Hydrogels
A topical collection in Polymers (ISSN 2073-4360). This collection belongs to the section "Polymer Chemistry".
Viewed by 65679
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
Topical Collection Information
Polymeric hydrogels are finding a plethora of interesting applications, for the environment, removing pollutants from water as well as from the air; in biomedical applications, where they can be used as scaffolds for cell proliferation; and in other specific applications such as drug delivery. The aim of this Special Issue is to collect the most recent advances in the field of hydrogels and their synthesis, characterization and applications.
Prof. Dr. Marco Sangermano
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Polymers is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Published Papers (9 papers)
Open AccessArticle
Tailoring Hydrogel Sheet Properties through Co-Monomer Selection in AMPS Copolymer Macromers
by
Jinjutha Daengmankhong, Thanyaporn Pinthong, Sudarat Promkrainit, Maytinee Yooyod, Sararat Mahasaranon, Winita Punyodom, Sukunya Ross, Jirapas Jongjitwimol, Brian J. Tighe, Matthew J. Derry, Paul D. Topham and Gareth M. Ross
Viewed by 1470
Abstract
This study investigates hydrogels based on 2-Acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid sodium salt (AMPS) copolymers, incorporating N-hydroxyethyl acrylamide (HEA) and 3-sulfopropyl acrylate potassium salt (SPA). The addition of HEA and SPA is designed to fine-tune the hydrogels’ water absorption and mechanical properties, ultimately enhancing their characteristics
[...] Read more.
This study investigates hydrogels based on 2-Acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid sodium salt (AMPS) copolymers, incorporating N-hydroxyethyl acrylamide (HEA) and 3-sulfopropyl acrylate potassium salt (SPA). The addition of HEA and SPA is designed to fine-tune the hydrogels’ water absorption and mechanical properties, ultimately enhancing their characteristics and expanding their potential for biomedical applications. A copolymer of AMPS, 2-carboxyethyl acrylate (CEA) combined with methacrylic acid (MAA) as poly(AMPS-stat-CEA-stat-MAA, PACM), was preliminarily synthesized. CEA and MAA were modified with allyl glycidyl ether (AGE) through ring-opening, yielding macromers with pendant allyl groups (PACM-AGE). Copolymers poly(AMPS-stat-HEA-stat-CEA-stat-MAA) (PAHCM) and poly(AMPS-stat-SPA-stat-CEA-stat-MAA) (PASCM) were also synthesized and modified with AGE to produce PAHCM-AGE and PASCM-AGE macromers. These copolymers and macromers were characterized by
1H NMR, FT-IR, and GPC, confirming successful synthesis and functionalization. The macromers were then photocrosslinked into hydrogels and evaluated for swelling, water content, and mechanical properties. The results revealed that the PASCM-AGE hydrogels exhibited superior swelling ratios and water retention, achieving equilibrium water content (~92%) within 30 min. While the mechanical properties of HEA and SPA containing hydrogels show significant differences compared to PACM-AGE hydrogel (tensile strength 2.5 MPa, elongation 47%), HEA containing PAHCM-AGE has a higher tensile strength (5.8 MPa) but lower elongation (19%). In contrast, SPA in the PASCM-AGE hydrogels led to both higher tensile strength (3.7 MPa) and greater elongation (92%), allowing for a broader range of hydrogel properties. An initial study on drug delivery behavior was conducted using PACM-AGE hydrogels loaded with photosensitizers, showing effective absorption, release, and antibacterial activity under light exposure. These AMPS-based macromers with HEA and SPA modifications demonstrate enhanced properties, making them promising for wound management and drug delivery applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Preparation and Characterization of Alginate Hydrogels with High Water-Retaining Capacity
by
Ivana M. Savić Gajić, Ivan M. Savić and Zorica Svirčev
Cited by 46 | Viewed by 20567
Abstract
Hydrogels are very attractive materials due to their multifunctional properties. Many natural polymers, such as polysaccharides, are used for the preparation of hydrogels. The most important and commonly used polysaccharide is alginate because of its biodegradability, biocompatibility, and non-toxicity. Since the properties of
[...] Read more.
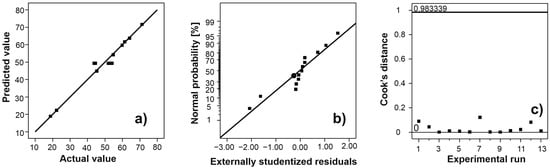
Hydrogels are very attractive materials due to their multifunctional properties. Many natural polymers, such as polysaccharides, are used for the preparation of hydrogels. The most important and commonly used polysaccharide is alginate because of its biodegradability, biocompatibility, and non-toxicity. Since the properties of alginate hydrogel and its application depend on numerous factors, this study aimed to optimize the gel composition to enable the growth of inoculated cyanobacterial crusts for suppressing the desertification process. The influence of alginate concentration (0.1–2.9%, m/v) and CaCl
2 concentration (0.4–4.6%, m/v) on the water-retaining capacity was analyzed using the response surface methodology. According to the design matrix, 13 formulations of different compositions were prepared. The water-retaining capacity was defined as the system response maximized in optimization studies. The optimal composition of hydrogel with a water-retaining capacity of about 76% was obtained using 2.7% (m/v) alginate solution and 0.9% (m/v) CaCl
2 solution. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was used for the structural characterization of the prepared hydrogels, while the water content and swelling ratio of hydrogels were determined using gravimetric methods. It was concluded that alginate and CaCl
2 concentrations play the most important role regarding the gelation time, homogeneity, water content, and swelling ratio of the hydrogel.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Granular Disulfide-Crosslinked Hyaluronic Hydrogels: A Systematic Study of Reaction Conditions on Thiol Substitution and Injectability Parameters
by
Luis Andrés Pérez, Rebeca Hernández, José María Alonso, Raúl Pérez-González and Virginia Sáez-Martínez
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3804
Abstract
Granular polymer hydrogels based on dynamic covalent bonds are attracting a great deal of interest for the design of injectable biomaterials. Such materials generally exhibit shear-thinning behavior and properties of self-healing/recovery after the extrusion that can be modulated through the interactions between gel
[...] Read more.
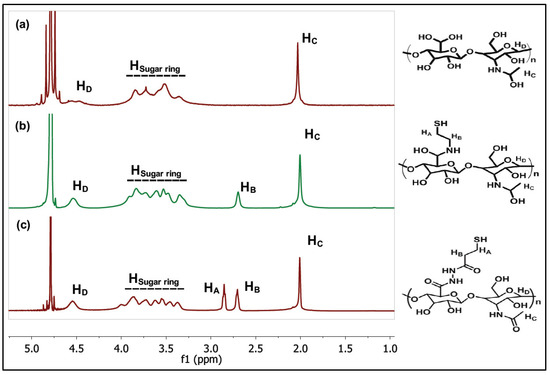
Granular polymer hydrogels based on dynamic covalent bonds are attracting a great deal of interest for the design of injectable biomaterials. Such materials generally exhibit shear-thinning behavior and properties of self-healing/recovery after the extrusion that can be modulated through the interactions between gel microparticles. Herein, bulk macro-hydrogels based on thiolated-hyaluronic acid were produced by disulphide bond formation using oxygen as oxidant at physiological conditions and gelation kinetics were monitored. Three different thiol substitution degrees (SD%: 65%, 30% and 10%) were selected for hydrogel formation and fully characterized as to their stability in physiological medium and morphology. Then, extrusion fragmentation technique was applied to obtain hyaluronic acid microgels with dynamic disulphide bonds that were subsequently sterilized by autoclaving. The resulting granular hyaluronic hydrogels were able to form stable filaments when extruded through a syringe. Rheological characterization and cytotoxicity tests allowed to assess the potential of these materials as injectable biomaterials. The application of extrusion fragmentation for the formation of granular hyaluronic hydrogels and the understanding of the relation between the autoclaving processes and the resulting particle size and rheological properties should expand the development of injectable materials for biomedical applications.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
UV-Cured Chitosan-Based Hydrogels Strengthened by Tannic Acid for the Removal of Copper Ions from Water
by
Rossella Sesia, Sara Ferraris, Marco Sangermano and Silvia Spriano
Cited by 22 | Viewed by 3345
Abstract
In this work, a new environmentally friendly material for the removal of heavy metal ions was developed to enhance the adsorption efficiency of photocurable chitosan-based hydrogels (CHg). The acknowledged affinity of tannic acid (TA) to metal ions was investigated to improve the properties
[...] Read more.
In this work, a new environmentally friendly material for the removal of heavy metal ions was developed to enhance the adsorption efficiency of photocurable chitosan-based hydrogels (CHg). The acknowledged affinity of tannic acid (TA) to metal ions was investigated to improve the properties of hydrogels obtained from natural and renewable sources (CHg-TA). The hydrogel preparation was performed via a simple two-step method consisting of the photocrosslinking of methacrylated chitosan and its subsequent swelling in the TA solution. The samples were characterized using ATR-FTIR, SEM, and Folin–Ciocalteu (F&C) assay. Moreover, the mechanical properties and the ζ potential of CHg and CHg-TA were tested. The copper ion was selected as a pollutant model. The adsorption capacity (Q
e) of CHg and CHg-TA was assessed as a function of pH. Under acidic conditions, CHg-TA shows a higher Q
e than CHg through the coordination of copper ions by TA. At an alkaline pH, the phenols convert into a quinone form, decreasing the Q
e of CHg-TA, and the performance of CHg was found to be improved. A partial TA release can occur in the copper solution due to its high hydrophilicity and strong acidic pH conditions. Additionally, the reusability of hydrogels was assessed, and the high number of recycling cycles of CHg-TA was related to its high mechanical performance (compression tests). These findings suggest CHg-TA as a promising green candidate for heavy metal ion removal from acidic wastewater.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessEditor’s ChoiceReview
Novel Trends in Hydrogel Development for Biomedical Applications: A Review
by
Pablo Sánchez-Cid, Mercedes Jiménez-Rosado, Alberto Romero and Víctor Pérez-Puyana
Cited by 191 | Viewed by 15579
Abstract
Nowadays, there are still numerous challenges for well-known biomedical applications, such as tissue engineering (TE), wound healing and controlled drug delivery, which must be faced and solved. Hydrogels have been proposed as excellent candidates for these applications, as they have promising properties for
[...] Read more.
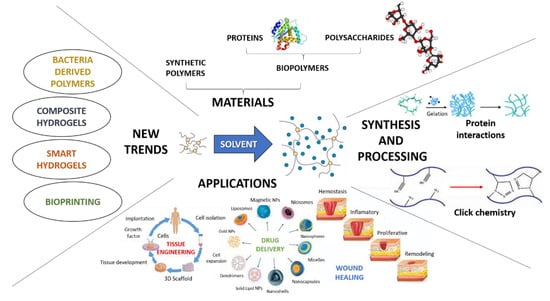
Nowadays, there are still numerous challenges for well-known biomedical applications, such as tissue engineering (TE), wound healing and controlled drug delivery, which must be faced and solved. Hydrogels have been proposed as excellent candidates for these applications, as they have promising properties for the mentioned applications, including biocompatibility, biodegradability, great absorption capacity and tunable mechanical properties. However, depending on the material or the manufacturing method, the resulting hydrogel may not be up to the specific task for which it is designed, thus there are different approaches proposed to enhance hydrogel performance for the requirements of the application in question. The main purpose of this review article was to summarize the most recent trends of hydrogel technology, going through the most used polymeric materials and the most popular hydrogel synthesis methods in recent years, including different strategies of enhancing hydrogels’ properties, such as cross-linking and the manufacture of composite hydrogels. In addition, the secondary objective of this review was to briefly discuss other novel applications of hydrogels that have been proposed in the past few years which have drawn a lot of attention.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
UV-Cured Chitosan and Gelatin Hydrogels for the Removal of As(V) and Pb(II) from Water
by
Camilla Noè, Michael Zanon, Amaya Arencibia, María-José López-Muñoz, Nieves Fernández de Paz, Paola Calza and Marco Sangermano
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 5234
Abstract
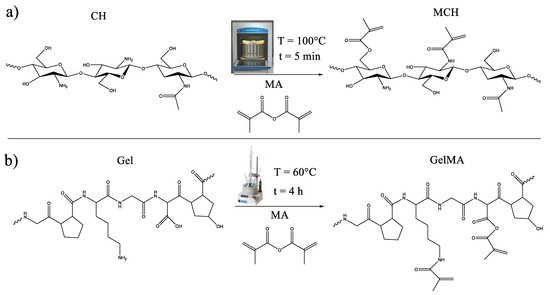
In this study, new photocurable biobased hydrogels deriving from chitosan and gelatin are designed and tested as sorbents for As(V) and Pb(II) removal from water. Those renewable materials were modified by a simple methacrylation reaction in order to make them light processable. The
[...] Read more.
In this study, new photocurable biobased hydrogels deriving from chitosan and gelatin are designed and tested as sorbents for As(V) and Pb(II) removal from water. Those renewable materials were modified by a simple methacrylation reaction in order to make them light processable. The success of the reaction was evaluated by both
1H-NMR and FTIR spectroscopy. The reactivity of those formulations was subsequently investigated by a real-time photorheology test. The obtained hydrogels showed high swelling capability reaching up to 1200% in the case of methacrylated gelatin (GelMA). Subsequently, the Z-potential of the methacrylated chitosan (MCH) and GelMA was measured to correlate their electrostatic surface characteristics with their adsorption properties for As(V) and Pb(II). The pH of the solutions proved to have a huge influence on the As(V) and Pb(II) adsorption capacity of the obtained hydrogels. Furthermore, the effect of As(V) and Pb(II) initial concentration and contact time on the adsorption capability of MCH and GelMA were investigated and discussed. The MCH and GelMA hydrogels demonstrated to be promising sorbents for the removal of heavy metals from polluted waters.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
HPMC Hydrogel Formation Mechanisms Unveiled by the Evaluation of the Activation Energy
by
Saray Perez-Robles, Claudia Carotenuto and Mario Minale
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 5445
Abstract
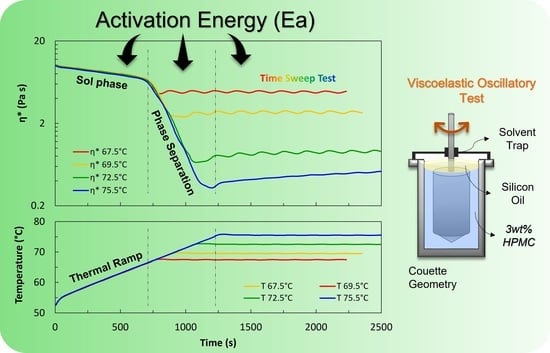
Aqueous solutions of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) show inverse thermoreversible gelation, i.e., they respond to small temperature variations exhibiting sol–gel transition during heating, and reversibly gel–sol transition during cooling. According to the pertinent literature on HPMC aqueous systems, at room temperature, the loss modulus
[...] Read more.
Aqueous solutions of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) show inverse thermoreversible gelation, i.e., they respond to small temperature variations exhibiting sol–gel transition during heating, and reversibly gel–sol transition during cooling. According to the pertinent literature on HPMC aqueous systems, at room temperature, the loss modulus (G”) is higher than the storage modulus (G’). During the heating ramp, the viscoelastic response follows a peculiar path: initially, G” and G’ smoothly decrease, then drop to a minimum and finally increase. Eventually, G’ overcomes G”, indicating the gel formation. A recent explanation of this behaviour considers a two-step mechanism: first, phase separation occurs, then fibrils form from a polymer-rich phase and entangle, leading to a three-dimensional network. Based on this, our research focuses on the rheological analysis of the different steps of the sol–gel transition of an HPMC aqueous solution. We perform different viscoelastic tests: thermal ramps, time sweeps, and frequency sweeps at selected characteristic temperatures. We couple classical analysis of the SAOS experiments with an innovative approach based on the evaluation of the activation energy (
Ea), made possible by the instrument intrinsic temperature oscillations around the target value. Results show that
Ea can be a valid tool that contributes to further clarifying the peculiar microstructural evolution occurring in this kind of thermoreversible gel.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Systematic Evaluation of a Novel Self-Healing Poly(acrylamide-co-vinyl acetate)/Alginate Polymer Gel for Fluid Flow Control in High Temperature and High Salinity Reservoirs
by
Jingyang Pu, Baojun Bai and Thomas P. Schuman
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3586
Abstract
Preferential fluid flow often occurs when water and CO
2 is injected into mature oilfields, significantly reducing their injection efficiency. Particle gels have been evaluated and applied to control the short circulation problems. This study systematically investigated a novel poly(acrylamide-co-vinyl acetate)/alginate-based interpenetrated gel
[...] Read more.
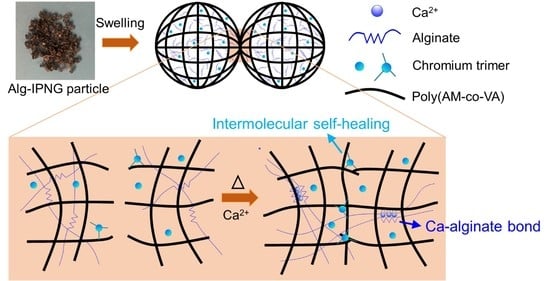
Preferential fluid flow often occurs when water and CO
2 is injected into mature oilfields, significantly reducing their injection efficiency. Particle gels have been evaluated and applied to control the short circulation problems. This study systematically investigated a novel poly(acrylamide-co-vinyl acetate)/alginate-based interpenetrated gel system (Alg-IPNG) which is designed to control the preferential fluid flow problems in high-temperature reservoirs. Chromium acetate was incorporated into the gel system to provide the delayed crosslinking feature of the particle gels. The alginate polymer system can also take advantage of the Ca
2+ ions in the formation water, which exist in most reservoirs, to reinforce its strength by capturing the Ca
2+ to form Ca–alginate bonds. In this paper, various characterizations for the Alg-IPNGs before and after the self-healing process were introduced: (1) the elastic modulus is set at up to 1890 Pa, and (2) the water uptake ratio is set at up to 20. In addition, we also discuss their possible self-healing and reinforcement mechanisms. In particular, the self-healing starting time of the Alg-IPNG particles are modified between 38 to 60 h, which is related to the water uptake ratio, Ca
2+ concentration, and temperature. The reinforced Alg-IPNG gel has an enhanced thermal stability (180 days) at the temperature up to 110 °C.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Removal of a Past Varnish Treatment from a 19th-Century Belgian Wall Painting by Means of a Solvent-Loaded Double Network Hydrogel
by
Ehab Al-Emam, Victoria Beltran, Steven De Meyer, Gert Nuyts, Vera Wetemans, Karolien De Wael, Joost Caen and Koen Janssens
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 4628
Abstract
Polymeric materials have been used by painting conservator-restorers as consolidants and/or varnishes for wall paintings. The application of these materials is carried out when confronting loose paint layers or as a protective coating. However, these materials deteriorate and cause physiochemical alterations to the
[...] Read more.
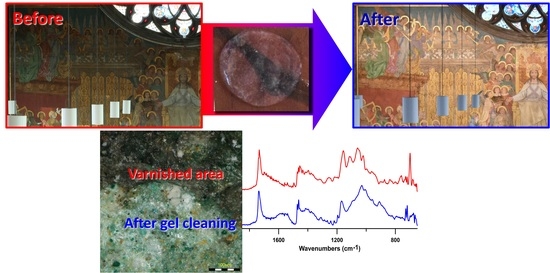
Polymeric materials have been used by painting conservator-restorers as consolidants and/or varnishes for wall paintings. The application of these materials is carried out when confronting loose paint layers or as a protective coating. However, these materials deteriorate and cause physiochemical alterations to the treated surface. In the past, the monumental neo-gothic wall painting ‘The Last Judgment’ in the chapel of Sint-Jan Berchmanscollege in Antwerp, Belgium was treated with a synthetic polymeric material. This varnish deteriorated significantly and turned brown, obscuring the paint layers. Given also that the varnish was applied to some parts of the wall painting and did not cover the entire surface, it was necessary to remove it in order to restore the original appearance of the wall painting. Previous attempts carried out by conservator-restorers made use of traditional cleaning methods, which led to damage of the fragile paint layers. Therefore, gel cleaning was proposed as a less invasive and more controllable method for gently softening and removing the varnish. The work started by identifying the paint stratigraphy and the deteriorated varnish via optical microscopy (OM), scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. A polyvinyl alcohol–borax/agarose (PVA–B/AG) hydrogel loaded with a number of solvents/solvent mixtures was employed in a series of tests to select the most suitable hydrogel composite. By means of the hydrogel composite loaded with 10% propylene carbonate, it was possible to safely remove the brown varnish layer. The results were verified by visual examinations (under visible light ‘VIS’ and ultraviolet light ‘UV’) as well as OM and FTIR spectroscopy.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures