Experimental Investigation on Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber–Nanoclay–Epoxy Composites Under Water-Soaking: A Comparative Study Using RSM and ANN
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Preparation of Composites
2.2. Water-Soaking Conditions
2.3. Mechanical Testing and Analysis
2.3.1. Tensile Test
2.3.2. SEM Analysis
2.3.3. Flexural Test
2.4. Design of Experiments
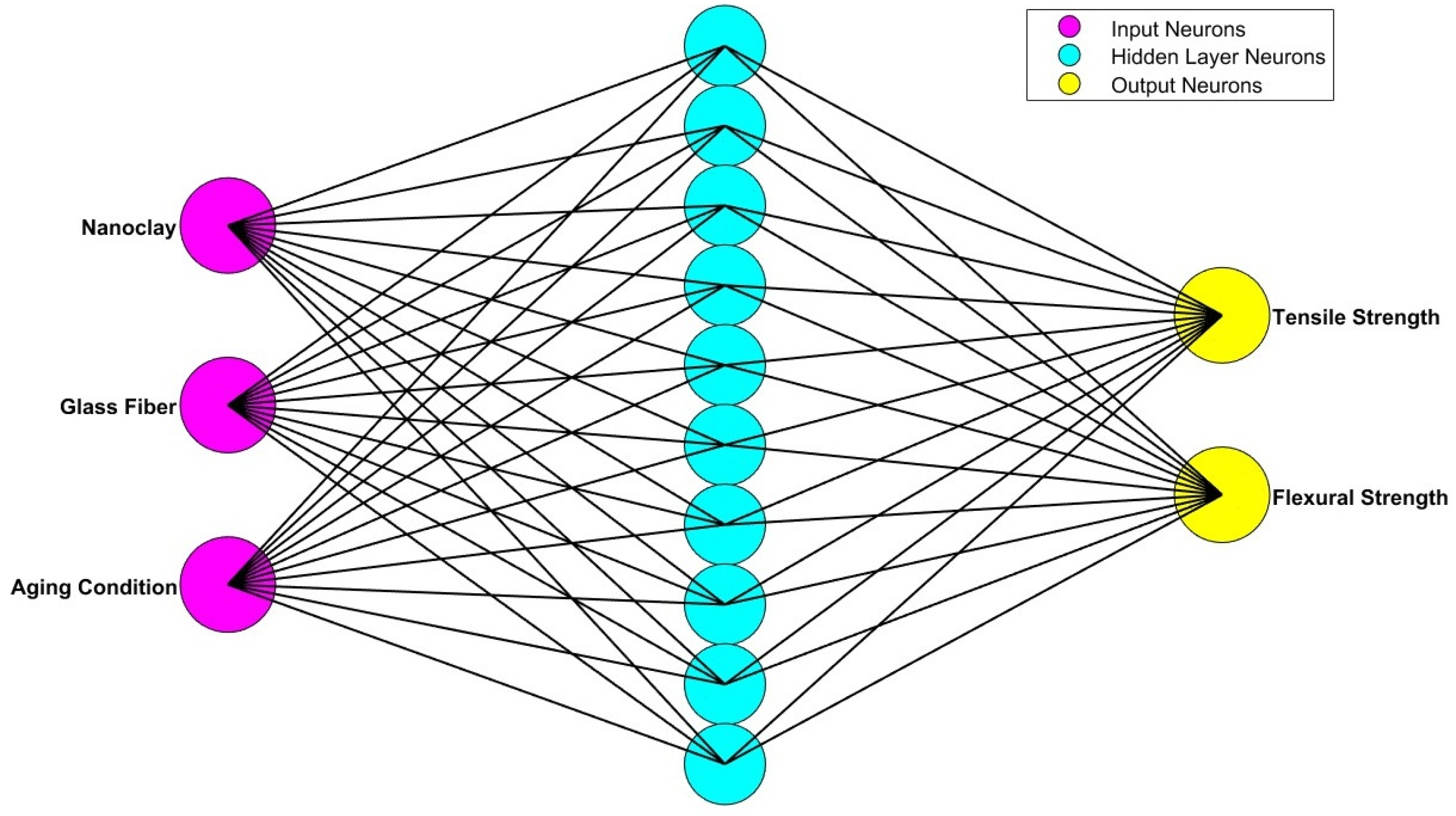
2.5. Artificial Neural Network
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Response Surface Methodology—Central Composite Design
3.1.1. ANOVA
3.1.2. Regression Equation and Residual Plots
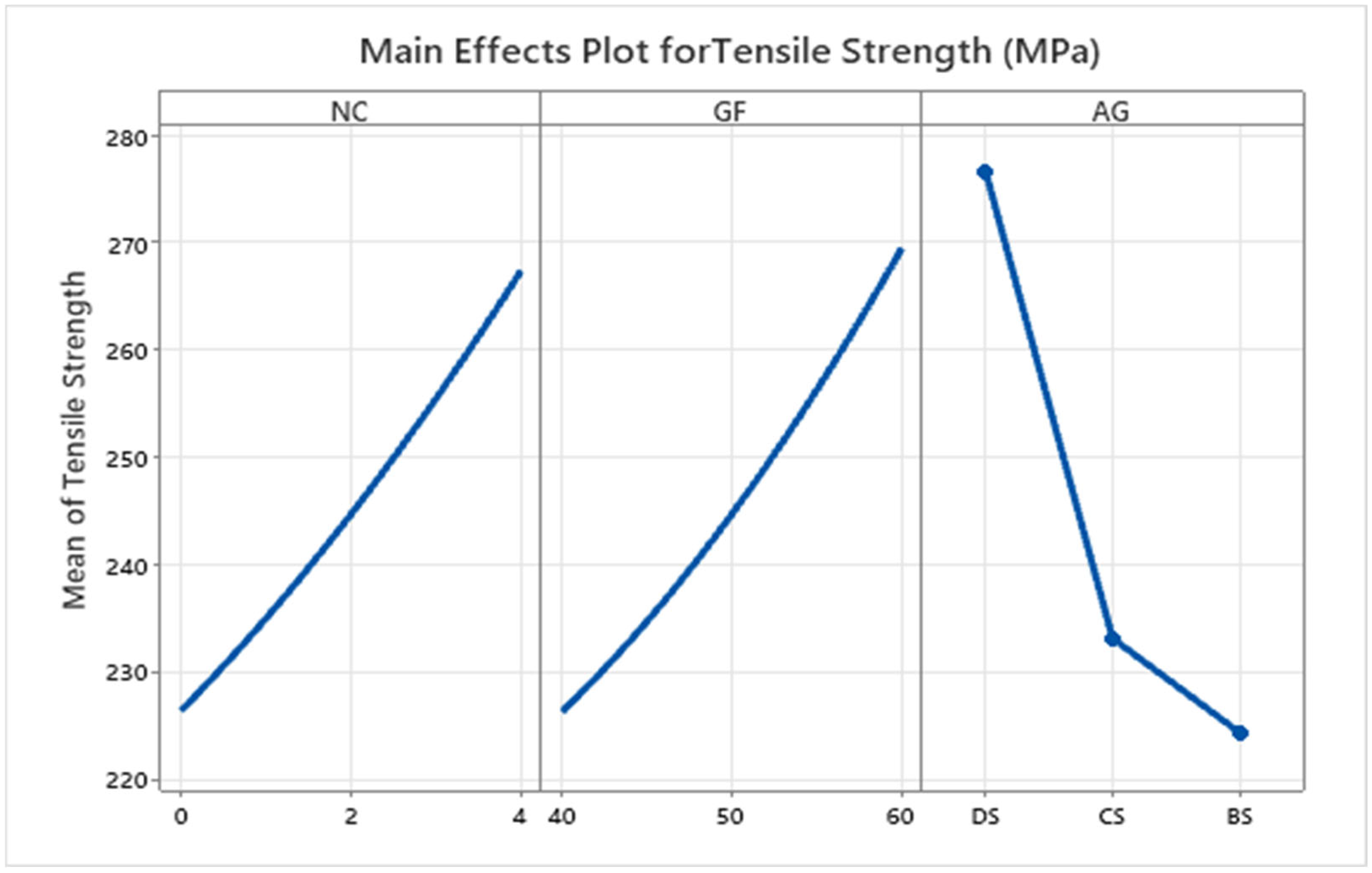
3.1.3. Main Effects Plots
3.1.4. Interaction Plots
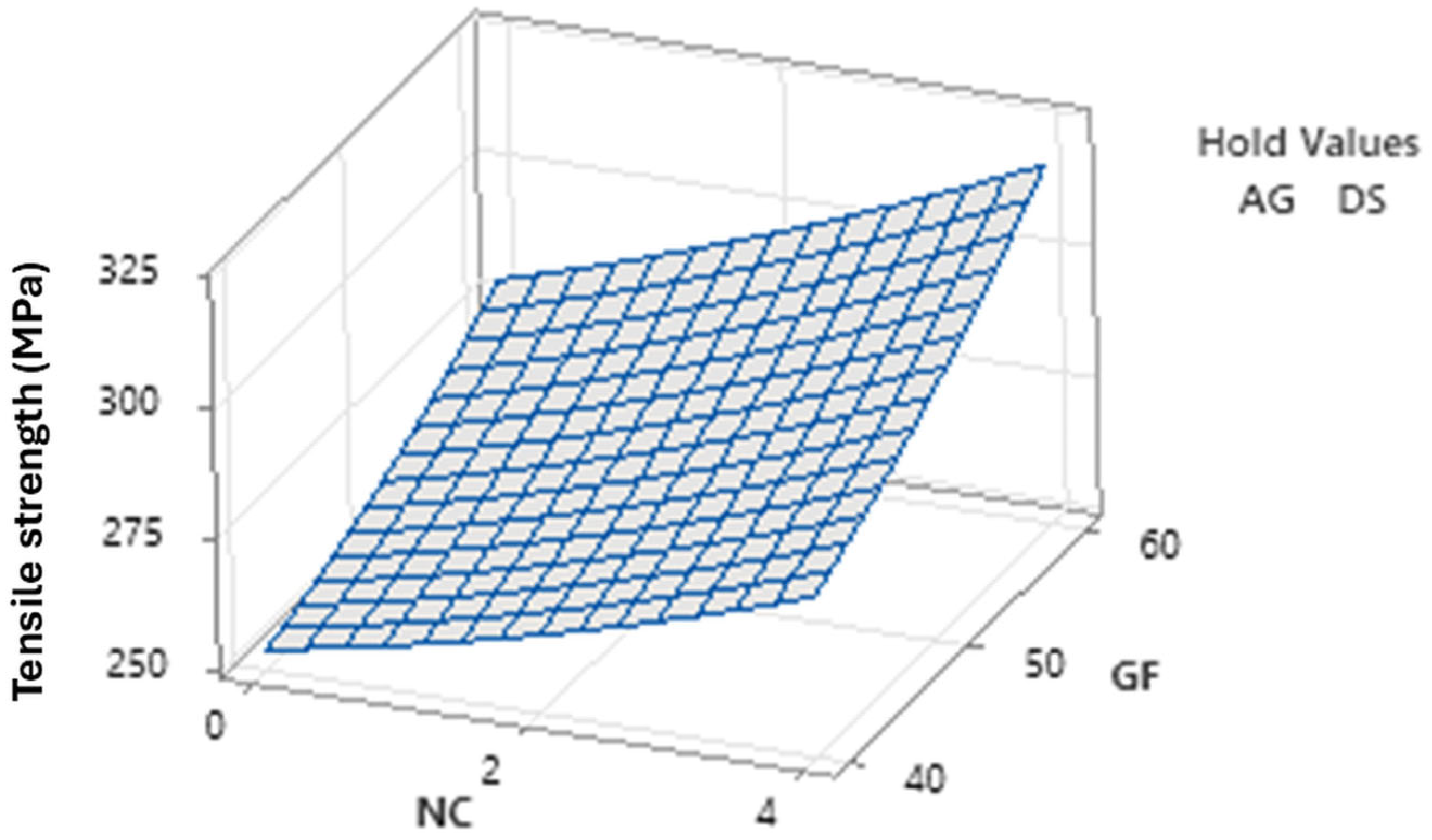
3.1.5. Surface Plots
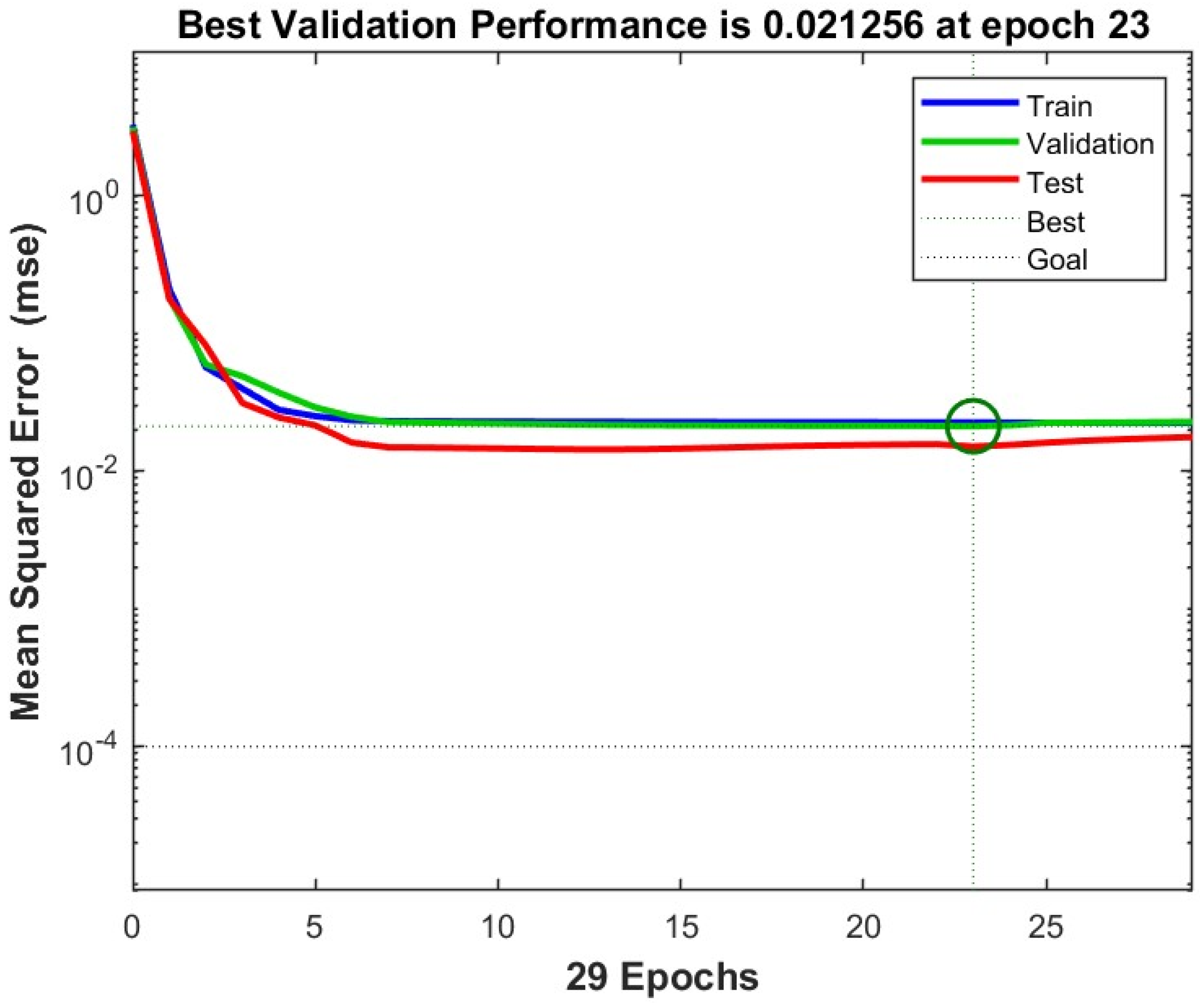
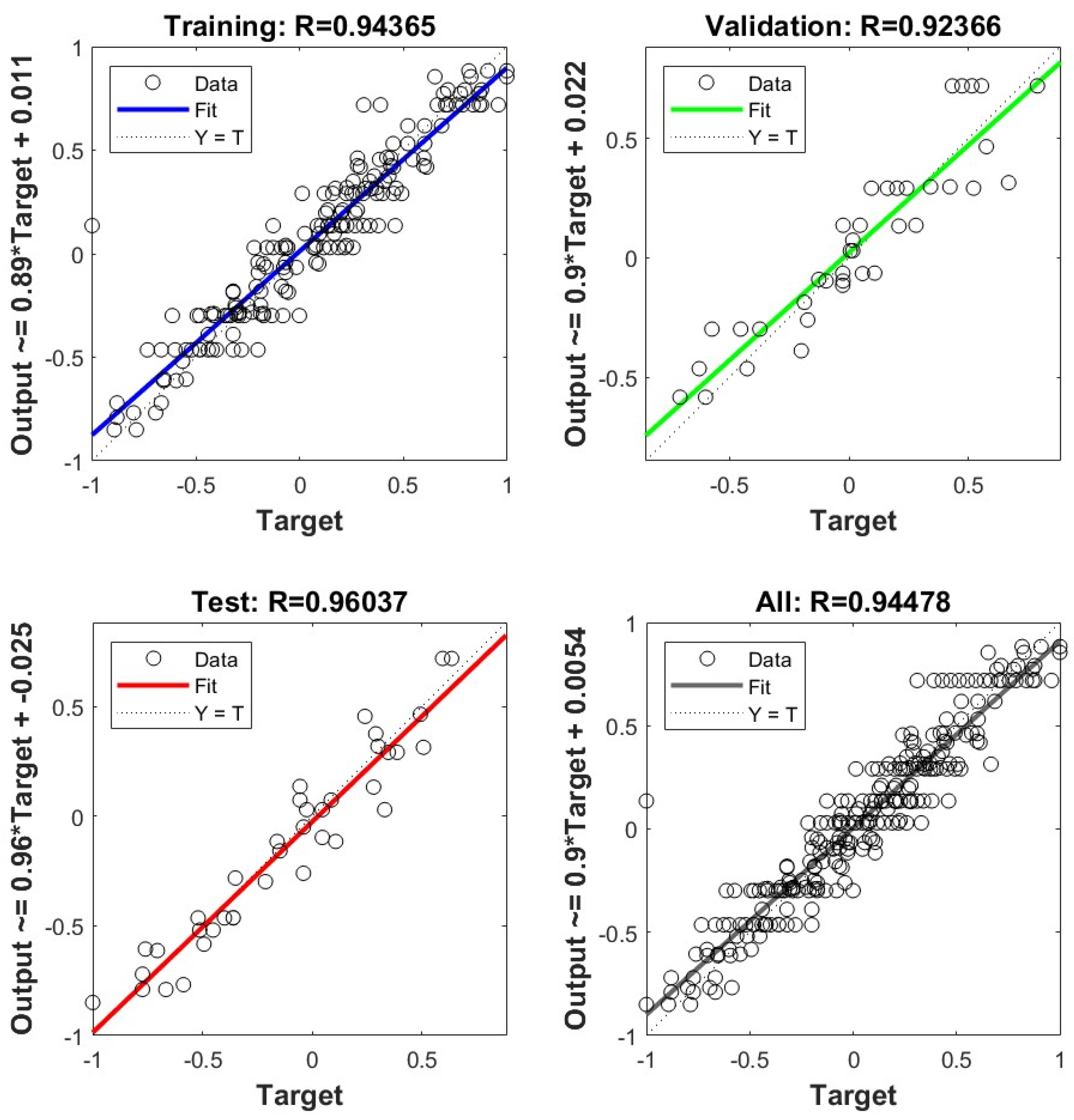
3.2. Artificial Neural Network
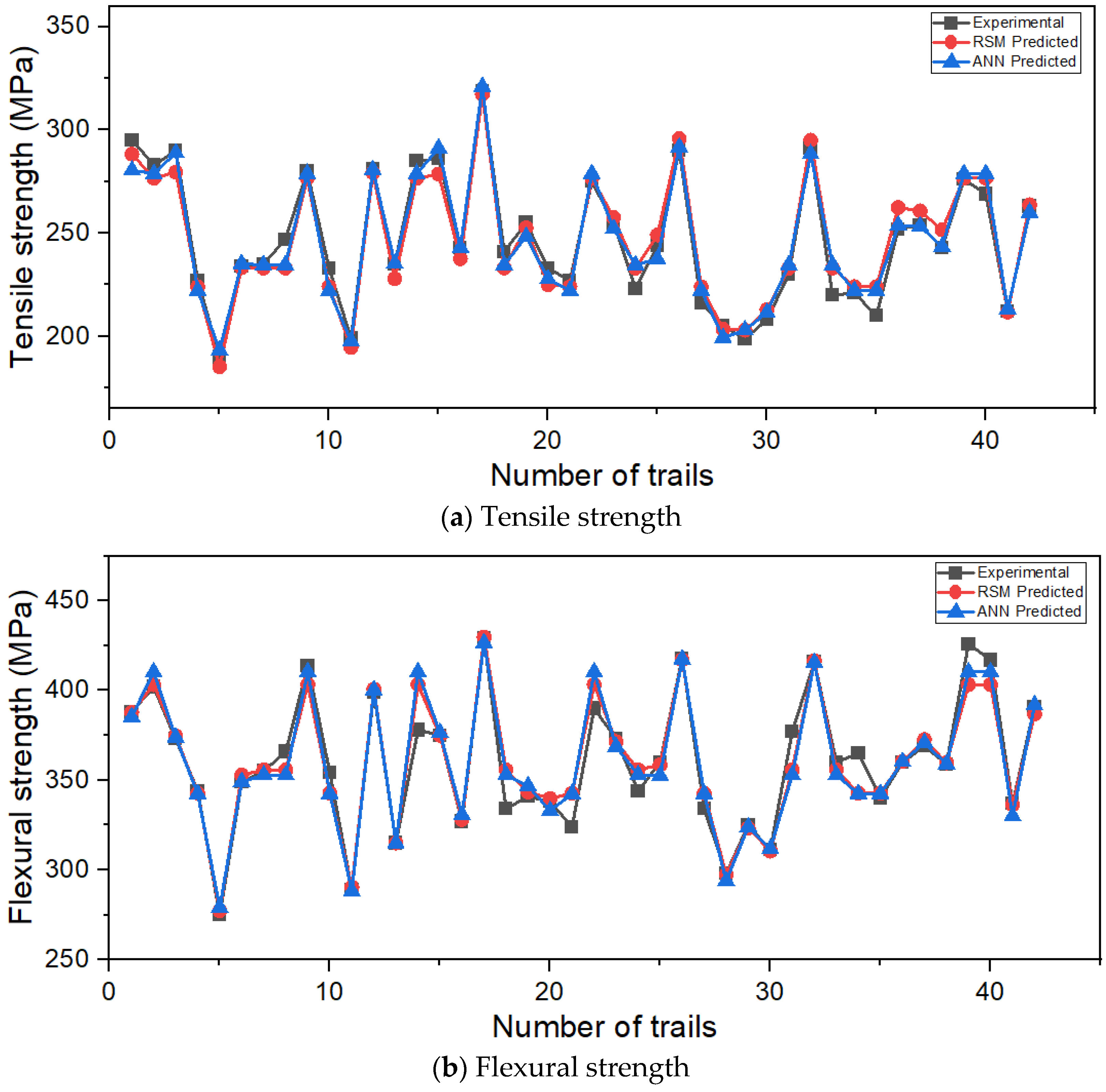
3.3. Comparison Data
3.4. SEM Analysis
4. Conclusions
- The increase in wt.% of glass fiber and nanoclay enhances the strength of the composites and declines the effect of aging conditions.
- The composite with 4 wt.% nanoclay and 60 wt.% glass fiber under dry (as-made) conditions displays the highest tensile and flexural strengths, i.e., 319 (±12) and 429 (±15) MPa, respectively.
- The composite with 40 wt.% glass fiber and without nanoclay under boiling water-soaking conditions display the lowest tensile and flexural strengths, i.e., 190 (±13) and 275 (±14) MPa, respectively.
- RSM provided highly accurate predictions for tensile strength due to its structured polynomial approach.
- The ANN model exhibited enhanced accuracy in predicting flexural strength by effectively modeling the intricate nonlinear relationship.
- SEM analysis of the fracture surfaces reveals the reasons for specimen failure under tensile load, with apparent differences for dry, cold, and boiling water-soaked specimens.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diniță, A.; Ripeanu, R.G.; Ilincă, C.N.; Cursaru, D.; Matei, D.; Naim, R.I.; Tănase, M.; Portoacă, A.I. Advancements in Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composites: A Comprehensive Analysis. Polymers 2023, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzat, A.K.; Murad, M.S.; Adediran, I.A.; Asmatulu, E.; Asmatulu, R. Fiber-reinforced composites for aerospace, energy, and marine applications: An insight into failure mechanisms under chemical, thermal, oxidative, and mechanical load conditions. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2025, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmare, S.; Yoseph, B.; Jamir, T.M. Investigating the impact resistance of E-glass/Polyester composite materials in variable fiber-to-matrix weight ratio composition. Cogent Eng. 2023, 10, 2178110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, H.; Ahmad, Z.; Mazlan, S.A.; Faizal Johari, M.A.; Siebert, G.; Petrů, M.; Rahimian Koloor, S.S. Lightweight Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composite for Automotive Bumper Applications: A Review. Polymers 2022, 15, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Cao, Y. Strength degradation of GFRP cross-ply laminates in hydrothermal conditions. APL Mater. 2024, 12, 031113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, J.; Xypolias, G. Hydrothermal Ageing of Glass Fibre Reinforced Vinyl Ester Composites: A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Cao, Y. Investigation of the hygrothermal aging behavior of GFRP laminates used for a marine unmanned aerial vehicle structure. AIP Adv. 2023, 13, 045107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merah, N.; Ashraf, F.; Shaukat, M.M. Mechanical and Moisture Barrier Properties of Epoxy–Nanoclay and Hybrid Epoxy–Nanoclay Glass Fibre Composites: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiratli, S.; Aslan, Z. Investigation of mechanical properties of nanoclay modified E-glass/epoxy composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2023, 57, 2501–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, W.W.; Jumahat, A.; Mahmud, J. Effect of nanoclay content on flexural properties of glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) composites. J. Teknol. 2015, 76, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, A.; Merah, N. Nanoclay enhancement of flexural properties and water uptake resistance of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy composites at different temperatures. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antil, S.K.; Antil, P.; Singh, S.; Kumar, A.; Pruncu, C.I. Artificial Neural Network and Response Surface Methodology Based Analysis on Solid Particle Erosion Behavior of Polymer Matrix Composites. Materials 2020, 13, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopparthi, P.K.; Kundavarapu, V.R.; Dasari, V.R.; Kaki, V.R.; Pathakokila, B.R. Modeling of glass fiber reinforced composites for optimal mechanical properties using teaching learning based optimization and artificial neural networks. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoth, V.; Sathiyamurthy, S.; Saravanakumar, S.; Senthilkumar, R. Integrating response surface methodology and machine learning for analyzing the unconventional machining properties of hybrid fiber-reinforced composites. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 6077–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, S.J.; Saravanan, R.; Sathish, T.; Giri, J.; Kanan, M. Mechanical assessment for enhancing hybrid composite performance through silane treatment using RSM and ANN. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, S.J.; Saravanan, R.; Sathish, T.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Giri, J.; Kumar, A. Enhancing mechanical performance of MWCNT filler with jute/kenaf/glass composite: A statistical optimization study using RSM and ANN. Mater. Technol. 2024, 39, 2381156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladaci, N.; Saadia, A.; Belaadi, A.; Boumaaza, M.; Chai, B.X.; Abdullah, M.M.S.; Al-Khawlani, A.; Ghernaout, D. ANN and RSM Prediction of Water Uptake of Recycled HDPE Biocomposite Reinforced with Treated Palm Waste W. filifera. J. Nat. Fibers 2024, 21, 2356697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.M.; Gowrishankar, M.C.; Shettar, M. Effect of boiling water soaking on the mechanical properties and durability of nanoclay-enhanced bamboo and glass fiber epoxy composites. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3039; Test Method for Tensile Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2008. [CrossRef]
- ASTM D7264; Test Method for Flexural Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Withers, G.J.; Yu, Y.; Khabashesku, V.N.; Cercone, L.; Hadjiev, V.G.; Souza, J.M.; Davis, D.C. Improved mechanical properties of an epoxy glass–fiber composite reinforced with surface organomodified nanoclays. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 72, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyakumar, R.; Sampath, P.S.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ramakrishnan, T. Structural, morphological and mechanical behaviour of glass fibre reinforced epoxy nanoclay composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annappa, A.R.; Basavarajappa, S.; Davim, J.P. Effect of organoclays on mechanical properties of glass fiber-reinforced epoxy nanocomposite. Polym. Bull. 2021, 79, 5085–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çava, K.; İpek, H.; Uşun, A.; Aslan, M. Examine the mechanical properties of woven glass fiber fabric reinforced composite plate manufactured with vat-photopolymerization. Polym. Compos. 2024, 45, 17105–17120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shettar, M.; Kini, U.A.; Sharma, S.; Hiremath, P.; Gowrishankar, M.C. Hygrothermal chamber aging effect on mechanical behavior and morphology of glass fiber-epoxy-nanoclay composites. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, C.S.P.; Akhavan-Safar, A.; Marques, E.A.S.; Carbas, R.J.C.; Ueffing, C.; Weißgraeber, P.; da Silva, L.F.M. Effect of Water Ingress on the Mechanical and Chemical Properties of Polybutylene Terephthalate Reinforced with Glass Fibers. Materials 2021, 14, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, U.A.; Shettar, M.; Sharma, S.; Hiremath, P.; Gowrishankar, M.C.; Hegde, A.; Siddhartha, D. Effect of hygrothermal aging on the mechanical properties of nanoclay-glass fiber-epoxy composite and optimization using full factorial design. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 065311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Rashid, A.; Haque, M.; Islam, S.M.M.; Labib, K.R.U. Nanotechnology-enhanced fiber-reinforced polymer composites: Recent advancements on processing techniques and applications. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merah, N.; Mohamed, O. Nanoclay and Water Uptake Effects on Mechanical Properties of Unsaturated Polyester. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 8130419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaichanawong, J.; Thongchuea, C.; Areerat, S. Effect of moisture on the mechanical properties of glass fiber reinforced polyamide composites. Adv. Powder Technol. 2016, 27, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati Giv, A.; Rastegar, S.; Özcan, M. Influence of nanoclays on water uptake and flexural strength of glass–polyester composites. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2020, 18, 228080002093018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Material Name | Properties |
|---|---|
| Glass fiber—Plain bi-directional woven, 360 GSM | Tensile strength—1720–1950 MPa Tensile modulus—72–76 GPa Density—2.5 g/cm3 |
| Epoxy resin (L-12) and hardener (K-6) (Mixing ratio 10:1) | Tensile strength—55–70 MPa Tensile modulus—2.5–04 GPa Flexural strength—120–140 MPa Density—1.15 g/cm3 |
| Nanoclay (Montmorillonite (MMT)) | Appearance (color)—White to off-white Appearance (form)—Powder Size—<20 µm Bulk density—200–500 kg/m3 Surface-modified contains 15–35 wt.% octadecylamine, 0.5–5 wt.% aminopropyltriethoxysilane. |
| Factors | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nanoclay (NC) wt.% | 0 | 2 | 4 |
| Glass fiber (GF) wt.% | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| Aging conditions (AG) | Dry Specimens (DS) | Cold water-soaking (CS) | Boiling water-soaking (BS) |
| Nanoclay (NC) wt.% | Glass Fiber (GF) wt.% | Aging Conditions (AG) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 60 | CS | 295 | 388 |
| 2 | 50 | DS | 283 | 402 |
| 4 | 60 | BS | 290 | 373 |
| 2 | 50 | BS | 227 | 344 |
| 0 | 40 | BS | 190 | 275 |
| 4 | 40 | CS | 234 | 349 |
| 2 | 50 | CS | 235 | 355 |
| 2 | 50 | CS | 247 | 366 |
| 2 | 50 | DS | 280 | 414 |
| 2 | 50 | BS | 233 | 354 |
| 0 | 40 | CS | 199 | 289 |
| 4 | 40 | DS | 281 | 399 |
| 0 | 60 | BS | 235 | 315 |
| 2 | 50 | DS | 285 | 378 |
| 0 | 60 | DS | 286 | 375 |
| 0 | 60 | CS | 243 | 327 |
| 4 | 60 | DS | 319 | 429 |
| 2 | 50 | CS | 241 | 334 |
| 0 | 40 | DS | 255 | 341 |
| 4 | 40 | BS | 233 | 338 |
| 2 | 50 | BS | 227 | 324 |
| 2 | 50 | DS | 275 | 390 |
| 4 | 50 | CS | 255 | 373 |
| 2 | 50 | CS | 223 | 344 |
| 4 | 50 | BS | 244 | 360 |
| 2 | 60 | DS | 290 | 418 |
| 2 | 50 | BS | 216 | 334 |
| 0 | 50 | BS | 205 | 298 |
| 2 | 40 | BS | 199 | 325 |
| 0 | 50 | CS | 208 | 311 |
| 2 | 50 | CS | 230 | 377 |
| 4 | 50 | DS | 291 | 416 |
| 2 | 50 | CS | 220 | 360 |
| 2 | 50 | BS | 221 | 365 |
| 2 | 50 | BS | 210 | 340 |
| 0 | 50 | DS | 252 | 360 |
| 2 | 60 | CS | 254 | 369 |
| 2 | 60 | BS | 243 | 359 |
| 2 | 50 | DS | 276 | 426 |
| 2 | 50 | DS | 269 | 417 |
| 2 | 40 | CS | 212 | 337 |
| 2 | 40 | DS | 263 | 391 |
| Source | DF | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 12 | 40,291.4 | 3357.6 | 163.21 | 0.000 |
| Blocks | 1 | 1108.8 | 1108.8 | 53.90 | 0.000 |
| Linear | 4 | 37,919.7 | 9479.9 | 460.80 | 0.000 |
| Nanoclay | 1 | 7564.5 | 7564.5 | 367.70 | 0.000 |
| Glass fiber | 1 | 8406.7 | 8406.7 | 408.64 | 0.000 |
| Aging conditions | 2 | 21,948.4 | 10,974.2 | 533.44 | 0.000 |
| Square | 2 | 188.9 | 94.5 | 4.59 | 0.019 |
| Nanoclay*Nanoclay | 1 | 39.2 | 39.2 | 1.91 | 0.178 |
| Glass fiber*Glass fiber | 1 | 83.2 | 83.2 | 4.04 | 0.054 |
| 2-Way Interaction | 5 | 548.4 | 109.7 | 5.33 | 0.001 |
| Nanoclay*Glass fiber | 1 | 108.0 | 108.0 | 5.25 | 0.029 |
| Nanoclay* Aging conditions | 2 | 157.0 | 78.5 | 3.82 | 0.034 |
| Glass fiber* Aging conditions | 2 | 283.4 | 141.7 | 6.89 | 0.004 |
| Error | 29 | 596.6 | 20.6 | ||
| Lack-of-Fit | 17 | 345.9 | 20.3 | 0.97 | 0.532 |
| Pure Error | 12 | 250.7 | 20.9 | ||
| Total | 41 | 40,888.0 | |||
| S—4.53571 R-sq—98.56% R-sq(adj)—97.94% R-sq(pred)—96.89% | |||||
| Source | DF | Adj SS | Adj MS | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 12 | 53,294.7 | 4441.2 | 34.87 | 0.000 |
| Blocks | 1 | 231.3 | 231.3 | 1.82 | 0.188 |
| Linear | 4 | 50,071.7 | 12,517.9 | 98.28 | 0.000 |
| Nanoclay | 1 | 15,842.0 | 15,842.0 | 124.38 | 0.000 |
| Glass fiber | 1 | 5304.5 | 5304.5 | 41.65 | 0.000 |
| Aging conditions | 2 | 28,925.2 | 14,462.6 | 113.55 | 0.000 |
| Square | 2 | 2194.8 | 1097.4 | 8.62 | 0.001 |
| Nanoclay*Nanoclay | 1 | 1781.4 | 1781.4 | 13.99 | 0.001 |
| Glass fiber*Glass fiber | 1 | 12.9 | 12.9 | 0.10 | 0.753 |
| 2-Way Interaction | 5 | 66.3 | 13.3 | 0.10 | 0.990 |
| Nanoclay*Glass fiber | 1 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 0.04 | 0.839 |
| Nanoclay* Aging conditions | 2 | 25.0 | 12.5 | 0.10 | 0.907 |
| Glass fiber* Aging conditions | 2 | 36.0 | 18.0 | 0.14 | 0.869 |
| Error | 29 | 3693.7 | 127.4 | ||
| Lack-of-Fit | 17 | 239.0 | 14.1 | 0.05 | 1.000 |
| Pure Error | 12 | 3454.7 | 287.9 | ||
| Total | 41 | 56,988.4 | |||
| S—11.2858 R-sq—93.52% R-sq(adj)—90.84% R-sq(pred)—91.17% | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shettar, M.; Bhat, A.; Katagi, N.N.; Gowrishankar, M.C. Experimental Investigation on Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber–Nanoclay–Epoxy Composites Under Water-Soaking: A Comparative Study Using RSM and ANN. J. Compos. Sci. 2025, 9, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9040195
Shettar M, Bhat A, Katagi NN, Gowrishankar MC. Experimental Investigation on Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber–Nanoclay–Epoxy Composites Under Water-Soaking: A Comparative Study Using RSM and ANN. Journal of Composites Science. 2025; 9(4):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9040195
Chicago/Turabian StyleShettar, Manjunath, Ashwini Bhat, Nagaraj N. Katagi, and Mandya Channegowda Gowrishankar. 2025. "Experimental Investigation on Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber–Nanoclay–Epoxy Composites Under Water-Soaking: A Comparative Study Using RSM and ANN" Journal of Composites Science 9, no. 4: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9040195
APA StyleShettar, M., Bhat, A., Katagi, N. N., & Gowrishankar, M. C. (2025). Experimental Investigation on Mechanical Properties of Glass Fiber–Nanoclay–Epoxy Composites Under Water-Soaking: A Comparative Study Using RSM and ANN. Journal of Composites Science, 9(4), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs9040195






