Innovation in Energy Security and Long-Term Energy Efficiency Ⅲ
A project collection of Energies (ISSN 1996-1073). This project collection belongs to the section "B: Energy and Environment".
Papers displayed on this page all arise from the same project. Editorial decisions were made independently of project staff and handled by the Editor-in-Chief or qualified Editorial Board members.
Viewed by 36098
Share This Project Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Manuela Tvaronavičienė
Prof. Dr. Manuela Tvaronavičienė
 Prof. Dr. Manuela Tvaronavičienė
Prof. Dr. Manuela Tvaronavičienė
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Department of Business Technologies and Entrepreneurship, Vilnius Gediminas Technical University, 10223 Vilnius, Lithuania
Interests: economic growth; investments; innovations; sustainable development; sector development; energy security; energy effciency
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Project Overview
Dear Colleagues,
The sustainable development of our planet depends on the use of energy. The increasing population of the world inevitably causes an increase in the demand for energy, which, on the one hand, threatens us with the potential to encounter a shortage of energy supply, and, on the other hand, causes the deterioration of the environment.
Therefore, our task is to reduce this demand through different innovative solutions (i.e., both technological and social). Social marketing and economic policies can also play their role by affecting the behavior of households and companies, by causing behavioral change oriented to energy stewardship, and an overall switch to renewable energy resources. This Special Issue provides a platform for the exchange of a wide range of ideas, which, ultimately, would facilitate in driving societies to long-term energy efficiency.
Prof. Dr. Manuela Tvaronavičienė
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Energies is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- energy security
- energy consumption
- energy demand
- renewables
- technological innovations
- social innovations
- behavioral change
- energy efficiency
Related Special Issues
Published Papers (9 papers)
Open AccessArticle
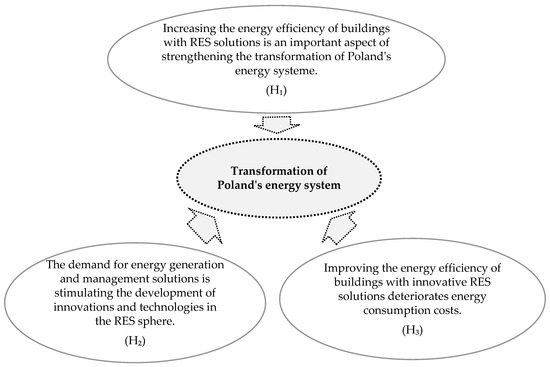
Energy Innovation for Individual Consumers in Poland—Analysis of Potential and Evaluation of Practical Applications in Selected Areas
by
Ewa Chomać-Pierzecka, Joanna Rogozińska-Mitrut, Monika Różycka, Dariusz Soboń and Jacek Stasiak
Cited by 12 | Viewed by 1327
Abstract
Green technologies are undergoing strong development. These are created by global formal and legal regulations enforcing the reduction of the share of non-renewable energy sources in the energy systems of economies and the minimisation of harmful emissions through the development of technologies based
[...] Read more.
Green technologies are undergoing strong development. These are created by global formal and legal regulations enforcing the reduction of the share of non-renewable energy sources in the energy systems of economies and the minimisation of harmful emissions through the development of technologies based on renewable energy sources. In addition, the development of green technologies is driven by the need to reduce the rising cost of electricity, particularly affecting households in countries heavily reliant on coal-fired power generation, where green technologies are only just gaining popularity (e.g., Poland). With this in mind, it was considered important to present the formal and legal background of the development of the Polish energy system towards sustainability and to discuss the green technology market in Poland, including innovative solutions in this field, which are or could be, applied to small individual consumers (households). The main objective of the study was to analyse the interest of households in innovative green technology solutions, determined by the surface area and cubic capacity of buildings, in order to strengthen the source material that can be used by decision-makers when designing a strategy for the development of the green energy market in Poland, with a special focus on individual consumers. The study was carried out based on a critical analysis of the available literature, regulations, and industry reports, as well as survey material enabling practical evaluation of solutions by users of innovative technologies. The practical research dimension was reinforced by statistical instrumentation, using the statistical instrument PQstat version 1.8.4.164. The main findings of this study show a significant level of openness of households in Poland to innovative green technologies and a clear relationship between the area and volume of a building and the range of choices made. The most popular solutions in this respect include photovoltaics, followed by heat pumps. Furthermore, it was noted that the area and cubic volume of a building determines the potential and scale of future strengthening of the RES dimension by small individual consumers.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Role of Local Governments in Green Deal Multilevel Governance: The Energy Context
by
Māris Pūķis, Jānis Bičevskis, Staņislavs Gendelis, Edvīns Karnītis, Ģirts Karnītis, Andris Eihmanis and Uģis Sarma
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 1701
Abstract
The sustainability of the climate is a global problem that requires the involvement of all levels of public governance and the private sector. Energy issues play a crucial role in the Green Deal (GD), and many of these issues are being addressed at
[...] Read more.
The sustainability of the climate is a global problem that requires the involvement of all levels of public governance and the private sector. Energy issues play a crucial role in the Green Deal (GD), and many of these issues are being addressed at the local government (LG) level. The division of competences within the framework of the GD among the European Union (EU), national governments, LGs, and the private sector has not been sufficiently discussed. Existing studies often neglect the specific role of LGs. The aim of this study was to evaluate the extent to which the role of LGs aligns with the core principles of public governance, namely sustainability, solidarity, subsidiarity, and proportionality. The novelty of this study’s methodology lies in the comprehensive and integrated application of all four principles to assess the distribution of competences necessary to achieve global goals. The conclusion of the study demonstrates that, although the functionality and competences of LGs generally comply with these principles, the role of LGs as consultants to and co-legislators with national and EU authorities should be further discussed and expanded. Overall, this study highlights the importance of strengthening the role of LGs as valuable contributors to the governance process.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
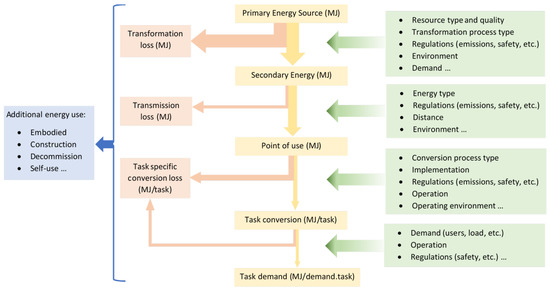
Rethinking Notions of Energy Efficiency in a Global Context
by
Patrick Moriarty and Damon Honnery
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1590
Abstract
Energy efficiency is, in principle, a simple idea: an output of human value, for example, vehicle-km traveled, divided by the needed input energy. Efficiency improvements are regarded as an important means of mitigating not only climate change, but also other environmental problems. Despite
[...] Read more.
Energy efficiency is, in principle, a simple idea: an output of human value, for example, vehicle-km traveled, divided by the needed input energy. Efficiency improvements are regarded as an important means of mitigating not only climate change, but also other environmental problems. Despite the vast number of articles published on energy efficiency, a few people question whether it is a useful or accurate measure in its present form; nearly all papers are either engineering studies, or address barriers to efficiency improvements. This review addresses this issue via a critical review of the literature, including not only papers on energy efficiency, but those on adjacent areas of research that can help broaden the scope, both geographically and conceptually. These shortcomings are illustrated in case studies of buildings/cities and road passenger transport. The main findings of this review are that (1) energy efficiency inevitably has an ethical dimension, as well as a technical one, in that feedbacks are more widespread than they have generally considered to be, and (2) that conventional efficiency measures omit important energy input items, particularly those concerned with the mining the materials needed for renewable energy plants. The key conclusions are that present efficiency measures are not adequate, and future research is needed to overcome these shortcomings.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
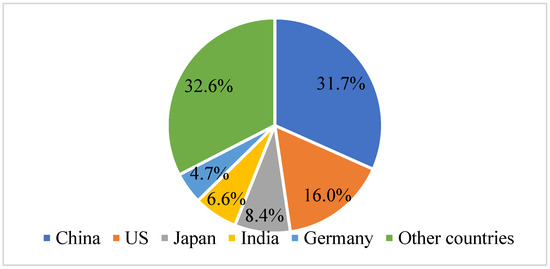
A Review on Solar Energy Policy and Current Status: Top 5 Countries and Kazakhstan
by
Saulesh Minazhova, Ruslan Akhambayev, Timur Shalabayev, Amangeldy Bekbayev, Bolat Kozhageldi and Manuela Tvaronavičienė
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 5326
Abstract
The article describes the world’s experience in developing the solar industry. It discusses the mechanisms of state support for developing renewable energy sources in the cases of five countries that are the most successful in this area—China, the United States, Japan, India, and
[...] Read more.
The article describes the world’s experience in developing the solar industry. It discusses the mechanisms of state support for developing renewable energy sources in the cases of five countries that are the most successful in this area—China, the United States, Japan, India, and Germany. Furthermore, it contains a brief review of state policy in producing electricity by renewable energy facilities in Kazakhstan. This paper uses statistical information from the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), the International Energy Agency (IEA), British Petroleum (BP), and the Renewable Energy Network (REN21), and peer-reviewed sources. The research methodology includes analytical research and evaluation methods to examine the current state of solar energy policy, its motivators and incentives, as well as the prospects for its development in Kazakhstan and in the world. Research shows that solar energy has a huge development potential worldwide and is sure to take its place in gross electricity production. This paper focuses on the selected economic policies of the top five countries and Kazakhstan, in what may be considered a specific research limitation. Future research suggestions for the expansion of Renewable Energy (RE) in Kazakhstan could include analysing the impact of introducing dedicated policies and incentives for solar systems and exploring the benefits and challenges of implementing large RE zones with government–business collaboration.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
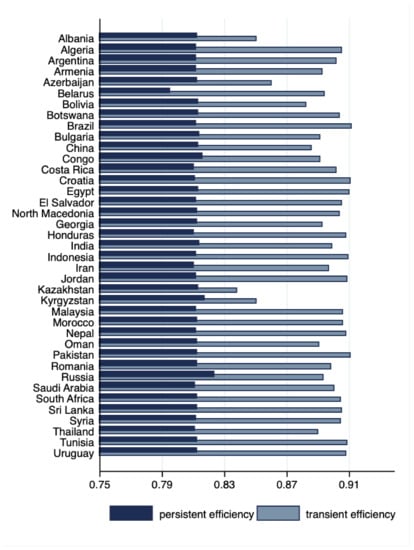
Energy Demand and Energy Efficiency in Developing Countries
by
Lester C. Hunt and Paraskevas Kipouros
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 6217
Abstract
This paper investigates relative aggregate energy efficiency for a panel of 39 developing countries by econometrically estimating an energy-demand function (EDF) using the stochastic frontier analysis (SFA) approach to provide relative energy efficiency scores over the period 1989 to 2008. Energy efficiency is
[...] Read more.
This paper investigates relative aggregate energy efficiency for a panel of 39 developing countries by econometrically estimating an energy-demand function (EDF) using the stochastic frontier analysis (SFA) approach to provide relative energy efficiency scores over the period 1989 to 2008. Energy efficiency is arguably difficult to define or even conceptualise with several interpretations in the literature but here it is based on an economists’ perspective of efficiency. Hence, the estimates of ‘true’ energy efficiency found in the paper using this approach approximate the economically efficient use of energy capturing both technical and allocative efficiency and the results confirm that energy intensity should not be considered as a de facto standard indicator of energy efficiency. While, by controlling for a range of socio-economic factors, the measurements of energy efficiency obtained by the analysis are deemed more appropriate and hence it is argued that this analysis should be undertaken to avoid potentially misleading advice to policy makers. This study contributes to the literature since it is, as far as is known, the first attempt to apply the benchmarking parametric stochastic frontier technique to econometrically estimate energy efficiency for a large panel of only developing counties around the world. Moreover, the results from such analysis are arguably particularly relevant in a world dominated by environmental concerns, especially in the aftermath of energy price increase as a result of the unrest in Ukraine.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Energy Security Assessment Based on a New Dynamic Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Framework
by
Paweł Ziemba
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 1788
Abstract
Access to energy resources and broadly understood energy security are some of the critical factors influencing the economic development of countries. This article deals with the problem of assessing the energy security of countries, considering this problem in various periods of time, examining
[...] Read more.
Access to energy resources and broadly understood energy security are some of the critical factors influencing the economic development of countries. This article deals with the problem of assessing the energy security of countries, considering this problem in various periods of time, examining the past, present and forecasted future conditions at the same time. For this purpose, the Dynamic Multi-Criteria Decision Making (DMCDM) methodology was developed and applied, based on the classic and fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) methods and the International Energy Security Risk Index (IESRI). In particular, the Simple Additive Weighting (SAW)/Fuzzy SAW and New Easy Approach to Fuzzy PROMETHEE II (NEAT F-PROMETHEE) methods were used. These methods are significantly different from each other in the calculation procedures used. The study showed that methodological differences between these methods cause large differences in the results of the assessment of energy security of countries. However, both methodological approaches indicated the high energy security of New Zealand, Norway, Denmark and the United States, and the very low security of Ukraine, Thailand and South Korea. The results of the assessment of energy security of countries over the 2015–2025 period are the main practical contribution of this article. The scientific contribution of the article consists in developing a framework for dynamic energy security assessment that allows for the aggregation of many periods of time and that defines the aggregation strategies, capturing data from the past, present and future state forecasts while taking into account changes in the weights of criteria and changes in the sets of alternatives and criteria.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Identification of the Strategy of the Energy and Utilities Sector from the G7 Group Countries, from the Perspective of a Dominant Strategy Approach
by
Jerzy Niemczyk, Kamil Borowski, Rafał Trzaska, Mateusz Trzaska, Aleksandra Sus and Maciej Matuszewski
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 1795
Abstract
The aim of the research, the effect of which is this article, is to identify the hierarchy of selected approaches to building a strategy in companies from the sector of Energy and Utilities included in seven stock market indexes of the G7 countries
[...] Read more.
The aim of the research, the effect of which is this article, is to identify the hierarchy of selected approaches to building a strategy in companies from the sector of Energy and Utilities included in seven stock market indexes of the G7 countries The obtained results are related to the isolation of cognitive knowledge about the preferred approaches to the strategy in energy companies currently undergoing intensive changes and that are listed in the stock indexes of the G7 countries. The Authors proved that the strategy implementation in companies representing Energy and Utilities sectors is mainly based on the resource approach. Moreover, such an approach is supported by the classic tools of the positional school, resulting in shaping the competitive position in the sector of differentiating the Chamberlin’s rent.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Energy Security and Energy Transition to Achieve Carbon Neutrality
by
Mohammad Fazle Rabbi, József Popp, Domicián Máté and Sándor Kovács
Cited by 131 | Viewed by 11977
Abstract
Successful energy transitions, also referred to as leapfrog development, present enormous prospects for EU nations to become carbon neutral by shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. Along with climate change, EU countries must address energy security and dependency issues, exacerbated by
[...] Read more.
Successful energy transitions, also referred to as leapfrog development, present enormous prospects for EU nations to become carbon neutral by shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources. Along with climate change, EU countries must address energy security and dependency issues, exacerbated by factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic, rising energy costs, conflicts between Russia and Ukraine, and political instability. Diversifying energy sources, generating renewable energy, increasing energy efficiency, preventing energy waste, and educating the public about environmental issues are proposed as several strategies. The study draws the conclusion that central European countries may transition to a clean energy economy and become carbon neutral on economic and strategic levels by locating alternative clean energy supply sources, reducing energy use, and producing renewable energy. According to the study, the EU energy industry can be decarbonised and attain energy security using three basic strategies, such as supply diversification, energy savings, and quicker adoption of renewable energy to replace fossil fuels. The energy transformation industry still needs to improve energy efficiency, incorporate a circular and sustainable bioeconomy, and support renewable energies, including solar, wind, hydropower, nuclear, and hydrogen.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Energy Efficiency of Small Wind Turbines in an Urbanized Area—Case Studies
by
Adam Zagubień and Katarzyna Wolniewicz
Cited by 13 | Viewed by 3109
Abstract
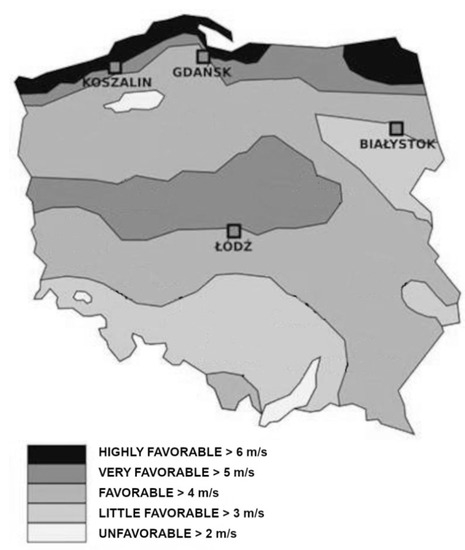
This study aimed to determine whether the wind zone that characterizes a given area of the country in open area is reflected in the built-up area lying within the zone. Analysis included four Polish cities located in different wind zones. The two-parameter Weibull
[...] Read more.
This study aimed to determine whether the wind zone that characterizes a given area of the country in open area is reflected in the built-up area lying within the zone. Analysis included four Polish cities located in different wind zones. The two-parameter Weibull density distribution function was used to present the wind conditions at each location. Two 3 kW VAWT devices were selected to evaluate the productivity of wind turbines at the locations analyzed. It was shown that the wind zones characterizing the wind potential of a region in an open area have no significant influence on the wind conditions in the built-up area located in that area. It was determined that the study location’s did not exhibit wind potential that could be economically justified by a wind turbine. WTs in the city do not reach their nominal productivity. A decisive advantage of very light winds was observed (up to 2 m/s) and a large proportion of so-called atmospheric calms. It was shown that the installation of small wind turbines in an urbanized area requires a minimum of annual wind measurements at the exact location and height of each future turbine planned.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures