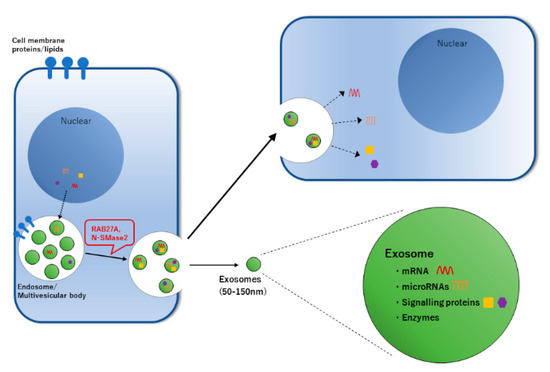
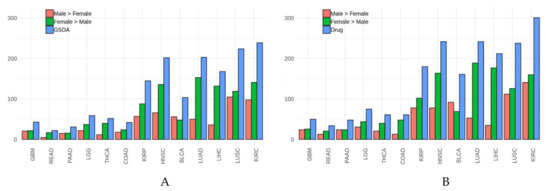
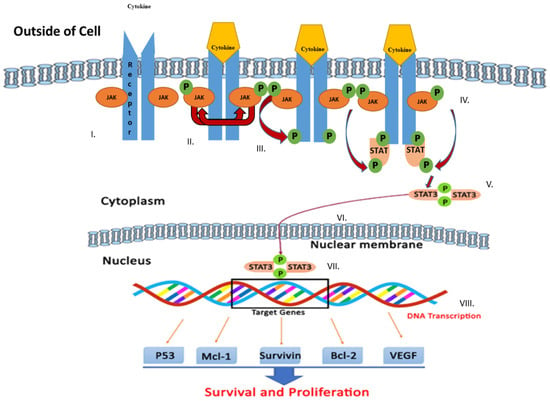
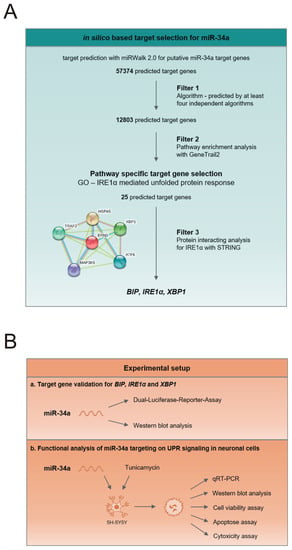
Targeting Signal Transduction Pathways and Non-coding RNAs as Potential Therapy in Cancer and Aging
A topical collection in Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This collection belongs to the section "Cell Signaling".
Viewed by 77485Editors
Interests: cancer; hepatocellular carcinoma; targeted therapy; cell signaling; apoptosis; ER stress; nutraceutics
Interests: signaling pathways; chemotherapeutic drugs and ionizing radiation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: cancer
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
World Health Organization estimates indicate that death from cancer will be the leading cause of death in the world in the next decade, with approximately 22 million new cases per year. It is known that the risk of cancer increases with an individual’s age. If we consider that in the coming decades, the number of people over 65 will double, it is clear that the prevalence of oncological disease will increase in parallel with the aging of the global population.
Cancer is a complex disease in which mutations in the DNA cause the activation of aberrant cellular signals that ultimately affect numerous cellular functions, such as those impacting cell survival, proliferation, and metabolism, as well as communication between different cell types in the cancer microenvironment. Together, these distinctive traits allow tumors to develop, grow, metastasize, and resist therapies.
Aging is also a complex process in which DNA damage and alterations of numerous cellular signals lead to the development of aging-related diseases.
For this Topical Collection, we would like to invite original research articles as well as review articles that address the application of cellular and molecular biology to cancer research and aging, from the identification and validation of biomarkers to new therapies and targeted mechanistic studies.
Potential topics include but are not limited to the following:
- Changes in signaling pathways in cancer and aging;
- Factors that influence signal transduction in cancer and aging;
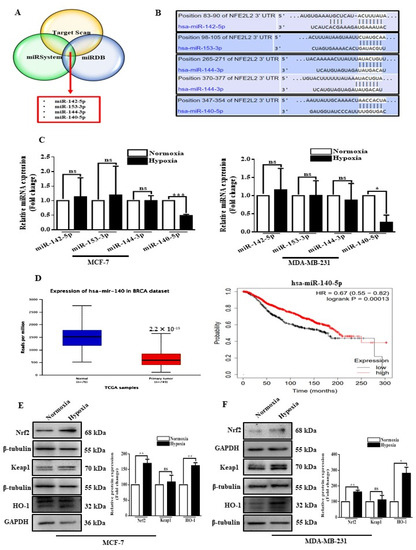
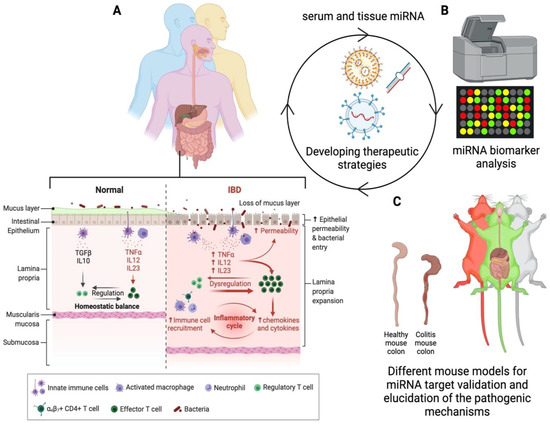
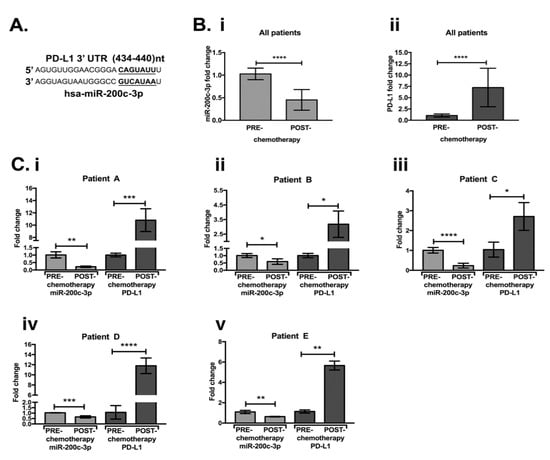
- Roles of microRNAs (miRs) and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in cancer and aging;
- New possibilities for targeted therapies in cancer and aging;
- Optimization of cancer combination therapies.
Dr. Melchiorre Cervello
Prof. Dr. James Albert McCubrey
Dr. Giuseppa Augello
Dr. Antonella Cusimano
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- cancer
- aging
- signaling pathways
- targted therapy
- oncogenes
- noncoding RNA
- miR
- lncRNA
- tumor suppressor genes