Thermomechanical Treatment of SRF for Enhanced Fuel Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
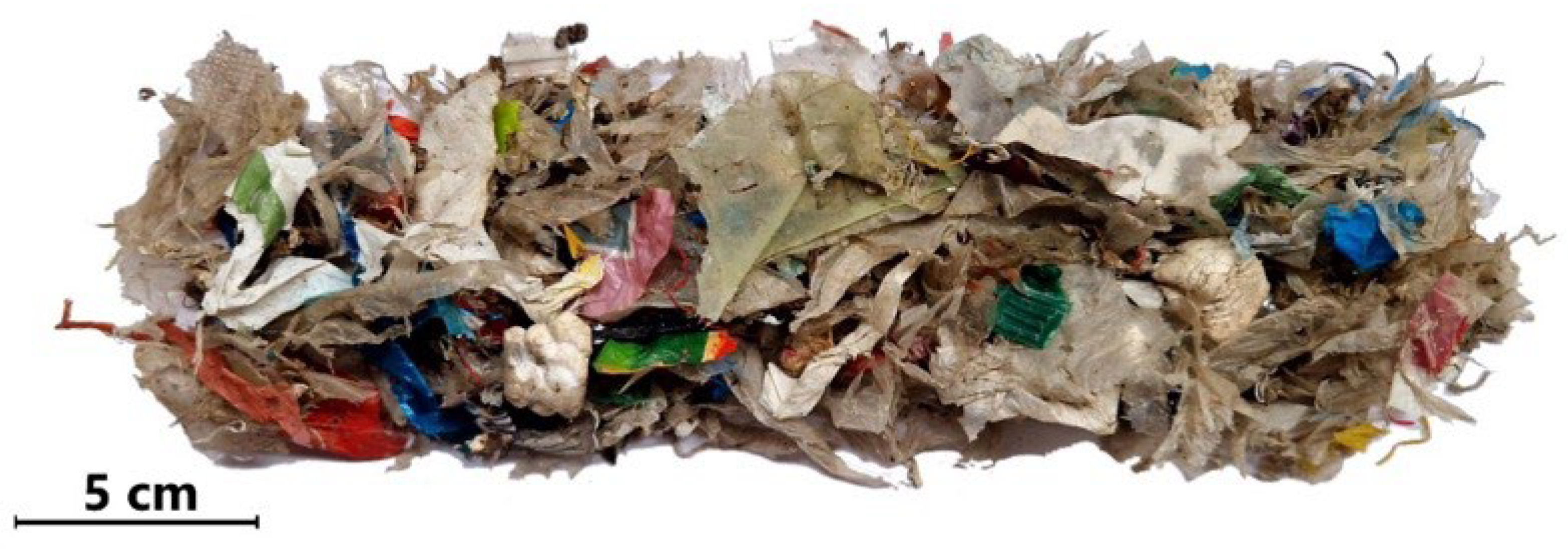
2.1. Input Material
2.2. Pelletisation Process Description
2.3. Determination of the Physical Properties
2.3.1. Particle Size Distribution and Particle Shape
2.3.2. Ultimate and Proximate Analysis
2.3.3. Wettability Index Determination
2.3.4. Pellet Durability Index
2.3.5. Hardness
2.3.6. Bulk Density
2.3.7. Particle Density
3. Results
3.1. Characterisation of Raw Input Material and Pelletisation Process
3.1.1. Particle Size Distribution of SRF
3.1.2. The Ultimate and Proximate Analysis
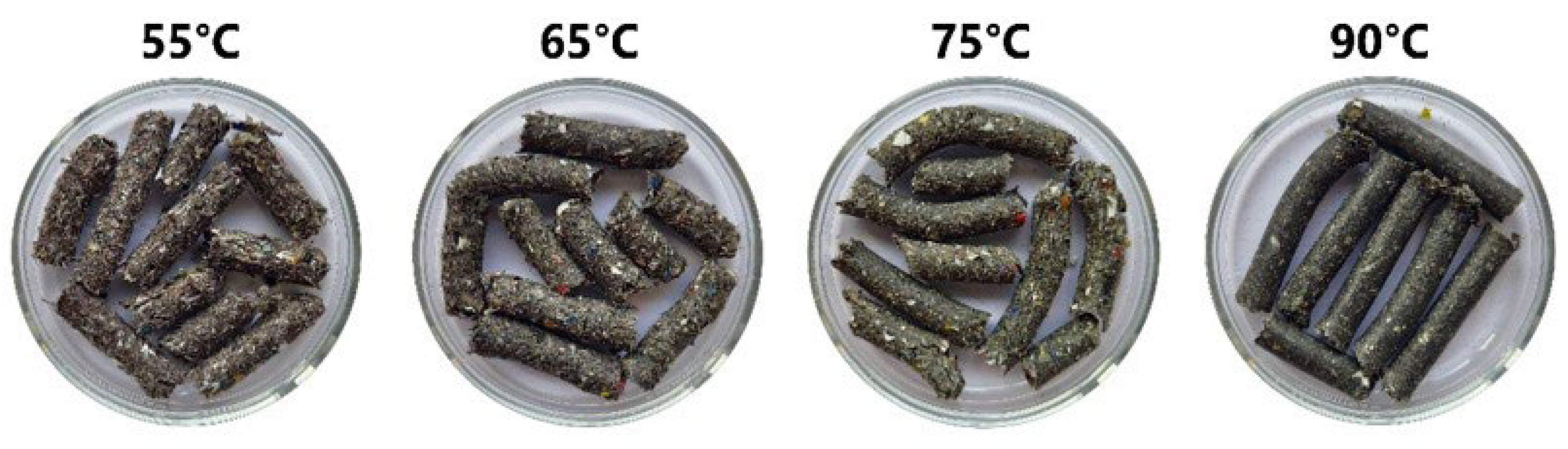
3.1.3. Pelletisation Process
3.2. Physical Properties of Pellets
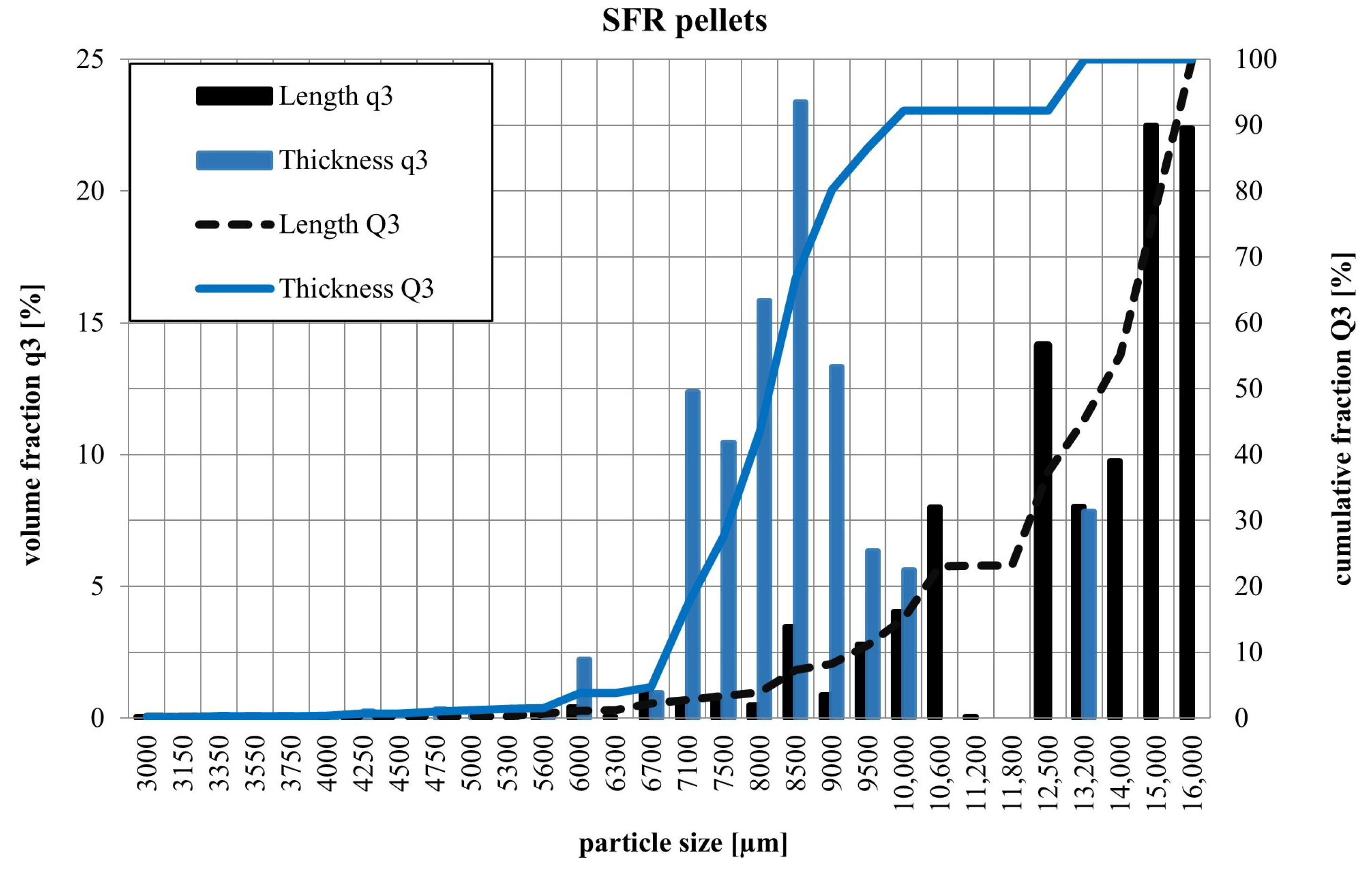
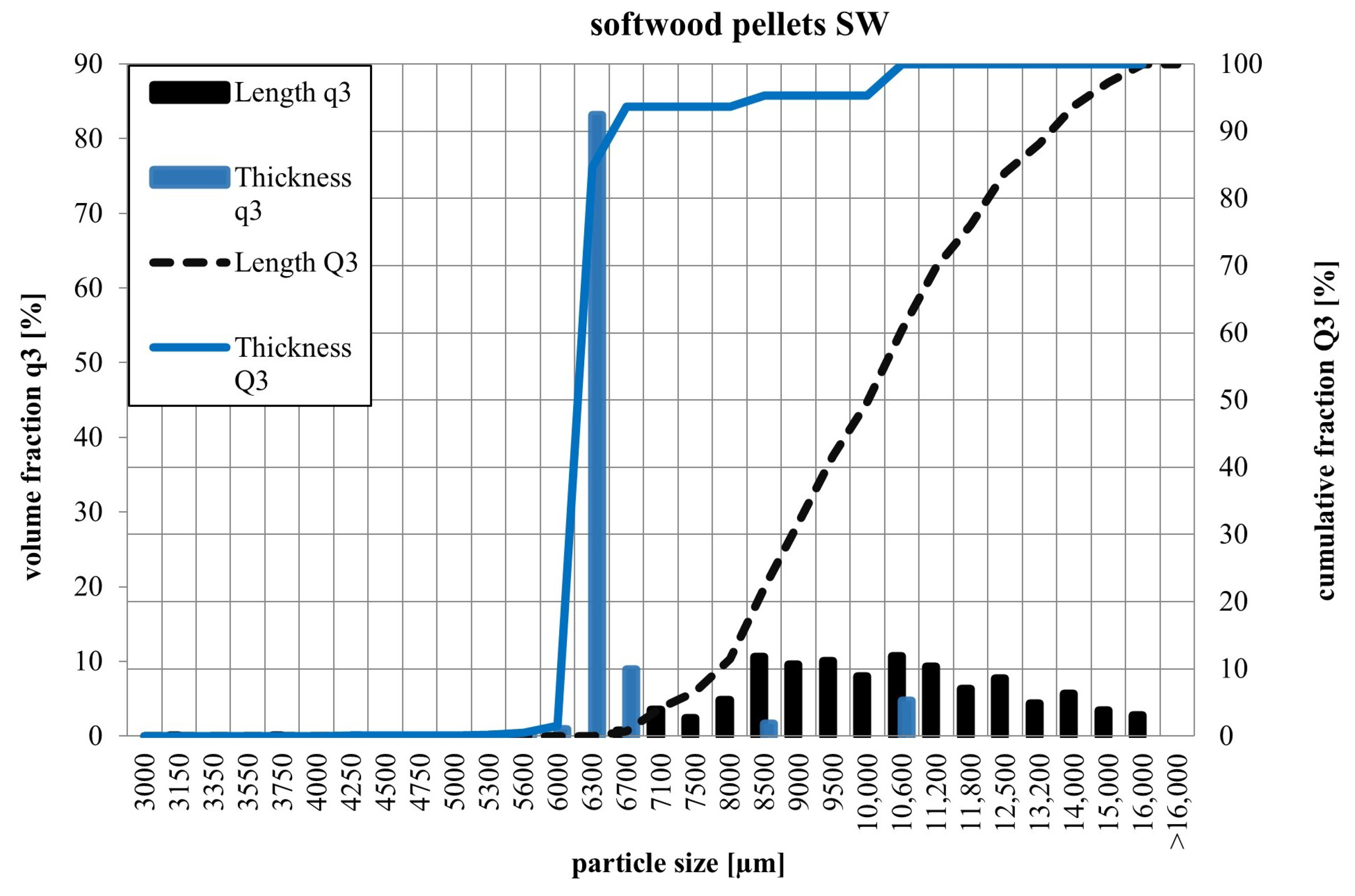
3.2.1. Particle Size Distribution of Pellets
3.2.2. Particle Shape
3.2.3. Wettability Index
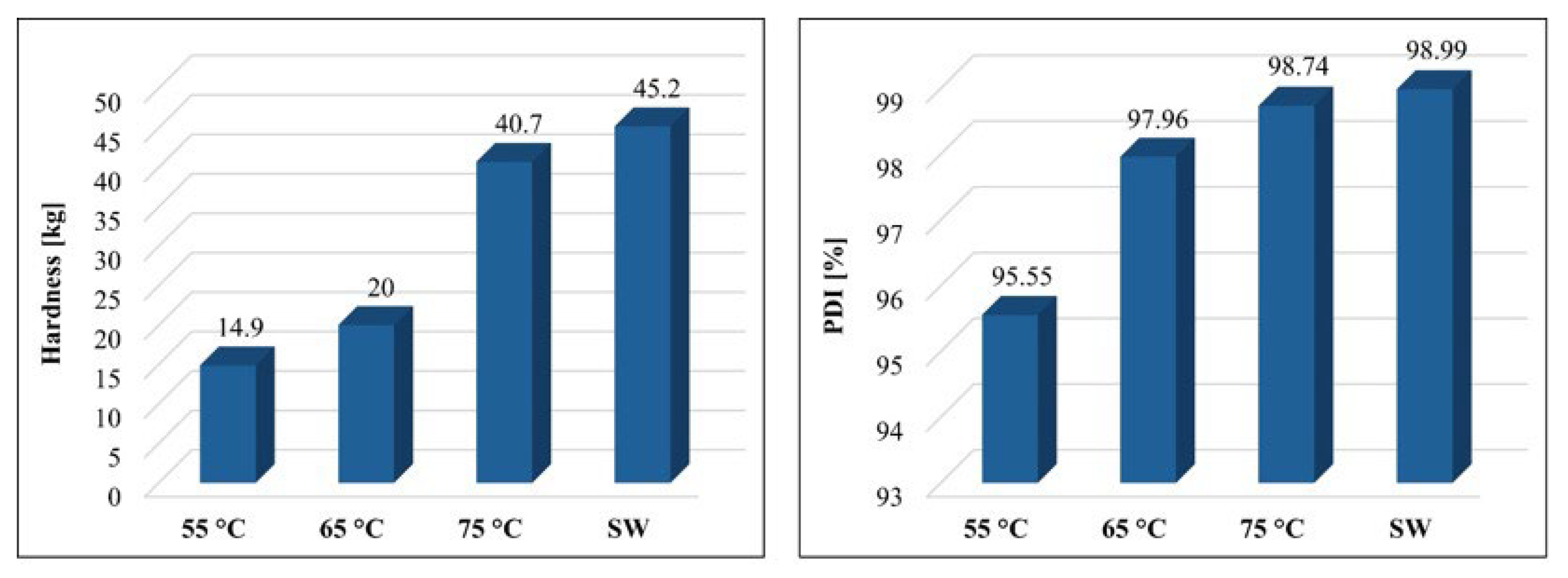
3.2.4. Hardness and Pellet Durability Index
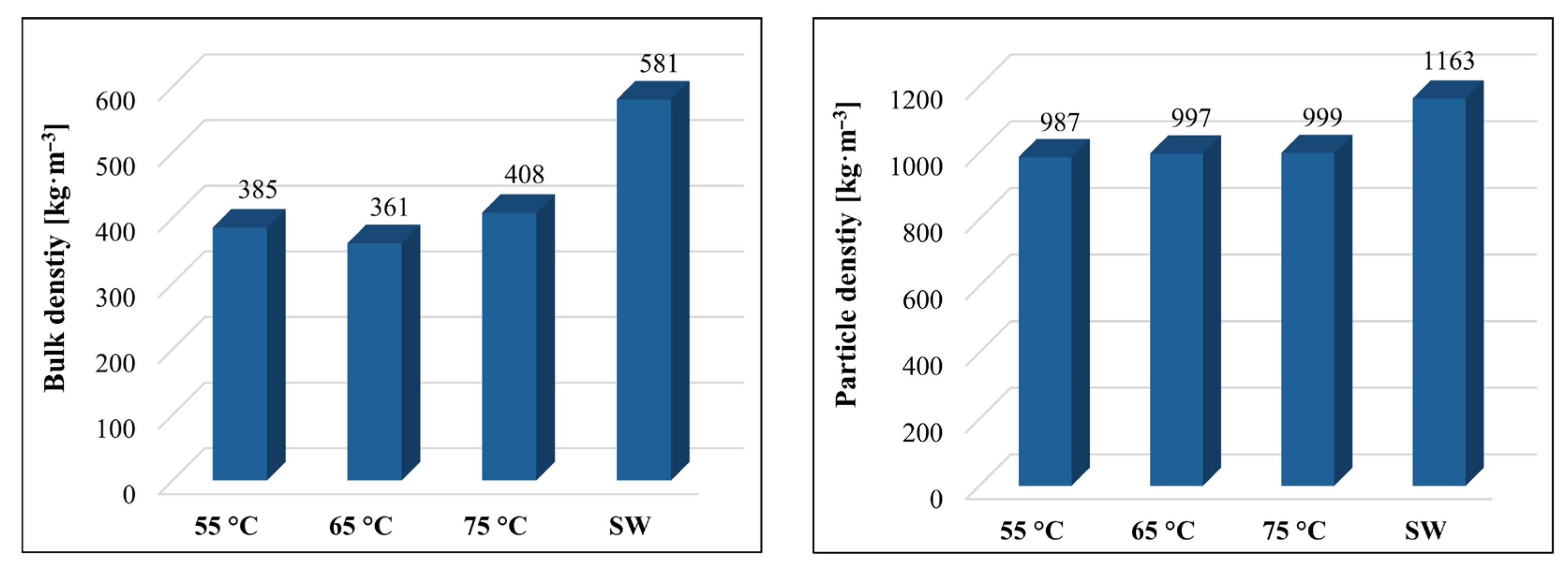
3.2.5. Bulk Density and Particle Density
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| HDPE | High density polyethylene |
| LHV | Lower heating value |
| MSW | Municipal solid waste |
| PCDD/F | Polychlorinated dibenzodioxins/polychlorinated dibenzofurans |
| PDI | Pellet durability index |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| q3 | Volume fraction |
| Q3 | Cumulative fraction |
| SPHT | Sphericity |
| SRF | Solid recovered fuel |
| SW | Softwood |
| WHO | World Health Organisation |
| WI | Wettability index |
References
- Tokmurzin, D.; Nam, J.Y.; Lee, T.R.; Park, S.J.; Nam, H.; Yoon, S.J.; Mun, T.-Y.; Yoon, S.M.; Moon, J.H.; Lee, J.G.; et al. High Temperature Flash Pyrolysis Characteristics of Waste Plastics (SRF) in a Bubbling Fluidized Bed: Effect of Temperature and Pelletizing. Fuel 2022, 326, 125022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Samadder, S.R. A Review on Technological Options of Waste to Energy for Effective Management of Municipal Solid Waste. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrullah, M.; Vainikka, P.; Hannula, J.; Hurme, M. Elemental Balance of SRF Production Process: Solid Recovered Fuel Produced from Commercial and Industrial Waste. Fuel 2015, 145, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valin, S.; Ravel, S.; Pons de Vincent, P.; Thiery, S.; Miller, H. Fluidized Bed Air Gasification of Solid Recovered Fuel and Woody Biomass: Influence of Experimental Conditions on Product Gas and Pollutant Release. Fuel 2019, 242, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerzak, W.; Mlonka-Mędrala, A.; Gao, N.; Magdziarz, A. Potential of Products from High-Temperature Pyrolysis of Biomass and Refuse-Derived Fuel Pellets. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 183, 107159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recari, J.; Berrueco, C.; Puy, N.; Alier, S.; Bartrolí, J.; Farriol, X. Torrefaction of a Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF) to Improve the Fuel Properties for Gasification Processes. Appl. Energy 2017, 203, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragon-Briceño, C.; Pożarlik, A.; Bramer, E.; Brem, G.; Wang, S.; Wen, Y.; Yang, W.; Pawlak-Kruczek, H.; Niedźwiecki, Ł.; Urbanowska, A.; et al. Integration of Hydrothermal Carbonization Treatment for Water and Energy Recovery from Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste Digestate. Renew. Energy 2022, 184, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čespiva, J.; Jadlovec, M.; Výtisk, J.; Serenčíšová, J.; Ochodek, T.; Honus, S. Softwood and Srf Gasification Residual Chars as Sorbents for Flue Gas Mercury Capture. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 29, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čespiva, J.; Wnukowski, M.; Skřínský, J.; Perestrelo, R.; Jadlovec, M.; Výtisk, J.; Trojek, M.; Câmara, J.S. Production Efficiency and Safety Assessment of the Solid Waste-Derived Liquid Hydrocarbons. Environ. Res. 2024, 244, 117915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikkema, R.; Steiner, M.; Junginger, M.; Hiegl, W.; Hansen, M.T.; Faaij, A. The European Wood Pellet Markets: Current Status and Prospects for 2020. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2011, 5, 250–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibitoye, S.E.; Jen, T.-C.; Mahamood, R.M.; Akinlabi, E.T. Densification of Agro-Residues for Sustainable Energy Generation: An Overview. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelte, W.; Sanadi, A.R.; Shang, L.; Holm, J.K.; Ahrenfeldt, J.; Henriksen, U.B. Recent Developments in Biomass Pelletization—A Review. Bioresources 2012, 7, 4451–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Zotto, L.; Tallini, A.; Di Simone, G.; Molinari, G.; Cedola, L. Energy Enhancement of Solid Recovered Fuel within Systems of Conventional Thermal Power Generation. Energy Procedia 2015, 81, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, R.; Xu, Z.; Xing, Y.; Liu, W.; Wu, X.; Jia, T.; Sun, S.; He, Y. Global Status of Dioxin Emission and China’s Role in Reducing the Emission. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Chen, K.; Huang, T.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Mao, X.; Gao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Z. New Emission Inventory Reveals Termination of Global Dioxin Declining Trend. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Maraver, A.; Rodriguez, M.L.; Serrano-Bernardo, F.; Diaz, L.F.; Zamorano, M. Factors Affecting the Quality of Pellets Made from Residual Biomass of Olive Trees. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 129, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorber, K.E.; Sarc, R.; Aldrian, A. Design and Quality Assurance for Solid Recovered Fuel. Waste Manag. Res. J. A Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2012, 30, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridout, A.J.; Carrier, M.; Görgens, J. Fast Pyrolysis of Low and High Ash Paper Waste Sludge: Influence of Reactor Temperature and Pellet Size. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 111, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruszelnicka, W.; Hlosta, J.; Diviš, J.; Gierz, Ł. Study of the Relationships between Multi-Hole, Multi-Disc Mill Performance Parameters and Comminution Indicators. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velis, C.A.; Longhurst, P.J.; Drew, G.H.; Smith, R.; Pollard, S.J.T. Production and Quality Assurance of Solid Recovered Fuels Using Mechanical—Biological Treatment (MBT) of Waste: A Comprehensive Assessment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 40, 979–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Torre-Bayo, J.J.; Zamorano, M.; Torres-Rojo, J.C.; Rodríguez, M.L.; Martín-Pascual, J. Analyzing the Production, Quality, and Potential Uses of Solid Recovered Fuel from Screening Waste of Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 172, 950–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Žurovec, D.; Jezerská, L.; Nečas, J.; Hlosta, J.; Diviš, J.; Zegzulka, J. Spiral Vibration Cooler for Continual Cooling of Biomass Pellets. Processes 2021, 9, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, R.; González-Vázquez, M.P.; Rubiera, F.; Pevida, C.; Gil, M.V. Co-Pelletization of Pine Sawdust and Refused Derived Fuel (RDF) to High-Quality Waste-Derived Pellets. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 328, 129635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DD CEN/TS 15359:2006; Solid Recovered Fuels—Specifications and Classes. European Commission, European Committee for Standardisation: Brussels, Belgium, 2006.
- PD CEN/TR 15508:2006; Key Properties on Solid Recovered Fuels to Be Used for Establishing a Classification System. European Commission, European Committee for Standardisation: Brussels, Belgium, 2006.
- Prismantoko, A.; Karuana, F.; Ghazidin, H.; Ruhiyat, A.S.; Adelia, N.; Prayoga Moch, Z.E.; Romelan, R.; Utomo, S.M.; Cahyo, N.; Hartono, J.; et al. Ash Deposition Behavior during Co-Combustion of Solid Recovered Fuel with Different Coals. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2024, 48, 102404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos Casado, R.; Arenales Rivera, J.; Borjabad García, E.; Escalada Cuadrado, R.; Fernández Llorente, M.; Bados Sevillano, R.; Pascual Delgado, A. Classification and Characterisation of SRF Produced from Different Flows of Processed MSW in the Navarra Region and Its Co-Combustion Performance with Olive Tree Pruning Residues. Waste Manag. 2016, 47, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Výtisk, J.; Čespiva, J.; Jadlovec, M.; Kočí, V.; Honus, S.; Ochodek, T. Life Cycle Assessment Applied on Alternative Production of Carbon-Based Sorbents—A Comparative Study. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2023, 35, e00563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryšavý, J.; Horák, J.; Kuboňová, L.; Jaroch, M.; Hopan, F.; Krpec, K.; Kubesa, P. Beech Leaves Briquettes’ and Standard Briquettes’ Combustion: Comparison of Flue Gas Composition. Int. J. Energy Prod. Manag. 2021, 6, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhang, Q.; Arnold, L.; Yang, W.; Blasiak, W. A Study of the Pyrolysis Behaviors of Pelletized Recovered Municipal Solid Waste Fuels. Appl. Energy 2013, 107, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9276-6:2008; Representation of Results of Particle Size Analysis—Part 6: Descriptive and Quantitative Representation of Particle Shape and Morphology. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/39389.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- ISO 13322-2:2021; Particle Size Analysis—Image Analysis Methods—Part 2: Dynamic Image Analysis Methods. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/72566.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Brown, D.J.; Vickers, G.T.; Collier, A.P.; Reynolds, G.K. Measurement of the Size, Shape and Orientation of Convex Bodies. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2005, 60, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchigolla, K.; Wilkinson, D. Crystal Shape Characterisation of Dry Samples Using Microscopic and Dynamic Image Analysis. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2009, 26, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.F.; Hawkins, S.M.; Meyer, J.L.L.; Sharman, A.R.C. Evaluation of Different Particle Size Distribution and Morphology Characterization Techniques. Addit. Manuf. Lett. 2022, 3, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 16993:2016; Solid Biofuels—Conversion of Analytical Results from one Basis to Another. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/70098.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- ISO 18125:2017; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Calorific Value. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/61517.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Mahadeo, K. Study on Physical and Chemical Properties of Crop Residues Briquettes for Gasification. Am. J. Energy Eng. 2014, 2, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knarr, L.E.; Bowen, K.M.; Ferrel, J.; Moritz, J.S. Azomite, a Dacitic (Rhyolitic) Tuff Breccia, Included at 0.25% in Feed Manufactured with 32, 38, and 45 Mm Pellet Die Thicknesses Increased Pellet Production Rate by 5.0, 7.9, and 11.8%, Respectively. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2024, 33, 100389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 17831-1:2015; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Mechanical Durability of Pellets and Briquettes. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/60695.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- ISO 17225-6:2021; Solid Biofuels—Fuel Specifications and Classes Part 6: Graded Non-Woody Pellets. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/76093.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- ISO 22167:2021; Solid Recovered Fuels—Determination of Content of Volatile Matter. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/72716.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- ISO 18134-2:2024; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Moisture Content Part 2: Simplified Method. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/86024.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- ISO 18122:2022; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Ash Content. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/83190.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- ISO 16948:2015; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Total Content of Carbon, Hydrogen and Nitrogen. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/58004.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- ISO 16994:2016; Solid Biofuels—Determination of Total Content of Sulfur and Chlorine. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/70097.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- ISO 11724:2019; Solid Mineral Fuels—Determination of Total Fluorine in Coal, Coke and Fly Ash. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/75881.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- ISO 18806:2019; Solid Mineral Fuels—Determination of Chlorine Content. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/75466.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- ISO 15237:2016; Solid Mineral Fuels—Determination of Total Mercury Content of Coal. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/70207.html (accessed on 30 December 2024).
- Koppejan, J.; van Ioo, S. The Handbook of Biomass Combustion and Co-Firing; Earthscan: Oxford, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Alakoski, E.; Jämsén, M.; Agar, D.; Tampio, E.; Wihersaari, M. From Wood Pellets to Wood Chips, Risks of Degradation and Emissions from the Storage of Woody Biomass—A Short Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ye, X.; Cheng, T.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R. A Laboratory Study of Agricultural Crop Residue Combustion in China: Emission Factors and Emission Inventory. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8432–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Glarborg, P.; Frandsen, F.J.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Jensen, P.A.; Sander, B. Trace Elements in Co-Combustion of Solid Recovered Fuel and Coal. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 105, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čespiva, J.; Skřínský, J.; Vereš, J.; Wnukowski, M.; Serenčíšová, J.; Ochodek, T. Solid Recovered Fuel Gasification in Sliding Bed Reactor. Energy 2023, 278, 127830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daouk, E.; Sani, R.; Pham Minh, D.; Nzihou, A. Thermo-Conversion of Solid Recovered Fuels under Inert and Oxidative Atmospheres: Gas Composition and Chlorine Distribution. Fuel 2018, 225, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarc, R.; Lorber, K.; Pomberger, R.; Rogetzer, M.; Sipple, E. Design, Quality, and Quality Assurance of Solid Recovered Fuels for the Substitution of Fossil Feedstock in the Cement Industry. Waste Manag. Res. J. A Sustain. Circ. Econ. 2014, 32, 565–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edo-Alcón, N.; Gallardo, A.; Colomer-Mendoza, F.J. Characterization of SRF from MBT Plants: Influence of the Input Waste and of the Processing Technologies. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 153, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziok, T.; Bury, M.; Burmistrz, P. Mercury Release from Municipal Solid Waste in the Thermal Treatment Process. Fuel 2022, 329, 125528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, I.; Skawińska, A.; Sajdak, M. Analysis of Chlorine Forms in Hard Coal and the Impact of Leaching Conditions on Chlorine Removal. J. Energy Inst. 2021, 94, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, T.; Arora, A.; Pawlak-Kruczek, H.; Rafajłowicz, W.; Wietrzych, J.; Niedźwiecki, Ł.; Vishwajeet Mościcki, K. Non-Destructive Diagnostic Methods for Fire-Side Corrosion Risk Assessment of Industrial Scale Boilers, Burning Low Quality Solid Biofuels—A Mini Review. Energies 2021, 14, 7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullett, B.K.; Sarofim, A.F.; Smith, K.A.; Procaccini, C. The Role of Chlorine in Dioxin Formation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2000, 78, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bury, M.; Dziok, T.; Borovec, K.; Burmistrz, P. Influence of RDF Composition on Mercury Release during Thermal Pretreatment. Energies 2023, 16, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilber, T.; Thorwarth, H.; Stack-Lara, V.; Schneider, M.; Maier, J.; Scheffknecht, G. Fate of Mercury and Chlorine during SRF Co-Combustion. Fuel 2007, 86, 1935–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stogiannis, P.; Triantafillidis, A.; Amarantos, P.; Kontodimos, I.; Ketikidis, C.; Grammelis, P. Measuring the Concentration of Mercury for Automotive Shredded Residues Using the Direct Mercury Analyser. Eng. Proc. 2023, 56, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Pudasainee, D.; Duan, Y.; Gupta, R.; Liu, M.; Lu, J. A Review on Mercury in Coal Combustion Process: Content and Occurrence Forms in Coal, Transformation, Sampling Methods, Emission and Control Technologies. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2019, 73, 26–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grycova, B.; Klemencova, K.; Jezerska, L.; Zidek, M.; Lestinsky, P. Effect of Torrefaction on Pellet Quality Parameters. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 13235–13243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sykorova, V.; Jezerska, L.; Sassmanova, V.; Honus, S.; Peikertova, P.; Kielar, J.; Zidek, M. Biomass Pellets with Organic Binders—Before and after Torrefaction. Renew. Energy 2024, 221, 119771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Peng, J.; Li, H.; Bi, X.T.; Legros, R.; Lim, C.J.; Sokhansanj, S. Oxidative Torrefaction of Biomass Residues and Densification of Torrefied Sawdust to Pellets. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 127, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Niedzwiecki, L.; Arora, A.; Mościcki, K.; Pawlak-Kruczek, H.; Krochmalny, K.; Baranowski, M.; Tiwari, M.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, T.; et al. Influence of Torrefaction and Pelletizing of Sawdust on the Design Parameters of a Fixed Bed Gasifier. Energies 2020, 13, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




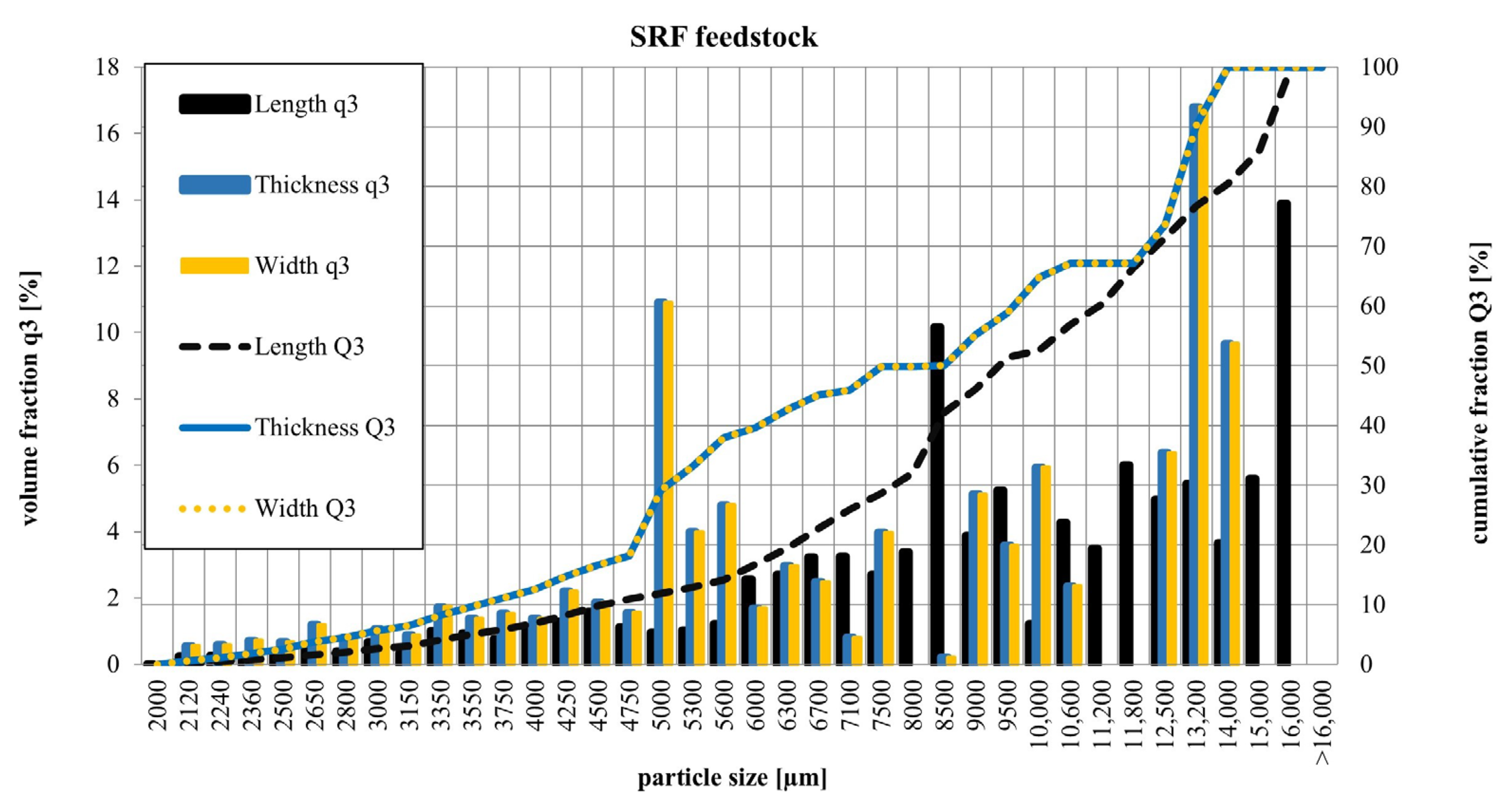

| d10 | Standard Deviation | d50 | Standard Deviation | d90 | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [µm] | [µm] | [µm] | [µm] | [µm] | [µm] | |
| Length | 4541 | 341 | 9389 | 724 | 15,749 | 1716 |
| Width | 3588 | 265 | 8494 | 662 | 12,808 | 1063 |
| Thickness | 3588 | 265 | 8494 | 662 | 12,808 | 1063 |
| Parameter | Unit | SW | SRF | Standard | Uncertainty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower heating value (LHVr) | [MJ·kg−1] | 17.41 | 30.5 | EN 18125 [35] | 3.0% |
| Volatile matter (Vr) | [wt.%] | 75.75 | 83.13 | EN ISO 22167 [42] | 1.9% |
| Water (Wr) | [wt.%] | 7.12 | 1.59 | EN ISO 18134-2 [43] | 3.1% |
| Ash (Ar) | [wt.%] | 0.24 | 10.27 | EN ISO 18122 [44] | 9.0% |
| Carbon (Cr) | [wt.%] | 47.09 | 66.9 | EN ISO 16948 [45] | 4.6% |
| Oxygen (Or) | [wt.%] | 39.70 | 10.42 | EN ISO 16993 [36] | - |
| Hydrogen (Hr) | [wt.%] | 5.63 | 8.61 | EN ISO 16948 [45] | 3.1% |
| Nitrogen (Nr) | [wt.%] | 0.20 | 0.57 | EN ISO 16948 [45] | 6.1% |
| Total sulphur (Sr) | [wt.%] | <0.02 | 0.09 | EN ISO 16994 [46] | 6.4% |
| Chlorine (Clr) | [wt.%] | <0.01 | 1.18 | ISO 11724:2019 [47] | 37% |
| Fluorine (Fr) | [wt.%] | <0.02 | <0.02 | ISO 18806:2019 [48] | - |
| Mercury (Hgr) | [mg·kg−1] | <0.1 | 0.1 | ISO 15237:2016 [49] | 0.01% |
| d10 | Standard Deviation | d50 | Standard Deviation | d90 | Standard Deviation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [µm] | [µm] | [µm] | [µm] | [µm] | [µm] | ||
| SW pellets | Length | 7892 | 497 | 10,004 | 710 | 13,433 | 1236 |
| Thickness | 6069 | 73 | 6182 | 69 | 6349 | 84 | |
| Width | 6069 | 73 | 6182 | 69 | 6349 | 84 | |
| SRF pellets | Length | 9264 | 723 | 13,911 | 1141 | 15,538 | 1461 |
| Thickness | 6826 | 89 | 8162 | 171 | 9641 | 231 | |
| Width | 6826 | 89 | 8162 | 171 | 9641 | 231 |
| Sphericity SPHT [–] | Circularity C [–] | Aspect Ratio b/l [–] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Standard Deviation | Mean | Standard Deviation | Mean | Standard Deviation | |
| SRF pellets | 0.37 | 0.06 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.67 | 0.06 |
| SW pellets | 0.68 | 0.09 | 0.82 | 0.06 | 0.70 | 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prokeš, R.; Diviš, J.; Ryšavý, J.; Jezerská, L.; Niedźwiecki, Ł.; Vilas, D.P.; Mościcki, K.; Mlonka-Mędrala, A.; Yan, W.-M.; Žurovec, D.; et al. Thermomechanical Treatment of SRF for Enhanced Fuel Properties. Fire 2025, 8, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8020057
Prokeš R, Diviš J, Ryšavý J, Jezerská L, Niedźwiecki Ł, Vilas DP, Mościcki K, Mlonka-Mędrala A, Yan W-M, Žurovec D, et al. Thermomechanical Treatment of SRF for Enhanced Fuel Properties. Fire. 2025; 8(2):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8020057
Chicago/Turabian StyleProkeš, Rostislav, Jan Diviš, Jiří Ryšavý, Lucie Jezerská, Łukasz Niedźwiecki, David Patiño Vilas, Krzysztof Mościcki, Agata Mlonka-Mędrala, Wei-Mon Yan, David Žurovec, and et al. 2025. "Thermomechanical Treatment of SRF for Enhanced Fuel Properties" Fire 8, no. 2: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8020057
APA StyleProkeš, R., Diviš, J., Ryšavý, J., Jezerská, L., Niedźwiecki, Ł., Vilas, D. P., Mościcki, K., Mlonka-Mędrala, A., Yan, W.-M., Žurovec, D., & Čespiva, J. (2025). Thermomechanical Treatment of SRF for Enhanced Fuel Properties. Fire, 8(2), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/fire8020057













