The Effect of High-Pressure Pre-Soaking on the Water Absorption, Gelatinization Properties, and Microstructural Properties of Wheat Grains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Samples Preparation and Analysis
2.3. HHP Treatment
2.4. Water Absorption during HHP Treatment
2.5. Convective Drying
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.7. Stereo Microscope
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
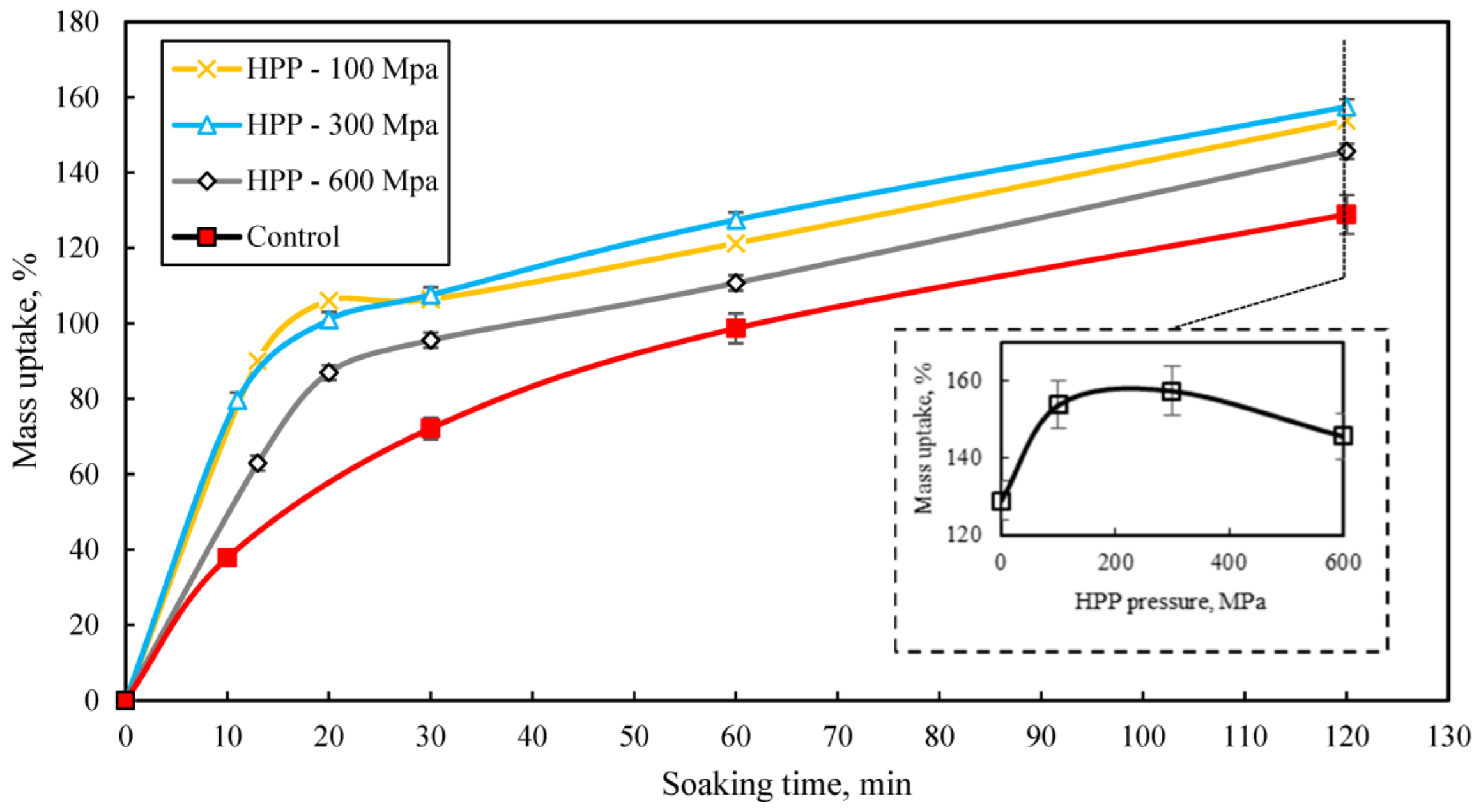
3.1. Effects of HHP on Mass Uptake
3.2. Microscopic Analysis of Untreated and HHP-Treated Wheat Grains
3.3. Effect of HHP on the Gelatinization Properties of Wheat Grains
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aganovic, K.; Hertel, C.; Vogel, R.F.; Johne, R.; Schlüter, O.; Schwarzenbolz, U.; Jäger, H.; Holzhauser, T.; Bergmair, J.; Roth, A.; et al. Aspects of high hydrostatic pressure food processing: Perspectives on technology and food safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 3225–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, J.; Mulla, M.; Al-Ruwaih, N.; Arfat, Y.A. Effect of high-pressure treatment prior to enzymatic hydrolysis on rheological, thermal, and antioxidant properties of lentil protein isolate. Legum. Sci. 2019, 1, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.Y.; Kil, D.Y.; Kong, C.; Kim, B.G. Comparison of oven-drying methods for determination of moisture content in feed ingredients. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 1615–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba, F.J.; Terefe, N.S.; Buckow, R.; Knorr, D.; Orlien, V. New opportunities and perspectives of high pressure treatment to improve health and safety attributes of foods: A review. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 725–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacha, J.S.; Zhang, L.; Ofoedu, C.E.; Suleiman, R.A.; Dotto, J.M.; Roobab, U.; Agunbiade, A.O.; Duguma, H.T.; Mkojera, B.T.; Hossaini, S.M.; et al. Revisiting non-thermal food processing and preservation methods—Action mechanisms, pros and cons: A technological update (2016–2021). Foods 2021, 10, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forst, P.; Werner, F.; Delgado, A. The viscosity of water at high pressures—Especially at subzero degrees centigrade. Rheol. Acta 2000, 39, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebishy, E.; Buffa, M.; Guamis, B.; Blasco-Moreno, A.; Trujillo, A.J. Physical and oxidative stability of whey protein oil-in-water emulsions produced by conventional and ultra high-pressure homogenization: Effects of pressure and protein concentration on emulsion characteristics. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 32, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-L.; Jao, C.-L.; Hsu, K.-C. Effects of Hydrostatic Pressure/Heat Combinations on Water Uptake and Gelatinization Characteristics of Japonica Rice Grains: A Kinetic Study Materials and Methods. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, E442–E448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulathunga, J.; Reuhs, B.L.; Zwinger, S.; Simsek, S. Comparative study on kernel quality and chemical composition of ancient and modern wheat species: Einkorn, emmer, spelt and hard red spring wheat. Foods 2021, 10, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurpiewska, K.; Biela, A.; Loch, J.I.; Lipowska, J.; Siuda, M.; Lewiński, K. Towards understanding the effect of high pressure on food protein allergenicity: β-lactoglobulin structural studies. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bail, P.; Chauvet, B.; Simonin, H.; Rondeau-Mouro, C.; Pontoire, B.; De Carvalho, M.; Le-Bail, A. Formation and stability of amylose ligand complexes formed by high pressure treatment. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 18, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chao, C.; Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Copeland, L. New insights into starch gelatinization by high pressure: Comparison with heat-gelatinization. Food Chem. 2020, 318, 126493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meretukov, Z.A.; Koshevoy, E.; Shorstkii, I.; Okpala, C.O.R. Porous granules formation from oil crops by extrusion process: A theoretical perspective. OCL 2021, 28, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei-Ling, L.; Xiao-Song, H.; Qun, S. Effect of high hydrostatic pressure on starches: A review. Starch/Staerke 2010, 62, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, N.K.; Raghavarao, K.S.M.S.; Balasubramaniam, V.M.; Niranjan, K.; Knorr, D. Opportunities and challenges in high pressure processing of foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 69–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathjen, J.R.; Strounina, E.V.; Mares, D.J. Water movement into dormant and non-dormant wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) grains. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 1619–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevkani, K.; Singh, N.; Bajaj, R.; Kaur, A. Wheat starch production, structure, functionality and applications—A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 38–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Słomińska, L.; Zielonka, R.; Jarosławski, L.; Krupska, A.; Szlaferek, A.; Kowalski, W.; Tomaszewska-Gras, J.; Nowicki, M. High pressure impact on changes in potato starch granules. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2015, 17, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topin, V.; Radjaï, F.; Delenne, J.-Y.; Sadoudi, A.; Mabille, F. Wheat endosperm as a cohesive granular material. J. Cereal Sci. 2008, 47, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushakov, D.S.; Shepelev, V.V.; Patlasov, Y.O. Marketing researches of the modified starch market and the technologies of its production. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 6th International Conference on Agriproducts Processing and Farming, Voronezh, Russian, 17–18 October 2019; Volume 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, G.V.; Barbosa-Cánovas, H.L.L. High Pressure Processing of Food: Principles, Technology and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Li, D.; Wang, L.J. Drying Damage on Physiological Properties of Rice Seed Associated with Ultrastructure Changes. Int. J. Food Eng. 2017, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welti-Chanes, J.; López-Malo, A.; Palou, E.; Bermúdez, D.; Guerrero-Beltrán, J.A.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Fundamentals and Applications of High Pressure Processing to Foods; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ge, L.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Wang, C.; Zhan, Y.; Zhu, S. Effect of high-pressure processing on moisture sorption properties of brown rice. Dry. Technol. 2016, 34, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Qi, X.G.; Wu, G. Research on migration path and structuring role of water in rice grain during soaking. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 92, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.M.; Hu, F.F.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Zhang, Q.T. Effect of High Pressure Treatment and Degree of Milling on Gelatinization and Structural Properties of Brown Rice. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



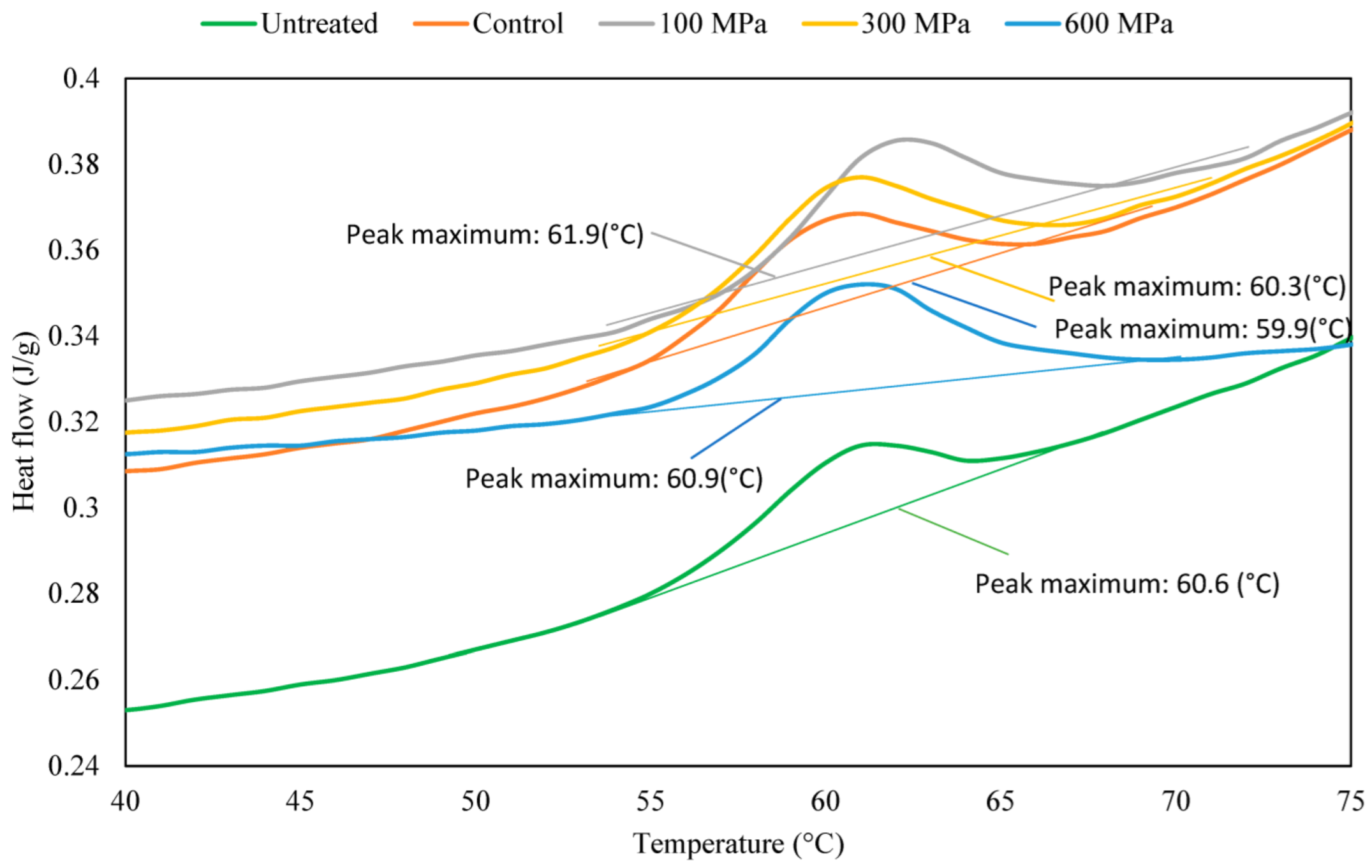
| Sample | Untreated | Control | HHP | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 MPa | 300 MPa | 600 MPa | |||
| Transition temperature, Tpeak, [°C] | 60.6 ± 0.4 | 59.9 ± 0.3 | 61.9 ± 0.1 | 60.4 ± 0.1 | 60.9 ± 0.1 |
| Heat flow, Qpeak, [W/g] | 0.3 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.4 ± 0.1 |
| Total enthalpy, ∆H [J/g] | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 1.4 ± 0.5 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 1.9 ± 0.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shorstkii, I.; Sosnin, M.; Mounassar, E.H.A.; Bindrich, U.; Heinz, V.; Aganovic, K. The Effect of High-Pressure Pre-Soaking on the Water Absorption, Gelatinization Properties, and Microstructural Properties of Wheat Grains. AgriEngineering 2022, 4, 1153-1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering4040071
Shorstkii I, Sosnin M, Mounassar EHA, Bindrich U, Heinz V, Aganovic K. The Effect of High-Pressure Pre-Soaking on the Water Absorption, Gelatinization Properties, and Microstructural Properties of Wheat Grains. AgriEngineering. 2022; 4(4):1153-1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering4040071
Chicago/Turabian StyleShorstkii, Ivan, Maxim Sosnin, Emad Hussein Ali Mounassar, Ute Bindrich, Volker Heinz, and Kemal Aganovic. 2022. "The Effect of High-Pressure Pre-Soaking on the Water Absorption, Gelatinization Properties, and Microstructural Properties of Wheat Grains" AgriEngineering 4, no. 4: 1153-1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering4040071
APA StyleShorstkii, I., Sosnin, M., Mounassar, E. H. A., Bindrich, U., Heinz, V., & Aganovic, K. (2022). The Effect of High-Pressure Pre-Soaking on the Water Absorption, Gelatinization Properties, and Microstructural Properties of Wheat Grains. AgriEngineering, 4(4), 1153-1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering4040071










