Radiomics-Based Machine Learning Models Improve Acute Pancreatitis Severity Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
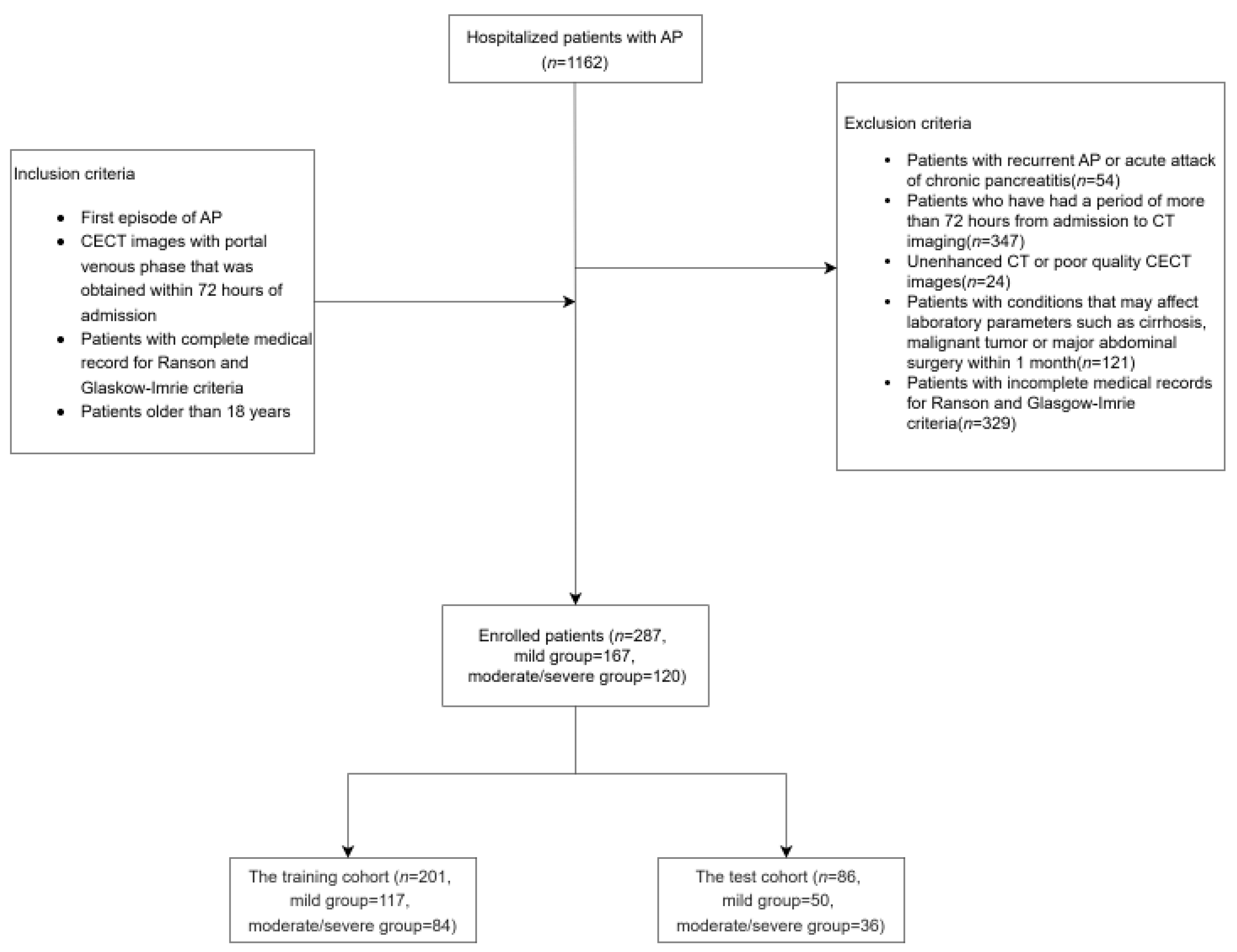
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
- Patients aged ≥ 18 years.
- First episode of AP.
- CECT with portal venous phase acquired within 72 h of admission.
- Complete medical records for Ranson and Glasgow-Imrie scoring.
- Incomplete medical records for Ranson and Glasgow-Imrie scoring.
- History of recurrent AP or acute exacerbations of chronic pancreatitis.
- Conditions potentially affecting laboratory results, including cirrhosis, malignancy, or major abdominal surgery within the past month.
- CECT was performed more than 72 h after admission.
- Unenhanced or poor-quality CECT images.
2.2. CT Image Acquisition
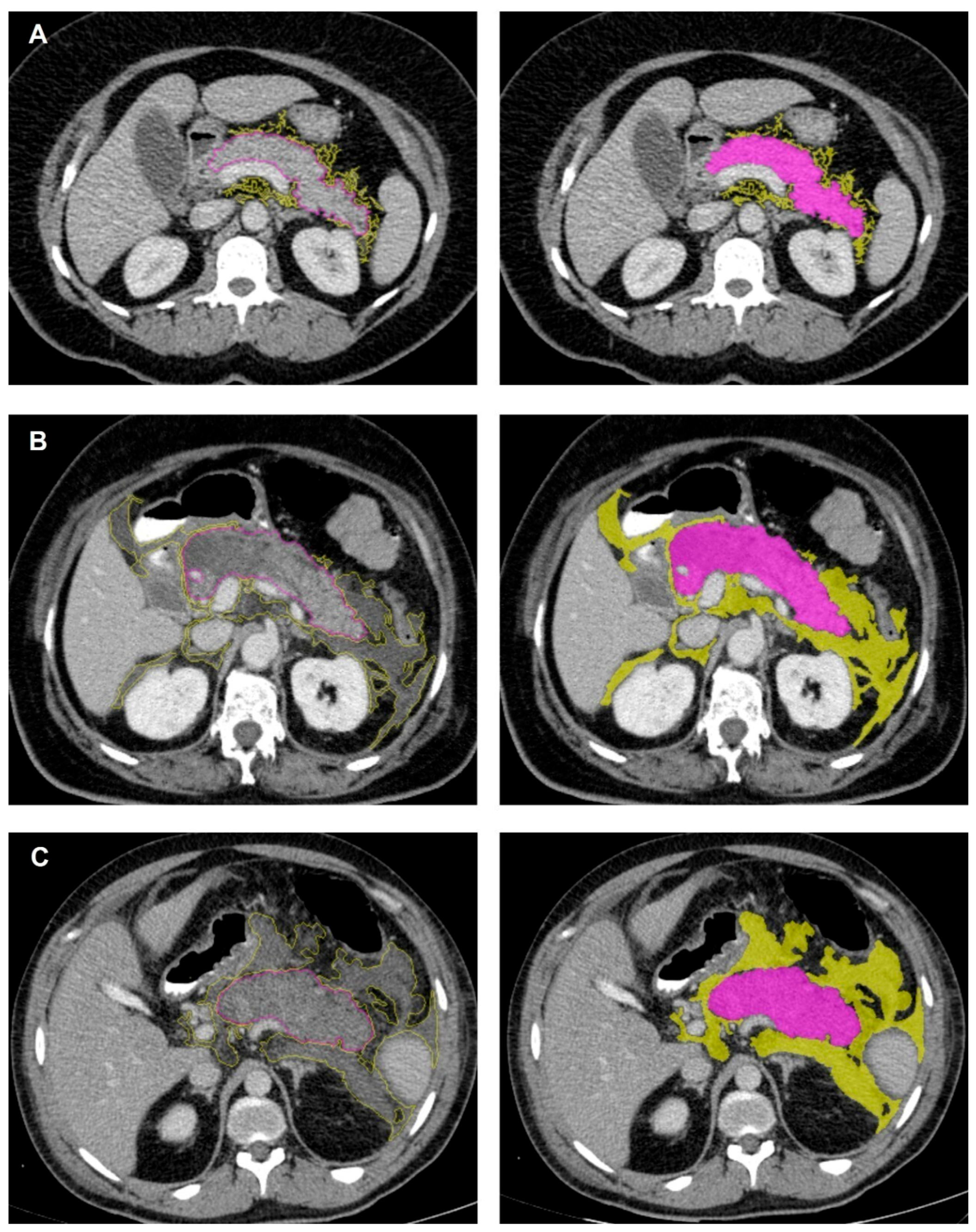
2.3. CT Image Interpretation and Feature Extraction
2.4. Intra-Observer Reliability and Inter-Observer Agreement
2.5. Feature Selection
2.6. Classification with Machine Learning Algorithms
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szatmary, P.; Grammatikopoulos, T.; Cai, W.; Huang, W.; Mukherjee, R.; Halloran, C.; Beyer, G.; Sutton, R. Acute pancreatitis: Diagnosis and treatment. Drugs 2022, 82, 1251–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, M.S.; Yadav, D. Global epidemiology and holistic prevention of pancreatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habtezion, A.; Gukovskaya, A.S.; Pandol, S.J. Acute pancreatitis: A multifaceted set of organelle and cellular interactions. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1941–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S. Classification of acute pancreatitis2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2012, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papachristou, G.I.; Muddana, V.; Yadav, D.; O’COnnell, M.; Sanders, M.K.; Slivka, A.; Whitcomb, D.C. Comparison of BISAP, Ranson’s, APACHE-II, and CTSI scores in predicting organ failure, complications, and mortality in acute pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 105, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Cho, C.M. Predicting severity of acute pancreatitis. Med. Kaunas 2022, 58, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capurso, G.; de Leon Pisani, R.P.; Lauri, G.; Archibugi, L.; Hegyi, P.; Papachristou, G.I.; Pandanaboyana, S.; Maisonneuve, P.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; De-Madaria, E. Clinical usefulness of scoring systems to predict severe acute pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis with pre and post-test probability assessment. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2023, 11, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharwani, N.; Patel, S.; Prabhudesai, S.; Fotheringham, T.; Power, N. Acute pancreatitis: The role of imaging in diagnosis and management. Clin. Radiol. 2010, 66, 164–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanier, B.W.M.; Nio, Y.; Van der Hulst, R.W.M.; Tuynman, H.A.R.E.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.W.; Bruno, M.J. Practice and yield of early CT scan in acute pancreatitis: A Dutch observational multicenter study. Pancreatology 2010, 10, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenner, B.; Chari, S.T.; Kelsen, D.; Klimstra, D.S.; Pandol, S.J.; Rosenthal, M.; Rustgi, A.K.; Taylor, J.A.; Yala, A.; Abul-Husn, N.; et al. Artificial intelligence and early detection of pancreatic cancer: 2020 summative review. Pancreas 2021, 50, 251–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinesh, M.G.; Bacanin, N.; Askar, S.S.; Abouhawwash, M. Diagnostic ability of deep learning in detection of pancreatic tumour. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Jha, D.; Biswas, K.; Zhang, Z.; Velichko, Y.; Yazici, C.; Tirkes, T.; Borhani, A.; Turkbey, B.; Medetalibeyoglu, A.; et al. Detection of peri-pancreatic edema using deep learning and radiomics techniques. In Proceedings of the 46th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Orlando, FL, USA, 15–19 July 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bette, S.; Canalini, L.; Feitelson, L.-M.; Woźnicki, P.; Risch, F.; Huber, A.; Decker, J.A.; Tehlan, K.; Becker, J.; Wollny, C.; et al. Radiomics-based machine learning model for diagnosis of acute pancreatitis using computed tomography. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nioche, C.; Orlhac, F.; Boughdad, S.; Reuzé, S.; Goya-Outi, J.; Robert, C.; Pellot-Barakat, C.; Soussan, M.; Frouin, F.; Buvat, I. LIFEx: A freeware for radiomic feature calculation in multimodality imaging to accelerate advances in the characterization of tumor heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4786–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, J.H.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsmark, C.E.; Baillie, J. AGA Institute technical review on acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2022–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, J.; Xiao, B.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, Y.; He, W. Early prediction of acute pancreatitis severity based on changes in pancreatic and peripancreatic computed tomography radiomics nomogram. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.; Ji, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, H.; Yang, D.; Chen, A.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X.M. Radiomics model of contrast-enhanced MRI for early prediction of acute pancreatitis severity. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 51, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Wang, Z.-Q.; Liu, G.-Y.; Zhang, X.-M. Chest computed tomography semi-quantitative pleural effusion and pulmonary consolidation are early predictors of acute pancreatitis severity. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2020, 10, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxhoorn, L.; Voermans, R.P.; Bouwense, S.A.; Bruno, M.J.; Verdonk, R.C.; Boermeester, M.A.; van Santvoort, H.C.; Besselink, M.G. Acute pancreatitis. Lancet 2020, 396, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Category | Total (n, %) | Training (n, %) | Test (n, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild AP 1 | 167 (58.2%) | 117 (70.1%) | 50 (29.9%) |
| Moderate/Severe AP 1 | 120 (41.8%) | 84 (70.0%) | 36 (30.0%) |
| Total | 287 | 201 | 86 |
| Characteristic | Mild | Moderate-Severe | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total (n = 287) | n = 167 | % | n = 120 | % | |
| Age (median, range) | 53 (18–92) | 55(24–96) | 0.383 | ||
| Sex | 0.039 | ||||
| Female | 86 | 51.5 | 47 | 39.2 | |
| Male | 81 | 48.5 | 73 | 60.8 | |
| Atlanta 1 AP type | <0.001 | ||||
| Edematous | 166 | 99.4 | 38 | 31.7 | |
| Necrotizing | 1 | 0.6 | 82 | 68.3 | |
| Obesity | 83 | 49.7 | 47 | 39.2 | 0.077 |
| Hypertension | 73 | 43.7 | 58 | 48.3 | 0.438 |
| Hepatic steatosis | 59 | 35.3 | 43 | 35.8 | 0.930 |
| Etiology | |||||
| Gallstones | 68 | 40.7 | 56 | 46.7 | 0.313 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 30 | 18 | 14 | 11.7 | |
| Alcohol | 1 | 0.6 | 2 | 1.6 | |
| Other | 68 | 40.7 | 48 | 40 | |
| 2 AKI | 0 | 0 | 13 | 10.8 | <0.001 |
| 2 AKI, at 48th Hours | 2 | 1.2 | 13 | 10.8 | <0.001 |
| Fluid loss > 4/6 * L within 48 h | 17 | 10.2 | 59 | 49.2 | <0.001 |
| 3 MODS | 0 | 0 | 9 | 7.5 | <0.001 |
| Death, within 1 month | 1 | 0.6 | 13 | 10.8 | <0.001 |
| Scoring System | 1 AUC | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | 2 F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ranson at Admission | 0.593 | 0.589 | 0.483 | 0.665 | 0.509 | 0.496 |
| Ranson at 48 h | 0.696 | 0.669 | 0.508 | 0.784 | 0.629 | 0.562 |
| Cumulative Ranson | 0.677 | 0.627 | 0.600 | 0.635 | 0.541 | 0.569 |
| Glasgow-Imrie | 0.663 | 0.645 | 0.575 | 0.695 | 0.575 | 0.575 |
| Model | Group | 1 AUC | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | Precision | 7 F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 LR | Training | 0.825 | 0.751 | 0.746 | 0.786 | 0.702 | 0.723 |
| Test | 0.746 | 0.686 | 0.555 | 0.780 | 0.645 | 0.597 | |
| 3 RF | Training | 0.876 | 0.801 | 0.833 | 0.778 | 0.729 | 0.778 |
| Test | 0.747 | 0.733 | 0.833 | 0.660 | 0.638 | 0.723 | |
| 4 SVM | Training | 0.791 | 0.751 | 0.655 | 0.820 | 0.724 | 0.688 |
| Test | 0.777 | 0.721 | 0.528 | 0.860 | 0.730 | 0.613 | |
| 5 ANN | Training | 0.826 | 0.736 | 0.667 | 0.786 | 0.655 | 0.661 |
| Test | 0.767 | 0.686 | 0.528 | 0.800 | 0.728 | 0.612 | |
| 6 kNN | Training | 0.653 | 0.607 | 0.631 | 0.675 | 0.582 | 0.606 |
| Test | 0.677 | 0.674 | 0.694 | 0.660 | 0.595 | 0.641 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karkas, A.Y.; Durak, G.; Babacan, O.; Cebeci, T.; Uysal, E.; Aktas, H.E.; Ilhan, M.; Medetalibeyoglu, A.; Bagci, U.; Cakir, M.S.; et al. Radiomics-Based Machine Learning Models Improve Acute Pancreatitis Severity Prediction. AI 2025, 6, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6040080
Karkas AY, Durak G, Babacan O, Cebeci T, Uysal E, Aktas HE, Ilhan M, Medetalibeyoglu A, Bagci U, Cakir MS, et al. Radiomics-Based Machine Learning Models Improve Acute Pancreatitis Severity Prediction. AI. 2025; 6(4):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6040080
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarkas, Ahmet Yasin, Gorkem Durak, Onder Babacan, Timurhan Cebeci, Emre Uysal, Halil Ertugrul Aktas, Mehmet Ilhan, Alpay Medetalibeyoglu, Ulas Bagci, Mehmet Semih Cakir, and et al. 2025. "Radiomics-Based Machine Learning Models Improve Acute Pancreatitis Severity Prediction" AI 6, no. 4: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6040080
APA StyleKarkas, A. Y., Durak, G., Babacan, O., Cebeci, T., Uysal, E., Aktas, H. E., Ilhan, M., Medetalibeyoglu, A., Bagci, U., Cakir, M. S., & Erturk, S. M. (2025). Radiomics-Based Machine Learning Models Improve Acute Pancreatitis Severity Prediction. AI, 6(4), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/ai6040080







