Risk Assessment in Landslide-Prone Terrain within a Complex Geological Setting at Kadugannawa, Sri Lanka: Implications for Highway Maintenance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
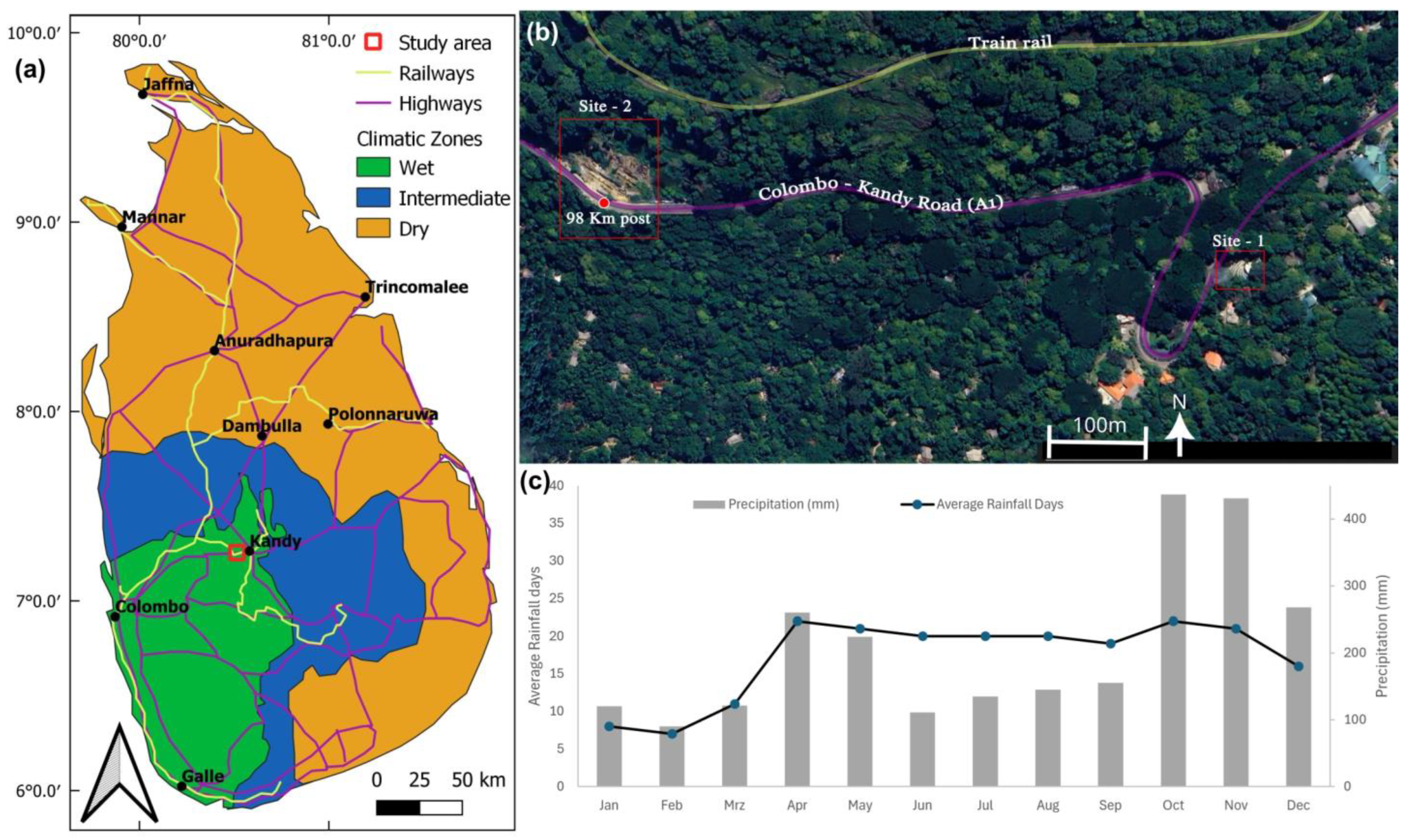
2. General Setting of the Study Area
2.1. Climate, Geomorphology, and Vegetation
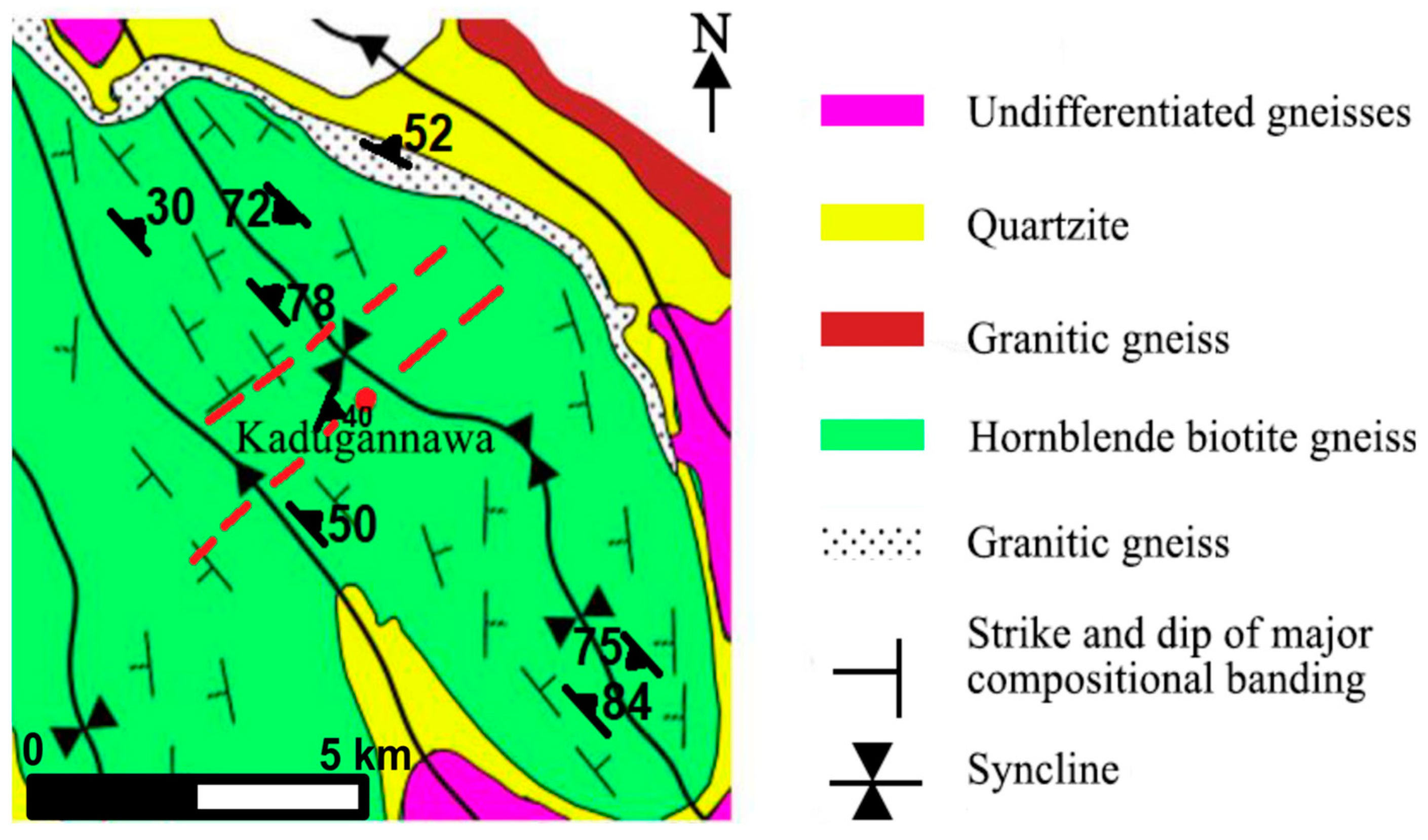
2.2. Geological Setting and Subsurface Conditions
3. Methodology
4. Results and Discussion
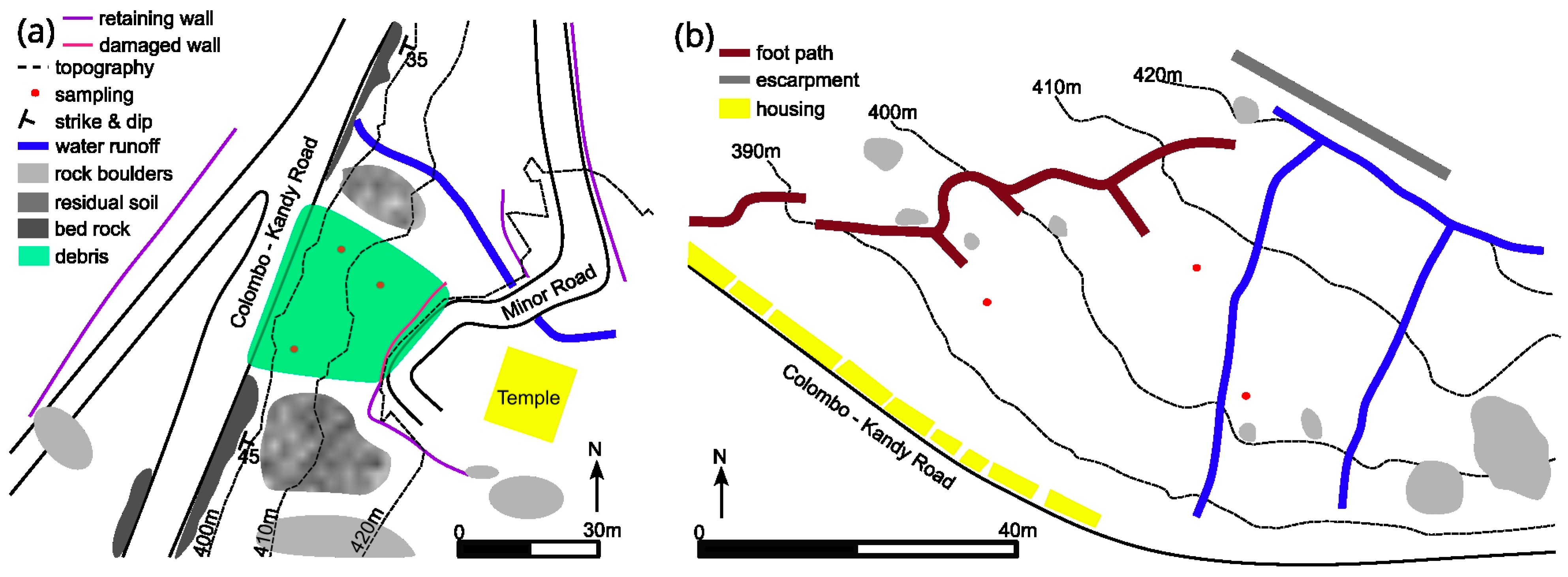
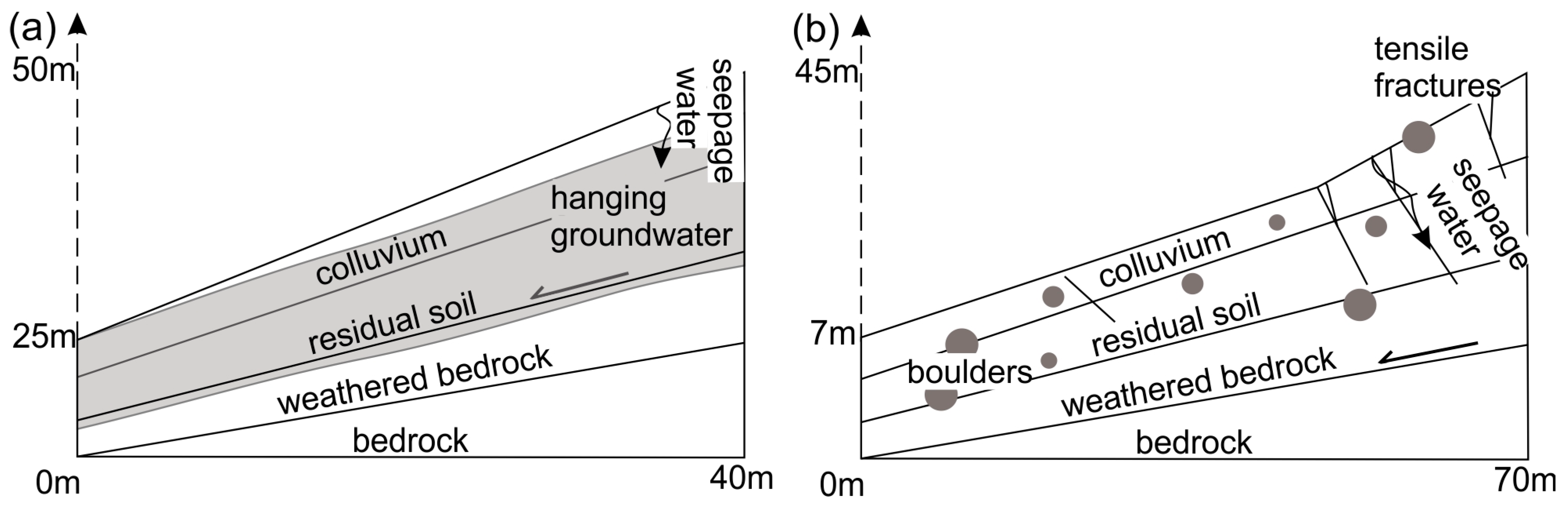
4.1. Distinguished Features of the Slope Failures at the Study Sites
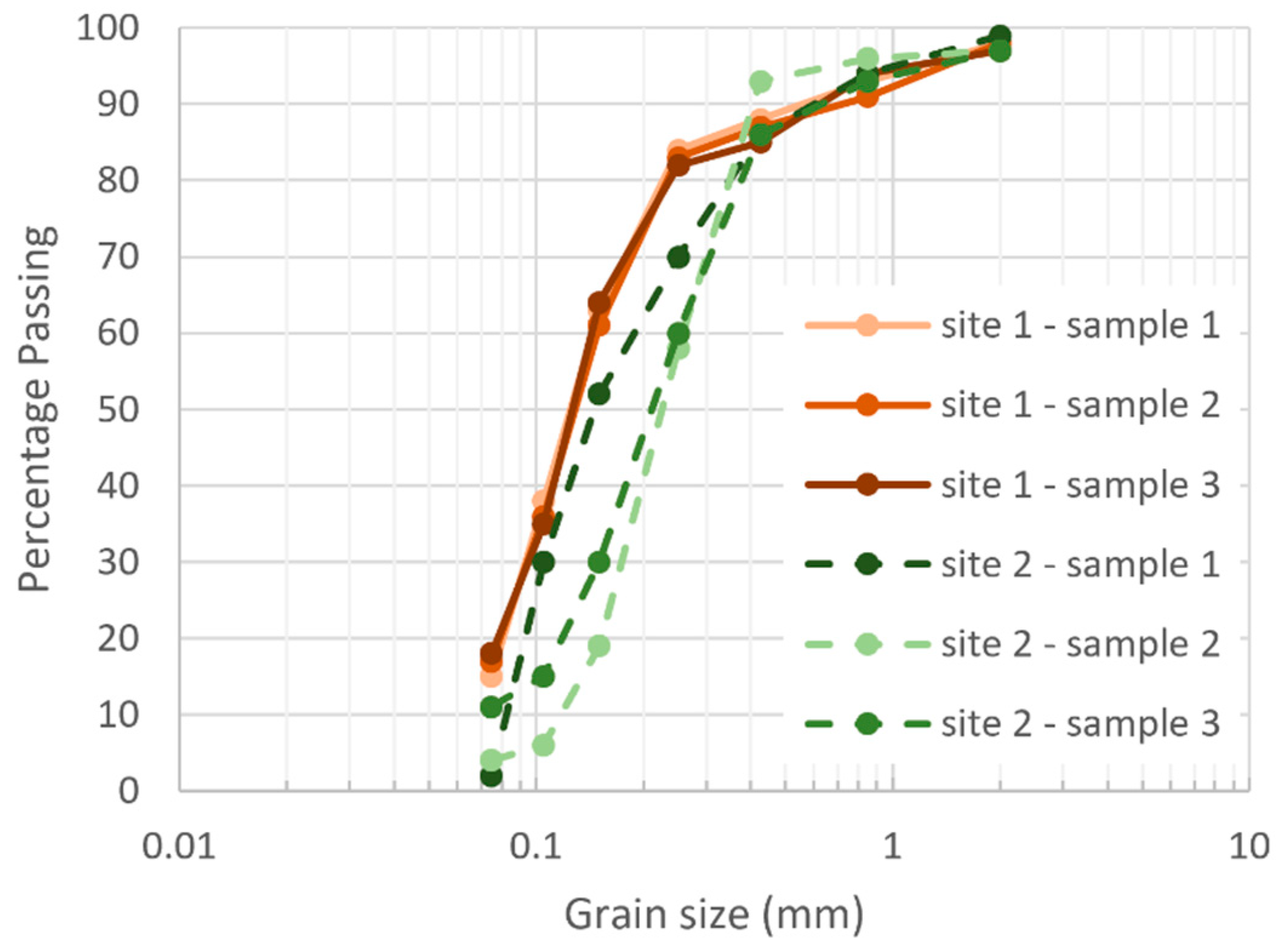
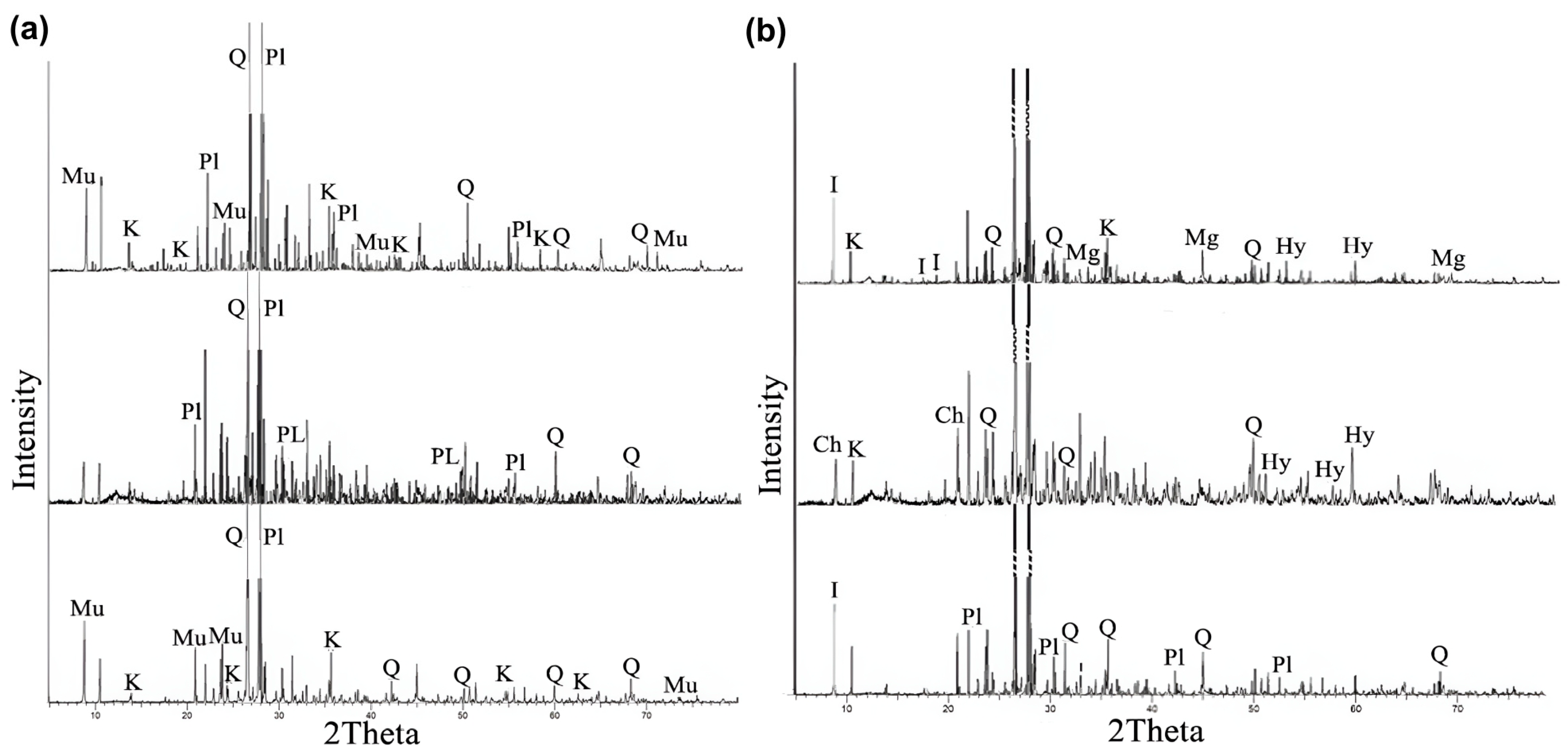
4.2. Soil Texture and Clay Mineralogy
4.3. Subsurface Saturation and Pore Water Pressure
4.4. Influence of Regional Geological and Hydrogeological Conditions
4.5. Summary on Failure Modes and Mechanisms
4.6. Proposed Mitigation Measures
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bukhari, M.H.; da Silva, P.F.; Pilz, J.; Istanbulluoglu, E.; Görüm, T.; Lee, J.; Karamehic-Muratovic, A.; Urmi, T.; Soltani, A.; Wilopo, W.; et al. Community perceptions of landslide risk and susceptibility: A multi-country study. Landslides 2023, 20, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, U.; Blum, P.; Da Silva, P.F.; Andersen, P.; Pilz, J.; Chalov, S.R.; Malet, J.P.; Auflič, M.J.; Andres, N.; Poyiadji, E.; et al. Fatal landslides in Europe. Landslides 2016, 13, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, S.T. Landslide causes and triggers. In Landslide Hazards, Risks, and Disasters, 2nd ed.; Davies, T., Rosser, N., Shroder, J.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Margottini, C.; Canuti, P.; Sassa, K. Landslide Science and Practice, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alupoae, D. Landslides—A result of urban expansion in the metropolitan area of Iasi City. Bull. Polytech. Inst. Jassy Constr. Archit. Sect. 2013, 59, 69–78. [Google Scholar]
- Kazmi, D.; Qasim, S.; Harahap, I.S.H.; Baharom, S.; Imran, M.; Moin, S. A study on the contributing factors of major landslides in Malaysia. Civ. Eng. J. 2016, 2, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanyas, H.; Görüm, T.; Kirschbaum, D.; Lombardo, L. Could road constructions be more disastrous than an earthquake in terms of landsliding? Nat. Hazards 2022, 112, 639–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igwe, O.; Ayogu, C.N.; Maduka, R.I.; Ayogu, N.O.; Ugwoke, T.A. Slope failures and safety index assessment of waste rock dumps in Nigeria’s major mines. Nat. Hazards 2023, 115, 1331–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, B.; Singh, H.O.; Singh, P.K.; Kainthola, A.; Singh, T.N. Stability analysis of potential failure zones along NH-305, India. Nat. Hazards 2016, 83, 1341–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnard, C.; Noverraz, F. Influence of climate change on large landslides: Assessment of long-term movements and trends. In Proceedings of the International Conference on landslides-Causes, Impacts and Countermeasures, Davos, Switzerland, 17–21 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gariano, S.L.; Guzzetti, F. Landslides in a changing climate. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 162, 227–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, M. Landslides in a changing climate. In Landslide Hazards, Risks, and Disasters, 2nd ed.; Davies, T., Rosser, N., Shroder, J.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 505–579. [Google Scholar]
- Neranjan, S.; Uchida, T.; Yamakawa, Y.; Hiraoka, M.; Kawakami, A. Geometrical Variation Analysis of Landslides in Different Geological Settings Using Satellite Images: Case Studies in Japan and Sri Lanka. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracko, T.; Zlender, B.; Jelusic, P. Implementation of Climate Change Effects on Slope Stability Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzolan, E.; Holcombe, E.A.; Pianosi, F.; Marchesini, I.; Alvioli, M.; Wagener, T. A mechanistic approach to include climate change and unplanned urban sprawl in landslide susceptibility maps. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subasinghe, C.N.; Kawasaki, A. Assessment of physical vulnerability of buildings and socio-economic vulnerability of residents to rainfall induced cut slope failures: A case study in central highlands, Sri Lanka. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2021, 65, 102550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnaweera, T.D.; Palihawadana, M.P.; Rangana, H.L.L.; Nawagamuwa, U.P. Effects of climate change on landslide frequencies in landslide prone districts in Sri Lanka. In Civil Engineering Research Exchange Symposium; University of Ruhuna: Ruhuna, Sri Lanka, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnayake, U.; Herath, S. Changing rainfall and its impact on landslides in Sri Lanka. J. Mt. Sci. 2005, 2, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senanayake, S.; Pradhan, B. Predicting soil erosion susceptibility associated with climate change scenarios in the Central Highlands of Sri Lanka. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 308, 114589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrajith, R. Geology and geomorphology. In The Soils of Sri Lanka, 1st ed.; Mapa, R.B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooray, P.G. The Geology of Sri Lanka, 2nd ed.; National Museum of Sri Lanka: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 1984.
- Vanacker, V.; von Blanckenburg, F.; Hewawasam, T.; Kubik, P.W. Constraining landscape development of the Sri Lankan escarpment with cosmogenic nuclides in river sediment. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2007, 253, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Blanckenburg, F.; Hewawasam, T.; Kubik, P.W. Cosmogenic nuclide evidence for low weathering and denudation in the wet, tropical highlands of Sri Lanka. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2004, 109, F03008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, M.M.; Bryson, L.S. Assessment of active landslides using field electrical measurements. Eng. Geol. 2018, 233, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.J.; Ma, P.H.; Peng, J.B. Characteristics of loess landslides triggered by different factors in the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 3218–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilake, K.L.W.I.; Jayathilake, P.P.G.; Fernando, N.; Jayasinghe, N.; Amaratunga, D.; Haigh, R. Living with Landslide Risks: A Case of Resistance to Relocation Among Vulnerable Households Residing in the Kegalle District of Sri Lanka. In Rebuilding Communities after Displacement; Hamza, M., Amaratunga, D., Haigh, R., Malalgoda, C., Jayakody, C., Senanayake, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Hou, T.S.; Jiang, X.D. Study on stability of exit slope of Chenjiapo tunnel under extreme rainstorm conditions. Nat. Hazards 2021, 107, 1387–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S. Impacts of Road Construction on Landsliding in Nepal. Ph.D. Dissertation, Durham University, Durham, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ryabukhin, A.K.; Leyer, D.V.; Lubarskiy, N.N. Peculiarities of designing landslide constructions on the example of engineering protection of buildings and roads in the city of Sochi (Russia). In Proceedings of the International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference: SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 16–25 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Perera, E.N.C.; Jayawardana, D.T.; Jayasinghe, P.; Bandara, R.M.S.; Alahakoon, N. Direct impacts of landslides on socio-economic systems: A case study from Aranayake, Sri Lanka. Geoenviron. Disasters 2018, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, R.M.S.; Jayasingha, P. Landslide disaster risk reduction strategies and present achievements in Sri Lanka. Geosci. Res. 2018, 3, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, A.; Alemdağ, S.; Dağ, S.; Gürocak, Z. Stability assessment of high-steep cut slope debris on a landslide (Gumushane, NE Turkey). Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2016, 75, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yin, G.; Wang, J.G.; Wan, L.; Jin, L. Stability analysis and supporting system design of a high-steep cut soil slope on an ancient landslide during highway construction of Tehran–Chalus. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 67, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, M.E.; Sasahara, K. Engineering measures for landslide disaster mitigation. In Landslides–Disaster Risk Reduction, 1st ed.; Sassa, K., Canuti, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 609–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paswan, A.P.; Shrivastava, A.K. Modelling of rainfall-induced landslide: A threshold-based approach. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmi, D.; Qasim, S.; Harahap, I.S.H.; Baharom, S.; Mehmood, M.; Siddiqui, F.I.; Imran, M. Slope remediation techniques and overview of landslide risk management. Civ. Eng. J. 2017, 3, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, R.P.; Lacerda, W.A.; Coelho Netto, A.L. Relevant geological-geotechnical parameters to evaluate the terrain susceptibility for shallow landslides: Nova Friburgo, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, F.C.; Lee, C.F.; Ngai, Y.Y. Landslide risk assessment and management: An overview. Eng. Geol. 2002, 64, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, R.M.S.; Weerasinghe, K.M. Overview of Landslide Risk Reduction Studies in Sri Lanka. In Landslide Science and Practice; Margottini, C., Canuti, P., Sassa, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, J.; Kervyn, M.; de Hontheim, A.; Dewitte, O.; Jacobs, L.; Mertens, K.; Vanmaercke, M.; Vranken, L.; Poesen, J. Landslide risk reduction measures: A review of practices and challenges for the tropics. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2017, 41, 191–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Grecco, O.; Oggeri, C. Reinforcement design and control of rock slopes above tunnel portals in northern Italy. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2004, 41, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Uchimura, T.; Wang, G.; Selvarajah, H.; Maqsood, Z.; Shen, Q.; Mei, G.; Qiao, S. Predicting the sliding behavior of rotational landslides based on the tilting measurement of the slope surface. Eng. Geol. 2020, 269, 105554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Miao, M.; Tang, H.; Jia, S.; Dong, A.; An, P.; Zhang, B. Insights into the deformation and failure characteristic of a slope due to excavation through multi-field monitoring: A model test. Acta Geotech. 2023, 18, 1001–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Heinze, T.; Budler, J.; Gunatilake, T.; Kemna, A.; Huisman, J.A. Combining Site Characterization, Monitoring and Hydromechanical Modeling for Assessing Slope Stability. Land 2021, 10, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara-Ayala, I.; Garnica-Peña, R.J. Landslide Warning Systems in Low-And Lower-Middle-Income Countries: Future Challenges and Societal Impact. In Progress in Landslide Research and Technology; Sassa, K., Konagai, K., Tiwari, B., Arbanas, Ž., Sassa, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Dong, A.; Tang, H.; An, P.; Wang, Q.; Jia, S.; Zhang, B. Development of an easy-assembly and low-cost multi-smartphone photogrammetric monitoring system for rock slope hazards. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2024, 174, 105655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konagai, K.; Karunawardena, A.; Bandara, K.N.; Sassa, K.; Onishi, R.; Uzuoka, R.; Asano, S.; Sasahara, K.; Jayakody, S.; Ariyarathna, I. Early Warning System against Rainfall-Induced Landslide in Sri Lanka. In Progress in Landslide Research and Technology; Sassa, K., Konagai, K., Tiwari, B., Arbanas, Ž., Sassa, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punyawardena, B.W.R. Climate. In The Soils of Sri Lanka, 1st ed.; Mapa, R.B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitanage, P. Post-Precambrian uplifts and regional neotectonic movements in Ceylon. In Proceedings of the 24th IGC, Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–31 August 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Cooray, P.G. The Precambrian of Sri Lanka: A historical review. Precambrian Res. 1994, 66, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröner, A. African linkage of precambrian Sri Lanka. Geol. Rundsch. 1991, 80, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athurupana, B.M.B.; Perera, L.R.K. Is Kadugannawa Complex-Highland Complex Boundary a Transitional Contact? In Proceedings of the 29th Technical Sessions of Geological Society of Sri Lanka, Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 25 February 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Tani, Y.; Yoshida, M. The structural evolution of the Arena Gneisses and its bearing on Proterozoic tectonics of Sri Lanka. J. Southeast Asian Earth Sci. 1996, 14, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Sassa, K.; Dang, K.; Konagai, K.; Karunawardena, A.; Bandara, R.M.S.; Tang, H.; Sato, G. Estimation of the past and future landslide hazards in the neighboring slopes of the 2016 Aranayake landslide, Sri Lanka. Landslides 2020, 17, 1727–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassanayake, A.R.; Senarath, A.; Hettiarachchi, L.S.K.; Mapa, R.B. Major Soils of the Wet Zone and Their Classification. In The Soils of Sri Lanka, 1st ed.; Mapa, R.B., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2020; pp. 83–94. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasinghe, P. Social geology and landslide disaster risk reduction in Lanka. J. Trop. For. Environ. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, D.J.; McLaren, S.J. Geochemical Sediments and Landscapes, 1st ed.; Whiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mugagga, F.; Kakembo, V.; Buyinza, M. A characterization of the physical properties of soil and the implications for landslide occurrence on the slopes of Mount Elgon, Eastern Uganda. Nat. Hazards 2012, 60, 1113–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Yin, X.; Iglauer, S. A review on clay wettability: From experimental investigations to molecular dynamics simulations. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 285, 102266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, B.; Adhikari, D.P. Role of clay minerals in the occurrence of landslides along Narayangarh-Mugling Highway section, central Nepal. J. Nepal Geol. Soc. 2011, 43, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summa, V.; Margiotta, S.; Medici, L.; Tateo, F. Compositional characterization of fine sediments and circulating waters of landslides in the southern Apennines–Italy. Catena 2018, 171, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Foster, A.S.; Alava, M.J.; Laurson, L. Stick-slip control in nanoscale boundary lubrication by surface wettability. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 095502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, M.P.; Kulathilaka, S.A.S.; Robert, D.J.; Zhou, A.; Jayathissa, H.A.G. Risk assessment and management of rainfall-induced landslides in tropical regions: A review. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 2179–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.A.V.; Abayakoon, S.B.S.; Bhandari, R.K. Discrete Boundary Shear Strength of a Landslide at High Rainfall Precipitation Zone in Sri Lanka. In Landslide Science for a Safer Geoenvironment; Sassa, K., Canuti, P., Yin, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarasinghe, U.B. Mechanism of slow-moving slope failure in Kahagolla, Sri Lanka. J. Geol. Soc. Sri Lanka 2022, 23, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.F.; Rogers, J.D.; Ismail, E.H. A regional level preliminary landslide susceptibility study of the Upper Indus River Basin. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 47, 343–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.U.; Cho, Y.C.; Kim, M.; Jang, S.J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S. The effects of different geological conditions on landslide-triggering rainfall conditions in South Korea. Water 2022, 14, 2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourghasemi, H.R.; Pradhan, B.; Gokceoglu, C.; Moezzi, K.D. Landslide susceptibility. In Terrigenous Mass Movements, 1st ed.; Pradhan, B., Buchroithner, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, B.A.; Burbank, D.W. Bedrock fracturing, threshold hillslopes, and limits to the magnitude of bedrock landslides. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 297, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.P.; Siddique, T. Stability assessment of landslide-prone road cut rock slopes in Himalayan terrain: A finite element method based approach. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 12, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, H. A review on different types of soil stabilization techniques. Int. J. Transp. Eng. Technol. 2017, 3, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huat, B.B.; Gue, S.S.; Ali, F.H. Tropical Residual Soils Engineering, 1st ed.; Routledge: Milton Park, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Komadja, G.C.; Pradhan, S.P.; Oluwasegun, A.D.; Roul, A.R.; Stanislas, T.T.; Laïbi, R.A.; Adebayo, B.; Onwualu, A.P. Geotechnical and geological investigation of slope stability of a section of road cut debris-slopes along NH-7, Uttarakhand, India. Results Eng. 2021, 10, 100227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Samanta, M.; Sarkar, S. Soil nailing: An effective slope stabilization technique. In Landslides: Theory, Practice and Modelling, 1st ed.; Pradhan, S.P., Vishal, V., Singh, T.N., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzano, B.; Tarantino, A.; Ridley, A. Preliminary analysis on the impacts of the rhizosphere on occurrence of rainfall-induced shallow landslides. Landslides 2019, 16, 1885–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevikbilen, G. Slope Stability of Soils. In Handbook of Research on Trends and Digital Advances in Engineering Geology, 1st ed.; Ceryan, N., Ed.; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 380–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, O.U.; Bashir, D.; Islam, T. Slope Stability Analysis and Mitigation for Landslide Hazards along Mughal Road in Kashmir Valley, Northwestern Himalayas. i-Manag. J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pitawala, S.M.; Wimalakeerthi, H.; Heinze, T. Risk Assessment in Landslide-Prone Terrain within a Complex Geological Setting at Kadugannawa, Sri Lanka: Implications for Highway Maintenance. Geotechnics 2024, 4, 564-580. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics4020031
Pitawala SM, Wimalakeerthi H, Heinze T. Risk Assessment in Landslide-Prone Terrain within a Complex Geological Setting at Kadugannawa, Sri Lanka: Implications for Highway Maintenance. Geotechnics. 2024; 4(2):564-580. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics4020031
Chicago/Turabian StylePitawala, Sunera Mahinsa, Harindu Wimalakeerthi, and Thomas Heinze. 2024. "Risk Assessment in Landslide-Prone Terrain within a Complex Geological Setting at Kadugannawa, Sri Lanka: Implications for Highway Maintenance" Geotechnics 4, no. 2: 564-580. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics4020031
APA StylePitawala, S. M., Wimalakeerthi, H., & Heinze, T. (2024). Risk Assessment in Landslide-Prone Terrain within a Complex Geological Setting at Kadugannawa, Sri Lanka: Implications for Highway Maintenance. Geotechnics, 4(2), 564-580. https://doi.org/10.3390/geotechnics4020031








