Effects of Pollutants on Fish
A topical collection in Animals (ISSN 2076-2615). This collection belongs to the section "Aquatic Animals".
Submission Status: Closed | Viewed by 101872Editors
Interests: aquatic physiology; transport stress livestock; biomarkers stress
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: animal welfare; homeostasis; livestock; oxidative stress; redox balance
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
2. Institute for Marine Biological Resources and Biotechnology (IRBIM), National Research Council (CNR), Section of Messina, 98100 Messina, Italy
Interests: otolith; fisheries; teleost; elasmobranchs; biodiversity; microplastics; environmental conservation; aquaculture; fish respiration; fish immunology; marine zoology; zoomorphology; taxonomy
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: seafood analysis; shelf life; parasitology
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
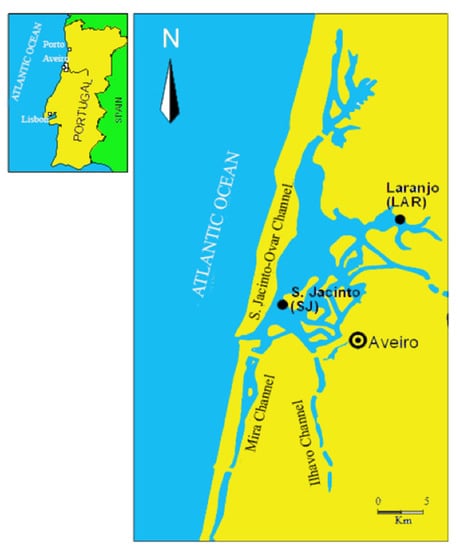
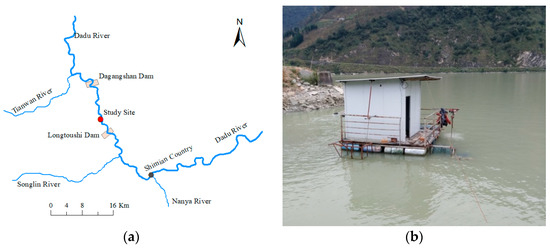
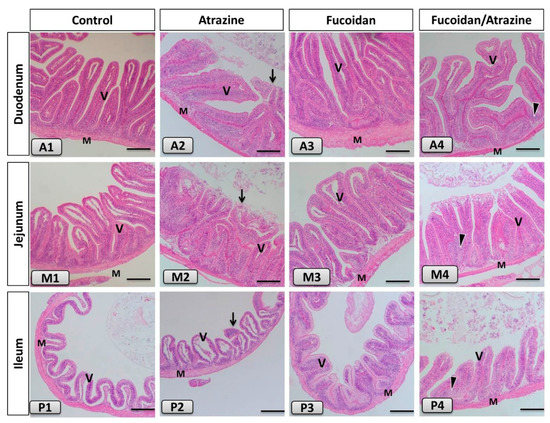
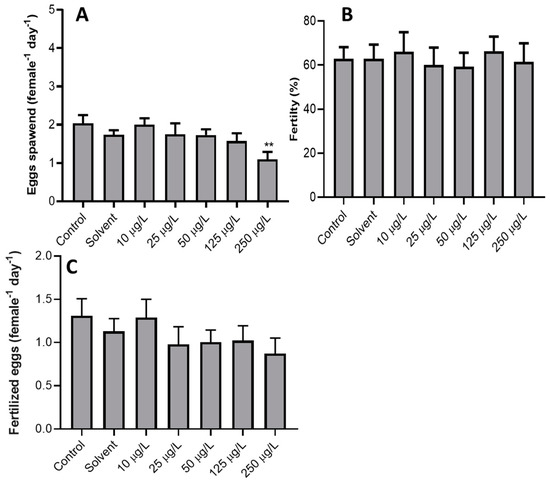
Today, environmental pollution is one of the most serious problems of our planet and it causes serious harm to many aquatic organisms. A great part of pollutants exhibit biomagnification and bioaccumulation capabilities with a broad spectrum of impacts and can stress aquatic organisms. Fish have been widely documented as useful indicators of environmental water quality. The analyses of bioaccumulation of contaminants in the biotic components of ecosystems and of modifications of blood parameters represent an important and useful tool for understanding persistence, movement, and allocation of pollutants. This Topical Collection also welcomes epidemiological studies on the presence and accumulation of pollutants in wild and farmed fish in order to give a comprehensible comparison on the presence of toxicants, such as heavy metals, POPs, veterinary drugs, etc., in fish reared in different conditions. Epidemiological studies focused on the analysis of the accumulation levels of pollutants in the tissues of benthonic, demersal, and pelagic fish are also welcome.
Potential topics include:
- Hematological response to environmental pollution in fish
- Chemical pollution in aquatic environment and oxidative stress in teleost
- Pollution and immune response in fish
- Aquatic animal (fish) models for bioaccumulation
- The toxicological effects of pollutants on physiological functions in fish
- Effects of chemical stressors at the biochemical and cellular levels
- Epidemiological studies on the presence of pollutants in fish
- Morpho-physiological adaptations of fish to water pollutants
Prof. Dr. Francesco Fazio
Dr. Stefano Cecchini Gualandi
Dr. Gioele Capillo
Dr. Gaetano Cammilleri
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Animals is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Aquatic environment
- fish
- hematological and hemato-chemical parameters
- immunity
- oxidative stress
- pollutions
- xenobiotics.