Epigenetic Alterations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—The Critical Role of Extracellular Matrix
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epigenetic Alterations in TNBC: ECM/EMT Interplay
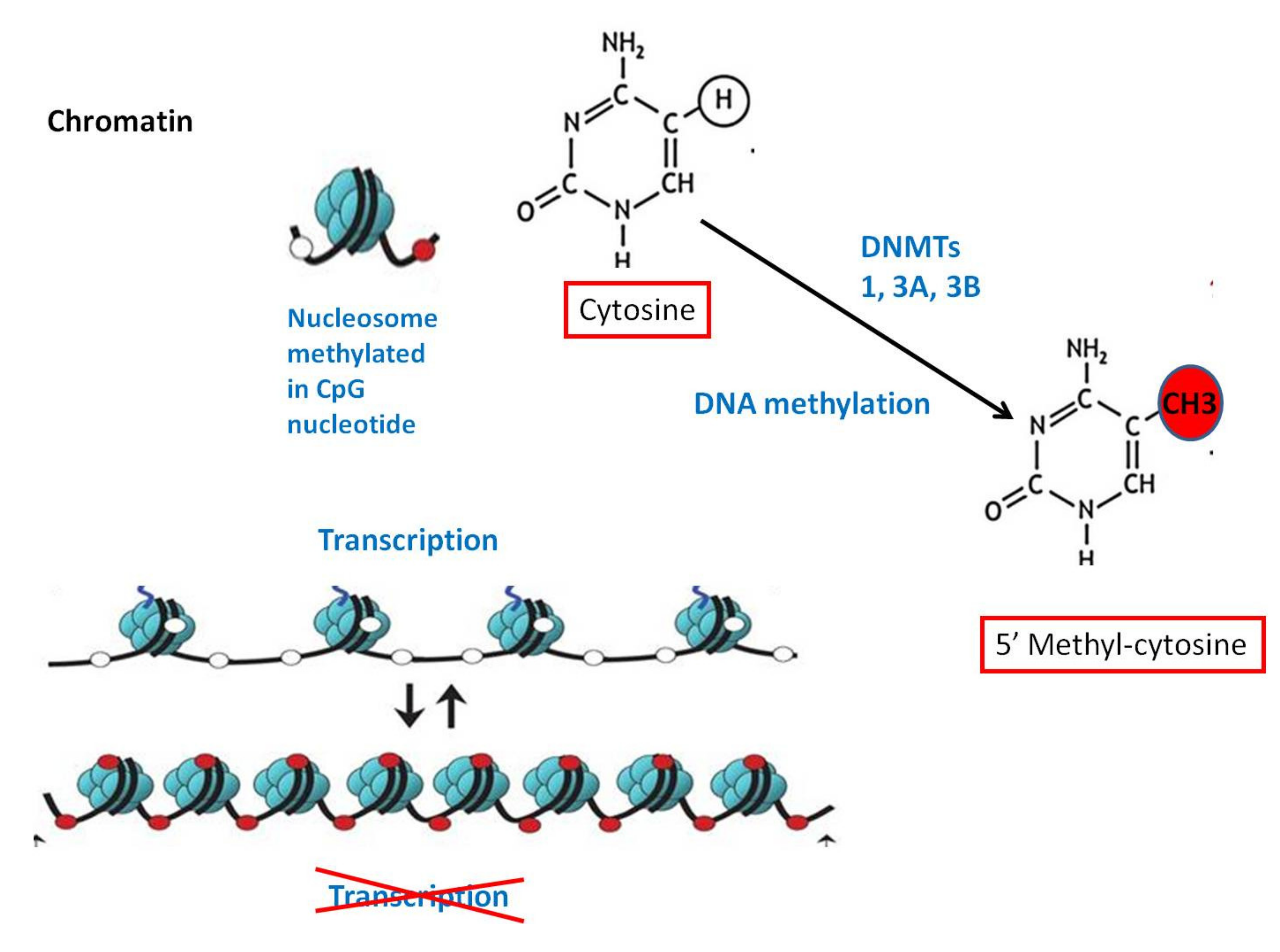
2.1. DNA Methylation
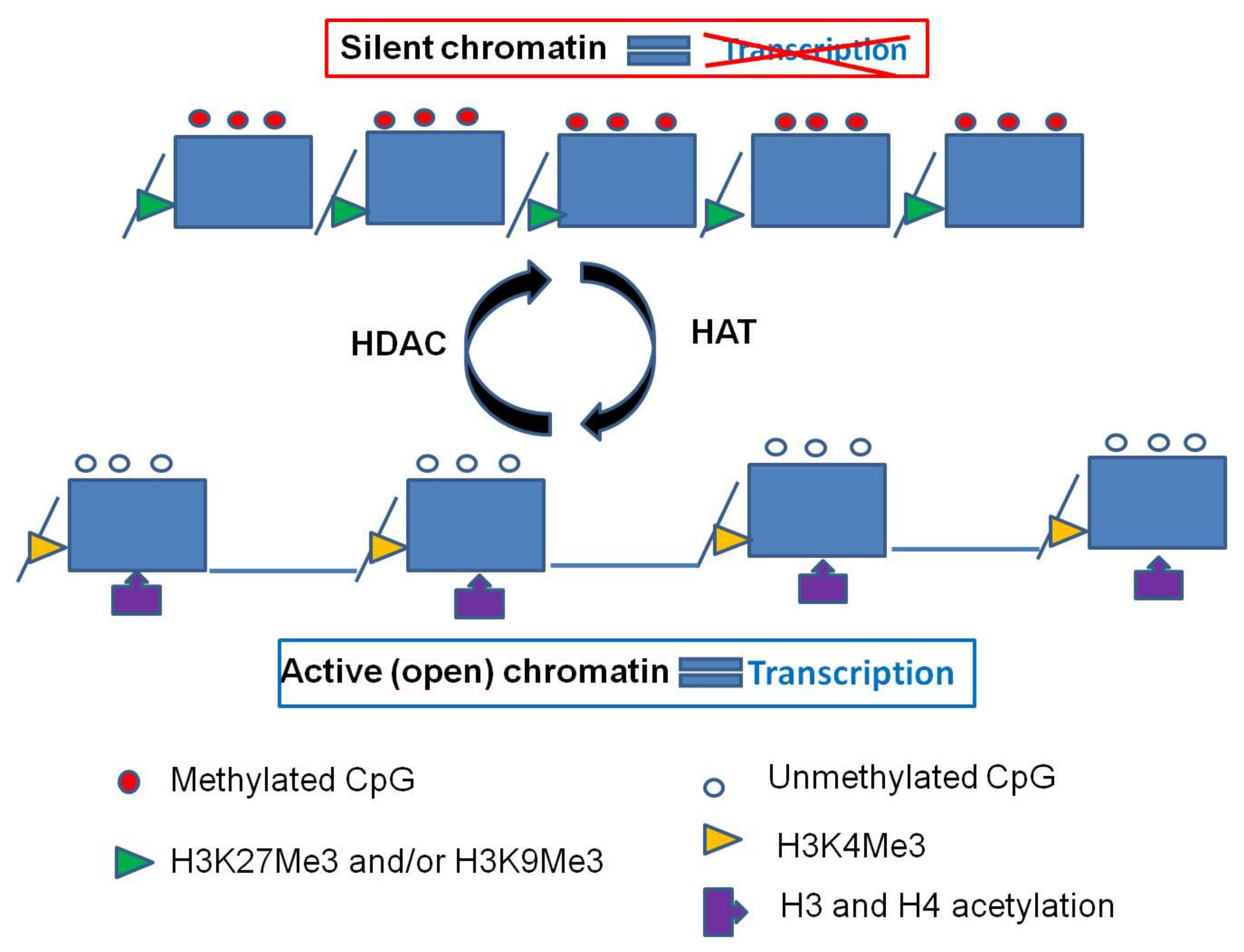
2.2. Histone Modifications
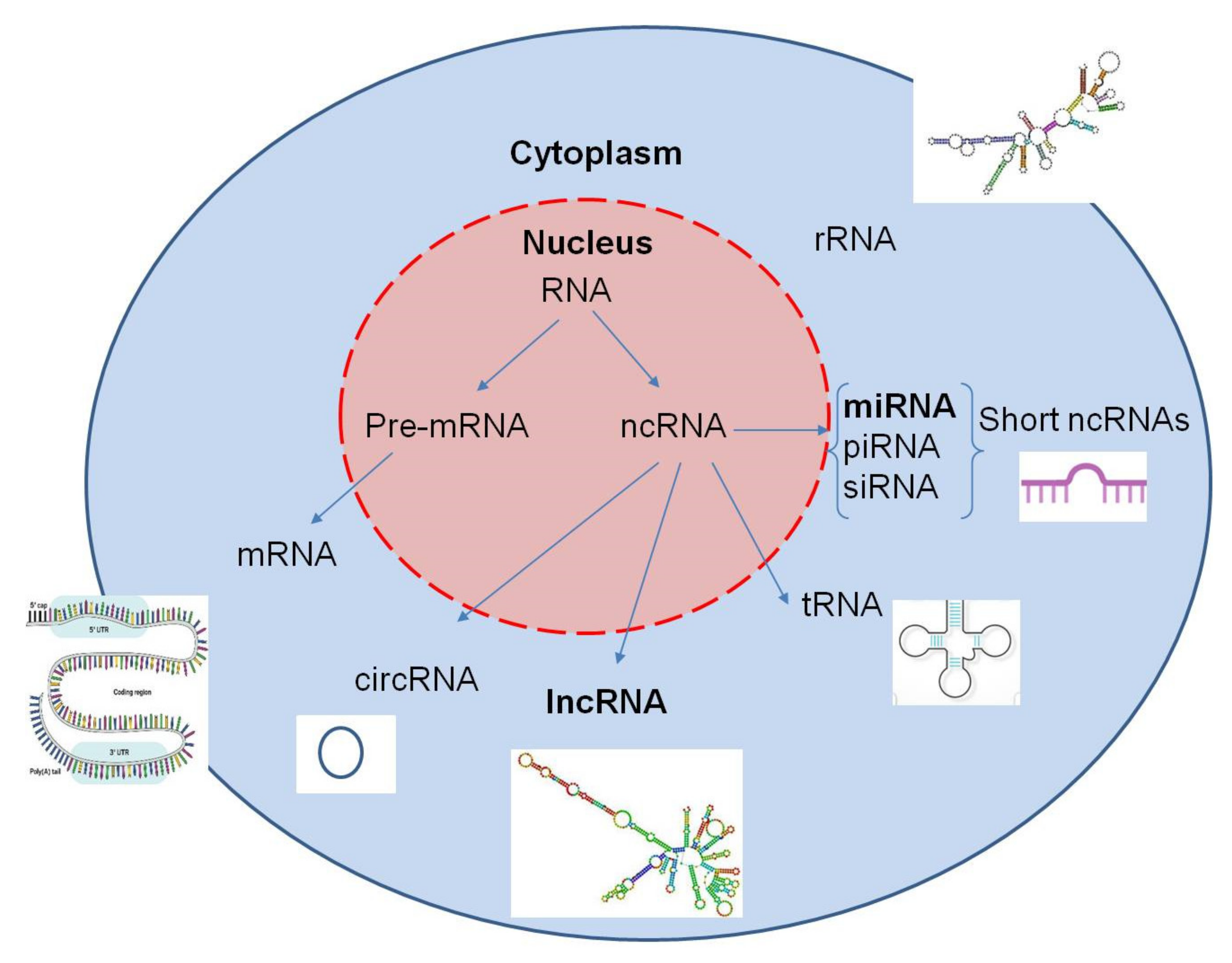
2.3. MicroRNA Expression
2.4. Long Non-Coding RNAs
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foulkes, W.D.; Smith, I.E.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.P.; Roth, A.; Goya, R.; Oloumi, A.; Ha, G.; Zhao, Y.; Turashvili, G.; Ding, J.; Tse, K.; Haffari, G.; et al. The clonal and mutational evolution spectrum of primary triple-negative breast cancers. Nature 2012, 486, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, A.; Parker, J.S.; Karginova, O.; Fan, C.; Livasy, C.; Herschkowitz, J.I.; He, X.; Perou, C.M. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of the claudin-low intrinsic subtype of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farmer, P.; Bonnefoi, H.; Becette, V.; Tubiana-Hulin, M.; Fumoleau, P.; Larsimont, D.; MacGrogan, G.; Bergh, J.; Cameron, D.; Goldstein, D.; et al. Identification of molecular apocrine breast tumours by microarray analysis. Oncogene 2005, 24, 4660–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Jovanović, B.; Chen, X.; Estrada, M.V.; Johnson, K.N.; Shyr, Y.; Moses, H.L.; Sanders, M.E.; Pietenpol, J.A. Refinement of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Molecular Subtypes: Implications for Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Selection. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamanos, N.K. Special issue: Translating extracellular matrix: From cancer progression to therapeutics. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 62, iii–v. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C. The extracellular matrix in breast cancer predicts prognosis through composition, splicing, and crosslinking. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 343, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deville, S.S.; Cordes, N. The Extracellular, Cellular, and Nuclear Stiffness, a Trinity in the Cancer Resistome—A Review. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, J. The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Angelo, E.; Lindoso, R.S.; Sensi, F.; Pucciarelli, S.; Bussolati, B.; Agostini, M.; Collino, F. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Modulators of the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition: Driving the Fate of Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kong, G. Roles and epigenetic regulation of epithelial–mesenchymal transition and its transcription factors in cancer initiation and progression. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4643–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrian, F.; Lelièvre, S.A. Mining the epigenetic landscape of tissue polarity in search of new targets for cancer therapy. Epigenomics 2015, 7, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piperigkou, Z.; Karamanos, N.K. Dynamic Interplay between miRNAs and the Extracellular Matrix Influences the Tumor Microenvironment. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperigkou, Z.; Götte, M.; Theocharis, A.D.; Karamanos, N.K. Insights into the key roles of epigenetics in matrix macromolecules-associated wound healing. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 129, 16–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustakas, A.; Heldin, P. TGFβ and matrix-regulated epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2014, 1840, 2621–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, M.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, E.J.; Chung, Y.R.; Park, S.Y. Expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition–related markers in triple-negative breast cancer: ZEB1 as a potential biomarker for poor clinical outcome. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, W.L.; Weiberg, R.A. The epigenetics of epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer. Nature Med. 2013, 19, 1438–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourguignon, L.Y.W. Matrix Hyaluronan-CD44 Interaction Activates MicroRNA and LncRNA Signaling Associated With Chemoresistance, Invasion, and Tumor Progression. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepak, K.G.K.; Vempati, R.; Nagaraju, G.P.; Dasari, V.R.; Nagini, S.; Rao, D.N.; Malla, R.R. Tumor microenvironment: Challenges and opportunities in targeting metastasis of triple negative breast cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 153, 104683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, J.G.; Baylin, S.B. Gene Silencing in Cancer in Association with Promoter Hypermethylation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2042–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Laird, P.W. Interplay between the Cancer Genome and Epigenome. Cell 2013, 153, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stirzaker, C.; Zotenko, E.; Song, J.Z.; Qu, W.; Nair, S.S.; Locke, W.J.; Stone, A.; Armstong, N.J.; Robinson, M.D.; Dobrovic, A.; et al. Methylome sequencing in triple-negative breast cancer reveals distinct methylation clusters with prognostic value. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Branham, M.T.; Marzese, D.M.; Laurito, S.R.; Gago, F.E.; Orozco, J.I.; Tello, O.M.; Vargas-Roig, L.M.; Roqué, M. Methylation profile of triple-negative breast carcinomas. Oncogenesis 2012, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avery-Kiejda, K.A.; Mathe, A.; Scott, R.J. Genome-wide miRNA, gene and methylation analysis of triple negative breast cancer to identify changes associated with lymph node metastases. Genom. Data 2017, 14, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathe, A.; Wong-Brown, M.; Locke, W.J.; Stirzaker, C.; Braye, S.G.; Forbes, J.F.; Clark, S.J.; Avery-Kiejda, K.A.; Scott, R.J. DNA methylation profile of triple negative breast cancer-specific genes comparing lymph node positive patients to lymph node negative patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Dai, X. DNA methylation profiles capturing breast cancer heterogeneity. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dookeran, K.A.; Zhang, W.; Stayner, L.; Argos, M. Associations of two-pore domain potassium channels and triple negative breast cancer subtype in The Cancer Genome Atlas: Systematic evaluation of gene expression and methylation. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Xiao, G.; Wang, H.; Yang, G.; Li, Y.; Tang, S.-C.; Qin, S.; Du, N.; et al. MYC and DNMT3A-mediated DNA methylation represses microRNA-200b in triple negative breast cancer. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 6262–6274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khaled, N.; Bidet, Y. New insights into the implication of epigenetic alterations in the EMT of triple negative breast cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, A.K.; Mellor, P.; Smith, S.E.; Kendall, S.; Just, N.A.; Vizeacoumar, F.S.; Sarker, S.; Phillips, Z.; Alvi, R.; Saxena, A.; et al. Epigenetic silencing of CREB3L1 by DNA methylation is associated with high-grade metastatic breast cancers with poor prognosis and is prevalent in triple negative breast cancers. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Lv, Z.-D.; Wang, Y.; Jin, L.-Y.; Ding, L.; Yang, Z.-C. Down-regulation of BRMS1 by DNA hypermethylation and its association with metastatic progression in triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 11076–11083. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Yu, H.; Tian, J.; Yuan, F.; Fan, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y.; et al. DUSP1 promoter methylation in peripheral blood leukocyte is associated with triple-negative breast cancer risk. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elsheikh, S.E.; Green, A.R.; Rakha, E.A.; Powe, D.G.; Ahmed, R.A.; Collins, H.M.; Soria, D.; Garibaldi, J.M.; Paish, C.E.; Ammar, A.A.; et al. Global histone modifications in breast cancer correlate with tumor phenotypes, prognostic factors, and patient outcome. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3802–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tye, C.E.; Boyd, J.R.; Messier, T.L.; Browne, G.; Gordon, J.A.R.; Stein, G.S.; Stein, J.L.; Lian, J.B. Histone H3 lysine 4 acetylation and methylation dynamics define breast cancer subtypes. Oncotarget 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, W.; Tanaka, K.; Allton, K.L.; Richardson, D.; Li, J.; Franco, H.L.; Nagari, A.; Malladi, V.S.; et al. Histone modification profiling in breast cancer cell lines highlights commonalities and differences among subtypes. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Fang, M.; Bai, H.; Xu, Y. The chromatin remodeling protein BRM regulates the transcription of tight junction proteins: Implication in breast cancer metastasis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Kimball, S.; Liu, H.; Holowatyj, A.; Yang, Z.-Q. Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morcillo-Garcia, S.; Noblejas-Lopez, M.d.M.; Nieto-Jimenez, C.; Perez-Peña, J.; Nuncia-Cantarero, M.; Győrffy, B.; Amir, E.; Pandiella, A.; Galan-Moya, E.M.; Ocana, A. Genetic mutational status of genes regulating epigenetics: Role of the histone methyltransferase KMT2D in triple negative breast tumors. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Roberts, C.W.M. Targeting EZH2 in cancer. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.K. DNMT1: A key drug target in triple-negative breast cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, D.; Ma, W.; An, K.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, C.; Du, F.; Han, X.; Chang, S.; et al. Transcriptomic and epigenetic analysis of breast cancer stem cells. Epigenomics 2018, 10, 765–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, C.R.; Rhodes, L.V.; Segar, H.C.; Driver, J.L.; Pounder, F.N.; Burow, M.E.; Collins-Burow, B.M. Targeting triple-negative breast cancer cells with the histone deacetylase inhibitor panobinostat. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schech, A.; Kazi, A.; Yu, S.; Shah, P.; Sabnis, G. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Entinostat Inhibits Tumor-Initiating Cells in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Y.; Hopfinger, N.R.; Nguyen, T.D.; Pogash, T.J.; Santucci-Pereira, J.; Russo, J. Epigenetic reprogramming of epithelial mesenchymal transition in triple negative breast cancer cells with DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibitors. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liz, J.; Esteller, M. lncRNAs and microRNAs with a role in cancer development. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2016, 1859, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svoronos, A.A.; Engelman, D.M.; Slack, F.J. OncomiR or Tumor Suppressor? Duplicity MicroRNAs Cancer 2016, 76, 3666–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marsico, A.; Huska, M.R.; Lasserre, J.; Hu, H.; Vucicevic, D.; Musahl, A.; Orom, U.; Vingron, M. PROmiRNA: A new miRNA promoter recognition method uncovers the complex regulation of intronic miRNAs. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piasecka, D.; Braun, M.; Kordek, R.; Sadej, R.; Romanska, H. MicroRNAs in regulation of triple-negative breast cancer progression. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, J.-O.; Lee, J.-M.; Cho, K.-W.; Kwak, S.; Kwon, H.-J.; Lee, M.-J.; Cho, S.-W.; Kim, K.-S.; Jung, H.-S. MiR-200b is involved in Tgf-β signaling to regulate mammalian palate development. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 137, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperigkou, Z.; Franchi, M.; Riethmüller, C.; Götte, M.; Karamanos, N.K. miR-200b restrains EMT and aggressiveness and regulates matrix composition depending on ER status and signaling in mammary cancer. Matrix Biol. Plus 2020, 6–7, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Györffy, B.; Lanczky, A.; Eklund, A.C.; Denkert, C.; Budczies, J.; Li, Q.; Szallasi, Z. An online survival analysis tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer prognosis using microarray data of 1809 patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 123, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piovan, C.; Palmieri, D.; Di Leva, G.; Braccioli, L.; Casalini, P.; Nuovo, G.; Tortoreto, M.; Sasso, M.; Plantamura, I.; Triulzi, T.; et al. Oncosuppressive role of p53-induced miR-205 in triple negative breast cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Han, J.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Lv, Y. MicroRNA-203 Regulates Growth and Metastasis of Breast Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Wei, D.; Yan, F. MicroRNA-145 functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting matrix metalloproteinase 11 and Rab GTPase family 27a in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shin, V.Y.; Siu, M.T.; Ho, J.C.W.; Cheuk, I.; Kwong, A. miR-199a-5p confers tumor-suppressive role in triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Nikokar, I.; Zokaei, M.; Bozorgzadeh, E. Design, development and evaluation of microRNA-199a-5p detecting electrochemical nanobiosensor with diagnostic application in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Talanta 2018, 189, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Bian, X.; Shim, H. Downregulation of microRNA-206 promotes invasion and angiogenesis of triple negative breast cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, G.; Zhao, Y. MicroRNA-211, a direct negative regulator of CDC25B expression, inhibits triple-negative breast cancer cells’ growth and migration. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 5001–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, I.; Sareyeldin, R.M.; Al-Hashimi, I.; Al-Thawadi, H.A.; Farsi, H.A.; Vranic, S.; Moustafa, A.E. Al Triple negative breast cancer profile, from gene to microRNA, in relation to ethnicity. Cancers 2019, 11, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zuo, W.; Zheng, W. MicroRNA-223 Increases the Sensitivity of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Stem Cells to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis by Targeting HAX-1. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayraktar, R.; Pichler, M.; Kanlikilicer, P.; Ivan, C.; Bayraktar, E.; Kahraman, N.; Aslan, B.; Oguztuzun, S.; Ulasli, M.; Arslan, A.; et al. MicroRNA 603 acts as a tumor suppressor and inhibits triple-negative breast cancer tumorigenesis by targeting elongation factor 2 kinase. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 11641–11658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Browne, G.; Dragon, J.A.; Hong, D.; Messier, T.L.; Gordon, J.A.R.; Farina, N.H.; Boyd, J.R.; VanOudenhove, J.J.; Perez, A.W.; Zaidi, S.K.; et al. MicroRNA-378-mediated suppression of Runx1 alleviates the aggressive phenotype of triple-negative MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 8825–8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.K.; Gromisch, C.; Ozturk, S.; Papageorgis, P.; Abdolmaleky, H.M.; Reinhard, B.M.; Thiagalingam, A.; Thiagalingam, S. MicroRNA-4417 is a tumor suppressor and prognostic biomarker for triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago-Ferrante, R.; Pentimalli, F.; Carlisi, D.; De Blasio, A.; Saliba, C.; Baldacchino, S.; Degaetano, J.; Debono, J.; Caruana-Dingli, G.; Grech, G.; et al. Suppressive role exerted by microRNA-29b-1-5p in triple negative breast cancer through SPIN1 regulation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28939–28958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.-L.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Yi, Z.-B.; Li, J.-J. MicroRNA-211-5p suppresses tumour cell proliferation, invasion, migration and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer by directly targeting SETBP1. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Xu, P.; Wang, H.; Niu, Z.; Zhu, D.; Lin, Q.; Tang, L.; Ren, L. MicroRNA-150 suppresses triple-negative breast cancer metastasis through targeting HMGA2. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 2319–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, D.; Lei, M.; Han, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, R. MicroRNA-645 targets urokinase plasminogen activator and decreases the invasive growth of MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 7733–7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Chen, W.; Zheng, L.; Xi, T.; Wang, A.; Lu, Y. MicroRNA-9 and breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 122, 109687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piperigkou, Z.; Franchi, M.; Götte, M.; Karamanos, N.K. Estrogen receptor beta as epigenetic mediator of miR-10b and miR-145 in mammary cancer. Matrix Biol. 2017, 64, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Ouyang, H.; He, D.; Yu, C.; Tang, G. MicroRNA-based potential diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic applications in triple-negative breast cancer. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2800–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collina, F.; Aquino, G.; Brogna, M.; Cipolletta, S.; Buonfanti, G.; De Laurentiis, M.; Di Bonito, M.; Cantile, M.; Botti, G. LncRNA HOTAIR up-regulation is strongly related with lymph nodes metastasis and LAR subtype of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2018–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Li, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Burow, M.E.; Collins-, B.; Xue, M.; Song, C.; Shan, B. Induction of HOXA9 expression in three-dimensional organotypic culture of the Claudin-low breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 51503–51514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, A.; Li, C.; Xing, Z.; Hu, Q.; Liang, K.; Han, L.; Wang, C.; Hawke, D.H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The LINK-A lncRNA activates normoxic HIF1α signalling in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, O.; Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Lv, L.; Ma, R.; Chen, C.; Wang, J.; Tan, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Xia, E.; et al. C-MYC-induced upregulation of lncRNA SNHG12 regulates cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration in triple-negative breast cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 533–545. [Google Scholar]
- Aram, R.; Dotan, I.; Hotz-Wagenblatt, A.; Canaani, D. Identification of a novel metastasis inducing lncRNA which suppresses the KAI1/CD82 metastasis suppressor gene and is upregulated in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Sang, Y.; Yu, B.; Lv, D.; Zhang, W.; Feng, H. LncRNA PVT1 regulates triple-negative breast cancer through KLF5/beta-catenin signaling. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4723–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yu, D.; Shi, H.; Li, J.; Meng, L. Reduced lncRNA Aim enhances the malignant invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells mainly by activating Wnt/β-catenin/mTOR/PI3K signaling. Pharmazie 2017, 72, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Tang, H.; Ling, L.; Li, N.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Shi, L.; Yin, J.; Qiu, N.; et al. LINC01638 lncRNA activates MTDH-Twist1 signaling by preventing SPOP-mediated c-Myc degradation in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 6166–6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ke, H.; Zhang, H.; Ma, Y.; Ao, L.; Zou, L.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Nie, J.; Wu, C.; et al. LncRNA MIR100HG promotes cell proliferation in triple-negative breast cancer through triplex formation with p27 loci. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, X.; Song, C.; Li, M. LncRNA AWPPH promotes the growth of triple-negative breast cancer by up-regulating frizzled homolog 7 (FZD7). Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20181223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, A.; Qu, H.; Gong, W.; Xiang, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, W. LncRNA AWPPH and miRNA-21 regulates cancer cell proliferation and chemosensitivity in triple-negative breast cancer by interacting with each other. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 14860–14866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Meng, X.; Yu, Y.; Pan, L.; Zheng, Q.; Lin, W. LncRNA POU3F3 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis of cancer cells in triple-negative breast cancer by inactivating caspase 9. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Luan, T.; Zhou, S.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W.; Tong, X.; Jiang, W. LncRNA HCP5 promotes triple negative breast cancer progression as a ceRNA to regulate BIRC3 by sponging miR-219a-5p. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 4389–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Geng, C.; Dong, Q. LncRNA PAPAS may promote triple-negative breast cancer by downregulating miR-34a. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 300060519850724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, E.; Wang, H. LncRNA LUCAT1 facilitates tumorigenesis and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer through modulating miR-5702. Biosci. Rep. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.-Z.; Liu, Y.-R.; Xu, X.-E.; Jin, X.; Hu, X.; Yu, K.-D.; Shao, Z.-M. Transcriptome Analysis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Reveals an Integrated mRNA-lncRNA Signature with Predictive and Prognostic Value. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2105–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, G.; Li, H.; Sun, R.; Li, P.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yin, C. Long non-coding RNA ZEB2-AS1 promotes the proliferation, metastasis and epithelial mesenchymal transition in triple-negative breast cancer by epigenetically activating ZEB2. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3271–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. LncRNA DLX6-AS1 Contributes to Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Cisplatin Resistance in Triple-negative Breast Cancer via Modulating Mir-199b-5p/Paxillin Axis. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 096368972092998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, D.; Wu, X.; Zeng, Y.; Li, L.; Hou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, Z. Long non-coding RNA (LncRNA) RMST in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC): Expression analysis and biological roles research. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6603–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z. LncRNA NEF is downregulated in triple negative breast cancer and correlated with poor prognosis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Hou, M.; Zhan, Y.; Sheng, X. LncRNA PTCSC3 inhibits triple-negative breast cancer cell proliferation by downregulating lncRNA H19. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 15083–15088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Dong, G.; Shi, H.; Zhang, J.; Ning, Z.; Bao, X.; Liu, C.; Hu, J.; Liu, M.; Xiong, B. LncRNA MIR503HG inhibits cell migration and invasion via miR-103/OLFM4 axis in triple negative breast cancer. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4738–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, J.; Wang, R.; Wu, Z. LncRNA TCONS_l2_00002973 correlates with less advanced tumor stage and favorable survival, and also inhibits cancer cells proliferation while enhancing apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer. J. BUON 2019, 24, 535–542. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hou, L.; Yin, L.; Zhao, S. LncRNA XIST interacts with miR-454 to inhibit cells proliferation, epithelial mesenchymal transition and induces apoptosis in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Biosci. 2020, 45, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Non-Coding RNAs | Major Affected ECM/EMT Mediators |
|---|---|
| miRNAs | |
| miR-7 | Fibronectin; interleukin-1β |
| miR-9 | CDH1; β-catenin; VEGF; MYC |
| miR-10b | HOXD10; uPA/uPAR; syndecan-1; Twist; CDH1; vimentin; fibronectin; Snail2/Slug; IGF-IR; HER2; VEGF; MMP-2,-7,-9,-14 |
| miR-21 | PTEN; TIMP1; TIMP3; PDCD4; PI3K/AKT |
| miR-145 | CDH1; vimentin; fibronectin; Snail2; HER2; MMP-2,-9,-11; Rab GTPase family 27a |
| miR-152 | CDH1; DNMT1/DNMT3A |
| miR-199a-5p | CDH1; ZEB1; Twist |
| miR-200b | CDH1; vimentin; Snail2/Slug; fibronectin; ZEB1/2; BMI1; MMP-2,-7,-9,-14; Erk1/2; ERα/β |
| miR-203 | Snail2/Slug |
| miR-205 | Laminin gamma 1; CDH1 |
| miR-206 | VEGF; MAPK3; SOX9 |
| miR-211 | CDC25B; MMP-9 |
| miR-214 | PTEN-PI3K/AKT; collagen type IV alpha 1 |
| miR-221/222 | CDH1; Snail1; Snail2/Slug |
| miR-223 | CD44; TRAIL |
| miR-378 | Runx1 |
| miR-603 | eEF2K; IGF-IR |
| miR-4417 | EGFR; IGF-IR; cyclin D1; CDH1; vimentin; p38 MAPK |
| Long non-coding RNAs | |
| HAS2-AS1 | HAS2 |
| HOTAIR | HOXA9; PTEN; AR |
| LINK-A | HIF1α; EGFR |
| SNHG12 | MMP-13 |
| SKAI1BC | KAI1 |
| Aim, PVT1 | KLF5; β-catenin |
| LINC01638 | Twist; metadherin |
| MIR100HG | CDK18; WEE1; CCNF; CDKN1B; CDC25A |
| AWPPH | FZD7 |
| POU3F3 | Caspase 9 |
| ZEB2-AS1 | ZEB2 |
| LINC01638 | c-Myc; Twist1 |
| MIR503HG | Olfactomedin 4; MMP-9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zolota, V.; Tzelepi, V.; Piperigkou, Z.; Kourea, H.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Argentou, M.-I.; Karamanos, N.K. Epigenetic Alterations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—The Critical Role of Extracellular Matrix. Cancers 2021, 13, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040713
Zolota V, Tzelepi V, Piperigkou Z, Kourea H, Papakonstantinou E, Argentou M-I, Karamanos NK. Epigenetic Alterations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—The Critical Role of Extracellular Matrix. Cancers. 2021; 13(4):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040713
Chicago/Turabian StyleZolota, Vasiliki, Vasiliki Tzelepi, Zoi Piperigkou, Helen Kourea, Efthymia Papakonstantinou, Maria-Ioanna Argentou, and Nikos K. Karamanos. 2021. "Epigenetic Alterations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—The Critical Role of Extracellular Matrix" Cancers 13, no. 4: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040713
APA StyleZolota, V., Tzelepi, V., Piperigkou, Z., Kourea, H., Papakonstantinou, E., Argentou, M.-I., & Karamanos, N. K. (2021). Epigenetic Alterations in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer—The Critical Role of Extracellular Matrix. Cancers, 13(4), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040713









