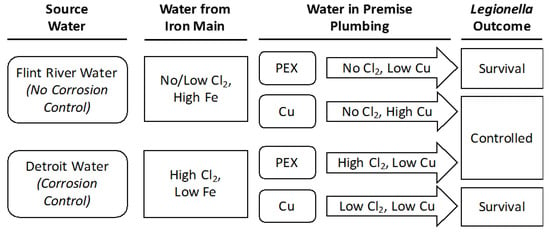
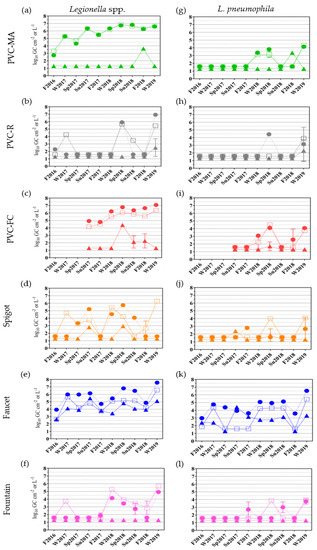
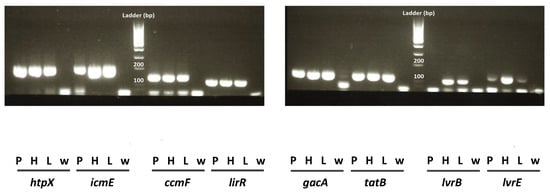
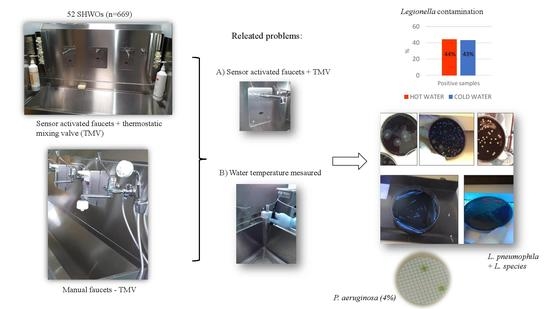
Waterborne Pathogens: Epidemiology, Surveillance, Control and Risk (Closed)
A topical collection in Pathogens (ISSN 2076-0817). This collection belongs to the section "Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases".
Viewed by 17392Editors
Interests: emerging pathogens; environment; antibiotic resistance; molecular methods; water; food
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Interests: methods for the detection of Legionella in water; study of disinfection method against waterborne pathogens; evaluation of microbiological air quality
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
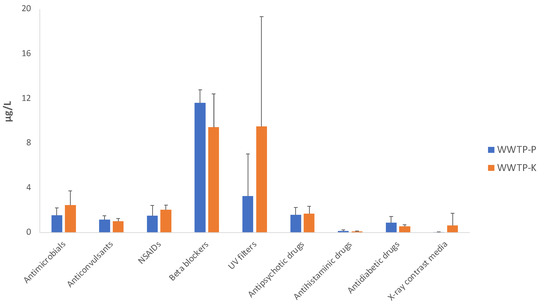
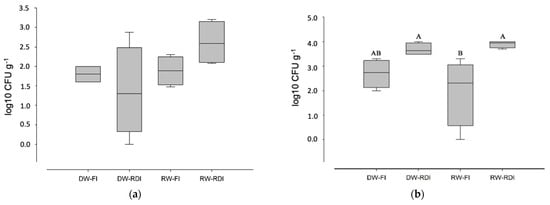
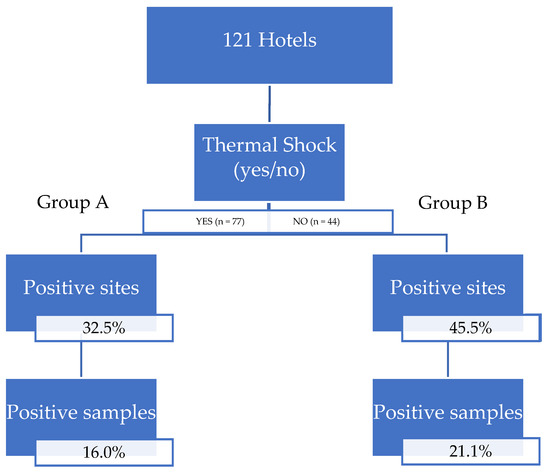
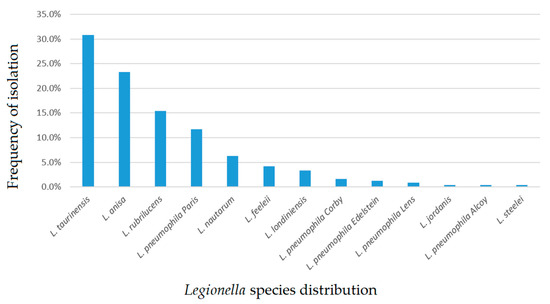
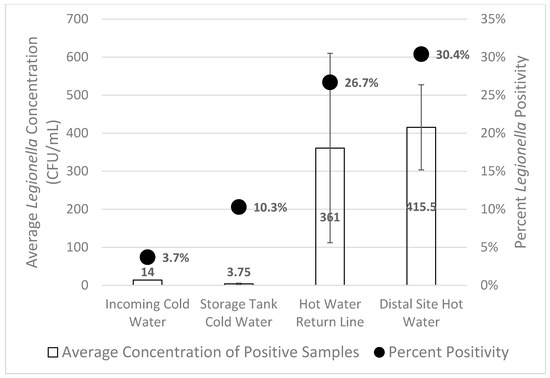
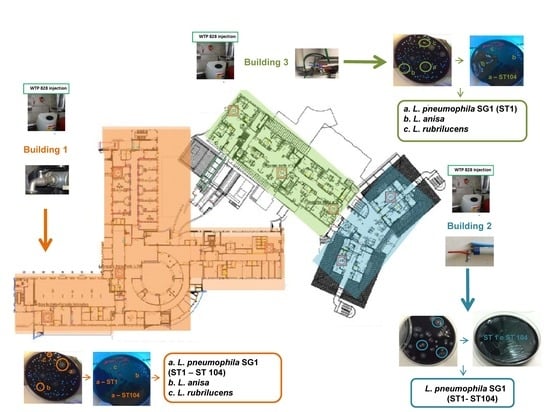
Waterborne diseases are a major global problem, associated with high morbidity and mortality, and massive economic costs; they are responsible for between 1.6 and 12 million deaths annually. Although the burden is the highest in developing countries, outbreaks of the disease still occur in developed countries. In the USA, in 2013–2014, 42 drinking water-associated outbreaks were reported, accounting for at least 1006 cases of illness, 124 hospitalizations, and 13 deaths. In developed countries, waterborne pathogens include classic and emerging bacteria (e.g. pathogenic Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., Campylobacter spp., Legionella), viruses (e.g. norovirus, adenovirus) and protozoa (Cryptosporidium spp. and Giardia spp.). Emerging pathogens have lately had an increased interest from the scientific community, and they are now considered to be a major microbiologic public health threat, including antibiotic resistant bacteria. The main causes for drinking water contamination can be the intrusion of animal feces or wastewater due to heavy rain; discharge of wastewater into the water source; malfunctioning of the disinfection equipment in the treatment plants and cross-connections; pipe breaks and wastewater intrusion into the network. The environmental monitoring of pathogens in water and wastewater is an essential tool for detecting and preventing or minimizing the further spread of this microorganisms. Currently, conventional methods based on a culture approach are used to detect pathogens, however, they have several limits, including lengthy experimental turnaround times for results. For this reason, in recent decades, alternative tools for the rapid, sensitive, and specific detection of pathogens in water and wastewater samples have been proposed (e.g., real-time PCR, biosensors). Moreover, studies leveraging next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies are providing new insights into the ecology of microbially mediated processes that influence pathogen dissemination.
We invite you to submit a review article or original research article related to these issues.
Potential topics include, but are not limited to:
- Waterborne pathogens occurrence in environment (e.g. wastewater, water distribution system, surface water);
- Risk assessment of waterborne pathogens;
- Effectiveness of control procedures in reducing waterborne pathogens contamination;
- New methods for the detection of waterborne pathogen;
- Role of climate changes in waterborne pathogen spreading.
Dr. Silvia Bonetta
Dr. Sara Bonetta
Collection Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Pathogens is an international peer-reviewed open access monthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2200 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- Water environment
- Environmental monitoring
- Detection methods
- Control procedures
- Climate changes
- Risk assessment
Related Special Issue
- Legionella Contamination in Water Environment in Pathogens (17 articles - displayed below)