The Design and Testing of a Special Drinker for Meat Ducks Based on Reverse Engineering
Abstract
:1. Introduction
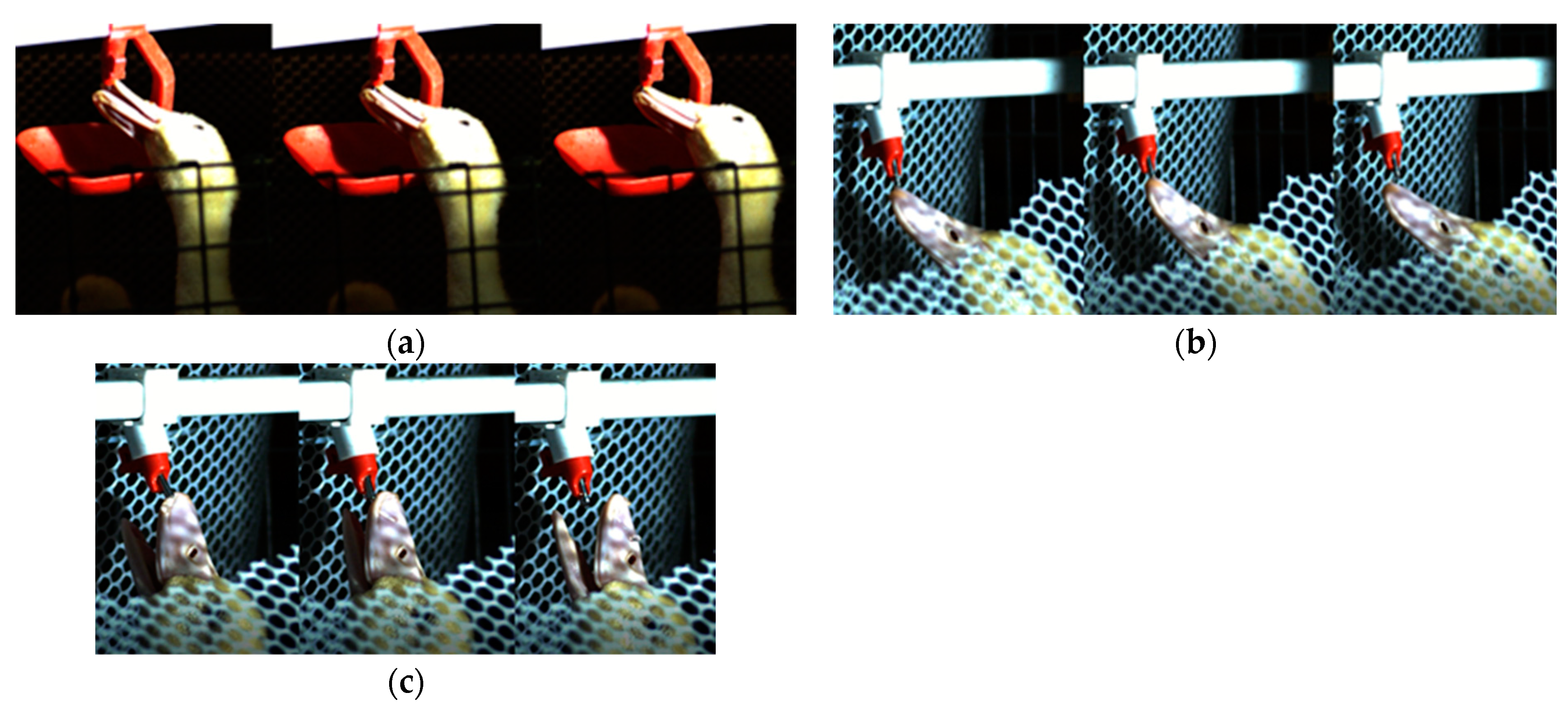
2. Observation and Analysis of the Drinking Habits of Meat Ducks
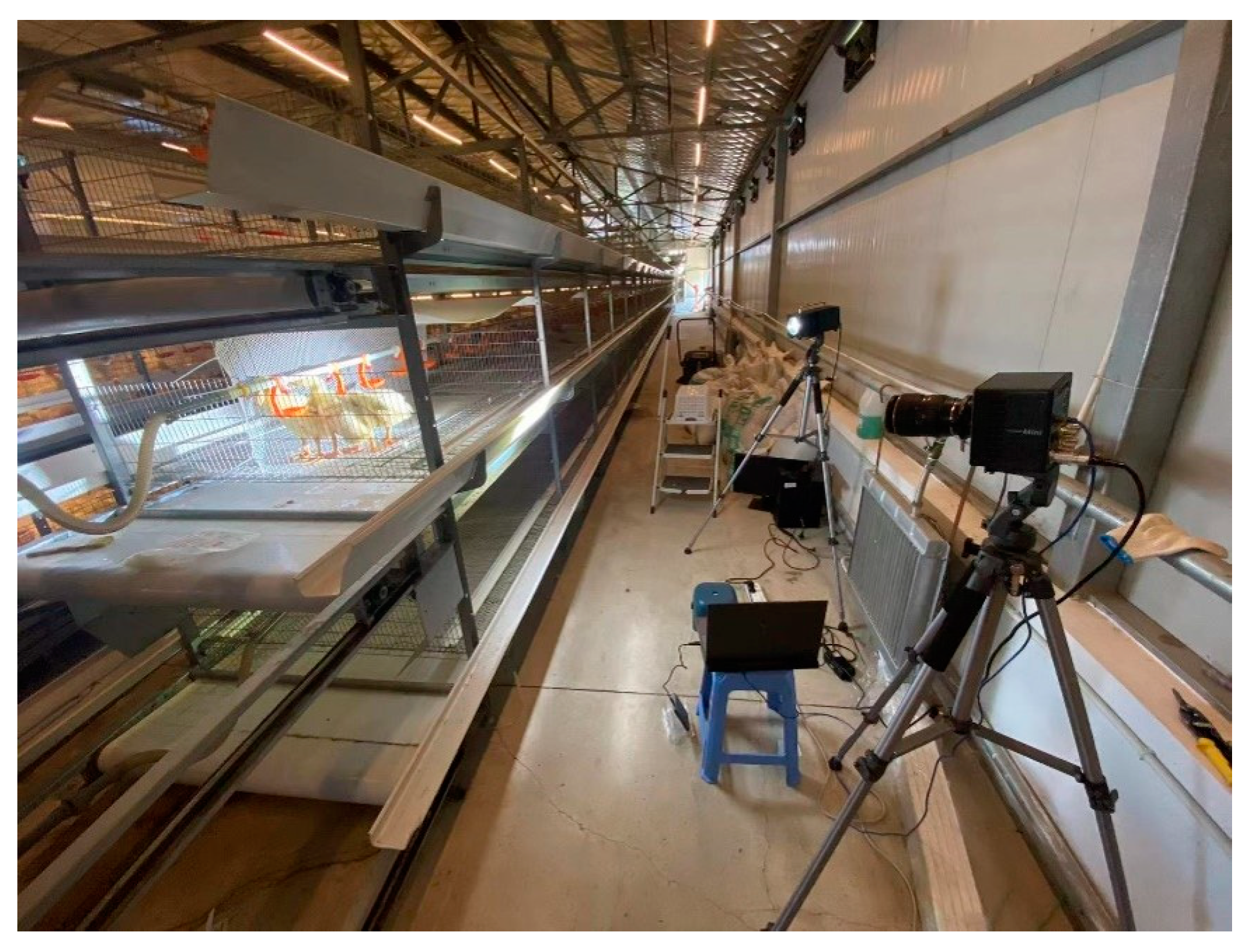
2.1. Materials and Methods
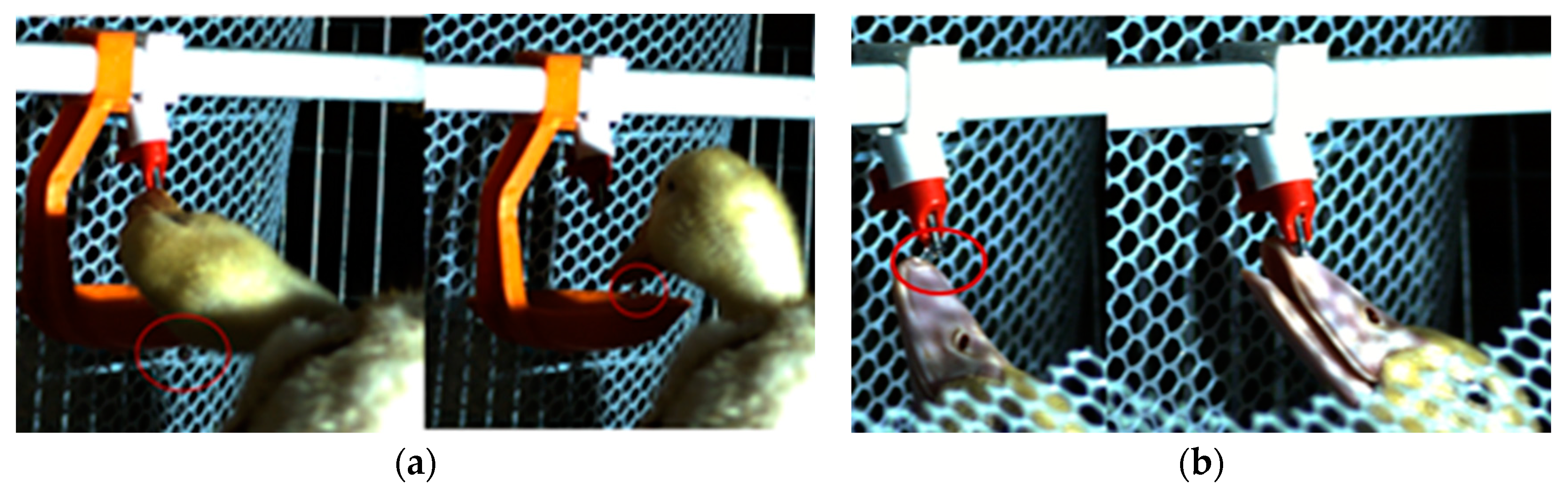
2.2. Analysis of High-Speed Video Results
3. Design Scheme of a Special Water Drinker for Meat Ducks
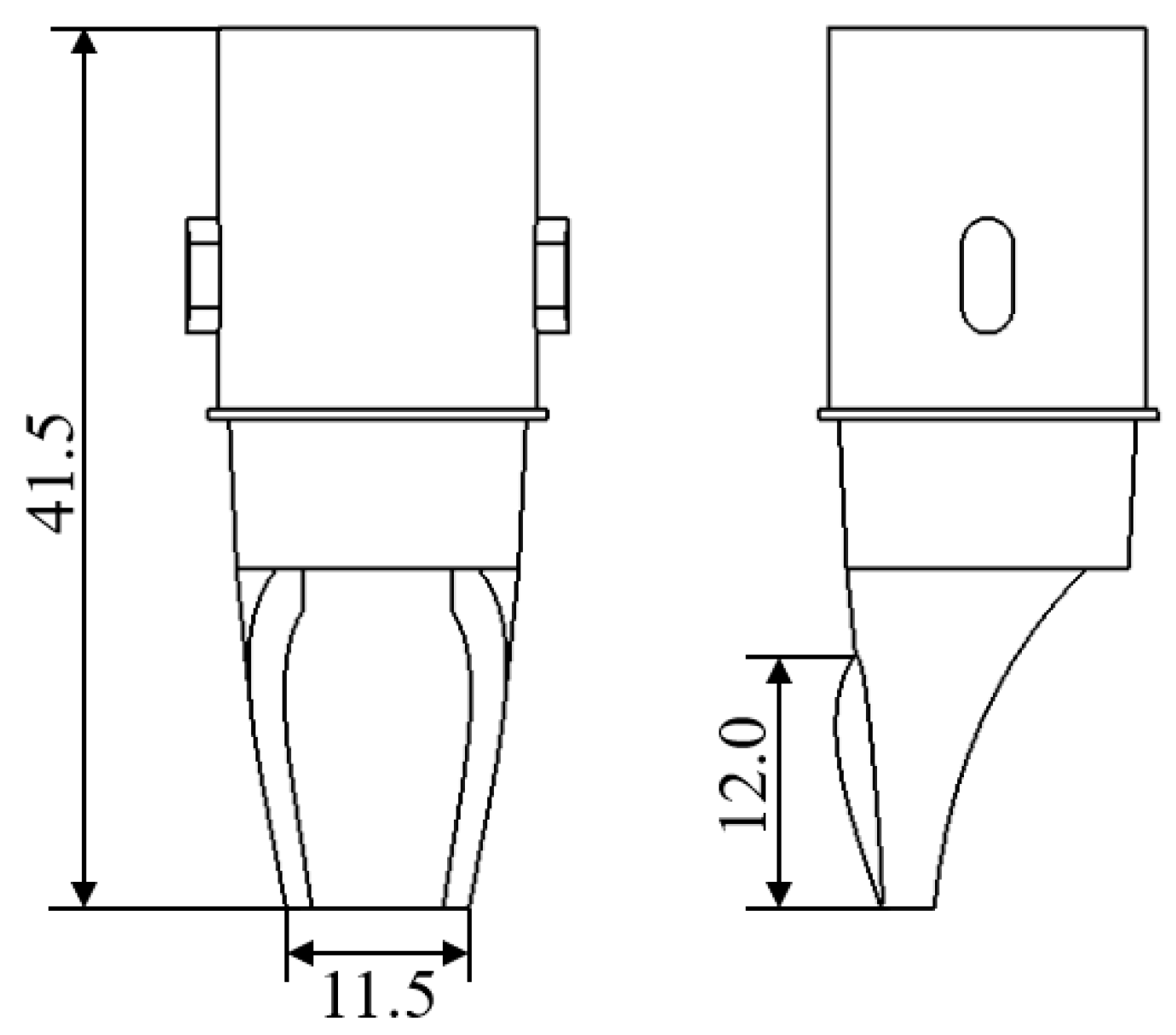
3.1. Design and Modeling of the Water Outlet Structure of the Drinker
3.2. Design and Modeling of the Drinker Shell
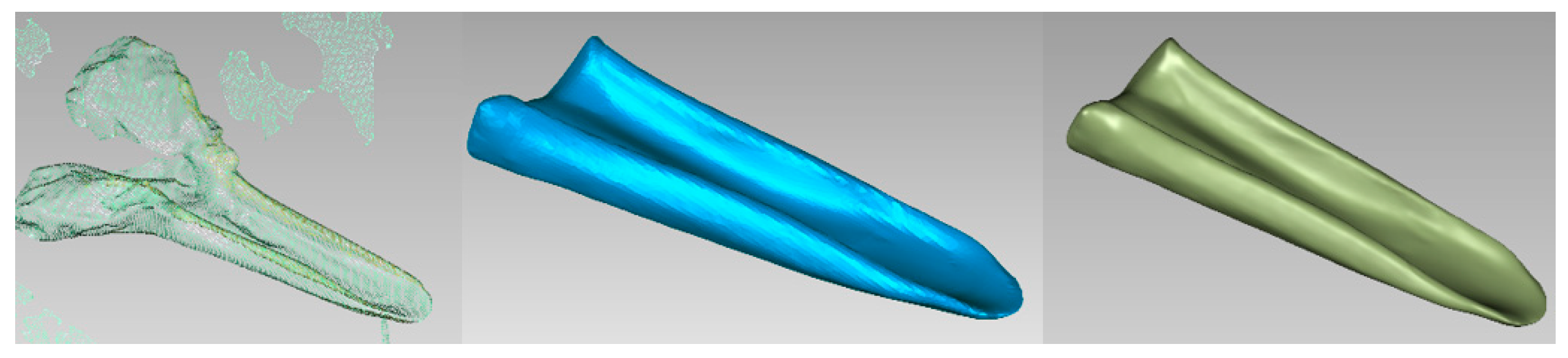
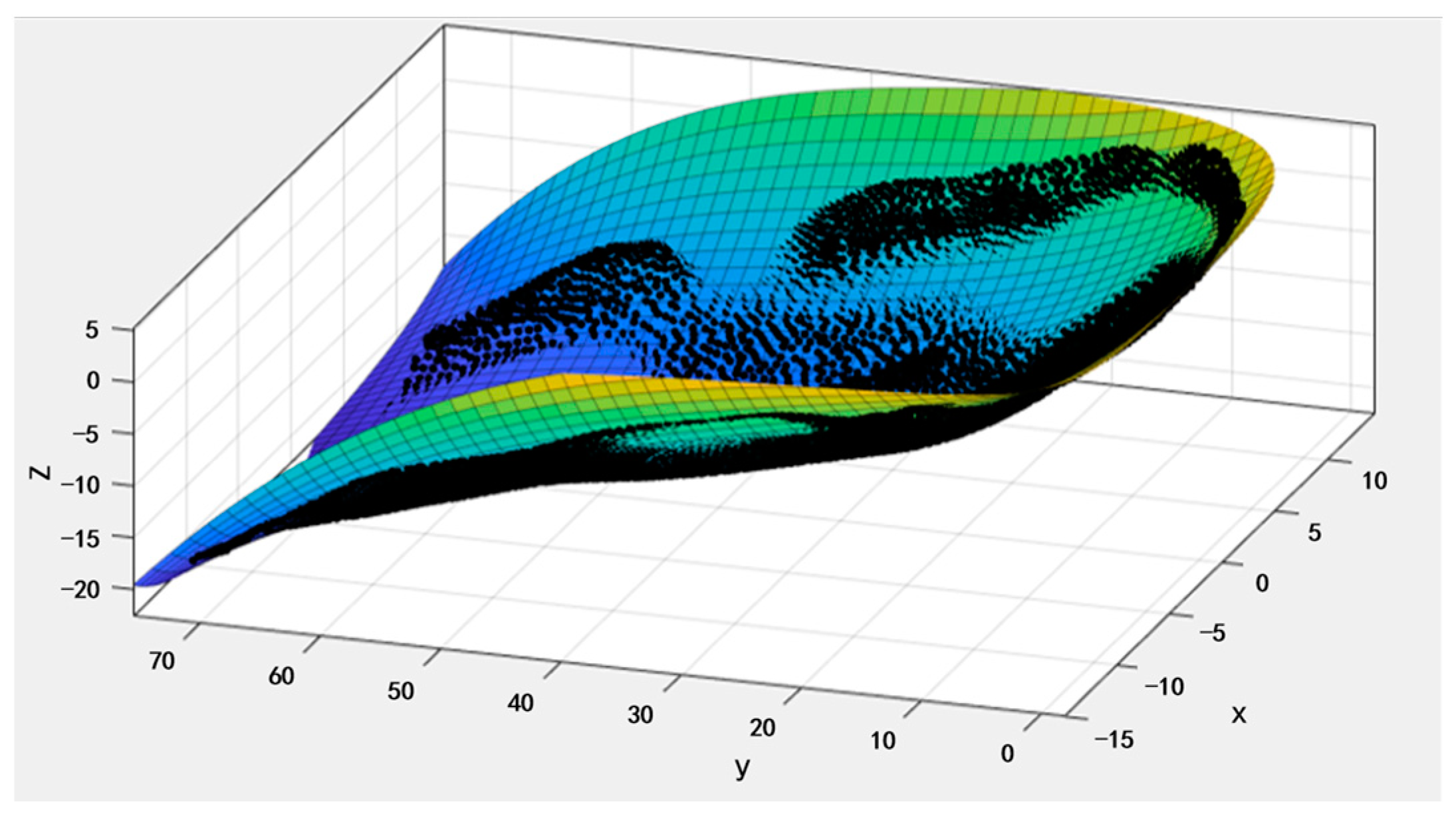
3.2.1. Acquisition of the Point Cloud Data for the Meat Duck Beak
3.2.2. Modeling of the Drinker Shell
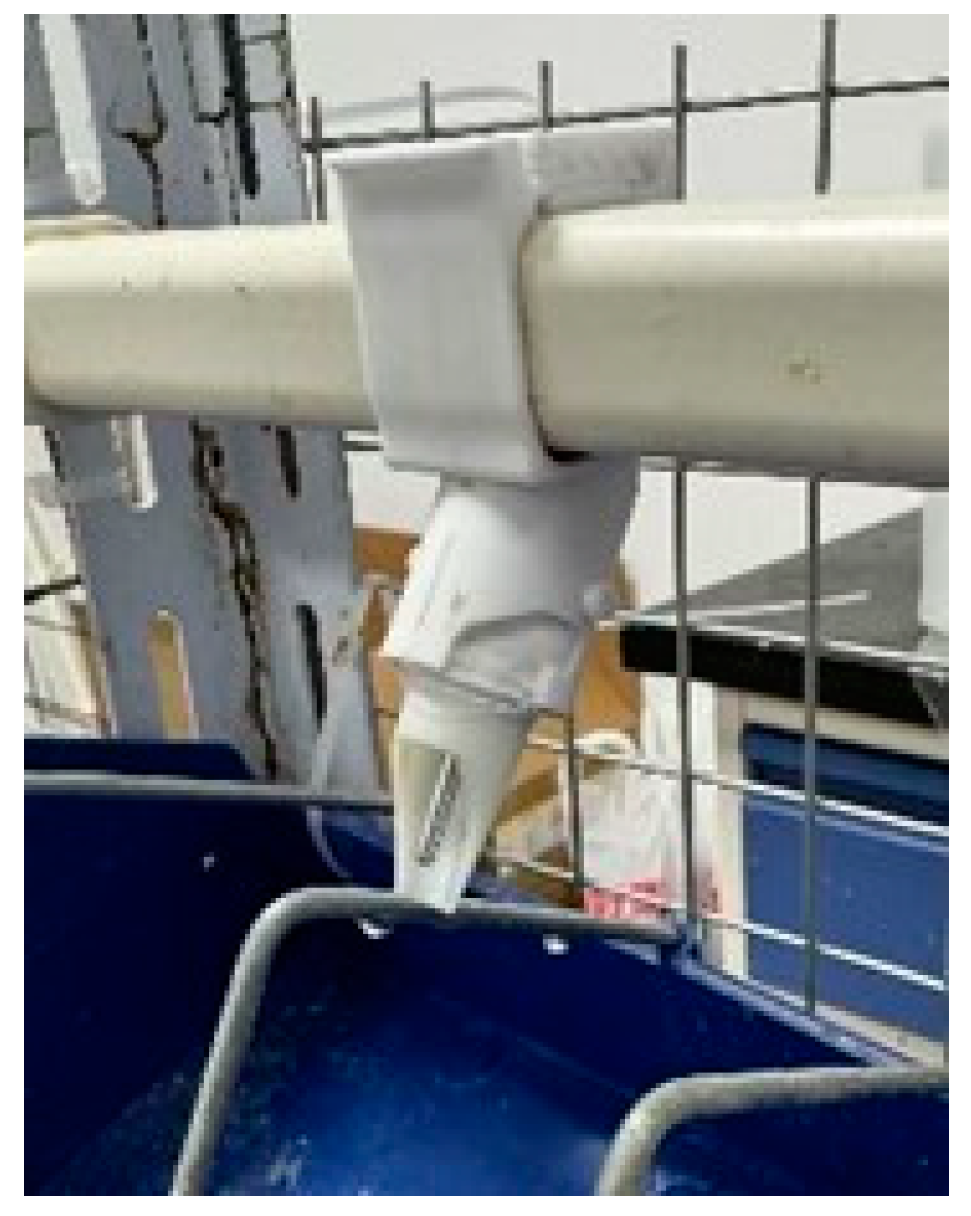
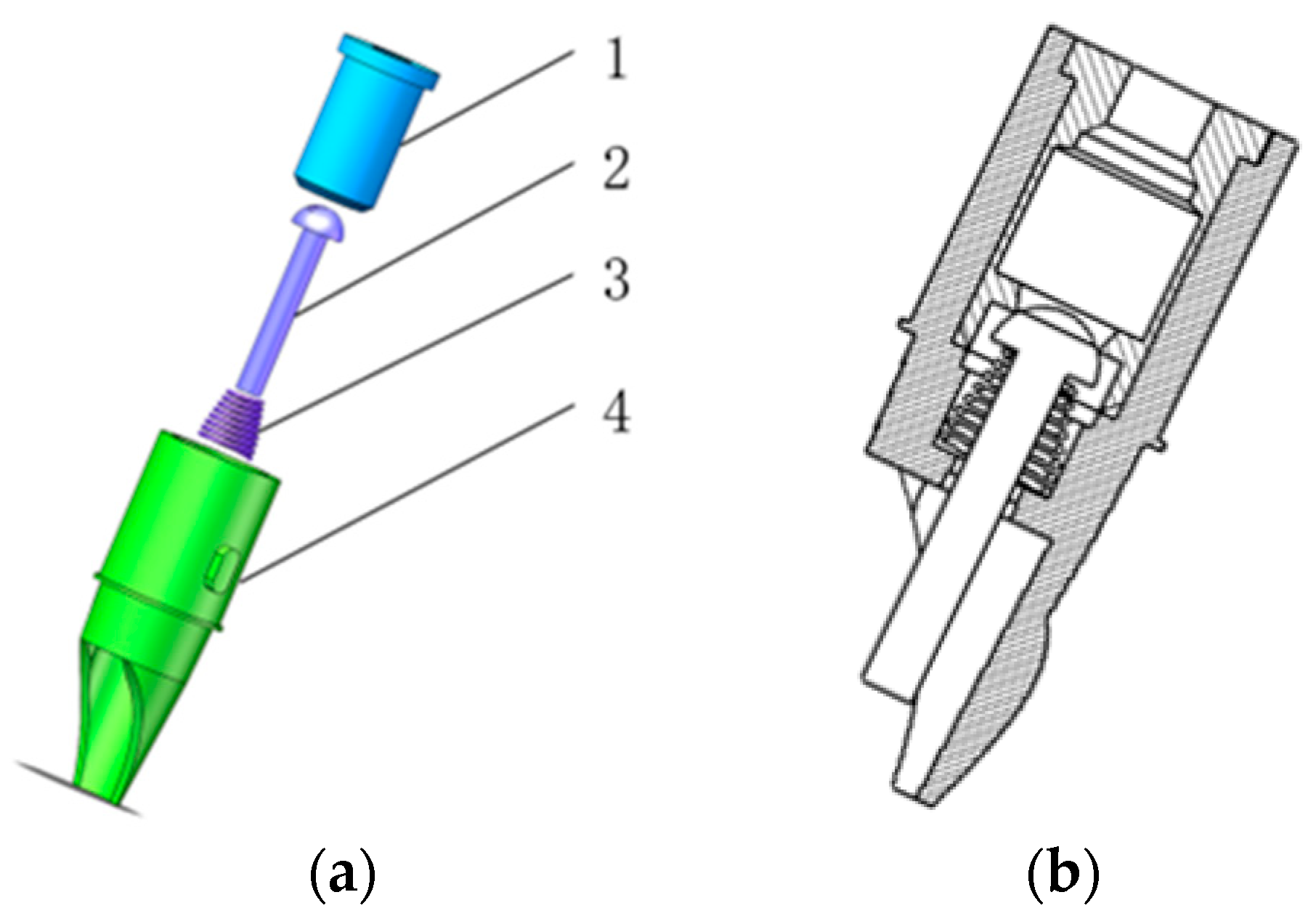
3.3. Overall Structure and Working Principle of the Drinker
3.4. Manufacturing of Prototype for Meat Duck-Specific Drinker
4. Performance Testing of Water Drinker
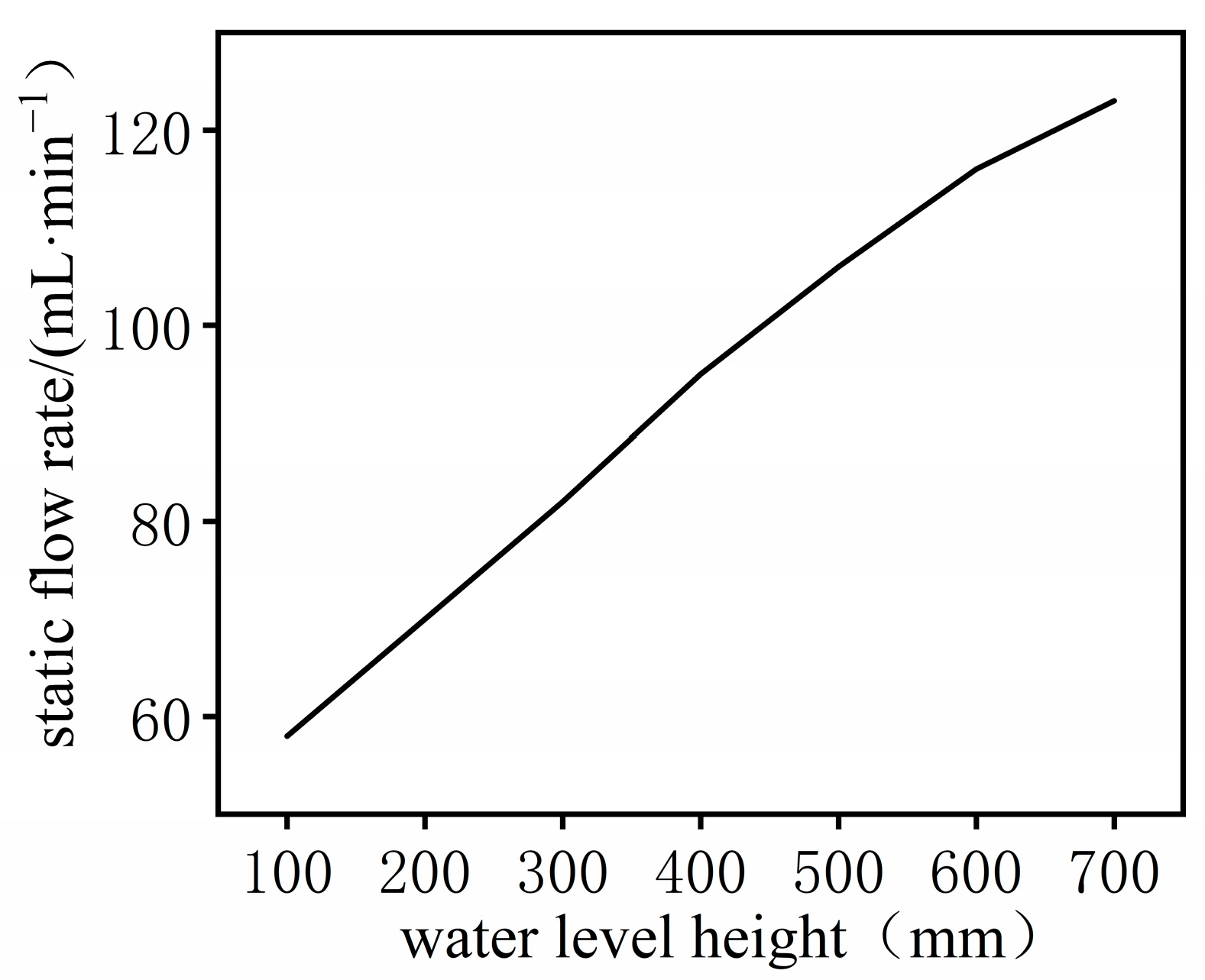
4.1. Laboratory Test
4.2. Breeding Test
Result and Analysis
5. Conclusions
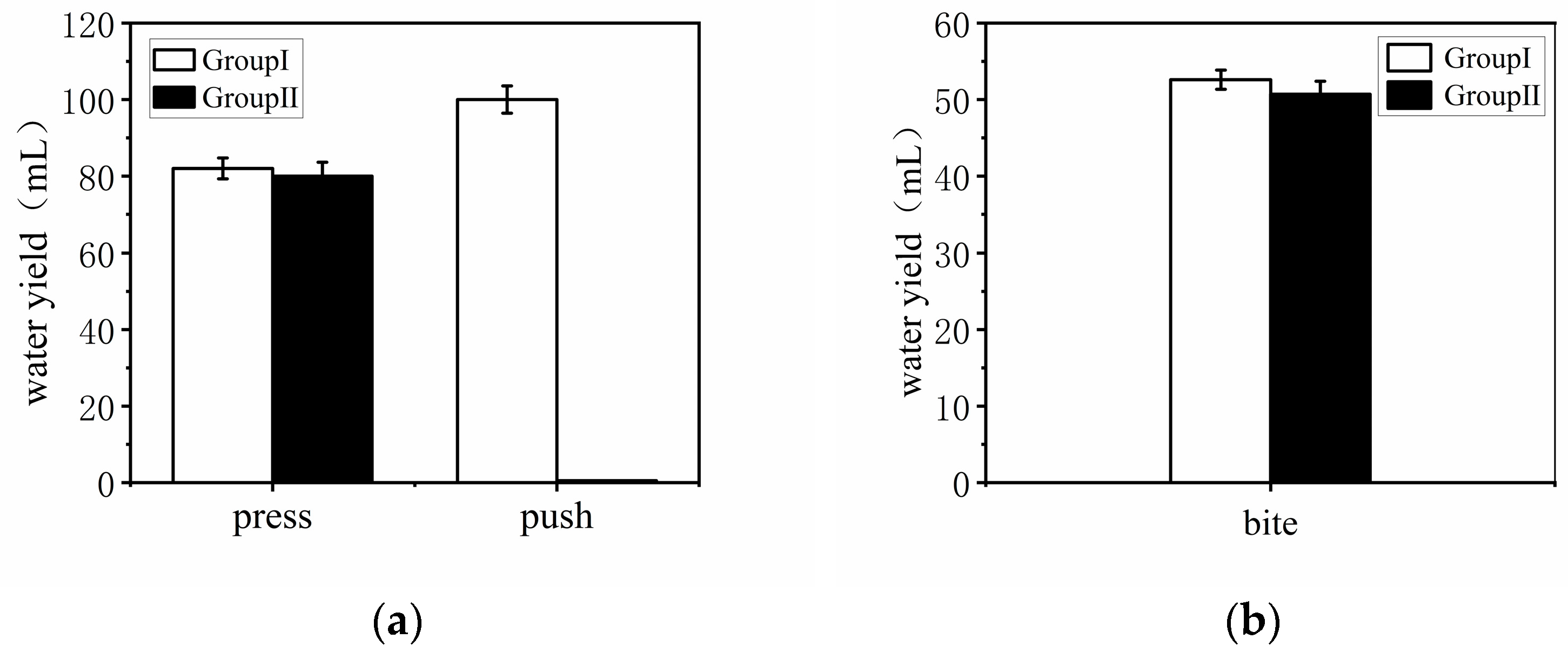
- The drinking behavior of meat ducks was recorded, and it was found that the biting action is the most efficient drinking action when kept in cages. Therefore, biting was selected as the method for water release in the new type of meat duck drinkers, achieving optimal effective drinking without the need for training the ducks.
- Using reverse engineering, an original model of the head of meat ducks was created, and its features were repaired and reconstructed. The characteristic surface equation for the lower jaw of meat ducks was obtained, which could be applied to the subsequent engineering designs.
- The improved and optimized meat duck drinking device showed a 15.3% reduction in water loss compared to the nipple drinker and features a simple structure. It can meet the drinking needs of meat ducks during the farming process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, S.; Zhou, Z. The past, present, and future of the meat duck breeding industry. China Anim. Husb. 2021, 18, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Dai, W.; Xia, L. Effects of Different Environmental Control Methods on the Environment in Layered Cages for Meat Ducks in Summer. China Poult. 2024, 46, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Ying, S.; Dai, Z. Comparative analysis of production performance and economic benefits of a new breeding model for meat ducks. China Poult. 2020, 42, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, Z. Design and construction of three-dimensional intelligent cage systems for duck farms. China Poult. 2018, 40, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, G. Comparative analysis of production performance and economic benefits between cage and three-dimensional net systems for meat ducks. China Poult. 2019, 41, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Rodenburg, T.B.; Bracke, M.B.M.; Berk, J.; Cooper, J.; Faure, J.; Guémené, D.; Guy, G.; Harlander, A.; Jones, T.; Knierim, U.; et al. Welfare of ducks in European duck husbandry systems. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2005, 61, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Ying, S.J.; Dai, Z.C. Comparative analysis of production performance and economic benefits of a novel meat duck farming model. China Poult. 2020, 42, 80–85. [Google Scholar]
- Tjoa, G.W.; Aribowo, A.; Putra, A.S. Design of Automatic Drinking Water Supply System for Poultry Cage. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference on New Media Studies (CONMEDIA), Bali, Indonesia, 9–11 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, G.H.; Peterson, R.A.; Jones, W.T.; Daly, K.; Hypes, W. Effects of two nipple drinker types with different flow rates on the productive performance of broiler chickens during summerlike growing conditions. Poult. Sci. 1992, 71, 1450–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branton, S.L.; Simmons, J.D.; Lott, B.D.; Miles, D.M.; Maslin, W.R. Chick mortality associated with elevated water lines and consumption of wet litter. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2001, 10, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quichimbo, C.; Quintana, J.; Rodríguez-Saldaña, D.; López-Coello, C.; Gómez, S.; Castellanos, F.; de CV, M.L. Effect of Nipple Type Drinker Height on Productive Parameters of Broilers. Int. J. Poult. Sci. 2013, 12, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, Y. Challenges faced by the meat duck industry in China. Contemp. Anim. Husb. 2021, 8, 71–73. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Mai, Y.; Zhao, W. Current status and prospects of duck farming systems and environmental control in China. China Poult. 2012, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pueo, B. High Speed Cameras for Motion Analysis in Sports Science. J. Hum. Sport Exerc. 2016, 11, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qi, L.; Yang, X. Current issues and countermeasures in meat duck farming. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2006, S2, 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, J.; Su, T.; Chen, G. Comparison of bite force between two closely related bird species, the house sparrow and tree sparrow. J. Zool. 2016, 51, 771–776. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Gan, D.; Li, W.T. Surface modeling and innovative design based on reverse engineering. Plast. Technol. 2020, 48, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y. 3D scanning and reverse modeling technology applications. Mech. Eng. Autom. 2019, 6, 202–203. [Google Scholar]
- JB/T 7720-2007; Poultry Equipment—Nipple Drinkers. China National Institute of Standardization: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Vande Pol, K.D.; Grohmann, N.; Weber, T.; Ritter, M.J.; Ellis, M. Effect of drinker design on growth and water disappearance of nursery pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100 (Suppl. S2), 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosete, A.; Sarda, R. Nipple drinkers versus bell drinkers for on-bed housed chickens. Rev. Cuba. Cienc. Avíc. 2006, 30, 89–92. [Google Scholar]
- Quilumba, C.; Quijia, E.; Gernat, A.; Murillo, G.; Grimes, J. Evaluation of Different Water Flow Rates of Nipple Drinkers on Broiler Productivity. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2015, 24, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| xnym | SSE | RMSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| x1y1 | 4755 | 1.4111 | 0.73999 |
| x1y2 | 4100 | 1.3109 | 0.77580 |
| x1y3 | 4088 | 1.3095 | 0.77647 |
| x1y4 | 4024 | 1.2998 | 0.77995 |
| x2y1 | 2222 | 0.9651 | 0.87847 |
| x2y2 | 1137 | 0.6903 | 0.93786 |
| x2y3 | 1034 | 0.6589 | 0.94350 |
| x2y4 | 1004 | 0.6496 | 0.94510 |
| x3y1 | 2120 | 0.9429 | 0.88410 |
| x3y2 | 1042 | 0.6614 | 0.94284 |
| x3y3 | 1025 | 0.6560 | 0.94398 |
| x3y4 | 932 | 0.6261 | 0.94905 |
| x4y1 | 1894 | 0.8961 | 0.89641 |
| x4y2 | 951 | 0.6323 | 0.94799 |
| x4y3 | 933 | 0.6265 | 0.94898 |
| x4y4 | 930 | 0.6257 | 0.94914 |
| Day | Effective Drinking Volume L | Water Yield a | Effective Drinking Water Rate η | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 157.4 | 223.5 | 70.4 |
| 15 | 217.1 | 324.8 | 66.8 | |
| 20 | 288.4 | 465.6 | 61.9 | |
| 25 | 313.2 | 549.5 | 56.9 | |
| 30 | 328.2 | 663.5 | 49.4 | |
| 35 | 375.4 | 798.8 | 46.9 | |
| 40 | 423.2 | 865.1 | 48.9 | |
| Average | 57.3 | |||
| 2 | 10 | 168.7 | 236.6 | 71.3 |
| 15 | 245.4 | 349.8 | 70.1 | |
| 20 | 363.5 | 493.7 | 73.6 | |
| 25 | 446.3 | 583.6 | 76.4 | |
| 30 | 511.8 | 705.2 | 72.5 | |
| 35 | 547.1 | 774.1 | 70.6 | |
| 40 | 613.9 | 832.7 | 73.7 | |
| Average | 72.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, T.; Wang, H.; Duan, E.; Ma, G.; Bai, Z. The Design and Testing of a Special Drinker for Meat Ducks Based on Reverse Engineering. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7040126
Sun T, Wang H, Duan E, Ma G, Bai Z. The Design and Testing of a Special Drinker for Meat Ducks Based on Reverse Engineering. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(4):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7040126
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Tao, Huixin Wang, Enze Duan, Gang Ma, and Zongchun Bai. 2025. "The Design and Testing of a Special Drinker for Meat Ducks Based on Reverse Engineering" AgriEngineering 7, no. 4: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7040126
APA StyleSun, T., Wang, H., Duan, E., Ma, G., & Bai, Z. (2025). The Design and Testing of a Special Drinker for Meat Ducks Based on Reverse Engineering. AgriEngineering, 7(4), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7040126






