Selenium and Heavy Metals in Soil–Plant System in a Hydrogeochemical Province with High Selenium Content in Groundwater: A Case Study of the Lower Dniester Valley
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Geochemical Characteristics of the Lower Dniester Valley (LDV)
2.2. Field Studies and Sample Preparation
2.3. Chemical Analysis and Extraction
2.4. Bioccumulation Assessment and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Total Se and Heavy Metals Content in Soils
3.1.1. Soil Physicochemical Characteristics
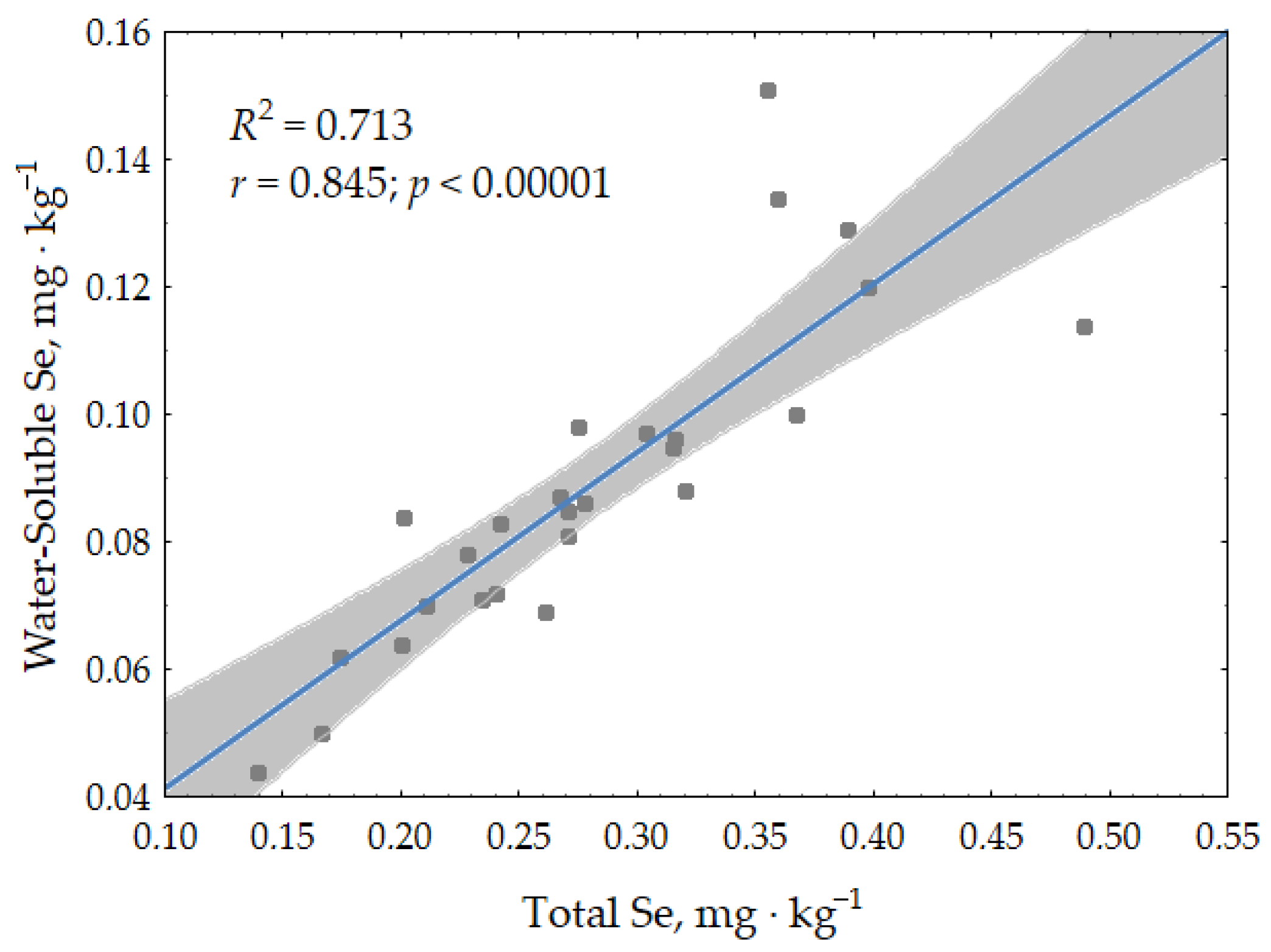
3.1.2. Selenium in Soils
3.1.3. Heavy Metals in Soils
Manganese
Zinc
Copper
3.2. Se, Mn, Zn, and Cu Concentrations in Plants and Their Bioaccumulation
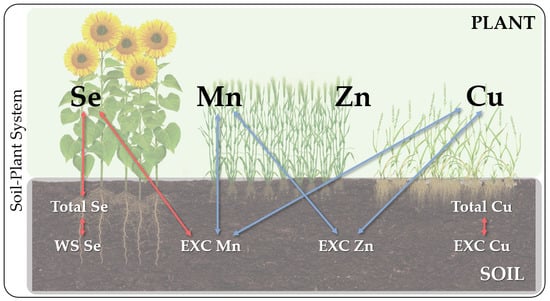
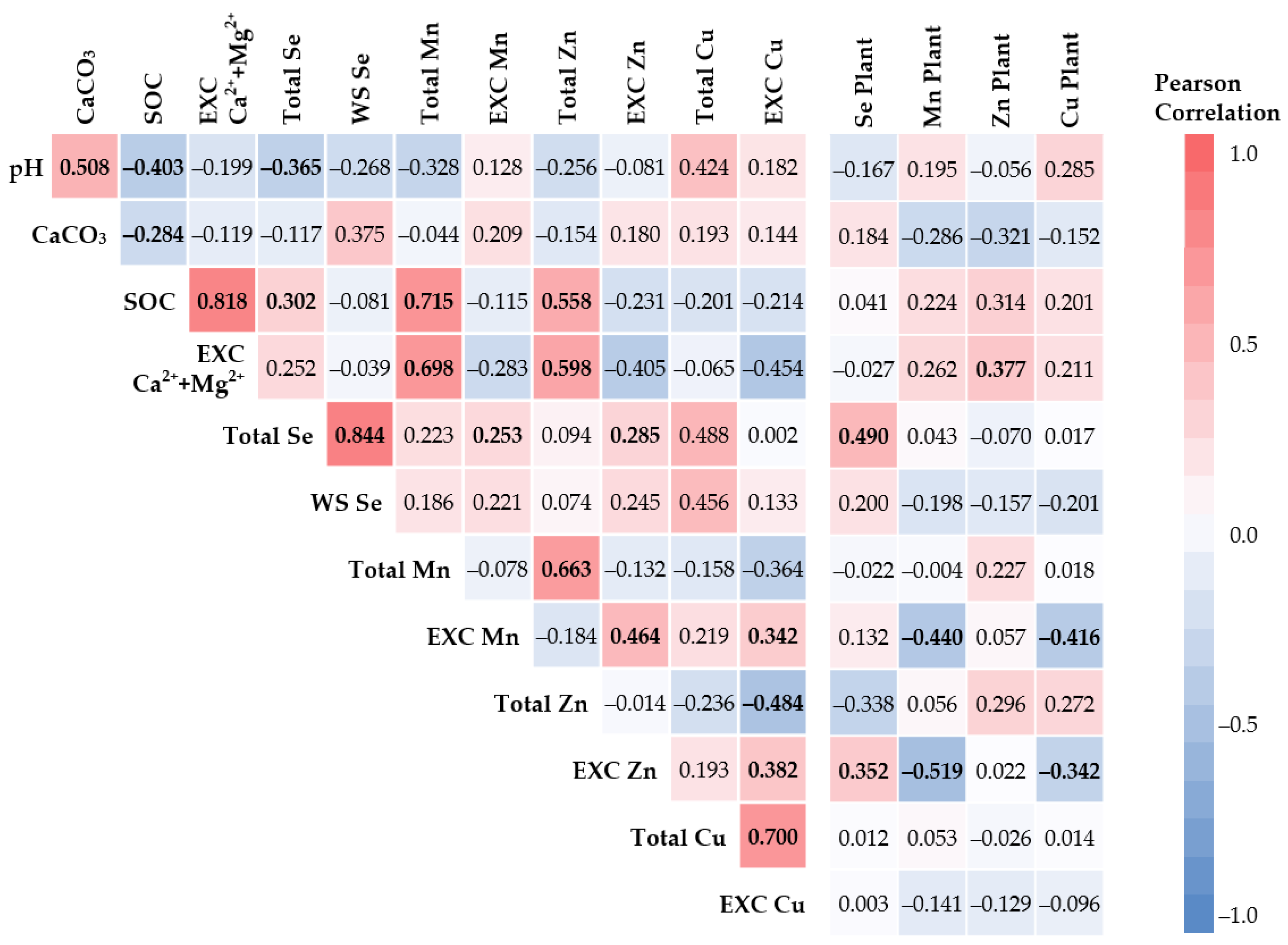
3.3. Se and HMs Interactions in Soil–Plant System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szynkowska, M.I.; Pawlaczyk, A.; Maćkiewicz, E. Bioaccumulation and Biomagnification of Trace Elements in the Environment. In Recent Advances in Trace Elements; Chojnacka, K., Saeid, A., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 251–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaid, H.; Ma, L.; Nader, S.E.; Hashimi, M.H.; Sharifi, S.; Kakar, H.; Ni, J.; Ni, C. Heavy Metal Contamination Status of Water, Agricultural Soil, and Plant in the Semiarid Region of Kandahar, Afghanistan. ACS Earth Space Chem. 2023, 7, 1446–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massas, I.; Kairis, O.; Gasparatos, D.; Ioannou, D.; Vatougios, D.; Zafeiriou, I. Impaired Soil Health in Agricultural Areas Close to Fe-Ni Mines on Euboea Island, Greece, Caused by Increased Concentrations of Potentially Toxic Elements, and the Associated Impacts on Human Health. Environments 2023, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, H.; Yang, X. Quantifying Ecological and Human Health Risks of Heavy Metals from Different Sources in Farmland Soils within a Typical Mining and Smelting Industrial Area. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 5669–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Mo, L.; Yu, X.-X.; Shi, H.-D.; Fei, Y. Enrichment Characteristics, Source Apportionment, and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Industrial and Mining Area of Northern Guangdong Province. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2023, 44, 1636–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhou, K.; Qin, W.; Tian, C.; Qi, M.; Yan, X.; Han, W. A Review on Heavy Metals Contamination in Soil: Effects, Sources, and Remediation Techniques. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2019, 28, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natasha; Shahid, M.; Niazi, N.K.; Khalid, S.; Murtaza, B.; Bibi, I.; Rashid, M.I. A Critical Review of Selenium Biogeochemical Behavior in Soil-Plant System with an Inference to Human Health. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 915–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alengebawy, A.; Abdelkhalek, S.T.; Qureshi, S.R.; Wang, M.-Q. Heavy Metals and Pesticides Toxicity in Agricultural Soil and Plants: Ecological Risks and Human Health Implications. Toxics 2021, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Lin, W.; Jiao, H.; Liu, J.; Chan, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, R.; Chen, T. Uptake, Transport, and Metabolism of Selenium and Its Protective Effects against Toxic Metals in Plants: A Review. Metallomics 2021, 13, mfab040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farman, M.; Nawaz, F.; Majeed, S.; Ahmad, K.S.; Rafeeq, R.; Shehzad, M.A.; Shabbir, R.N.; Usmani, M.M. Interplay between Selenium and Mineral Elements to Improve Plant Growth and Development. In Handbook of Bioremediation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xiao, C.; Qiu, T.; Deng, J.; Cheng, H.; Cong, X.; Cheng, S.; Rao, S.; Zhang, Y. Selenium Regulates Antioxidant, Photosynthesis, and Cell Permeability in Plants under Various Abiotic Stresses: A Review. Plants 2022, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guignardi, Z.; Schiavon, M. Biochemistry of Plant Selenium Uptake and Metabolism. In Selenium in Plants; Pilon-Smits, E.A.H., Winkel, L.H.E., Lin, Z.-Q., Eds.; Plant Ecophysiology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2017; Volume 11, pp. 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P. The Importance of Selenium to Human Health. Lancet 2000, 356, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Sami, U.; Hasnain, U.; Arsalan, S.; Sohaib, N.; Zarmina, A.; Hamza, J.M.; Zain, U.A.; Rimsha, Z. Effects of Heavy Metals on Soil Properties and Their Biological Remediation. Indian J. Pure Appl. Biosci. 2022, 10, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, W.; Pang, F. Selenium in Soil–Plant-Microbe: A Review. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 108, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveed, S.; Oladoye, P.O.; Alli, Y.A. Toxic Heavy Metals: A Bibliographic Review of Risk Assessment, Toxicity, and Phytoremediation Technology. Sustain. Chem. Environ. 2023, 2, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraru, C. Groundwater Quality in the Republic of Moldova. In Management of Water Quality in Moldova; Duca, G., Ed.; Water Science and Technology Library; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2014; Volume 69, pp. 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannigan, R.E.; Bogdevich, O.P.; Izmailova, D.N. Selenium in Soils and Groundwater of Moldova. Environ. Geosci. 2006, 13, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kapitalchuk, I.; Golubkina, N.; Kapitalchuk, M.; Sheshnitsan, S. Selenium in Soils of Moldova. J. Environ. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 3, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubkina, N.; Sheshnitsan, S.; Kapitalchuk, M. Ecological Importance of Insects in Selenium Biogenic Cycling. Int. J. Ecol. 2014, 2014, 835636. [Google Scholar]
- Golubkina, N.A.; Sheshnitsan, S.S.; Kapitalchuk, M.V.; Erdenotsogt, E. Variations of Chemical Element Composition of Bee and Beekeeping Products in Different Taxons of the Biosphere. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubkina, N.A.; Kapitalchuk, M.V.; Sheshnitsan, S.S.; Grishina, T.L.; Kapitalchuk, I.P. Selenium Accumulation by Mushrooms of the Dniester River Valley. Trace Elem. Med. Mosc. 2014, 15, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kapitalchuk, M.V.; Golubkina, N.A.; Kapitalchuk, I.P. Hair Concentrations of Selenium in the Moldovan Population. Ekol. Cheloveka Hum. Ecol. 2023, 30, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botnaru, V.; Mirlean, N.; Quintana, G.C.R. Informative Eco-Geochemical Assessment of Soil Layer Pollution in Chisinau during the Peak Period of Industrial Activity. Bull. Inst. Geol. Seismol. 2022, 1, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubcov, E.; Zubcov, N. The Dynamics of the Content and Migration of Trace Metals in Aquatic Ecosystems of Moldova. E3S Web Conf. 2013, 1, 32009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Hramco, C.; Duliu, O.G.; Vergel, K.; Culicov, O.A.; Frontasyeva, M.V.; Duca, G. Air Pollution Study in the Republic of Moldova Using Moss Biomonitoring Technique. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 98, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Duliu, O.; Culicov, O.A.; Frontasyeva, M.; Sturza, R. Major and Trace Elements Distribution in Moldavian Soils. Romanian Rep. Phys. 2018, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zinicovscaia, I.; Sturza, R.; Duliu, O.; Grozdov, D.; Gundorina, S.; Ghendov-Mosanu, A.; Duca, G. Major and Trace Elements in Moldavian Orchard Soil and Fruits: Assessment of Anthropogenic Contamination. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabata-Pendias, A. Trace Elements in Soils and Plants, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosyak, G. Atlas of Moldavian SSR; Main Directorate of Geodesy and Cartography: Moscow, Russia, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Grebenshchikov, V.P.; Grebenshchikova, N.V. Hydrogeological Features of the Territory of Tiraspol. Sci. Dev. Trends Educ. 2019, 56, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjemstad, J.; Baldock, J. Total and Organic Carbon. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 2nd ed.; Carter, M., Gregorich, E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaimukhametov, M.S. On the Methods of Exchangeable Ca and Mg Determination in Chernozemic Soils. Eurasian Soil Sci. 1993, 12, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 11047:1998; Soil Quality—Determination of Cadmium, Chromium, Cobalt, Copper, Lead, Manganese, Nickel and Zinc—Flame and Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometric Methods. German Institute for Standardization: Berlin, Germany, 1998. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/24010.html (accessed on 10 September 2023).
- Gupta, U.; Hettiarachchi, G. Boron, Molybdenum, and Selenium. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis, 2nd ed.; Carter, M., Gregorich, E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfthan, G. A Micromethod for the Determination of Selenium in Tissues and Biological Fluids by Single-Test-Tube Fluorimetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 1984, 165, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Abbas, Y.; ur-Rahman, S.; Ali, H.; Zafar, M.; Ali, S.; Ashraf, M.N.; Zehra, Q.; Espinoza, S.T.L.; Valderrama, J.R.D. Metal and Metalloids Speciation, Fractionation, Bioavailability, and Transfer toward Plants. In Metals Metalloids Soil Plant Water Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 29–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Liu, C.; Cui, G.; Tong, S. Research on the Migration and Transformation Behaviors of Soil Selenium in the Flood Irrigation Process. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2021, 67, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.D.; Winkel, L.H.E. Multi-Scale Factors and Processes Controlling Selenium Distributions in Soils. In Selenium in Plants; Pilon-Smits, E.A.H., Winkel, L.H.E., Lin, Z.-Q., Eds.; Plant Ecophysiology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2017; Volume 11, pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.V.; Stockdale, E.A.; Brookes, P.C.; Goulding, K.W.T. Impact of Microorganisms on Chemical Transformations in Soil. In Soil Biological Fertility; Abbott, L.K., Murphy, D.V., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jump, R.K.; Sabey, B.R. Soil Test Extractants for Predicting Selenium in Plants. In SSSA Special Publications; Jacobs, L.W., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America and American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2015; pp. 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gao, Y. Biogeochemical Cycling of Selenium in Chinese Environments. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, W.; Li, R.; Hou, S.; Wang, D.; Yang, L. Selenium in Soil and Endemic Diseases in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 284, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriluk, V.P. Trace Elements in the Components of the Biosphere of Moldova; Pontos: Chișinău, Moldova, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, H.; Hattori, T. Forms of Soluble Selenium in Soil. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1989, 35, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čuvardić, M.S. Selenium in Soil. Proc. Nat. Sci. 2003, 104, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Gondi, F.; Pantó, G.; Fehér, J.; Bogye, G.; Alfthan, G. Selenium in Hungary: The Rock-Soil-Human System. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1992, 35, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapitalchuk, I.P.; Sheshnitsan, T.L.; Sheshnitsan, S.S.; Kapitalchuk, M.V. Migration of Manganese, Zinc, Copper and Molybdenum in Landscape-Geochemical Catena of the Lower Dniester Valley. South Russ. Ecol. Dev. 2018, 13, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapozhnikova, Y.; Zubcov, N.; Hungerford, S.; Roy, L.A.; Boicenco, N.; Zubcov, E.; Schlenk, D. Evaluation of Pesticides and Metals in Fish of the Dniester River, Moldova. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udeigwe, T.K.; Eichmann, M.; Eze, P.N.; Ogendi, G.M.; Morris, M.N.; Riley, M.R. Copper Micronutrient Fixation Kinetics and Interactions with Soil Constituents in Semi-Arid Alkaline Soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2016, 62, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Lian, W.; Lianggang, Z.; Dezhi, C. Expression of Copper and Cadmium Plant Availability in Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 33, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Blanco, R.; Nóvoa-Muñoz, J.C.; Arias-Estévez, M.; Fernández-Calviño, D.; Pérez-Rodríguez, P. Changes in Cu Accumulation and Fractionation along Soil Depth in Acid Soils of Vineyards and Abandoned Vineyards (Now Forests). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 339, 108146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Gong, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yang, S.; Ma, J.; Zhao, L.; Hou, H. Status of Copper Accumulation in Agricultural Soils across China (1985–2016). Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.J. Selenium Accumulation by Plants. Ann. Bot. 2016, 117, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu, M.E.; Bras, R.L. Dataset on the Global Distribution of Shallow Groundwater. Data Brief 2023, 47, 108973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liang, D.; Wang, D.; Wei, W.; Fu, D.; Lin, Z. Selenium Fractionation and Speciation in Agriculture Soils and Accumulation in Corn (Zea mays L.) under Field Conditions in Shaanxi Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 427–428, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliopoulos, G.D.; Eliopoulos, I.-P.D.; Tsioubri, M.; Economou-Eliopoulos, M. Distribution of Selenium in the Soil–Plant–Groundwater System: Factors Controlling Its Bio-Accumulation. Minerals 2020, 10, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Hawrylak-Nowak, B.; Islam, T.; Fujita, M. (Eds.) Biostimulants for Crop Production and Sustainable Agriculture; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.U.; Wang, X.; Shahzad, M.; Bashir, O.; Li, Y.; Cheng, H. A Review of the Influence of Nanoparticles on the Physiological and Biochemical Attributes of Plants with a Focus on the Absorption and Translocation of Toxic Trace Elements. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, G.D.S.; De Brito, P.O.B.; Lima, T.D.A.; Aderaldo, F.Í.C.; De Carvalho, G.T.; De Sousa Filho, E.D.N.; Gondim, F.A. Assessment of the Effects of Selenium Application on Leaves or Substrate on the Growth of Sunflower Plants: Avaliação Dos Efeitos Da Aplicação de Selênio Nas Folhas Ou No Substrato Sobre o Crescimento de Plantas de Girassol. Braz. J. Anim. Environ. Res. 2022, 5, 3972–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Soil Type | pH | SOC | CaCO3 | Exchangeable Cations Ca2+ + Mg2+ | Texture |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g·kg−1) | (g·kg−1) | (mg (eq)·100 g−1) | |||
| Fluvisols | 8.09 ± 0.10 ab | 13.9 ± 5.9 a | 67.2 ± 38.0 ab | 25.0 ± 8.9 a | Sandy loam |
| Luvy-Calcic Chernozems | 8.17 ± 0.11 a | 13.6 ± 6.3 a | 43.9 ± 23.8 b | 32.8 ± 10.0 a | Loam |
| Vorony-Calcic Chernozems | 7.88 ± 0.24 b | 8.4 ± 8.1 a | 28.4 ± 37.0 c | 18.2 ± 10.5 a | Loam |
| Voronic Chernozems | 7.95 ± 0.10 b | 27.1 ± 1.5 b | 12.6 ± 7.9 c | 46.4 ± 4.8 b | Silt loam |
| Soil Type | Se | Mn | Zn | Cu | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | WS | Total | EXC | Total | EXC | Total | EXC | |
| Fluvisols | 0.36 ± 0.09 ab | 0.11 ± 0.03 a | 429 ± 173 ab | 96.1 ± 24.0 a | 35.5 ± 25.0 a | 1.91 ± 1.29 a | 27.6 ± 10.9 ab | 0.35 ± 0.22 ab |
| Luvy-Calcic Chernozems | 0.32 ± 0.16 b | 0.09 ± 0.02 a | 458 ± 122 a | 76.2 ± 25.0 ab | 29.3 ± 16.4 a | 0.97 ± 0.70 ab | 39.1 ± 10.8 a | 0.52 ± 0.51 a |
| Vorony-Calcic Chernozems | 0.33 ± 0.12 b | 0.08 ± 0.03 a | 374 ± 115 ab | 64.6 ± 12.5 ab | 25.2 ± 10.3 a | 0.46 ± 0.19 b | 13.1 ± 8.5 b | 0.18 ± 0.03 b |
| Voronic Chernozems | 0.23 ± 0.07 bc | 0.08 ± 0.01 a | 565 ± 17 b | 56.1 ± 6.2 b | 44.0 ± 16.2 a | 0.82 ± 1.25 ab | 26.2 ± 7.7 b | 0.09 ± 0.05 b |
| All soil types | 0.33 ± 0.13 | 0.09 ± 0.03 | 464 ± 129 | 75.7 ± 24.5 | 33.8 ± 18.4 | 1.04 ± 0.90 | 31.2 ± 12.7 | 0.41 ± 0.45 |
| Pollution Level | Cu | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | AS | EXC | ||
| Unpolluted and low-polluted soils | Mean ± SD | 27.3 ± 8.1 a | 6.2 ± 3.5 a | 0.23 ± 0.19 a |
| (n = 14) | Min–max | 12.1–38.3 | 2.0–11.5 | 0.03–0.52 |
| Highly polluted soils | Mean ± SD | 73.7 ± 57.7 b | 53.8 ± 43.7 b | 8.00 ± 10.71 b |
| (n = 4) | Min–max | 28.9–158.3 | 20.6–115.8 | 0.85–23.70 |
| Plant Species | Se | Mn | Zn | Cu | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (mg·kg−1) | BAF | (mg·kg−1) | BAF | (mg·kg−1) | BAF | (mg·kg−1) | BAF | ||
| Sunflower (Helianthus annuus) | Mean ± SD | 0.23 ± 0.17 a | 0.70 ± 0.41 a | 94.9 ± 46.7 a | 0.18 ± 0.08 a | 21.2 ± 5.5 b | 0.74 ± 0.46 a | 5.1 ± 6.4 a | 0.15 ± 0.13 a |
| Min–max | 0.08–0.58 | 0.30–1.43 | 43.6–166.0 | 0.08–0.30 | 14.6–27.7 | 0.36–1.35 | 1.5–16.4 | 0.06–0.38 | |
| Wheat (Titicum aestivum) | Mean ± SD | 0.15 ± 0.08 ab | 0.53 ± 0.26 ab | 90.4 ± 28.5 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 a | 30.1 ± 4.4 a | 0.75 ± 0.22 a | 3.1 ± 0.9 a | 0.11 ± 0.04 a |
| Min–max | 0.07–0.36 | 0.29–1.05 | 26.1–126.5 | 0.19–0.20 | 22.4–35.6 | 0.55–1.06 | 1.9–4.3 | 0.06–0.15 | |
| Couch grass (Elytrigia repens) | Mean ± SD | 0.12 ± 0.07 b | 0.43 ± 0.20 b | 78.2 ± 37.4 a | 0.20 ± 0.17 a | 25.4 ± 7.7 b | 1.03 ± 0.56 a | 3.3 ± 1.6 a | 0.14 ± 0.13 a |
| Min–max | 0.06–0.32 | 0.20–0.86 | 26.2–152.5 | 0.05–0.49 | 13.3–43.4 | 0.32–2.58 | 1.5–7.9 | 0.04–0.49 | |
| Chemical Elements | World Soils [30] | Soils of Moldova [20,45] | Soils of the LDV (This Study) | Threshold Levels [30] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Total | EXC | Total | EXC | MAC | TAV | ||
| Se | Mean | 0.44 | 0.25 | – | 0.33 | 0.09 * | – | – |
| Min–max | – | 0.10–0.65 | – | 0.08–0.65 | 0.04–0.15 * | – | 3–10 | |
| Mn | Mean | 488 | 790 | 2.4 | 464 | 75.7 | – | – |
| Min–max | – | 150–2250 | 0.4–195 | 196–676 | 43–136 | – | – | |
| Zn | Mean | 70 | 71 | 1.4 | 33.8 | 1.04 | – | – |
| Min–max | – | 10–166 | 0.1–4.9 | 13.2–63.0 | 0.14–3.34 | 100–130 | 200–1500 | |
| Cu | Mean | 38.9 | 32 | 1.6 | 31.2 ** | 0.41 ** | – | – |
| Min–max | – | 2–400 | 0.1–60 | 7.0–158.3 | 0.01–23.70 | 60–150 | 60–500 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheshnitsan, S.; Golubkina, N.; Sheshnitsan, T.; Murariu, O.C.; Tallarita, A.V.; Caruso, G. Selenium and Heavy Metals in Soil–Plant System in a Hydrogeochemical Province with High Selenium Content in Groundwater: A Case Study of the Lower Dniester Valley. Soil Syst. 2024, 8, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8010007
Sheshnitsan S, Golubkina N, Sheshnitsan T, Murariu OC, Tallarita AV, Caruso G. Selenium and Heavy Metals in Soil–Plant System in a Hydrogeochemical Province with High Selenium Content in Groundwater: A Case Study of the Lower Dniester Valley. Soil Systems. 2024; 8(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheshnitsan, Sergey, Nadezhda Golubkina, Tatiana Sheshnitsan, Otilia Cristina Murariu, Alessio Vincenzo Tallarita, and Gianluca Caruso. 2024. "Selenium and Heavy Metals in Soil–Plant System in a Hydrogeochemical Province with High Selenium Content in Groundwater: A Case Study of the Lower Dniester Valley" Soil Systems 8, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8010007
APA StyleSheshnitsan, S., Golubkina, N., Sheshnitsan, T., Murariu, O. C., Tallarita, A. V., & Caruso, G. (2024). Selenium and Heavy Metals in Soil–Plant System in a Hydrogeochemical Province with High Selenium Content in Groundwater: A Case Study of the Lower Dniester Valley. Soil Systems, 8(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/soilsystems8010007