Rapid, Precise and Affordable Estimation of Venlafaxine and Its Metabolites in Highly Polluted Effluent Waters: Proof-of-Concept for Methodology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Proposed Reaction Mechanism
2.2. Reaction Stoichiometry
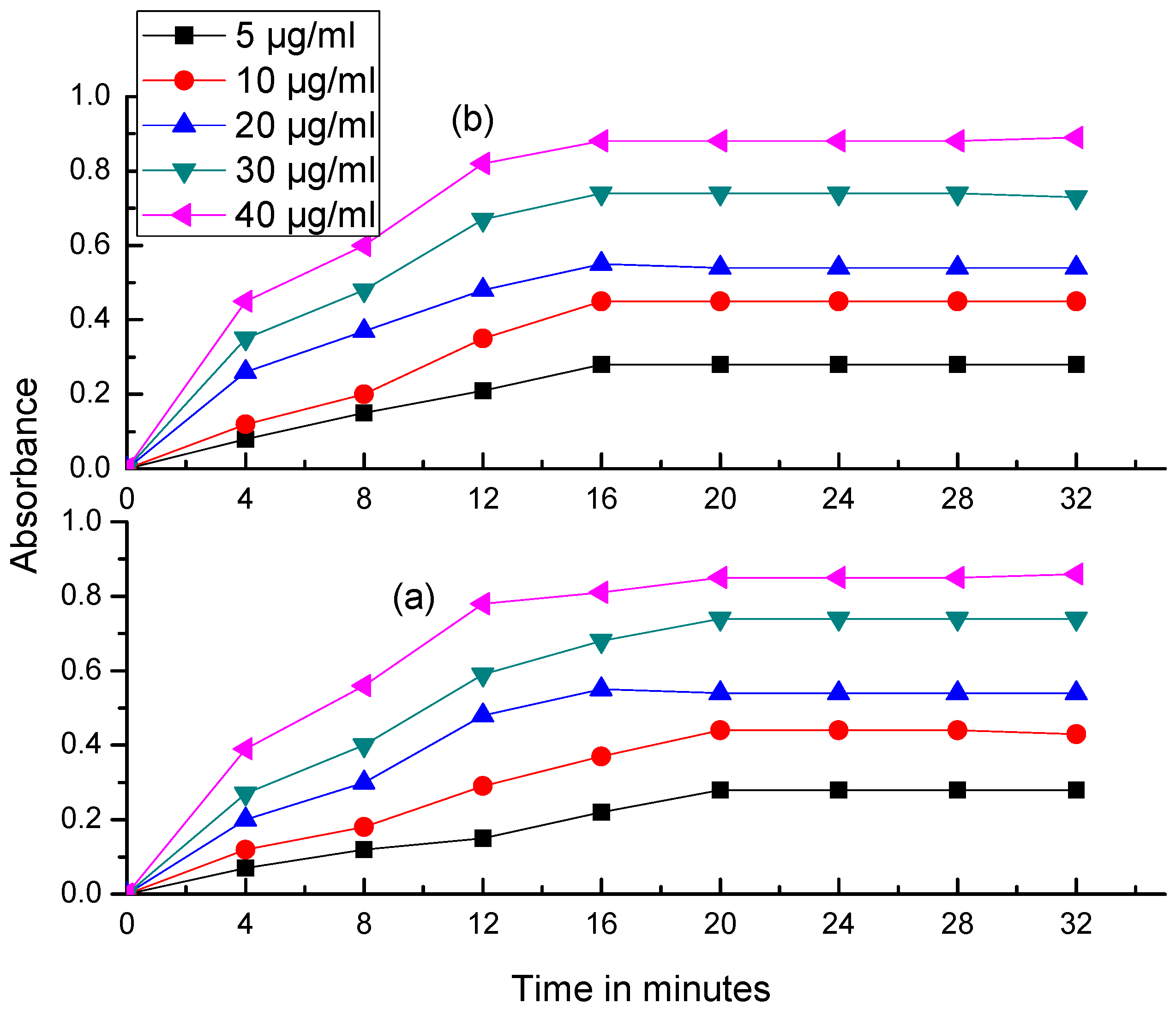
2.3. Effects of Reagent Concentration
2.4. Method Validation
2.5. Interference Study
2.6. Effect of Adding Metabolites into VEN Tablet Samples
2.7. Kinetic Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Instrumental
3.3. Method Development
3.4. Optimization of Reaction Conditions and Procedures
3.4.1. VEN
3.4.2. NDV and Cyclic VEN
3.5. Calibration Curve
3.6. Procedure for VEN Tablets (Recovery Studies)
3.7. Effects of Surfactants and Excipients
3.8. Standard Addition of Metabolites into VEN Tablet Solution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drugs in the Water. Available online: https://www.health.harvard.edu/newsletter_article/drugs-in-the-water (accessed on 12 August 2020).
- Shaaban, H.; Alghamdi, H.; Alhamed, N.; Alziadi, A.; Mostafa, A. Environmental Contamination by Pharmaceutical Waste: Assessing Patterns of Disposing Unwanted Medications and Investigating the Factors Influencing Personal Disposal Choices. J. Pharmacol. Pharm. Res. 2018, 1, 003. [Google Scholar]
- Painter, M.M.; Buerkley, M.A.; Julius, M.L.; Vajda, A.M.; Norris, D.O.; Barber, L.B.; Furlong, E.T.; Schultz, M.M.; Schoenfuss, H.L. Antidepressants at environmentally relevant concentrations affect predator avoidance behavior of larval fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2677–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.M.; Furlong, E.T.; Kolpin, D.W.; Werner, S.L.; Schoenfuss, H.L.; Barber, L.B.; Blazer, V.S.; Norris, D.O.; Vajda, A.M. Antidepressant Pharmaceuticals in Two U.S. Effluent-Impacted Streams: Occurrence and Fate in Water and Sediment, and Selective Uptake in Fish Neural Tissue. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, C.; Melnyk-Lamont, N.; Gesto, M.; Vijayan, M.M. Environmental levels of the antidepressant venlafaxine impact the metabolic capacity of rainbow trout. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 155, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minguez, L.; Farcy, E.; Ballandonne, C.; Lepailleur, A.; Serpentini, A.; Lebel, J.-M.; Bureau, R.; Halm-Lemeille, M.-P. Acute toxicity of 8 antidepressants: What are their modes of action? Chemosphere 2014, 108, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisesi, J.H.; Bridges, W.; Klaine, S.J. Effects of the antidepressant venlafaxine on fish brain serotonin and predation behavior. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 148, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González Alonso, S.; Catalá, M.; Maroto, R.R.; Gil, J.L.R.; de Miguel, Á.G.; Valcárcel, Y. Pollution by psychoactive pharmaceuticals in the Rivers of Madrid metropolitan area (Spain). Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia-Lor, E.; Sancho, J.V.; Hernández, F. Simultaneous determination of acidic, neutral and basic pharmaceuticals in urban wastewater by ultra high-pressure liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopala, K.N.; Tratrat, C.; Chandrashekharappa, S.; Attimarad, M.; Sreeharsha, N.; Nair, A.B.; Pottathil, S.; Venugopala, R.; Al-Attraqchi, O.H.A.; Morsy, M.A.; et al. Anti-tubercular Potency and Computationally-assessed Drug-likeness and Toxicology of Diversely Substituted Indolizines. Indian J. Pharma. Edu. Res. 2019, 53, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, M.; Kirischian, N.; Higgins, S.; Purdy, J.; Chow, J.; Rangaranjan, S.; Li, H.; Metcalfe, C.; Wilson, J.Y. Chronic, low concentration exposure to pharmaceuticals impacts multiple organ systems in zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 132–133, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muth, E.A.; Moyer, J.A.; Haskins, J.T.; Andree, T.H.; Husbands, G.E.M. Biochemical, neurophysiological, and behavioral effects of Wy-45,233 and other identified metabolites of the antidepressant venlafaxine. Drug Dev. Res. 1991, 23, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klamerus, K.J.; Moloney, K.; Rudolph, R.L.; Sisenwine, S.F.; Jusko, W.J.; Chiang, S.T. Introduction of a Composite Parameter to the Pharmacokinetics of Venlafaxine and its Active O-Desmethyl Metabolite. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1992, 32, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, S.R.; Husbands, G.E.M.; Scatina, J.A.; Sisenwine, S.F. Metabolic disposition of 14C-venlafaxine in mouse, rat, dog, rhesus monkey and man. Xenobiotica 1993, 23, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogelman, S.M.; Schmider, J.; Venkatakrishnan, K.; von Moltke, L.L.; Harmatz, J.S.; Shader, R.I.; Greenblatt, D.J. O- and N-demethylation of Venlafaxine In Vitro by Human Liver Microsomes and by Microsomes from cDNA-Transfected Cells: Effect of Metabolic Inhibitors and SSRI Antidepressants. Neuropsychopharmacology 1999, 20, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Ma, R.; Wang, B.; Yang, J.; Duan, L.; Yu, G. Enantiospecific toxicity, distribution and bioaccumulation of chiral antidepressant venlafaxine and its metabolite in loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) co-exposed to microplastic and the drugs. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 370, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.; Bagnall, J.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Enantiomeric profiling of a chemically diverse mixture of chiral pharmaceuticals in urban water. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 230, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, B.; Barden, R.; Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. A review on emerging contaminants in wastewaters and the environment: Current knowledge, understudied areas and recommendations for future monitoring. Water Res. 2015, 72, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SreeHarsha, N.; Hiremath, J.G.; Rawre, B.K.; Puttaswamy, N.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Venugopala, K.N.; Akrawi, S.H.; Meravanige, G.; Attimarad, M.; Nair, A.B. Formulation and Evaluation of Tamoxifen Citrate Loaded Transdermal Reservoir Gel Drug Delivery Systems. Indian J. Pharma Educ. Res. 2019, 53, S596–S606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.M.; Boillot, C.; Munaron, D.; Fenet, H.; Casellas, C.; Gomez, E. Occurrence of venlafaxine residues and its metabolites in marine mussels at trace levels: Development of analytical method and a monitoring program. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelsbach, M.; Buchberger, W.; Klampfl, C.W. Determination of antidepressants in surface and waste water samples by capillary electrophoresis with electrospray ionization mass spectrometric detection after preconcentration using off-line solid-phase extraction. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 1220–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KPMG International. The Indian Pharmaceutical Industry: Collaboration for Growth. 2006. Available online: http://www.in.kpmg.com/pdf/Indian%20pharma%20outlook.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Reddy, A.G.S.; Boraa, S.; Ganji, S. Hydrogeochemical characterization of contaminated groundwater in Patancheru industrial area, Southern India. Environ. Monit. Assess 2012, 184, 3557–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, G.; Unnikrishnan, M.K. The emerging environmental burden from pharmaceuticals. Econ. Polit Week 2012, 47, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Mike, A. India’s Waterways: A Toxic Stew of Pharmaceutical Chemicals Dumped from Big Pharma Factories. Natural News. 2009. Available online: http://www.naturalnews.com/025415.html (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Schertow, J.A. India’s Waterways Used as Dumping Grounds for Big Pharma. 2009. Available online: http://intercontinentalcry.org/indias-waterways-used-as-dumpinggrounds-for-big-pharma/ (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- CBS Investigates. Indian stream a Cocktail of Drugs. CBS News. 2009. Available online: http://www.cbsnews.com/2100-202_162-4752641.html (accessed on 28 September 2020).
- Ryu, A. Pharmaceutical pollution of water in India: International market failure. Harv. Health Policy Rev. 2013, 14, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Kummerer, K. Pharmaceuticals in the Environment: Sources, Fate, Effects and Risks; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Vijay, G. Systemic failure of regulation: The political economy of pharmaceutical and bulk drug manufacturing. In The Politics of the Pharmaceutical Industry and Access to Medicines: World Pharmacy and India; Lofgren, H., Ed.; Social Science Press: New Delhi, India, 2012; pp. 73–107. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Bisht, B.S.; Joshi, V.D.; Singh, A.K.; Talwar, A. Physical, chemical and bacteriological study of water from rivers of Uttarakhand. J. Hum. Ecol. 2010, 32, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, V.; Singh, P.; Sharma, B.; Upadhyay, K.; Singh, R. Environmental and health hazards due to pharmaceutical effluents. Int. J. Phar. Rev. Res. 2014, 4, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Chander, V.; Sharma, B.; Negi, V.; Aswal, R.S.; Singh, P.; Singh, R.; Dobhal, R. Pharmaceutical compounds in drinking water. J. Xenobiot 2016, 6, 5774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; de Pedro, C.; Paxeus, N. Effluent from drug manufactures contains extremely high levels of pharmaceuticals. J. Hazard Mater. 2007, 148, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, J.; Söderström, H.; Lindberg, R.H.; Phan, C.; Tysklind, M.; Larsson, D.J. Contamination of surface, ground, and drinking water from pharmaceutical production. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 2522–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollman, J.; Dominic, J.A.; Achari, G.; Langford, C.H.; Tay, J. Effect of UV dose on degradation of venlafaxine using UV/H2O2: Perspective of augmenting UV units in wastewater treatment. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharpa, K.; Basavaiah, K.; Revanasiddappa, H.D.; Vinay, K.B. Spectrophotometric determination of isoxsuprine hydrochloride using 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolinone hydrazone hydrochloride in spiked human urine and pharmaceuticals. Talanta 2010, 81, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J. Advanced Physico-Chemical Experiments. A 1wTextbook of Practical Physical Chemistry and Calculations; Pitman: London, UK, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology Q2 (R1), ICH Harmonized Tripartite Guideline. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use, London, UK, November 2005; pp. 1–15. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q2_R1__Guideline.pdf (accessed on 3 October 2020).


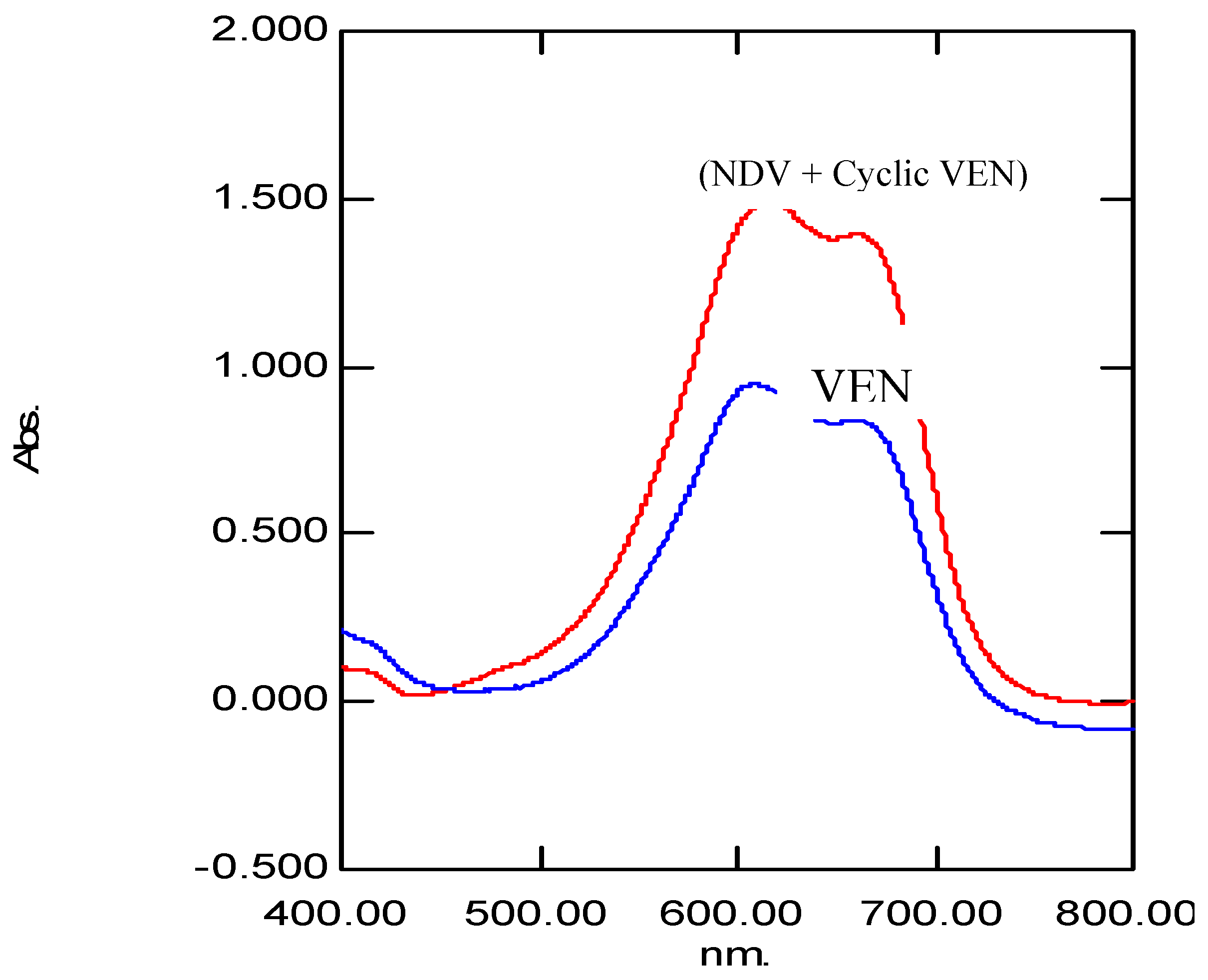
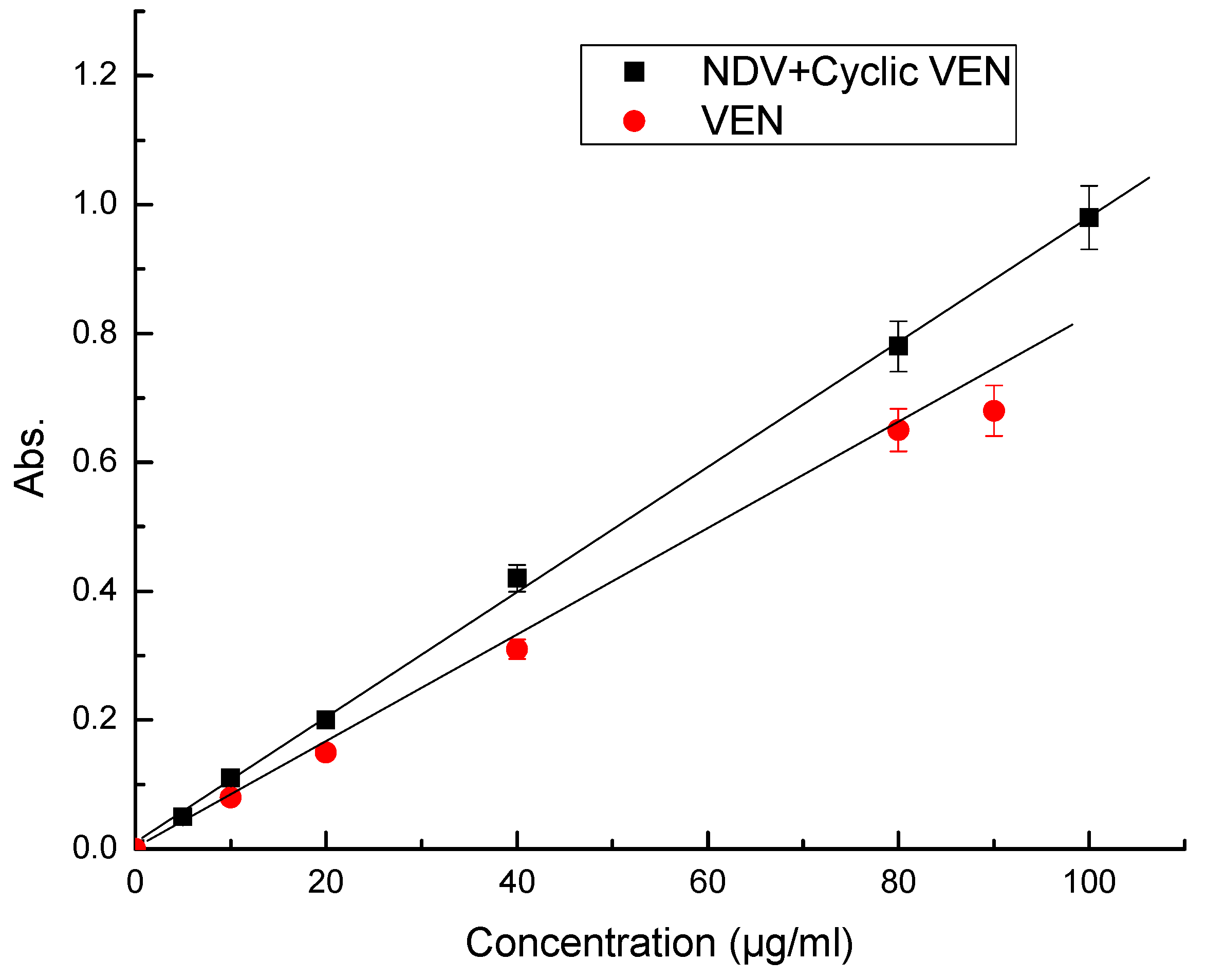
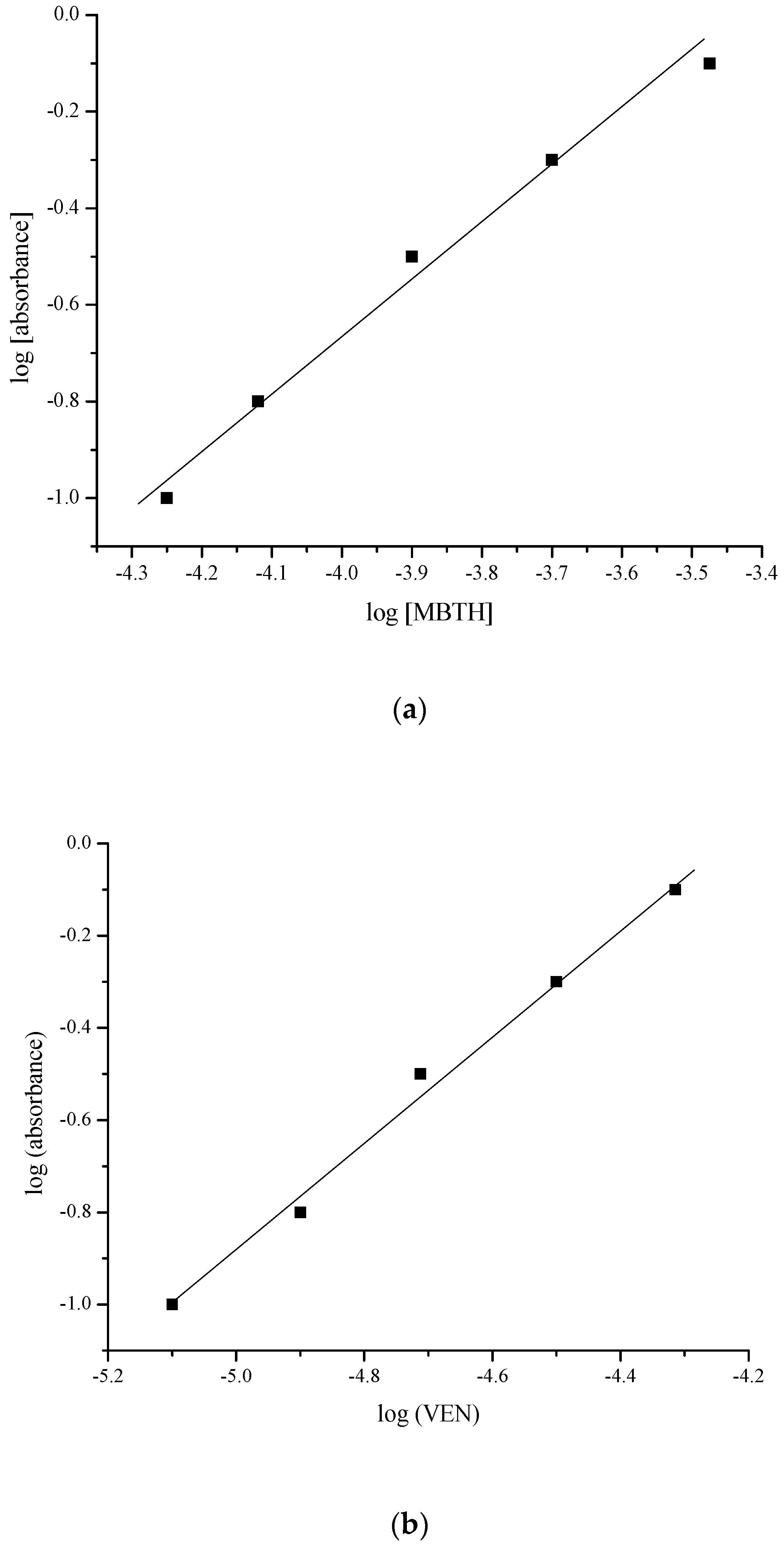
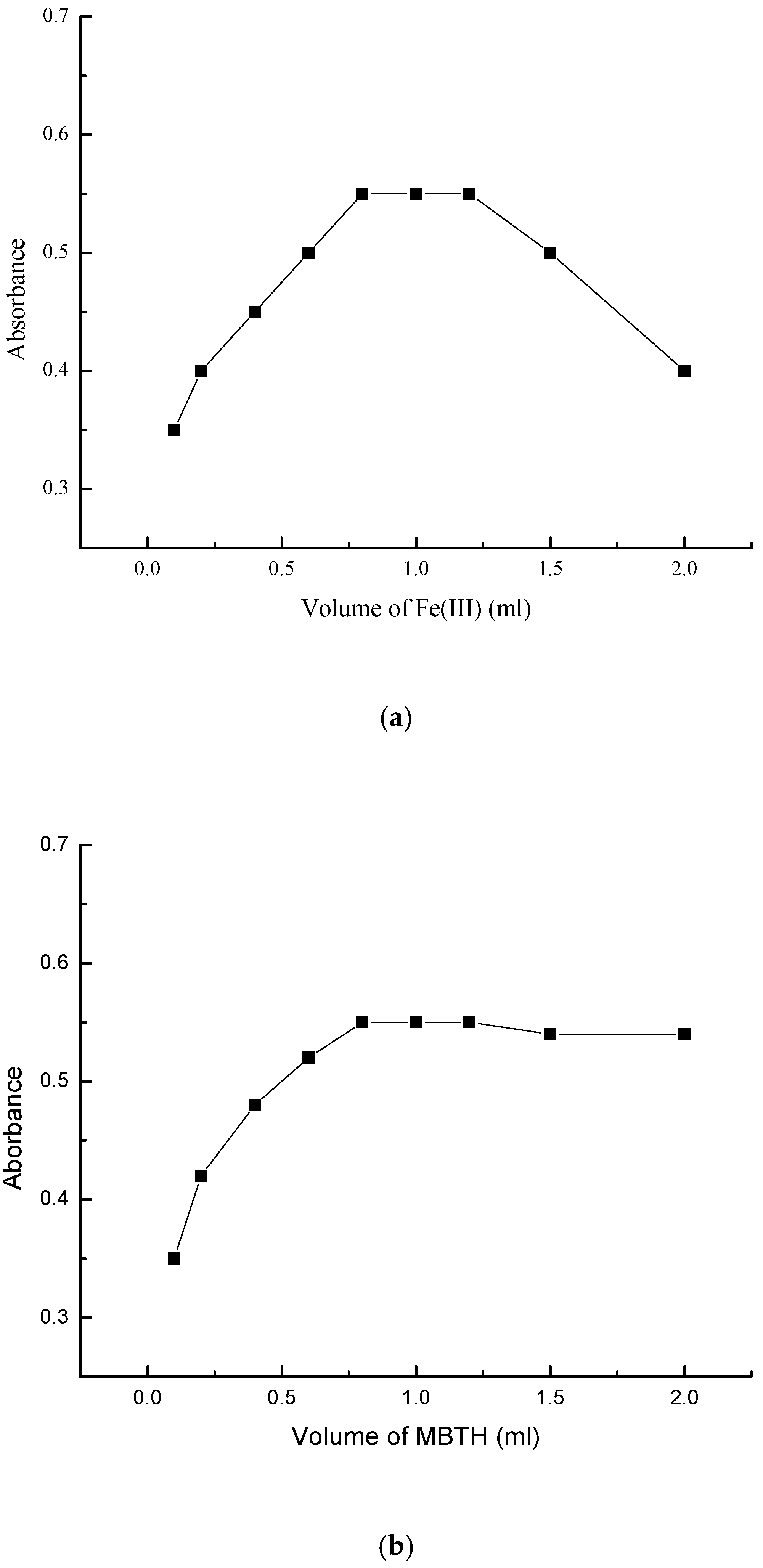
| Parameter | VEN | (NDV + Cyclic VEN) |
|---|---|---|
| λMax, nm | 608.5 | 616.5 nm |
| Beer’s Law range, µg/mL | 10–100 | 5–100 |
| Molar extinction coefficient (l mol−1cm−1) | 0.61 × 105 | 0.94 × 105 |
| Limit of detection, µg/mL | 1.38 | 1.13 |
| Limit of quantification, µg/mL | 3.4 | 4.1 |
| Sandell sensitivity | 0.1638 | 0.2533 |
| Regression Equation * | ||
| Intercept | −0.0035 | 0.0109 |
| Slope | 0.0097 | 0.0080 |
| Sa | 0.01235 | 0.01297 |
| Sb | 0.00014 | 0.00016 |
| Correlation Coefficient | 0.99958 | 0.99933 |
| Intra-Day Assessment | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VEN Added (µg/mL) | VEN Obtained (µg/mL) | % RE | % RSD | (NDV + Cyclic VEN) Added (µg/mL) | (NDV + Cyclic VEN) Obtained (µg/mL) | % RE | % RSD |
| 2.0 | 1.980 | 1.00 | 2.9141 | 2.0 | 1.990 | 0.50 | 2.8994 |
| 4.0 | 3.950 | 1.25 | 1.7877 | 4.0 | 3.970 | 0.75 | 1.7787 |
| 6.0 | 5.930 | 1.17 | 0.5029 | 6.0 | 5.940 | 1.00 | 0.5020 |
| Inter-Day Assessment | |||||||
| VEN added (µg/mL) | VEN obtained (µg/mL) | % RE | % RSD | (NDV + Cyclic VEN) added (µg/mL) | (NDV + Cyclic VEN) obtained (µg/mL) | % RE | % RSD |
| 2.0 | 1.970 | 1.50 | 2.9288 | 2.0 | 1.980 | 1.00 | 2.9141 |
| 4.0 | 3.940 | 1.50 | 1.7923 | 4.0 | 3.960 | 1.00 | 1.7832 |
| 6.0 | 5.920 | 1.33 | 0.5037 | 6.0 | 5.920 | 1.33 | 0.5037 |
| Sl. No. | Excipient | Quantity of Excipient (µg/mL) 1 | Recovery 2 % |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Talc | 100 | 99.87 ± 0.85 |
| 2 | Starch | 150 | 99.74 ± 0.82 |
| 3 | Cellulose | 200 | 99.8 ± 0.78 |
| 4 | Alginate | 100 | 99.3 ± 0.96 |
| 5 | Gum Arabic | 100 | 100.2 ± 0.55 |
| 6 | Lactose | 100 | 99.6 ± 0.85 |
| 7 | Dextrose | 100 | 99.8 ± 0.77 |
| Sl. No. | Surfactant Added | Amount Added (µg/mL) | Absorbance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No surfactant | 0 | 0.61 |
| 2 | Sodium lauryl sulfate | 5 | 0.62 |
| 3 | Gelatin | 5 | 0.65 |
| 4 | Sodium stearate | 10 | 0.60 |
| 5 | Polysorbate | 10 | 0.60 |
| Sl. No. | VEN Taken (µg/mL) | (NDV + Cyclic VEN) Added (µg/mL) | Absorbance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20.0 | 0.0 | 0.456 |
| 2 | 20.0 | 0.5 | 0.462 |
| 3 | 20.0 | 1.0 | 0.478 |
| 4 | 20.0 | 2.0 | 0.502 |
| 5 | 20.0 | 4.0 | 0.546 |
| 6 | 20.0 | 6.0 | 0.583 |
| 7 | 20.0 | 8.0 | 0.606 |
| 8 | 20.0 | 10.0 | 0.655 |
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hussain, S.; Ramnarayanan, C.; Roopashree, T.S.; Anwer, M.K.; Sreeharsha, N.; Nair, A.B. Rapid, Precise and Affordable Estimation of Venlafaxine and Its Metabolites in Highly Polluted Effluent Waters: Proof-of-Concept for Methodology. Molecules 2020, 25, 4793. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204793
Hussain S, Ramnarayanan C, Roopashree TS, Anwer MK, Sreeharsha N, Nair AB. Rapid, Precise and Affordable Estimation of Venlafaxine and Its Metabolites in Highly Polluted Effluent Waters: Proof-of-Concept for Methodology. Molecules. 2020; 25(20):4793. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204793
Chicago/Turabian StyleHussain, Snawar, Chandramouli Ramnarayanan, Teeka S. Roopashree, Md. Khalid Anwer, Nagaraja Sreeharsha, and Anroop B. Nair. 2020. "Rapid, Precise and Affordable Estimation of Venlafaxine and Its Metabolites in Highly Polluted Effluent Waters: Proof-of-Concept for Methodology" Molecules 25, no. 20: 4793. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204793
APA StyleHussain, S., Ramnarayanan, C., Roopashree, T. S., Anwer, M. K., Sreeharsha, N., & Nair, A. B. (2020). Rapid, Precise and Affordable Estimation of Venlafaxine and Its Metabolites in Highly Polluted Effluent Waters: Proof-of-Concept for Methodology. Molecules, 25(20), 4793. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25204793








