Circularity Between Aquaponics and Anaerobic Digestion for Energy Generation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials Used in the Anaerobic Digestion Process
2.2. Anaerobic Biodigester
2.3. Biomass Characterization
2.4. Biogas Yield
2.5. Flame Test
2.6. Biogas Composition Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Characterization of the Substrate and Digestate
3.2. Biogas, Digestion, and Ambient Environment Temperature Profile
3.3. Biogas Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Anaerobic Digestion |
| AE | Aquaponic Effluent |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| BD | Biodegradability |
| CH4 | Methane |
| CHP | Combined Heat and Power |
| CM | Cattle Manure |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| CoAD | Anaerobic Mono-Digestion |
| COD | Chemical Oxygen Demand |
| D | Digestate |
| EC | Electrical Conductivity |
| FIPERJ | Fishing Institute Foundation of the State of Rio de Janeiro |
| H2S | Hydrogen Sulfide |
| L | Liters |
| L kg−1 | Liters per Kilogram |
| LabGERAR | Laboratory of the Renewable and Alternative Rural Energy Group |
| MC | Moisture Content |
| MoAD | Anaerobic Mono-Digestion |
| NH3 | Ammonia |
| N-NO3 | Total Nitrogen–Nitrate |
| OLR | Organic Loading Rates |
| RAS | Recirculating Aquaculture System |
| S | Substrate |
| TA | Total Alkalinity |
| TOC | Total Organic Carbon |
| TS | Total Solids |
| UFRRJ | Federal Rural University of Rio de Janeiro |
| VFA | Volatile Fatty Acids |
| VTS | Volatile Total Solids |
| W | Water |
References
- Cifuentes-Torres, L.; Correa-Reyes, G.; Mendoza-Espinosa, L.G. Can reclaimed water be used for sustainable food production in aquaponics? Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 669984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baganz, G.F.M.; Junge, R.; Portella, M.C.; Goddek, S.; Keesman, K.J.; Baganz, D.; Staaks, G.; Shaw, C.; Lohrberg, F.; Kloas, W. The aquaponic principle—It is all about coupling. Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okomoad, V.T.; Oladimeji, S.A.; Solomon, S.G.; Olufeagba, S.O.; Ogah, S.I.; Ikhwanuddin, M. Aquaponics production system: A review of historical perspective, opportunities, and challenges of its adoption. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandramenon, P.; Aggoun, A.; Tchuenbou-Magaia, F. Smart approaches to aquaponics 4.0 with focus on water quality—comprehensive review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 225, 109256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerreiro, S.L.M.; Cabral Júnior, J.F.G.; Eiras, B.J.C.F.; Miranda, B.D.S.; Lopes, P.C.A.; Melo, N.F.A.C.D.; Luz, R.K.; Sterzelecki, F.C.; Palheta, G.D.A. Integrating aquaponics with Macrobrachium Amazonicum (Palaemonidae: Decapoda) cultivation for the production of microgreens: A sustainable approach. AgriEngineering 2024, 6, 2718–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yep, B.; Zheng, Y. Aquaponic trends and challenges—A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1586–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, A.; Lepine, C.; Witarsa, F.; Good, C. Anaerobic digestion challenges and resource recovery opportunities from land-based aquaculture waste and seafood processing byproducts: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 354, 127144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yogev, U.; Keesman, K.J.; Gross, A. Onsite anaerobic treatment of aquaponics lettuce waste: Digestion efficiency and nutrient recovery. Aquac. Int. 2021, 29, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yogev, U.; Goddek, S.; Yang, F.; Keesman, K.J.; Gross, A. Carbon dynamics and energy recovery in a novel near-zero waste aquaponics system with onsite anaerobic treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.H.; Pinho, S.M.; Agostinho, F.; Costa, J.I.; Portella, M.C.; Keesman, K.J.; Garcia, F. Sustainability of urban aquaponics farms: An emergy point of view. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 331, 129896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, M.; Bergman, J.; Van Willigenburg, L.G.; Keesman, K.J. Towards a zero-waste aquaponics-centered eco-industrial food park. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 454, 142109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagh, M.S.; S, S.; Nath, P.C.; Chakraborty, A.; Amrit, R.; Mishra, B.; Mishra, A.K.; Mohanta, Y.K. Valorisation of agro-industrial wastes: Circular bioeconomy and biorefinery process—A sustainable symphony. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 183, 708–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alengebawy, A.; Ran, Y.; Osman, A.I.; Jin, K.; Samer, M.; Ai, P. Anaerobic digestion of agricultural waste for biogas production and sustainable bioenergy recovery: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2024, 22, 2641–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Yogev, U.; Keesman, K.J.; Gross, A. Promoting circular economy: Comparison of novel coupled aquaponics with anaerobic digestion and conventional aquaponic systems on nutrient dynamics and sustainability. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 208, 107716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ganeshan, P.; Sar, T.; Xu, S.; Rajendran, K.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Anaerobic digestion in global bio-energy production for sustainable bioeconomy: Potential and research challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 208, 114985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaghat, A.H.; Merenda, A.; Seccombe, D.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K. From waste to high-value fertilisers: Harvesting nutrients from liquid anaerobic digestate for a circular bioeconomy. Desalination 2025, 596, 118266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaimes-Estévez, J.; Mercado, E.V.; Jaramillo, J.G.; Rodríguez, P.; Martí-Herrero, J.; Escalante, H.; Castro, L. From laboratory to farm-scale psychrophilic anaerobic co-digestion of cheese whey and cattle manure. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 19, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyropoulos, C.; Thomopoulos, V.; Petrakis, T.; Kavga, A. Implementing circular economy in the production of biogas from plant and animal waste: Opportunities in greenhouse heating. AgriEngineering 2024, 6, 4675–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garkoti, P.; Ni, J.-Q.; Thengane, S.K. Energy management for maintaining anaerobic digestion temperature in biogas plants. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 199, 114430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casallas-Ojeda, M.; Cabeza, I.; Sanchez, N.; Caicedo-Concha, D.M.; Astals, S. Cheese whey and dairy manure anaerobic co-digestion at psychrophilic conditions: Technical and environmental evaluation. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kébé, N.N.; Rieker, C.; Fall, P.A.; Diouf, D.; Ndiaye, D.; Mockenhaupt, T.; Beuel, P.; Bursche, J. Anaerobic co-digestion of fish processing waste with cow manure and waste of market (rests of fruits and vegetables): A lab scale batch test. J. Sustain. Bioenergy Syst. 2021, 11, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Montiel, R.; Medina-Pérez, G.; Afanador-Barajas, L.; Ibarra-Sánchez, C.; Prince, S.; Pérez-Ríos, S.; Hernández-Niño, J. Anaerobic co-digestion of bovine manure and residual sludge from tilapia fish (Oreochromis niloticus) breeding ponds. Agro Product. 2022, 15, i11.2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhr, K.I.; Letelier-Gordo, C.O.; Lund, I. Anaerobic digestion of solid waste in RAS: Effect of reactor type on the Biochemical Acidogenic Potential (BAP) and assessment of the Biochemical Methane Potential (BMP) by a batch assay. Aquac. Eng. 2015, 65, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Ma, N.; Li, P.; Tan, H.; Liu, W. Enhancement of anaerobic digestion to treat saline sludge from recirculating aquaculture systems. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 479101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.-J. Influence of acidogenic fermented fish by-products with rice bran for sludge reduction and biogas recovery in anaerobic co-digestion. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 26, 190409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Lv, L.; Li, W.; Ren, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Gao, W.; Sun, L.; Zhang, G. A comprehensive review on food waste anaerobic co-digestion: Research progress and tendencies. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xiao, G.; Peng, L.; Su, H.; Tan, T. The anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and cattle manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwabie, M.; VanderZaag, A.; Nji, P.; Tembong, G.; Chenwi, T. Assessment of gaseous emissions from cattle abattoir wastes in Cameroon. AgriEngineering 2019, 1, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, M.G.; Sousa, S.S.O.D.; Arruda, V.C.M.D.; El-Deir, S.G. Impactos socioambientais dos dejetos da pecuária no âmbito rural: Uma revisão de literatura. Rev. AIDIS Ing. Cienc. Ambient. 2022, 15, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Qin, K.; Ding, J.; Xue, M.; Yang, C.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Q. Optimization of the co-digestion of sewage sludge, maize straw and cow manure: Microbial responses and effect of fractional organic characteristics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Krooneman, J.; Euverink, G.J.W. Strategies to boost anaerobic digestion performance of cow manure: Laboratory achievements and their full-scale application potential. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freepik Company S.L.—Flaticon. Available online: https://www.flaticon.com/ (accessed on 24 January 2025).
- Paes, J.L.; Costa, L.M.P.; Fernandes, P.L.B.G.; Vargas, B.C.; Cecchin, D. Biogas production by anaerobic digestion of coffee husks and cattle manure. Eng. Agrícola 2023, 43, e20220126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.D.; Franson, M.A.H. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water & Wastewater, 23rd ed.; American Public Health Association—APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Carmo, D.L.D.; Silva, C.A. Métodos de quantificação de carbono e matéria orgânica em resíduos orgânicos. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Solo 2012, 36, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazil’s National Institute of Meteorology (INMET). Available online: https://tempo.inmet.gov.br/TabelaEstacoes/A001 (accessed on 24 January 2025).
- Kunz, A.; Sulzbach, A. Kit biogas portátil. Concórdia: EMBRAPA—CNPSA. 2007. 2p. Available online: https://www.embrapa.br/suinos-e-aves/busca-de-publicacoes/-/publicacao/439433/kit-biogas-portatil-para-analise-de-concentracao-de-gas-metano-amonia-e-gas-sulfidrico-em-biogas (accessed on 24 January 2025).
- Ferreira, D.F. SISVAR: A computer analysis system to fixed effects split plot type designs. Rev. Bras. Biom. 2019, 37, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slopiecka, K.; Liberti, F.; Massoli, S.; Bartocci, P.; Fantozzi, F. Chemical and physical characterization of food waste to improve its use in anaerobic digestion plants. Energy Nexus 2022, 5, 100049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franqueto, R.; da Silva, J.D.; Konig, M. Effect of temperature variation on codigestion of animal waste and agricultural residue for biogas production. BioEnergy Res. 2020, 13, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, R.; Eikebrokk, B. Mesophilic anaerobic treatment of sludge from salmon smolt hatching. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 2389–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Jin, T.; Chen, H.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, Y. Conductive materials as fantastic toolkits to stimulate direct interspecies electron transfer in anaerobic digestion: New insights into methanogenesis contribution, characterization technology, and downstream treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, A.; Zhang, L.; Guo, W.; Sajjad, W.; Ilahi, N.; Banerjee, A.; Faisal, S.; Usman, M.; Chen, T.; Zhang, W. Temperature-dependent transformation of microbial community: A systematic approach to analyzing functional microbes and biogas production. Environ. Res. 2024, 249, 118351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
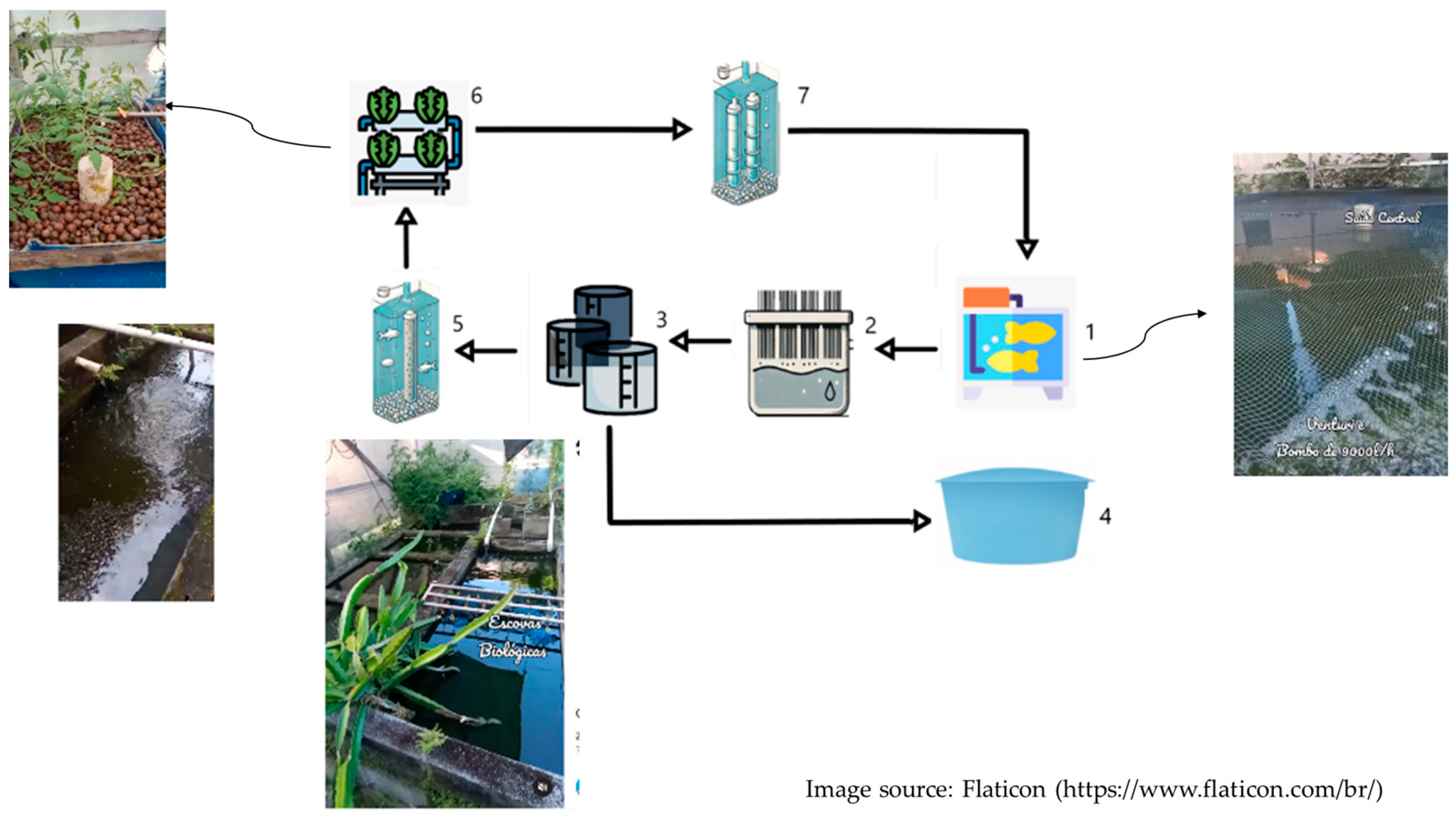
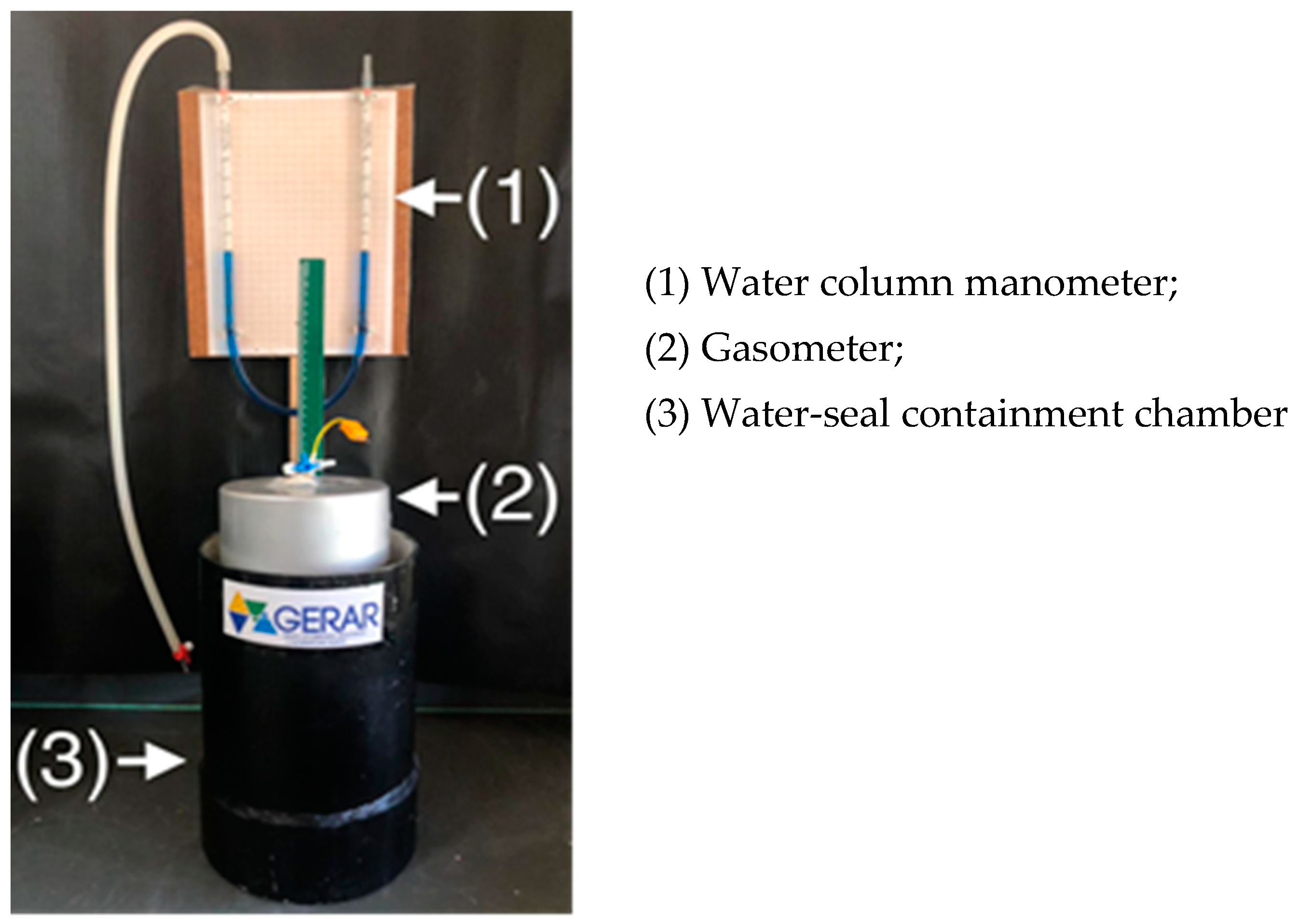
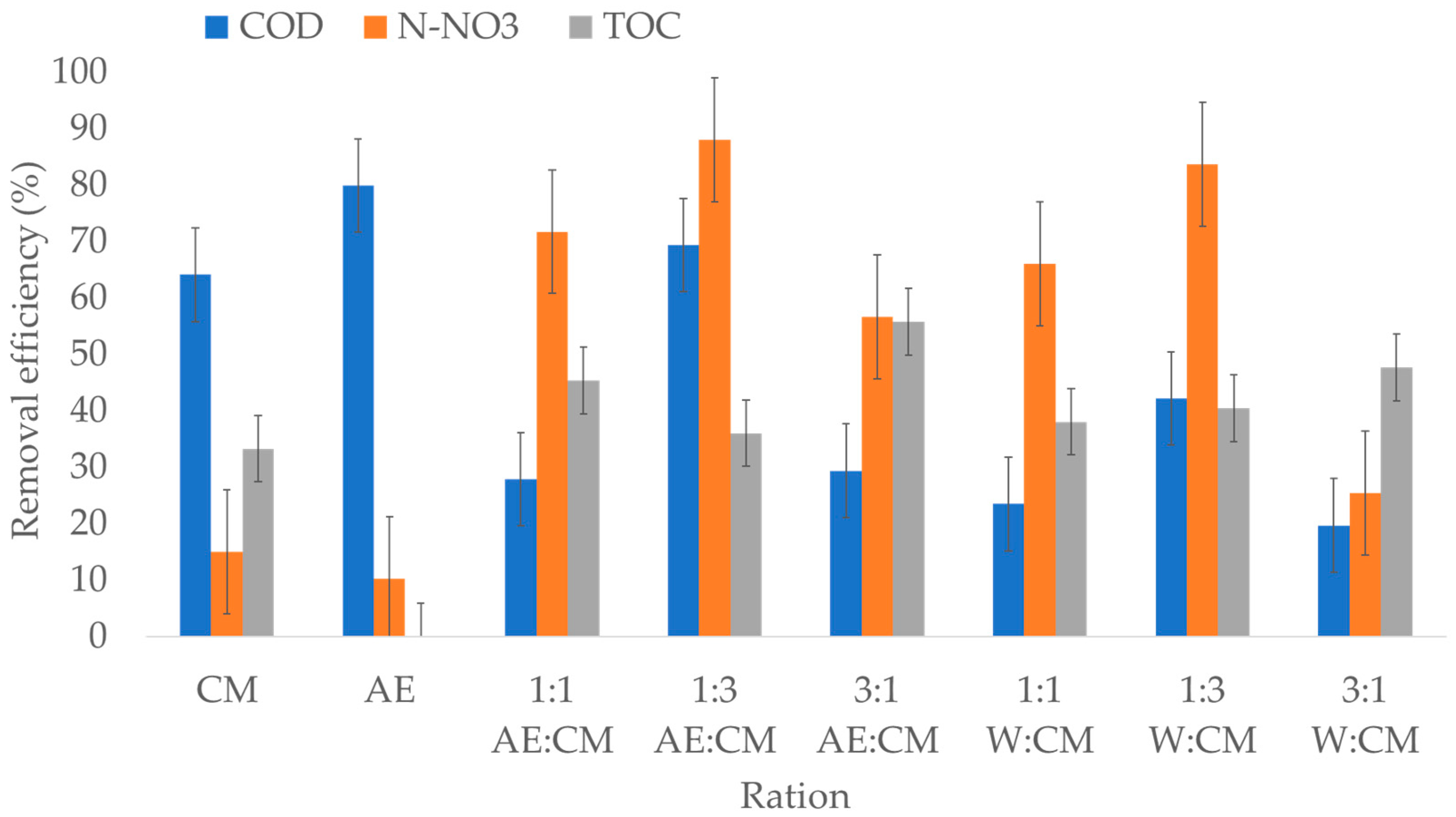


| Process | Ratio | MC (%) | TS (%) | VTS (%) | BD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | D | S | D | S | D | S | D | ||
| MoAD | CM | 83.32 Bf | 87.40 Ae | 16.68 Aa | 12.60 Ba | 13.22 Aa | 8.78 Ba | 0.79 Aa | 0.70 Ba |
| AE | 99.93 Aa | 100 Aa | 0.07 Af | 0.00 Ae | 0.00 Ag | 0.00 Ae | 0.00 Ab | 0.00 Ab | |
| CoAD | 1:1 AE:CM | 92.32 Bd | 95.18 Ac | 7.68 Ac | 4.81 Bc | 5.97 Ac | 3.32 Bc | 0.77 Aa | 0.69 Ba |
| 1:3 AE:CM | 89.78 Be | 92.94 Ad | 10.22 Ab | 7.06 Bb | 8.10 Ab | 5.01 Bb | 0.79 Aa | 0.71 Ba | |
| 3:1 AE:CM | 94.95 Bc | 97.48 Ab | 5.04 Ad | 2.51 Bd | 4.19 Ae | 1.82 Bd | 0.83 Aa | 0.72 Ba | |
| MoAD | 1:1 W:CM | 92.90 Bd | 95.41 Ac | 7.10 Ac | 4.59 Bc | 5.34 Ad | 3.10 Bc | 0.75 Aa | 0.67 Ba |
| 1:3 W:CM | 89.66 Be | 93.37 Ad | 10.34 Ab | 6.63 Bb | 7.95 Ab | 4.60 Bb | 0.77 Aa | 0.69 Ba | |
| 3:1 W:CM | 96.33 Bb | 98.11 Ab | 3.67 Ae | 1.89 Bd | 2.82 Af | 1.31 Bd | 0.77 Aa | 0.68 Ba | |
| Ratio | pH | EC (ds m−1) | TA (gCaCO3 L−1) | VFA (g eq HAc L−1) | VFA/TA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | D | S | D | S | D | S | D | S | D | |
| CM | 7.24 Aa | 7.36 Aa | 0.32 Ad | 0.82 Ac | 3.54 Ba | 5.62Aa | 1.06 Aa | 0.80 Ba | 0.29 Ab | 0.14 Ba |
| AE | 7.03 Ab | 7.12 Ab | 0.34 Ad | 0.31 Ac | 0.02 Ad | 0.05Ad | 0.01Ad | 0.01 Ac | 0.46 Aa | 0.14 Ba |
| 1:1 AE:CM | 6.61 Bc | 6.82 Ac | 4.04 Aa | 3.56 Aa | 1.63 Bb | 2.69 Ac | 0.48 Ac | 0.20 Bc | 0.30 Ab | 0.08 Ba |
| 1:3 AE:CM | 6.80 Bc | 7.36 Aa | 4.41 Aa | 4.23 Aa | 2.33 Bb | 4.02Ab | 0.86 Ab | 0.58 Bb | 0.37 Aa | 0.15 Ba |
| 3:1 AE:CM | 6.63 Bc | 6.84 Ac | 3.19Ab | 2.95 Ab | 1.04Bc | 2.63Ac | 0.43 Ac | 0.19 Bc | 0.41 Aa | 0.07 Ba |
| 1:1 W:CM | 6.73 Bc | 6.95 Ac | 3.79 Aa | 3.80Aa | 1.94 Bb | 3.72 Ab | 0.49 Ac | 0.20 Bc | 0.25 Ab | 0.05 Ba |
| 1:3 W:CM | 6.78 Bc | 7.15 Ab | 2.55 Ac | 2.70 Ab | 2.10 Bb | 3.62Ab | 0.69 Ab | 0.25 Bc | 0.33 Ab | 0.07 Ba |
| 3:1 W:CM | 6.42 Bd | 6.76 Ac | 3.17 Ab | 2.93 Ab | 1.96 Bb | 3.91Ab | 0.46 Ac | 0.13 Bc | 0.24 Ab | 0.03 Ba |
| Ratio | Week | Biogas Yield (L kg−1) | Biogas Composition | Cumulative Biogas Yield (L kg−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 (%) | CO2 (%) | H2S (ppmv) | NH3 (ppmv) | ||||
| CM | 12 | 5.83 | 76.5 | 23.5 | 20 | 15 | 57.58 |
| AE | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 1:1 AE:CM | 4 | 7.21 | 75.0 | 25.0 | 15 | 20 | 56.92 |
| 1:3 AE:CM | 5 | 7.09 | 77.5 | 22.5 | 15 | 20 | 69.72 |
| 3:1 AE:CM | 4 | 6.36 | 75.0 | 25.0 | 15 | 20 | 32.49 |
| 1:1 W:CM | 12 | 5.84 | 60.0 | 40.0 | 20 | 15 | 47.85 |
| 1:3 W:CM | 5 | 5.07 | 77.5 | 22.5 | 20 | 15 | 40.92 |
| 3:1 W:CM | 5 | 4.09 | 75.0 | 25.0 | 20 | 15 | 31.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lobo Paes, J.; Guimarães, C.G.; Gomes, A.d.S.; Valadão, R.C.; Cecchin, D.; Menino, R. Circularity Between Aquaponics and Anaerobic Digestion for Energy Generation. AgriEngineering 2025, 7, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7050129
Lobo Paes J, Guimarães CG, Gomes AdS, Valadão RC, Cecchin D, Menino R. Circularity Between Aquaponics and Anaerobic Digestion for Energy Generation. AgriEngineering. 2025; 7(5):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7050129
Chicago/Turabian StyleLobo Paes, Juliana, Cirlene Gomes Guimarães, Alexia de Sousa Gomes, Romulo Cardoso Valadão, Daiane Cecchin, and Regina Menino. 2025. "Circularity Between Aquaponics and Anaerobic Digestion for Energy Generation" AgriEngineering 7, no. 5: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7050129
APA StyleLobo Paes, J., Guimarães, C. G., Gomes, A. d. S., Valadão, R. C., Cecchin, D., & Menino, R. (2025). Circularity Between Aquaponics and Anaerobic Digestion for Energy Generation. AgriEngineering, 7(5), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/agriengineering7050129









