Ionic Liquid Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Sugarcane Cellulose to Produce Reducing Sugar
Abstract
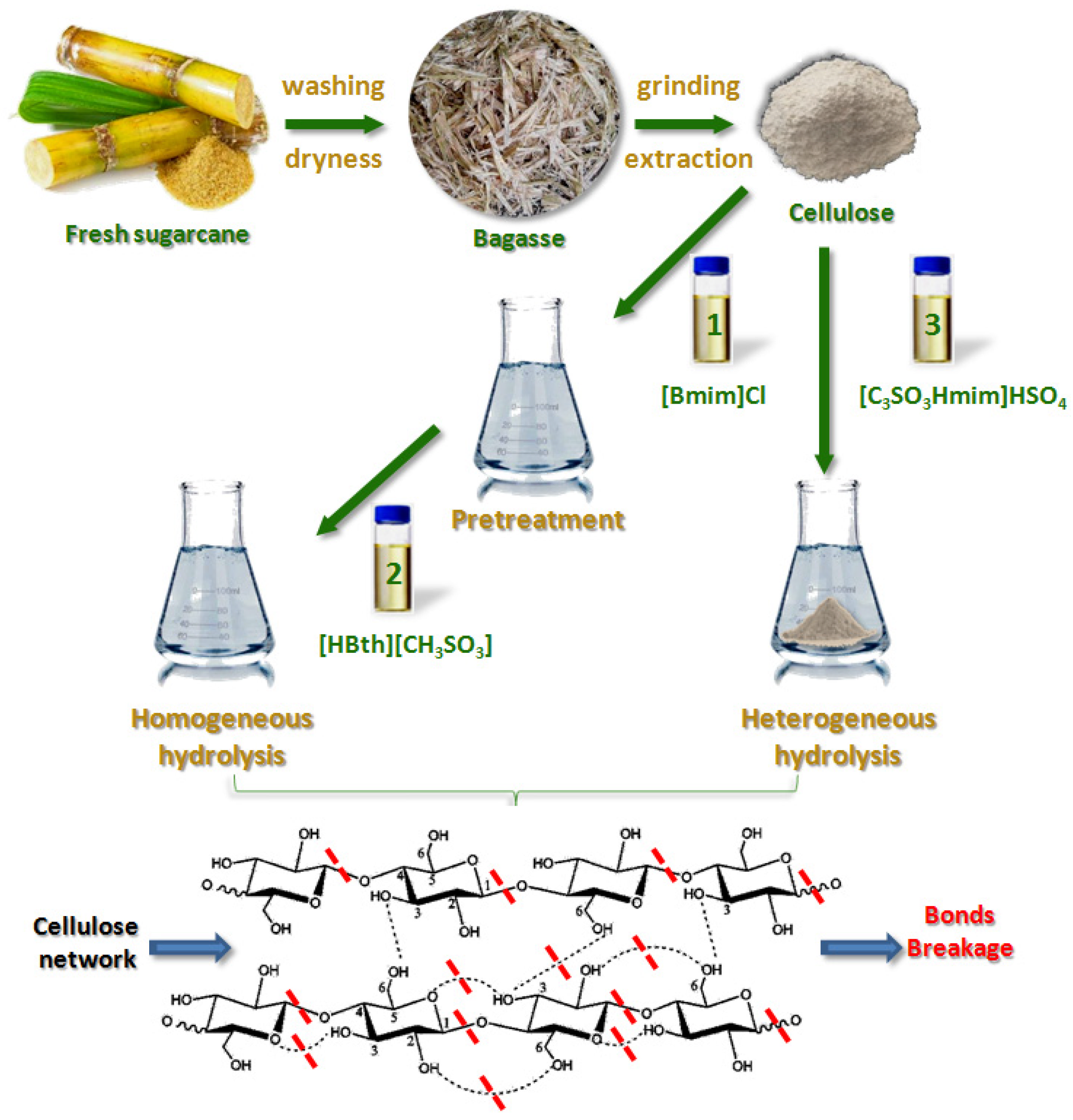
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Preparation of Ionic Liquids
2.3. Hydrolysis of Sugarcane Cellulose by Ionic Liquids
2.3.1. Homogeneous System Hydrolysis
2.3.2. Heterogeneous System Hydrolysis
2.4. Determination of Reducing Sugar in Hydrolysis Product
2.5. Development of Standard Curves for Related Objectives
2.6. Characterization of Sugarcane Cellulose before and after Hydrolysis
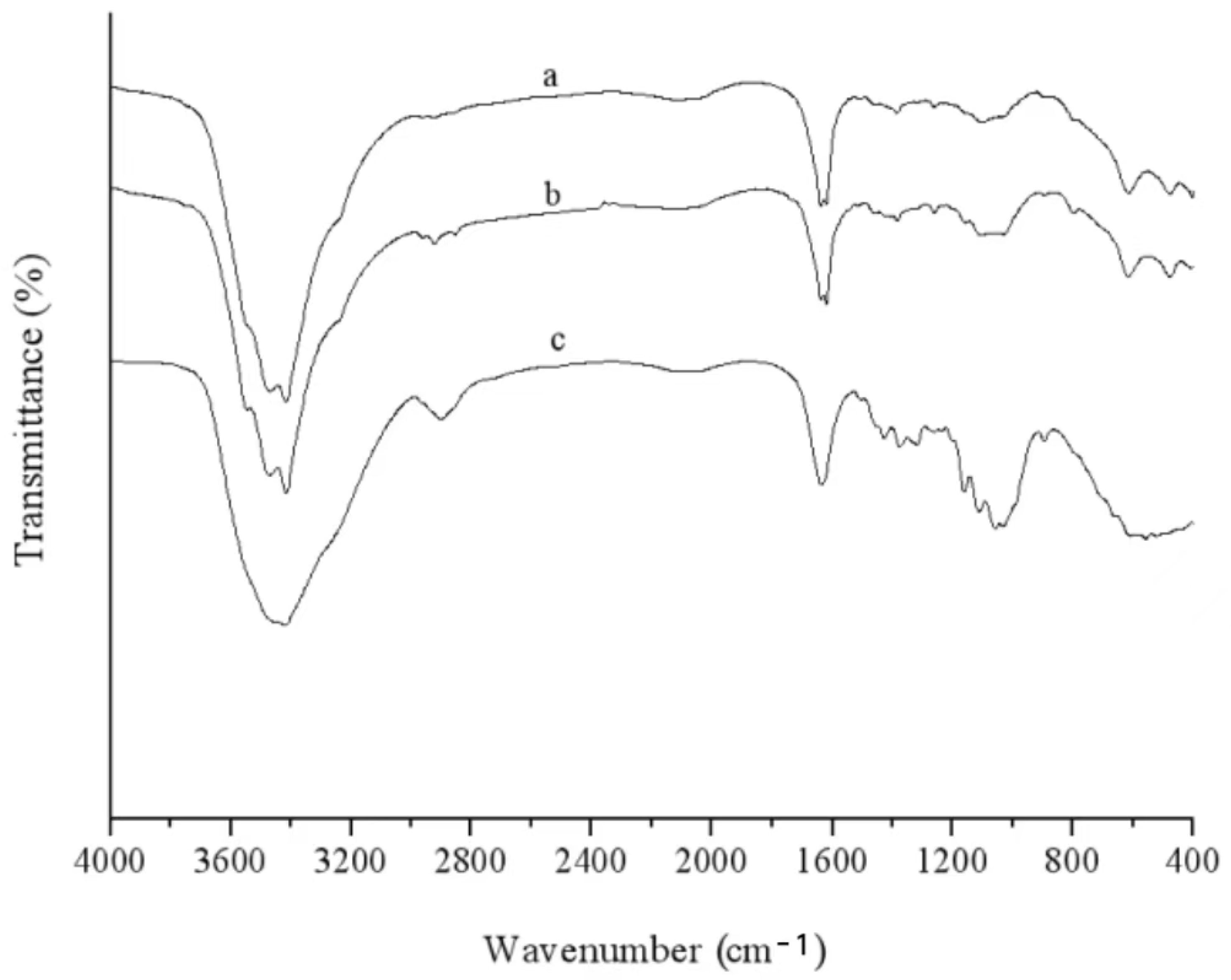
2.6.1. Infrared (IR) Spectroscopic Analysis
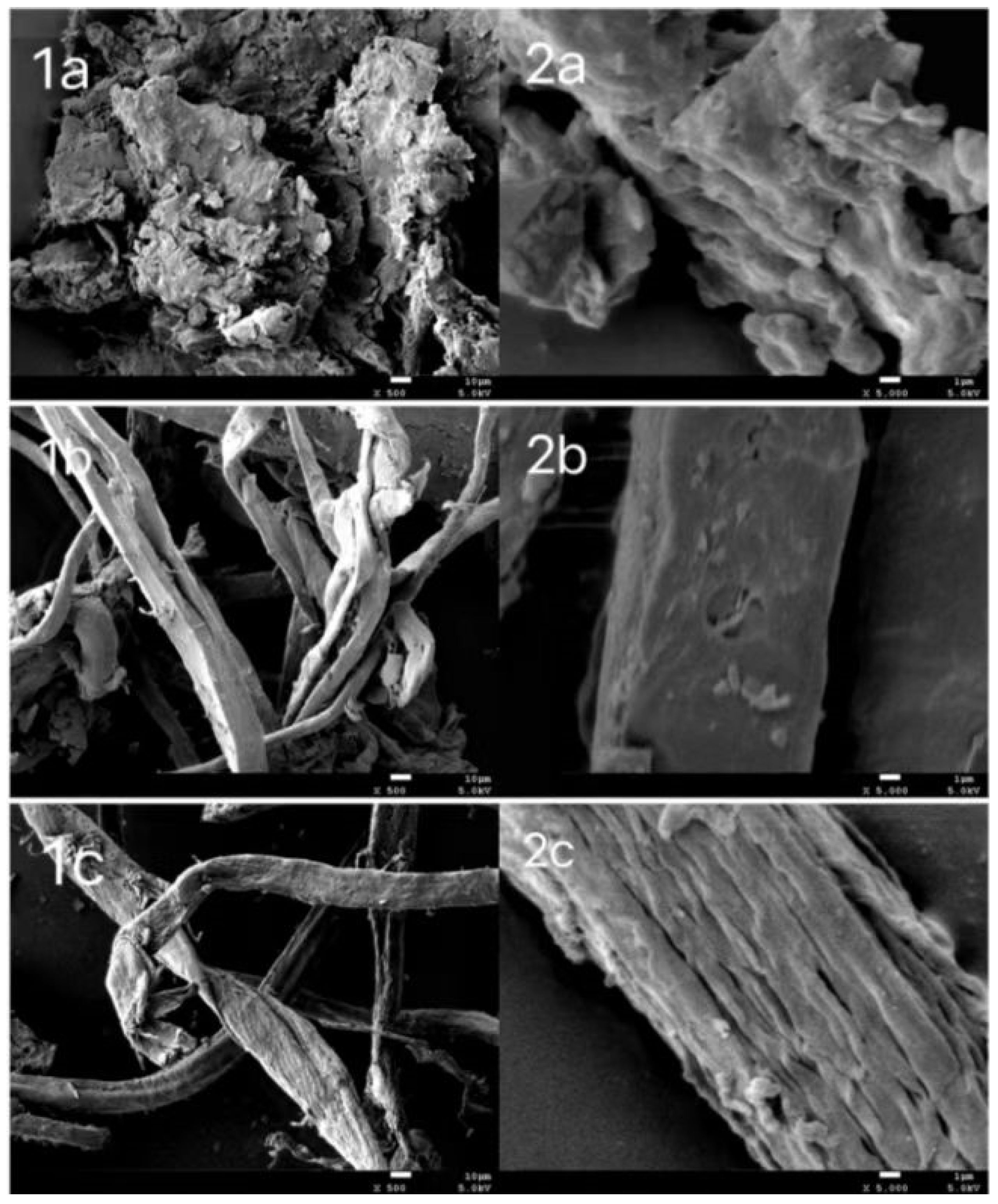
2.6.2. SEM Analysis
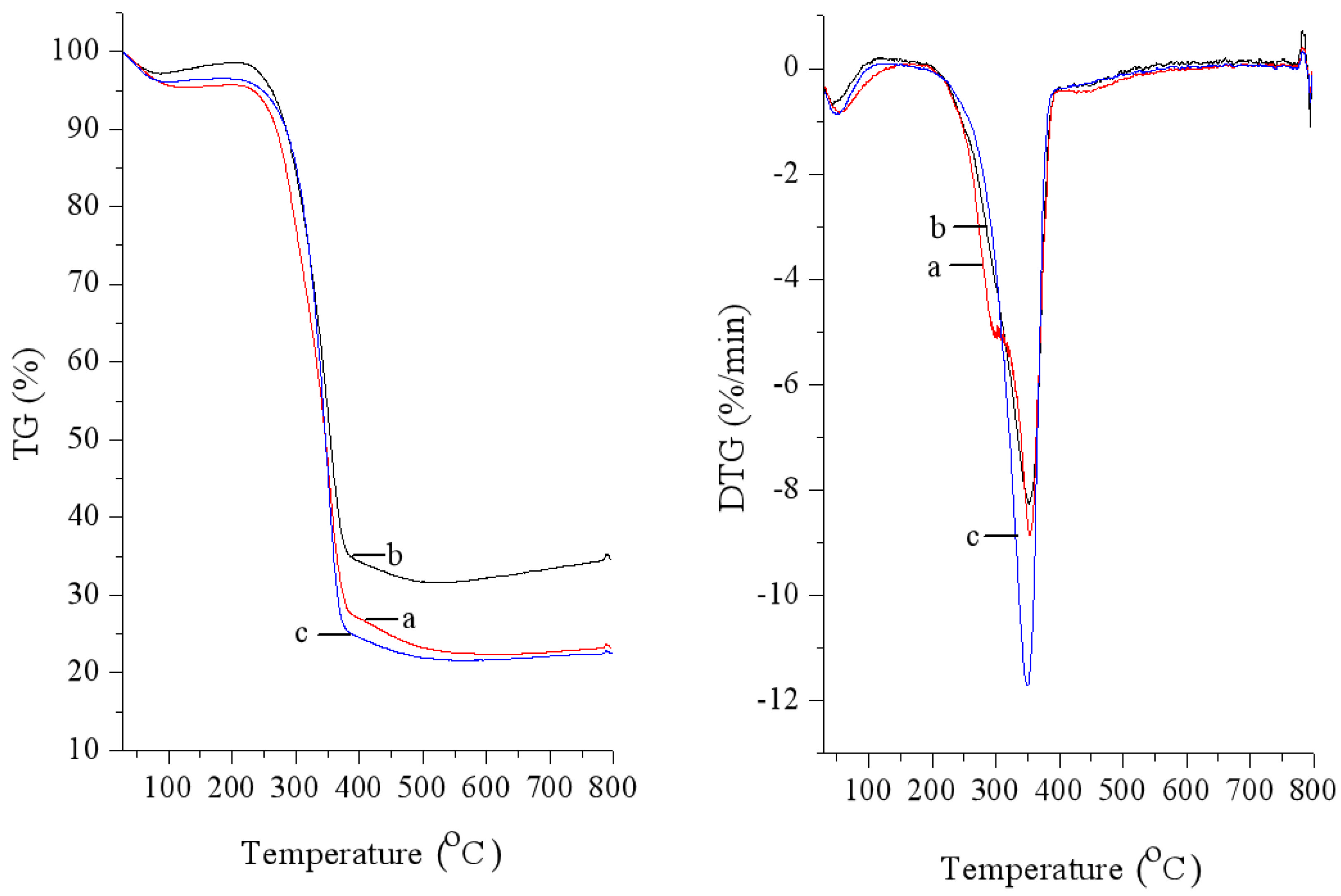
2.6.3. Thermogravimetric (TGA) Analysis
2.7. Separation of Ionic Liquids from the Hydrolysis Product in Post-Treatment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Homogeneous Catalytic Hydrolysis with [HBth][CH3SO3]
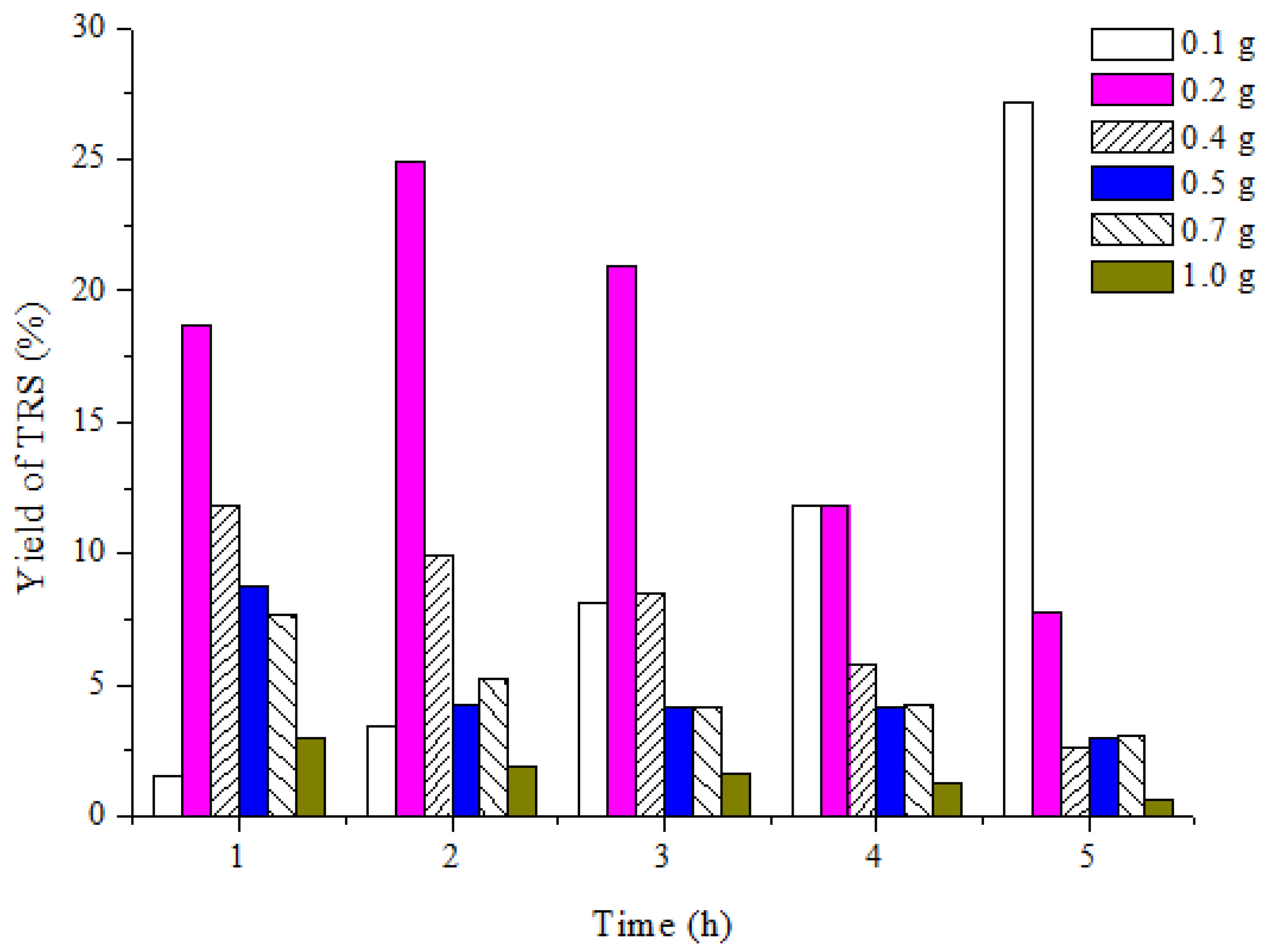
3.1.1. Effect of Catalyst Dosage on Yield of Reducing Sugar
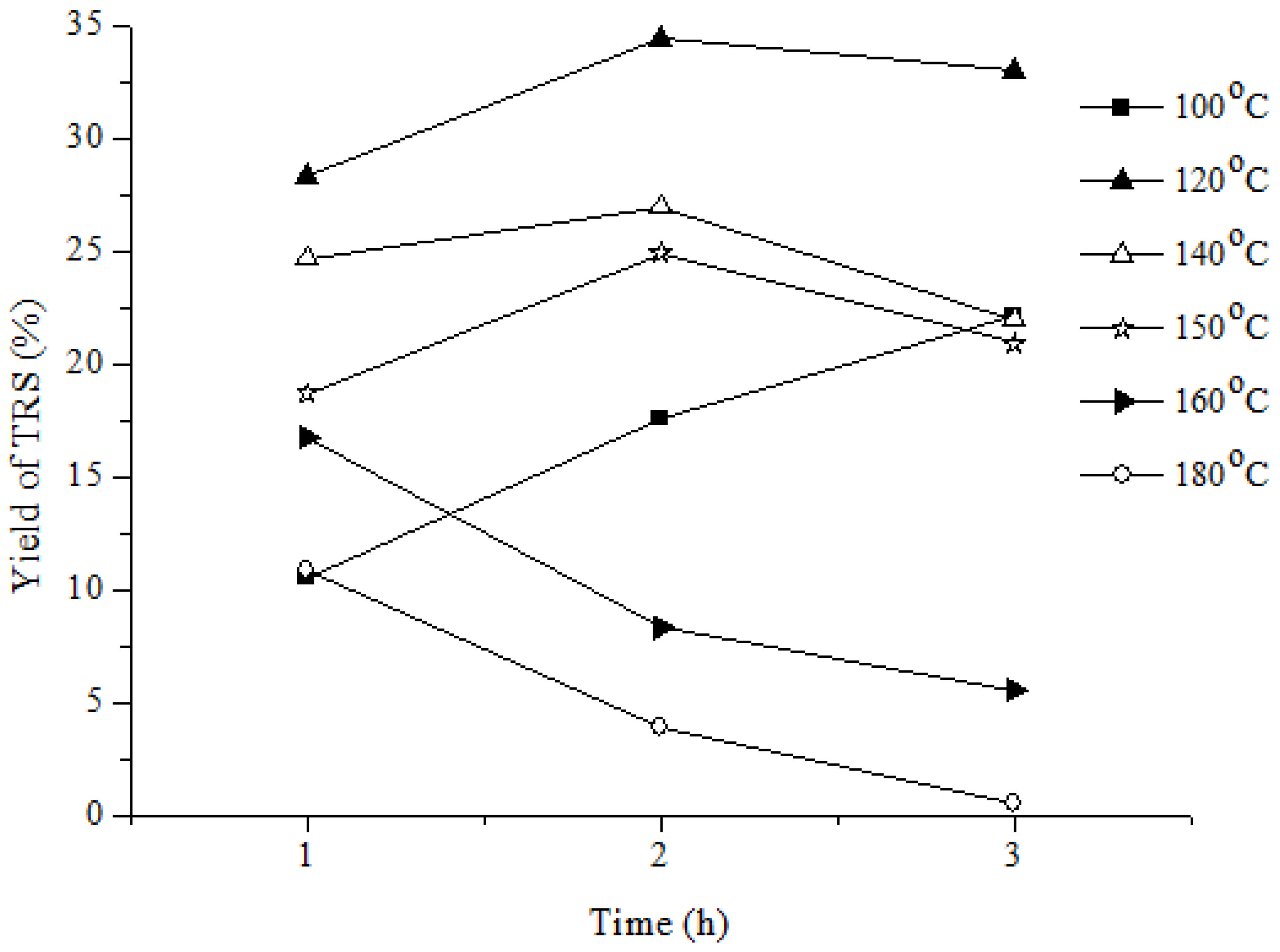
3.1.2. Effect of Reaction Temperature on Yield of Reducing Sugar
3.1.3. Comparison on [HBth][CH3SO3] and Water
3.1.4. Comparison on Pretreatment with Different ILs
3.2. Characterization on Products after Hydrolysis
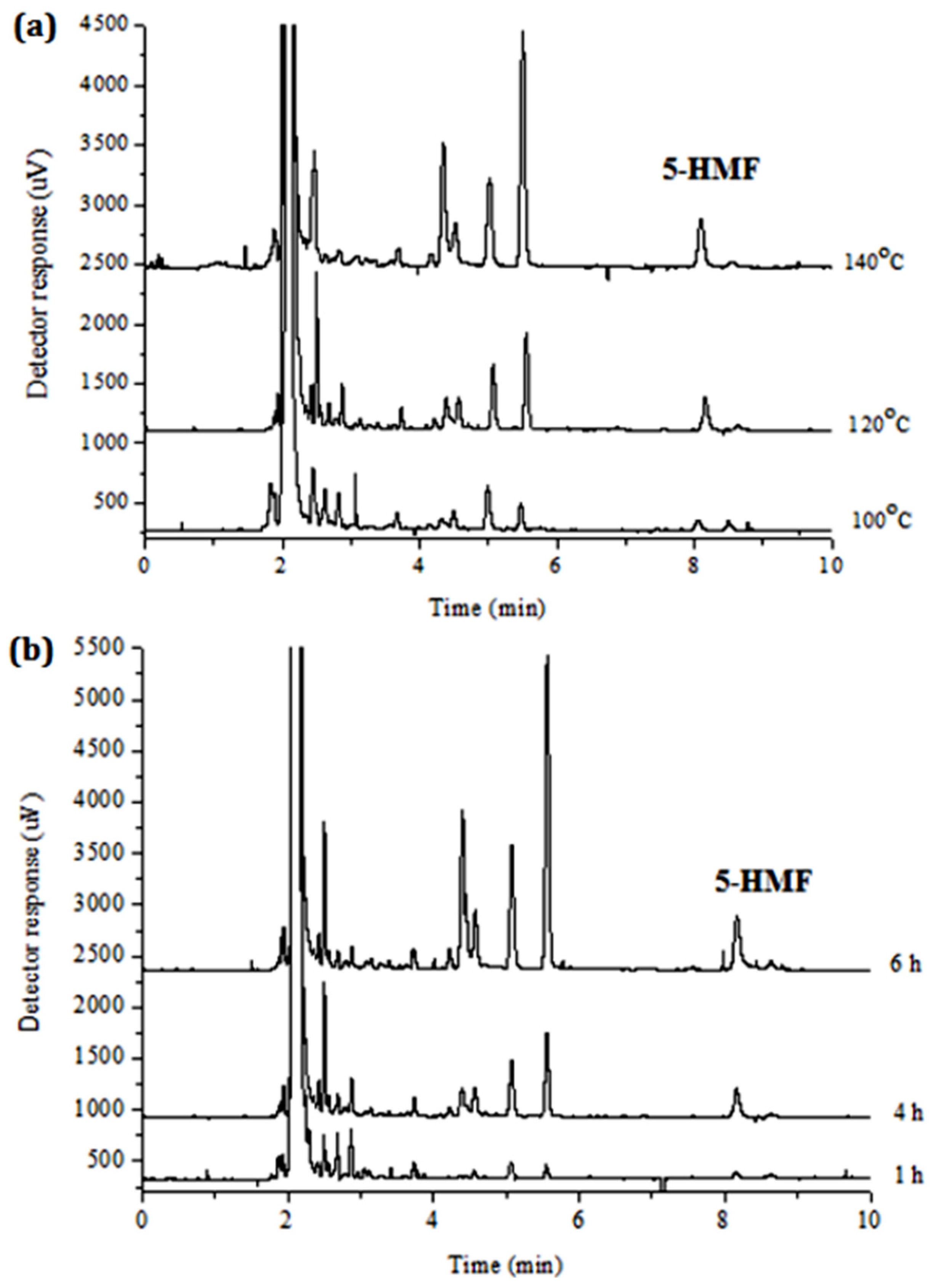
3.3. Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrolysis with [C3SO3Hmim]HSO4
3.4. Separation of Ionic Liquids from Reducing Sugars
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olszewski, A.; Kosmela, P.; Piszczyk, Ł. Bio-polyols synthesized by liquefaction of cellulose: Influence of liquefaction solvent molecular weight. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, 1–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, J.; Chen, M.J.; Szeto, Y.S.; Yan, S. Comparative study of liquefaction process and liquefied products from bamboo using different organic solvents. Biores. Technol. 2009, 100, 6674–6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosier, N.S.; Sarikaya, A.; Ladisch, C.M. Characterization of dicarboxylic acids for cellulose hydrolysis. Biotechnol. Progr. 2001, 17, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganuma, S.; Nakajima, K.; Kitano, M.; Yamaguchi, D.; Kato, H.; Hara, M. Hydrolysis of cellulose by amorphous carbon bearing SO3H, COOH, and OH groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12787–12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagaki, A.; Tagusagawa, C.; Domen, K. Glucose production from saccharides using layered transition metal oxide and exfoliated nanosheets as a water-tolerant solid acid catalyst. Chem. Commun. 2008, 130, 5363–5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogaki, Y.; Shinozuka, Y.; Hatakeyama, M.; Hara, T.; Ichikuni, N.; Shimazu, S. Selective production of xylose and xylooligosaccharides from bamboo biomass by sulfonated allophane solid acid catalyst. Chem. Lett. 2009, 38, 1176–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, T.C.; Guo, G.L.; Chen, W.H.; Hwang, W.S. Effect of dilute acid pretreatment of rice straw on structural properties and enzymatic hydrolysis. Biores. Technol. 2010, 101, 4907–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Jones, C.L.; Baker, G.A.; Xia, S.Q.; Olubajo, O.; Person, V.N. Regenerating cellulose from ionic liquids for an accelerated enzymatic hydrolysis. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 139, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putrino, M.F.; Tedesco, M.; Bodini, B.R.; Oliveria, L.A. Study of supercritical carbon dioxide pretreatment processes on green coconut fiber to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose. Biores. Technol. 2020, 309, 123387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Deng, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Li, K.X. Efficient in situ saccharification of microcrystalline cellulose over immobilized cellulase on magnetic biochar in ionic liquid media. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 485, 149990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Wang, X.K.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Wang, M.; Yi, Y.; Ji, M.; Wang, H.L.; Shao, Z.F.; Liang, C.H. A schiff base modified Pd catalyst for selective hydrogenation of 2- butyne-1,4- diol to 2- butene- 1,4- diol. Catal. Lett. 2020, 150, 2150–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Jian, X.; Wang, J.Y. Preparation of high temperature resistant polycarbonate via ionic liquid activation of bisphenol fluorene under mild conditions. High. Perform. Polym. 2024, 36, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lin, Y. Solidification and conformation of ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium trifluoroacetate under high pressure. Int. J. Heat. Technol. 2023, 41, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiori, S.; Yuko, T.; Masahiro, R.; Masahiro, Y.F. Brønsted acidic ionic liquids for cellulose hydrolysis in an aqueous medium: Structural effects on acidity and glucose yield. RSC. Adv. 2018, 8, 14623–14632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriporn, T.; Worawut, K. Recent progress in processing cellulose using ionic liquids as solvents. Polysaccharides 2022, 3, 671–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Xu, Q.; Liu, J.Y.; Yin, D.L.; Su, S.P.; Ding, H. Hydrolysis of cellulose into reducing sugars in ionic liquids. Fuel 2016, 164, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuke, K.; Kyohei, M.; Heri, S.; Kenji, T.; Kazuaki, N.; Kenji, T. Hydrolysis of cellulose using an acidic and hydrophobic ionic liquid and subsequent separation of glucose aqueous solution from the ionic liquid and 5-(Hydroxymethyl)furfural. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 3352–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.K. Solid acid and microwave-assisted hydrolysis of cellulose in ionic liquid. Carbohyd. Res. 2009, 344, 2069–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, Z.K. Efficient acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of cellulose in ionic liquid. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 1847–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, R.; Palkovits, R.; Schiith, F. Depolymerization of cellulose using solid catalysts in ionic liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8047–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, F.; Song, H.; Yang, J.; Chou, L. Catalytic hydrolysis of cellulose into furans in MnCl2-ionic liquid system. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 85, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.J.; Li, Z.C.; Huang, W.C.; Ali, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G.; Yao, S. Recovery and post-treatment processes for ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 402, 124767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Wei, D. New advances on the pretreatment technology of bagasse for high-effective digestion. J. Cell. Sci. Technol. 2008, 16, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wu, Y.Q. Fabrication and mechanical properties of bagasse fiber reinforced polypropylene composites. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2007, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.F.; He, J.R.; Li, H.; Jin, X.D.; Li, W.G.; Huang, B.Z.; Yu, K.X. Evaluation on feeding value of sugarcane bagasse. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bulletin. 2021, 37, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.; Wang, X.L. Manufacture and performance analysis of bagasse biomass plates. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.K.; Kaur, D.; Chaudhry, S.; Sharma, M.; Arya, S. Approaches for converting sugarcane trash, a promising agro residue, into pulp and paper using soda pulping and elemental chlorine-free bleaching. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Lo, Y.C.; Shu, C.J. Multicomponent cellulase production by Cellulomonas biazotea NCIM-2550 and its applications for cellulosic biohydrogen production. Biotechnol. Progr. 2010, 26, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, Ó.J.; Cardona, C.A. Trends in biotechnological production of fuel ethanol from different feedstocks. Biores. Technol. 2008, 99, 5270–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, M.; Viksø-Nielsen, A.; Meyer, A.S. Monosaccharide yields and lignin removal from wheat straw in response to catalyst type and pH during mild thermal pretreatment. Process Biochem. 2010, 45, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.X.; Zhou, Y.G.; Li, Y.B. Liquid hot water and alkaline pretreatment of soybean straw for improving cellulose digestibility. Biores. Technol. 2011, 102, 6254–6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gu, Y.G.; Yang, Y.; Song, H.; Yao, S. Novel brønsted-acidic ionic liquids based on benzothiazolium cations as catalysts for the acetalization reactions. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 396–398, 1969–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Z.; Fu, Z.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Dai, B.H.; Zou, Y.H.; Gong, X.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Deng, X.L.; Wu, H.T.; Xu, Q. Ionic liquid-functionalized biochar sulfonic acid as a biomimetic catalyst for hydrolysis of cellulose and bamboo under microwave irradiation. Green. Chem. 2014, 14, 1928–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Zhang, Y.W.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, Z.D.; Yao, S.; Song, H. Synthesis and physicochemical properties of new benzothiazole ionic liquids. Chin. J. Syn. Chem. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, F.; Song, H.; Chou, L. Catalytic conversion of cellulose to chemicals in ionic liquid. Carbohyd. Res. 2011, 346, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.Q.; Yi, N.; Zhao, W.Q.; Qiu, N.W. Drawing of standard curves in biological experiments. Exp. Sci. Technol. 2014, 12, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.H.; Wang, W.C.; Zhang, R.L.; Hua, D.; Wang, H.P. Dissolution and regeneration of colored waste cotton fabric in [Bmim]Cl/DMSO. Shanghai Text. Technol. 2022, 50, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.F.; Liu, X.M.; Zhou, S.Y.; Li, S. Synthesis of benzooxanthracene catalyzed by the functionalized ionic liquid [C3SO3Hnhm]HSO4. Household Chem. Ind. 2018, 48, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.S.; Wang, H.Y. Polymer solid electrolyte based on polyionic liquid was prepared by in-situ polymerization. Battery 2023, 53, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhong, L.C. Research progress on dissolution and functional modification of cellulose in ionic liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2008, 142, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Sun, X.F.; Sun, R. Chemical, structural and thermal characterizations of alkali-soluble lignins and hemicelluloses, and cellulose from maize stems, rye straw and rice straw. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 2001, 74, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.N.; Ruan, D.; Zhou, J.P. Structure and properties of regenerated cellulose films prepared from cotton linters in NaOH/urea aqueous solution. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 5923–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Chakrabarty, D. Isolation of nanocellulose from waste sugarcane bagasse (SCB) and its characterization. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 86, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, G.; Zhang, Y.G.; Ying, J.Y. Efficient catalytic system for the selective production of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural from glucose and fructose. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9345–9348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| No. | H2O Volume (μL) | IL Dosage (g) | TRS Yield (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 0.5 | 16.65 |
| 2 | 0 | 0.5 | 9.50 |
| 3 | 100 | 0 | 6.16 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 1.78 |
| ILs | TRS Yield (wt.%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | 2 h | 3 h | |
| [Amim]Cl | 7.99 | 5.05 | 2.87 |
| [Emim]Br | 4.78 | 1.55 | 1.42 |
| [Prmim]Br | 3.96 | 1.12 | 1.27 |
| [Bmim]Br | 3.09 | 1.91 | 0.80 |
| HCl Concentration (%) | [Bmim]+-Loaded Resin | [Bmim]+·[HBth]+-Loaded Resin | |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Bmim]Cl Desorption Rate (%) | [Bmim]Cl Desorption Rate (%) | [HBth]+ Desorption Rate (%) | |
| 1 | 16.55 | 12.47 | 5.58 |
| 5 | 58.01 | 55.10 | 28.35 |
| 10 | 77.06 | 73.95 | 48.55 |
| 15 | 92.05 | 90.04 | 52.95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Li, J.; Liu, E.; Ali, A.; Li, Z.; Yao, S. Ionic Liquid Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Sugarcane Cellulose to Produce Reducing Sugar. Biomass 2024, 4, 886-903. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass4030049
Liu R, Li J, Liu E, Ali A, Li Z, Yao S. Ionic Liquid Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Sugarcane Cellulose to Produce Reducing Sugar. Biomass. 2024; 4(3):886-903. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass4030049
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ruihuan, Jiying Li, Enming Liu, Ahmad Ali, Zicheng Li, and Shun Yao. 2024. "Ionic Liquid Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Sugarcane Cellulose to Produce Reducing Sugar" Biomass 4, no. 3: 886-903. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass4030049
APA StyleLiu, R., Li, J., Liu, E., Ali, A., Li, Z., & Yao, S. (2024). Ionic Liquid Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Sugarcane Cellulose to Produce Reducing Sugar. Biomass, 4(3), 886-903. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass4030049









