Cosmeceutical Applications of Phlorotannins from Brown Seaweeds
Abstract
1. Introduction
Phlorotannins
2. Cosmeceutical Applications of Phlorotannins Isolated from Brown Seaweeds
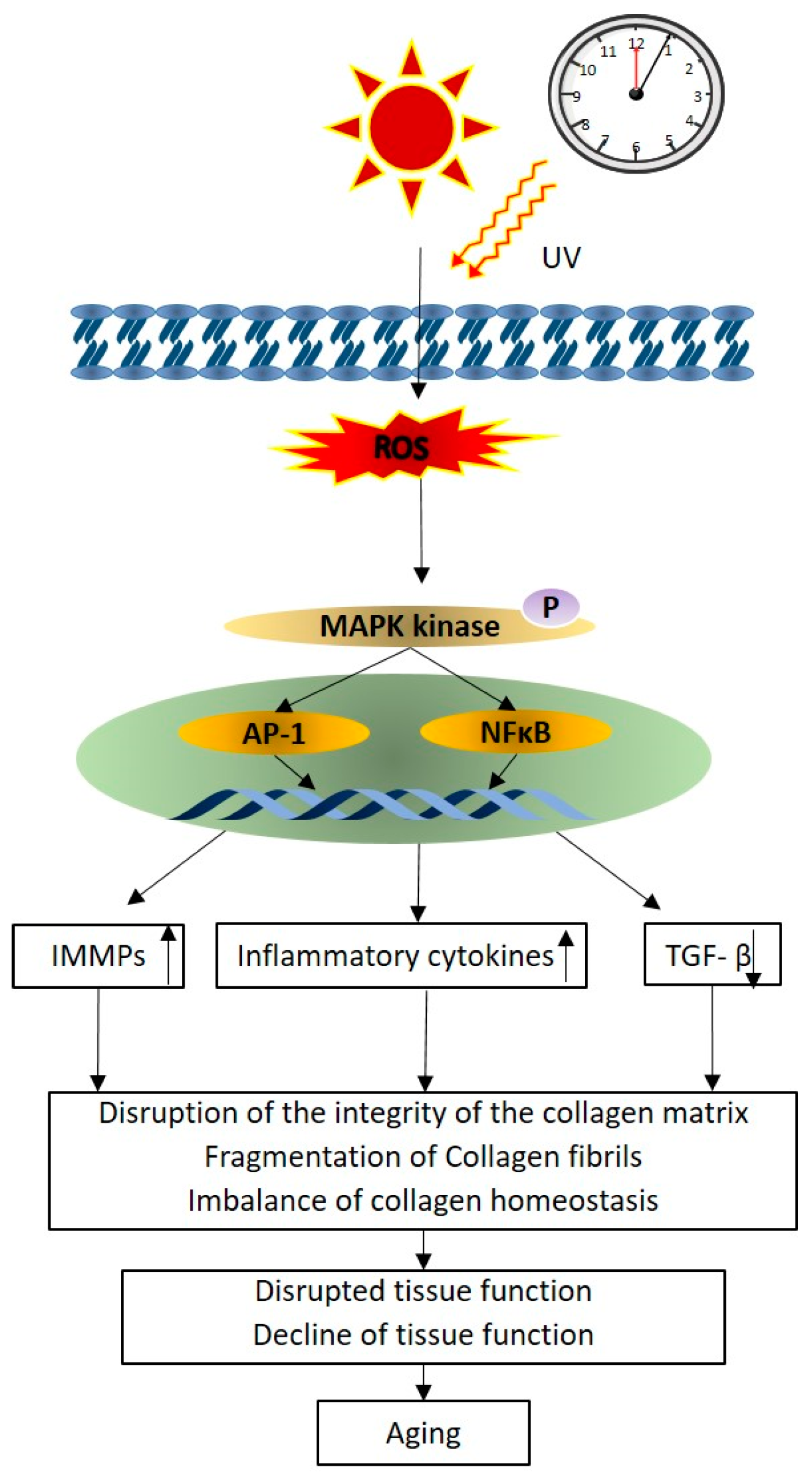
2.1. Photo-Protective and Anti-Aging Properties of Phlorotannins
2.2. Whitening Properties of Phlorotannins
2.3. Antioxidant Activity
2.4. Anti-Acne Potential of Phlorotannins
2.5. Hair Growth Activities of Phlorotannins
2.6. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Allergenic Activities of Phlorotannins
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| PGU | Phloroglucinol units |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| GAGs | Glycosaminoglycans |
| PGs | Proteoglycans |
| UHPLC | Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| UVR | Ultraviolet radiation |
| DNA | Deoxyribosnucleic acid |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-κb |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| HDF | Human dermal fibroblast |
| EGCG | Epigallocatechin gallate |
| PT | Phlorotannins |
| EC | E. Cava |
| PBE | Padina boryana |
| EV | Extracellular vesicle |
| HSP70 | Heat shock protein 70 |
| α-MSH | A-melanocyte-stimulating hormone |
| EC50 | Effective concentration 50 |
| AP-1 | Activator protein 1 |
| TRP | Tyrosinase-related protein |
| MITF | Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor |
| INCI | International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients |
| BHT | Butylated hydroxytoluene |
| BHA | Butylated hydroxyanisole |
| TBHQ | Tert-butylhydroquinone |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| IL | Interleukin |
| DPCs | Dermal papilla cells |
| hfSCs | Hair follicle stem cells |
| AGA | Androgenetic alopecia |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| JAK | Janus Kinases |
| STAT | Transducers and Activators of Transcription |
References
- Dini, I.; Laneri, S. The New Challenge of Green Cosmetics: Natural Food Ingredients for Cosmetic Formulations. Molecules 2021, 26, 3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.; Kroumpouzos, G. Beauty perception: A historical and contemporary review. Clin. Dermatol. 2023, 41, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnuqaydan, A.M. The dark side of beauty: An in-depth analysis of the health hazards and toxicological impact of synthetic cosmetics and personal care products. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1439027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalasariya, H.S.; Pereira, L. Dermo-Cosmetic Benefits of Marine Macroalgae-Derived Phenolic Compounds. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço-Lopes, C.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Jimenez-Lopez, C.; Pereira, A.G.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Carpena, M.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Metabolites from Macroalgae and Its Applications in the Cosmetic Industry: A Circular Economy Approach. Resources 2020, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalasariya, H.S.; Maya-Ramírez, C.E.; Cotas, J.; Pereira, L. Cosmeceutical Significance of Seaweed: A Focus on Carbohydrates and Peptides in Skin Applications. Phycology 2024, 4, 276–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Kim, K.B.; Yoon, S.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, B.-M. Risk assessment of unintentional phthalates contaminants in cosmetics. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 115, 104687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagarasaiyar, K.; Goh, B.-H.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Yow, Y.-Y. Algae Metabolites in Cosmeceutical: An Overview of Current Applications and Challenges. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, P.L.M.; Nieri, V.; Moreli, F.d.C.; Constantino, E.; de Souza, J.; Oshima-Franco, Y.; Grotto, D. Unveiling New Horizons: Advancing Technologies in Cosmeceuticals for Anti-Aging Solutions. Molecules 2024, 29, 4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, D.S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Jayawardena, T.U. What is Seaweed? General Facts about Seaweeds. In The Role of Seaweeds in Blue Bioeconomy; Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Chukwuma, O.C.; Tan, S.P.; Hughes, H.; McLoughlin, P.; O’Toole, N.; McCarthy, N. The potential of seaweeds as a rich natural source for novel bioherbicide formulation/development. Weed Sci. 2024, 72, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Kareem, M.S.M.; ElSaied, A.A.F.; Abdel-Kareem, M.S.M.; ElSaied, A.A.F. Global seaweeds diversity. In Handbook of Algal Biofuels; El-Sheekh, M., Abomohra, A.E.-F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 39–55. [Google Scholar]
- Anjana, K.; Arunkumar, K. Brown algae biomass for fucoxanthin, fucoidan and alginate; update review on structure, biosynthesis, biological activities and extraction valorisation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280 Pt 2, 135632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cikoš, A.-M.; Šubarić, D.; Roje, M.; Babić, J.; Jerković, I.; Jokić, S. Recent advances on macroalgal pigments and their biological activities (2016–2021). Algal Res. 2022, 65, 102748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remya, R.R.; Samrot, A.V.; Kumar, S.S.; Mohanavel, V.; Karthick, A.; Chinnaiyan, V.K.; Umapathy, D.; Muhibbullah, M.; Nassar, A. Bioactive Potential of Brown Algae. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 9104835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, A.; Baroutian, S. Current status and trends in extraction of bioactives from brown macroalgae using supercritical CO2 and subcritical water. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.V.; Diyya AS, M.; Ghafour, D.D.; Kim, S.-K. Marine Algal Phlorotannins and their Biological Importance. In Encyclopedia of Marine Biotechnology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1535–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, L. A Bioactive Substance Derived from Brown Seaweeds: Phlorotannins. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.R.G.; Paul, P.T.; Anas, K.K.; Tejpal, C.S.; Chatterjee, N.S.; Anupama, T.K.; Mathew, S.; Ravishankar, C.N. Phlorotannins-bioactivity and extraction perspectives. J. Appl. Phycol. 2022, 34, 2173–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Kim, E.A.; Son, K.T.; Jeon, Y.J. Bioactive properties and potentials cosmeceutical applications of phlorotannins isolated from brown seaweeds: A review. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2016, 162, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiviya, P.; Gamage, A.; Gama-Arachchige, N.S.; Merah, O.; Madhujith, T. Seaweeds as a Source of Functional Proteins. Phycology 2022, 2, 216–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, I.; Huovinen, P. Brown Algal Phlorotannins: An Overview of Their Functional Roles. In Antarctic Seaweeds; Gómez, I., Huovinen, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 365–388. [Google Scholar]
- Pradhan, B.; Nayak, R.; Bhuyan, P.P.; Patra, S.; Behera, C.; Sahoo, S.; Ki, J.-S.; Quarta, A.; Ragusa, A.; Jena, M. Algal Phlorotannins as Novel Antibacterial Agents with Reference to the Antioxidant Modulation: Current Advances and Future Directions. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Agar, O.T.; Barrow, C.J.; Dunshea, F.R.; Suleria, H.A.R. Improving potential strategies for biological activities of phlorotannins derived from seaweeds. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 65, 833–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Mu, T.; Sun, H.; Garcia-Vaquero, M. Phlorotannins: A review of extraction methods, structural characteristics, bioactivities, bioavailability, and future trends. Algal Res. 2021, 60, 102484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, L.; Theodoridou, K.; Sheldrake, G.N.; Walsh, P.J. A critical review of analytical methods used for the chemical characterisation and quantification of phlorotannin compounds in brown seaweeds. Phytochem. Anal. 2019, 30, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardari, R.R.R.; Prothmann, J.; Gregersen, O.; Turner, C.; Karlsson, E.N. Identification of Phlorotannins in the Brown Algae, Saccharina latissima and Ascophyllum nodosum by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to High-Resolution Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 26, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catarino, M.D.; Pires, S.M.G.; Silva, S.; Costa, F.; Braga, S.S.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Overview of Phlorotannins’ Constituents in Fucales. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Zhang, W.; Smid, S.D. Phlorotannins: A review on biosynthesis, chemistry and bioactivity. Food Biosci. 2021, 39, 100832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.A.; Hargest, R. Surgical anatomy of the skin. Surgery 2022, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Workman, V.L.; Giblin, A.V.; Green, N.H.; MacNeil, S.; Hearnden, V. Development of a tissue-engineered skin model with epidermal, dermal and hypodermal components. Vitr. Models 2023, 2, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, J.; Du, R.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, P. Collagen study advances for photoaging skin. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2024, 40, e12931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardhana, H.H.A.C.K.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Liyanage, N.M.; Nagahawatta, D.P.; Lee, H.-G.; Kim, J.-I.; Jeon, Y.-J. Marine Algal Polyphenols as Skin Protective Agents: Current Status and Future Prospectives. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; He, X.; Liu, N.; Deng, H. Role of reactive oxygen species in ultraviolet-induced photodamage of the skin. Cell Div. 2024, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gromkowska-Kępka, K.J.; Puścion-Jakubik, A.; Markiewicz-Żukowska, R.; Socha, K. The impact of ultraviolet radiation on skin photoaging—Review of in vitro studies. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 3427–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Chen, X.; Yin, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, C. Matrix Metalloproteinases on Skin Photoaging. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2024, 23, 3847–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.-J.; Ji, Y.; Jang, Y.-P.; Choung, S.-Y. Acer tataricum subsp. ginnala Inhibits Skin Photoaging via Regulating MAPK/AP-1, NF-κB, and TGFβ/Smad Signaling in UVB-Irradiated Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Molecules 2021, 26, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, N. Potential Active Marine Peptides as Anti-Aging Drugs or Drug Candidates. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gager, L.; Connan, S.; Molla, M.; Couteau, C.; Arbona, J.F.; Coiffard, L.; Cerantola, S.; Pouvreau, V.S. Active phlorotannins from seven brown seaweeds commercially harvested in Brittany (France) detected by 1H NMR and in vitro assays: Temporal variation and potential valorization in cosmetic applications. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 2375–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Kim, H.-S.; Je, J.-G.; Fu, X.; Huang, C.; Ahn, G.; Oh, J.-Y.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Xu, J.; Gao, X.; et al. In Vitro and In Vivo Photoprotective Effects of (-)-Loliode Isolated from the Brown Seaweed, Sargassum horneri. Molecules 2021, 26, 6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsukh, S.; Oh, S.; Lee, J.M.; Joo, J.H.; Son, K.H.; Byun, K. Extracellular Vesicles from Ecklonia cava and Phlorotannin Promote Rejuvenation in Aged Skin. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; John, J. Identification of polyphenols using UPLC-QTOF MS/MS, in-vitro photoprotective and antiaging activities of brown macroalga Padina tetrastromatica. Algal Res. 2023, 75, 103255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalasariya, H.S.; Pereira, L.; Patel, N.B. Pioneering Role of Marine Macroalgae in Cosmeceuticals. Phycology 2022, 2, 172–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa-Cansigno, C.; Serviere-Zaragoza, E.; Morales-Martínez, T.K.; Ascacio-Valdes, J.A.; Morreeuw, Z.P.; Gauyat, C.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Reyes, A.G. The antioxidant and anti-elastase activity of the brown seaweed Sargassum horridum (Fucales, Phaeophyceae) and their early phenolics and saponins profiling for green cosmetic applications. Algal Res. 2023, 75, 103271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.C.D.; Levi, P.M.; Vidal, P.S.A.L.; Carlos, C.M.R.; Negrão, C.D.; Guilherme, W.B.; Letícia, M.S.A.; Marcela, C.O.J. Dermocosmetic properties of bioproducts from Sargassum macroalgae: Chemical aspects, challenges, and opportunities. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1500778. (In English) [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero-Higareda, S.; Carrillo-Nieves, D. Green extraction cascade of UV-absorbing compounds, alginate, and fucoidan from Sargassum using ethanol and natural deep eutectic solvents. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunkumar, K.; Raj, R.; Raja, R.; Carvalho, I.S. Brown seaweeds as a source of anti-hyaluronidase compounds. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 139, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, B.J.L.S.L. Innovation in cosmetic products with Sargassam sp. Life Sci. Leafl. 2024, 166, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, L.; Lee, S.G.; Lim, K.T.; Kim, H.-R. Potential Anti-Aging Substances Derived from Seaweeds. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirata, S.; Asnaghi, V.; Chiantore, M.; Salis, A.; Benvenuti, M.; Damonte, G.; Scarfì, S. Photoprotective and Anti-Aging Properties of the Apical Frond Extracts from the Mediterranean Seaweed Ericaria amentacea. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utami, D.T.; Setyowati, E.P.; Murti, Y.B.; Meiyanto, E. Marine resources with melanogenic regulatory properties: Seagrass, seaweed, and marine sponges as anti-melanogenic agents. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 14, 045–058. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, A.; Sousa, E.; Kijjoa, A.; Pinto, M. Marine-Derived Compounds with Potential Use as Cosmeceuticals and Nutricosmetics. Molecules 2020, 25, 2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-K. Natural products in cosmetics. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2022, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, A.; Wang, J.; Huang, D.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qu, Q.; Ma, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhu, M.; et al. Potential application of natural bioactive compounds as skin-whitening agents: A review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 6669–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gam, D.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Hong, J.-W.; Jeon, S.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.-W. Effects of Sargassum thunbergii Extract on Skin Whitening and Anti-Wrinkling through Inhibition of TRP-1 and MMPs. Molecules 2021, 26, 7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Bhatt, K.; Shrivastava, R.; Nadda, A.K. Chapter 14—Tyrosinase and Oxygenases: Fundamentals and Applications. In Biotechnology of Microbial Enzymes, 2nd ed.; Brahmachari, G., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carradori, S.; Melfi, F.; Rešetar, J.; Şimşek, R. Tyrosinase enzyme and its inhibitors: An update of the literature. In Metalloenzymes; Supuran, C.T., Donald, W.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2024; pp. 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arguelles, E.; Sapin, A. Bioprospecting of Turbinaria ornata (Fucales, phaeophyceae) for cosmetic application: Antioxidant, tyrosinase inhibition and antibacterial activities. J. Int. Soc. Southeast Asian Agric. Sci. 2020, 26, 30–41. [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardena, T.U.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, H.G.; Wang, L.; Lee, D.S.; Jeon, Y.J. Padina boryana, a brown alga from the Maldives: Inhibition of α-MSH-stimulated melanogenesis via the activation of ERK in B16F10 cells. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Kondo, S.; Tajima, K.; Shibata, T.; Itoh, T. Effect of Phlorotannins Isolated from Eisenia bicyclis on Melanogenesis in Mouse B16 Melanoma Cells. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2021, 16, 1934578X211019264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, X.; Han, X.; Lee, S.-J.; Oh, G.; Jin, H.; Oh, H.-J.; Kim, E.; Kim, J.; Lee, B.-Y.; Choi, S.-I.; et al. In-Depth Understanding of Ecklonia stolonifera Okamura: A Review of Its Bioactivities and Bioactive Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chen, H.; Qiao, K.; Xu, M.; Wu, J.; Su, Y.; Shi, Y.; Ke, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q. Anti-Melanogenic Activities of Sargassum fusiforme Polyphenol-Rich Extract on α-MSH-Stimulated B16F10 Cells via PI3K/Akt and MAPK/ERK Pathways. Foods 2024, 13, 3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Huh, Y.; Lim, K.-M. Anti-Pigmentary Natural Compounds and Their Mode of Action. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, K.-A.; Park, Y.; Oh, S.; Batsukh, S.; Son, K.H.; Byun, K. Co-Treatment with Phlorotannin and Extracellular Vesicles from Ecklonia cava Inhibits UV-Induced Melanogenesis. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirindage, K.G.I.S.; Jayasinghe, A.M.K.; Ko, C.L.; Ahn, T.S.; Heo, S.J.; Oh, J.Y.; Kim, E.A.; Cha, S.H.; Ahn, G. Unveiling the potential of ultrasonic-assisted ethanol extract from Sargassum horneri in inhibiting tyrosinase activity and melanin production in B16F10 murine melanocytes. Front. Biosci. 2024, 29, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Dias, M.K.H.M.; Madusanka, D.M.D.; Han, E.J.; Kim, M.J.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Ahn, G. Step gradient alcohol precipitation for the purification of low molecular weight fucoidan from Sargassum siliquastrum and its UVB protective effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-K.; Ryu, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Jeong, H.H.; Baek, J.; Van, J.Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Jung, W.-K.; Lee, B. Potential Beneficial Effects of Sargassum spp. in Skin Aging. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Jeong, J.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, C.-S. Comparative analysis of biological activities and phenolic content between fresh and steamed Sargassum fusiforme in different extraction solvents. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.; Chung, H.; Jung, H.; Song, H.-K.; Park, E.; Choi, H.S.; Jung, K.; Choe, H.; Yang, S.; Oh, E.-S. Extracellular vesicles from Korean Codium fragile and Sargassum fusiforme negatively regulate melanin synthesis. Mol. Cells 2021, 44, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.W.; Yim, M.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, M.S.; Lee, D.S.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kim, K.T.; Kim, Y.M.; Eom, S.H. Tyrosinase inhibition effects of Korean edible brown, green, and red seaweed extracts. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2024, 27, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.V.; Diyya, A.S.M.; Ghafour, D.D.; Kim, S.K.J. Marine Algal Phlorotannins and their biological importance. Encycl. Mar. Biotechnol. 2020, 3, 1535–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Lee, W.; Ahn, G. Marine algal flavonoids and phlorotannins; an intriguing frontier of biofunctional secondary metabolites. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2022, 42, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotas, J.; Leandro, A.; Monteiro, P.; Pacheco, D.; Figueirinha, A.; Gonçalves, A.M.M.; da Silva, G.J.; Pereira, L. Seaweed Phenolics: From Extraction to Applications. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arguelles, E. Bioactive properties of Halymenia durvillei Bory 1828 for pharmaceutical application: Antioxidant, antidiabetic, antiwrinkling and skin-whitening activities. Yuz. Yıl Univ. J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 32, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V.; Xie, C.; Dunshea, F.R.; Barrow, C.J.; Suleria, H.A.R. The Quest for Phenolic Compounds from Seaweed: Nutrition, Biological Activities and Applications. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 39, 5786–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, K.; Tsuruta, D. What Are Reactive Oxygen Species, Free Radicals, and Oxidative Stress in Skin Diseases? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jayawardena, T.U.; Wang, K.; Ahn, G.; Cha, S.-H.; Jeon, Y.-J. Protective effect of the brown seaweed Padina boryana against UVB-induced photoaging in vitro in skin cells and in vivo in zebrafish. Algal Res. 2023, 76, 103316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcov, D.; Zbranca-Toporas, A.; Suteu, D. Bioactive Compounds for Combating Oxidative Stress in Dermatology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, H.T.; Moon, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C. Natural Antioxidants from Plant Extracts in Skincare Cosmetics: Recent Applications, Challenges and Perspectives. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima Cherubim, D.J.; Martins, C.V.B.; Farina, L.O.; da Silva de Lucca, R.A. Polyphenols as natural antioxidants in cosmetics applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Qiu, J. Oxidative stress in the skin: Impact and related protection. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, R.; Howlader, S.; Mamun-Or-Rashid, A.N.M.; Rafiquzzaman, S.M.; Ashraf, G.M.; Albadrani, G.M.; Sayed, A.A.; Peluso, I.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Uddin, M.S. Antioxidant and Signal-Modulating Effects of Brown Seaweed-Derived Compounds against Oxidative Stress-Associated Pathology. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 9974890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, R.; Martins, A.; Silva, J.; Alves, C.; Pinteus, S.; Alves, J.; Teodoro, F.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Gonçalves, L.; Petrovski, Ž.; et al. Highlighting the Biological Potential of the Brown Seaweed Fucus spiralis for Skin Applications. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xiong, P.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Analysis, occurrence, toxicity and environmental health risks of synthetic phenolic antioxidants: A review. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Sun, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Yu, C.; Qi, H. Preparation, Characterization and Antioxidant Activities of Kelp Phlorotannin Nanoparticles. Molecules 2020, 25, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Je, J.-G.; Yang, H.-W.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Lee, S. Dieckol, an Algae-Derived Phenolic Compound, Suppresses UVB-Induced Skin Damage in Human Dermal Fibroblasts and Its Underlying Mechanisms. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddheshiya, S.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, W.; Zakir, F.; Aggarwal, G. Essential oils for the treatment of skin anomalies: Scope and potential. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 151, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abozeid, D.; Fawzy, G.; Issa, M.; Abdeltawab, N.; Soliman, F.J.B.R.A.C. Medicinal Plants and their Constituents in the Treatment of Acne vulgaris. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 13, 189. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, A.K.; Barankin, B.; Lam, J.M.; Leong, K.F.; Hon, K.L. Dermatology: How to manage acne vulgaris. Drugs Context 2021, 10, 2021-8-6. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dréno, B.; Dagnelie, M.A.; Khammari, A.; Corvec, S. The Skin Microbiome: A New Actor in Inflammatory Acne. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallo, M.; Patel, K.; Hebert, A.A. Topical Antibiotic Treatment in Dermatology. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S.; Noorizadeh, K.; Zadmehr, O.; Rasekh, S.; Mohammadi-Samani, S.; Dehghan, D. Novel topical drug delivery systems in acne management: Molecular mechanisms and role of targeted delivery systems for better therapeutic outcomes. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 74, 103595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, W.; Han, E.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Ahn, G.; Kim, K.N. Eckol from Ecklonia cava ameliorates TNF-alpha/IFN-gamma-induced inflammatory responses via regulating MAPKs and NF-kappaB signaling pathway in HaCaT cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 82, 106146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, E.; Shabanpour, B.; Pourashouri, P.; Payamnoor, V.; Sharifian, S.; Bita, S. Nanoliposome-encapsulated and biopolymer-coated phlorotannin extract of Sargassum tenerrimum: A promising approach for enhanced antibacterial activity against acne-related bacteria. Iran. J. Fish. Sci. 2024, 23, 31–49. (In English) [Google Scholar]
- Ramsis, T.; Refat, M.S.H.M.; Elseedy, H.; Fayed, E.A. The role of current synthetic and possible plant and marine phytochemical compounds in the treatment of acne. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 24287–24321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besednova, N.N.; Andryukov, B.G.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Kryzhanovsky, S.P.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Fedyanina, L.N.; Makarenkova, I.D.; Zvyagintseva, T.N. Algae Polyphenolic Compounds and Modern Antibacterial Strategies: Current Achievements and Immediate Prospects. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lim, Y.J.; Kim, H.S.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, J.N.; Lee, J.H.; Bae, S. Phloroglucinol Enhances Anagen Signaling and Alleviates H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in Human Dermal Papilla Cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 812–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadgrove, N.; Batra, S.; Barreto, D.; Rapaport, J. An Updated Etiology of Hair Loss and the New Cosmeceutical Paradigm in Therapy: Clearing ‘the Big Eight Strikes’. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisuitiprot, V.; Ingkaninan, K.; Chakkavittumrong, P.; Wisuitiprot, W.; Neungchamnong, N.; Chantakul, R.; Waranuch, N. Effects of Acanthus ebracteatus Vahl. extract and verbascoside on human dermal papilla and murine macrophage. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.; Handa, M.; Ujjwal, R.R.; Singh, V.; Kesharwani, P.; Shukla, R. Potential of nanoparticulate based delivery systems for effective management of alopecia. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 208, 112050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manandhar, B.; Paudel, P.; Seong, S.H.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Characterizing Eckol as a Therapeutic Aid: A Systematic Review. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.-m.; Xue, W.-t.; Liao, L.-y.; Ling, X.; Yu, D.; Lan, X.-l.; Zhou, W.-q.; Li, L. Anti-allergic activity of natural plant products for the treatment of sensitive skin: A review. Pharmacol. Res. Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 3, 100117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, M.J.M.P. Contact sensitization and allergens in the composition of cosmetic products-current knowledge. Med. Rev. 2021, 74, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Hu, S.; Lou, Z.; Gao, J. The macrophage polarization in inflammatory dermatosis and its potential drug candidates. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 161, 114469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hyun, C.-G. Natural Products for Cosmetic Applications. Molecules 2023, 28, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, E.S.; Nweze, E.J.; Chibuogwu, C.C.; Anaduaka, E.G.; Chukwudozie, K.I.; Ezeorba, T.P.C. Aquatic Phlorotannins and Human Health: Bioavailability, Toxicity, and Future Prospects. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2021, 16, 1934578X211056144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirindage, K.G.I.S.; Jayasinghe, A.M.K.; Han, E.-J.; Han, H.-J.; Kim, K.-N.; Wang, L.; Heo, S.-J.; Jung, K.-S.; Ahn, G. Phlorofucofuroeckol-A refined by edible brown algae Ecklonia cava indicates anti-inflammatory effects on TNF-α/IFN-γ-stimulated HaCaT keratinocytes and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate-induced ear edema in BALB/c mice. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 109, 105786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bong, S.-K.; Park, N.-J.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, A.T.; Liu, X.; Kim, S.M.; Yang, M.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.-N. Trifuhalol A Suppresses Allergic Inflammation through Dual Inhibition of TAK1 and MK2 Mediated by IgE and IL-33. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.A.M.; Félix, R.; Félix, C.; Januário, A.P.; Alves, N.; Novais, S.C.; Dias, J.R.; Lemos, M.F.L. A Biorefinery Approach to the Biomass of the Seaweed Undaria pinnatifida (Harvey Suringar, 1873): Obtaining Phlorotannins-Enriched Extracts for Wound Healing. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catarino, M.D.; Silva, A.; Cruz, M.T.; Mateus, N.; Silva, A.M.S.; Cardoso, S.M. Phlorotannins from Fucus vesiculosus: Modulation of Inflammatory Response by Blocking NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phasanasophon, K.; Kim, S.M. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the Phlorotannin Trifuhalol A Using LPS-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells Through NF-κB and MAPK Main Signaling Pathways. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 1934578X19849798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name of the Seaweed | Activity | References |
|---|---|---|
| Padina tetrastromatica | Anti-tyrosinase Anti-elastase Anti-collagenase | [42,43] |
| Sargassum horridum | Anti-elastase | [44,45,46] |
| Sargassum tenerrimum | Anti-hyaluronidase | [47,48] |
| Ecklonia cava | Downregulating matrix metalloproteinases | [8,33,39,41,43,49] |
| Ericaria amentacea | Anti-tyrosinase Anti-hydrolytic | [50,51] |
| Laminaria japonica (Kombu) | Anti-hyaluronidase Anti-tyrosinase Anti-UVB-induced | [8,52] |
| Name of Brown Seaweed | Activities | References |
|---|---|---|
| Sargassum horridum | Antioxidant | [44,63] |
| Ecklonia stolonifera Okamura | Tyrosinase inhibition | [18,63] |
| Ecklonia cava | Anti-melanogenesis | [8,64] |
| Sargassum horneri | Antioxidant | [40,45,65] |
| Sargassum siliquastrum | Photoprotective effect | [45,66,67] |
| Sargassum fusiforme | Anti-melanogenesis, downregulated the expression of tyrosinase-1 (TRP-1) | [45,62,68,69] |
| Ishige okamurae | Tyrosinase inhibition | [70,71,72] |
| Padina tetrastromatica | Photoprotective effect | [42,73,74] |
| Ecklonia bicyclis | Tyrosinase inhibition | [18,60,73,75] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gunasekara, D.M.N.M.; Wang, L.; Herath, K.H.I.N.M.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A. Cosmeceutical Applications of Phlorotannins from Brown Seaweeds. Phycology 2025, 5, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5020015
Gunasekara DMNM, Wang L, Herath KHINM, Sanjeewa KKA. Cosmeceutical Applications of Phlorotannins from Brown Seaweeds. Phycology. 2025; 5(2):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5020015
Chicago/Turabian StyleGunasekara, D. M. N. M., Lei Wang, K. H. I. N. M. Herath, and K. K. A. Sanjeewa. 2025. "Cosmeceutical Applications of Phlorotannins from Brown Seaweeds" Phycology 5, no. 2: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5020015
APA StyleGunasekara, D. M. N. M., Wang, L., Herath, K. H. I. N. M., & Sanjeewa, K. K. A. (2025). Cosmeceutical Applications of Phlorotannins from Brown Seaweeds. Phycology, 5(2), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology5020015








