- Article
A Nested U-Network with Temporal Convolution for Monaural Speech Enhancement in Laser Hearing
- Bomao Zhou,
- Jin Tang and
- Fan Guo
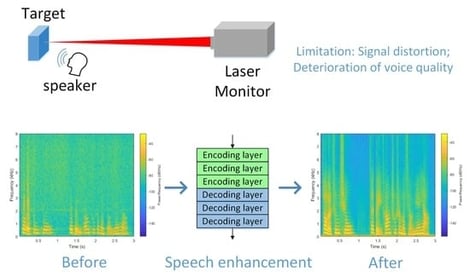
Laser Doppler vibrometer (LDV) has the characteristics of long-distance, non-contact, and high sensitivity, and plays an increasingly important role in industrial, military, and security fields. Remote speech acquisition technology based on LDV has progressed significantly in recent years. However, unlike microphone receivers, LDV-captured signals have severe signal distortion, which affects the quality of the LDV-captured speech. This paper proposes a nested U-network with gated temporal convolution (TCNUNet) to enhance monaural speech based on LDV. Specifically, the network is based on an encoder-decoder structure with skip connections and introduces nested U-Net (NUNet) in the encoder to better reconstruct speech signals. In addition, a temporal convolutional network with a gating mechanism is inserted between the encoder and decoder. The gating mechanism helps to control the information flow, while temporal convolution helps to model the long-range temporal dependencies. In a real-world environment, we designed an LDV monitoring system to collect and enhance voice signals remotely. Different datasets were collected from various target objects to fully validate the performance of the proposed network. Compared with baseline models, the proposed model achieves state-of-the-art performance. Finally, the results of the generalization experiment also indicate that the proposed model has a certain degree of generalization ability for different languages.
3 February 2026