The Role of Genomics and Transcriptomics in Characterizing and Predicting Patient Response to Treatment in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
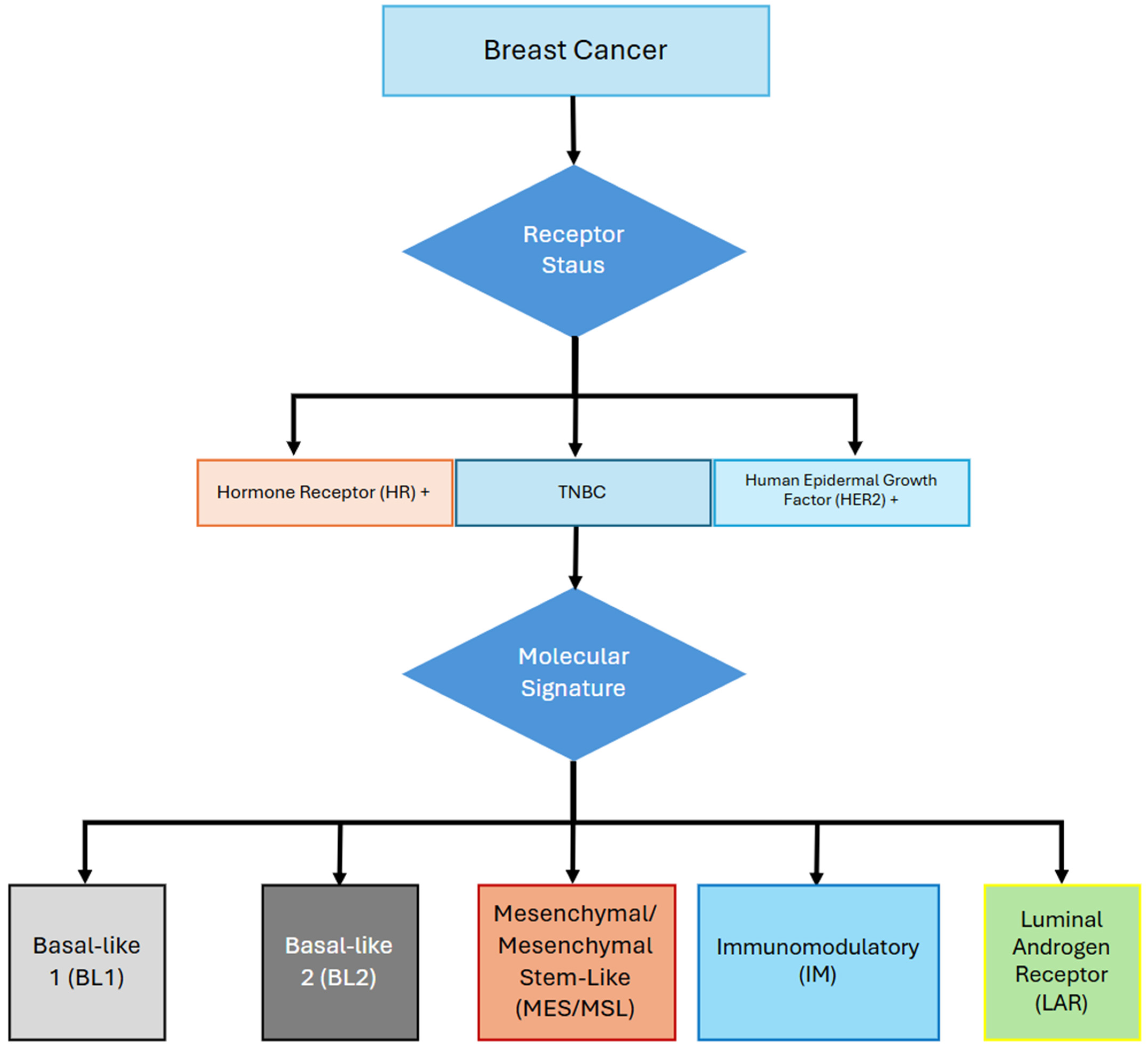
2. Molecular Subtypes of TNBC
3. Genomics and Transcriptomics in TNBC
4. Chemotherapy and Antibody Drug Conjugates
4.1. Chemotherapy
4.2. Antibody-Drug Conjugates
5. Immunotherapy
5.1. Pembrolizumab
5.2. Atezolizumab
5.3. Molecular Predictors of Resistance to Prembrolizumab
6. Targeted Therapy
6.1. PARP Inhibitors
6.2. PIK3/AKT/mTOR Inhibitors
6.3. Other Targeted Therapies
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SEER. Cancer Stat Facts: Female Breast Cancer. National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Newman, L.A.; Freedman, R.A.; Smith, R.A.; Star, J.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Breast cancer statistics 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 477–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrantia-Borunda, E.; Anchondo-Nuñez, P.; Acuña-Aguilar, L.E.; Gómez-Valles, F.O.; Ramírez-Valdespino, C.A. Subtypes of Breast Cancer. In Breast Cancer; Mayrovitz, H.N., Ed.; Exon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2022; Chapter 3. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK583808/ (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- Marra, A.; Trapani, D.; Viale, G.; Criscitiello, C.; Curigliano, G. Practical classification of triple-negative breast cancer: Intratumoral heterogeneity, mechanisms of drug resistance, and novel therapies. npj Breast Cancer 2020, 6, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Merkher, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, N.; Leonov, S.; Chen, Y. Recent advances in therapeutic strategies for triple-negative breast cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Harris, E.E.R.; Small, J. Intraoperative Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Osgood, C.L.; Amatya, A.K.; Fiero, M.H.; Pierce, W.F.; Nair, A.; Herz, J.; Robertson, K.J.; Mixter, B.D.; Tang, S.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Pembrolizumab for Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Treatment of Patients with High-Risk Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 5249–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, S.; Roesch, E. Breast cancer survivorship. J. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 130, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, G.; Yau, T.C.C.; Chiu, J.W.; Tse, E.; Kwong, Y.L. Pembrolizumab (Keytruda). Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2016, 12, 2777–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.K. Personalized medicine. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2002, 4, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, R.Q.; Yan, L.; Zhang, L.; Ma, H.X.; Wang, H.W.; Bu, P.; Xi, Y.F.; Lian, J. Genomic characterization reveals distinct mutational landscapes and therapeutic implications between different molecular subtypes of triple-negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporikova, Z.; Koudelakova, V.; Trojanec, R.; Hajduch, M. Genetic Markers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e841–e850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkel, Ç. Retrospective Analysis of Transcriptomic Differences between Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) and non-TNBC. Eur. J. Biol. 2024, 83, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.; Reddy, S.; Ashok, P.; Hariri, D.; Sokol, E.; Sivakumar, S.; Quintanilha, J.; Pavlick, D.; Levy, M.A.; Ross, J.S.; et al. Impact of HER2 low status on genomic signatures in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42 (Suppl. S16), 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidula, N.; Ellisen, L.; Bardia, A.; Yau, C. Abstract PO5-03-12: Genomic differences of primary triple negative breast cancer in patients younger than 45 years vs. patients older than 45 years of age. Cancer Res. 2024, 84 (Suppl. S9), PO5-03-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.F.; Mardis, E.R. The emerging clinical relevance of genomics in cancer medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balmain, A.; Gray, J.; Ponder, B. The genetics and genomics of cancer. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33 (Suppl. S3), 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarno, F.; Tenorio, J.; Perea, S.; Medina, L.; Pazo-Cid, R.; Juez, I.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Feliu, J.; Guillen-Ponce, C.; Lopez-Casa, P.P.; et al. A Phase III Randomized Trial of Integrated Genomics and Avatar Models for Personalized Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer: The AVATAR Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 31, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.; Li, Y.; Shi, Q.; Tian, J.; Lou, H.; Feng, Y. Omics sciences for cervical cancer precision medicine from the perspective of the tumor immune microenvironment. Oncol. Res. 2025, 33, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Afzal, M.Z.; Vahdat, L.T. Evolving Management of Breast Cancer in the Era of Predictive Biomarkers and Precision Medicine. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Jeon, S.H.; Nam, H.; Jung, J.H.; Jeon, M.; Kim, E.S.; Bae, S.J.; Ahn, J.; Yoo, T.K.; et al. CD39+ tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells with a clonal overlap across compartments mediate antitumor immunity in breast cancer. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 7, eabn8390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugo, M.; Huang, C.S.; Egle, D.; Bermejo, B.; Zamagni, C.; Seitz, R.S.; Nielsen, T.J.; Thill, M.; Anton, A.; Russo, S.; et al. Abstract PD10-06: Predictive value of RT-qPCR 27-gene IO score and comparison with RNA-Seq IO score in the NeoTRIPaPDL1 trial. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, PD10-06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn, T.; Denkert, C.; Weber, K.E.; Holtrich, U.; Hanusch, C.; Sinn, B.V.; Higgs, B.W.; Jank, P.; Sinn, H.P.; Huober, J.; et al. Tumor mutational burden and immune infiltration as independent predictors of response to neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibition in early TNBC in GeparNuevo. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denkert, C.; Wienert, S.; Poterie, A.; Loibl, S.; Budczies, J.; Badve, S.; Bago-Horvath, Z.; Bane, A.; Bedri, S.; Brock, J.; et al. Standardized evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in breast cancer: Results of the ring studies of the international immuno-oncology biomarker working group. Mod. Pathol. 2016, 29, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachelot, T.; Filleron, T.; Bieche, I.; Arnedos, M.; Campone, M.; Dalenc, F.; Coussy, F.; Sablin, M.P.; Debled, M.; LefeuvrePlesse, C.; et al. Durvalumab compared to maintenance chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer: The randomized phase II SAFIR02-BREAST IMMUNO trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korde, L.A.; Somerfield, M.R.; Carey, L.A.; Crews, J.R.; Denduluri, N.; Hwang, E.S.; Khan, S.A.; Loibl, S.; Morris, E.A.; Perez, A.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy, Endocrine Therapy, and Targeted Therapy for Breast Cancer: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1485–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.M.; Aguirre, B.; Liu, L.; Mah, V.; Balko, J.M.; Tsui, J.; Wadehra, N.P.; Moatamed, N.A.; Khoshchehreh, M.; Dillard, C.M.; et al. EMP2 Serves as a Functional Biomarker for Chemotherapy Resistant Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Stecklein, S.R.; Yoder, R.; Staley, J.M.; Schwensen, K.; O’dea, A.; Nye, L.; Satelli, D.; Crane, G.; Madan, R.; et al. Clinical and Biomarker Findings of Neoadjuvant Pembrolizumab and Carboplatin Plus Docetaxel in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer NeoPACT Phase 2 Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2024, 10, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Liu, L.; Yu, T.; Yu, L.; Feng, M.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X.; Teng, G.; Ma, Z.; Zhou, W.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of breast cancer identifies novel signatures associated with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Genome Med. 2024, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusby, R.; Zhang, Z.; Mahesh, A.; Tiwari, V.K. Decoding gene regulatory circuitry underlying TNBC chemoresistance reveals biomarkers for therapy response and therapeutic targets. npj Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akshatha, C.R.; Halanaik, D.; Ganesh, R.N.; Kishore, N.; Ganesan, P.; Kayal, S.; Kumar, H.; Dubashi, B. Assessment of novel prognostic biomarkers to predict pathological complete response in patients with non-metastatic triple-negative breast cancer using a window of opportunity design. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2024, 16, 17588359241248329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, M.; Stecklein, S.R.; Gluz, O.; Villacampa, G.; Monte-Millán, M.; Nitz, U.; Cobo, S.; Christgen, M.; Brasó-Maristany, F.; Álvarez, E.L.; et al. TNBC-DX genomic test in early-stage triple-negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant taxane-based therapy. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 36, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, B.S.; Esteva, F.J. Next-Generation HER2-Targeted Antibody-Drug Conjugates in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Jacot, W.; Yamashita, T.; Sohn, J.; Vidal, M.; Tokunaga, E.; Tsurutani, J.; Ueno, N.T.; Prat, A.; Chae, Y.S.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Low Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 387, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Tolaney, S.M.; Loirat, D.; Punie, K.; Oliveira, M.; Brufsky, A.; Sardesai, S.D.; Kalinsky, K.; Zelnak, A.B.; et al. Sacituzumab Govitecan in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascione, L.; Guidi, L.; Prakash, A.; Trapani, D.; LoRusso, P.; Lou, E.; Curigliano, G. Unlocking the Potential: Biomarkers of Response to Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2024, 44, e431766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xue, J.; Li, J.; Yi, J.; Bu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, P.; Gu, X. Advances in immunotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Current researches in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.; Rugo, H.S.; Cescon, D.W.; Im, S.; Yusof, M.M.; Gallardo, C.; Lipatov, O.; Barrios, C.H.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Iwata, H.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buisseret, L.; Bareche, Y.; Venet, D.; Girard, E.; Gombos, A.; Emonts, P.; Majjaj, S.; Rouas, G.; Serra, M.; Debien, V.; et al. The long and winding road to biomarkers for immunotherapy: A retrospective analysis of samples from patients with triple-negative breast cancer treated with pembrolizumab. ESMO Open 2024, 9, 102964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.Q.; Shao, Z.M. Identification of immune-related prognostic biomarkers in triple-negative breast cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 1707–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugo, M.; Huang, C.S.; Egle, D.; Bermejo, B.; Zamagni, C.; Seitz, R.S.; Nielsen, T.J.; Thill, M.; Antón-Torres, A.; Russo, S.; et al. The Immune-Related 27-Gene Signature DetermaIO Predicts Response to Neoadjuvant Atezolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 4900–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Gou, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, L.; Chen, F.; Bao, C.; Bu, H. Gene panel predicts neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy response and benefit from immunotherapy in HER2-negative breast cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e009587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, T.G. Targeted Therapies for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2019, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagia, E.; Mahalingam, D.; Cristofanilli, M. Landscape of Targeted Therapies in TNBC. Cancers 2020, 12, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannoudis, A.; Sokol, E.S.; Bhogal, T.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; Razis, E.D.; Bartsch, R.; Shaw, J.A.; McGregor, K.; Clark, A.; Huang, R.; et al. Breast cancer brain metastases genomic profiling identifies alterations targetable by immune-checkpoint and PARP inhibitors. npj Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Däster, K.; Hench, J.; Diepenbruck, M.; Volkmann, K.; Rouchon, A.; Palafox, M.; Miragaya, J.G.; Preca, B.T.; Kurzeder, C.; Weber, W.P.; et al. BRCA promoter methylation in triple-negative breast cancer is preserved in xenograft models and represents a potential therapeutic marker for PARP inhibitors. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 209, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitri, Z.I.; Creason, A.L.; Stommel, J.M.; Bottomly, D.; Ozmen, T.Y.; Rames, M.J.; Ozmen, F.; Jeong, B.; Lukashchuk, N.; Ashton, J.; et al. Adaptive Responses to PARP Inhibition Predict Response to Olaparib and Durvalumab: Multi-omic Analysis of Serial Biopsies in the AMTEC Trial. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulgarelis, D.; Forment, J.V.; Ropero, A.H.; Polychronopoulos, D.; Cohen-Setton, J.; Bender, A.; Serra, V.; O’connor, M.J.; Yates, J.W.T.; Bulusu, K.C. Understanding tumour growth variability in breast cancer xenograft models identifies PARP inhibition resistance biomarkers. npj Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, P.; Turner, N.C.; Barrios, C.H.; Isakoff, S.J.; Kim, S.; Sabline, M.; Saji, S.; Savas, P.; Vidal, G.A.; Oliveria, M.; et al. First-Line Ipatasertib, Atezolizumab, and Taxane Triplet for Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical and Biomarker Results. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Cui, H.; Dai, L.; Chang, L.; Liu, D.; Yan, W.; Zhao, X.; Kang, H.; Ma, X. PIK3CA mutation-driven immune signature as a prognostic marker for evaluating the tumor immune microenvironment and therapeutic response in breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulet, S.; Dai, M.; Wang, N.; Yan, G.; Boudreault, J.; Daliah, G.; Guillevin, A.; Nguyen, H.; Galal, S.; Ali, S.; et al. Genome-wide in vivo CRISPR screen identifies TGFβ3 as an actionable biomarker of palbociclib resistance in triple negative breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medford, A.J.; Oshry, L.; Boyraz, B.; Kiedrowski, L.; Menshikova, S.; Butusova, A.; Dai, C.S.; Gogakos, T.; Keenan, J.C.; Occhiogrosso, R.H.; et al. TRK inhibitor in a patient with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer and NTRK fusions identified via cell-free DNA analysis. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2023, 15, 17588359231152844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, M.; Velez, M. Larotrectinib in NTRK3 fusion-positive metastatic secretory carcinoma of the breast: A case study. Curr Prob Cancer Case Rep. 2025, 17, 100334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, R. Microbiome Immunotherapy Neoadjuvant Assessment (MINA) [Clinical Trials: NCT06709651]; University of Cork: Cork, Ireland, 2025. [Google Scholar]

| TNBC Subtype | Most Common Mutations | Potential Targets |
|---|---|---|
| Basal-Like Immunosuppressed (BLIS) (BL1 and BL2) | ABL1, AKT1, ALK, ARAF, ATM, BRAF, BRCA1, BRD4, CCNE1, CDKN2A, CDKN2B, CTNNB1, DDR2, EGFR, EPHA5, ERBB2, ESR1, EZH2, FBXW7, FGFR2, FGFR3, IDH1, IGF1R, JAK2, MCL1, MLL, NF1, PDGFRA, PIK3CA *, PTCH1, PTEN, RB1 *, STK11, TP53 *, TSC1, XPO1 | Inhibitors: SRC, novel ephrin, JAK2, IGFR1-R, IDH, FGFR, FAK, EZH2, endocrine, CDK4/6, CDK2, bromodomain, AKT, WNT, RAF, PI3K **, PARP **, MTOR **, MEK **, HDAC **, cell cycle **, CDK **, ALK Targeted therapy: dasatinib, lapatinib ** Monoclonal antibodies: trastuzumab ** Others: TKIs, selective inhibitors of nuclear export, p53 specific gene therapy **, immunotherapy **, anti-tubulin chemotherapy, anti-RTK therapy **, anti-HER2 therapy, anti-EGFR TKIs ** |
| Mesenchymal and Mesenchymal Stem-Like (MES/MSL) | PIK3CA *, RB1 *, ROS1, SMARCA4, TP53 *, XPO1 | Inhibitors: anti-EGFR therapy, FGFR, AKT, PI3K **, PARP **, Notch, MTOR **, MEK **, HDAC **, cell cycle **, CDK ** Targeted therapy: crizotinib, lapatinib ** Monoclonal antibodies: trastuzumab ** Others: selective inhibitors of nuclear export, p53 specific gene therapy **, immunotherapy **, anti-tubulin chemotherapy, anti-RTK therapy **, anti-EGFR TKIs ** |
| Luminal Androgen Receptor (LAR) | AKT1, ALK, ATM, BAP1, BRAF, BRCA1, BRCA2, CTNNB1, EGFR, ERBB2, ERBB3, MCL1, NF1, NOTCH1, NOTCH2, PIK3CA *, PIK3R1, PTEN, RB1 *, SMO, TP53 *, TSC2, XPO1 | Inhibitors: WNT, RAF, PI3K **, PARP **, Notch, MTOR **, MEK **, HER3, hedgehog, HDAC **, cell cycle **, CDK ** Targeted therapy: lapatinib ** Monoclonal antibodies: trastuzumab ** Others: TKIs, selective inhibitors of nuclear export, p53 specific gene therapy **, immunotherapy **, anti-tubulin chemotherapy, anti-RTK therapy **, anti-HER2 therapy, anti-EGFR TKIs ** |
| Immunomodulatory (IM) | AKT3, ALK, ATM, BRCA1, BRCA2, BRD4, CDK6, CDKN2A, CTNNB1, EGFR, ERBB2, ERBB4, FGFR3, FLT3, IDH1, KRAS, MCL1, MLL, NF1, NOTCH1, NOTCH2, PDGFRA, PIK3CA *, PTEN, RB1 *, RET, TP53 *, TSC1 | Inhibitors: RET, FLT3, anti-EGFR therapy, IDH, FGFR, CDK4/6, bromodomain, AKT, WNT, RAF, PI3K **, PARP **, Notch, MTOR **, MEK **, HDAC **, cell cycle **, CDK **, ALK Targeted therapy: lapatinib ** Monoclonal antibodies: trastuzumab ** Others: p53 specific gene therapy **, immunotherapy **, anti-RTK therapy **, anti-HER2 therapy, anti-EGFR TKIs ** |
| Biomarker | Prognostic Association | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| TDO2 | Protective | Tryptophan metabolism role: catalysis of kynurenine. Kynurenine prevents detection of the tumor by the host immune system |
| CHIT1 | Protective | Chitotriosidase, which is part of the glycosyl hydrolase family 18 (GH18), which in a previous study, increased levels were detected in patients with primary breast cancer |
| CARMIL2 | Protective | A characteristic of CARMIL2 is impaired T-cell activation |
| HLA-C | Protective | Part of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) family, this protein is the subject of many investigations not just in cancer but also in autoimmune disorders |
| ADIRF | Unfavorable | No justification given by authors |
| C19orf33 | Unfavorable | Multiple studies have shown that mutations of C19orf116 are present in ovarian carcinoma and nonmuscle-invasive bladder cancer. Deficiency of C19orf116 has shown to be a poor prognostic indicator in prostate cancer. Abnormal expression of C19orf116 has been found in pancreatic and many other cancers. |
| CA8 | Unfavorable | Excessive CA8 was found to enhance proliferation and migration of cells in renal cell carcinoma |
| AHNAK2 | Unfavorable | Increased levels of AHNAK2 have been found in thyroid carcinoma stimulating the NF-κB, advancing progression |
| RHOV | Unfavorable | Within the JNK/c-Jun pathway, increased RHOV enhances growth and spread of lung adenocarcinoma |
| OPLAH | Unfavorable | OPLAH has been found to be a prognostic factor in gastric cancer and squamous cell carcinoma in previous studies |
| THEM6 | Unfavorable | Part of the thioesterase superfamily and an indicator of resistance to ADT in prostate cancer |
| NEBL | Unfavorable | Previous studies have found that NEBL plays a crucial role in ovarian cancer advancement |
| NCT# | Actively Recruiting Studies | Intervention | Methods and Biomarkers | Early, Locally Advanced, or Metastatic | Location(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05916755 | Predictive Biomarkers of Response to Checkpoint Inhibitors in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Multiomics Platform (PORTRAIT) | NACT with and without ICI | WGS and RNA-seq, ctDNA, TCR-β, PD-L1, and TILs (B- and T-lymphocytes) | Locally advanced | Spain |
| NCT06355037 | Dasatinib Combined with Quercetin to Reverse Chemo Resistance in Triple Negative Breast Cancer | Dasatinib and quercetin with NACT | Age-related secretory factors, IHC of senescent fibroblasts, and number and area of neutrophil extracellular traps | Metastatic | China |
| NCT06709651 | Microbiome Immunotherapy Neoadjuvant Assessment (MINA) | Neoadjuvant chemo and immunotherapy | Microbiota present in breast tissue | Locally advanced | Ireland |
| NCT06182306 | Prospective Evaluation of AI R&D Tool for Patient Stratification—MoA Evaluation in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (PEAR-MET) | PearBio, a novel AI tool that uses biomarker data, recommendations v. standard of care-guided medical oncologists | Various including RNAseq, MSI testing, TMB, and more | Metastatic | United Kingdom |
| NCT06418126 | Prediction of Radiotherapy Efficacy in Patients with Triple-negative Breast Cancer (TNBC-RT2023) | NACT/ACT with radiotherapy | IL-1β, Il-5, and IL-6 | Locally advanced | France |
| NCT05552001 | A2-ESO-1 TCR-Engineered T Cells for Relapsed/Refractory Advanced or Metastatic NY-ESO-1 Overexpression Positive Triple Negative Breast Cancer | anti-HLA-A2/NY-ESO-1 TCR-transduced autologous T lymphocytes | PD-1, NY-ESO-1-specific T cell, T regulatory cells | Locally advanced and metastatic | United states of America |
| NCT05192798 | Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel Combined with Antiangiogenic Agents in First-line Treatment of Relapsed or Metastatic TNBC | Nab paclitaxel, nab paclitaxel and apatinib mesylate, nab paclitaxel and bevacizumab | Serum VEGF-A | Metastatic | China |
| NCT04877821 | The Efficacy and Safety of Sintilimab Plus Anlotinib Combined with Chemotherapy as Neoadjuvant Therapy in TNBC (NeoSACT) | Sintilimab and anlotinib with NACT or NACT followed by surgery | Immune biomarkers (PDL1, CD8, TILs, HRD) | Locally advanced | China |
| NCT05949021 | OCTANE: Adjuvant Liposomal Doxorubicin and Carboplatin for Early-stage Triple-negative Breast Cancer | Liposomal doxorubicin and carboplatin | ctDNA | Early | United States of America |
| NCT03740893 | PHOENIX DDR/Anti-PD-L1 Trial: A Pre-surgical Window of Opportunity and Post-surgical Adjuvant Biomarker Study of DNA Damage Response Inhibition and/or Anti-PD-L1 Immunotherapy in Patients with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Resistant Residual Triple Negative Breast Cancer (PHOENIX) | AZD6738, olaparib, and durvalumab followed by surgery | DDR biomarkers (53BP1, RAD51, RPA, RPA32, pRPA, BRCA1/2, PARP, immune checkpoint ligands and receptors | Locally advanced | United Kingdom |
| NCT04947189 | Seviteronel in Combination with Chemotherapy in Androgen-receptor Positive Metastatic Triple-negative Breast Cancer (4CAST) | Seviteronel and dexamethasone (SEVI-D) with and without NACT | RNAseq, androgen receptor, ZEB1, ctDNA analysis | Metastatic | Australia |
| NCT05174832 | Induction of Cisplatin/Nab-paclitaxel/Pembrolizumab Followed by Olaparib/Pembrolizumab Maintenance in mTNBC Patients | Cisplatin/Nab-paclitaxel/Pembrolizumab followed by olaparib/pembrolizumab | Unspecified | Metastatic | China |
| NCT05556200 | A Phase II Trial of Camrelizumab in Combination with Apatinib for Neoadjuvant Treatment of Early-stage TNBC With a High Proportion of TILs | Camrelizumab with apatinib | Tumor and stromal PD-L1, and TILs (B and T lymphocytes) | Early | China |
| NCT05914961 | Immunotherapy-related CRP Kinetics in Early and Metastatic Triple-negative Breast Cancer | Immunotherapy | CRP | Early, locally advanced, or metastatic | Germany |
| NCT06246786 | Breast/Cyclosporin A/TNBC (Triple Negative Breast Cancer) | Cyclosporin A prior to surgery | g-H2Ax, apoptosis markers | Early and locally advanced | United States of America |
| NCT05831553 | TIP in Patients Affected by Metastatic TNBC (TIP) | Atezolizumab plus Nab-paclitaxel | Tissue Immune Profile (TILs, PD-L1, CD73) | Metastatic | Italy |
| NCT04986852 | Olinvacimab with Pembrolizumab in Patients with mTNBC | Olinvacimab with pembrolizumab | Tumor exome sequencing, MDSC, other unspecified biomarkers | Metastatic | Australia |
| NCT06162351 | A Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Toxicities of PLX038, in Patients with Locally Advanced or Metastatic Triple-negative Breast Cancer (TOPOLOGY) | PLX038 with prior NACT exposure | Replication stress-related biomarkers (SLFN11, RB1) | Locally advanced or metastatic | France |
| NCT03213041 | Pembrolizumab and Carboplatin in Treating Patients with Circulating Tumor Cells Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer | Carboplatin with pembrolizumab | PD-L1, CAMLs, ctDNA, circulating tumor cells | Metastatic | United States of America |
| NCT06134375 | A Study of Tetrathiomolybdate (TM) Plus Capecitabine | Capecitabine and pembrolizumab with and without tetrathiomolybdate | VEGFR2+ EPCs, LOXL-2, ctDNA, and other unspecified | Locally advanced or metastatic | United States of America |
| NCT05422794 | Testing the Addition of Anti-Cancer Drug, ZEN003694 (ZEN-3694) and PD-1 Inhibitor (Pembrolizumab), to Standard Chemotherapy (Nab-Paclitaxel) Treatment in Patients with Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer | ZEN003694 with and without pembrolizumab and nab-paclitaxel | Pancytokeratin, CD8, PD-1, PD-L1, and CD31 | Locally advanced | United States of America |
| NCT06240195 | Biomarkers of Efficacy and Tolerability of Sacituzumab-Govitecan in the Treatment of Patients with Triple-negative Breast Cancer in the Metastatic Phase: Prospective Multicenter Real-world Study (BIO-PROSA) | Sacituzumab govecitan | Unspecified | Metastatic | Italy |
| NCT05082259 | ASTEROID: A Trial of ASTX660 in Combination with Pembrolizumab (ASTEROID) | ASTX660 with pembrolizumab | PD-L1, cytokines, immune transcriptome changes | Metastatic | United Kingdom |
| NCT04360941 | PAveMenT: Palbociclib and Avelumab in Metastatic AR+ Triple Negative Breast Cancer (PAveMenT) | Palbociclib and avelumab | ctDNA, RB1, PIK3CA, PTEN, T-cell and T-cell receptor clonality | Locally advanced or metastatic | United Kingdom |
| NCT06649331 | Platform Study of ADC Rechallenge in ADC-treated Metastatic Breast Cancer | SHR-A1811, SHR-A1921, SHR-A2009, SHR-A2102 | HER2, TROP2, HER3, Nectin4 | Locally advanced or metastatic | China |
| NCT06230185 | ctDNA Based MRD Testing for NAC Monitoring in TNBC (B-STRONGER-I) | NACT | ctDNA | Early to locally advanced | United States of America |
| NCT01042379 | I-SPY TRIAL: Neoadjuvant and Personalized Adaptive Novel Agents to Treat Breast Cancer (I-SPY) | Various treatment regimens in combination with NACT | Unspecified | Locally advanced or metastatic | United States of America |
| NCT03606967 | Testing the Addition of an Individualized Vaccine to Durvalumab and Tremelimumab and Chemotherapy in Patients with Metastatic Triple Negative Breast Cancer | Nab-paclitaxel, durvalumab, tremelimumab with and without synthetic long peptide vaccine | TIL percentage, PD-L1 on TILs and tumor, genomic and transcriptomic evaluation | Metastatic | United States of America |
| NCT05037825 | The Gut Microbiome and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Solid Tumors (PARADIGM) | Immunotherapy, diet, prebiotics and probiotics | Microbiome and metabolite analysis | Early, locally advanced, and metastatic | United States of America |
| NCT02276443 | Molecular Testing and Imaging in Improving Response in Patients with Stage I-III Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy MDACC Breast Moonshot Initiative | Personalized regimen versus standard NACT | Genomic signature | Early to locally advanced | United States of America |
| NCT06261918 | Transcriptional and Epimetabolic Profile of Breast Carcinoma with Luminal or HER2+ or Locally Advanced Triple-negative Histotype in Patients With/Without Previous Clinical History of Metabolic Syndrome (PROMETA) | NACT | Unspecified | Locally advanced | Italy |
| NCT04348747 | Dendritic Cell Vaccines Against Her2/Her3 and Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Brain Metastasis from Triple Negative Breast Cancer or HER2+ Breast Cancer | Dendritic cell vaccines against HER2/HER3 with pembrolizumab | CTLs, PD-L1, cytokine expression | Metastatic | United States of America |
| NCT02945579 | Multicenter Trial for Eliminating Breast Cancer Surgery or Radiotherapy in Exceptional Responders to Neoadjuvant Systemic Therapy | Radiation therapy after systemic NACT with and without surgery | CTC and cDNA | Early | United States of America |
| NCT02993068 | Stand up to Cancer: MAGENTA (Making Genetic Testing Accessible) | Online module versus phone call genetics evaluation and education | Various genetic panels | Early, locally advanced, or metastatic | United States of America |
| NCT05180006 | Impact of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy in Early-Stage Breast Cancer Before Standard Therapy (BIS-Program) | Atezolizumab with and without ipatasertib/bevacizumab/trastuzumab/pertuzumab | GzmB+ CD8+ T lymphocytes, GzmB/CD8, CD8/FoxP3, CD8/CD68, PD-L1, MHC-I, RNA-Seq | Early | France |
| NCT05253053 | To Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of TT-00420 (Tinengotinib) as Monotherapy and Combination Therapy in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors | T-00420 with and without atezolizumab or nab-paclitaxel | FGFR2, PD-L1, dMMR, MSI, TNBC subtype, TMB | Locally advanced or metastatic | China |
| NCT05955105 | A Study of ILB2109 and Toripalimab in Patients with Advanced Solid Malignancies | ILB2109 and toripalimab | Adenosine Signature gene panel, TMB, MSI status, PD-L1, CD68, A2aR, CD8 | Locally advanced or metastatic | China |
| NCT05958199 | A Study of NPX267 for Subjects with Solid Tumors Known to Express HHLA2/B7-H7 | NPX267 | Unspecified | Unspecified | United States of America |
| NCT05076760 | MEM-288 Oncolytic Virus Alone and in Combination with Nivolumab in Solid Tumors Including Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | MEM-288 with and without nivolumab | CD40L, type 1 IFN, and other biomarkers of anti-tumor activity, immunogenicity and immune activation | Locally advanced or metastatic | United States of America |
| NCT05565417 | Study of the Monoclonal Antibody IMT-009 in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors or Lymphomas | IMT-009 post treatment with NACT, sacituzumab govitecan, a PD-L1 inhibitor, or PARP inhibitor | Unspecified | Unspecified | United States of America |
| NCT03475953 | A Phase I/II Study of Regorafenib Plus Avelumab in Solid Tumors (REGOMUNE) | Regorafenib with and without avelumab | Cytokines, lymphocytes, and other angiogenic and immunologic biomarkers | Locally advanced and metastatic | France |
| NCT05107674 | A Study of NX-1607 in Adults with Advanced Malignancies | NX-1607 with and without paclitaxel after standard NACT | Inflammatory cytokines, tumor-infiltrating immune cells | Locally advanced and metastatic | United States of America and United Kingdom |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Corea-Dilbert, F.E.; Afzal, M.Z. The Role of Genomics and Transcriptomics in Characterizing and Predicting Patient Response to Treatment in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC). Onco 2025, 5, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco5020018
Corea-Dilbert FE, Afzal MZ. The Role of Genomics and Transcriptomics in Characterizing and Predicting Patient Response to Treatment in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC). Onco. 2025; 5(2):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco5020018
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorea-Dilbert, Franklin Eduardo, and Muhammad Zubair Afzal. 2025. "The Role of Genomics and Transcriptomics in Characterizing and Predicting Patient Response to Treatment in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC)" Onco 5, no. 2: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco5020018
APA StyleCorea-Dilbert, F. E., & Afzal, M. Z. (2025). The Role of Genomics and Transcriptomics in Characterizing and Predicting Patient Response to Treatment in Triple Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC). Onco, 5(2), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/onco5020018






