Microseismic Monitoring of Geothermal Systems
A special issue of Energies (ISSN 1996-1073). This special issue belongs to the section "H: Geo-Energy".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (30 June 2021) | Viewed by 2430
Special Issue Editor
Interests: Microseismic monitoring; enhanced geothermal systems; induced seismicity; signal processing
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
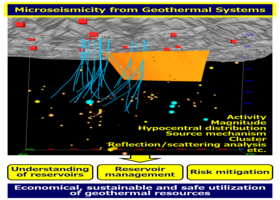
Microseismic monitoring is one of the most practical and effective means to collect both wide and 3D information of dynamic behaviour of geothermal reservoirs associated with various kinds of operation, including production, injection, and build-up. Microseismic monitoring of geothermal reservoirs has a long history, and activities, spatio-temporal distribution of hypocenters, and magnitude have been mainly used for estimation of location and motion of fracture system, in which geothermal energy is stored. Recent progress in hardware and processing techniques in seismology enables us to acquire more reliable and detailed information of the reservoirs. Furthermore, induced seismicity with large magnitude in creation and production of/from enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) is considered one of the largest environmental burden in utilization of geothermal energy. Scientific understanding of physics behind the large induced earthquake has been deepened after some unexpected and unfortunate experiences in EGS development worldwide.
The Special Issue of Energies on microseismic monitoring covers a wide area of science and technologies related to microseismicity in the geothermal field. I believe that sharing experiences and knowledge through this SI will greatly contribute to better microseismic monitoring for stable and sustainable green geothermal energies and reduction of the risks of damaging earthquakes in the future.
Dr. Hiroshi Asanuma
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Characteristics of microseismicity from geothermal systems
- Estimation of distribution of flow and pressure
- Induced seismicity
- Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS)
- Downhole seismic monitoring system





