Real-Time Automated Segmentation and Classification of Calcaneal Fractures in CT Images
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fractures Classification in Calcaneus
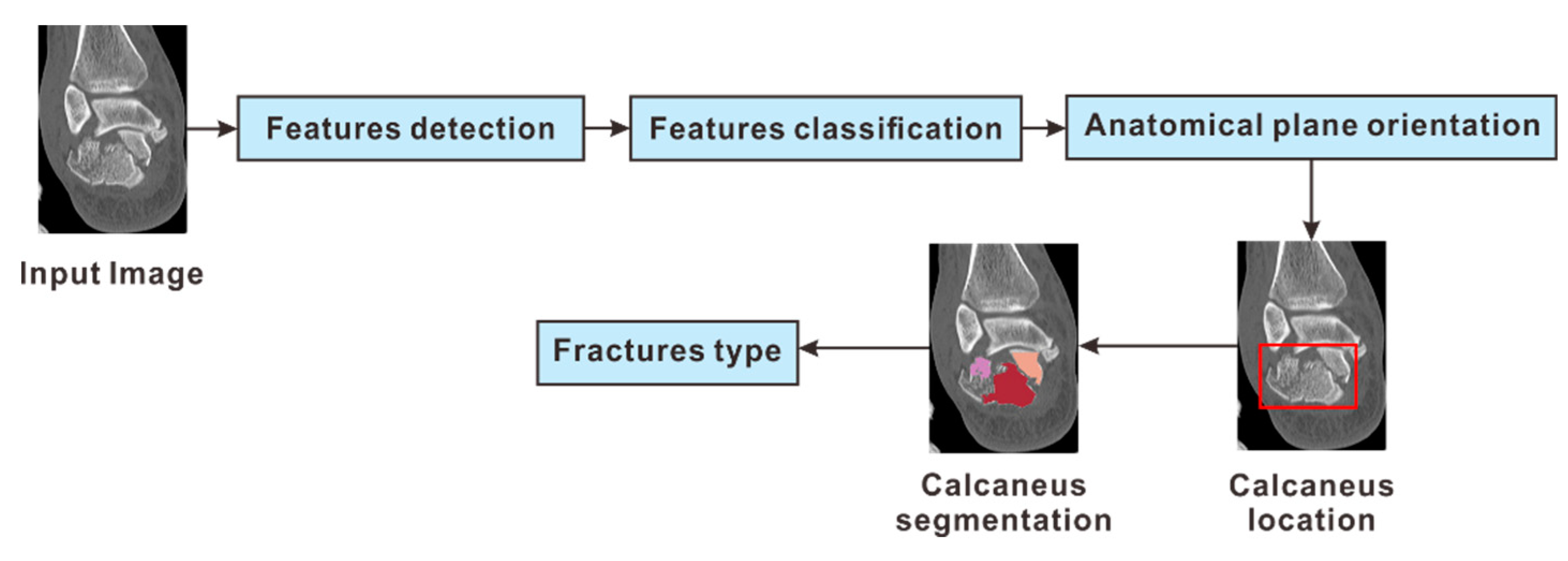
2.3. System Overview
2.4. Step 1: Detection of Calcaneus Location
2.5. Step 2: Segmentation of the Calcaneus Fragments
2.5.1. Classification of Calcaneal Fractures in Coronal and Transverse Images
2.5.2. Contour Detection
- If the current pixel value is 1, change the scan direction to the left and move 1 pixel. Conversely, when the pixel value is 0, change the scan direction to the right and move 1 pixel.
- Continue sub-steps 2a until the current contour point returns to the starting point.
| Algorithm 1: Build Contour Hierarchies. |
| S = corresponding LNDB S’ = new contour found If S = OUTER and S’ = OUTER If S = HOLE and S’ = HOLE Build the same hierarchy parent for S and S’ Add S to the last of children linked list of S’ Else Let S’ be the parent of S If SS’S child = 0 Let S to be the first child of S’ Else Add S to the last of children linked list of S’ End End End |
2.5.3. Classification of Calcaneal Fractures in Sagittal Images
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
- Bone structure is detected as a fracture,
- The fracture in the image is too similar to the bone structure, so it is not recognized as a fracture.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Badillo, K.; Pacheco, J.A.; Padua, S.O.; Gomez, A.A.; Colon, E.; Vidal, J.A. Multidetector CT evaluation of calcaneal fractures. Radiographics 2011, 31, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, S.A.; Clare, M.P.; Sanders, R.W. Management of Intra-Articular Fractures of the Calcaneus. Foot Ankle Clin. 2008, 13, 659–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rammelt, S.; Zwipp, H. Calcaneus fractures: Facts, controversies and recent developments. Injury 2004, 35, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Lee, D.Y. Surgical treatment of sanders type 2 calcaneal fractures using a sinus tarsi approach. Indian J. Orthop. 2017, 51, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Shui, X.; Ying, X.; Cai, L.; Yu, Y.; Hong, J. Closed Reduction and Percutaneous Fixation of Calcaneal Fractures in Children. Orthopedics 2016, 39, e744–e748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoelscher-Doht, S.; Frey, S.P.; Kiesel, S.; Meffert, R.H.; Jansen, H. Subtalar Dislocation: Long-Term Follow-Up and CT-Morphology. Open J. Orthop. 2015, 5, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mostafa, M.F.; El-Adl, G.; Hassanin, E.Y.; Abdellatif, M.S. Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture using a single small lateral approach. Strat. Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2010, 5, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rammelt, S.; Godoy-Santos, A.L.; Schneiders, W.; Fitze, G.; Zwipp, H. Foot and ankle fractures during childhood: Review of the literature and scientific evidence for appropriate treatment. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2016, 51, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, M.S.; Prabhakar, S. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneus fractures: A current concepts review. SICOT-J 2017, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, K.M.; Hassaan, M.A.E.; Moharram, A.N.; Elmahdi, M.D. The role of multidetector CT in evaluation of calcaneal fractures. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2015, 46, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daftary, A.; Haims, A.H.; Baumgaertner, M.R. Fractures of the Calcaneus: A Review with Emphasis on CT. Radiographics 2005, 25, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzo, M.; Greco, F.; Pietragalla, M.; De Renzis, A.; Carbone, M.; Zappia, M.; Maggialetti, N.; D’andrea, A.; Caracchini, G.; Miele, V. Calcaneal fractures: Radiological and CT evaluation and classification systems. Acta Biomed. 2018, 89, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harnroongroj, T.; Suntharapa, T.; Arunakul, M. The new intra-articular calcaneal fracture classification system in term of sustentacular fragment configurations and incorporation of posterior calcaneal facet fractures with fracture components of the calcaneal body. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2016, 50, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Davuluri, P.; Ward, K.R.; Cockrell, C.; Hobson, R.; Najarian, K. Fracture Detection in Traumatic Pelvic CT Images. Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, H.R.; Wang, Y.; Yao, J.; Lu, L.; Burns, J.E.; Summers, R.M. Deep convolutional networks for automated detection of posterior-element fractures on spine CT. Med. Imaging 2016 Comput. Aided Diagn. 2016, 9785, 97850. [Google Scholar]
- Long, C.; Fang, Y.; Huang, F.G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.L.; Yang, T.F.; Liu, L. Sanders II–III calcaneal fractures fixed with locking plate in elderly patients. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2016, 19, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biz, C.; Barison, E.; Ruggieri, P.; Iacobellis, C. Radiographic and functional outcomes after displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: A comparative cohort study among the traditional open technique (ORIF) and percutaneous surgical procedures (PS). J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2016, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, M.S.; Bali, K.; Prabhakar, S. Controversies in calcaneus fracture management: A systematic review of the literature. Musculoskelet. Surg. 2011, 95, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranata, Y.D.; Wang, K.C.; Wang, J.C.; Idram, I.; Lai, J.Y.; Liu, J.W.; Hsieh, I.H. Deep learning and SURF for automated classification and detection of calcaneus fractures in CT images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 171, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, R.; Fortin, P.; DiPasquale, T.; Walling, A. Operative treatment in 120 displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results using a prognostic computed tomography scan classification. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1993, 290, 87–95. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, R. Displaced Intra-Articular Fractures of the Calcaneus. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2000, 82, 225–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janzen, D.L.; Connell, D.G.; Munk, P.L.; E Buckley, R.; Meek, R.N.; Schechter, M.T. Intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus: Value of CT findings in determining prognosis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1992, 158, 1271–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Shan, C.; Ardabilian, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Local Binary Patterns and its application to facial image analysis: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C 2011, 41, 765–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, O.; Nunes, U.J.C.; Ribeiro, B.; Premebida, C. Improving the generalization capacity of cascade classifiers. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2013, 43, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Moulin, P. Regularized Adaboost learning for identification of time-varying content. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2014, 9, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M.J. Robust real-time object detection. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 57, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Be, K. Topological structural analysis of digitized binary images by border following. Comput. Vis. Graph. Image Process. 1985, 30, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shen, X.; Long, J.; Chen, H. An improved median-based otsu image thresholding algorithm. AASRI Procedia 2012, 3, 468–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.C.; Woods, R.E. Digital Image Processing; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002; ISBN 0201180758. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, J.; Chae, S.; Shim, J.; Kim, D.; Cheong, C.; Han, T.D. Fast Contour-Tracing Algorithm Based on a Pixel-Following Method for Image Sensors. Sensors 2016, 16, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Huang, C. An Improved Median Filtering Algorithm for Image Noise Reduction. Phys. Procedia 2012, 25, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.M.; Chen, C.C.; Wu, M.C.; Horng, G.; Wu, H.C.; Hsueh, S.H.; Ho, H.Y. Automatic Contrast Enhancement of Brain MR Images Using Hierarchical Correlation Histogram Analysis. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2015, 35, 724–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
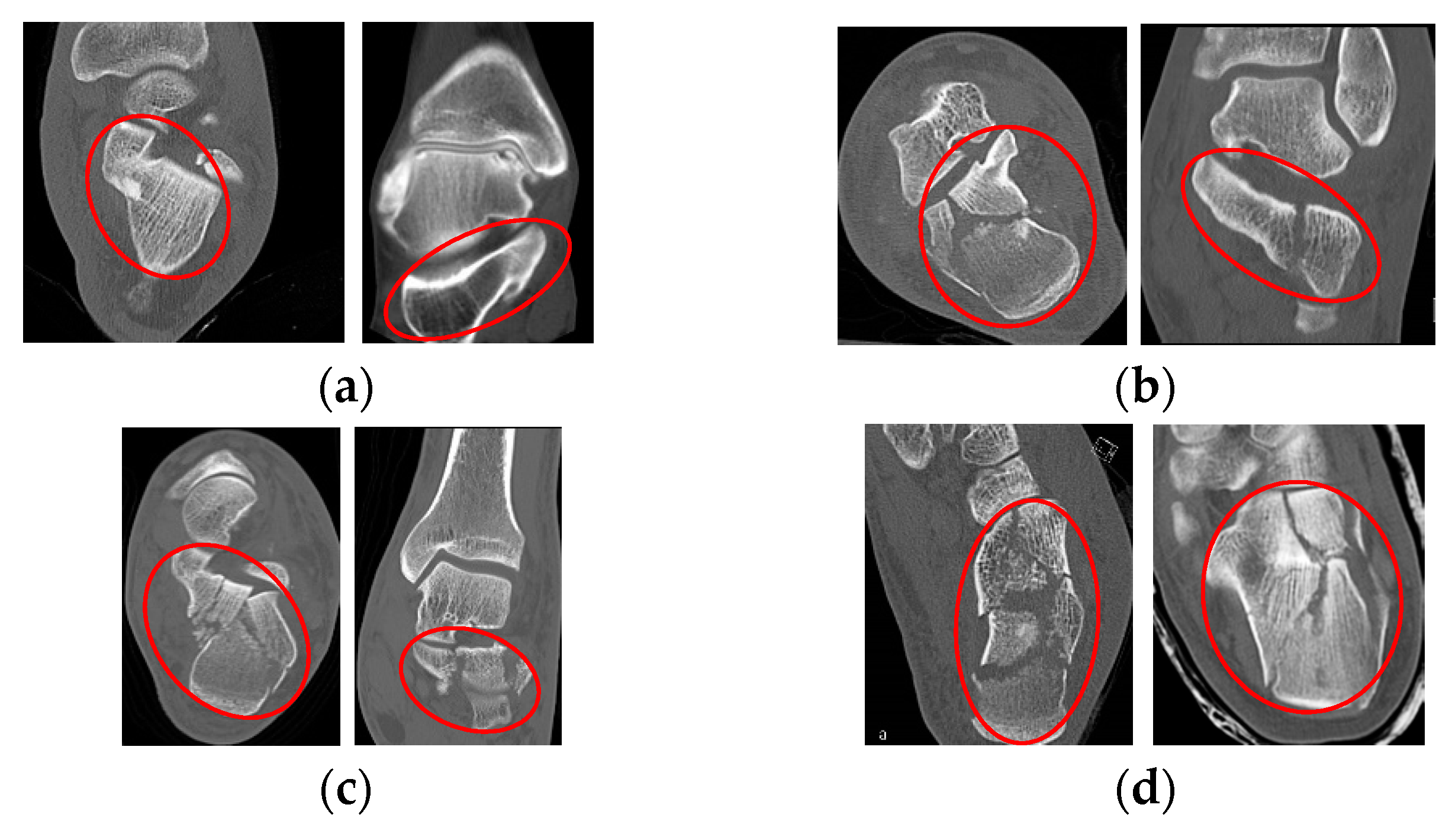

















| Fractures Type | Coronal (%) | Transverse (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | 88 | 84 |
| Type II | 86 | 81 |
| Type III | 83 | 80 |
| Type IV | 92 | 88 |
| Average | 87.25 | 83.25 |
| Fractures Type | Sagittal (%) |
|---|---|
| Type A | 81 |
| Type B | 85 |
| Type C | 80 |
| Average | 82 |
| Anatomical Plane | Average fps |
|---|---|
| Coronal | 92.33 |
| Transverse | 146.67 |
| Sagittal | 160.33 |
| Anatomical Plane | TP | FP | FN | PR | Recall | F-Measure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coronal | 92 | 13 | 7 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.89 |
| Transverse | 87 | 11 | 10 | 0.88 | 0.89 | 0.88 |
| Sagittal | 82 | 15 | 12 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.86 |
| Average Accuracy | 87 | 13 | 9.6 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.8 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahmaniar, W.; Wang, W.-J. Real-Time Automated Segmentation and Classification of Calcaneal Fractures in CT Images. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153011
Rahmaniar W, Wang W-J. Real-Time Automated Segmentation and Classification of Calcaneal Fractures in CT Images. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(15):3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153011
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahmaniar, Wahyu, and Wen-June Wang. 2019. "Real-Time Automated Segmentation and Classification of Calcaneal Fractures in CT Images" Applied Sciences 9, no. 15: 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153011
APA StyleRahmaniar, W., & Wang, W.-J. (2019). Real-Time Automated Segmentation and Classification of Calcaneal Fractures in CT Images. Applied Sciences, 9(15), 3011. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9153011






