Impact of Hepatitis B Virus Genetic Variation, Integration, and Lymphotropism in Antiviral Treatment and Oncogenesis
Abstract
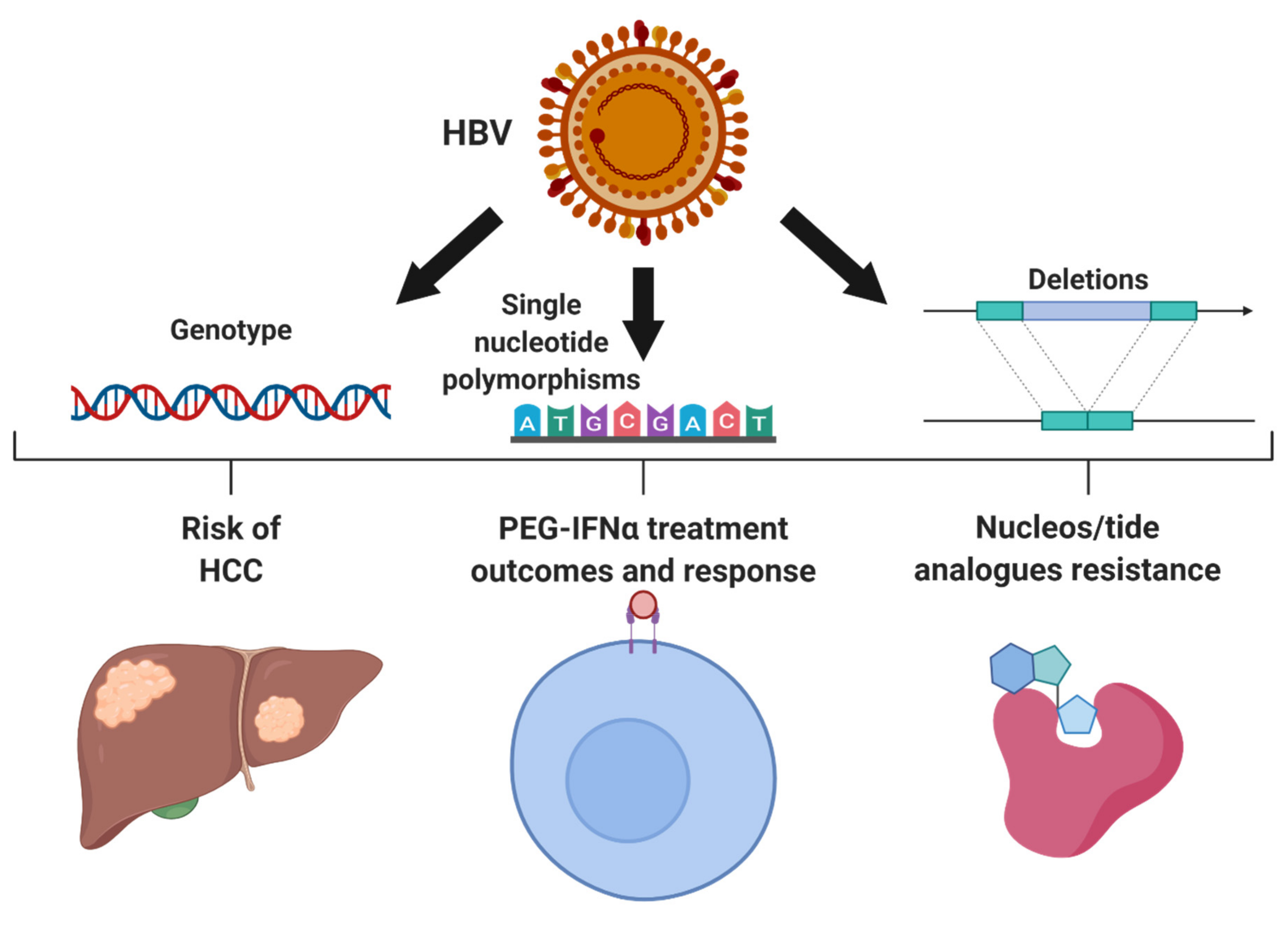
:1. Introduction
1.1. Natural History of Chronic HBV Infection
1.2. Current Treatment of Chronic HBV Infection
2. Genetic Variations within HBV
2.1. HBV Genotypes
2.2. Resistance to Anti-Viral Treatment
2.3. HBV Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms Associated with HCC
3. Unique Features of HBV that Impact Treatment and Oncogenesis
3.1. Oncogenic Implications of HBV Integration
3.2. Extrahepatic HBV Infection and Lymphotropism
4. Considerations for Novel HBV Therapeutics
4.1. HBV Genetic Variation as Predictor Factors
4.2. Occult HBV Infection
4.3. Therapeutic Management of HBV Lymphoid Reservoirs
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Global Hepatitis Report 2017; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Naghavi, M.; Abajobir, A.A.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abera, S.F.; Aboyans, V.; Adetokunboh, O.; Afshin, A.; Agrawal, A.; et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1151–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schweitzer, A.; Horn, J.; Mikolajczyk, R.T.; Krause, G.; Ott, J.J. Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. Lancet 2015, 386, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.C.; Shaheen, A.A.; Aspinall, A.A.; Ba, T.R.; Mba, K.Q.; Congly, S.E.; Borman, M.A.; Jayakumar, S.; Eksteen, B.; Lee, S.S.; et al. Hepatitis B virus testing and linkage to care in a Canadian urban tertiary referral centre: A retrospective cohort study. CMAJ Open 2017, 5, E431–E436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trépo, C.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Lok, A. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet 2014, 384, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginzberg, D.; Wong, R.J.; Gish, R. Global HBV burden: Guesstimates and facts. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.-F.; Chen, D.-S.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Lau, D.T.Y.; Locarnini, S.A.; Peters, M.G.; Lai, C.-L. Hepatitis B virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 18035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajoriya, N.; Combet, C.; Zoulim, F.; Janssen, H.L. How viral genetic variants and genotypes influence disease and treatment outcome of chronic hepatitis B. Time for an individualised approach? J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1281–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coffin, C.S.; Fung, S.K.; Alvarez, F.; Cooper, C.L.; Doucette, K.; Fournier, C.; Kelly, E.; Ko, H.H.; Ma, M.M.; Martin, S.R.; et al. Management of Hepatitis B Virus Infection: 2018 Guidelines from the Canadian Association for the Study of the Liver and Association of Medical Microbiology and Infectious Disease Canada. Can. Liver J. 2018, 1, 156–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlich, W.H.; Glebe, D.; Kramvis, A.; Magnius, L. Peculiarities in the designations of hepatitis B virus genes, their products, and their antigenic specificities: A potential source of misunderstandings. Virus Genes 2020, 56, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, K.-N.; Kuo, C.-F.; Ou, J.-H.J. Mechanisms of Hepatitis B Virus Persistence. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Revill, P. Overview of hepatitis B viral replication and genetic variability. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S4–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuen, M.-F.; Wong, D.K.; Fung, J.; Ip, P.P.C.; But, D.; Hung, I.F.-N.; Lau, K.; Yuen, J.C.; Lai, C.-L. HBsAg Seroclearance in Chronic Hepatitis B in Asian Patients: Replicative Level and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Gehring, A.J. Immune Therapeutic Strategies in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection: Virus or Inflammation Control? PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konerman, M.A.; Lok, A.S. Interferon Treatment for Hepatitis B. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 645–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, G.; Yi, Z.; Song, H.; Xu, F.; Li, F.; Aliyari, R.; Zhang, H.; Du, P.; Ding, Y.; Niu, J.; et al. Type-I-IFN-Stimulated Gene TRIM5gamma Inhibits HBV Replication by Promoting HBx Degradation. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 3551–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, G.; Xu, F.; Song, H.; Yuan, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, F.; Qin, F.X.-F.; Cheng, G. Identification of TRIM14 as a Type I IFN-Stimulated Gene Controlling Hepatitis B Virus Replication by Targeting HBx. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Xiao, Q.; Song, H.; Ma, F.; Xu, F.; Peng, D.; Li, N.; Wang, X.; Niu, J.; Gao, P.; et al. Type I IFN augments IL-27-dependent TRIM25 expression to inhibit HBV replication. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 15, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Niklasch, M.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Shi, B.; Yuan, W.; Baumert, T.F.; Yuan, Z.; Tong, S.; Nassal, M.; et al. Interferon-inducible MX2 is a host restriction factor of hepatitis B virus replication. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, C.R.; Funami, K.; Oshiumi, H.; Mengao, D.; Takaki, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Aly, H.H.; Watashi, K.; Chayama, K.; Seya, T. Interferon-stimulated gene of 20 kDa protein (ISG20) degrades RNA of hepatitis B virus to impede the replication of HBV in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 68179–68193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Nie, H.; Mao, R.; Mitra, B.; Cai, D.; Yan, R.; Guo, J.-T.; Block, T.M.; Mechti, N.; Guo, H. Interferon-inducible ribonuclease ISG20 inhibits hepatitis B virus replication through directly binding to the epsilon stem-loop structure of viral RNA. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, L.; Allweiss, L.; Guerrieri, F.; Pediconi, N.; Volz, T.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M.; Levrero, M. IFN-α inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Campagna, M.; Qi, Y.; Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Xu, C.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Block, T.M.; Chang, J.; et al. Alpha-Interferon Suppresses Hepadnavirus Transcription by Altering Epigenetic Modification of cccDNA Minichromosomes. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buster, E.H.; Hansen, B.E.; Lau, G.K.; Piratvisuth, T.; Zeuzem, S.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Janssen, H.L.A. Factors That Predict Response of Patients with Hepatitis B e Antigen–Positive Chronic Hepatitis B to Peginterferon-Alfa. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flink, H.J.; Van Zonneveld, M.; Hansen, B.E.; De Man, R.A.; Schalm, S.W.; Janssen, H.L.; for the HBV 99-01 Study Group. Treatment with Peg-Interferon alpha-2b for HBeAg-Positive Chronic Hepatitis B: HBsAg Loss Is Associated with HBV Genotype. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.L.Y.; Fung, S.; Seto, W.K.; Chuang, W.-L.; Chen, C.-Y.; Kim, H.J.; Hui, A.J.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Chowdhury, A.; Tsang, T.Y.O.; et al. Tenofovir alafenamide versus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for the treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B virus infection: A randomised, double-blind, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-J.; Yang, H.-I.; Su, J.; Jen, C.-L.; You, S.-L.; Lu, S.-N.; Huang, G.-T.; Iloeje, U.H.; for the REVEAL-HBV Study Group. Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Across a Biological Gradient of Serum Hepatitis B Virus DNA Level. JAMA 2006, 295, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, C.-L.; Yuen, M.-F. Prevention of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma with antiviral therapy. Hepatology 2013, 57, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASL. EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 370–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.F.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.-M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochaksaraei, G.S.; Castillo, E.; Osman, M.; Simmonds, K.; Scott, A.N.; Oshiomogho, J.I.; Lee, S.S.; Myers, R.P.; Martin, S.R.; Coffin, C.S. Clinical course of 161 untreated and tenofovir-treated chronic hepatitis B pregnant patients in a low hepatitis B virus endemic region. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 23, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.Q.; Duan, Z.; Dai, E.; Zhang, S.; Han, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zou, H.; Zhu, B.; Zhao, W.; et al. Tenofovir to Prevent Hepatitis B Transmission in Mothers with High Viral Load. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2324–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, M.H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, J.H.; Je, J.H.; Yoo, Y.J.; Yeon, J.E.; Byun, K.S. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The efficacy and safety of tenofovir to prevent mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boucheron, P.; Lu, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Zhao, T.; Funk, A.L.; Lunel-Fabiani, F.; Guingané, A.; Tuaillon, E.; Van Holten, J.; Chou, R.; et al. Accuracy of HBeAg to identify pregnant women at risk of transmitting hepatitis B virus to their neonates: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlich, W.H. Good news from WHO on prevention of peripartum hepatitis B transmission. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, A.L.; Lu, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Zhao, T.; Boucheron, P.; Van Holten, J.; Chou, R.; Bulterys, M.; Shimakawa, Y. Efficacy and safety of antiviral prophylaxis during pregnancy to prevent mother-to-child transmission of hepatitis B virus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Prevention of Mother-to-Child Transmission of Hepatitis B Virus: Guidelines on Antiviral Prophylaxis in Pregnancy; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, C.-F.; Li, T.-C.; Huang, H.-Y.; Lin, J.-H.; Chen, W.-S.; Shyu, W.-C.; Wu, H.-C.; Peng, C.-Y.; Su, I.-J.; Jeng, L.-B. Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Quantitative Detection of Hepatitis B Virus Pre-S Mutants in Plasma Predicts Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence. Viruses 2020, 12, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-L.; Kao, J.-H. Hepatitis B Virus Genotypes and Variants. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.-J.; Kao, J.-H. Global perspective on the natural history of chronic hepatitis B: Role of hepatitis B virus genotypes A to J. Semin. Liver Dis. 2013, 33, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramvis, A. Genotypes and Genetic Variability of Hepatitis B Virus. Intervirology 2014, 57, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaughton, A.L.; Revill, P.A.; Littlejohn, M.; Matthews, P.C.; Ansari, M.A. Analysis of genomic-length HBV sequences to determine genotype and subgenotype reference sequences. J. Gen. Virol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; He, K.; Wu, B.; Xu, M.; Du, L.; Liu, W.; Liao, P.; Liu, Y.; He, M. A systematic genotype and subgenotype re-ranking of hepatitis B virus under a novel classification standard. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Congly, S.E.; Wong, P.; Al-Busafi, S.A.; Doucette, K.; Fung, S.K.; Ghali, P.; Fonseca, K.; Myers, R.P.; Osiowy, C.; Coffin, C.S. Characterization of hepatitis B virus genotypes and quantitative hepatitis B surface antigen titres in North American tertiary referral liver centres. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, C.S.; Ramji, A.; Cooper, C.L.; Miles, D.; Doucette, K.E.; Wong, P.; Tam, E.; Wong, D.K.; Wong, A.; Ukabam, S.; et al. Epidemiologic and clinical features of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in 8 Canadian provinces: A descriptive study by the Canadian HBV Network. CMAJ Open 2019, 7, E610–E617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zoulim, F.; Habersetzer, F.; Xiong, S.; Trépo, C. Analysis of hepatitis B virus genotypes and pre-core region variability during interferon treatment of HBe antigen negative chronic hepatitis B. J. Med. Virol. 1996, 48, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhardt, A.; Blondin, D.; Hauck, K.; Sagir, A.; Kohnle, T.; Heintges, T.; Häussinger, D. Response to interferon alfa is hepatitis B virus genotype dependent: Genotype A is more sensitive to interferon than genotype D. Gut 2005, 54, 1009–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ye, S.; Wang, T.; Zhao, R.; Chen, F.; Abe, K.; Jin, X. The response to interferon is influenced by hepatitis B virus genotype in vitro and in vivo. Virus Res. 2013, 171, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, C. HBV genotype B is associated with better response to interferon therapy in HBeAg(+) chronic hepatitis than genotype C. Hepatology 2002, 36, 1425–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kao, J.-H.; Chen, P.-J.; Lai, M.-Y.; Chen, P.-J. Hepatitis B genotypes correlate with clinical outcomes in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-J.; Iloeje, U.H.; Yang, H.-I. Long-Term Outcomes in Hepatitis B: The REVEAL-HBV Study. Clin. Liver Dis. 2007, 11, 797–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tang, G.; Wang, Y.; Xue, G.; Zhou, W.; Sun, S. Characterization of the genotype and integration patterns of hepatitis B virus in early- and late-onset hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1821–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhou, B.; Tanaka, Y.; Kurbanov, F.; Orito, E.; Gong, Z.; Xu, L.; Lu, J.; Jiang, X.; Lai, W.; et al. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) genotypes/subgenotypes in China: Mutations in core promoter and precore/core and their clinical implications. J. Clin. Virol. 2007, 39, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, C.S.; Osiowy, C.; Gao, S.; Nishikawa, S.; Van Der Meer, F.; Van Marle, G. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) variants fluctuate in paired plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells among patient cohorts during different chronic hepatitis B (CHB) disease phases. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 22, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Duan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Van Der Meer, F.; Lee, S.S.; Osiowy, C.; Van Marle, G.; Coffin, C.S. Compartmental HBV evolution and replication in liver and extrahepatic sites after nucleos/tide analogue therapy in chronic hepatitis B carriers. J. Clin. Virol. 2017, 94, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, C.S.; Mulrooney-Cousins, P.M.; Peters, M.G.; Van Marle, G.; Roberts, J.P.; Michalak, T.I.; Terrault, N.A. Molecular characterization of intrahepatic and extrahepatic hepatitis B virus (HBV) reservoirs in patients on suppressive antiviral therapy. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 18, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sonneveld, M.J.; Rijckborst, V.; Zeuzem, S.; Heathcote, E.J.; Simon, K.; Senturk, H.; Pas, S.D.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L.A. Presence of precore and core promoter mutants limits the probability of response to peginterferon in hepatitis B e antigen-positive chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 2012, 56, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, M.J.; Rijckborst, V.; Zwang, L.; Zeuzem, S.; Heathcote, E.J.; Simon, K.; Zoutendijk, R.; Akarca, U.; Pas, S.D.; Hansen, B.E.; et al. Hepatitis B e antigen levels and response to peginterferon: Influence of precore and basal core promoter mutants. Antivir. Res. 2013, 97, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Duan, Z.-P.; Coffin, C.S. Clinical relevance of hepatitis B virus variants. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1086–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoulim, F.; Locarnini, S. Hepatitis B Virus Resistance to Nucleos(t)ide Analogues. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1593–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Gao, Z.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, J.; Cheng, J.; Chen, C.; Mao, Q.; Zhao, W.; Ren, H.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis B: 5-year results. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Corsa, A.C.; Buti, M.; Cathcart, A.L.; Flaherty, J.F.; Miller, M.D.; Kitrinos, K.M.; Marcellin, P.; Gane, E.J. No detectable resistance to tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in HBeAg+ and HBeAg− patients with chronic hepatitis B after 8 years of treatment. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 24, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.H.; Song, M.J.; Jang, J.W.; Bae, S.H.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoon, S.K.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, C.W.; Song, D.S.; Chang, U.I.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate in Treatment-Naïve Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B in Korea. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2019, 64, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcellin, P.; Wong, D.K.; Sievert, W.; Buggisch, P.; Petersen, J.; Flisiak, R.; Manns, M.; Kaita, K.; Krastev, Z.; Lee, S.S.; et al. Ten-year efficacy and safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate treatment for chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1868–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cathcart, A.L.; Chan, H.L.-Y.; Bhardwaj, N.; Liu, Y.; Marcellin, P.; Pan, C.Q.; Shalimar; Buti, M.; Cox, S.; Parhy, B.; et al. No Resistance to Tenofovir Alafenamide Detected through 96 Weeks of Treatment in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Song, C.; Zeng, H.; Wang, X. Entecavir resistance mutations rtL180M/T184L/M204V combined with rtA200V lead to tenofovir resistance. Liver Int. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.-S.; Lee, A.R.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.-H.; Yoo, J.-J.; Ahn, S.H.; Sim, H.; Park, S.; Kang, H.S.; Won, J.; et al. Identification of a quadruple mutation that confers tenofovir resistance in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Gu, C.; Yin, J.; He, Y.; Xie, J.; Cao, G. Associations Between Hepatitis B Virus Mutations and the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 1066–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Hung, C.; Chen, W.; Hu, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Lu, S.-N.; Changchien, C. Pre-S Deletion and Complex Mutations of Hepatitis B Virus Related to Advanced Liver Disease in HBeAg-Negative Patients. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-N.; Chisari, F.V. Strong, sustained hepatocellular proliferation precedes hepatocarcinogenesis in hepatitis B surface antigen transgenic mice. Hepatology 1995, 21, 620–626. [Google Scholar]
- Pollicino, T.; Cacciola, I.; Saffioti, F.; Raimondo, G. Hepatitis B virus PreS/S gene variants: Pathobiology and clinical implications. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, I.-J.; Wang, H.-C.; Wu, H.-C.; Huang, W.-Y. Ground glass hepatocytes contain pre-S mutants and represent preneoplastic lesions in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadziyannis, S.; Gerber, M.A.; Vissoulis, C.; Popper, H. Cytoplasmic hepatitis B antigen in “ground-glass” hepatocytes of carriers. Arch. Pathol. 1973, 96, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.-C.; Huang, W.; Lai, M.-D.; Su, I.-J. Hepatitis B virus pre-S mutants, endoplasmic reticulum stress and hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Chen, W. HBV X gene point mutations are associated with the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 4, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, H.-G. Key role of hepatitis B virus mutation in chronic hepatitis B development to hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.M.; Jang, J.W.; Yoo, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, I.M.; Park, S.J.; Jang, Y.S.; Lee, S.J. Combinations of eight key mutations in the X/preC region and genomic activity of hepatitis B virus are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Viral Hepat. 2013, 21, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Song, C.; Jiang, D.; Jin, T.; Dai, J.; Zhu, L.; An, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, S.; Qin, N.; et al. Hepatitis B virus genotype, mutations, human leukocyte antigen polymorphisms and their interactions in hepatocellular carcinoma: A multi-centre case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, H.; Han, L.; Lu, W.; Shen, Q.; Xu, G.; Dong, H.; Shen, J.; et al. Association Between the Various Mutations in Viral Core Promoter Region to Different Stages of Hepatitis B, Ranging of Asymptomatic Carrier State to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, B.-F.; Cheng, M.-L.; Zhao, X.-K.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Y.-X.; Liu, H.-J.; Mu, M.; Wang, B.; Yang, G.-Z.; et al. Quantitative assessment of mutations in hepatitis B virus genome with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma development. Oncotarget 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Yao, Z.; Hu, K.; Zhong, Y.; Li, M.; Xiong, Z.; Deng, M. Hepatitis B Virus Core Promoter A1762T/G1764A (TA)/T1753A/T1768A Mutations Contribute to Hepatocarcinogenesis by Deregulating Skp2 and P53. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 60, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, W.; Hadziyannis, S.; McGarvey, M.J.; Jacyna, M.; Karayiannis, P.; Makris, A.; Thomas, H. Mutation Preventing Formation of Hepatitis B E Antigen in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. Lancet 1989, 334, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammeh, S.; Tavner, F.; Watson, R.; Thomas, H.C.; Karayiannis, P. Effect of basal core promoter and pre-core mutations on hepatitis B virus replication. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferns, R.B.; Naoumov, N.V.; Gilson, R.J.; Tedder, R.S. Presence of hepatitis B virus core promoter mutations pre-seroconversion predict persistent viral replication after HBeAg loss. J. Clin. Virol. 2007, 39, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.M.; Huang, G.-M.; Li, J.-G.; Huang, Y.-S.; Mei, Y.-Y.; Gao, Z.-L. High level of hepatitis B virus DNA after HBeAg-to-anti-HBe seroconversion is related to coexistence of mutations in its precore and basal core promoter. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 3131–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S. HBV DNA Integration: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Viruses 2017, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Summers, J. Illegitimate replication of linear hepadnavirus DNA through nonhomologous recombination. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 4029–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bill, C.A.; Summers, J. Genomic DNA double-strand breaks are targets for hepadnaviral DNA integration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11135–11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.-H.; Liu, X.; Yan, H.-X.; Li, W.-Y.; Zeng, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.-P.; Zhuang, X.-H.; Lin, C.; et al. Genomic and oncogenic preference of HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, P.; Dai, X.; Sun, J.; He, C.; Huang, C.; Zhou, R.; Cao, Z.; Ye, L. Different types of viral-host junction found in HBV integration breakpoints in HBV-infected patients. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 19, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S. Hepatitis B virus DNA integration occurs early in the viral life cycle in an in vitro infection model via NTCP-dependent uptake of enveloped virus particles. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02007-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, T.; Mason, W.S.; Clouston, A.; Shackel, N.A.; McCaughan, G.W.; Yeh, M.M.; Schiff, E.R.; Ruszkiewicz, A.R.; Chen, J.W.; Harley, H.A.J.; et al. Clonal expansion of hepatocytes with a selective advantage occurs during all stages of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 737–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, W.S.; Gill, U.S.; Litwin, S.; Zhou, Y.; Peri, S.; Pop, O.; Hong, M.L.; Naik, S.; Quaglia, A.; Bertoletti, A.; et al. HBV DNA Integration and Clonal Hepatocyte Expansion in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients Considered Immune Tolerant. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chauhan, R.; Churchill, N.D.; Mulrooney-Cousins, P.M.; Michalak, T.I. Initial sites of hepadnavirus integration into host genome in human hepatocytes and in the woodchuck model of hepatitis B-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, M.; Tanaka, H.; Shiraishi, Y.; Unida, T.; Imamura, M.; Fujimoto, A.; Fujita, M.; Sasaki, A.-O.; Maejima, K.; Nakano, K.; et al. Characterization of HBV integration patterns and timing in liver cancer and HBV-infected livers. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 25075–25088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sung, W.-K.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Lee, N.P.; Lee, W.H.; Ariyaratne, P.N.; Tennakoon, C.; et al. Genome-wide survey of recurrent HBV integration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Urban, S.; Tu, T. Cellular Genomic Sites of Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration. Genes 2018, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, T.; Budzinska, M.A.; Shackel, N.A.; Jilbert, A.R. Conceptual models for the initiation of hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 1786–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterlini-Brechot, P.; Saigo, K.; Murakami, Y.; Chami, M.; Gozuacik, D.; Mugnier, C.; Lagorce, D.; Brechot, C.; Paterlini-Br, P. Eacute, Hepatitis B virus-related insertional mutagenesis occurs frequently in human liver cancers and recurrently targets human telomerase gene. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3911–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferber, M.J.; Montoya, D.P.; Yu, C.; Aderca, I.; McGee, A.; Thorland, E.C.; Nagorney, D.M.; Gostout, B.S.; Burgart, L.J.; Boix, L.; et al. Integrations of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) and human papillomavirus (HPV) into the human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) gene in liver and cervical cancers. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3813–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gozuacik, D.; Murakami, Y.; Saigo, K.; Chami, M.; Mugnier, C.; Lagorce, D.; Okanoue, T.; Urashima, T.; Brechot, C.; Paterlini-Brechot, P. Identification of human cancer-related genes by naturally occurring Hepatitis B Virus DNA tagging. Oncogene 2001, 20, 6233–6240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toh, S.T.; Jin, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Babrzadeh, F.; Gharizadeh, B.; Ronaghi, M.; Toh, H.C.; Chow, P.K.; Chung, A.Y.-F.; et al. Deep sequencing of the hepatitis B virus in hepatocellular carcinoma patients reveals enriched integration events, structural alterations and sequence variations. Carcinogenesis 2012, 34, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zeng, X.; Lee, N.P.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.; Guo, B.; Yi, S.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, G.; et al. HIVID: An efficient method to detect HBV integration using low coverage sequencing. Genomics 2013, 102, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nault, J.-C.; Calderaro, J.; Di Tommaso, L.; Balabaud, C.; Zafrani, E.S.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Roncalli, M.; Zucman-Rossi, J. Telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutation is an early somatic genetic alteration in the transformation of premalignant nodules in hepatocellular carcinoma on cirrhosis. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nault, J.C.; Mallet, M.; Pilati, C.; Calderaro, J.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Laurent, C.; Laurent, A.; Cherqui, D.; Balabaud, C.; Zucman, J.-R. High frequency of telomerase reverse-transcriptase promoter somatic mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma and preneoplastic lesions. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murakami, Y.; Saigo, K.; Takashima, H.; Minami, M.; Okanoue, T.; Bréchot, C.; Paterlini-Brechot, P. Large scaled analysis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA integration in HBV related hepatocellular carcinomas. Gut 2005, 54, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, L.; Qian, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, G.; Chen, Y.; Xie, X.; Ye, Q.; Zang, J.; Ren, Z.-G.; et al. Identification of HBV-MLL4 Integration and Its Molecular Basis in Chinese Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Jacob, L.S.; Slack, F.J. Non-coding RNA networks in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 18, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.J.; Wong, S.Y.; Huang, F.; Lim, S.; Chong, S.S.; Ooi, L.L.; Kon, O.L.; Lee, C.G.L. Roles and Regulation of Long Noncoding RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5131–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.-C.; Sun, T.; Ching, A.K.; He, M.; Li, J.W.; Wong, A.M.; Na Co, N.; Chan, A.W.; Li, P.-S.; Lung, R.W.; et al. Viral-Human Chimeric Transcript Predisposes Risk to Liver Cancer Development and Progression. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michalak, T.I.; Mulrooney, P.M.; Coffin, C.S. Low doses of hepadnavirus induce infection of the lymphatic system that does not engage the liver. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 1730–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lew, Y.-Y.; Michalak, T.I. In Vitro and In Vivo Infectivity and Pathogenicity of the Lymphoid Cell-Derived Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus. J. Virol. 2001, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulrooney-Cousins, P.M.; Michalak, T.I. Repeated Passage of Wild-Type Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus in Lymphoid Cells Does Not Generate Cell Type-Specific Variants or Alter Virus Infectivity. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7540–7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korba, B.E.; Cote, P.J.; Gerin, J.L. Mitogen-induced replication of woodchuck hepatitis virus in cultured peripheral blood lymphocytes. Science 1988, 241, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffin, C.S.; Mulrooney-Cousins, P.M.; Van Marle, G.; Roberts, J.P.; Michalak, T.I.; Terrault, N. Hepatitis B virus quasispecies in hepatic and extrahepatic viral reservoirs in liver transplant recipients on prophylactic therapy. Liver Transplant. 2011, 17, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Minami, M.; Daimon, Y.; Okanoue, T. Hepatitis B virus DNA in liver, serum, and peripheral blood mononuclear cells after the clearance of serum hepatitis B virus surface antigen. J. Med Virol. 2003, 72, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brind, A.; Jiang, J.; Samuel, D.; Gigou, M.; Féray, C.; Bréchot, C.; Kremsdorf, D. Evidence for selection of hepatitis B mutants after liver transplantation through peripheral blood mononuclear cell infection. J. Hepatol. 1997, 26, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, N. Configuration and replication competence of hepatitis B virus DNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from chronic hepatitis B patients and patients who have recovered from acute self-limited hepatitis. Hepatol. Res. 2003, 25, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.L.; Wick, M.; White, H.; Perrillo, R. Hepatitis B virus replication in diverse cell types during chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 1993, 18, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoffe, B.; Burns, D.K.; Bhatt, H.S.; Combes, B. Extrahepatic hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in patients with acute hepatitis B infection. Hepatology 1990, 12, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Yueng, Y.-H.; Cheung, K.-F.; Luk, J.M.; Wang, F.-S.; Lau, G.K.-K. Intracellular levels of hepatitis B virus DNA and pregenomic RNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of chronically infected patients. J. Viral Hepat. 2009, 16, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Nishikawa, S.; Gao, S.; Eksteen, J.B.; Czub, M.; Gill, M.J.; Osiowy, C.; Van Der Meer, F.; Van Marle, G.; Coffin, C.S. Detection of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Genomes and HBV Drug Resistant Variants by Deep Sequencing Analysis of HBV Genomes in Immune Cell Subsets of HBV Mono-Infected and/or Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type-1 (HIV-1) and HBV Co-Infected Individuals. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trippler, M.; Büschenfelde, K.-H.M.Z.; Gerken, G. HBV viral load within subpopulations of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in HBV infection using limiting dilution PCR. J. Virol. Methods 1999, 78, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemin, I.; Vermot-Desroches, C.; Baginski, I.; Saurin, J.C.; Laurent, F.; Zoulim, F.; Bernaud, J.; Lamelin, J.P.; Hantz, O.; Rigal, D.; et al. Selective detection of human hepatitis B virus surface and core antigens in peripheral blood mononuclear cell subsets by flow cytometry. J. Viral Hepat. 1994, 1, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Lan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fan, R.; Liu, L.; Song, S.; Li, Y. Hepatitis B virus replication is upregulated in proliferated peripheral blood lymphocytes. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3581–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Yan, Q.; Fan, R.; Song, S.; Ren, H.; Li, Y.; Lan, Y. Hepatitis B Virus Replication in CD34+ Hematopoietic Stem Cells from Umbilical Cord Blood. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.C.; Joshi, S.S.; Gao, S.; Giles, E.; Swidinsky, K.; Van Marle, G.; Bathe, O.F.; Urbanski, S.J.; Terrault, N.A.; Burak, K.W.; et al. Oncogenic HBV variants and integration are present in hepatic and lymphoid cells derived from chronic HBV patients. Cancer Lett. 2020, 480, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouffard, P.; Lamelin, J.-P.; Zoulim, F.; Lepot, D.; Trepo, C. Phytohemagglutinin and concanavalin A activate hepatitis B virus in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 1992, 37, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Pan, H.; Yang, P.; Ye, P.; Cao, H.; Zhou, H. Both chronic HBV infection and naturally acquired HBV immunity confer increased risks of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, X.; Xing, L.; Yue, W.; Yin, H.; He, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, J. HBV infection potentiates resistance to S-phase arrest-inducing chemotherapeutics by inhibiting CHK2 pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Song, Y.; Young, K.H.; Hu, S.; Ding, N.; Song, W.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Hepatitis B virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Unique clinical features, poor outcome, and hepatitis B surface antigen-driven origin. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25061–25073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engels, E.A.; Cho, E.R.; Jee, S.H. Hepatitis B virus infection and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in South Korea: A cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Gan, Y.; Fan, C.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Meng, Z.; Xu, D.; Tu, H. Hepatitis B virus and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: An updated meta-analysis of 58 studies. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.-H.; Liu, C.-J.; Tseng, T.-C.; Chou, S.-W.; Liu, C.-H.; Yang, H.-C.; Wu, S.-J.; Chen, P.-J.; Chen, D.-S.; Chen, C.-L.; et al. Chronic hepatitis B is associated with an increased risk of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and multiple myeloma. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, M.; Rao, C.R.; Premalata, C.S.; Shafiulla, M.; Lakshmaiah, K.C.; Jacob, L.A.; Babu, G.K.; Viveka, B.K.; Appaji, L.; Subramanyam, J.R. Plasma Epstein–Barr virus and Hepatitis B virus in non-Hodgkin lymphomas: Two lymphotropic, potentially oncogenic, latently occurring DNA viruses. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2016, 37, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalia, S.; Chavez, J.; Castillo, J.J.; Sokol, L. Hepatitis B infection increases the risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Pan, S.; Hu, T.; Shen, J.; Zheng, H.; Xie, S.; Xie, Y.; Renquan, L.; Guo, L. Capable Infection of Hepatitis B Virus in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Lan, Y.; Cao, F.; Teng, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, F.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y. Infected hematopoietic stem cells and with integrated HBV DNA generate defective T cells in chronic HBV infection patients. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, e39–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitta, C.; Tripodi, G.; Barbera, A.; Bertuccio, A.; Smedile, A.; Ciancio, A.; Raffa, G.; SanGiovanni, A.; Navarra, G.; Raimondo, G.; et al. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA integration in patients with occult HBV infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 2311–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sinha, M.; Sundar, K.; Premalata, C.S.; Asati, V.; Murali, A.; Bajpai, A.K.; Davuluri, S.; Acharya, K.K.; Lakshmaiah, K.C.; Babu, G.K.; et al. Pro-oncogenic, intra host viral quasispecies in Diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients with occult Hepatitis B Virus infection. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14516–14518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikitina, E.; Larionova, I.; Choinzonov, E.L.; Kzhyshkowska, J. Monocytes and Macrophages as Viral Targets and Reservoirs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oropeza, C.E.; Tarnow, G.; Sridhar, A.; Taha, T.Y.; Shalaby, R.E.; McLachlan, A. The Regulation of HBV Transcription and Replication. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1179, 39–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.-M.; Churchill, N.D.; Michalak, T.I. Protease-activated lymphoid cell and hepatocyte recognition site in the preS1 domain of the large woodchuck hepatitis virus envelope protein. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanning, G.C.; Zoulim, F.; Hou, J.; Bertoletti, A. Therapeutic strategies for hepatitis B virus infection: Towards a cure. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, T.C.; Lok, A.S.-F. How Do We Determine Whether a Functional Cure for HBV Infection Has Been Achieved? Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimondo, G.; Allain, J.-P.; Brunetto, M.R.; Buendia, M.A.; Chen, P.-J.; Colombo, M.; Craxi, A.; Donato, F.; Ferrari, C.; Gaeta, G.B.; et al. Statements from the Taormina expert meeting on occult hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2008, 49, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, G.; Caccamo, G.; Filomia, R.; Pollicino, T. Occult HBV infection. Semin. Immunopathol. 2012, 35, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yip, T.C.-F.; Wong, G.L. Current Knowledge of Occult Hepatitis B Infection and Clinical Implications. Semin. Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, G.; Locarnini, S.; Pollicino, T.; Levrero, M.; Zoulim, F.; Lok, A.S.; Taormina Workshop on Occult HBV Infection Faculty Members. Update of the statements on biology and clinical impact of occult hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mak, L.-Y.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Pollicino, T.; Raimondo, G.; Hollinger, F.B.; Yuen, M.-F. Occult hepatitis B infection and hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology, virology, hepatocarcinogenesis and clinical significance. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, J.; Bulkow, L.; McMahon, B.J.; Homan, C.; Snowball, M.; Negus, S.; Williams, J.; Livingston, S.E. Clearance of hepatitis B surface antigen and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in a cohort chronically infected with hepatitis B virus. Hepatology 2009, 51, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Someya, T.; Saitoh, S.; Hosaka, T.; Akuta, N.; Suzuki, F.; Suzuki, Y.; Arase, Y.; Kumada, H. Occult hepatitis B virus infection increases hepatocellular carcinogenesis by eight times in patients with non-B, non-C liver cirrhosis: A cohort study. J. Viral Hepat. 2009, 16, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wu, Y.H.; Wu, W.; Zhang, W.J.; Yang, J.; Chen, Z. Association between occult hepatitis B infection and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2011, 32, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, N.; Onorato, L.; Iodice, V.; Starace, M.; Minichini, C.; Farella, N.; Liorre, G.; Filippini, P.; Sagnelli, E.; De Stefano, G. Occult HBV infection in HCC and cirrhotic tissue of HBsAg-negative patients: A virological and clinical study. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 62706–62714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, D.K.H.; Huang, F.Y.; Lai, C.-L.; Poon, R.T.P.; Seto, W.; Fung, J.; Hung, I.F.-N.; Yuen, M.-F. Occult hepatitis B infection and HBV replicative activity in patients with cryptogenic cause of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2011, 54, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, J.; Sugiyama, M.; Shirabe, K.; Mukaide, M.; Kirikae-Muto, I.; Ikegami, T.; Yoshizumi, T.; Yamashita, Y.-I.; Maehara, Y.; Mizokami, M. Frequency and Characteristics of Occult Hepatitis B Infection Among Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients in Japan. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.K.-H.; Cheng, S.C.Y.; Mak, L.L.-Y.; To, E.W.-P.; Lo, R.C.-L.; Cheung, T.-T.; Seto, W.-K.; Fung, J.; Man, K.; Lai, C.-L.; et al. Among Patients with Undetectable Hepatitis B Surface Antigen and Hepatocellular Carcinoma, a High Proportion Has Integration of HBV DNA into Hepatocyte DNA and No Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.-P.; Long, X.; Jia, W.-L.; Wu, H.-J.; Zhao, J.; Liang, H.-F.; Laurence, A.; Zhu, J.; Dong, D.; Chen, Y.; et al. Viral integration drives multifocal HCC during the occult HBV infection. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tajima, K.; Takahashi, N.; Ishizawa, K.; Murai, K.; Akagi, T.; Noji, H.; Sasaki, O.; Wano, M.; Itoh, J.; Kato, Y.; et al. High prevalence of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in occult hepatitis B virus-infected patients in the Tohoku district in Eastern Japan. J. Med. Virol. 2016, 88, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, N.; Huang, C.; Li, X.; Li, J. High risk of occult hepatitis B virus infection in leukemia patients from China. Arch. Virol. 2016, 162, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-H.; Hsiao, L.-T.; Chiou, T.-J.; Liu, J.-H.; Gau, J.-P.; Teng, H.-W.; Wang, W.-S.; Chao, T.-C.; Yen, C.-C.; Chen, P.-M. High prevalence of occult hepatitis B virus infection in patients with B cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2008, 87, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, W.; Chan, T.C.; Leung, N.; Lam, W.Y.; Mo, F.K.; Chu, M.T.; Chan, H.L.; Hui, E.P.; Lei, K.I.; Mok, T.S.-K.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in Lymphoma Patients With Prior Resolved Hepatitis B Undergoing Anticancer Therapy With or Without Rituximab. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumoto, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Ueda, R.; Mizokami, M. Reactivation of hepatitis B virus following rituximab-plus-steroid combination chemotherapy. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 46, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, W.; Chan, T.S.; Hwang, Y.-Y.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Fung, J.; Liu, K.S.-H.; Gill, H.; Lam, Y.-F.; Lie, A.K.; Lai, C.-L.; et al. Hepatitis B Reactivation in Patients With Previous Hepatitis B Virus Exposure Undergoing Rituximab-Containing Chemotherapy for Lymphoma: A Prospective Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3736–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allweiss, L.; Dandri, M. Experimental in vitro and in vivo models for the study of human hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S17–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lau, K.C.K.; Burak, K.W.; Coffin, C.S. Impact of Hepatitis B Virus Genetic Variation, Integration, and Lymphotropism in Antiviral Treatment and Oncogenesis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101470
Lau KCK, Burak KW, Coffin CS. Impact of Hepatitis B Virus Genetic Variation, Integration, and Lymphotropism in Antiviral Treatment and Oncogenesis. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(10):1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101470
Chicago/Turabian StyleLau, Keith C.K., Kelly W. Burak, and Carla S. Coffin. 2020. "Impact of Hepatitis B Virus Genetic Variation, Integration, and Lymphotropism in Antiviral Treatment and Oncogenesis" Microorganisms 8, no. 10: 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101470
APA StyleLau, K. C. K., Burak, K. W., & Coffin, C. S. (2020). Impact of Hepatitis B Virus Genetic Variation, Integration, and Lymphotropism in Antiviral Treatment and Oncogenesis. Microorganisms, 8(10), 1470. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8101470






