Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors for Water Quality Monitoring in Aquaculture Systems: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
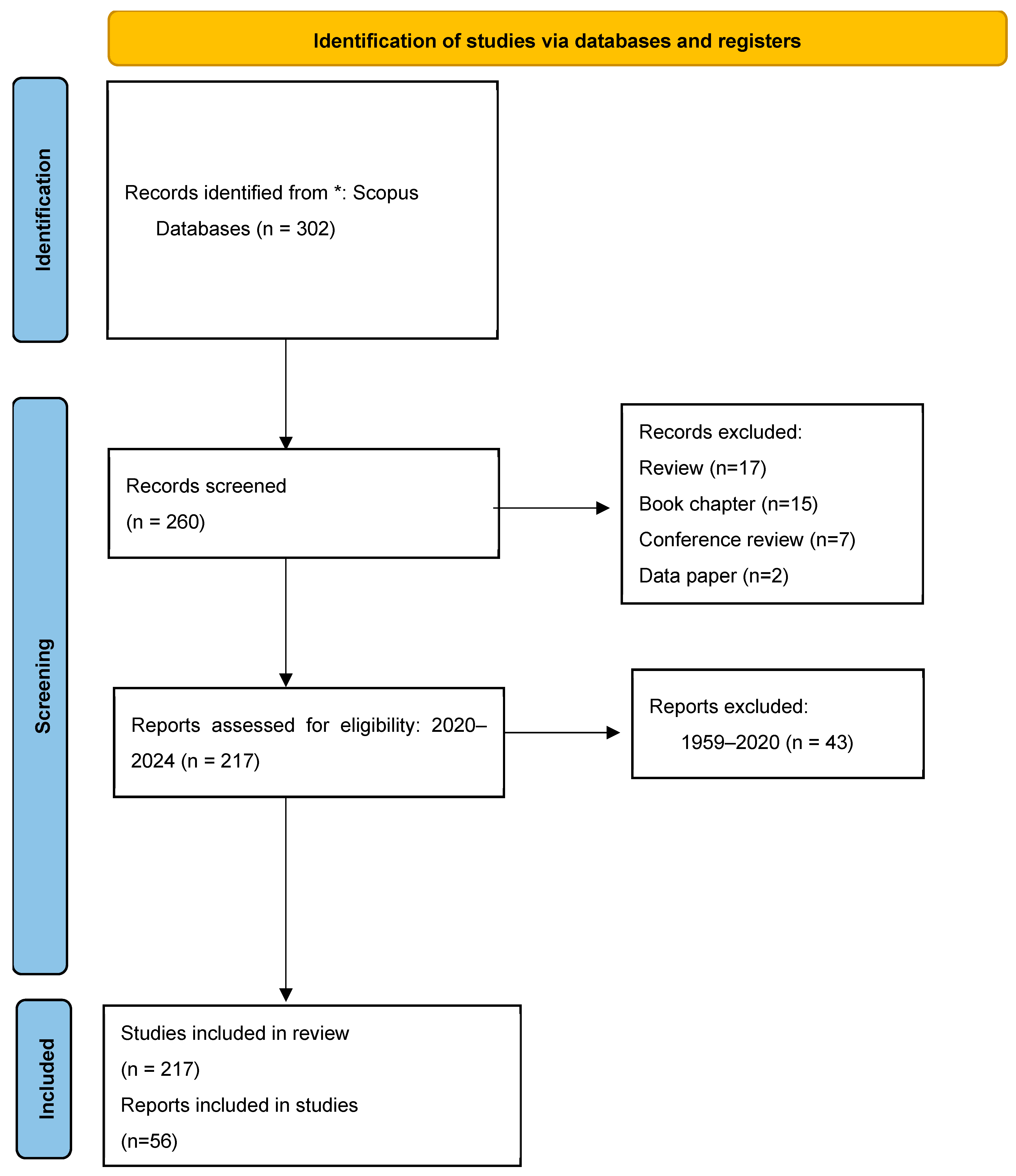
2. Methodology
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Bibliometrics Analysis
3. Performance and Network Analyses
3.1. Annual Scientific Output
3.2. Scientific Production by Country
3.3. Authors Contribution
3.4. Contribution of Affiliations
3.5. Keyword Analysis
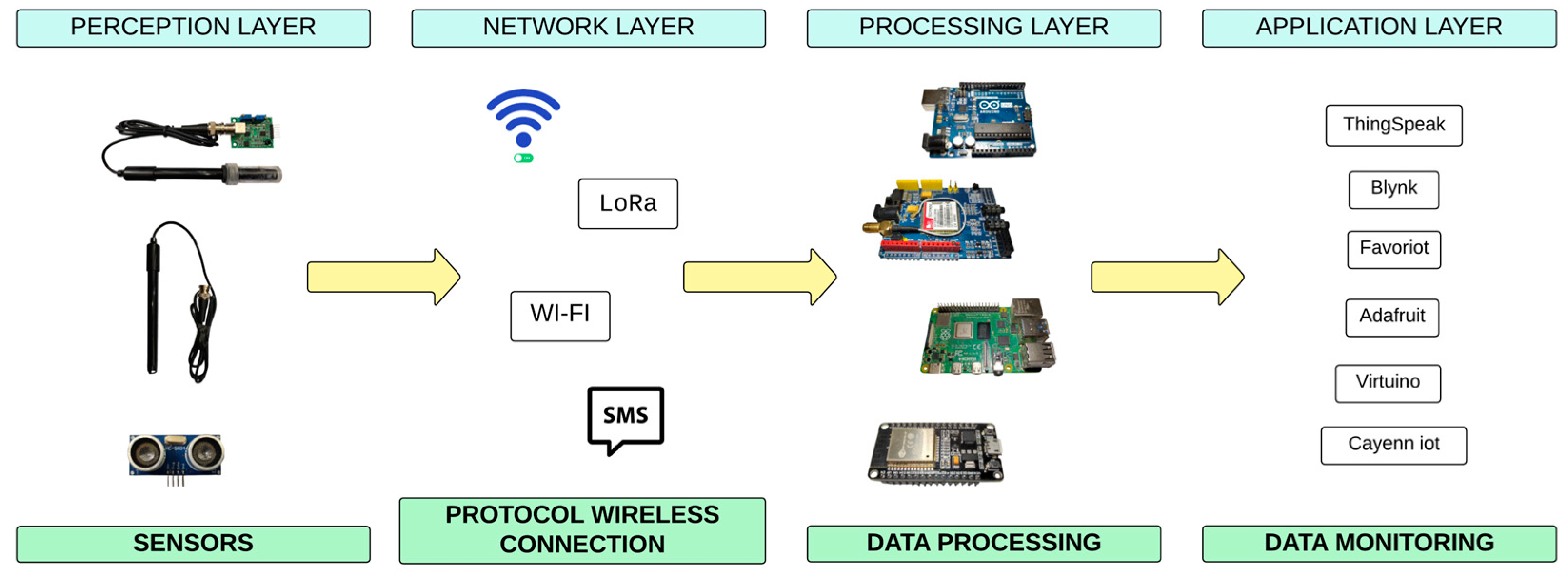
4. Internet of Things (IoT) in Aquaculture
4.1. Parameters Monitored Using IoT Sensors
| Reference | Sensor | Data Analysis and Processing | Data Transmission | Network Technology | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nayoun et al. [56] | pH, T° (DS18B20), Water level | Arduino Nano (ATmega328P), NodeMcu Esp-12E (Based ESP8266) | Arduino IOT cloud | Wi-Fi | - Oxygen level prediction |
| M et al. [53] | T°(DS18B20), pH (SEN0169), DO (SEN0237), Salinity (SLP2000) | Raspberry Pi, Edge server | Smartphone | Wi-Fi | - Development of a real-time water monitoring system using sensors and deep learning. |
| Shaghaghi et al. [82] | DO (MAX30102), T° and Humidity (DHT11) | Wisen Whisper Node, Arduino Nano | EPIC IoT | LoRa | - Development of an optical sensor for dissolved oxygen measurement. |
| Arif et al. [58] | T° (DS18B20), pH (SEN0161), Turbidity (SEN0189) | Arduino UNO | GSM SIM 900A, Smartphone | SMS (2G) | - Real-time monitoring. - SMS alerts when parameters are critical. |
| Islam et al. [19] | pH, T° (DS18B20), Turbidity, Water level (HC-SR04), DBO | Arduino UNO | ThingSpeak (rest-API) | Wi-Fi | - Determination of survival in aquaculture ponds based on physicochemical water parameters. |
| Nabi & Kharaz [83] | DO (OxyGuard DO 420 model) | ARM Cortex-M3 | N/R | SIM card (2G/3G). | - Development of early warning to oxygenate water. |
| Dutta et al. [84] | pH, T° and Humidity (DHT11), Water level (HCSR04) | Arduino UNO (ATmeda328P), Node MCU | Blynk App and ThingSpeak—Smartphone | Wi-Fi | - Real-time pH evaluation. - Bicarbonate solution dispensing device. |
| Chen et al. [59] | pH, T°, DO (ZTWL-SZO2-485), EC (ZT-SZEC-1001) | STM32F103 chip | FreeCloud (Mobile App) | SMS 4G | - System design for real-time monitoring. |
| Xu et al. [85] | T°, pH, DO, Ammonia nitrogen | RS485, GD32F303 and ESP8266 | OneNet cloud | Wi-Fi | - Development of a portable system to evaluate water quality parameters in aquaculture. |
| Singh et al. [86] | EC, pH, DO (ORP) | N/R | The Things Network | LoRaWAN | - Long-distance monitoring of water quality parameters. |
| Hawari & Hazwan [87] | T° (DS18820), Turbidity (SEN0189), pH (SEN0161) | Arduino, Orange Pi | Telegram notification/Google Drive | Wi-Fi | - Real-time monitoring. |
| Rohan et al. [88] | T° (DS18B20), Turbidity (SEN0189) | Raspberry Pi 3 Model B | ThingSpeakView App | Wi-Fi | - Increased productivity in aquaculture. |
| Uddin et al. [89] | Humidity, T°, Water level, Turbidity, pH, and DO | Arduino UNO R3 | DWIFS and IoT cloud servers | Wi-Fi and SMS | - Water quality control in fish and rice farming. |
| Tsai et al. [51] | pH, DO, EC, T° (DS18B20) | ESP32 | ThingSpeakView App | Wi-Fi | - Salinity prediction. |
| Lin et al. [68] | T° (DS18B20), pH. Dissolved Oxygen (DO), EC | Modulo SoC ESP-WROOM-32 (basado en ESP8266) | ThingSpeak IoT (MATLAB R2021b) | Wi-Fi and Bluetooth | - Real-time monitoring. |
| Q. Zhang et al. [60] | pH, Turbidity, DO | STM32F103ZT6 | OneNet cloud | NB-IoT | - Aquaculture water quality monitoring in a UAV. |
| Boonsong et al. [61] | pH, DO (Kit-ATLAS SCIENTIFIC), T° (DS18B20) | ATmega328 | Server Cloud | ZIGBEE | - Real-time monitoring. |
4.2. Application in Aquaculture
Cultures Employing IoT Sensors
5. Application of IoT Sensor in Cultivation Systems
5.1. Biofloc Technology (BFT)
5.2. Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS)
5.3. Aquaponic System
6. Challenges and Prospects
6.1. Challenges
6.2. Future Trending
- ⮚
- Flexible sensors, such as the nonplanar multi-chamber array dissolved oxygen sensor developed by Xu et al. [159], enable real-time monitoring in aquaculture systems such as Biofloc. These soft sensors improve efficiency by adapting to dynamic aquatic environments and overcoming the limitations of traditional rigid sensors, but they still present challenges in scalability and cost.
- ⮚
- AI-driven digital twins, such as the model integrated by Ubina et al. [160], use big data and cloud computing to predict fish growth in real time. This approach, applicable to RAS or aquaponics systems, improves decision support and productivity but requires robust infrastructure and data integration, areas that continue to evolve.
- ⮚
- Nanosensors, developed by Abdelaziz et al. [161], such as an optical ammonia detection probe using dendritic nanoparticles, improve sensitivity in monitoring nitrogenous compounds, which is crucial for aquaponics and BFT. Despite their high sensitivity, their scalability and large-scale deployment remain a challenge.
- ⮚
- High-speed connectivity powered by 5G enables real-time monitoring in large-scale aquaculture farms, as reviewed in the study by Li et al. [162]. This improves data transmission compared to technologies such as LoRaWAN or Wi-Fi, but it requires a large infrastructure investment, limiting its immediate adoption in rural areas.
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Section and Topic | Item # | Checklist Item | Location Where Item Is Reported |
|---|---|---|---|
| TITLE | |||
| Title | 1 | Identify the report as a systematic review. | L.3 |
| ABSTRACT | |||
| Abstract | 2 | See the PRISMA 2020 for Abstracts checklist. | L.21 |
| INTRODUCTION | |||
| Rationale | 3 | Describe the rationale for the review in the context of existing knowledge. | L.60 |
| Objectives | 4 | Provide an explicit statement of the objective(s) or question(s) the review addresses. | L.85 |
| METHODS | |||
| Eligibility criteria | 5 | Specify the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the review and how studies were grouped for the syntheses. | L.117 |
| Information sources | 6 | Specify all databases, registers, websites, organisations, reference lists and other sources searched or consulted to identify studies. Specify the date when each source was last searched or consulted. | L.112 |
| Search strategy | 7 | Present the full search strategies for all databases, registers and websites, including any filters and limits used. | L.120 |
| Selection process | 8 | Specify the methods used to decide whether a study met the inclusion criteria of the review, including how many reviewers screened each record and each report retrieved, whether they worked independently, and if applicable, details of automation tools used in the process. | L.117-119 |
| Data collection process | 9 | Specify the methods used to collect data from reports, including how many reviewers collected data from each report, whether they worked independently, any processes for obtaining or confirming data from study investigators, and if applicable, details of automation tools used in the process. | L.112-121 |
| Data items | 10a | List and define all outcomes for which data were sought. Specify whether all results that were compatible with each outcome domain in each study were sought (e.g., for all measures, time points, analyses), and if not, the methods used to decide which results to collect. | |
| 10b | List and define all other variables for which data were sought (e.g., participant and intervention characteristics, funding sources). Describe any assumptions made about any missing or unclear information. | ||
| Study risk of bias assessment | 11 | Specify the methods used to assess risk of bias in the included studies, including details of the tool(s) used, how many reviewers assessed each study and whether they worked independently, and if applicable, details of automation tools used in the process. | |
| Effect measures | 12 | Specify for each outcome the effect measure(s) (e.g., risk ratio, mean difference) used in the synthesis or presentation of results. | |
| Synthesis methods | 13a | Describe the processes used to decide which studies were eligible for each synthesis (e.g., tabulating the study intervention characteristics and comparing against the planned groups for each synthesis (item #5)). | |
| 13b | Describe any methods required to prepare the data for presentation or synthesis, such as handling of missing summary statistics, or data conversions. | ||
| 13c | Describe any methods used to tabulate or visually display results of individual studies and syntheses. | ||
| 13d | Describe any methods used to synthesize results and provide a rationale for the choice(s). If meta-analysis was performed, describe the model(s), method(s) to identify the presence and extent of statistical heterogeneity, and software package(s) used. | ||
| 13e | Describe any methods used to explore possible causes of heterogeneity among study results (e.g., subgroup analysis, meta-regression). | ||
| 13f | Describe any sensitivity analyses conducted to assess robustness of the synthesized results. | ||
| Reporting bias assessment | 14 | Describe any methods used to assess risk of bias due to missing results in a synthesis (arising from reporting biases). | |
| Certainty assessment | 15 | Describe any methods used to assess certainty (or confidence) in the body of evidence for an outcome. | |
| RESULTS | |||
| Study selection | 16a | Describe the results of the search and selection process, from the number of records identified in the search to the number of studies included in the review, ideally using a flow diagram. | L. 248 |
| 16b | Cite studies that might appear to meet the inclusion criteria, but which were excluded, and explain why they were excluded. | ||
| Study characteristics | 17 | Cite each included study and present its characteristics. | L.356 |
| Risk of bias in studies | 18 | Present assessments of risk of bias for each included study. | |
| Results of individual studies | 19 | For all outcomes, present, for each study: (a) summary statistics for each group (where appropriate) and (b) an effect estimate and its precision (e.g., confidence/credible interval), ideally using structured tables or plots. | |
| Results of syntheses | 20a | For each synthesis, briefly summarise the characteristics and risk of bias among contributing studies. | |
| 20b | Present results of all statistical syntheses conducted. If meta-analysis was done, present for each the summary estimate and its precision (e.g., confidence/credible interval) and measures of statistical heterogeneity. If comparing groups, describe the direction of the effect. | ||
| 20c | Present results of all investigations of possible causes of heterogeneity among study results. | ||
| 20d | Present results of all sensitivity analyses conducted to assess the robustness of the synthesized results. | ||
| Reporting biases | 21 | Present assessments of risk of bias due to missing results (arising from reporting biases) for each synthesis assessed. | |
| Certainty of evidence | 22 | Present assessments of certainty (or confidence) in the body of evidence for each outcome assessed. | |
| DISCUSSION | |||
| Discussion | 23a | Provide a general interpretation of the results in the context of other evidence. | L.429 |
| 23b | Discuss any limitations of the evidence included in the review. | L.547 | |
| 23c | Discuss any limitations of the review processes used. | L.553 | |
| 23d | Discuss implications of the results for practice, policy, and future research. | L.595 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | |||
| Registration and protocol | 24a | Provide registration information for the review, including register name and registration number, or state that the review was not registered. | L.241 |
| 24b | Indicate where the review protocol can be accessed, or state that a protocol was not prepared. | L.108 | |
| 24c | Describe and explain any amendments to information provided at registration or in the protocol. | L.109 | |
| Support | 25 | Describe sources of financial or non-financial support for the review, and the role of the funders or sponsors in the review. | L.650 |
| Competing interests | 26 | Declare any competing interests of review authors. | L.657 |
| Availability of data, code and other materials | 27 | Report which of the following are publicly available and where they can be found: template data collection forms; data extracted from included studies; data used for all analyses; analytic code; any other materials used in the review. | L.655 |
Appendix B
References
- Apine, E.; Ramappa, P.; Bhatta, R.; Turner, L.M.; Rodwell, L.D. Challenges and Opportunities in Achieving Sustainable Mud Crab Aquaculture in Tropical Coastal Regions. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 242, 106711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. El Estado Mundial de la Pesca y la Acuicultura 2022; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [CrossRef]
- FAO. La Sostenibilidad en Acción; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Higuita, F.; Acosta-Coll, M.; Ballester-Merelo, F.; De-la-Hoz-Franco, E. Implementation of Information and Communication Technologies to Increase Sustainable Productivity in Freshwater Finfish Aquaculture—A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 408, 137124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wen, X.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z. A Systematic Review on Aquaculture Wastewater: Pollutants, Impacts, and Treatment Technology. Environ. Res. 2024, 262, 119793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Li, G.; Wu, H.B.; Liu, X.G.; Yao, Y.H.; Tao, L.; Liu, H. An Integrated Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS) for Land-Based Fish Farming: The Effects on Water Quality and Fish Production. Aquac. Eng. 2011, 45, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.M.; Nayan, A.-A.; Rahman, M.O.; Simi, S.A.; Saha, J.; Kibria, M.G. IoT Based Smart Water Quality Prediction for Biofloc Aquaculture. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shete, R.P.; Bongale, A.M.; Dharrao, D. IoT-Enabled Effective Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring Method for Aquaculture. MethodsX 2024, 13, 102906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, B.; Yang, P.; Wang, X.; Li, D.; Wang, J. Water Quality Parameter Analysis Model Based on Fish Behavior. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 203, 107500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegari, H.; Nadi, F.; Lam, S.S.; Ikhwanuddin, M.; Kasan, N.A.; Rahmat, R.F.; Mahari, W.A.W. Internet of Things in Aquaculture: A Review of the Challenges and Potential Solutions Based on Current and Future Trends. Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 4, 100187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabelli, R.; Bernatin, T. Water Quality Monitoring and Controlling Systems for Aquaculture. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Science, Machine Learning and Applications, Hyderabad, India, 26–27 December 2022; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; Volume 1038, ISBN 9789819920570. [Google Scholar]
- Ogello, E.O.; Outa, N.O.; Obiero, K.O.; Kyule, D.N.; Munguti, J.M. The Prospects of Biofloc Technology (BFT) for Sustainable Aquaculture Development. Sci. Afr. 2021, 14, e01053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovski, A.; Ajdari, J.; Zenuni, X. IoT-Based Solutions in Aquaculture: A Systematic Literature Review. In Proceedings of the 2021 44th International Convention on Information, Communication and Electronic Technology, MIPRO 2021, Opatija, Croatia, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 1358–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Gouiza, N.; Jebari, H.; Reklaoui, K. IoT in Smart Farming: A Review; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; Volume 930, ISBN 9783031543180. [Google Scholar]
- Londhe, A.; Apare, R.; Borhade, R. Aqua Status Prediction Using IoT and Optimization in Aquaculture: A Comprehensive Review. In Proceedings of the 2024 MIT Art, Design and Technology School of Computing International Conference (MITADTSoCiCon 2024), Pune, India, 25–27 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Iannacci, J. Internet of Things (IoT); Internet of Everything (IoE); Tactile Internet; 5G—A (Not so Evanescent) Unifying Vision Empowered by EH-MEMS (Energy Harvesting MEMS) and RF-MEMS (Radio Frequency MEMS). Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 272, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.K. Optical Wireless Communications for Broadband Global Internet Connectivity: Fundamentals and Potential Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; ISBN 9780128133651. [Google Scholar]
- Udanor, C.N.; Ossai, N.I.; Nweke, E.O.; Ogbuokiri, B.O.; Eneh, A.H.; Ugwuishiwu, C.H.; Aneke, S.O.; Ezuwgu, A.O.; Ugwoke, P.O.; Christiana, A. An Internet of Things Labelled Dataset for Aquaponics Fish Pond Water Quality Monitoring System. Data Brief 2022, 43, 108400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.M.; Kashem, M.A.; Alyami, S.A.; Moni, M.A. Monitoring Water Quality Metrics of Ponds with IoT Sensors and Machine Learning to Predict Fish Species Survival. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2023, 102, 104930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Jais, N.A.; Abdullah, A.F.; Mohd Kassim, M.S.; Abd Karim, M.M.; Abdulsalam, M.; Muhadi, N. Improved Accuracy in IoT-Based Water Quality Monitoring for Aquaculture Tanks Using Low-Cost Sensors: Asian Seabass Fish Farming. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, S.; Oza, P.; Kakkar, R.; Tanwar, S.; Jetani, V.; Undhad, J.; Singh, A. Analysis and Recommendation System-Based on PRISMA Checklist to Write Systematic Review. Assess. Writ. 2024, 61, 100866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Visualizing Bibliometric Networks. In Measuring Scholarly Impact; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 285–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsman, E.B.M.; Baba, A.; Offringa, M. PRISMA-COSMIN 2024: New Guidance Aimed to Enhance the Reporting Quality of Systematic Reviews of Outcome Measurement Instruments. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2024, 160, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, K.F.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Goh, K.H. Aquaculture Efficiency and Productivity: A Comprehensive Review and Bibliometric Analysis. Aquaculture 2021, 544, 736881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, Q.; Hu, R.G.; Cong, W.; Li, S.; Kang, Y.H. The Evaluation of Bacteriophage Therapy in Aquaculture: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Aquaculture 2024, 588, 740925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegaard, O.; Wallin, J.A. The Bibliometric Analysis of Scholarly Production: How Great Is the Impact? Scientometrics 2015, 105, 1809–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passas, I. Bibliometric Analysis: The Main Steps. Encyclopedia 2024, 4, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iber, B.T.; Ikyo, B.C.; Nor, M.N.M.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Shafie, M.S.B.; Manan, H.; Abdullah, M.I.; Kasan, N.A. Application of Biofloc Technology in Shrimp Aquaculture: A Review on Current Practices, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. J. Agric. Food Res. 2025, 19, 101675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarosh, S.; Kulkarni, R.M.; Varma, E.; Sirivibha, S.P.; Ramaswami, S. Recirculating Aquaculture System and Nitrification: A Review. J. Indian Inst. Sci. 2024, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.-C.; Lee, Y.-H.; Chou, H.-Y. Study on the Removal of Nitrogen-Containing Waste Outside the Aquaculture Pond by the Method of Electric Flocculation and Quasi Circulating Aquaculture. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 691, 012009. [Google Scholar]
- Prapti, D.R.; Shariff, A.R.M.; Man, H.C.; Ramli, N.M.; Perumal, T.; Shariff, M. An Overview of Water Quality Monitoring in IoT Based Aquaculture. In Proceedings of the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers Annual International Meeting, ASABE 2021, Online, 12–16 July 2021; Volume 1, pp. 602–610. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Tan, T.; Du, X.; Feng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Bai, G.; Liu, Z.; Xia, S.; Song, S.; et al. Advancements in Freshwater Aquaculture Wastewater Management: A Comprehensive Review. Aquaculture 2025, 594, 741346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. VOS: A New Method for Visualizing Similarities between Objects. In Advances in Data Analysis, Proceedings of the 30th Annual Conference of the Gesellschaft für Klassifikation eV, Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 8–10 March 2006; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arepalli, P.G.; Naik, K.J. Water Contamination Analysis in IoT Enabled Aquaculture Using Deep Learning Based AODEGRU. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 79, 102405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arepalli, P.G.; Naik, K.J. A Deep Learning-Enabled IoT Framework for Early Hypoxia Detection in Aqua Water Using Light Weight Spatially Shared Attention-LSTM Network. J. Supercomput. 2024, 80, 2718–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arepalli, P.G.; Khetavath, J.N. An IoT Framework for Quality Analysis of Aquatic Water Data Using Time-Series Convolutional Neural Network. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 125275–125294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danh, L.V.Q.; Dung, D.V.M.; Danh, T.H.; Ngon, N.C. Design and Deployment of an IoT-Based Water Quality Monitoring System for Aquaculture in Mekong Delta. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Robot. Res. 2020, 9, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai-Nghe, N.; Hung, T.T.; Ngon, N.C. A Forecasting Model for Monitoring Water Quality in Aquaculture and Fisheries IoT Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Advanced Computing and Applications, ACOMP 2020, Quy Nhon, Vietnam, 25–27 November 2020; pp. 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Thai-Nghe, N.; Thanh-Hai, N.; Ngon, N.C. Deep Learning Approach for Forecasting Water Quality in IoT Systems. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2020, 11, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blancaflor, E.; Baccay, M. Design of a Solar Powered IoT (Internet of Things) Remote Water Quality Management System for a Biofloc Aquaculture Technology. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd Blockchain and Internet of Things Conference, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 8–10 July 2021; pp. 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Blancaflor, E.B.; Baccay, M. Assessment of an Automated IoT-Biofloc Water Quality Management System in the Litopenaeus vannamei’s Mortality and Growth Rate. Automatika 2022, 63, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozie, F.; Syarif, I.; Al Rasyid, M.U.H. Design and Implementation of Intelligent Aquaponics Monitoring System Based on IoT. In Proceedings of the IES 2020—International Electronics Symposium: The Role of Autonomous and Intelligent Systems for Human Life and Comfort, Surabaya, Indonesia, 29–30 September 2020; pp. 534–540. [Google Scholar]
- Al Rasyid, M.U.H.; Sukaridhoto, S.; Dzulqornain, M.I.; Rifa’i, A. Integration of IoT and Chatbot for Aquaculture with Natural Language Processing. Telkomnika 2020, 18, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arepalli, P.G.; Jairam Naik, K. An IoT Based Smart Water Quality Assessment Framework for Aqua-Ponds Management Using Dilated Spatial-Temporal Convolution Neural Network (DSTCNN). Aquac. Eng. 2024, 104, 102373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palconit, M.G.B.; Concepcion, R.S.; Tobias, R.R.; Alejandrino, J.; Almero, V.J.D.; Bandala, A.A.; Vicerra, R.R.P.; Sybingco, E.; Dadios, E.P. Development of IoT-Based Fish Tank Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 13th International Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Information Technology, Communication and Control, Environment, and Management, HNICEM 2021, Manila, Philippines, 28–30 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Baldovino, R.G.; Magallanes, F.N.; Santos, E.J.C.; Conti, K.D.; Sia, P.D.L. Smart IoT-Based Feeder System for Koi Fish (Cyprinus rubrofuscus) Aquaculture. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Mechatronics Engineering, ICOM 2024, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–14 August 2024; 2024; pp. 240–244. [Google Scholar]
- Espena, G.D.; Libao, F.J.D.; Comedia, V.J.G.; De Luna, N.A.P.U.; Mojica, A.J.N.; Rivera, M.D. Enhancing Water Quality Control and Monitoring in Shrimp Farms with LoRaWAN Technology. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 15th International Conference on Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Information Technology, Communication and Control, Environment, and Management, HNICEM 2023, Coron, Palawan, Philippines, 19–23 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Libao, F.J.D.; Villaverde, O.S.M.; De Luna, N.A.P.U.; Comedia, V.J.G.; Luna, M.O.; Atienza, A.M.C.; Espena, G.D. Automated Control and IoT-Based Water Quality Monitoring System for a Molobicus Tilapia Recirculating Aquaculture System (RAS). In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Sustainability, SusTech 2024, Portland, OR, USA, 14–17 April 2024; pp. 410–415. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, A.; Wills, P.S.; Garvey, J.E.; Fairman, W.; Karim, M.A.; Ouyang, B. Developing and Field Testing Path Planning for Robotic Aquaculture Water Quality Monitoring. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, B.; Wills, P.S.; Tang, Y.; Hallstrom, J.O.; Su, T.-C.; Namuduri, K.; Mukherjee, S.; Rodriguez-Labra, J.I.; Li, Y.; Den Ouden, C.J. Initial Development of the Hybrid Aerial Underwater Robotic System (HAUCS): Internet of Things (IoT) for Aquaculture Farms. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 14013–14027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-L.; Lin, J.-Y.; Lyu, W.-H. Design and Evaluation of Wireless Multi-Sensor IoT System for Monitoring Water Quality of Freshwater Aquaculture. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Automatic Control Conference, CACS 2021, Chiayi, Taiwan, 3–6 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Al Mamun, M.R.; Ashik-E-Rabbani, M.; Haque, M.M.; Upoma, S.M. IoT-Based Real-Time Biofloc Monitoring and Controlling System. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 9, 100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iniyan Arasu, M.; Subha Rani, S.; Thiyagarajan, K.; Ahilan, A. AQUASENSE: Aquaculture Water Quality Monitoring Framework Using Autonomous Sensors. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 9119–9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhaili, W.; Aziz, M.; Ramlee, H.; Patchmuthu, R.; Shams, S.; Mohamad, I.; Isa, M.; Nore, B. IoT Aquaculture System for Sea Bass and Giant Freshwater Prawn Farming in Brunei. In Proceedings of the 2023 13th International Conference on Information Technology in Asia, CITA 2023, Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia, 7–8 August 2023; pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-C.; Zhang, J.-X.; Chen, Y.-H. IoT-Based Fish Farm Water Quality Monitoring System. Sensors 2022, 22, 6700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayoun, M.N.I.; Hossain, S.A.; Rezaul, K.M.; Siddiquee, K.N.E.A.; Islam, M.S.; Jannat, T. Internet of Things-Driven Precision in Fish Farming: A Deep Dive into Automated Temperature, Oxygen, and PH Regulation. Computers 2024, 13, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, L.; Magbanua, M.J.; Manalang, L.M.; Enclona, E.; Dimalanta, M.A.; Mordeno, D.; Anacan, R.; Hiwatig, C.; Valondo, S.C. Design of Water Quality Control System for Commercial Tilapia Pond. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Open Conference of Electrical, Electronic and Information Sciences (eStream), Vilnius, Lithuania, 27 April 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.A.; Reza, M.R.; Mandal, A.B.; Mahmud Akib, M.A.; Shuma, F.M.; Fehir, S.S.M. Towards Developing an IoT-Based Aquaculture Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Sustainable Development, ICICT4SD 2023, Dhaka, Bangladesh, 21–23 September 2023; pp. 134–138. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Wang, M.; Liao, X.; Wu, Z. Design of IoT-Based Aquaculture Water Quality Parameter Monitoring System. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 16th International Conference on Electronic Measurement and Instruments, ICEMI 2023, Harbin, China, 9–11 August 2023; pp. 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lan, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L. Study of NB-IoT-Based Unmanned Surface Vehicle System for Water Quality Monitoring of Aquaculture Ponds. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Sensors and Instruments (ICSI 2021), Qingdao, China, 28–30 May 2021; Volume 11887. [Google Scholar]
- Boonsong, W.; Ismail, W.; Shinohara, N.; Nameh, S.M.I.S.; Alifah, S.; Kamaludin, K.H.; Anwar, T. Real-Time Water Quality Monitoring of Aquaculture Pond Using Wireless Sensor Network and Internet of Things. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2020, 98, 3573–3582. [Google Scholar]
- Shaghaghi, N.; Nguyen, T.; Patel, J.; Soriano, A.; Mayer, J. DOxy: Dissolved Oxygen Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Global Humanitarian Technology Conference, GHTC 2020, Seattle, WA, USA, 29 October–1 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Friuli, M.; Masciullo, A.; Blasi, F.S.; Mita, M.; Corbari, L.; Surano, I. A 4.0 Sustainable Aquaponic System Based on the Combined Use of Superabsorbing Natural Hydrogels and Innovative Sensing Technologies for the Optimization of Water Use. In Proceedings of the 6th International Forum on Research and Technology for Society and Industry, RTSI 2021, Online, 6–9 September 2021; pp. 429–434. [Google Scholar]
- Bresnahan, P.J.; Wirth, T.; Martz, T.; Shipley, K.; Rowley, V.; Anderson, C.; Grimm, T. Equipping Smart Coasts with Marine Water Quality IoT Sensors. Results Eng. 2020, 5, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarudin, M.; Septama, H.D.; Yulianti, T.; Yudamson, A.; Hendri, J.; Arafat, M.A.D. Multi Node Sensors for Water Quality Monitoring towards Precision Aquaculture. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 739, 012026. [Google Scholar]
- Eneh, A.H.; Udanor, C.N.; Ossai, N.I.; Aneke, S.O.; Ugwoke, P.O.; Obayi, A.A.; Ugwuishiwu, C.H.; Okereke, G.E. Towards an Improved Internet of Things Sensors Data Quality for a Smart Aquaponics System Yield Prediction. MethodsX 2023, 11, 102436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satra, R.; Hadi, M.S.; Sujito, S.; Febryan, F.; Fattah, M.H.; Busaeri, S.R. IoAT: Internet of Aquaculture Things for Monitoring Water Temperature in Tiger Shrimp Ponds with DS18B20 Sensors and WeMos D1 R2. J. Robot. Control 2024, 5, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-Y.; Tsai, H.-L.; Lyu, W.-H. An Integrated Wireless Multi-Sensor System for Monitoring the Water Quality of Aquaculture. Sensors 2021, 21, 8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haruo, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Arakawa, M.; Naka, I. Development and Evaluation of Environmental/Growth Observation Sensor Network System for Aquaponics. In Proceedings of the Digest of Technical Papers—IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–6 January 2020; Volume 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, G.; Cennamo, N.; Zeni, L.; Singh, R.; Kumar, S.; Fernandes, A.J.S.; Costa, F.; Pereira, S.O.; Marques, C. Innovative Optical PH Sensors for the Aquaculture Sector: Comprehensive Characterization of a Cost-Effective Solution. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 171, 110355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, T.G.; Seyhan, S. Fine-Tuning Growth Conditions: Leaf-Level Vapor Pressure Deficit Control for Optimized Photosynthesis. Lect. Notes Civ. Eng. 2024, 458, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyounsi, A.; Kalashnikov, A.N. Evaluating Suitability of a DS18B20 Temperature Sensor for Use in an Accurate Air Temperature Distribution Measurement Network. Engineering 2021, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Biswas, S.; Sarmah, S.; Karmakar, S.; Das, P. A Working Prototype Using DS18B20 Temperature Sensor and Arduino for Health Monitoring. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasnim, R.; Shaikat, A.S.; Al Amin, A.; Hussein, M.R.; Rahman, M.M. Design of a Smart Biofloc Monitoring and Controlling System Using IoT. J. Eng. Adv. 2022, 3, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Camargo, E.T.; Spanhol, F.A.; Slongo, J.S.; da Silva, M.V.R.; Pazinato, J.; de Lima Lobo, A.V.; Coutinho, F.R.; Pfrimer, F.W.D.; Lindino, C.A.; Oyamada, M.S.; et al. Low-Cost Water Quality Sensors for IoT: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2023, 23, 4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, R.; Paliuc, C.; Crisan-Vida, M.; Nimara, S.; Barmayoun, D. Low-Cost Internet-of-Things Water-Quality Monitoring System for Rural Areas. Sensors 2023, 23, 3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, W.L.; Hasanah, L.; Mulyanti, B.; Aminudin, A. Characterization of Turbidity Water Sensor SEN0189 on the Changes of Total Suspended Solids in the Water. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1280, 022064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstetter, D.; Fabian, E.; Lorenzoni, A.G. Ammonia Generation System for Poultry Health Research Using Arduino. Sensors 2021, 21, 6664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriasni, P.A.; Faizal, F.; Hermawan, W.; Subhan, U.; Panatarani, C.; Joni, I.M. IoT Water Quality Monitoring and Control System in Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor to Reduce Total Ammonia Nitrogen. Sensors 2024, 24, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diana, A.R.; Nugroho, E.R.; Wicaksono, S.R.; Azman, N. Industrial Internet of Things Solution for Monitoring Ammonia and Carbon Monoxide in Industrial Staging Areas. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2664, 030005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaoula, T.; Abdelouahid, R.A.; Ezzahoui, I.; Marzak, A. Architecture Design of Monitoring and Controlling of IoT-Based Aquaponics System Powered by Solar Energy. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 191, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaghaghi, N.; Fazlollahi, F.; Shrivastav, T.; Graham, A.; Mayer, J.; Liu, B.; Jiang, G.; Govindaraju, N.; Garg, S.; Dunigan, K.; et al. DOxy: A Dissolved Oxygen Monitoring System. Sensors 2024, 24, 3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, M.M.; Kharaz, A. Design and Deployment of Dissolved Oxygen Remote Monitoring and Control for The Environmental Agency Using IoT. In Proceedings of the 9th 2023 International Conference on Control, Decision and Information Technologies, CoDIT 2023, Rome, Italy, 3–6 July 2023; pp. 494–499. [Google Scholar]
- Dutta, L.; Bharali, S.; Barman, P.; Singh, A. An IoT-Enabled Smart PH Monitoring and Dispensing System for Precision Agriculture Application. Agric. Res. 2024, 13, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jin, J.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Q. Development and Evaluation of an IoT-Based Portable Water Quality Monitoring System for Aquaculture. INMATEH-Agric. Eng. 2023, 70, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Sharma, G.; Minhas, I.; Singh, G.; Mahajan, P.; Verma, P.; Manocha, G.C. LoRaWAN Gateway Architecture for Aquaculture Monitoring in Rural Area. In Proceedings of the 2023 6th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks, ISCON 2023, Mathura, India, 3–4 March 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hawari, H.F.; Hazwan, M.A. Development of Iot Monitoring System for Aquaculture Application. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Green Energy, Computing and Sustainable Technology, GECOST 2022, Online, 26–28 October 2022; 2022; pp. 330–334. [Google Scholar]
- Rohan, K.K.; Roria, O.; Raghavendra, C.G.; Awanti, S.S.; Shruthishree, C.; Chakravorty, S. Determining Water Quality for Productivity in Aquaculture Using Information and Communication Technologies. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing and Electrical Circuits and Electronics, ICDCECE 2022, Ballari, India, 23–24 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.A.; Kumar Dey, U.; Tonima, S.A.; Tusher, T.I. An IoT-Based Cloud Solution for Intelligent Integrated Rice-Fish Farming Using Wireless Sensor Networks and Sensing Meteorological Parameters. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 12th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference, CCWC 2022, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26–29 January 2022; pp. 568–573. [Google Scholar]
- Kozhiparamban, R.A.H.; Vettath Pathayapurayil, H. Review on Water Quality Monitoring Systems for Aquaculture. Lect. Notes Data Eng. Commun. Technol. 2020, 35, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, S.M.P.; Santos, C.L.B.; Briones, K.M.E.; Reyes, S.M.L.; Macasaet, M.A.G.; Pula, R. Automated Water Quality Monitoring and Control for Milkfish Pond. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Technology, Innovation and its Sustainability 2018, Manila, Philippines, 28–29 November 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljehani, F.; N’Doye, I.; Laleg-Kirati, T.-M. Feeding Control and Water Quality Monitoring on Bioenergetic Fish Growth Modeling: Opportunities and Challenges. Aquac. Eng. 2025, 109, 102511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Broeke, J.; Koster, T. Spectroscopic Methods for Online Water Quality Monitoring. Handb. Environ. Chem. 2019, 102, 283–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parija, S.P.; Mohanty, A.K.; Khaoash, S.; Mishra, P.; Gaen, E. Evaluation of Water Chemistry in the Coastal Aquifers of Eastern Odisha, India. Springer Proc. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, F2843, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobriyal, P.; Badola, R.; Tuboi, C.; Hussain, S.A. A Review of Methods for Monitoring Streamflow for Sustainable Water Resource Management. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2617–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rein, H.B.; Brown, C.; Quinn, R.; Breen, J. A Review of Sublittoral Monitoring Methods in Temperate Waters: A Focus on Scale. Underw. Technol. 2009, 28, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyacioglu, H.; Boyacioglu, H. Surface Water Quality Assessment by Environmetric Methods. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 131, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, F.; Siddiquei, H.R.; Alahi, M.E.E.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. An Internet of Things-Enabled System for Monitoring Multiple Water Quality Parameters. In Sensing Technologies for Real Time Monitoring of Water Quality; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 305–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Vanoye, J.A.; Fuentes-Penna, A.; Trejo-Macotela, F.R.; Campero-Jurado, I.; Ruiz-Jaimes, M.A.; Toledo-Navarro, Y.; Barrera-Cámara, R.A.; Díaz-Parra, O. Internet of Things on Sustainable Aquaculture System. In AI, Edge and IoT-Based Smart Agriculture; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divya, T.; Ramyadevi, R.; Vijaya Chamundeeswari, V. Smart Fish Monitoring System Using IoT. In Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain, Computing and Security Volume 2; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 270–273. [Google Scholar]
- Jayanthi, M.; Thirumurthy, S.; Muralidhar, M.; Ravichandran, P. Impact of Shrimp Aquaculture Development on Important Ecosystems in India. Glob. Environ. Change 2018, 52, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iber, B.T.; Kasan, N.A. Recent Advances in Shrimp Aquaculture Wastewater Management. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Bijoy, M.H.I.; Hemal, H.R.; Noori, S.R.H. Smart Aquaculture Analytics: Enhancing Shrimp Farming in Bangladesh through Real-Time IoT Monitoring and Predictive Machine Learning Analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasman, N.A.; Ahmad, I.; Rusli, J.R.; Marwangi Mohamad Maharum, S.; Thirunavakkarasu, P.; Mansor, Z. An IoT Water Quality Monitoring System for Shrimp Farming in Aquaculture. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Engineering Technology and Technopreneurship, ICE2T 2023, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 15–16 August 2023; pp. 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, M.; Idrus, S.M.; Yusof, K.M.; Azmi, A.I.; Ismail, W.; Kamaludin, K.H.; Ali, N.; Rani, A.; Yusof, F. Field Trial and Performance Evaluation of IoT Smart Aquaculture Monitoring System for Brackish Water Shrimp Farm. Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater. 2021, 14, 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Brian Ganda Pratama, F.A.; Hidayatullah, F.; Sari, E.L.I.P.; Ketut Agung Enriko, I.; Gustiyana, F.N.; Luthfi, A. Solar-Powered LoRa Wireless Water Quality Monitoring for Saline Tilapia Aquaculture. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Green Energy, Computing and Sustainable Technology, GECOST 2024, Miri Sarawak, Malaysia, 17–19 January 2024; pp. 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Medrano, K.; Hernandez, E.; Tejada, R.; Gonzalez, B.; Fuentes, N. Monitoring of Water Quality in Tilapia Farms with IoT Technology. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 41st Central America and Panama Convention (CONCAPAN XLI 2023), Tegucigalpa, Honduras, 8–10 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wibisono, A.B.; Jayadi, R. Experimental IoT System to Maintain Water Quality in Catfish Pond. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2024, 15, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joeng, P.I.; Halim, G.; Syuryansyah, W.; Perbangsa, A.S. Catfish Pond Information System Utilizing Internet of Things (IoT) Technology. In Proceedings of the 7th 2023 International Conference on New Media Studies (CONMEDIA 2023), Bali, Indonesia, 6–8 December 2023; pp. 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Muhammad, Z.; Jafri, N.M.; Hamid, S.A.; Bakar, S.J.A.; Leh, N.A.M. Monitoring Water Quality for Catfish Ponds Using PID Control with Internet of Thing. In Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Control System, Computing and Engineering, ICCSCE 2024, Penang, Malaysia, 23–24 August 2024; pp. 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sari, N.; Savitri, Y.; Wahyono, S.C.; Santoso, J.; Nasrulloh, A.V. Design of IoT-Based Monitoring System for Temperature and Dissolved Oxygen Levels in Catfish Aquaculture Pond Water. Int. J. Reconfig. Embed. Syst. 2024, 13, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, M.B. Farming Freshwater Prawns: A Manual for the Culture of the Giant River Prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2002; Volume 212. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Frinsko, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, G.; Gao, Q. Current Status of the Giant Freshwater Prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) Industry in China, with Special Reference to Live Transportation. Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, B.R.; Ponzoni, R.W.; Das Mahapatra, K.; Panda, D. Genetic Improvement of Giant Freshwater Prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii: A Review of Global Status. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 1285–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farook, M.A.; Mohamed, H.M.; Tariq, N.; Shariq, K.; Ahmed, I.A. Giant Freshwater Prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (De Man 1879): A Review. Int. J. Res. Anal. Rev. 2019, 6, 571–584. [Google Scholar]
- Prabu, E.; Rajagopalsamy, C.B.T.; Ahilan, B.; Jeevagan, I.J.M.A.; Renuhadevi, M. Tilapia—An Excellent Candidate Species for World Aquaculture: A Review. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2019, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, N.A.G.; Rapatsa, M.M. A Review of the Factors Affecting Tilapia Aquaculture Production in Southern Africa. Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelany, N.F.; Abdel-Mohsein, H.S.; Kotb, S.A.H.; Ismail, A.E.M.A. Significant Impact of Physicochemical Water Parameters in Tilapia Aquaculture. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 2024, 14, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Chandra Segaran, T.; Azra, M.N.; Piah, R.M.; Lananan, F.; Téllez-Isaías, G.; Gao, H.; Torsabo, D.; Kari, Z.A.; Noordin, N.M. Catfishes: A Global Review of the Literature. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; Torrans, E.L.; Tucker, C.S. Dissolved Oxygen and Aeration in Ictalurid Catfish Aquaculture. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2018, 49, 7–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalam, S.; Kandasamy, K.; Krishnamoorthy, I.; Narayanasamy, R. Survival and Growth of Fish (Lates calcarifer) under Integrated Mangrove-Aquaculture and Open-Aquaculture Systems. Aquac. Rep. 2018, 9, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niswar, M.; Wainalang, S.; Ilham, A.A.; Zainuddin, Z.; Fujaya, Y.; Muslimin, Z.; Paundu, A.W.; Kashihara, S.; Fall, D. IoT-Based Water Quality Monitoring System for Soft-Shell Crab Farming. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things and Intelligence System (IOTAIS 2018), Bali, Indonesia, 1–3 November 2018; pp. 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Babitha Rani, A.M.; Verma, A.K.; Maqsood, M. Biofloc Technology: An Emerging Avenue in Aquatic Animal Healthcare and Nutrition. Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaz, M.; Kubilay, A. Operating Parameters Affecting Biofloc Technology: Carbon Source, Carbon/Nitrogen Ratio, Feeding Regime, Stocking Density, Salinity, Aeration, and Microbial Community Manipulation. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 1121–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, M.H.; Mohammadi, A.; Emerenciano, M.G.C. Water Quality in Biofloc Technology (BFT): An Applied Review for an Evolving Aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 9321–9374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozumder, S.A.; Sharifuzzaman Sagar, A.S.M. Smart IoT Biofloc Water Management System Using Decision Regression Tree. Lect. Notes Netw. Syst. 2022, 437, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podder, S.; Sultan Anoy, M.F.; Salim Rafid, S.T.; Ajwad, A.J. Smart Biofloc System: Leveraging IoT for Enhanced Aquaculture Sustainability. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical, Control and Instrumentation Engineering, ICECIE, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 22–24 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhit, A.A.; Jamlos, M.F.; Nordin, M.A.H.; Jamlos, M.A.; Mamat, R.; Nawi, M.A.M.; Nugroho, A. Design of a Low-Cost IoT-Based Biofloc Water Quality Monitoring System. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Mech. 2024, 114, 153–162. Available online: https://semarakilmu.com.my/journals/index.php/appl_mech/article/view/5466 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Abid, M.A.; Amjad, M.; Munir, K.; Siddique, H.U.R.; Jurcut, A.D. IoT-Based Smart Biofloc Monitoring System for Fish Farming Using Machine Learning. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 86333–86345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhit, A.A.; Jamlos, M.F.; Alhaj, N.A.; Mamat, R. Biofloc Farming with IoT and Machine Learning Predictive Water Quality System. In Proceedings of the 2022 RFM IEEE International RF and Microwave Conference, RFM 2022, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 19–21 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, N.; Sufian, S.A.; Khandakar, M.S.; Shihab, K.Z.H.; Zishan, M.S.R. Design and Development of Smart System for Biofloc Fish Farming in Bangladesh. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES 2022), Coimbatore, India, 22–24 June 2022; pp. 1424–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, N.; Kawamata, M. Aquarium Recirculation System. In Application of Recirculating Aquaculture Systems in Japan; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinal, C.A.; Matulić, D. Recirculating Aquaculture Technologies. Aquaponics Food Prod. Syst. Comb. Aquac. Hydroponic Prod. Technol. Future 2019, 1, 35–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Kamalam, B.S.; Sarma, D. Recirculating Aquaculture System for Intensive Fish Farming in Indian Himalayan Region: An Overview. Fish. Aquac. Temp. Himalayas 2023, 173–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropicki, A.; Garlock, T.; Farzad, R.; Hazell, J.E. Recirculating Aquaculture System-Based Production as a Pathway to Increase Aquaculture in Developed Countries: The Case of United States Aquaculture. Aquac. Econ. Manag. 2024, 28, 515–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anani, O.A.; Olugbemi, O.T.; Adetunji, C.O.; Hefft, D.I.; Wilson, N.; Olayinka, A.S. IoT-Based Monitoring System for Freshwater Fish Farming: Analysis and Design. In AI, Edge and IoT-Based Smart Agriculture; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; ISBN 9780128236949. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Angani, A.; Thalluri, T.; Shin, K.J. Realization of Water Process Control for Smart Fish Farm. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Electronics, Information, and Communication (ICEIC 2020), Barcelona, Spain, 19–22 January 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandramenon, P.; Aggoun, A.; Tchuenbou-Magaia, F. Smart Approaches to Aquaponics 4.0 with Focus on Water Quality—Comprehensive Review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 225, 109256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, J.; Priyadarsini, M.; Rani, J.; Pandey, K.P.; Dhoble, A.S. Aquaponic Trends, Configurations, Operational Parameters, and Microbial Dynamics: A Concise Review. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 27, 213–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, L.A.; Shaghaleh, H.; El-Kassar, G.M.; Abu-Hashim, M.; Elsadek, E.A.; Alhaj Hamoud, Y. Aquaponics: A Sustainable Path to Food Sovereignty and Enhanced Water Use Efficiency. Water 2023, 15, 4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okomoda, V.T.; Oladimeji, S.A.; Solomon, S.G.; Olufeagba, S.O.; Ogah, S.I.; Ikhwanuddin, M. Aquaponics Production System: A Review of Historical Perspective, Opportunities, and Challenges of Its Adoption. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahayu, L.P.; Kindhi, B.A.; Pradika, C.D.; Adhim, F.I.; Priananda, C.W.; Musthofa, A.; Indasyah, E.; Istiqomah, F. Design of PH Control System and Water Recirculation in Aquaponic Cultivation Using Mamdani Fuzzy Logic Control. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Advanced Mechatronics, Intelligent Manufacture and Industrial Automation, ICAMIMIA 2021, Surabaya, Indonesia, 8–9 December 2021; pp. 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Pramono, T.B.; Qothrunnada, N.I.; Asadi, F.; Cenggoro, T.W.; Pardamean, B. Water Quality Monitoring System for Aquaponic Technology Using the Internet of Things (IoT). Commun. Math. Biol. Neurosci. 2023, 2023, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansor, M.N.; Hasan, M.Z.; Abdul Kader, M.M.M.; Mustafa, W.A.; Saidi, S.A.; Jamlos, M.A.; Talib, N.A.A. Aquaponic Ecosystem Monitoring with IOT Application. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2023, 31, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, C.L.; Kusuma, I.M.B.P.; Koh, Y.Y.; Tang, H.; Lim, A.B. Smart Aquaponics: An Automated Water Quality Management System for Sustainable Urban Agriculture. Electronics 2024, 13, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asma, T.H.; Mohamed, H.; Kaouther, L.O. IOT Design and Water Monitoring of an Aquaponic System. In Proceedings of the SCC 2023—IEEE 3rd International Conference on Signal, Control and Communication, Hammamet, Tunisia, 1–3 December 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandana, M.S.; Sridevi, C.; Chowdary, R.A.; Likhitha, D. Automated Aquaponics Farming Using Internet of Things (IoT). In Proceedings of the 2023 2nd International Conference on Electronics and Renewable Systems, ICEARS, Tuticorin, India, 2–4 March 2023; pp. 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobrini, A.; Belhakimi, A.; Remram, Y. Design and Implementation of a Cost-Effective IoT-Enabled Multi-Parameter System for Water Quality Monitoring in Aquaculture and Aquaponics. In Proceedings of the 2023 2nd International Conference on Electronics, Energy and Measurement, IC2EM, Medea, Algeria, 28–29 November 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, R.; Martinez, P.; Ahmad, R. Data Acquisition and Monitoring Dashboard for IoT Enabled Aquaponics Facility. In Proceedings of the 2022 10th International Conference on Control, Mechatronics and Automation, ICCMA, Belval, Luxembourg, 9–12 November 2022; pp. 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Dai, H.-N.; Wang, Q.; Shukla, M.K. On UAV-Assisted Data Acquisition for Underwater IoT in Aquaculture Surveillance. In Proceedings of the Developments in Maritime Technology and Engineering—5th International Conference on Maritime Technology and Engineering (MARTECH 2020), Glasgow, Scotland, UK, 16–19 November 2020; Volume 2, pp. 729–735. [Google Scholar]
- Setiawan, F.; Basuki, T.M.; Santosa, B.H.; Pramono, I.B.; Chulafak, G.A.; Rahmadya, A.; Nada, F.M.H. Developing Algorithms for Estimating Total Suspended Solids (TSS) Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle: A Case Study in the Upper Citarum River, Indonesia. J. Degrad. Min. Lands Manag. 2025, 12, 7379–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwenya, N.; Bangira, T.; Sibanda, M.; Kebede Gurmessa, S.; Mabhaudhi, T. UAV-Based Remote Sensing of Chlorophyll-a Concentrations in Inland Water Bodies: A Systematic Review. Geocarto Int. 2025, 40, 2452246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Cortez, O.O. A Low-Cost IoT System for Water Quality Monitoring in Developing Countries. In Proceedings of the IEEE Consumer Communications and Networking Conference, CCNC, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 6–9 January 2024; pp. 596–597. [Google Scholar]
- Kalim Amzad Chy, M.; Masum, A.K.M.; Hossain, M.E.; Golam Rabiul Alam, M.; Khan, S.I.; Alam, M.S. A Low-Cost Ideal Fish Farm Using IoT in the Context of Bangladesh Aquaculture System; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 89. [Google Scholar]
- Boppana, L.; Madhu, K.; Rama Vaibhav, C.P. Aquaculture Water Monitoring System Using LoRaWAN. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Humanitarian Technology Conference, R10-HTC, Rajkot, India, 16–18 October 2023; pp. 1095–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Rawi, R.; Salleh, S.; Husin, H.S. Shrimp Farming Water Parameter Monitoring System Using LoRa. In Proceedings of the IVIT 2022—1st International Visualization, Informatics and Technology Conference, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1–2 November 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Anupama, K.; Rao, Y.C.; Gurrala, V.K. A Machine Learning Approach to Monitor Water Quality in Aquaculture. Int. J. Perform. Eng. 2020, 16, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar]
- Bakhit, A.A.; Sabli, N.S.M.; Jamlos, M.F.; Jamlos, M.A.; Ramli, N.H.; Nordin, M.A.H.; Alhaj, N.A.; Ali, E. IoT-Based Machine Learning Comparative Models of Stream Water Parameters Forecasting for Freshwater Lobster. J. Adv. Res. Appl. Mech. 2024, 117, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Du, Z.; Bai, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Li, D. A Novel Nonplanar Multi-Chamber Flexible Array Dissolved Oxygen Sensor for Aquaculture Robotic Fish. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 230, 109903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubina, N.A.; Lan, H.Y.; Cheng, S.C.; Chang, C.C.; Lin, S.S.; Zhang, K.X.; Lu, H.Y.; Cheng, C.Y.; Hsieh, Y.Z. Digital Twin-Based Intelligent Fish Farming with Artificial Intelligence Internet of Things (AIoT). Smart Agric. Technol. 2023, 5, 100285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaziz, O.A.; Abdallah, R.M.; Khater, R.A.; Abo Dena, A.S.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Optical Ammonia-Sensing Probe Based on Surface-Plasmon Resonance of Silver-Nanoparticle-Decorated Superparamagnetic Dendritic Nanoparticles. Plasmonics 2023, 18, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Han, H.; Zhang, S.; Fang, H.; Fan, W.; Zhao, F.; Xu, C. Reviews on the Development of Digital Intelligent Fisheries Technology in Aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2025, 33, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



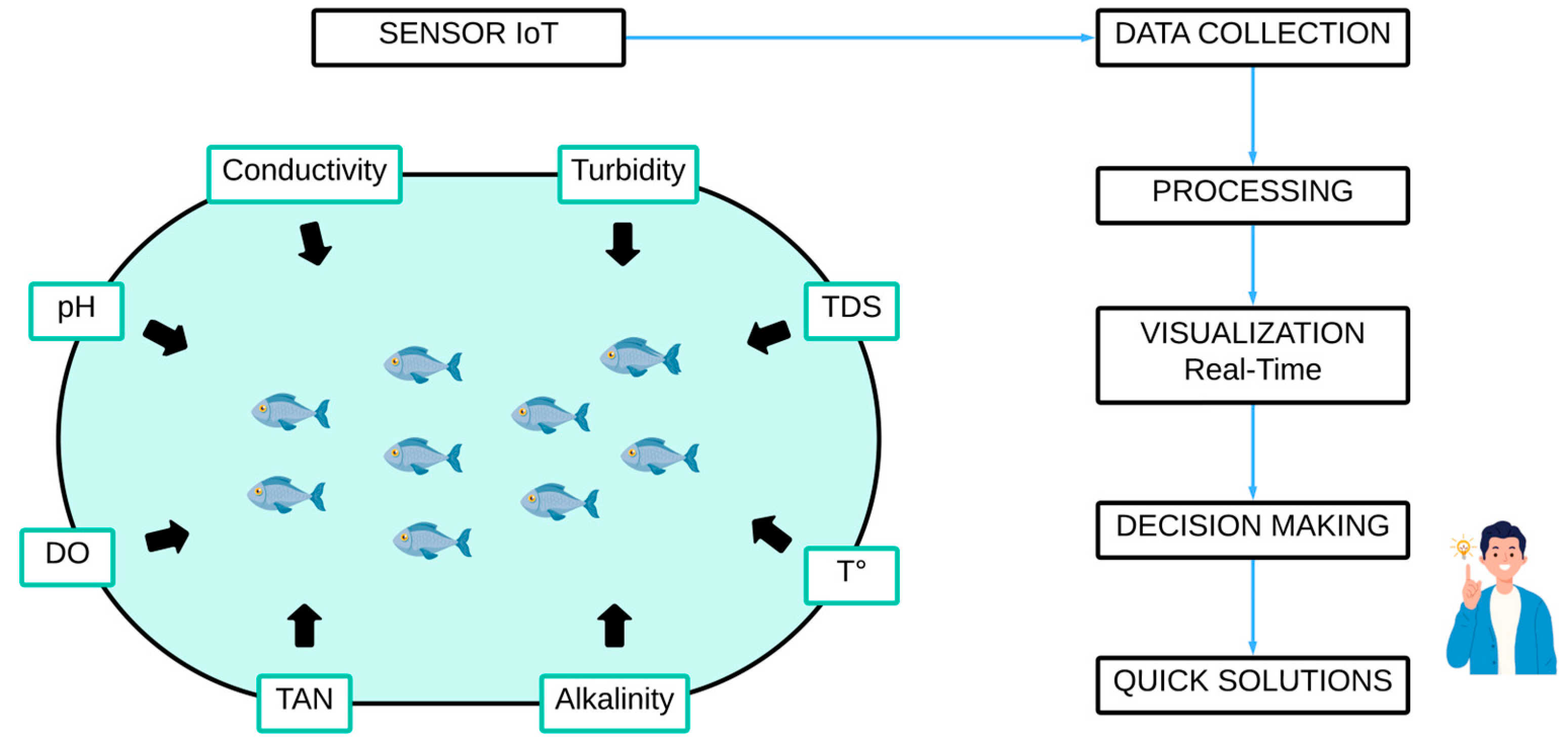
| Reference | Aquatic Organism | Sensor | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ahmed et al. [103] | Shrimp | pH, T°, TDS, EC, Salinity | - Early warning of atypical water quality ranges. |
| Espena et al. [47] | pH, Salinity, T°, DO | - Monitoring of water quality parameters in the culture. | |
| Hasman et al. [104] | T° (DS18B20), pH, Turbidity, DO | - Increased productivity in aquaculture. | |
| Abdullah et al. [105] | pH, DO, T° | - Reduction in operational costs. | |
| E.B Blancaflor & Baccay [41] | DO, T°, pH | - Managing culture growth and mortality through water quality. | |
| Brian Ganda Pratama et al. [106] | Tilapia | T°, pH, DO, EC | - Long-distance and real-time monitoring. |
| Libao et al. [48] | pH, Salinity, DO, T° | - Automated monitoring and comparison with human error. | |
| Shete et al. [8] | pH, DO, T° | - Real-time monitoring. | |
| Lopez et al. [57] | T° (DS18B20), pH, Turbidity | - Develop a prototype to dispense agricultural lime and aluminum sulfate and activate heaters and aerators based on temperature and pH values that are atypical. | |
| Medrano et al. [107] | pH, DO, T° (DS18B20) | - Real-time monitoring. | |
| Wibisono & Jayadi et al. [108] | Catfish | pH (SEN0169), T° (DS18B20), Water level (Ultrasonic) | - Disease prevention. |
| Joeng et al. [109] | T°, pH | - Automated monitoring. | |
| Muhammad et al. [110] | pH | - Real-time pH monitoring. | |
| Sari et al. [111] | DO (SEN0237), T° (DS18B20) | - Real-time monitoring of oxygen and temperature. | |
| Mohd Jais et al. [20] | Asian seabass | T° (DS18B20), pH (SKU SEN0161), Ammonia (MQ137), DO, Salinity (DFR0300) | - Development of a real-time water quality monitoring system. |
| Suhaili et al. [54] | Giant Freshwater Prawn | T°, Salinity, TDS, pH, DO | - Activation of emergency lights, heaters, and troughs |
| Reference | Parameter | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Abid et al. [129] | T°, pH, CO (MQ-7), TDS, Turbidity, Humidity (DHT11) | - Real-time monitoring and mortality prediction. |
| Al Mamun et al. [52] | T° (DS18B20), DO (DFRobot), Water level, TDS, Turbidity, pH (BNC) | - Real-time monitoring. |
| Bakhit et al. [128] | pH, DO, TDS, EC | - Real-time monitoring for temperature prediction by using ML. |
| Podder et al. [127] | T° (DS18B20), DO (Lutron DO-5509), pH (HANNA HI-98107), Water level, Turbidity, TDS (HM TDS-EZ) | - The heater and acid-basic solution dispenser are activated. |
| Bakhit et al. [130] | DO, pH, TDS, T°, Water level | - Real-time predictive analysis of water quality data. |
| E. B. Blancaflor & Baccay [41] | DO, T°, pH | - Mortality and growth management based on water quality monitoring. |
| Goswami et al. [131] | pH, T° (DS18B20), TDS, EC | - Real-time monitoring. |
| Mozumder & Sharifuzzaman Sagar [126] | pH, T° (DS18B20), Ammonia (MQ-135), TDS, EC | - Activation of heater and water pump. |
| Tasnim et al. [74] | pH, Turbidity, TDS, T° (DS18B20) | - Automated water level control. |
| Rashid et al. [7] | pH, T°, TDS | - Increase productivity based on water quality monitoring. |
| Reference | Sensor | Aquatic Organism | Filter | Findings | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical | Biofilter | ||||
| Libao et al. [48] | pH, Salinity, DO, T° | Tilapia | Mechanical filter | Bacterial | - Automated monitoring and comparison with human error. |
| Suriasni et al. [79] | DO (SEN0237), pH (SEN0161), TDS (SEN0244), T° (DS18B20), Water flow (YF-201) | Fish tanks | N/R | Nitrosobacter and Nitrosomonas | - Activation of aerators to oxygenate water for TAN removal. |
| Suhaili et al. [54] | T°, Salinity, TDS, pH, DO | Asian seabass and Giant Freshwater Prawn | Sponges and Aquarium wools | Bio-balls/K-1 and filters/ceramic | - Activation of emergency lights, heaters, and fish feeders. |
| Lee et al. [137] | T°, pH, DO, Water level | N/R | N/R | N/R | - Aquaculture water processing control. |
| Reference | Parameter | Plants | Aquatic Organism | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kok et al. [145] | pH (SEN0161), T°, Water level, Turbidity, TDS (SEN0244) | Vegetables | Catfish | - Automated control. |
| Asma et al. [146] | pH, T°, Humidity (DHTH) | N/R | N/R | - Real-time monitoring. |
| Chandana et al. [147] | pH, Humidity (DHT11), Water level | N/R | N/R | - Feed system control. |
| Ghobrini et al. [148] | pH, T°, TDS, Turbidity | N/R | Tilapia | - Real-time monitoring and automatic sensor calibration. |
| Mansor et al. [144] | pH, T° and humidity (DHT22) | Mustard | Aquarium fish | - Real-time monitoring. |
| Pramono et al. [143] | pH (pH-4502C), T° (DS18B20), DO (Gravity Analog), Ammonia (MQ-135) | Spinach | Tilapia | - Real-time monitoring and evaluation of spinach growth. |
| Abbasi et al. [149] | pH (pH-4502C), T° (DS18B20), DO (Gravity Analog), Humidity (DHT22) | Romaine lettuce | Aquarium fish | - Prediction of romaine lettuce growth by monitoring water quality. |
| Khaoula et al. [81] | pH (Grove-pH), Water level. T° (DS18B20), EC (Grove-EC), TDS (Grove-TDS), Humidity (SCD30) CO2, Taux Ammonia Nitrogen (TAN) | Vegetables | Aquarium fish | - Algorithm-based plant growth assessment (AI) and water quality monitoring. |
| Rahayu et al. [142] | pH (pH4502C), Turbidity | N/R | N/R | - Automatic water flow increase. - Dispensing of acid-basic solutions for automatic pH control. |
| Haruo et al. [69] | T°, pH, DO | N/R | N/R | - Plant growth monitoring through correlation of water quality data. |
| Rozie et al. [42] | T° (DS18S20), Turbidity, pH (pH-4502C), DO, TDS, Ammonia (MQ-135), Water level (HC-SR04) | Cabbage | Tilapia | - Ammonium level control. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Flores-Iwasaki, M.; Guadalupe, G.A.; Pachas-Caycho, M.; Chapa-Gonza, S.; Mori-Zabarburú, R.C.; Guerrero-Abad, J.C. Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors for Water Quality Monitoring in Aquaculture Systems: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7030078
Flores-Iwasaki M, Guadalupe GA, Pachas-Caycho M, Chapa-Gonza S, Mori-Zabarburú RC, Guerrero-Abad JC. Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors for Water Quality Monitoring in Aquaculture Systems: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(3):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7030078
Chicago/Turabian StyleFlores-Iwasaki, Manhiro, Grobert A. Guadalupe, Miguel Pachas-Caycho, Sandy Chapa-Gonza, Roberto Carlos Mori-Zabarburú, and Juan Carlos Guerrero-Abad. 2025. "Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors for Water Quality Monitoring in Aquaculture Systems: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis" AgriEngineering 7, no. 3: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7030078
APA StyleFlores-Iwasaki, M., Guadalupe, G. A., Pachas-Caycho, M., Chapa-Gonza, S., Mori-Zabarburú, R. C., & Guerrero-Abad, J. C. (2025). Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors for Water Quality Monitoring in Aquaculture Systems: A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis. AgriEngineering, 7(3), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7030078







