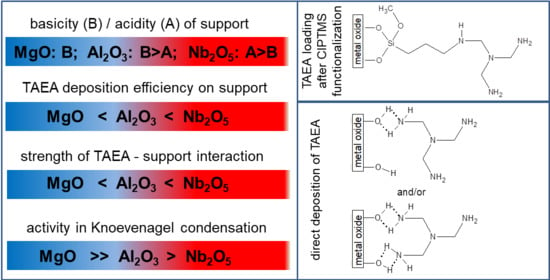
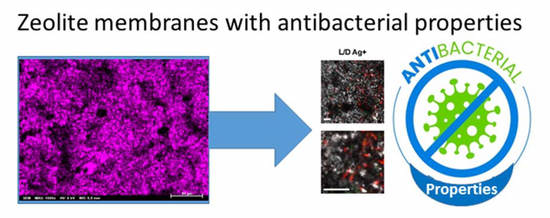
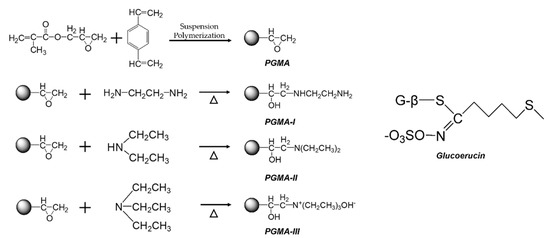
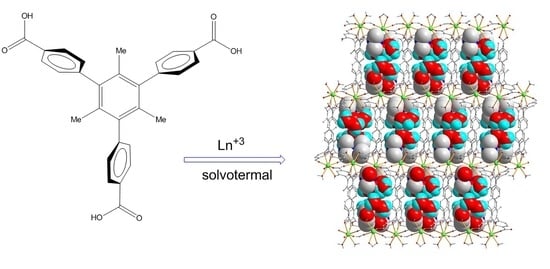
Porous Materials
A topical collection in Molecules (ISSN 1420-3049). This collection belongs to the section "Materials Chemistry".
Viewed by 77691Editors
Interests: synthesis of functional porous polymer gels; hybrid polymer-inorganic and nanocomposite materials; smart polymer systems; biomaterials; drug delivery systems; nanoparticles; characterisation of soft porous materials; novel materials for contaminated water remediation
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: zeolites; hierarchical materials; synthesis and characterization of porous materials; textural properties; structural properties; shaping of zeolites; molecular decontamination; energy storage or adsorption; catalysis
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Porous materials are vital elements for a range of industrial applications, such as catalysis, separation, ion exchange, gas storage, adsorbents, thermal insulators, acoustic absorbents, molecular decontamination, biomaterials, etc. as they possess a number of special properties (mechanical and thermal stabilities, etc.) associated with their low density and exiting textural properties, such as a large specific surface area and pore volume, etc. This Topic Collection aims to focus on all kinds of porous materials and their applications in many fields. The Topic Collection will provide an excellent opportunity for expert researchers of porous materials to publish their recent work after peer review. Topics of particular interest include but are not limited to:
Methods for textural and structural characterization of porous materials;
Molecular simulation to predict new porous structure or new properties;
Shaping of porous materials (films, pellets, beads, extrudates, membranes, etc.);
Molecular decontamination (water and air treatments):
- Gas storage;
- Ion-exchange;
- Molecular sieving (molecule separation, gas purification);
Catalytic applications;
Emerging applications:
- Energy storage;
- Sensors;
- Health (biomedical applications);
- Photovoltaic.
Dr. Irina Savina
Prof. Dr. T. Jean Daou
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Molecules is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- porous materials;
- microporous and mesoporous materials;
- zeolite; metal organic framework (MOF);
- covalent organic framework (COF);
- porous organic polymer (POP);
- membranes;
- adsorption;
- molecular structural characterization;
- gas adsorption;
- molecular simulation