Spatial and Temporal Variation of C, N, and S Stable Isotopes and Seagrass Coverage Related to Eutrophication Stress in Zostera marina
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
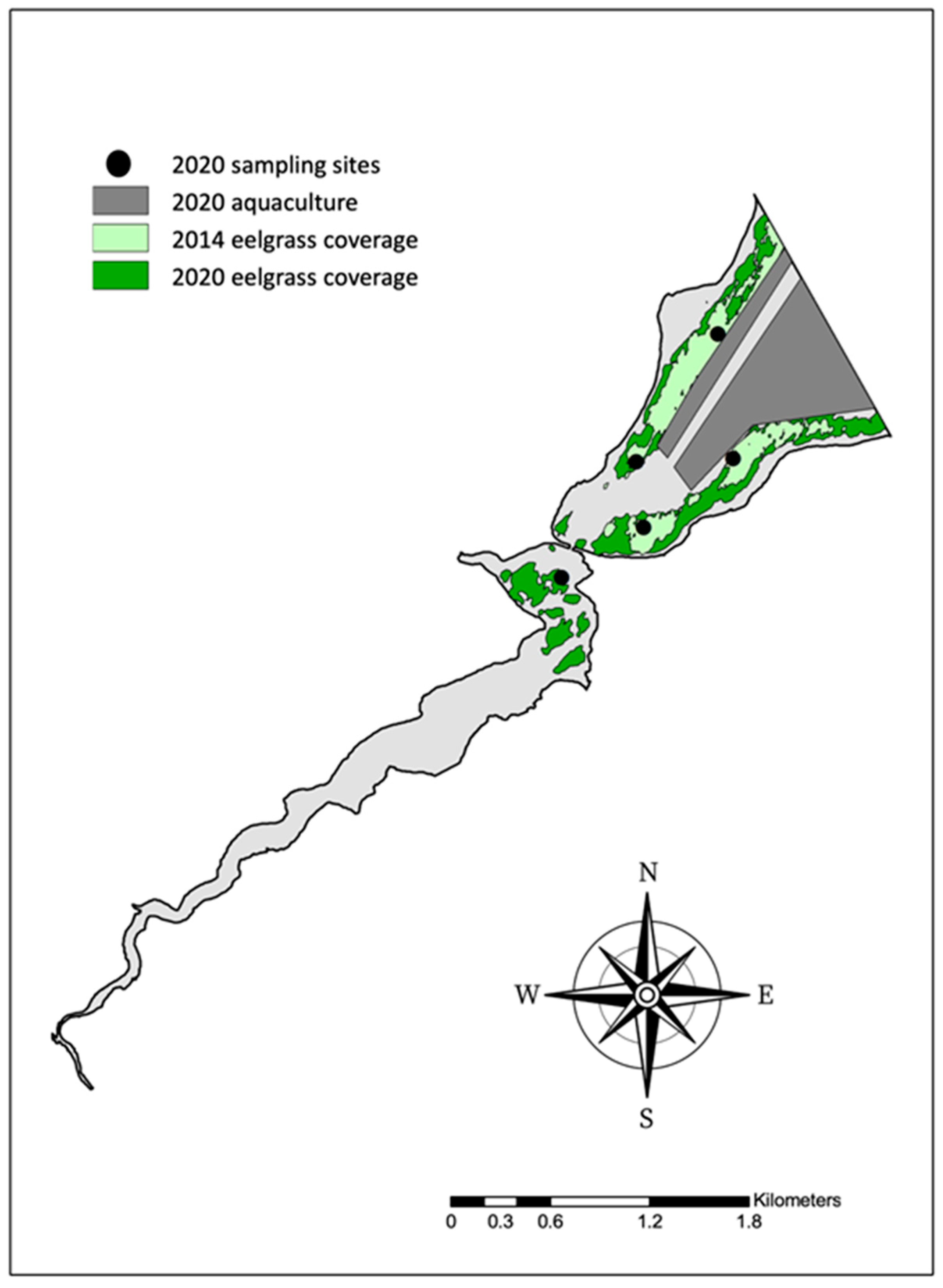
2.1. Study Area and Station Location
2.2. Historic External Nitrogen Load Calculations
2.3. Estuarine Water Quality
2.4. Submerged Aquatic Vegetation Sonar Survey
2.5. Eelgrass Tissue Collection and Biomass Measurements
2.6. Isotope Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Wheatley River Nitrate-N Loading
3.2. Eelgrass Coverage from 2014 and 2020
3.3. Eelgrass Bed Sampling Sediment and Water Chemistry
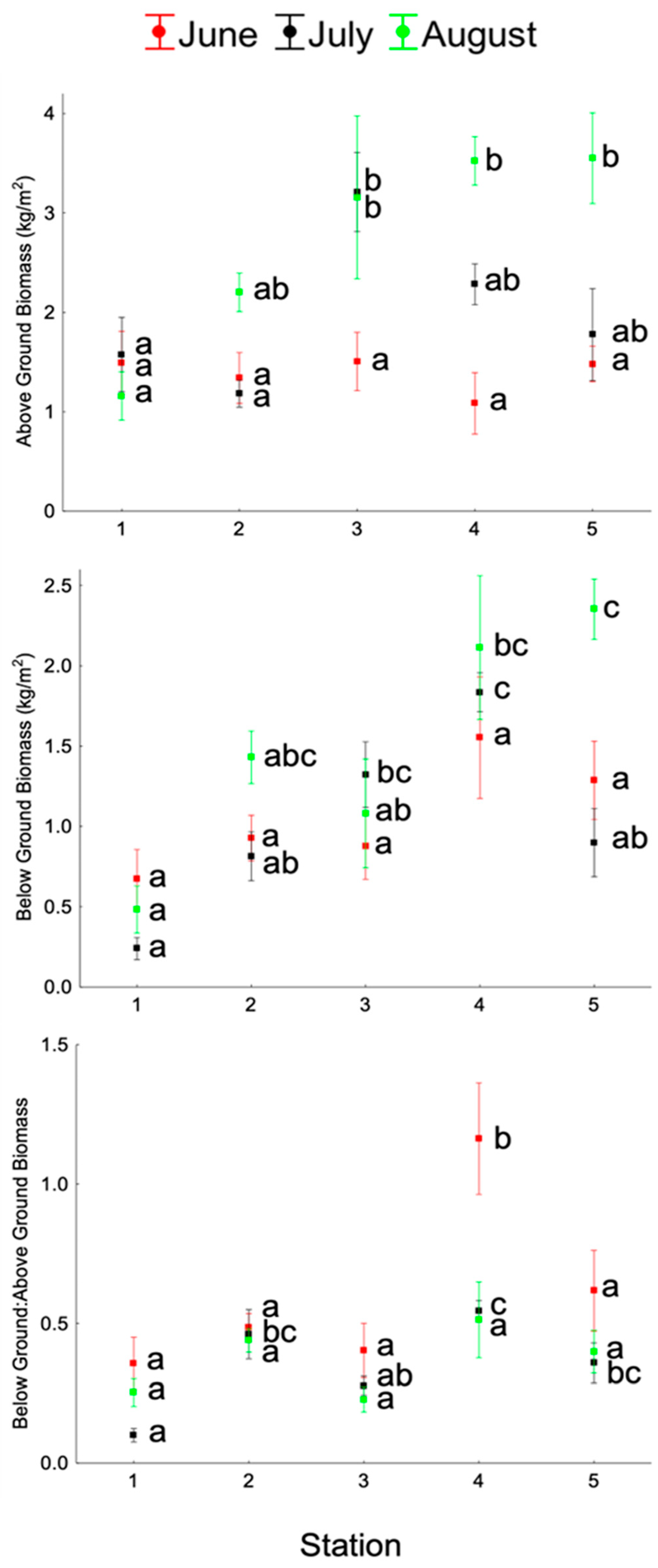
3.4. Eelgrass Biomass
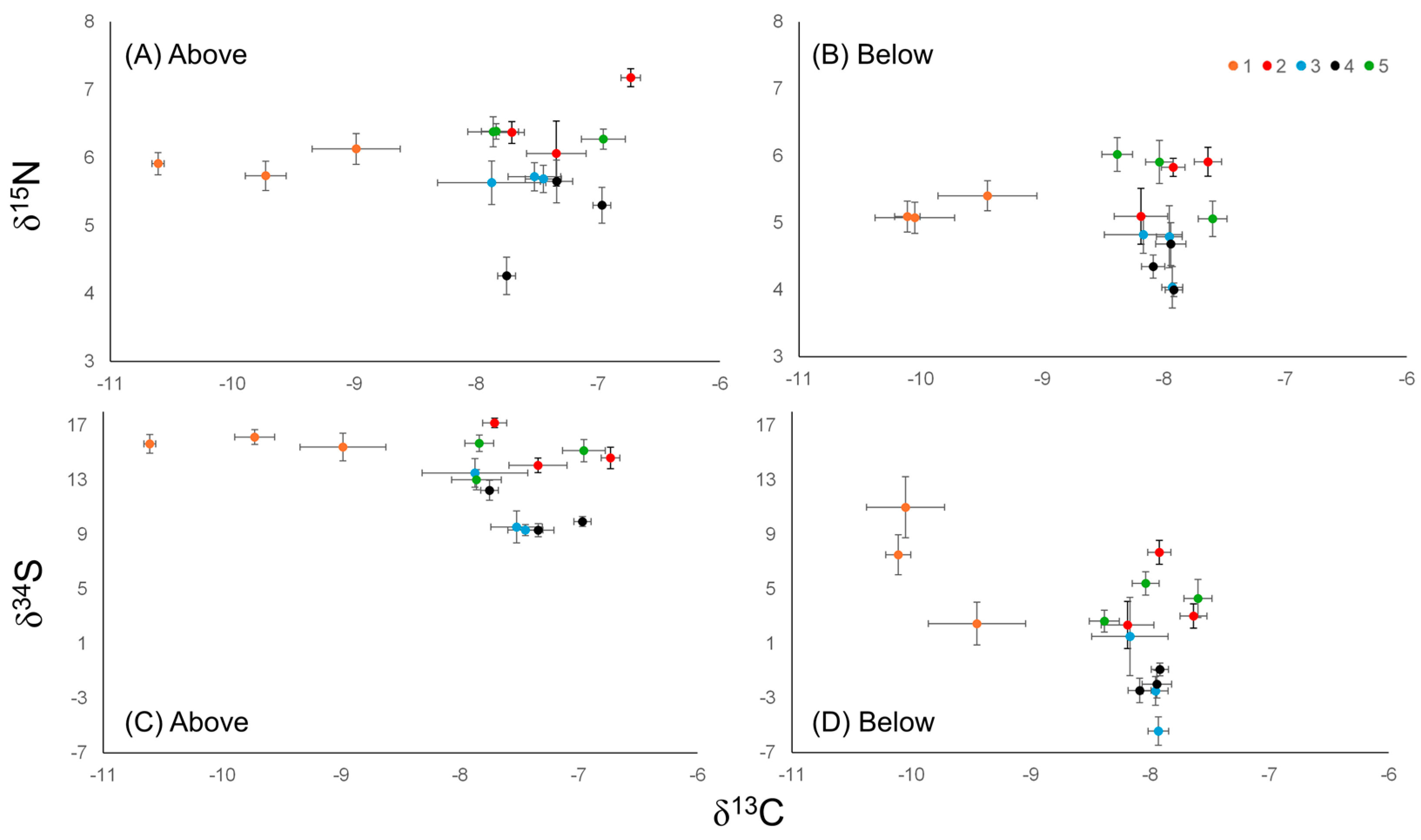
3.5. Eelgrass Tissue Isotopes
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vandermeulen, H.; An Introduction to Eelgrass (Zostera marina L.): The Persistent Ecosystem Engineer. Government of Canada. 2009. Available online: https://www.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/csas-sccs/publications/resdocs-docrech/2009/2009_085-eng.htm (accessed on 25 January 2024).
- Waycott, M.; Duarte, C.M.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Orth, R.J.; Dennison, W.C.; Olyarnik, S.; Calladine, A.; Fourqurean, J.W.; Heck, K.L., Jr.; Hughes, A.R.; et al. Accelerating loss of seagrasses across the globe threatens coastal ecosystems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12377–12381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiela, I.; McClelland, J.; Hauxwell, J.; Behr, P.J.; Hersh, D.; Foreman, K. Macroalgal blooms in shallow estuaries: Controls and ecophysiological and ecosystem consequences. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42 (Pt 2), 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Heuvel, M.R.; Hitchcock, J.K.; Coffin, M.R.S.; Pater, C.C.; Courtenay, S.C. Inorganic nitrogen has a dominant impact on estuarine eelgrass distribution in the Southern Gulf of St. Lawrence, Canada. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2019, 64, 2313–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudrey, J.M.P.; Kremer, J.N.; Branco, B.F.; Short, F.T. Eelgrass recovery after nutrient enrichment reversal. Aquat. Bot. 2010, 93, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, A.O.; Francis, T.B.; Feist, B.E.; Williams, G.D.; Lindquist, A.; Levin, P.S. Forty years of seagrass population stability and resilience in an urbanizing estuary. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 458–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.; Markon, C.; Douglas, D. Distribution and stability of eelgrass beds at Izembek Lagoon, Alaska. Aquat. Bot. 1997, 58, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.; Coles, R.; Fortes, M.; Victor, S.; Salik, M.; Isnain, I.; Andrew, J.; Seno, A. Monitoring in the Western Pacific region shows evidence of seagrass decline in line with global trends. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 83, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leblanc, M.L.; O’Connor, M.I.; Kuzyk, Z.Z.A.; Noisette, F.; Davis, K.E.; Rabbitskin, E.; Sam, L.L.; Neumeier, U.; Costanzo, R.; Ehn, J.K.; et al. Limited recovery following a massive seagrass decline in subarctic eastern Canada. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 432–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauxwell, J.; Cebrian, J.; Valiela, I. Eelgrass Zostera marina loss in temperate estuaries: Relationship to land-derived nitrogen loads and effect of light limitation imposed by algae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2003, 247, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, J.M.; Mason, K.M.; Glasgow, H.B., Jr. Water-column nitrate enrichment promotes decline of eelgrass Zostera marina: Evidence from seasonal mesocosm experiments. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 81, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Bondgaard, E.J. Photosynthesis and growth response of eelgrass to low oxygen and high sulfide concentrations during hypoxic events. Aquat. Bot. 2001, 70, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, L.W.; de Niro, M.J. Stable carbon isotope variability in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica: Evidence for light intensity effects. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1989, 50, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, M.L.; Zimmerman, R.C.; Hill, V.J. Predicting carbon isotope discrimination in Eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) from the environmental parameters—Light, flow, and [DIC]. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1875–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGlathery, K.J.; Sundbäck, K.; Anderson, I.C. Eutrophication in shallow coastal bays and lagoons: The role of plants in the coastal filter. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2007, 348, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, M.R.S.; Courtenay, S.C.; Pater, C.C.; van den Heuvel, M.R. An empirical model using dissolved oxygen as an indicator for eutrophication at a regional scale. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 133, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, J.M.; Tomasko, D.A.; Touchette, B.W. Seagrasses and eutrophication. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 350, 46–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, P.; Karez, R.; Reusch, T.; Dierking, J. Isotopic signatures of eelgrass (Zostera marina L.) as bioindicator of anthropogenic nutrient input in the western Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 72, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Frederiksen, M.S.; Møllegaard, H. Sulfur accumulation in eelgrass (Zostera marina) and effect of sulfur on eelgrass growth. Aquat. Bot. 2005, 81, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, J.K.; Courtenay, S.C.; Coffin, M.R.S.; Pater, C.C.; van den Heuvel, M.R. Eelgrass bed structure, leaf nutrient, and leaf isotope responses to natural and anthropogenic gradients in estuaries of the southern Gulf of St. Lawrence, Canada. Estuaries Coasts 2017, 40, 1653–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coffin, M.R.S.; Courtenay, S.C.; Knysh, K.M.; Pater, C.C.; van den Heuvel, M.R. Impacts of hypoxia on estuarine macroinvertebrate assemblages across a regional nutrient gradient. FACETS 2018, 3, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormier, J.M.; Coffin, M.R.S.; Pater, C.C.; Knysh, K.M.; Gilmour, R.F., Jr.; Guyondet, T.; Courtenay, S.C.; van den Heuvel, M.R. Internal nutrients dominate load and drive hypoxia in a eutrophic estuary. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schein, A.; Courtenay, S.C.; Crane, C.S.; Teather, K.L.; van den Heuvel, M.R. The role of submerged aquatic vegetation in structuring the nearshore fish community within an estuary of the southern Gulf of St. Lawrence. Estuaries Coasts 2012, 35, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizard, P.; MacQuarrie, K.; Jiang, Y. Land-use based modeling approach for determining freshwater nitrate loadings from small agricultural watersheds. Water Qual. Res. J. 2020, 55, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Nishimura, P.; van den Heuvel, M.R.; MacQuarrie, K.T.B.; Crane, C.S.; Xing, Z.; Raymond, B.G.; Thompson, B.L. Modeling land-based nitrogen loads from groundwater-dominated agricultural watersheds to estuaries to inform nutrient reduction planning. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, A.; St-Hilaire, A.; Courtenay, S.C.; van den Heuvel, M.R. Monitoring stream sediment loads in response to agriculture in Prince Edward Island, Canada. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, M.R.S.; Knysh, K.M.; Roloson, S.D.; Pater, C.C.; Theriaul, E.; Cormier, J.M.; Courtenay, S.C.; van den Heuvel, M.R. Influence of nutrient enrichment on temporal and spatial dynamics of dissolved oxygen within northern temperate estuaries. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauxwell, J.; Cerbian, J.; Furlong, C.; Valiela, I. Macroalgal canopies contribute to eelgrass (Zostera marina) decline in temperate estuarine ecosystems. Ecology 2001, 82, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, F.T.; Burdick, D.M.; Kaldy III, J.E. Mesocosm experiments quantify the effects of eutrophication on eelgrass, Zostera marina. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, Y.S.; Fox, S.E.; Teichberg, M.; Otter, M.; Valiela, I. δ15N and δ13C reveal differences in carbon flow through estuarine benthic food webs in response to the relative availability of macroalgae and eelgrass. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 421, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasko, D.; Alderson, M.; Burnes, R.; Hecker, J.; Leverone, J.; Raulerson, G.; Sherwood, E. Widespread recovery of seagrass coverage in Southwest Florida (USA): Temporal and spatial trends and management actions responsible for success. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greening, H.; Janicki, A. Toward reversal of eutrophic conditions in a subtropical estuary: Water quality and seagrass response to nitrogen loading reductions in Tampa Bay, Florida, USA. Environ. Manag. 2006, 38, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstensen, J.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Markager, S.; Timmermann, K.; Windolf, J. Water clarity and eelgrass responses to nitrogen reductions in the eutrophic Skive Fjord, Denmark. Hydrobiologia 2013, 704, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, G.; Aylward, M.; Hegge, B.; Cambridge, M.; Hillman, K.; Wyllie, A.; Lord, D. Changes in seagrass coverage in Cockburn Sound, Western Australia between 1967 and 1999. Aquat. Bot. 2002, 73, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaisted, H.; Novak, A.; Weigel, S.; Klein, A.; Short, F. Eelgrass genetic diversity influences resilience to stresses associated with eutrophication. Estuaries Coasts 2020, 43, 1245–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbà, N.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Alcoverro, T.; Birk, S.; Pedersen, A.; Neto, J.M.; Orfanidis, S.; Garmendia, J.M.; Muxika, I.; Borja, A.; et al. Diversity of European seagrass indicators: Patterns within and across regions. Hydrobiologia 2013, 704, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, G.; Alcoverro, T.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Balsby, T.J.S.; van Katwijk, M.M.; Marbà, N.; Santos, R.; Arthur, R.; Mascaró, O.; Fernández-Torquemada, Y.; et al. Response of seagrass indicators to shifts in environmental stressors: A global review and management synthesis. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 63, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, A.M.; Loneragan, N.R.; Dennison, W.C. Light intensity and the interactions between physiology, morphology, and stable isotope ratios in five species of seagrass. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1996, 195, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, M.J.; Smith, S.V. C:N:P ratios of benthic marine plants. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1983, 28, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M. Seagrass nutrient content. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1990, 67, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-S.; Short, F.T.; Burdick, D.M. Development of a nutrient pollution indicator using the seagrass, Zostera marina, along nutrient gradients in three New England estuaries. Aquat. Bot. 2004, 78, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schein, A.; Courtenay, S.C.; Kidd, K.; Campbell, A.; van den Heuvel, M.R. Food web structure within an estuary of the southern Gulf of St. Lawrence undergoing eutrophication. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 70, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminga, M.A.; Mateo, M.A. Stable carbon isotopes in seagrasses: Variability in ratios and use in ecological studies. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 140, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateman, A.S.; Kelly, S.D. Fertilizer nitrogen isotope signatures. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2007, 43, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClelland, J.W.; Valiela, I.; Michener, R.H. Nitrogen-stable isotope signatures in estuarine food webs: A record of increasing urbanization in coastal watersheds. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmer, M.; Baden, S.; Bostrom, C.; Moksnes, P.-O. Regional variation in eelgrass (Zostera marina) morphology, production and stable sulfur isotopic composition along the Baltic Sea and Skagerrak coasts. Aquat. Bot. 2009, 91, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, M.W.; Kendrick, G.A. Belowground stressors and long-term seagrass declines in a historically degraded seagrass ecosystem after improved water quality. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodersen, K.; Nielsen, D.; Ralph, P.; Kuhl, M. Oxic microshield and local pH enhancement protects Zostera muelleri from sediment-derived hydrogen sulphide. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 1264–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Station | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (m) | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.2 |
| Measured hypoxia (percentage of time < 4 mg/L) % | 29.1 | 8.1 | 6.8 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| Measured superoxia (percentage of time > 10 mg/L) % | 20.8 | 44.7 | 44.7 | 59.2 | 48.1 |
| Measured mean temperature (S.E.M., °C) | 21.3 (0.05) | 21.2 (0.06) | 20.9 (0.06) | 21.1 (0.05) | 21.1 (0.05) |
| Measured temperature range (°C) | 12.9–27.3 | 13.1–29.2 | 12.8–28.7 | 13.0–28.1 | 12.9–27.1 |
| Measured salinity (PSU) | 27.1 | 29.9 | 30.5 | 31.2 | 30.8 |
| Interpolated max chlorophyll a (μg/L) | 6.5 | 9.0 | 8.9 | 8.6 | 8.3 |
| Interpolated turbidity (NTU, grand mean) | 9.3 | 3.3 | 3.2 | 2.9 | 2.5 |
| Interpolated sediment %N | 0.3–0.8 | 0.2–0.1 | 0.2–0.1 | 0.1–0.1 | 0.0–0.0 |
| Interpolated N flux (mg/m2/h) | 3.4–4.5 | 0.7–0.8 | 0.7–0.8 | 0.6–0.7 | 0.6–0.5 |
| Interpolated P flux (mg/m2/h) | 1.6–0.4 | 0.3–0.7 | 0.3–0.6 | 0.2–0.4 | 0.3–0.1 |
| Interpolated sediment organic C (% d.w.) | 3.8–8.9 | 2.9–2.0 | 2.8–2.0 | 2.4–1.8 | 2.0–1.5 |
| Isotope/Date | Station | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| δ13C | |||||
| Above-ground | |||||
| June 15 | −8.98 (0.36) b | −7.71 (0.10) a | −7.87 (0.44) a | −7.75 (0.07) a | −7.84 (0.12) a |
| July 14 | −10.61(0.04) b | −7.34 (0.24) a | −7.52 (0.22) a | −6.97 (0.07) a | −6.96 (0.18) a |
| August 7 | −9.73 (0.16) c | −6.73 (0.08) a | −7.45 (0.15) b | −7.34 (0.13) ab | −7.86 (0.21) b |
| Below-ground | |||||
| June 15 | −9.45 (0.41) b | −7.92 (0.10) a | −8.17 (0.32) a | −7.92 (0.07) a | −8.04 (0.11) a |
| July 14 | −10.05 (0.33) b | −8.19 (0.22) a | −7.95 (0.11) a | −8.09 (0.10) a | −7.60 (0.12) a |
| August 7 | −10.11 (0.10) c | −7.64 (0.11) a | −7.93 (0.09) ab | −7.94 (0.12) ab | −8.38 (0.13) b |
δ15N | |||||
| Above-ground | |||||
| June 15 | 6.13 (0.23) a | 6.37 (0.16) a | 5.63 (0.32) a | 4.26 (0.27) b | 6.37 (0.11) a |
| July 14 | 5.91 (0.16) a | 6.06 (0.48) a | 5.72 (0.21) a | 5.30 (0.26) a | 6.27 (0.15) a |
| August 7 | 5.73 (0.22) b | 7.18 (0.13) a | 5.69 (0.20) b | 5.65 (0.31) b | 6.38 (0.22) ab |
| Below-ground | |||||
| June 15 | 5.40 (0.22) ab | 5.83 (0.14) a | 4.82 (0.28) bc | 4.00 (0.10) c | 5.91 (0.32) a |
| July 14 | 5.07 (0.23) a | 5.10 (0.42) a | 4.79 (0.46) a | 4.35 (0.17) a | 5.06 (0.26) a |
| August 7 | 5.09 (0.22) abc | 5.91 (0.22) a | 4.04 (0.31) c | 4.68 (0.32) c | 6.02 (0.25) ab |
δ34S | |||||
| Above-ground | |||||
| June 15 | 15.41 (1.01) ab | 17.17 (0.34) a | 13.51 (1.04) bc | 12.24 (0.74) c | 15.68 (0.60) ab |
| July 14 | 15.64 (0.69) a | 14.07 (0.53) a | 9.55 (1.17) b | 9.95 (0.36) b | 15.15 (0.81) a |
| August 7 | 16.14 (0.54) a | 14.61 (0.79) ab | 9.33 (0.40) c | 9.32 (0.48) c | 13.01 (0.74) b |
| Below-ground | |||||
| June 15 | 2.46 (1.57) ab | 7.68 (0.88) a | 1.51 (2.87) ab | −0.90 (0.47) b | 5.41 (0.86) ab |
| July 14 | 10.99 (2.23) a | 2.36 (1.72) bc | −2.48 (1.05) c | −2.45 (0.89) c | 4.30 (1.40) b |
| August 7 | 7.50 (1.47) a | 3.01 (0.89) ab | −5.43 (1.04) d | −1.99 (1.01) cd | 2.64 (0.80) bc |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Waddell, J.M.; Pater, C.C.; Coffin, M.R.S.; Gilmour, R.F., Jr.; Courtenay, S.C.; van den Heuvel, M.R. Spatial and Temporal Variation of C, N, and S Stable Isotopes and Seagrass Coverage Related to Eutrophication Stress in Zostera marina. Coasts 2024, 4, 419-436. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts4020021
Waddell JM, Pater CC, Coffin MRS, Gilmour RF Jr., Courtenay SC, van den Heuvel MR. Spatial and Temporal Variation of C, N, and S Stable Isotopes and Seagrass Coverage Related to Eutrophication Stress in Zostera marina. Coasts. 2024; 4(2):419-436. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts4020021
Chicago/Turabian StyleWaddell, Jerrica M., Christina C. Pater, Michael R. S. Coffin, Robert F. Gilmour, Jr., Simon C. Courtenay, and Michael R. van den Heuvel. 2024. "Spatial and Temporal Variation of C, N, and S Stable Isotopes and Seagrass Coverage Related to Eutrophication Stress in Zostera marina" Coasts 4, no. 2: 419-436. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts4020021
APA StyleWaddell, J. M., Pater, C. C., Coffin, M. R. S., Gilmour, R. F., Jr., Courtenay, S. C., & van den Heuvel, M. R. (2024). Spatial and Temporal Variation of C, N, and S Stable Isotopes and Seagrass Coverage Related to Eutrophication Stress in Zostera marina. Coasts, 4(2), 419-436. https://doi.org/10.3390/coasts4020021









