Abstract
Achieving net-zero carbon emissions, this study introduces a sustainable pathway for reducing strontium sulfate (SrSO4) and celestite ore to strontium sulfide (SrS) using biofuels (biomethane, bioethanol) derived from agro-industrial waste and green hydrogen. Traditional SrSO4 reduction methods, which rely on fossil-derived reductants like coal and operate at energy-intensive temperatures (1100–1200 °C), generate significant greenhouse gases and toxic byproducts, highlighting the need for eco-friendly alternatives. Experimental results demonstrate that bioethanol outperformed other reductants, achieving 97% conversion of synthetic SrSO4 at 950 °C within 24 min and 74% conversion of natural celestite ore over 6 h. Remarkably, this bioethanol-driven process matches the energy efficiency of the conventional black ash method while enabling carbon neutrality through renewable feedstock utilization, reducing CO2 emissions by 30–50%. By valorizing agro-industrial waste streams, this strategy advances circular economy principles and aligns with Mexico’s national agenda for sustainable industrial practices, including its commitment to decarbonizing heavy industries. This study contributes to sustainable development goals and offers a scalable solution for decarbonizing strontium compound production in the chemical industry.
1. Introduction
Strontium sulfide (SrS), renowned for its electrical/thermal conductivities, is essential in semiconductor technologies and next-generation energy storage systems [1]. As a precursor to strontium derivatives (e.g., SrCO3, Sr(NO3)2), which dominate ~70% of the global strontium market, SrS enables scalable production of compounds like SrTiO3 and SrCrO4 via cost-effective pathways (Figure S2) [2]. The global SrS market, valued at USD 100 million, is projected to grow at 13.3% CAGR (2024–2031), driven by applications in pyrotechnics, drilling fluids, phosphorescent materials, and medical devices [3,4]. SrS-derived materials further advance energy storage, photocatalysis, and solid oxide fuel cells, stressing SrS’s cross-industry versatility [2].
1.1. Production Challenges and Environmental Impact
SrS synthesis primarily relies on celestite (SrSO4), a mineral often containing BaSO4, CaCO3, and SiO2 impurities [3]. While high-purity Mexican celestite (70–94% SrSO4) simplifies processing, declining reserves and China’s surge in low-grade ore exports intensify supply-chain pressures [3,4]. Conventional carbothermic reduction, using coke at 1100–1200 °C, faces critical limitations, including low Sr recovery (60–80%), high CO2/SOx emissions caused by mineral impurities (SiO2, Al2O3, and Fe2O3) (Reactions (1)–(6)), and energy-intensive operations [5,6,7,8,9].
SrSO4 + 2C → SrS + 2CO2(g) ΔHR° = +201.390 kJ/mol
CO2(g) + C(s) → 2CO(g) ΔHR° = +172.358 kJ/mol
SrSO4 + 4CO → SrS + 4CO2(g) ΔHR° = −143.349 kJ/mol
SrSO4 + SiO2 → SrSiO3 + SO2(g) + 0.5O2(g) ΔHR° = +874.338 kJ/mol
SrSO4 + Al2O3 → Sr(AlO2)2 + SO2(g) + 0.5O2(g)
SrSO4 + Fe2O3 → Sr(FeO2)2 + SO2(g) + 0.5O2(g)
For every two moles of SrS produced, six moles of CO2 are emitted (Reactions (1) and (3)), exacerbating environmental concerns [6,7,8]. Although catalysts (e.g., Na2Cr2O3) and microwave-assisted methods improve efficiency (97% conversion in 10 min [10,11]), reliance on fossil-derived reductants persists as a sustainability barrier.
1.2. Emerging Reduction Strategies
Alternative approaches aim to mitigate these issues. Mechanochemical reduction with Mg/Al avoids CO2 but risks SrS re-oxidation and secondary phases (e.g., SrAl2O4), complicating purification [12,13,14]. Green gaseous reductants like methane and hydrogen show promise; CH4 reduces CO2 emissions by 50% (Reaction (7)) [15,16,17,18], while H2 enables fluidized-bed SrS synthesis at 950–1200 °C via synergistic CO/H2 pathways (Reactions (8)–(11)) [19,20,21]. Catalysts like ZnO and Ni further enhance kinetics, lowering temperatures by 200 °C [17,22]. However, scalability challenges, gas handling costs, and feedstock competition hinder widespread adoption.
SrSO4 + CH4 → SrS + CO2 + 2H2O ΔHR° = +97.339 kJ/mol
SrSO4 + 4H2→SrS + 4H2O ΔHR° = −155.581 kJ/mol
SrSO4 + 4CO→SrS + 4CO2 ΔHR° = −143.348 kJ/mol
C + H2O→CO + H2 ΔHR° = +175.416 kJ/mol
CO + H2O→CO2 + H2 ΔHR° = +3.058 kJ/mol
1.3. Toward Sustainable SrS: Bioethanol as a Renewable Reductant
Aligning with decarbonization goals (Kyoto Protocol, Paris Agreement), this study pioneers bioethanol—a second-generation biofuel from non-edible biomass—for SrSO4 reduction (Reaction (12)). Unlike carbothermal methods, bioethanol eliminates ash-related side reactions, operates at lower temperatures, and offsets CO2 via renewable feedstocks [23]. Despite systemic hurdles (e.g., food-vs-fuel debates for first-generation biofuels), bioethanol’s carbon neutrality and compatibility with circular economies offer a transformative pathway.
1.5SrSO4 + C2H6O → 1.5SrS + 2CO2 + 3H2O ΔHR° = +114.542 kJ/mol
While prior studies explored H2, CH4, and mechanochemical routes, bioethanol’s potential remains unexplored. This work systematically evaluated bioethanol, biomethane, and green H2 for SrS production, employing thermogravimetric, XRD, and SEM-EDS analyses to optimize conversion efficiency and scalability. By bridging renewable chemistry with industrial demands, this research advances sustainable strontium chemical transformation, addressing critical gaps in emission reduction and resource efficiency.
2. Experimental Methodology
2.1. Celestite Ore
The celestite ore (SrSO4) used in this study was obtained from Cuatro Ciénegas, Coahuila, Mexico, an area recognized for its high Sr concentration in sedimentary deposits. According to regional reports, the ore is primarily composed of SrSO4, with impurities such as BaSO4, CaSO4, SrCO3, and CaCO3 [4,7]. The material was crushed in an agate mortar and sieved using a #50 mesh to obtain particles with diameters smaller than 300 µm. The particle-size distributions are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Particle-Size Distribution of Celestite.
2.2. Synthesis of SrSO4 at Laboratory Scale
Strontium nitrate (5.29 g) was dissolved in 10 mL of distilled water under continuous magnetic stirring at ambient temperature. To the resultant aqueous solution, 1.5 mL of sulfuric acid (98%) was added dropwise, initiating the precipitation of strontium sulfate. The reaction mixture was stirred at 500 rpm for 10 min to ensure complete homogenization. The precipitate was isolated via vacuum filtration using a 125 mm diameter Whatman filter paper and subsequently washed with 600 mL of distilled water in aliquots to remove residual reactants. The retained SrSO4, identified by its characteristic white coloration, was dried at 80 °C for 4 h in a convection oven.
Theoretical yield calculations, incorporating an anticipated 80% reaction efficiency owing to stoichiometric and practical considerations, predicted a product mass of 3.672 g. Experimental quantification yielded 3.668 g of SrSO4, corresponding to 99.9% of the projected yield (79.9% of the maximum theoretical yield). This near-quantitative recovery demonstrates exceptional agreement between the experimental results and stoichiometric predictions.
The synthesis is illustrated by the following reaction:
Sr(NO3)2 + H2SO4 = SrSO4 + 2HNO3 ΔHR° = −9.095 kJ/mol
2.3. Thermodynamic Modeling and Sensitivity Analysis Procedures
Equilibrium-state thermodynamic modeling (TDM) was performed using Aspen Plus® software to identify and quantify equilibrium products during the reduction of SrSO4. The TDM employs a GIBBS reactor, which calculates the chemical equilibrium across multiphase systems (solid, liquid, and gas) by minimizing the Gibbs free energy. The reactor configuration illustrated in Figure S1 (Supplementary Material) included defined feed and output streams, with stream class parameters set to MIXCISLD and flow units standardized to kmol/h. The SOLIDS property method was selected to account for solid-phase interactions, with all simulations conducted at 1 bar and the operating temperatures specified under the sensitivity analysis.
The GIBBS reactor was chosen for its ability to resolve equilibrium compositions, detect solid-phase species, and quantify molar distributions. The phase interactions and reaction spontaneity were evaluated via Gibbs free energy minimization, and ΔG was analyzed as a function of temperature [24]. Sensitivity analysis (SA) was implemented to assess temperature-dependent variations (independent variable: 25–1500 °C) in molar flows (kmol/h) of output stream components, energy consumption (Q: Heat Duty, kJ), and equilibrium compositions (dependent variables).
Complementary enthalpy of reaction (ΔH, kJ/kmol) calculations were conducted using HSC Chemistry® software [25], which integrates thermodynamic databases to evaluate the effects of temperature on system equilibria. This dual-software approach ensured the robust validation of the energy profiles and phase behavior across the studied temperature range.
2.4. Structural Characterization and Elemental Analysis
Microstructural characterization of laboratory-synthesized SrSO4 and celestite ore was performed using X-ray diffraction (XRD). The XRD patterns were obtained in the range of 20–60° with a step size of 0.33°/s using a PANalytical X’pert Pro-Theta/2Theta diffractometer with a CuKα radiation source (λ = 1.54186 Å). Additionally, the obtained pattern from the celestite ore was refined using the Rietveld technique with Fullprof® software, adjusting the diffraction peaks to a Thompson–Cox–Hastings pseudo-Voigt function. Refinement was performed to accurately identify and quantify the phases present in the mineral. This process ensures precise determination of the crystalline structures, allowing for an estimate of the mineral composition and potential impurity content [26]. The morphology and elemental composition of the samples were analyzed using SEM-EDS with a JEOL field-emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM, model JSM-7401f. Energy), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was performed to determine the chemical composition of the laboratory-synthesized SrSO4 sample and celestite ore. The samples were prepared by dispersing the powder in isopropanol. A drop was then placed onto single-crystal silicon wafers using a capillary tube, and the samples were dried on a heating plate at approximately 80 °C. The elemental composition of the fresh and reduced celestite ore samples was quantified via inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES) using a Thermo Fisher Scientific iCAP 6500 spectrometer. This analysis provided critical insights into the compositional variations induced by the reduction processes, enabling a direct comparison of pre- and post-reduction elemental profiles.
2.5. Evaluation of Biofuel Reduction
The SrSO4 reduction reaction was conducted in a thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) equipped with an Evolved Gas Analysis (EGA) furnace. In all experiments, the total gas flow rate at the reactor outlet was maintained at 100 mL/min. Both laboratory-synthesized SrSO4 and natural celestite ore were used as starting materials. Methane and hydrogen were supplied in gaseous form through mass flow controllers to achieve precise volume concentration ratios. Ethanol was introduced via a liquid scrubber, with argon serving as the carrier gas to facilitate its controlled delivery and vaporization. These reducing agents were chosen as potential substitutes for biofuels such as methane (biogas), ethanol (bioethanol), and green hydrogen. The laboratory-synthesized sample underwent reduction at various temperatures (850, 900, and 950 °C) to determine the optimal reduction conditions for celestite ore. Additionally, the conversion efficiency of the three reducing agents was compared based on apparent kinetics and reduction time. Samples were heated at a controlled rate of 10 °C/min under an argon atmosphere. Once the target temperature was reached, a reducing atmosphere was introduced, consisting of 10% (v/v) methane, 10% (v/v) hydrogen, and 7% (v/v) ethanol, balance argon. The reducing conditions were maintained isothermally at 850 °C, 900 °C, and 950 °C until no further weight loss was observed, indicating the complete reduction of strontium sulfate to strontium sulfide. According to the stoichiometry of each reduction studied, the theoretical expected weight loss in the TGA for 100% conversion should be 34.84%wt.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Thermodynamic Modeling and Sensitivity Analysis Results
3.1.1. Black Ash Method
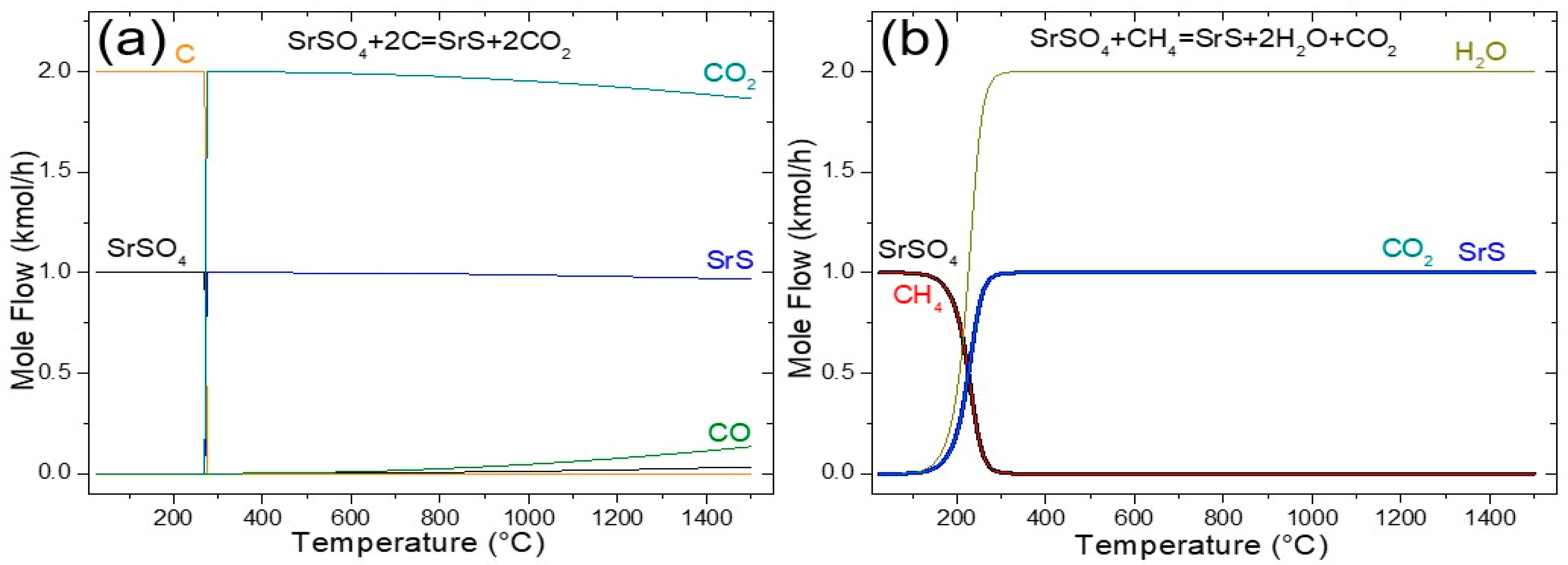
The results of the sensitivity analysis for the black ash method are presented in Figure 1a, which plots the equilibrium amount of each chemical species in the reaction system (kmol) against the reaction temperature (°C). The analysis revealed that temperatures below 280 °C resulted in negligible reactions between the feed components, 2 kmol of C, and 1 kmol of SrSO4. However, temperatures exceeding this threshold resulted in a high reactant conversion. According to Reaction (1), 2 kmol of CO2 is produced per 1 kmol of SrS. Notably, as the temperature increased above 280 °C, a slight decline in the equilibrium amounts of SrS and CO2 was observed. At 900 °C, the equilibrium composition comprised 0.9912 kmol of SrS, 1.9651 kmol of CO2, and 0.0348 kmol of CO, with only trace amounts of unreacted SrSO4 remaining. This corresponded to an equilibrium conversion of 99.12% for SrSO4, indicating a near-complete reaction under these conditions. In addition, TDM analysis revealed that Reaction (1) is non-spontaneous at lower temperatures (ΔG > 0) yet kinetically inhibited under these conditions. Significant activation barriers require elevated temperatures (≥900 °C) to achieve reasonable reaction rates, yielding conversion efficiencies approaching 90% [8,20].
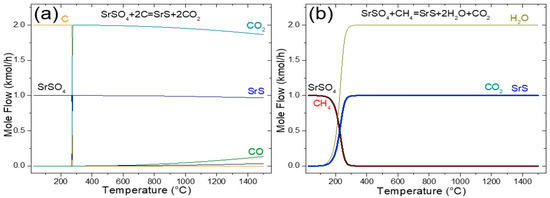
Figure 1.
Sensitivity analysis of the SrSO4 reduction by (a) black ash and (b) methane.
In addition, the Boudouard Reaction (2), at equilibrium, CO2(g) + C(s) ⇌ 2CO(g), exhibits a marked temperature dependence. Below 700 °C, the reverse reaction dominates, as evidenced by the thermodynamically unfavorable CO generation (ΔG > 0 for the forward reaction). At temperatures ≥700 °C, the endothermic forward reaction became both kinetically and thermodynamically favorable (ΔG < 0), driving CO production and concurrent CO2 reduction. This transition aligns with Le Chatelier’s principle, where elevated temperatures overcome kinetic barriers and favor an entropy-driven forward process, achieving equilibrium conversions of ~90%. In addition, CO generated via Reaction (2) serves as a critical reductant for SrSO4, enabling its conversion to SrS (Reaction (3)) [6,7,8]. However, this reduction process stoichiometrically releases two moles of CO2 per mole of SrSO4 converted, representing a significant environmental challenge due to greenhouse gas emissions.
3.1.2. Reduction with Methane
The utilization of methane (CH4) as a reductant for SrSO4 offers a promising pathway to mitigate CO2 emissions, achieving a 50% reduction compared with the conventional carbon-based black ash process [15]. As illustrated in Figure 1b, methane-driven reduction (Reaction (11)) became thermodynamically favorable above 200 °C, yielding SrS, H2O, and CO2. Significantly, the CO2 emissions generated in this pathway were stoichiometrically halved relative to carbon-based methods, positioning CH4 as a more sustainable alternative. According to Figure 1b, at 900 °C around 1 kmol of SrS, 2 kmol of H2O, and 1 kmol of CO2 were produced, which represents a complete equilibrium conversion of SrSO4 of 100%.
3.1.3. Reduction with Hydrogen
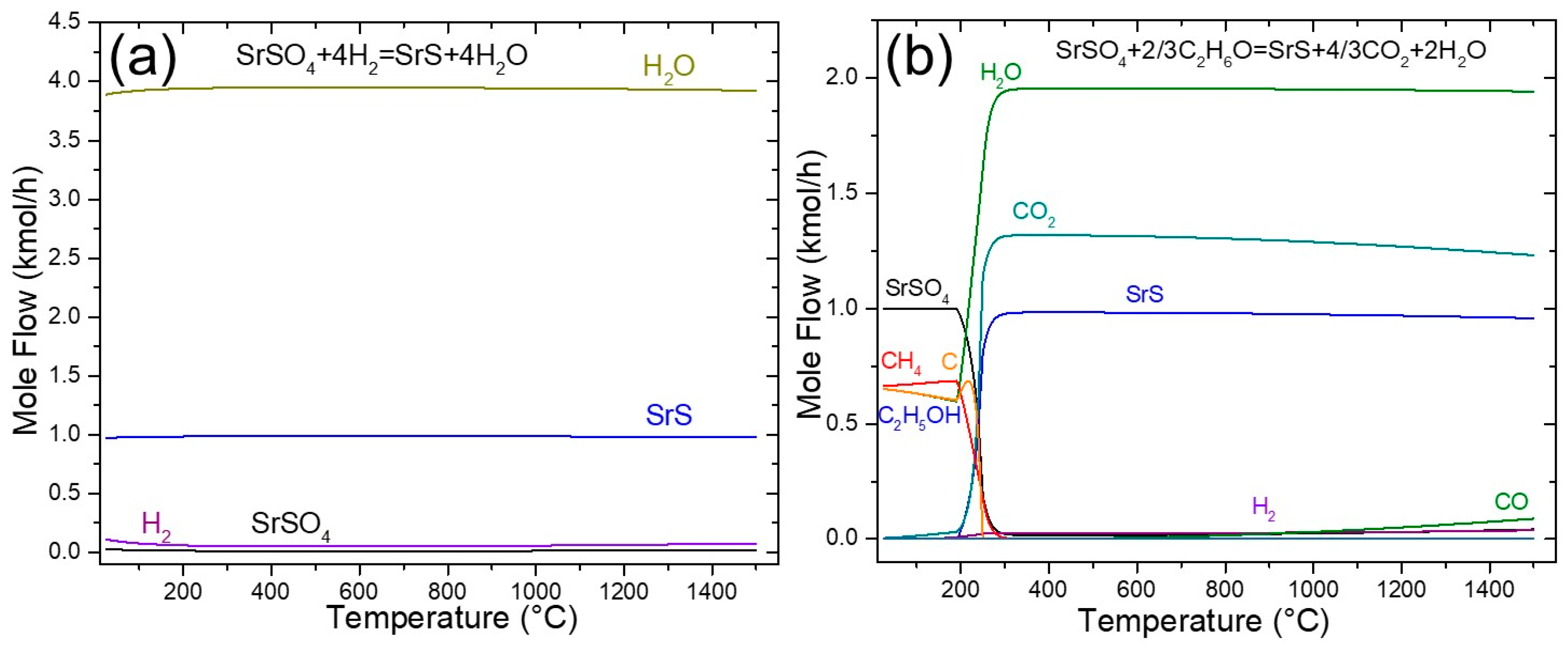
The use of green hydrogen (H2) as a reducing agent for SrSO4 is a viable and potentially cleaner alternative to traditional methods. The reduction with hydrogen is a potential sustainable alternative in this process. While it is true that hydrogen demand is high in other energy-intensive industries, the use of hydrogen in the strontium industry could become more realistic as green hydrogen production scales up and costs decrease. This scenario is aligned with future decarbonization strategies and ongoing efforts to diversify hydrogen applications in the metallurgical sector. In Reaction (8), the only byproduct generated was water vapor (4 mol), without CO2 emissions from stoichiometric amounts in the feed. As reported in the literature, this process requires prolonged reaction times (4.3 h) and high temperatures (>1000 °C) to achieve complete reduction of SrS [18]. Figure 2a shows that the reaction occurred across the entire temperature range according to the TDM analysis. In addition, the amounts of SrS and H2O products remained constant, indicating that the reaction reached equilibrium without significant changes in the composition throughout the analyzed temperature range. According to Figure 2a, at 900 °C, 0.9861 kmol of SrS and 3.9444 kmol of H2O were produced, which represents a complete equilibrium conversion of SrSO4 of 98.61%.
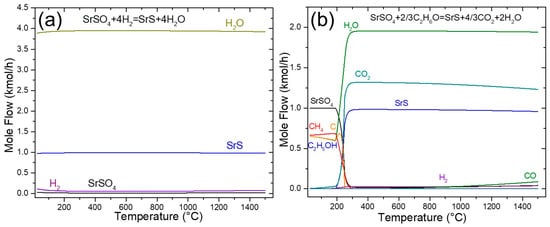
Figure 2.
Sensitivity analysis of the SrSO4 reduction by (a) hydrogen and (b) ethanol.
3.1.4. Reduction with Ethanol
The reduction of SrSO4 using ethanol has not been previously reported in the literature, thus positioning it as a novel and environmentally sustainable alternative for this process. A key advantage of ethanol over conventional carbon-based reductants (e.g., black ash) is its reduced environmental footprint. Unlike fossil-fuel-derived reductants, ethanol is renewable, biodegradable, and generates no solid waste or toxic byproducts, thus offering a cleaner and less polluting pathway [27].
The sensitivity analysis of ethanol decomposition (Figure 2b) revealed distinct temperature-dependent reaction pathways. Below ≈ 400 °C, ethanol predominantly decomposes via Reaction (14).
C2H6O → C + CH4 + H2O ΔHR° = −81.626 kJ/mol
This reaction is thermodynamically favored at lower temperatures (ΔG °< 0). At temperatures exceeding 700 °C, however, methane undergoes cracking (Reaction (15)) and steam reforming (Reaction (16)).
CH4 → C + 2H2 ΔHR° = +74.60 kJ/mol
CH4 + H2O → CO + 3H2 ΔHR° = +205.885 kJ/mol
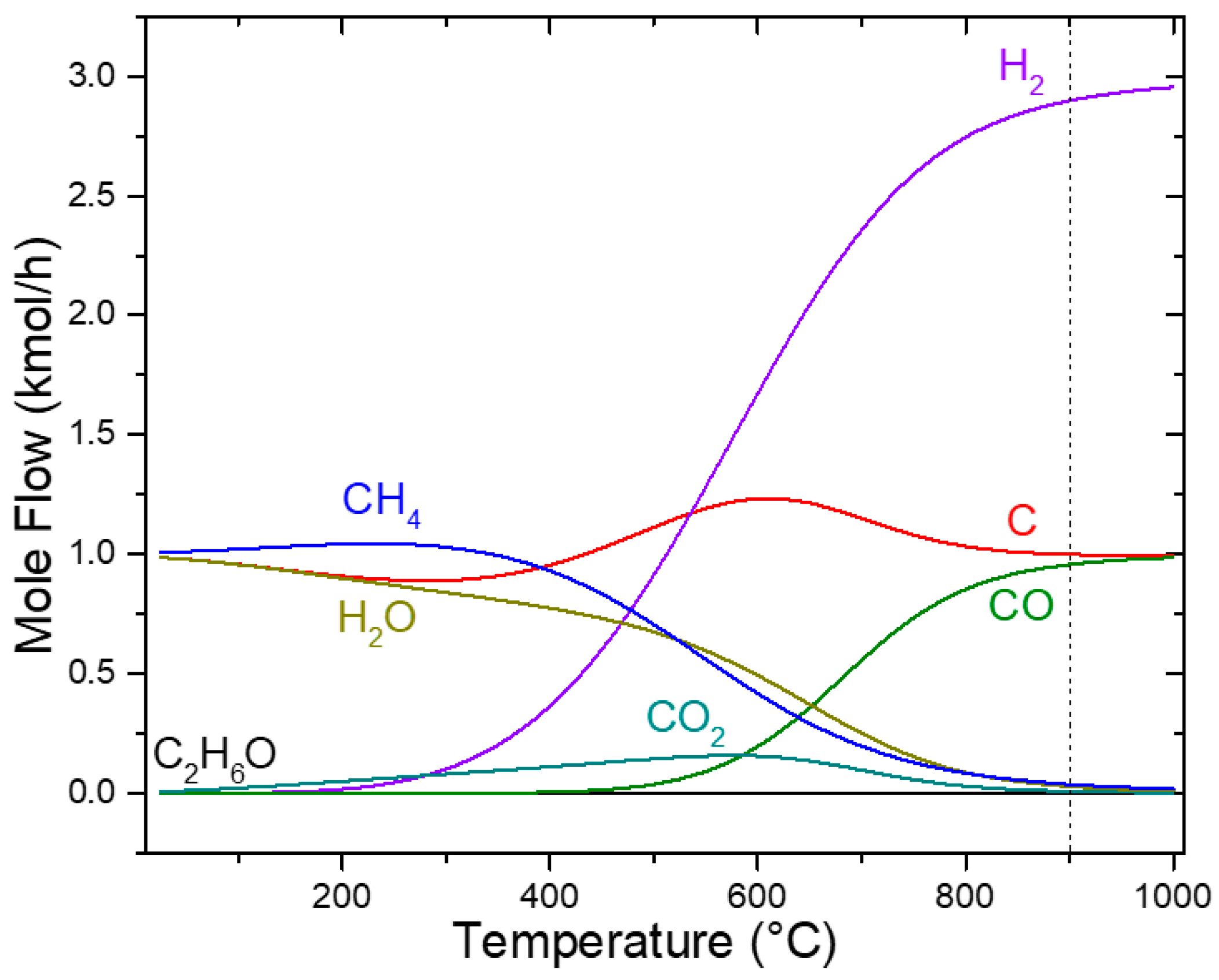
Simultaneously, the Boudouard Reaction (2) contributes to increasing CO levels at elevated temperatures, as illustrated in Figure 3. At 900 °C, these pathways collectively generated three reducing species (C, CO, and H2), which drove the reduction of SrSO4 to SrS. The highest H2 concentration was achieved between 900 and 950 °C, enhancing the reduction efficiency. This multi-stage decomposition mechanism features the effectiveness of ethanol as a reductant, enabling near-complete SrSO4 conversion with minimal environmental impact.
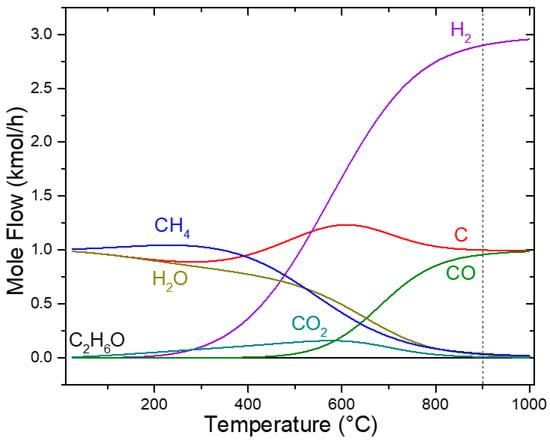
Figure 3.
Sensitivity analysis of ethanol decomposition.
Figure 2b presents a sensitivity analysis of the ethanol-driven reduction of SrSO4 (Reaction (20)). The stoichiometry of this reaction indicates that 1 kmol of SrSO4 reacts with 0.66 kmol of ethanol (C2H6O) to produce 1 kmol of SrS, 1.33 kmol of CO2, and 2 kmol of H2O, achieving a theoretical equilibrium conversion of 100%. However, at temperatures >700 °C, deviations emerged. A slight decline in SrS yield, increased CO formation, and reduced CO2 generation were observed. These trends align with the reverse Boudouard Reaction (2CO(g) ⇌ CO2(g) + C(s)), mirroring the behavior documented in the black ash method (Figure 1a). At 900 °C, the equilibrium conversion for the ethanol-based reduction (Reaction (20)) decreased slightly to 97.73%, reflecting the competing influence of secondary reactions at elevated temperatures.
While CO2 emissions persist in ethanol-mediated SrSO4 reduction, this pathway substantially mitigates hazardous byproducts such as carbon monoxide (CO) and sulfur-containing compounds (e.g., SOx), which are prevalent in conventional carbon-based reduction systems. Furthermore, the use of ethanol as a renewable feedstock enhances process sustainability by lowering the net carbon footprint relative to fossil-derived reductants [6,15]. However, the dual advantage of ethanol, consisting of reduced pollutant emissions and renewability, makes it a greener alternative for SrSO4 valorization, aligning with circular-economy principles.
3.1.5. SrSO4 Reduction Thermodynamic Comparison
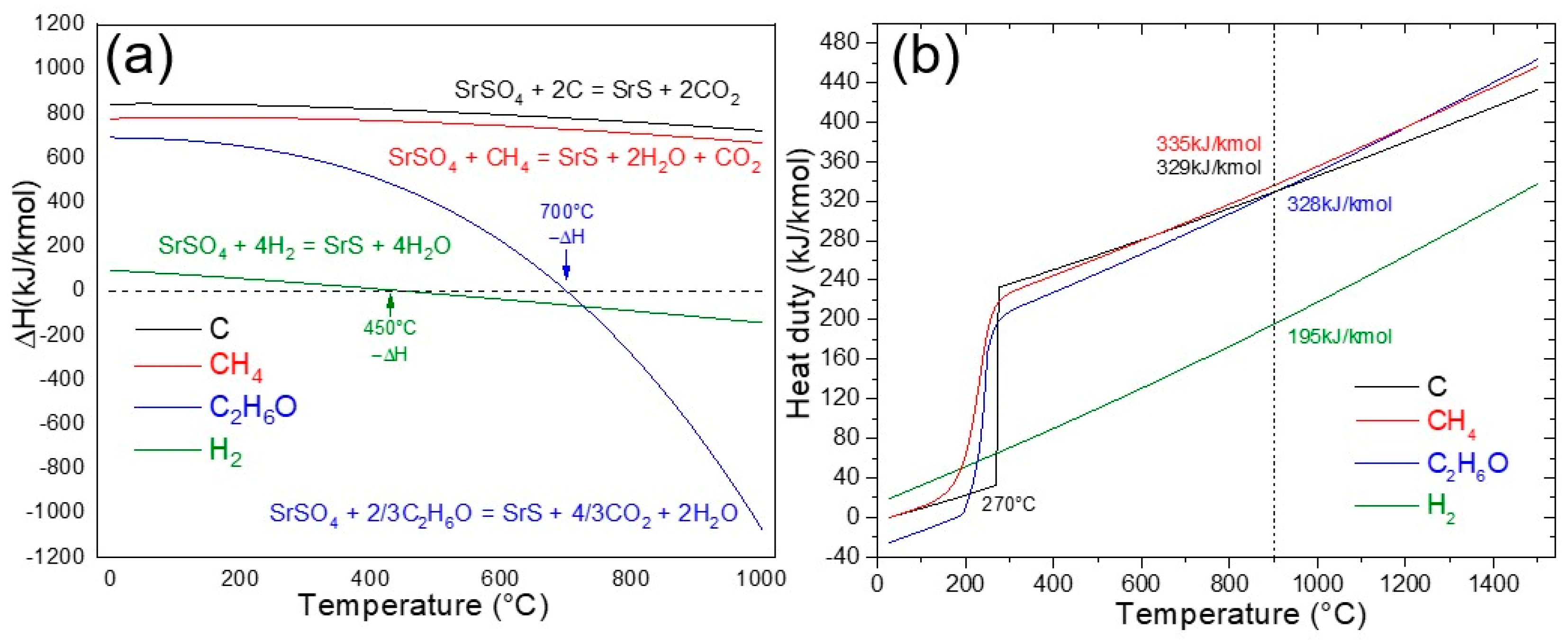
Figure 4a shows the reaction enthalpy (ΔH, kJ/mol) as a function of temperature (°C) for the reduction of SrSO4 using four distinct reducing agents: carbon (C), methane (CH4), hydrogen (H2), and ethanol (C2H6O). The analysis revealed important differences in the thermodynamic behavior of these agents. Both carbon and methane exhibit a strongly endothermic nature throughout the entire temperature range of 0–1000 °C, requiring continuous energy input to sustain the reduction process. Hydrogen, while similarly endothermic below 450 °C, transitions to a moderately exothermic regime at higher temperatures, reflecting a shift in its thermodynamic favorability.
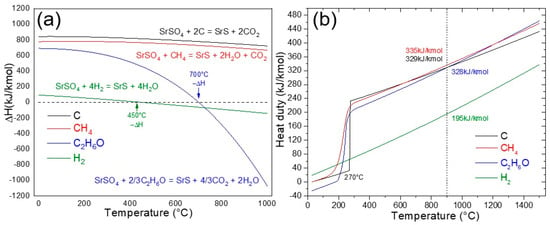
Figure 4.
(a) Reaction enthalpy and (b) Gibbs reactor heat duty for the reduction of SrSO4 using C, CH4, H2, and ethanol (C2H6O).
However, ethanol has a unique and industrially significant profile. Below 700 °C, the reduction of SrSO4 remains endothermic, aligning with conventional reductants. Remarkably, beyond this threshold, the reaction becomes strongly exothermic, reaching peak intensity near 900 °C, a temperature range in which kinetic conditions further enhance reaction rates. This dual behavior not only reduces the net energy required to drive the process at elevated temperatures but also positions ethanol as a more sustainable alternative to carbon- or methane-based methods. The exothermicity observed at high temperatures is particularly advantageous because it partially offsets the energy demands of the system, a feature absent in traditional reductants. This thermodynamic synergy between the reactivity of ethanol and energy efficiency demonstrates its potential for optimizing high-temperature industrial reduction processes.
Figure 4b shows the heat duty (kJ/kmol) required for SrSO4 reduction in a Gibbs reactor as a function of temperature (°C) across the four reducing agents: carbon (black ash method), methane, hydrogen, and ethanol. The black ash method exhibits an unusual thermal profile; at 270 °C, its heat duty surges abruptly, aligning with the onset of reactivity between carbon and SrSO4. Beyond this threshold, the energy demand increases steadily, peaking at 329 kJ/kmol at 900 °C, evidence of carbon’s persistently endothermic behavior and high operational energy cost. Methane follows a similar energy-intensive trajectory, with the heat duty escalating continuously from 200 °C, emphasizing the challenges of thermal management in methane-driven systems.
In contrast, hydrogen emerges as a comparatively efficient agent, requiring only 190 kJ/mol at 900 °C, nearly half the energy demanded by carbon or methane. However, even this reduced heat duty requires a significant external energy input, limiting its appeal for low-energy applications. However, ethanol presents a paradox: its heat duty of 328 kJ/kmol mirrors that of carbon and methane, suggesting comparable energy demands. Yet, at temperatures above 700 °C, ethanol decomposition generates carbon (C), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrogen (H2) in situ, enabling three simultaneous reduction pathways. This multi-mechanistic reactivity enhances SrSO4 conversion efficiency, effectively offsetting ethanol’s apparent energy penalty.
The interaction between the heat duty and mechanistic complexity makes ethanol a uniquely versatile reductant. While its thermal requirements align with those of conventional agents, its ability to self-generate reactive species in situ reduces reliance on external reductant feeds, offering a pathway to optimize both energy and material efficiency in high-temperature systems.
Table 2 provides a comparative analysis of heat duty, CO2 emissions, and reaction enthalpy for SrSO4 reduction at 900 °C using four reducing agents: hydrogen (H2), ethanol (C2H6O), methane (CH4), and carbon (black ash method). The data show the superior energy efficiency of hydrogen, which requires the lowest heat duty among all the agents. This positions green hydrogen produced via renewable energy as a compelling eco-friendly alternative to conventional carbon or methane-based methods, which demand significantly higher energy inputs.

Table 2.
Heat duty, conversion percentage, and CO2 generated at 900 °C by C, CH4, H2, and C2H6O.
The table further features evident contrasts in the CO2 emissions. Hydrogen uniquely generates no CO2, thus offering a zero-emission pathway. Carbon-based reduction, by contrast, produces 1.96 kmol of CO2 per kmol of SrSO4, the highest among the agents. Ethanol releases 1.33 kmol of CO2, but, crucially, its emissions originate from biological carbon cycles (e.g., plant-derived feedstocks), rendering it carbon-neutral over its lifecycle. While methane emits only 1 kmol of CO2, it lacks this renewable offset, resulting in a net-positive carbon footprint. However, this can be avoided if methane originates from biogas.
Thermodynamically, hydrogen and ethanol stand apart as the sole agents driving exothermic reactions at 900 °C. This inherent energy efficiency reduces the reliance on external heat inputs, enhancing their viability for industrial applications. Ethanol’s dual advantage—exothermicity and carbon-neutral emissions—positions it as a bridge between conventional reductants and zero-emission hydrogen. However, carbon and methane remain constrained by their endothermicity and high environmental costs, emphasizing the need to transition toward sustainable alternatives.
3.2. Microstructure and Reduction of Laboratory-Synthesized SrSO4
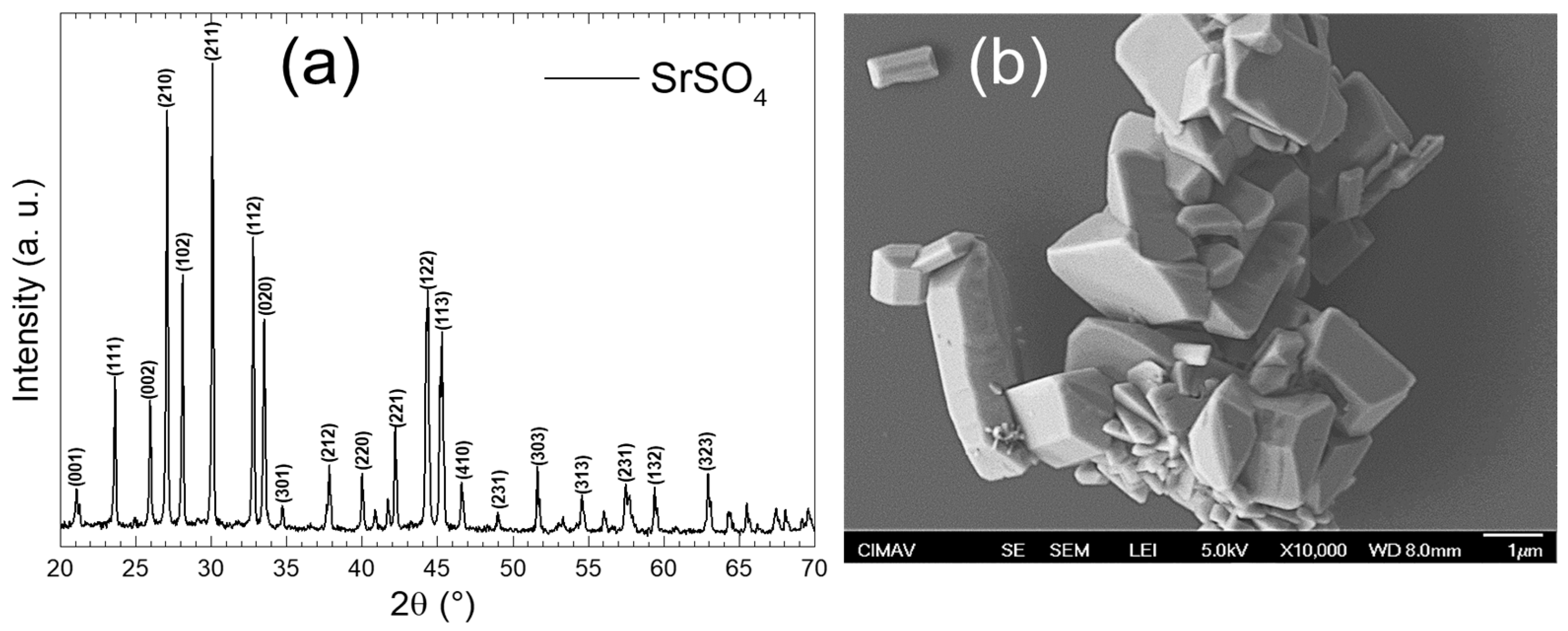
Figure 5a shows the XRD pattern of the laboratory-synthesized sample. These results indicate that SrSO4 with an orthorhombic crystalline phase was obtained, which fully matches the crystallographic card [00-005-0593]. This phase belongs to the space group Pnma (#62) and has lattice parameters of a = 6.87 Å, b = 8.371 Å, and c = 5.355 Å, a unit cell volume V = 307.96 Å3, and Z = 4. No reflections associated with the other crystalline phases were detected, confirming the purity of the material. The XRD pattern exhibited excellent crystallinity, as evidenced by sharp, well-defined, and high-intensity peaks, reflecting a highly ordered atomic arrangement [11]. This suggests minimal amorphous content and few structural defects. Furthermore, the peak intensities and positions aligned perfectly with those expected for the crystalline phase, corroborating the purity and quality of the synthesized material. On the other hand, Figure 5b presents a micrograph obtained using SEM at a magnification of 10,000×. In this image, agglomerated particles with well-defined edges and sizes in the micrometer range were observed. The absence of amorphous zones is evident because the SrSO4 particles exhibit a crystalline morphology with sharp shapes and clear edges [27]. Variability in the sizes and shapes of the crystals was noticeable, suggesting differences in the nucleation and growth conditions during synthesis. The presence of these well-defined crystalline forms confirms that SrSO4 has an ordered crystalline structure, which is consistent with the orthorhombic nature present in the XRD pattern.
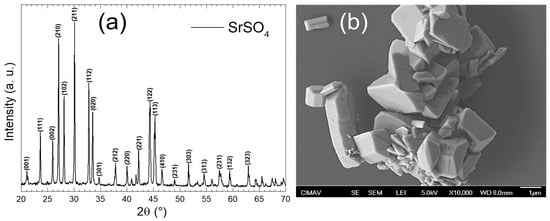
Figure 5.
(a) XRD pattern and (b) SEM micrograph of laboratory-synthesized SrSO4.
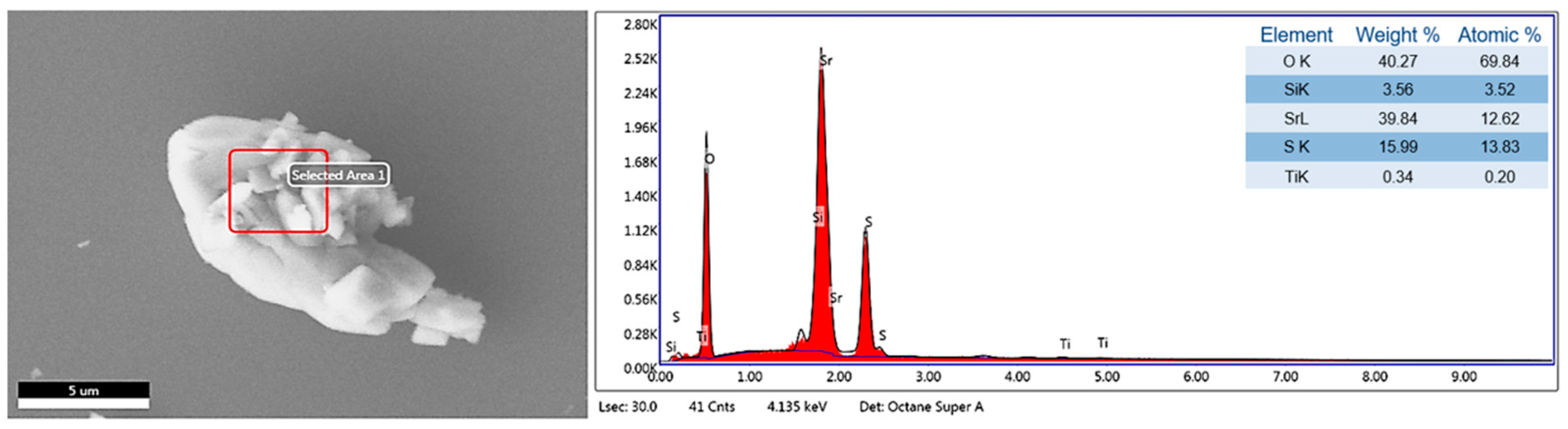
Figure 6 shows the EDS analysis of the laboratory-synthesized SrSO4 sample. The presence of oxygen (O), strontium (Sr), and sulfur (S) aligns with the expected composition of the SrSO4 phase, thereby confirming the purity of the material [28]. The detection of Silicon (Si) in the analysis was attributed to the substrates used during the sample preparation process, specifically because the sample was mounted on a monocrystalline silicon substrate for microscopy. Additionally, Titanium (Ti) is present in trace amounts, likely due to minor contamination during the analysis.
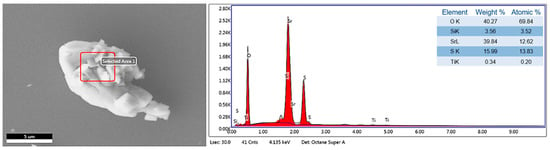
Figure 6.
EDS elemental analysis of the SrSO4 sample.
Based on the thermodynamic and environmental advantages outlined earlier, ethanol was selected as the reductant for the experimental SrSO4 reduction tests at multiple temperatures. This choice was driven not only by its carbon-neutral profile and multi-pathway reactivity, but also by the scarcity of prior studies exploring ethanol in this specific application (a gap underscored by Abu Tahari et al. [28]).
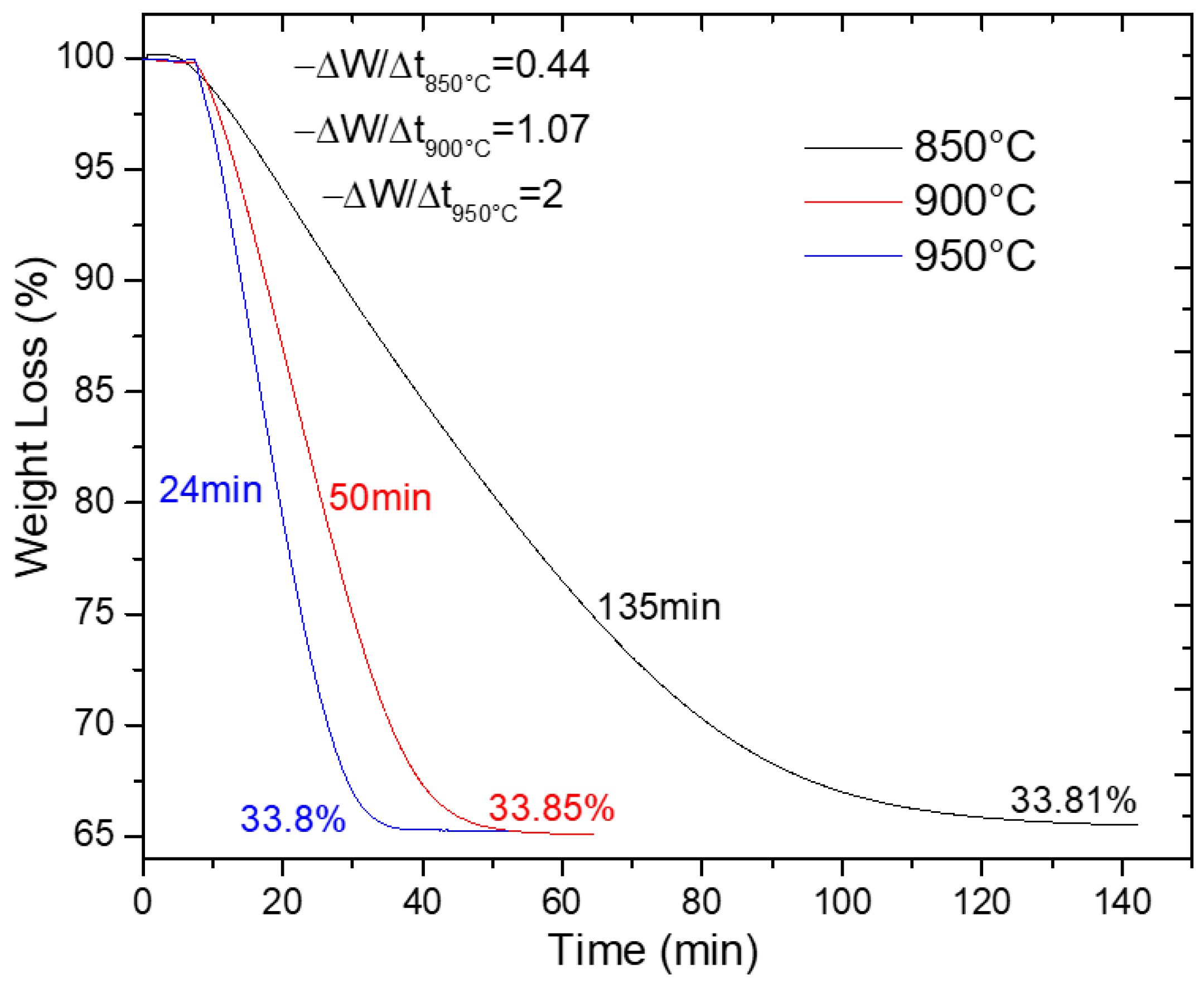
Figure 7 presents thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) results for synthesized SrSO4 reduction at 800 °C, 900 °C, and 950 °C, plotting weight change (%W) against temperature. These data confirm the efficient conversion of SrSO4 to SrS, which is a critical milestone in the production pathway. Notably, reduction times shortened dramatically at elevated temperatures (from 135 min at 800 °C to just 24 min at 950 °C, a five-fold acceleration attributed to enhanced reaction kinetics).
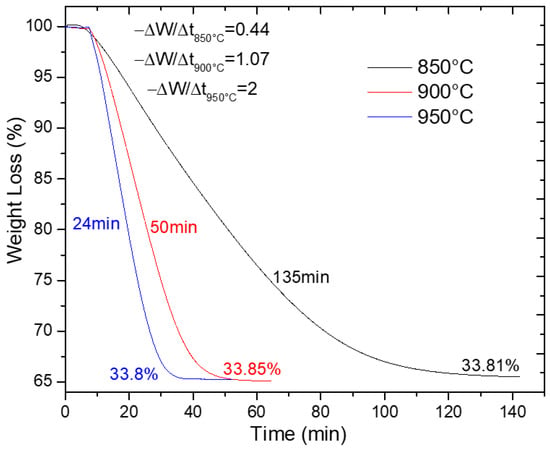
Figure 7.
SrSO4 reduction with ethanol at 850, 900, and 950 °C.
Reaction rates were quantified using the initial slope of the weight loss profile (−ΔW/Δt = −ra), revealing a clear kinetic hierarchy: 950 °C > 900 °C > 800 °C. This temperature dependence aligns with the expectations for a chemically controlled process, where thermal energy lowers the activation barriers and accelerates bond-breaking and reductant interactions. Despite these kinetic differences, all tests achieved near-identical weight losses (~33.8%), closely matching the theoretical value of 34.84%, indicating the consistent reduction efficacy of ethanol.
The 950 °C condition emerged as optimal, delivering rapid conversion without compromising yield. Consequently, this temperature was prioritized for subsequent comparative studies with other reductants. Beyond efficiency, the fast reduction kinetics of ethanol at high temperatures hold practical promise as shorter process durations translate to reduced energy consumption per batch, positioning ethanol not merely as an environmentally sound alternative but also as a cost-competitive solution for industrial scaling.
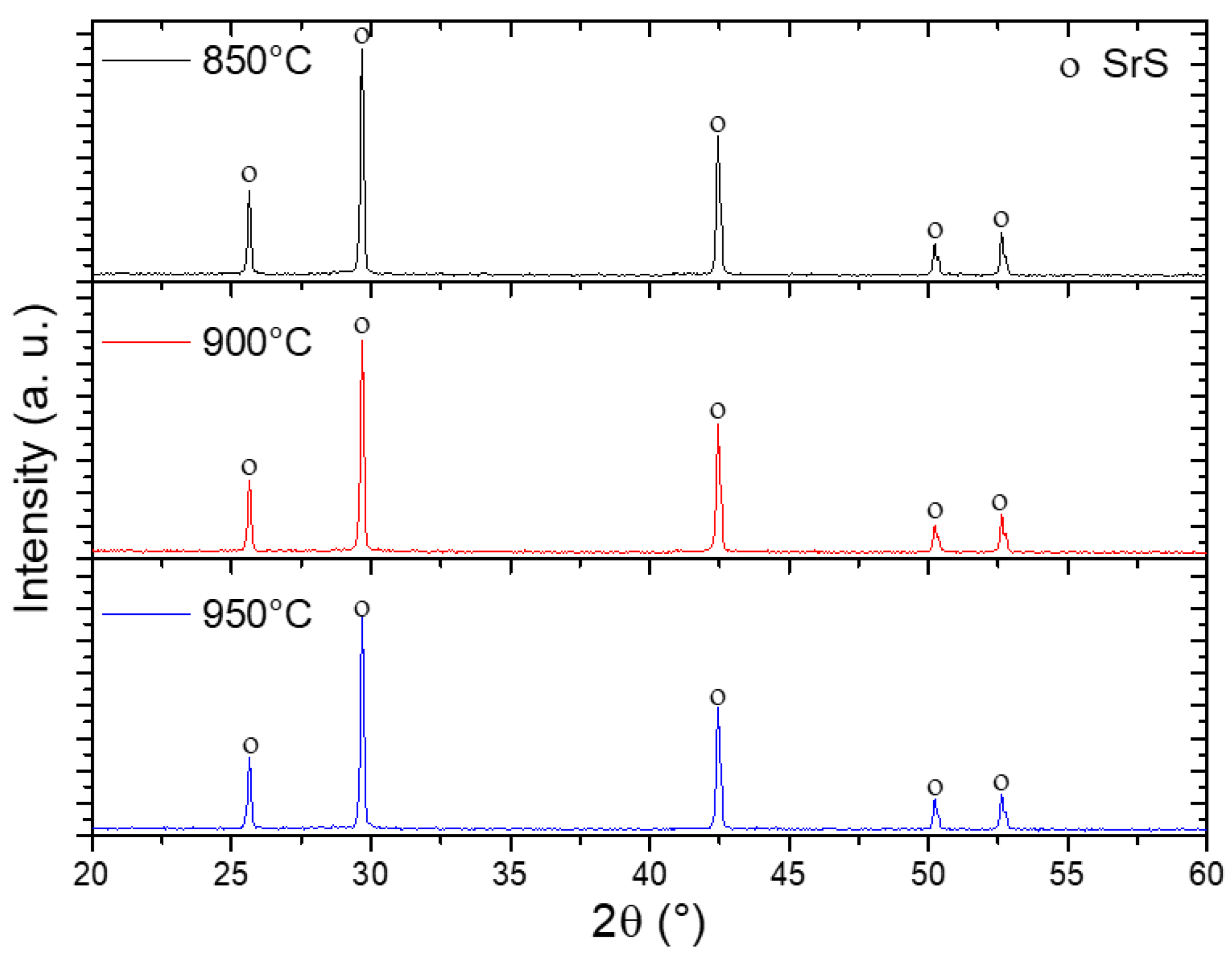
Figure 8 shows XRD patterns of SrSO4 samples after reduction with ethanol at 850, 900, and 950 °C. The presence of SrS with a cubic phase, space group Fm3m, indexed with the crystallographic card [00-008-0489] was detected at all reduction temperatures. The presence of SrS in this pattern indicates complete conversion of SrSO4.
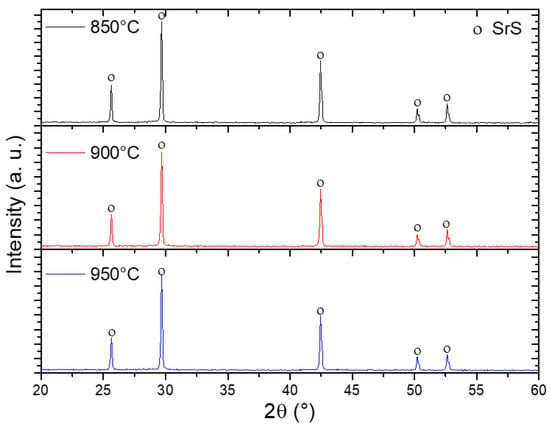
Figure 8.
XRD patterns of samples reduced with ethanol at different temperatures.
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Reducing Agents for SrSO4 Reduction
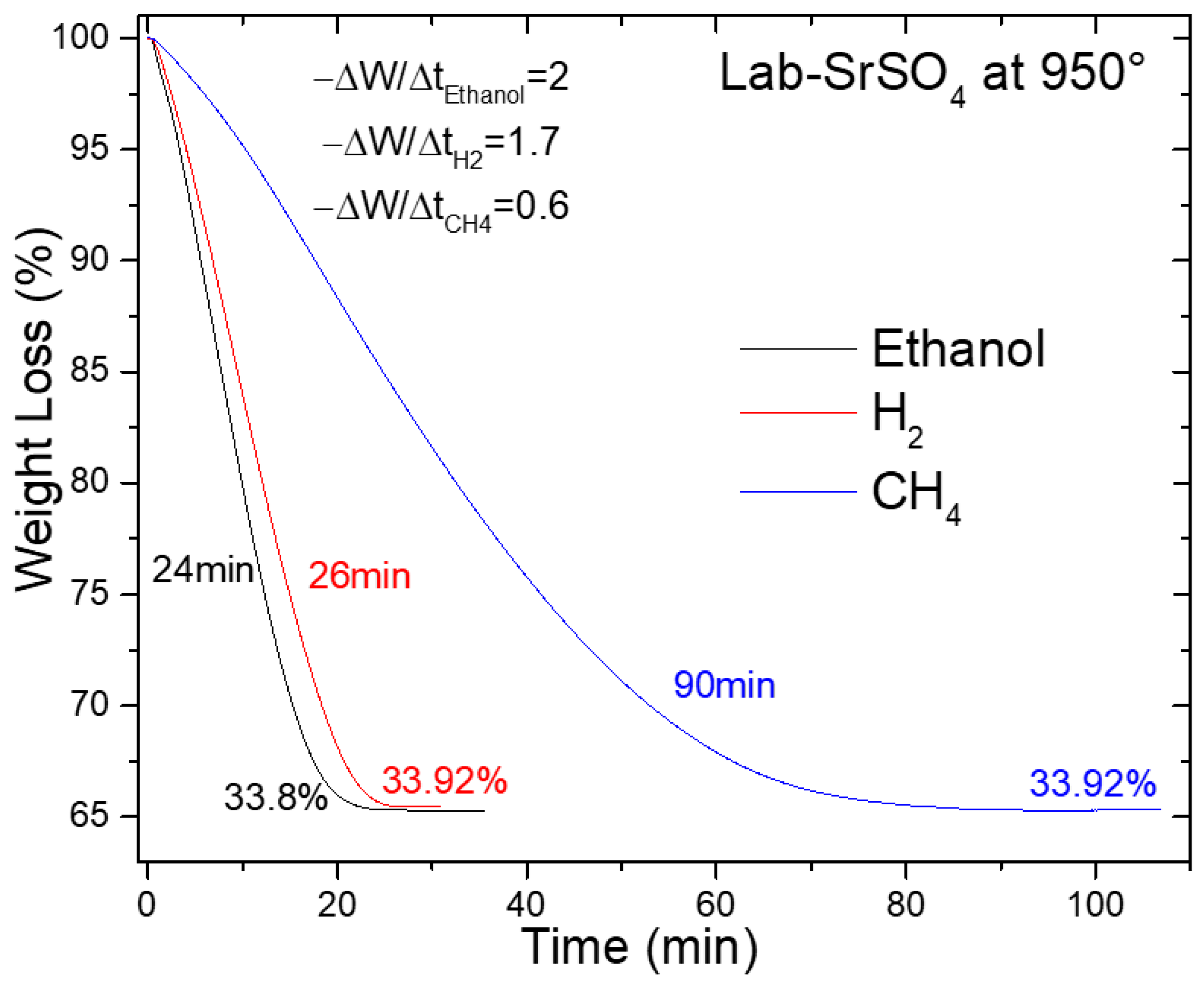
Figure 9 presents a thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) comparison of synthesized SrSO4 reduction using hydrogen (H2), ethanol (C2H6O), and methane (CH4), all evaluated at 950 °C. The plot follows the weight loss (%W) as a function of the reduction time, revealing evident contrasts in the kinetic efficiency among the agents.
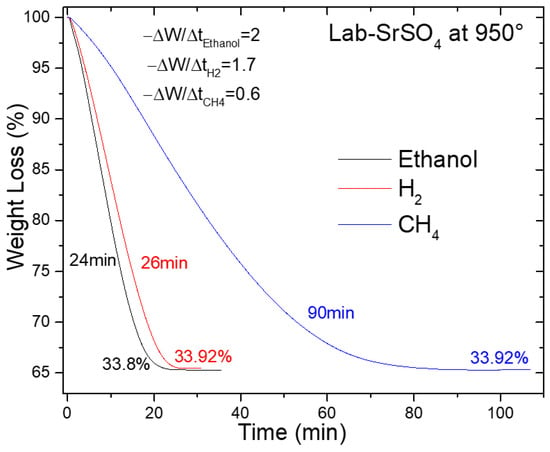
Figure 9.
SrSO4 reduction at 950 °C with ethanol, hydrogen, and methane.
Ethanol and hydrogen emerged as frontrunners, achieving complete reduction at 24 and 26 min, respectively. These times remarkably outperform traditional methods. The black ash process, for instance, requires 30 min at 1300 °C using 50% excess coke [29], whereas methane-based reductions require 90 min under similar conditions. Even more striking is the comparison with historical benchmarks, such as the 4.3 h reduction reported by Panek and Fitzner [18] and the 8 h duration cited by Wang et al. [19] for hydrogen-driven processes (Table S2).
The kinetic superiority is further quantified by the initial apparent reaction rate (−ra) derived from the linear slope of weight loss profiles. Ethanol leads with −ra = 2.0 min−1, followed closely by hydrogen at 1.7 min−1, both far exceeding methane’s sluggish 0.6 min−1. This hierarchy aligns with the agents’ mechanistic behavior. Ethanol decomposition generates CO and H2 in situ, enabling simultaneous gas- and solid-phase reduction pathways that accelerate SrSO4 conversion. Hydrogen, while lacking multi-pathway advantages, benefits from its inherently high reactivity. Methane, in contrast, suffers from kinetic limitations inherent to its stable C–H bonds, which prolong the reduction time.
The implications are twofold. First, ethanol’s rapid kinetics, achieved without extreme temperatures, suggest significant energy savings compared with the black ash method, which operates at 1300 °C. Second, the parity between ethanol and hydrogen highlights the potential of bioethanol as a renewable carbon-neutral alternative to fossil-derived reductants. Although biomethane remains a possible option, its impractical reaction time renders it unsuitable for industrial scaling.
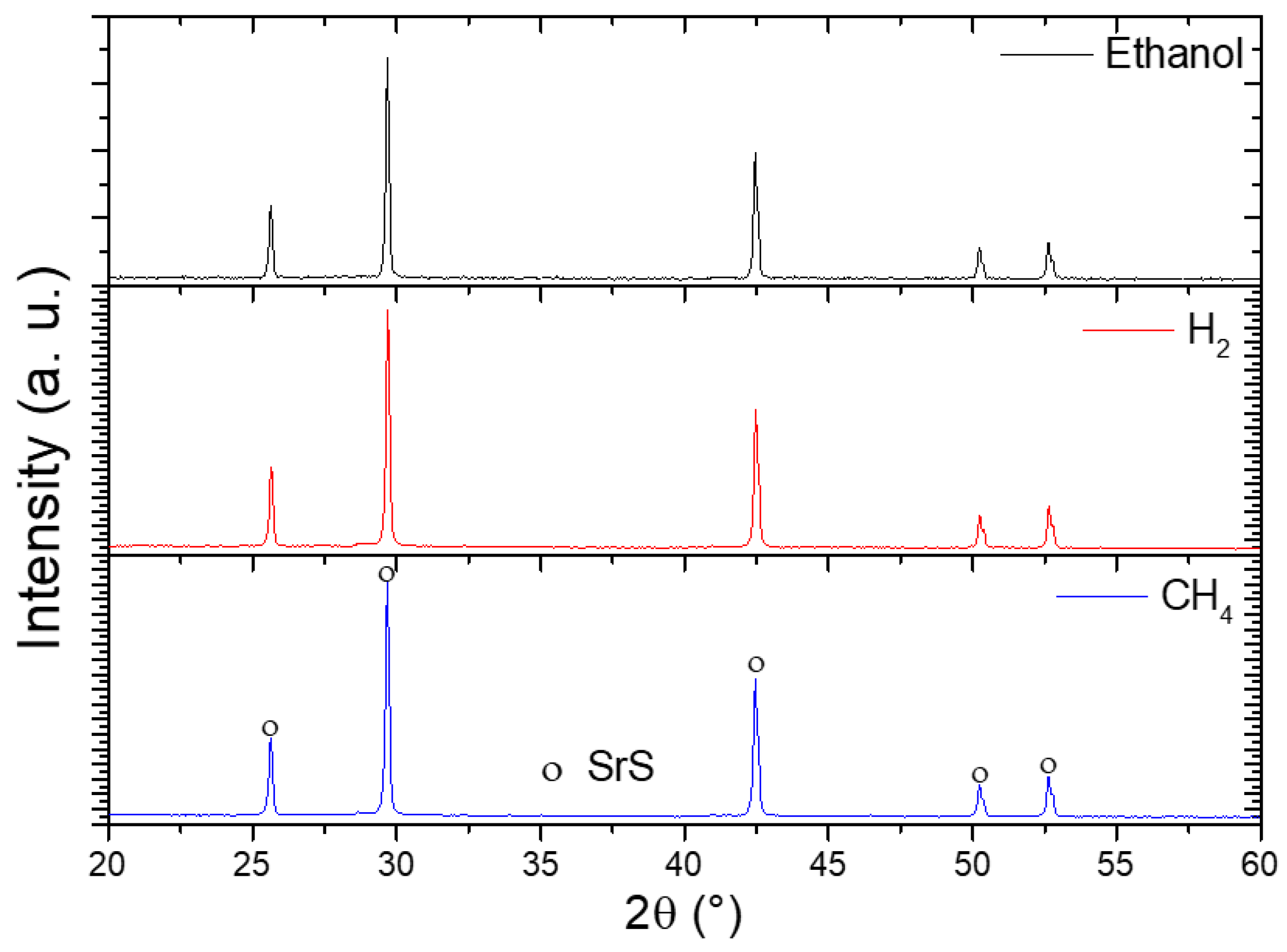
Figure 10 presents the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the synthesized SrSO4 sample following reduction with ethanol, hydrogen, and methane at 950 °C. The analysis conclusively identified SrS as the sole crystalline product in all cases, exhibiting a well-defined cubic phase (space group Fm3m) that aligned precisely with the reference crystallographic pattern ([00-008-0489]). Notably, the diffraction peaks corresponding to SrS remain consistent across all three reducing agents, with no detectable secondary phases or residual SrSO4 observed. This uniformity confirmed that the reduction pathway, whether driven by ethanol, hydrogen, or methane, yielded SrS as the exclusive solid product, emphasizing the robustness and selectivity of the process under the tested conditions.
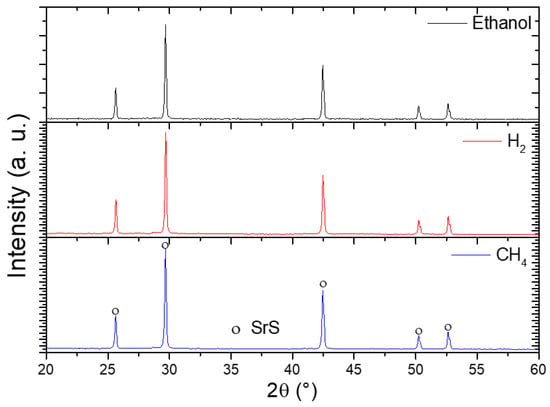
Figure 10.
XRD patterns of SrSO4 reduced with ethanol, hydrogen, and methane at 950 °C.
The structural fidelity of SrS across diverse reductants highlights the thermodynamic stability of its cubic phase at elevated temperatures, whereas the absence of competing byproducts reinforces the reliability of these reducing agents for targeted SrSO4 conversion. These findings provide a critical validation for industrial applications seeking adaptable and consistent methods to produce high-purity SrS.
In summary, this comparative analysis positions ethanol and hydrogen as transformative agents for SrSO4 reduction, balancing high reaction rates, efficiency, and sustainability, a critical advancement for industries seeking to decarbonize high-temperature processes. Consequently, ethanol at a temperature of 950 °C was selected for conducting further celestite ore reduction tests.
3.4. Reduction of Celestite Ore with Ethanol
3.4.1. Elemental Composition
Celestite ore typically contains between 80% and 95% SrSO4 by weight, depending on the extraction zone. Results obtained by ICP-OES analysis are presented in Table 3, showing the elemental content by weight of the mineral components. These results indicate a predominance of Sr content related to the SrSO4 phase in celestite ore as well as the presence of elements corresponding to the BaSO4, CaSO4, SrCO3, CaCO3, and Al2O3 phases. The sample reduced with ethanol at 950 °C fairly exhibits the stoichiometry corresponding to the obtained SrS, confirming the reduction of the mineral. The presence of Ba (2.23%wt) is attributed to the BaS phase that formed due to the BaSO4 decomposition in the original mineral.

Table 3.
ICP-OES results for celestite ore and the ethanol-reduced sample.
3.4.2. Microstructural Celestite Ore Characterization
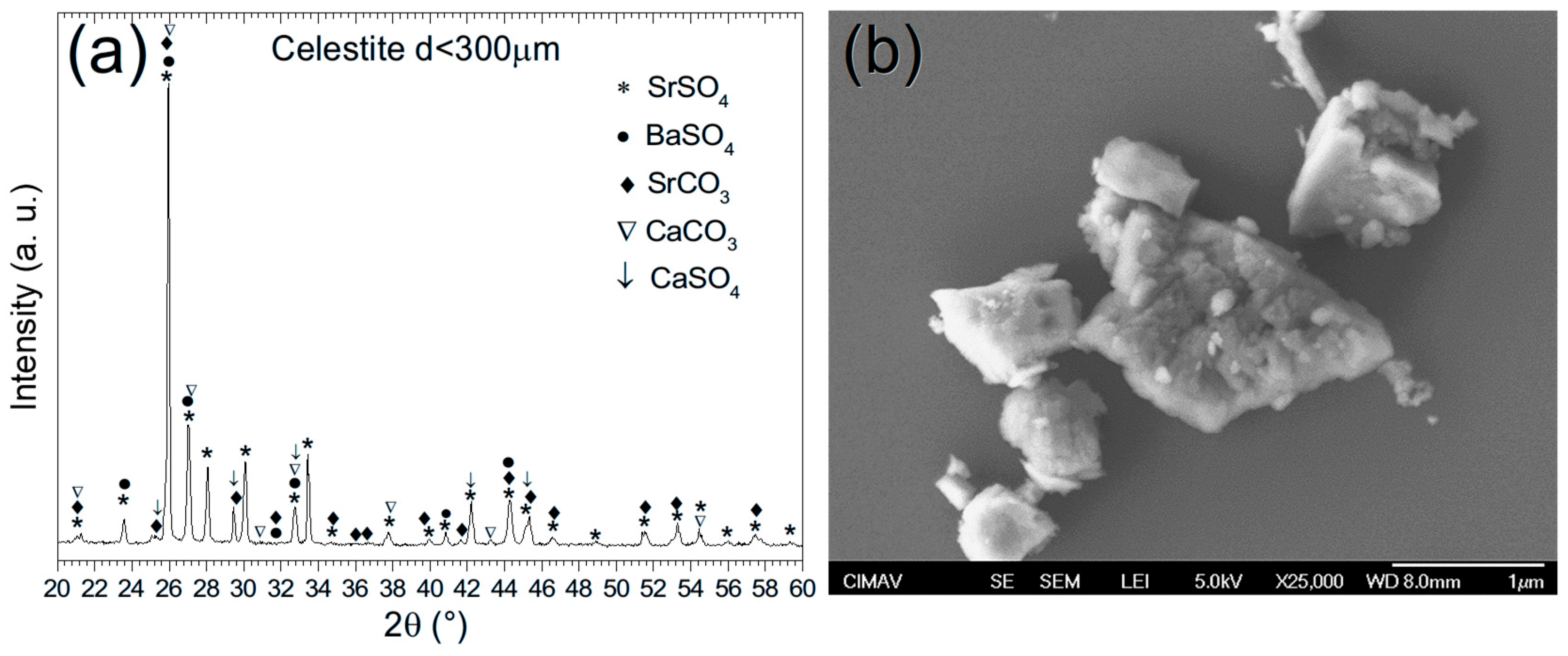
Figure 11a displays the X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of celestite sampled from Cuatro Ciénegas, Coahuila. The analysis reveals the presence of five distinct crystalline phases, marked by their corresponding symbols: (*) strontium sulfate (SrSO4), (●) barium sulfate (BaSO4), (♦) strontium carbonate (SrCO3), (∇) calcium carbonate (CaCO3), and (↓) calcium sulfate (CaSO4). All phases exhibit an orthorhombic crystal structure, consistent with the barite-type classification [30], and were indexed using crystallographic reference cards (SrSO4 [00-005-0593], BaSO4 [00-024-1035], SrCO3 [00-005-0418], CaCO3 [00-041-1475], and CaSO4 [00-083-0437]). Rietveld refinement quantified the relative contents of these phases as follows: SrSO4 (88.29%), BaSO4 (2.22%), SrCO3 (3.69%), CaCO3 (5.38%), and CaSO4 (0.425%). Particularly, earlier studies on celestite from the same region [31] reported a comparable composition dominated by SrSO4 (76.43%), with minor phases including SrCO3 (13.24%), CaCO3 (8.04%), and BaSO4 (2.20%). However, the current analysis identified an additional CaSO4 phase, although in trace amounts (0.425%), which was not documented in prior work. This discrepancy may reflect subtle variations in sample mineralogy or advances in the analytical resolution.
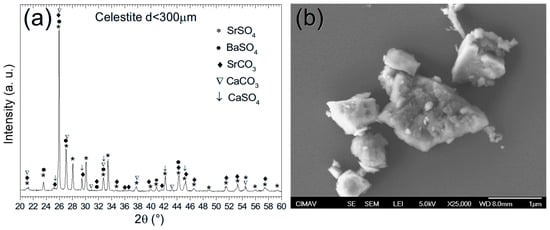
Figure 11.
(a) XRD pattern and (b) SEM micrograph of celestite ore.
Figure 11b presents a scanning electron microscopy (SEM) micrograph of the celestite ore captured at 25,000× magnification. The image features the mineral’s defining morphological details, consistent with strontium sulfate (SrSO4) as documented in barite-group sulfates. Well-defined crystalline structures dominate the micrograph, characterized by sharp geometric edges and a pronounced variation in particle dimensions, indicative of the natural growth history of the mineral. Angular and block-shaped morphologies, typical of sulfate minerals, were prominently observed, with particle sizes ranging from submicron fragments to larger, irregular aggregates. This heterogeneity aligns with findings from analogous studies [32], emphasizing how dynamic environmental conditions, such as shifts in temperature, pressure, or impurity influx (e.g., BaSO4, CaSO4, CaCO3), influenced crystallization. Such variables likely modulate the nucleation rates and crystal growth dynamics, yielding the observed diversity in size, shape, and textural complexity.
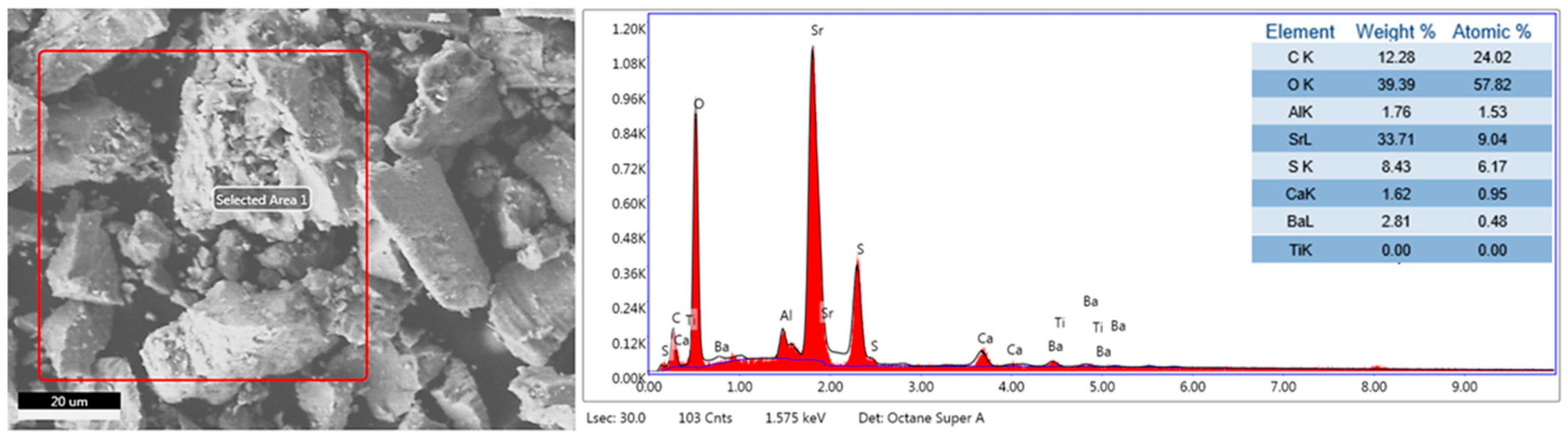
Furthermore, the EDS elemental analysis is shown in Figure 12, where the following elements were identified: C, O, Al, Sr, S, Ca, and Ba. These results confirm the presence of the following XRD phases: SrSO4, BaSO4, SrCO3, CaCO3, and CaSO4. Additionally, the presence of Al in the ore was attributed to the presence of Al2O3 in small, undetectable percentages by XRD.
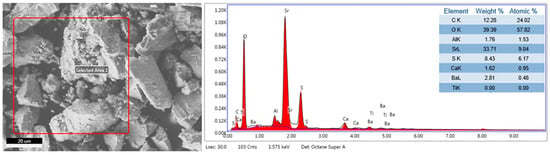
Figure 12.
EDS elemental analysis of celestite mineral ore.
3.4.3. Thermal Pretreatment
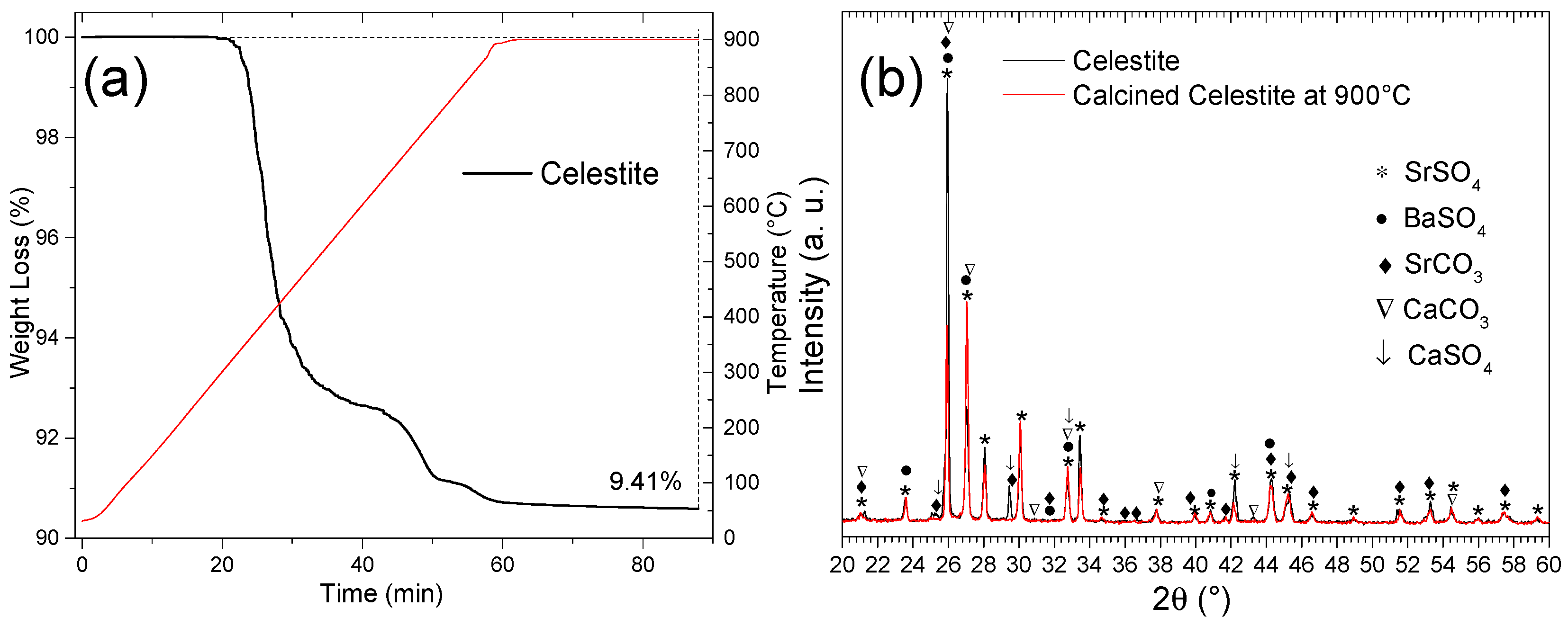
To remove impurities, such as carbonates and sulfates, which decompose below 900 °C, celestite particles (d < 300 µm) were calcined in a thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA) under an argon atmosphere. The temperature was increased from ambient to 900 °C at a rate of 15 °C/min, followed by a 30 min isothermal hold. As shown in Figure 13a, this process resulted in a total weight loss of 9.41%, consistent with the decomposition of SrCO3 and CaSO4 phases [32]. The reaction pathway aligns with the double decomposition mechanism of Reaction (17).
SrCO3 + CaSO4 = SrSO4 + CaCO3 ΔHR° = +0.003 kJ/mol
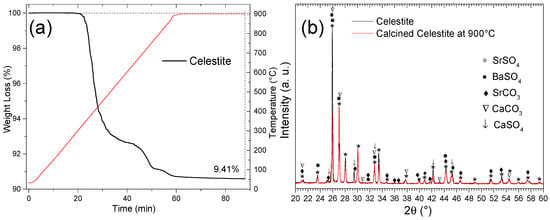
Figure 13.
(a) Calcination (TGA) of celestite (d < 300 µm) at 900 °C in an Ar atmosphere and (b) XRD diffractograms of natural and calcined celestite at 900 °C.
Figure 13b compares the XRD patterns of raw and calcined celestite (900 °C, Ar). Noticeable changes include the disappearance of peaks corresponding to SrCO3 (♦) and CaSO4 (↓) as well as reduced intensity for CaCO3 (∇), which undergoes decomposition at elevated temperatures [32]. Simultaneously, reflections associated with SrSO4 exhibit increased intensity in the calcined sample, confirming its stability and dominance post-treatment. These observations demonstrate the effectiveness of calcination in purifying celestite by selectively eliminating the thermally unstable phases.
3.4.4. Reduction Evaluation by TGA
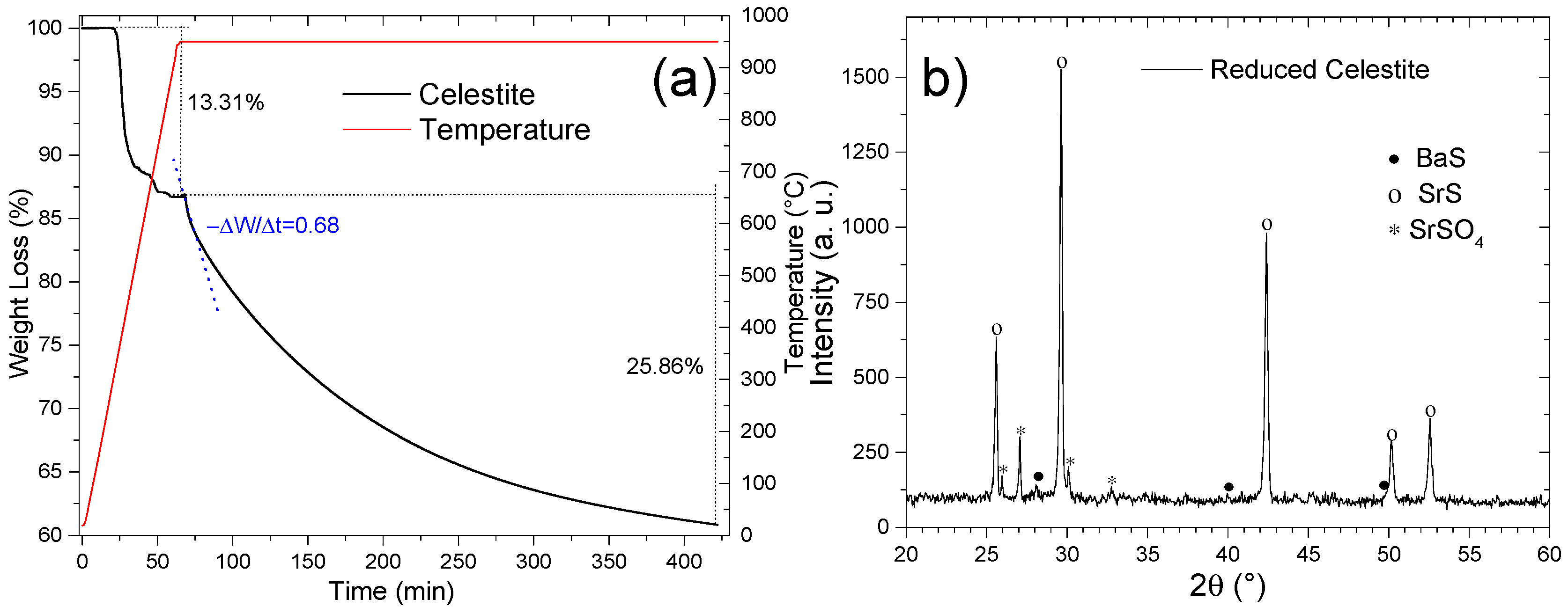
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) of natural celestite under ethanol-mediated reduction (Figure 14a) delineates two distinct mass-loss regimes. The initial 13.31% mass decline corresponds to the decomposition of thermally unstable phases—strontium carbonate (SrCO3), calcium sulfate (CaSO4), and calcium carbonate (CaCO3)—formed during pretreatment. The subsequent 25.86% mass loss is ascribed to the partial reduction of SrSO4 to SrS, achieving 74.2% conversion efficiency relative to the theoretical SrSO4-to-SrS mass loss (34.84%). This discrepancy is attributed to the concurrent reduction of barium sulfate (BaSO4) to BaS, as corroborated by the ICP-OES data and previous studies [15,16,33]. The post-reduction XRD analysis (Figure 14b) corroborates these findings, revealing dominant SrS [00-008-0489], minor BaS [00-075-0896], and residual SrSO4 [00-005-0593] phases, the latter emphasizing incomplete conversion.
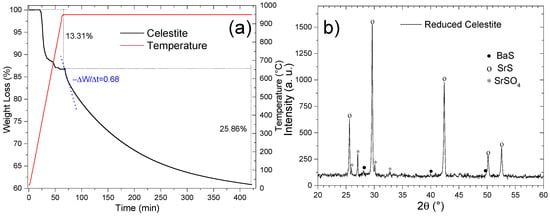
Figure 14.
(a) TGA and (b) XRD diffractogram of celestite reduced at 950 °C with ethanol.
The reduction kinetics at 950 °C exhibited an initial rate of 0.64 min−1, necessitating 6 h to attain substantial conversion. This duration aligns with conventional celestite reduction processes but contrasts with faster methodologies. For instance, the black ash process at 1000 °C in rotary kilns requires ~420 min (7 h) for complete conversion, whereas methane-assisted reduction (50% concentration, 950 °C) achieves 57.4% conversion in 110 min [15]. Notably, hydrogen reduction (100% H2, 1000 °C) achieved full SrS conversion within 50 min [18], highlighting the influence of reductant reactivity and process conditions.
While the present study demonstrates the feasibility of ethanol as a reductant, its slower kinetics compared with H2 or CH4 may reflect inherent limitations in ethanol’s reducing capacity or diffusional barriers under static conditions. Nevertheless, ethanol-mediated reduction offers a proof of concept for sustainable alternatives to conventional high-temperature or high-reductant-concentration methods. However, industrial scalability warrants further investigation, particularly for optimizing reactor configurations (e.g., rotary kilns) and ethanol concentrations to enhance mass transfer and reaction efficiency.
3.5. Proposed Reaction Mechanism
The reduction of celestite (SrSO4) via bioethanol proceeds through the well-defined reaction mechanism (12) supported by TDM and the dual role of bioethanol as a carbon and hydrogen donor. At elevated temperatures, bioethanol undergoes thermal decomposition according to
to yield a reactive syngas mixture of carbon monoxide (CO) and hydrogen (H2). These gases drive the reduction of SrSO4 via two parallel pathways.
2C2H6O + O2 → 4CO + 6H2 Δ HR° = +12.217 kJ/mol
SrSO4 + 4CO → SrS + 4CO2 ΔHR° = −143.348 kJ/mol
SrSO4 + 3H2 → SrS + 4H2O ΔHR° = −155.581 kJ/mol
This synergistic mechanism enhances the reaction efficiency by leveraging both reducing agents, whereas the renewable origin of bioethanol partially offsets CO2 emissions through carbon cycle closure. Crucially, the liquid phase of bioethanol and the lack of ash-forming impurities (e.g., SiO2 and Al2O3) suppress side reactions that generate toxic SO2 (a persistent drawback of solid reductants such as coke). Experimental validation confirms >75% SrSO4 conversion at 950 °C, a significant improvement over carbothermal methods requiring 1100–1200 °C, alongside 30–50% and 60–80% reductions in CO2 and SOx emissions, respectively.
3.5.1. Challenges and Comparative Advantages
Despite its potential, the proposed mechanism has practical limitations. Bioethanol decomposition requires a substantial energy input, even at lower temperatures than conventional processes. Catalytic promoters (e.g., Ni, Fe3O4) may be necessary to optimize gas utilization and kinetics, introducing cost and operational complexity. Scalability is further hindered by bioethanol’s competition with food-grade ethanol markets and the need to retrofit the infrastructure designed for solid reductants.
The comparative analysis focused on the intermediate practicality of bioethanol. Although hydrogen reduction achieves full conversion at 1000 °C in 50 min [18], its high storage and infrastructure costs limit its industrial feasibility. Methane-assisted reduction (57.4% conversion in 110 min at 950 °C [15]) outperformed bioethanol in kinetics but failed to match its emission profile or renewable synergy. Thus, bioethanol represents a balance, avoiding fossil-derived emissions while integrating into existing supply chains more seamlessly than hydrogen.
3.5.2. Toward Sustainable Strontium Chemistry
The proposed bioethanol-mediated mechanism bridges the gap between traditional SrS production and sustainable metallurgy. By combining renewable carbon cycles and dual reduction pathways, this study addresses the critical gaps in energy efficiency and emissions. However, industrial adoption hinges on advances in catalytic systems, reactor design (e.g., rotary kilns for enhanced mass transfer), and sustainable bioethanol sourcing. As decarbonization priorities intensify, this approach could redefine Sr chemistry, positioning it within the vanguard of green technology innovation.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrates the successful reduction of synthetic SrSO4 and natural celestite to SrS using sustainable reductants, with bioethanol emerging as a high-performance alternative. Ethanol achieved 97% conversion efficiency for synthetic SrSO4 at 950 °C within 24 min and 74% efficiency for pretreated celestite ore over 6 h, emphasizing its viability for both pure and mineral-based feedstocks. Significantly, thermal pretreatment (900 °C) eliminated carbonate/sulfate impurities, addressing kinetic barriers in raw celestite.
Replacing coal with bioethanol reduces reliance on fossil-derived reductants, decreases CO2 emissions, and lowers energy demands, aligning with global decarbonization targets. The liquid-phase nature of ethanol further simplifies process control, enabling precise dosing and operational flexibility.
As SrS is a crucial precursor for SrCO3 (essential in electronics, energy storage, and luminescent materials), this ethanol-driven process offers dual industrial advantages: enhancing production efficiency while advancing cleaner chemical transformations. Future work should prioritize scalable reactor designs (e.g., rotary kilns) to optimize gas–solid interactions and secure bioethanol supply chains, ensuring both economic and environmental sustainability.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/reactions6020028/s1, Figure S1: Flowsheet of the Gibbs-type reactor in the TDM; Figure S2: SrS as a platform for synthesizing various strontium compounds with diverse applications; Table S1: Chemical composition of mineral celestite from various sources; Table S2: Celestite ore (SrSO4) reduction methods in the literature. Refs. [34,35,36] cited in Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, formal analysis, writing—original draft preparation, J.E.M.-M.; formal analysis, A.B.J.-S.; methodology and investigation, J.L.D.-A.; visualization, B.C.H.-M.; validation, J.L.B.-E.; conceptualization, supervision, and writing—review and editing, A.L.-O.; project administration, V.H.C.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to express their sincere gratitude for the infrastructural support provided by Centro de Investigación en Materiales Avanzados S. C. (CIMAV). The authors would also like to express gratitude to the CIMAV staff members Andrés Isaak González Jacquez for the XRD analysis and César Cutberto Leyva Porras for the SEM-EDS analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| TDM | Thermodynamic Modeling |
| SA | Sensitivity analysis |
| ICP-OES | Inductively Coupled Plasma–Optical Emission Spectroscopy |
| SEM-EDS | Scanning Electron Microscopy–Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy |
| XRD | X-Ray Diffraction |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric Analysis |
References
- Abbas, W.; Mahmood, A.; Al-Masry, W.; Dunnill, C.W. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Strontium Sulfide/Nitrogen-Graphene Quantum Dot Composites for next-Generation Supercapattery Devices. Chalcogenide Lett. 2024, 21, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Duan, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, E. Research on the Distribution of S Species in the Pressure Oxidation Leaching Process of SrS Solution. Miner. Eng. 2023, 201, 108163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, D.; Gowda, V.; Ortega, F.; Bhadani, K.; Ariza-Rodríguez, N.; Asbjörnsson, G.; Brito-Parada, P.R. Strontium Minerals as Critical Raw Materials—Market Dynamics, Processing Techniques, and Future Challenges. Miner. Eng. 2025, 220, 109065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sánchez, F.; Camprubí, A.; González-Partida, E.; Puente-Solís, R.; Canet, C.; Centeno-García, E.; Atudorei, V. Regional Stratigraphy and Distribution of Epigenetic Stratabound Celestine, Fluorite, Barite and Pb–Zn Deposits in the MVT Province of Northeastern Mexico. Min. Depos. 2009, 44, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.-J.; Seo, Y. Production and Supply of Raw Materials for Radiometals Used in Radionuclide Imaging and Therapy in Korea. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2025, 59, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S. Method for Modifying Celestite High Temperature Reduction by Adding Catalyst. CN200310100262.7, 15 October 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, F.; Mancha, H. Reducción directa de minerales de celestita con monóxido de carbono. Rev. Metalurgia 1995, 31, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukiennik, M.; Malinowski, C.; Małecki, S. Kinetics of SrSO4 Reduction by Means of (CO + CO2) Gas Mixtures. Arch. Metall. 2024, 47, 81–93. [Google Scholar]
- Amirzadeh-Asl, D. Procedure for the Production of Barium or Strip Sulphide. ITMI981745, 20 July 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sonawane, R.S.; Apte, S.K.; Kale, B.B.; Dongare, M.K. Effect of a Catalyst on the Kinetics of Reduction of Celestite (SrSO4) by Active Charcoal. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2000, 31, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obut, A. Direct Conversion of Celestine to SrS by Microwave Heating. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 1320–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Mendoza, J.E.; Domínguez-Arvizu, J.L.; Hernández-Majalca, B.C.; Bueno-Escobedo, J.L.; López-Ortiz, A.; Collins-Martínez, V. Sustainable Mechanosynthesis and Reduction of Strontium Sulfate to Obtain Strontium Sulfide and Strontium Aluminates; Vide Leaf: Hyderabad, India, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Setoudeh, N.; Welham, N.J. Ball Milling Induced Reduction of SrSO4 by Al. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2011, 98, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setoudeh, N.; Welham, N.J. Mechanochemical Reduction of SrSO4 by Mg. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2012, 104–105, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale Ebrahim, H.; Jamshidi, E. Kinetic Study of Celestite Reduction by Methane. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2009, 118, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostamizadeh, M.A.; Afsahi, M.M.; Mousavi, M. Effect of Steam on the Barium Sulfate Reduction by Methane. Thermochim. Acta 2023, 730, 179610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, R.; Jamshidi, E.; Ale Ebrahim, H. Catalytic Effect of Zinc Oxide on the Reduction of Barium Sulfate by Methane. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 460, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panek, Z.; Fitzner, K. Determination of Phase Stability in the Sr-S-O System. Thermochim. Acta 1987, 113, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. Method for Producing High-Purity Strontium Carbonate by Using Hydrogen Metallurgy Technology. CN115432728B, 11 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel Halim, K.S.; Ibrahim, S.S.; El-Barawy, K.A. Isothermal Reduction Behaviour of Celestite Concentrate by Solid Carbon. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2009, 118, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Liu, F.; Liu, J.; Pan, F.; Fan, C.; Zhang, J. A Green Process for Producing Na2S from Waste Na2SO4 through Hydrogen Agglomerate Fluidized Bed Reduction of BaSO4. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 355, 131816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.Y.; Savic, M.; Padilla, R.; Han, G. A Novel Reaction System Involving BaS and BaSO4 to Elemental Sulfur without Generating Pollutants: Part II. Kinetics of the Hydrogen Reduction of BaSO4 to BaS. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 5088–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.A.; Hellier, P.; Ladommatos, N.; Almaleki, A. Pyrolytic Decomposition of Methanol, Ethanol, and Butanol at Various Temperatures and Residence Times in a High-Temperature Flow Reactor. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2024, 177, 106346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Saidi, M. Hydrogen-Rich Syngas Production via Integrated Configuration of Pyrolysis and Air Gasification Processes of Various Algal Biomass: Process Simulation and Evaluation Using Aspen Plus Software. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 18844–18856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roine, A. HSC Chemistry, Version 6.0 [Software]; Metso: Pori, Finland, 2023.
- Rodríguez-Carvajal, J. Recent Advances in Magnetic Structure Determination by Neutron Powder Diffraction. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1993, 192, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sun, R.; Xia, Z.; Du, H. Facile Room Temperature Morphology-Controlled Synthesis of SrSO4 Microcrystals. CrystEngComm 2012, 14, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Tahari, M.N.; Salleh, F.; Tengku Saharuddin, T.S.; Samsuri, A.; Samidin, S.; Yarmo, M.A. In-fluence of Hydrogen and Carbon Monoxide on Reduction Behavior of Iron Oxide at High Temper-ature: Effect on Reduction Gas Concentrations. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 24791–24805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemoğlu, M.; Canbazoğlu, M. The Leaching of SrS with Water and the Precipitation of SrCO3 from Leach Solution by Different Carbonating Agents. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 49, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanor, J.S. A Model for the Origin of Large Carbonate- and Evaporite-Hosted Celestine (SrSO4) Deposits. J. Sediment. Res. 2004, 74, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillejos, A.H.E.; de la Cruz del, F.P.B.; Uribe, A.S. The Direct Conversion of Celestite to Strontium Carbonate in Sodium Carbonate Aqueous Media. Hydrometallurgy 1996, 40, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Için, K.; Öztürk, S.; Sünbül, S.E. Investigation and Characterization of High Purity and Nano-Sized SrCO3 Production by Mechanochemical Synthesis Process. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 33897–33911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, R.; Bilen, A.; Hizli, İ.G.; Ertürk, S.; Arslan, C. Direct Conversion of Celestite to SrCO3 by Wet Milling. In TMS 2017 146th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings, San Diego, CA, USA, 26 February–2 March 2017; The Minerals, Metals &. Materials Society TMS, Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 609–614. [Google Scholar]
- Hessien, M.M.; Rashad, M.M.; Hassan, M.S.; El-Barawy, K. Synthesis and Magnetic Properties of Strontium Hexaferrite from Celestite Ore. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 476, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendón-Angeles, J.C.; Matamoros-Veloza, Z.; López-Cuevas, J.; Perez-Garibay, R.; Diaz-Algara, J.; Yanagisawa, K. Rotary-Hydrothermal Method Assisting the Conversion of Celestine into Scheelite SrWO4 in Alkaline Solutions. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 148, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylska, D.; Grzyb, T. Synthesis and Up-Conversion of Core/Shell SrF2:Yb3+,Er3+@SrF2:Yb3+,Nd3+ Nanoparticles under 808, 975, and 1532 Nm Excitation Wavelengths. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 831, 154797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).