm Oil Clinker Powder and Waste Rice Straw Ash for Sustainable Asphalt Paving Employing Response Surface Methodology: A Pilot Study. Clean. Mater. 2023, 8, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, P.; Mishra, P.K.; Mondal, M.K.; Srivastava, N. Non-Biodegradable Polymeric Waste Pyrolysis for Energy Recovery. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnood, A.; Modiri Gharehveran, M. Morphology, Rheology, and Physical Properties of Polymer-Modified Asphalt Binders. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112, 766–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Huang, W.; Chen, M.; Song, B.; Zeng, G.; Zhang, Y. (Micro)Plastic Crisis: Un-Ignorable Contribution to Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statista. Annual Production of Plastics Worldwide from 1950 to 2021 (in Million Metric Tons). Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/282732/global-production-of-plastics-since-1950/ (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Martin-Alfonso, J.E.; Cuadri, A.A.; Torres, J.; Hidalgo, M.E.; Partal, P. Use of Plastic Wastes from Greenhouse in Asphalt Mixes Manufactured by Dry Process. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 20, S265–S281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, S.; Hajimohammadi, A.; Haji Seyed Javadi, N.; Khalili, N. The Use of Plastic Waste in Asphalt: A Critical Review on Asphalt Mix Design and Marshall Properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, M.R.; Mikhailenko, P.; Piao, Z.; Bueno, M.; Poulikakos, L. Analysis of Waste Polyethylene (PE) and Its by-Products in Asphalt Binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 280, 122492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, G.M.; Faxina, A.L. High-Temperature Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binders Modified with Recycled Low-Density Polyethylene and Crumb Rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 298, 123852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- tur Rasool, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Improving the Aging Resistance of SBS Modified Asphalt with the Addition of Highly Reclaimed Rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar, Z.N.; Karim, M.R.; Mahrez, A. A Review of Using Waste and Virgin Polymer in Pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 33, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.K.; Shah, S.A.R.; Alhazmi, H. Recycling and Utilization of Polymers for Road Construction Projects: An Application of the Circular Economy Concept. Polymers 2021, 13, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Birgisson, B.; Kringos, N. Polymer Modification of Bitumen: Advances and Challenges. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 54, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.N.; Self, A.; Read, J. The Shell Bitumen Handbook, 6th ed.; ICE Publishing: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.; Jiang, C.; Yuan, J.; Xiao, F.; Wang, J. Low Temperature Performance Characteristics of Polyethylene Modified Asphalts—A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Z.; Padhan, R.K.; Sreeram, A. Production of a Sustainable Paving Material through Chemical Recycling of Waste PET into Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.; Hameed, M.A.; Dulaimi, A. Evaluation of the Properties of Modified Local Asphalt Binder by Using Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR) or Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE). Sci. Rev. Eng. Environ. Sci. 2022, 31, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, R.K.; Sreeram, A. Enhancement of Storage Stability and Rheological Properties of Polyethylene (PE) Modified Asphalt Using Cross Linking and Reactive Polymer Based Additives. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delva, L.; Hubo, S.; Cardon, L.; Ragaert, K. On the Role of Flame Retardants in Mechanical Recycling of Solid Plastic Waste. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abduljabbar, N.; Al-Busaltan, S.; Dulaimi, A.; Al-Yasari, R.; Sadique, M.; Nageim, H. Al the Effect of Waste Low-Density Polyethylene on the Mechanical Properties of Thin Asphalt Overlay. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 315, 125722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Jiang, X.; Tan, Z.; Yin, B.; Leng, Z.; Zhong, J. Enhancing Sustainability in Pavement Engineering: A-State-of-the-Art Review of Cement Asphalt Emulsion Mixtures. Clean. Mater. 2023, 9, 100204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, X.; Polaczyk, P.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, M.; Huang, B. The Utilization of Waste Plastics in Asphalt Pavements: A Review. Clean. Mater. 2021, 2, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamuddin, S.; Boom, Y.J.; Giustozzi, F. Sustainable Polymers from Recycled Waste Plastics and Their Virgin Counterparts as Bitumen Modifiers: A Comprehensive Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.; Hafeez, I.; Jamal; Ullah, R. Sustainable Use of Waste Plastic Modifiers to Strengthen the Adhesion Properties of Asphalt Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 235, 117496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.; Damen, P. Viability of Using Recycled Plastics in Asphalt and Sprayed Sealing Applications; ARRB Group Limited: Melbourne, Australia, 2019; ISBN 1925854515. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, E.M.I. Use of Low-Density Polyethylene in Flexible Pavement. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2023; Volume 1110, p. 012065. [Google Scholar]
- Akkouri, N.; Baba, K.; Simou, S.; ELfarissi, L.; Nounah, A. Recycled Thermoplastics Modified Bitumen Improved with Thermoplastic Elastomer. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2020; Volume 150, p. 02015. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, L.M.B.; Peralta, J.; Oliveira, J.R.M.; Silva, H.M.R.D. A New Life for Cross-Linked Plastic Waste as Aggregates and Binder Modifier for Asphalt Mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq Kakar, M.; Mikhailenko, P.; Piao, Z.; Poulikakos, L.D. High and Low Temperature Performance of Polyethylene Waste Plastic Modified Low Noise Asphalt Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 348, 128633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasileiro, L.; Moreno-Navarro, F.; Tauste-Martínez, R.; Matos, J.; del Carmen Rubio-Gámez, M. Reclaimed Polymers as Asphalt Binder Modifiers for More Sustainable Roads: A Review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sughanthy, S.A.P.; Ansari, M.N.M.; Atiqah, A. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis of Polyethylene Terephthalate/Hydroxyapatite Biocomposites for Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 2350–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherkhani, H.; Arshadi, M.R. Investigating the Mechanical Properties of Asphalt Concrete Containing Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 20, 381–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lastra-González, P.; Calzada-Pérez, M.A.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Vega-Zamanillo, Á.; Indacoechea-Vega, I. Comparative Analysis of the Performance of Asphalt Concretes Modified by Dry Way with Polymeric Waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Cortavitarte, M.; Lastra-González, P.; Calzada-Pérez, M.Á.; Indacoechea-Vega, I. Analysis of the Influence of Using Recycled Polystyrene as a Substitute for Bitumen in the Behaviour of Asphalt Concrete Mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 170, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, J.P.; Panda, M.; Sahoo, U.C. Use of Waste Polyethylene for Modification of Bituminous Paving Mixes Containing Recycled Concrete Aggregates. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashesh, G.J.; Joni, H.H.; Dulaimi, A. The Impact of Recycled Crumb Rubber Powder on the Behavior of the Asphalt Mixture. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT), Ankara, Turkey, 20–22 October 2022; pp. 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, L.; Benta, A.; Picado-Santos, L. Asphalt Rubber Concrete Fabricated by the Dry Process: Laboratory Assessment of Resistance against Reflection Cracking. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 160, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Dai, J.; Fu, Z.; Liu, J.; Dong, W.; Huang, Z. A New Type of Crumb Rubber Asphalt Mixture: A Dry Process Design and Performance Evaluation. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appiah, J.K.; Berko-Boateng, V.N.; Tagbor, T.A. Use of Waste Plastic Materials for Road Construction in Ghana. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2017, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Sun, C.; Yao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Ren, S. Utilization of Wax Residue as Compatibilizer for Asphalt with Ground Tire Rubber/Recycled Polyethylene Blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 116966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Xin, X.; Fan, W.; Wang, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yao, Z. Phase Behavior and Hot Storage Characteristics of Asphalt Modified with Various Polyethylene: Experimental and Numerical Characterizations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 203, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lin, W.; Partl, M.; Wang, D.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Z. Waste Packaging Tape as a Novel Bitumen Modifier for Hot-Mix Asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 193, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Gao, F.; Liu, S.; Yu, T. Integrated Utilization of Recycled Crumb Rubber and Polyethylene for Enhancing the Performance of Modified Bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 170, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahrodi, M.H.; Jazani, O.M.; Paran, S.M.R.; Formela, K.; Saeb, M.R. Modification of Thermal and Rheological Characteristics of Bitumen by Waste PET/GTR Blends. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalhat, M.A.; Al-Abdul Wahhab, H.I. Performance of Recycled Plastic Waste Modified Asphalt Binder in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2017, 18, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rahman, A.M.M.; El-Shafie, M.; Mohammedy, M.M.; Abo-Shanab, Z.L. Enhancing the Performance of Blown Asphalt Binder Using Waste EVA Copolymer (WEVA). Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joohari, I.B.; Giustozzi, F. Chemical and High-Temperature Rheological Properties of Recycled Plastics-Polymer Modified Hybrid Bitumen. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 123064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, P.; Liang, M.; Jiang, H.; Yao, Z.; Airey, G. Experimental Exploration of Influence of Recycled Polymer Components on Rutting Resistance and Fatigue Behavior of Asphalt Mixtures. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agha, N.; Hussain, A.; Ali, A.S.; Qiu, Y. Performance Evaluation of Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) Containing Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Using Wet and Dry Mixing Techniques. Polymers 2023, 15, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghrafy, Y.M.; Abd Alla, E.S.M.; El-Badawy, S.M. Rheological Properties and Aging Performance of Sulfur Extended Asphalt Modified with Recycled Polyethylene Waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 273, 121771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryaee, D.; Ameri, M.; Mansourkhaki, A. Utilizing of Waste Polymer Modified Bitumen in Combination with Rejuvenator in High Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 235, 117516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naga, I.A.; Ragab, M. Benefits of Utilization the Recycle Polyethylene Terephthalate Waste Plastic Materials as a Modifier to Asphalt Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 219, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Zhao, R.; Wang, R.; Xi, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xie, H. Microstructure and Performance of Epoxy Asphalt Binders Modified by Core-Shell Rubbers Containing Different Core Polymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 304, 124689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeganeh, S.; Ameri, M.; Dalmazzo, D.; Santagata, E. Experimental Investigation on the Use of Waste Elastomeric Polymers for Bitumen Modification. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.E.; Abd Kader, S.A.; Jaya, R.P.; Yaacob, H.; Hassan, N.A.; Wan, C.N.C. Effect of Waste Plastic as Bitumen Modified in Asphalt Mixture. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2017; Volume 103, p. 09018. [Google Scholar]
- Abd Kader, S.A.; Jaya, R.P.; Yaacob, H.; Hainin, M.R.; Hassan, N.A.; Ibrahim, M.H.W.; Mohamed, A.A. Stability and Volumetric Properties of Asphalt Mixture Containing Waste Plastic. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2017; Volume 103, p. 09002. [Google Scholar]
- Tshifularo, C.A.; Patnaik, A. Recycling of Plastics into Textile Raw Materials and Products. In Sustainable Technologies for Fashion and Textiles; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 311–326. [Google Scholar]
- Foti, D. Recycled Waste PET for Sustainable Fiber-Reinforced Concrete. Use of Recycled Plastics in Eco-Efficient Concrete; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 387–410. [Google Scholar]
- Aghayan, I.; Khafajeh, R. Recycling of PET in Asphalt Concrete. Use of Recycled Plastics in Eco-Efficient Concrete; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 269–285. [Google Scholar]
- Ameri, M.; Yeganeh, S.; Erfani Valipor, P. Experimental Evaluation of Fatigue Resistance of Asphalt Mixtures Containing Waste Elastomeric Polymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 198, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movilla-Quesada, D.; Raposeiras, A.C.; Olavarría, J. Effects of Recycled Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) on Stiffness of Hot Asphalt Mixtures. Adv. Civil. Eng. 2019, 2019, 6969826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandabad, A.S.; Motevalizadeh, S.M.; Sedghi, R.; Ayar, P.; Asgharzadeh, S.M. Fracture and Mechanical Properties of Asphalt Mixtures Containing Granular Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 259, 120410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Wu, Q.; Leng, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhai, Y.; Tu, Y.; Peng, C. Chemical Upcycling of Waste PET into Sustainable Asphalt Pavement Containing Recycled Concrete Aggregates: Insight into Moisture-Induced Damage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 360, 129632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, D.R.; Kuang, W.; Malhotra, D.; Petrossian, G.; Zhong, L.; Simmons, K.L.; Zhang, J.; Cosimbescu, L. Waste PET Chemical Processing to Terephthalic Amides and Their Effect on Asphalt Performance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5615–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, M.; Hong, J.; Lai, F.; Gao, Y. Molecular Dynamics Study on Improvement Effect of Bis(2-Hydroxyethyl) Terephthalate on Adhesive Properties of Asphalt-Aggregate Interface. Fuel 2021, 285, 119175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Z.; Sreeram, A.; Padhan, R.K.; Tan, Z. Value-Added Application of Waste PET Based Additives in Bituminous Mixtures Containing High Percentage of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (RAP). J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, M.; Martínez-Barrera, G.; Salgado-Delgado, R.; Gencel, O. Recycling Polypropylene and Polyethylene Wastes in Production of Polyester Based Polymer Mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 121487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragaert, K.; Delva, L.; Van Damme, N.; Kuzmanovic, M.; Hubo, S.; Cardon, L. Microstructural Foundations of the Strength and Resilience of LLDPE Artificial Turf Yarn. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teltayev, B.B.; Rossi, C.O.; Izmailova, G.G.; Amirbayev, E.D.; Elshibayev, A.O. Evaluating the Effect of Asphalt Binder Modification on the Low-Temperature Cracking Resistance of Hot Mix Asphalt. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2019, 11, e00238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.M.B.; Silva, H.M.R.D.; Peralta, J.; Oliveira, J.R.M. Using Waste Polymers as a Reliable Alternative for Asphalt Binder Modification—Performance and Morphological Assessment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 198, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizamuddin, S.; Jamal, M.; Gravina, R.; Giustozzi, F. Recycled Plastic as Bitumen Modifier: The Role of Recycled Linear Low-Density Polyethylene in the Modification of Physical, Chemical and Rheological Properties of Bitumen. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirkhanian, S. Utilization of Scrap Plastics in Asphalt Binders. In Eco-Efficient Pavement Construction Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 13–32. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, M.; Xin, X.; Fan, W.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Yao, Z. Comparison of Rheological Properties and Compatibility of Asphalt Modified with Various Polyethylene. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Yang, F.; Guo, G.; Ren, M.; Shi, J.; Tan, L. The Use of Polyurethane for Asphalt Pavement Engineering Applications: A State-of-the-Art Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, S.; Ergun Tuna, B. Evaluation of the Cyclic Fatigue Performance of Polyurethane Foam in Different Density and Category. Polym. Test. 2019, 76, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutar, Y.; Naïmi, S.; Mezlini, S.; Carbas, R.J.C.; da Silva, L.F.M.; Ben Sik Ali, M. Fatigue Resistance of an Aluminium One-Component Polyurethane Adhesive Joint for the Automotive Industry: Effect of Surface Roughness and Adhesive Thickness. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2018, 83, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Yuan, J.; Jiang, F.; Yu, X.; Xiao, F. Recent Applications and Developments of Polyurethane Materials in Pavement Engineering. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 304, 124639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Guo, N.; You, Z.; Wang, L.; Wen, Y.; Tan, Y. Rheological Properties and Micro-Characteristics of Polyurethane Composite Modified Asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awazhar, N.A.; Khairuddin, F.H.; Rahmad, S.; Fadzil, S.M.; Omar, H.A.; Nur, N.I.; Badri, K.H. Engineering and Leaching Properties of Asphalt Binders Modified with Polyurethane and Cecabase Additives for Warm-Mix Asphalt Application. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 238, 117699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Liu, F.; Wang, J. Improving the Performance of RET Modified Asphalt with the Addition of Polyurethane Prepolymer (PUP). Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 206, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Lastra-Gonzalez, P.; Rodriguez-Hernandez, J.; González González, M.; Castro-Fresno, D. Critical Assessment of New Polymer-Modified Bitumen for Porous Asphalt Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 307, 124957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, R.K.; Sreeram, A.; Mohanta, C.S. Chemically Recycled Polyvinyl Chloride as a Bitumen Modifier: Synthesis, Characterisation and Performance Evaluation. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2021, 22, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abdul Wahhab, H.I.; Dalhat, M.A.; Habib, M.A. Storage Stability and High-Temperature Performance of Asphalt Binder Modified with Recycled Plastic. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, M.; Shahryari, E.; Ahmadi, T. Investigate the use of recycled polyvinyl chloride (PVC) particles in improving the mechanical properties of stone mastic asphalt (SMA). Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 326, 126780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, A.; Sharma, G.; Kumar, G. A Sustainable Approach: Utilization of Waste PVC in Asphalting of Roads. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 54, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, P.; Nirmalkumar, K.; Uthra, R.; Vihash Kumar, K.S.; Vishnu, R. Study on Construction of Roads Using PVC Wastes-review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1145, 012105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Liu, X.; Yu, R.; Liu, P.; Lei, W. Preparation and Properties of Asphalt Modified with a Composite Composed of Waste Package Poly(Vinyl Chloride) and Organic Montmorillonite. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2014, 30, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, B.T.; Tech, M. A Study On Effect Of Pvc In The Performance Of The Bituminous Concrete Mix. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Commun. Eng. 2018, 4, 170–179. [Google Scholar]
- Arabani, M.; Yousefpour Taleghani, M. Rutting Behavior of Hot Mix Asphalt Modified by Polyvinyl Chloride Powder. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 1621–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, N.; Jaleel, Z. Effects of Waste PVC Addition on the Properties of (40-50) Grade Asphalt. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 162, 01046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziari, H.; Nasiri, E.; Amini, A.; Ferdosian, O. The Effect of EAF Dust and Waste PVC on Moisture Sensitivity, Rutting Resistance, and Fatigue Performance of Asphalt Binders and Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 203, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, E.N.; Abed, A.H. Enhancement Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Modified with Hybrid Polymers According to Superpave System. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 20, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Han, X.; Gong, J.; Xi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xie, H. Toughening Epoxy Asphalt Binder Using Core-Shell Rubber Nanoparticles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 119716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasileiro, L.L.; Moreno-Navarro, F.; Martínez, R.T.; del Sol-Sánchez, M.; Matos, J.M.E.; del Carmen Rubio-Gámez, M. Study of the Feasability of Producing Modified Asphalt Bitumens Using Flakes Made from Recycled Polymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Yan, K.; You, Z.; Xu, H. Modification Mechanism of Asphalt Binder with Waste Tire Rubber and Recycled Polyethylene. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, S.; Fiorentini, N.; Huang, J.; Losa, M. Crumb Rubber Modifier in Road Asphalt Pavements: State of the Art and Statistics. Coatings 2019, 9, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanjegowda, V.H.; Biligiri, K.P. Recyclability of Rubber in Asphalt Roadway Systems: A Review of Applied Research and Advancement in Technology. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 155, 104655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poovaneshvaran, S.; Mohd Hasan, M.R.; Putra Jaya, R. Impacts of Recycled Crumb Rubber Powder and Natural Rubber Latex on the Modified Asphalt Rheological Behaviour, Bonding, and Resistance to Shear. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanpour-Kasanagh, S.; Ahmedzade, P.; Fainleib, A.M.; Behnood, A. Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binders Modified with Recycled Materials: A Comparison with Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene (SBS). Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 117047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Roque, R.; Hernando, D.; Chun, S. Cracking Performance Characterisation of Asphalt Mixtures Containing Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement with Hybrid Binder. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2019, 20, 347–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.H.; Mazumder, M.; Lee, S.-J. Recycling of Aged Asphalt Binders with Wax Warm Additives. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2018, 19, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cong, P. Investigation on Physical and High Temperature Rheology Properties of Asphalt Binder Adding Waste Oil and Polymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 144, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzi, M.; Golestani, B.; Lee, K.W. Improving Moisture Sensitivity and Mechanical Properties of Sulfur Extended Asphalt Mixture by Nano-Antistripping Agent. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 133, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholy, S.A.; Abd El-Rahman, A.M.M.; El-Shafie, M.; Abo-Shanab, Z.L. Physical and Rheological Properties of Modified Sulfur Asphalt Binder. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2018, 11, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedik, A.; Lav, A.H. Determining Optimum Sulfur Content as Alternative Binder Additive in Asphaltic Concrete Pavements. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2016, 28, 04016040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghrafy, Y.M.; El-Badawy, S.M.; Abd Alla, E.-S.M. Rheological and Environmental Evaluation of Sulfur Extended Asphalt Binders Modified by High-and Low-Density Polyethylene Recycled Waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 307, 125008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawesah, H.A.; Sadique, M.; Harris, C.; Nageim, H.A.; Stopp, K.; Pearl, H. Polymer Modified Asphalt Binder–an Approach for Enhancing Temperature Sensitivity for Emergency Pavement Repair. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2022, 23, 4760–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.; Singh, D. Moisture Characteristics of Mixtures with Warm Mix Asphalt Technologies—A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 142, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Qian, Z. The Prediction of Adhesive Failure between Aggregates and Asphalt Mastic Based on Aggregate Features. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 183, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Tan, T. Adhesion between Modified Binders and Aggregate Minerals at Ambient Conditions Measured with Particle-Probe Scanning Force Microscopes. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2017, 29, 04017068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, S.; Kumar Roy, T. Influence of Plastic Waste on Chemical and Mechanical Properties of Modified Bitumen Used in the Bituminous Mix for Flexible Pavement. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2021, 33, 04020440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Leng, Z.; Yang, J.; Lu, G.; Huang, M.; Lan, J.; Zhang, H.; Bai, Y.; Dong, Z. Innovative Application of Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Derived Additive as an Antistripping Agent for Asphalt Mixture: Experimental Investigation and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Fuel 2021, 300, 121015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachariah, J.P.; Sarkar, P.P.; Pal, M. A Study on the Moisture Damage and Rutting Resistance of Polypropylene Modified Bituminous Mixes with Crushed Brick Aggregate Wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majidifard, H.; Jahangiri, B.; Rath, P.; Buttlar, W.G. Development of a Balanced Cracking Index for Asphalt Mixtures Tested in Semi-Circular Bending with Load-LLD Measurements. Measurement 2021, 173, 108658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, M.; Siyadati, S.A.; Aliha, M.R.M. Impact of Freeze–Thaw Cycles on Low Temperature Mixed Mode I/II Cracking Properties of Water Saturated Hot Mix Asphalt: An Experimental Study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 119939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliha, M.R.M.; Sarbijan, M.J. Effects of Loading, Geometry and Material Properties on Fracture Parameters of a Pavement Containing Top-down and Bottom-up Cracks. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2016, 166, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrassia, L.P.; Spinelli, P.; Paoloni, G.; Canestrari, F. Top-down Cracking in Italian Motorway Pavements: A Case Study. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 13, e00442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, H.R.; Khedri, E.; Aliha, M.R.M.; Shaker, H.; Haghighatpour, P.J. Repair Efficiency Evaluation for Cracked Asphalt Mixture Pavement in Different Ambient Temperatures Using Bitumen and Polymer Concrete as Repair Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnatenko, R.; Tsyrkunova, K.; Zhdanyuk, V. Technological Sides of Crack Sealing in Asphalt Pavements. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldagari, S.; Kabir, S.F.; Fini, E.H. Investigating Aging Properties of Bitumen Modified with Polyethylene-Terephthalate Waste Plastic. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 173, 105687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Capitão, S.; Bandeira, R.; Fonseca, M.; Picado-Santos, L. Performance of AC Mixtures Containing Flakes of LDPE Plastic Film Collected from Urban Waste Considering Ageing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.Z.; Hossain, Z.; Zaman, M. Nonrecoverable Compliance and Recovery Behavior of Polymer-Modified and Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement–Modified Binders in Arkansas. J. Test. Eval. 2018, 46, 2483–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan Mirhosseini, A.; Kavussi, A.; Tahami, S.A.; Dessouky, S. Characterizing Temperature Performance of Bio-Modified Binders Containing RAP Binder. J. Mater. Civil. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N. Investigation of the Properties of Asphalt Mixtures Incorporating Reclaimed SBS Modified Asphalt Pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 113, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H. Preparation of Rejuvenating Agent and Property Evaluation of Rejuvenated SBS Modified Asphalt Binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 233, 117911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behroozikhah, A.; Morafa, S.H.; Aflaki, S. Investigation of Fatigue Cracks on RAP Mixtures Containing Sasobit and Crumb Rubber Based on Fracture Energy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 141, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, M.; Mansourkhaki, A.; Daryaee, D. Evaluation of Fatigue Behavior of Asphalt Binders Containing Reclaimed Asphalt Binder Using Simplified Viscoelastic Continuum Damage Approach. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, M.; Mansourkhaki, A.; Daryaee, D. Evaluation of Fatigue Behavior of High Reclaimed Asphalt Binder Mixes Modified with Rejuvenator and Softer Bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 191, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabizadeh, H.; Haghshenas, H.F.; Kim, Y.-R.; Aragão, F.T.S. Effects of Rejuvenators on High-RAP Mixtures Based on Laboratory Tests of Asphalt Concrete (AC) Mixtures and Fine Aggregate Matrix (FAM) Mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 152, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryaee, D.; Habibpour, M.; Gulzar, S.; Underwood, B.S. Combined Effect of Waste Polymer and Rejuvenator on Performance Properties of Reclaimed Asphalt Binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 268, 121059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, C.; El Hanandeh, A. Systematic Literature Review, Meta-Analysis and Artificial Neural Network Modelling of Plastic Waste Addition to Bitumen. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, R.K.; Mohanta, C.; Sreeram, A.; Gupta, A. Rheological Evaluation of Bitumen Modified Using Antistripping Additives Synthesised from Waste Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawande, A.; Zamare, G.; Renge, V.C.; Tayde, S.; Bharsakale, G. An Overview on Waste Plastic Utilization in Asphalting of Roads. J. Eng. Res. Stud. 2012, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.; Fang, C.; Liu, P.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Storage Stability and Rheological Properties of Asphalt Modified with Waste Packaging Polyethylene and Organic Montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 104, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fethiza Ali, B.; Soudani, K.; Haddadi, S. Effect of Waste Plastic and Crumb Rubber on the Thermal Oxidative Aging of Modified Bitumen. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2022, 23, 222–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, Y. Polymer Modified Asphalt Binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2007, 21, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radeef, H.R.; Hassan, N.A.; Katman, H.Y.; Mahmud, M.Z.H.; Abidin, A.R.Z.; Ismail, C.R. The Mechanical Response of Dry-Process Polymer Wastes Modified Asphalt under Ageing and Moisture Damage. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 16, e00913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Oeser, M.; Wang, D. Recycling Waste Packaging Tape into Bituminous Mixtures towards Enhanced Mechanical Properties and Environmental Benefits. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, F.; Rubio, M.C.; Martinez-Echevarria, M.J. The Mechanical Performance of Dry-Process Crumb Rubber Modified Hot Bituminous Mixes: The Influence of Digestion Time and Crumb Rubber Percentage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahami, S.A.; Mirhosseini, A.F.; Dessouky, S.; Mork, H.; Kavussi, A. The Use of High Content of Fine Crumb Rubber in Asphalt Mixes Using Dry Process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 222, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, G.M.; Faxina, A.L. Asphalt Concrete Mixtures Modified with Polymeric Waste by the Wet and Dry Processes: A Literature Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 312, 125408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Ref. | Waste Polymer | Polymer Content (by Weight of Blend) | Asphalt | Mixing Method | Mixer | Mixing Parameters (Temperature, Speed, Time) | Tests |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [44] | HDPE and PP | 0.5–3% | bitumen AC-20 | Wet | High shear blending | 160–170 °C, 120 rpm, 30–60 min | FTIR spectroscopy Basic rheological parameters |
| [45] | Recycled PE | 15% | asphalt modified with GTR/PE | Dry | High shear mixer | 180 °C, 5000 rpm, 60 min | Temperature behavior Storage stability Morphology |
| [46] | PE of various densities | 5% | base asphalt (70/100) | - | High shear mixer | 150–170 °C, 500–4000 rpm, 30–150 min | Storage stability Morphology Fluorescence microscopy |
| [47] | PE (polyethylene waste packing tape) | 2%, 4%, 6%, and 8% | base bitumen (60/70) | Wet | High shear blending | 180 °C, 20,000 rpm, 60 min | Rutting and fatigue Rheological characterization |
| [48] | Composite, PE, and CR | PE (6%, 7%), CR (11%, 15%) | 70# base bitumen | Dry | High-speed shear process | 160 °C, 5000 rpm, 60 min | Physical and rheological performance Multiple Stress Creep Recovery (MSCR) Bending-Beam Rheometer (BBR) |
| [49] | wPET/GTR | 3%, 5%, 7% | road bitumen (60/70) | Dry | High shear mixer | 150 °C, 350–3000 rpm, 15–45 min | Rheological properties FTIR spectroscopy Morphology Thermal stability |
| [50] | PP, LDPE, and HDPE | 2%, 4%, 6%, 8% | refinery asphalt | Wet | High shear mixer | 160–190 °C, 5000 rpm, 50–60 min | Viscoelastic performance Resilient modulus Rutting, creep, and fatigue performance |
| [51] | EVA copolymer | 3%, 5%, 7% | blown asphalt | Wet | High shear mixer | 150 °C, 1500 rpm, 180 min | Physico-chemical characteristics |
| [52] | Various-density PE | 2% + 3% SBS | base bitumen C170 | Wet | Mechanical shear mixer | 180 °C, 3500 rpm, 180 min | Rheological behavior Thermal behavior Conventional bitumen test |
| [53] | PE | 0.2%, 0.3% | 70# base bitumen | Dry | - | 160 °C, 5 min | Uniaxial penetration, wheel tracking, and four-point bending |
| [54] | PET | 2%, 4%, 6%, 8%, 10% | bitumen (60/70) | Dry and wet | High shear laboratory-type mixer | 155–160 °C, 1100 rpm, 180 min | Susceptibility Test, Indirect Tensile Fatigue Test Flow and Marshall Stability Tests |
| [55] | rPW, rLDPE, rHDPE | 2%, 4%, 6%, 8% | sulfur-extended asphalt | Wet | high shear mixer | 50–145 °C, 10 min | Advanced rheological test Basic and rheological properties |
| [56] | PBR | 5%, 7.5%, 10% | RAP materials (60/70) | Wet | high shear mixer | 160 °C, 6000 rpm, 60 min | Moisture susceptibility Fatigue resistance, rutting resistance |
| [57] | PTP | 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12% | asphalt binder (60/70) | Dry | high shear mixer | 140–300 °C, 180 min | Basic and rheological properties, Marshall, indirect tensile, and rutting tests |
| [58] | CSR copolymer | 2% | hot-mix epoxy asphalt binder | Wet | high shear mixer | 150–160 °C, 200 rpm, 30 min, 180 min, 3d | Mechanical and tensile tests Thermogravimetric analysis Viscous measurement microscopy |
| [59] | PBR SBS | 3.0%, 4.0%, 5% | bitumen (50–70) | - | high shear mixer | 140–160 °C, 4000 rpm, 40 min | Preliminary Characterization Tests Chemical characterization Advanced Characterization Tests |
| [34] | PE | 5% | asphalt (70/100) | Dry | high shear mixer | 170 °C, 3500 rpm, 60 min | Semi-circular bending test cyclic compression test microscopy |
| Content of Main Modifier | Content of Other Modifier |
|---|---|
| 1% (Unsaturated Polyester Resin, UPR) | 15% (PU) |
| 5% (PU) | 5% (Pock Asphalt, RA) |
| 8–10% (Reactive Elastomeric Terpolymer, RET) | 1.5% (PU) |
| 9% (PU) | 2% (Organic Montmorillonite, OMMT) |
| 12% (PU) | 15% (CR) |
| Waste Polymer | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Wet process | ||
| PP |
|
|
| PE |
|
|
| EVA |
|
|
| PVC |
|
|
| CRM |
|
|
| Dry process | ||
| PE |
|
|
| Recycled polystyrene |
|
|
| PET |
|
|
| CR |
|
|
| PP |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jwaida, Z.; Dulaimi, A.; Mydin, M.A.O.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Jaya, R.P.; Ameen, A. The Use of Waste Polymers in Asphalt Mixtures: Bibliometric Analysis and Systematic Review. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7100415
Jwaida Z, Dulaimi A, Mydin MAO, Özkılıç YO, Jaya RP, Ameen A. The Use of Waste Polymers in Asphalt Mixtures: Bibliometric Analysis and Systematic Review. Journal of Composites Science. 2023; 7(10):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7100415
Chicago/Turabian StyleJwaida, Zahraa, Anmar Dulaimi, Md Azree Othuman Mydin, Yasin Onuralp Özkılıç, Ramadhansyah Putra Jaya, and Arman Ameen. 2023. "The Use of Waste Polymers in Asphalt Mixtures: Bibliometric Analysis and Systematic Review" Journal of Composites Science 7, no. 10: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7100415
APA StyleJwaida, Z., Dulaimi, A., Mydin, M. A. O., Özkılıç, Y. O., Jaya, R. P., & Ameen, A. (2023). The Use of Waste Polymers in Asphalt Mixtures: Bibliometric Analysis and Systematic Review. Journal of Composites Science, 7(10), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs7100415











