- Article
Multi-Agent Transfer Learning Based on Evolutionary Algorithms and Dynamic Grid Structures for Industrial Applications
- Marlon Löppenberg,
- Steve Yuwono and
- Andreas Schwung
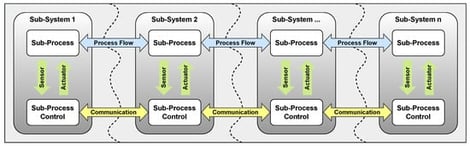
Distributed production systems have to increasingly balance economic goals such as energy efficiency and productivity with critical technical requirements such as flexibility, real-time capability, and reliability. This paper presents a novel approach for distributed optimization by means of Evolutionary State-based Potential Games with dynamic grid structures. More in detail, we leverage the combination of Potential Games which provide rigorous convergence guarantees with population-based optimization to improve the efficiency of the learning process. Specifically, we address challenges of previous approaches including inefficient best response strategies, insufficient coverage of the state–action space and the lack of knowledge transfer among agents. The developed strategies are evaluated on a industrial system of laboratory scale. The results highlight advances in evolutionary state-based knowledge transfer and an improved coverage resulting in efficient control policies. By leveraging dynamic grid structures, Evolutionary State-based Potential Games enable the maximization of weighted production targets while simultaneously eliminating process losses resulting in improvements in the considered metrics compared to state-of-the-art methods.
6 February 2026