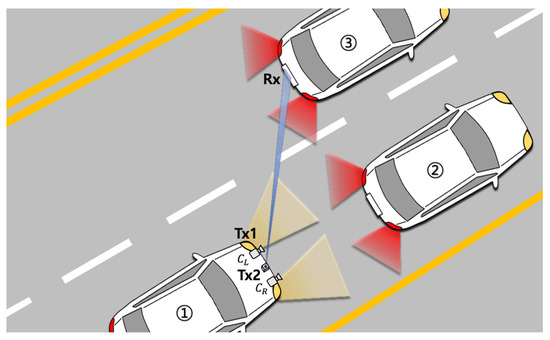
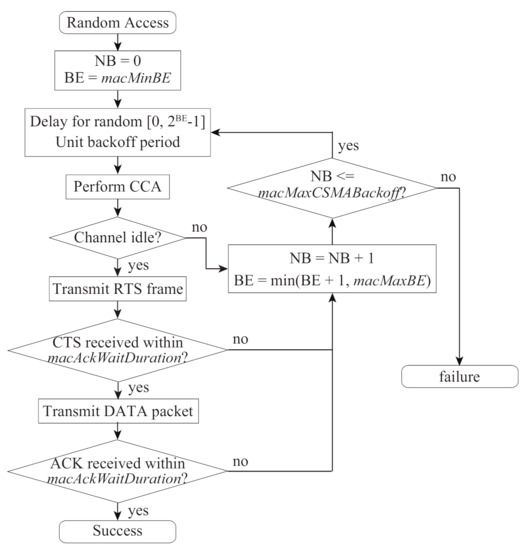
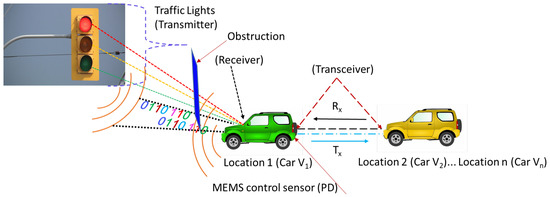
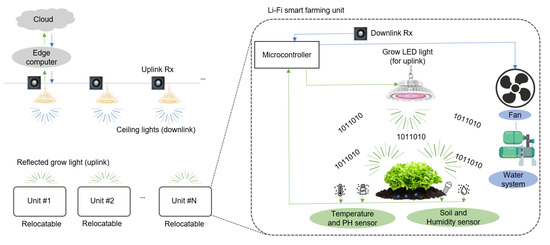
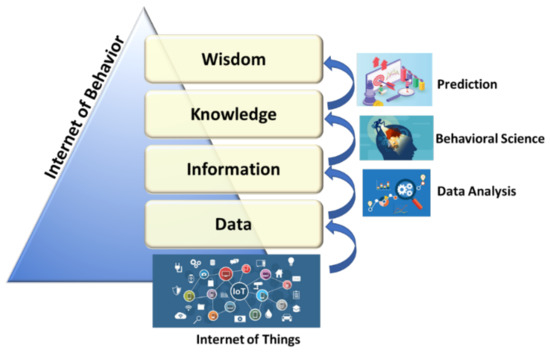
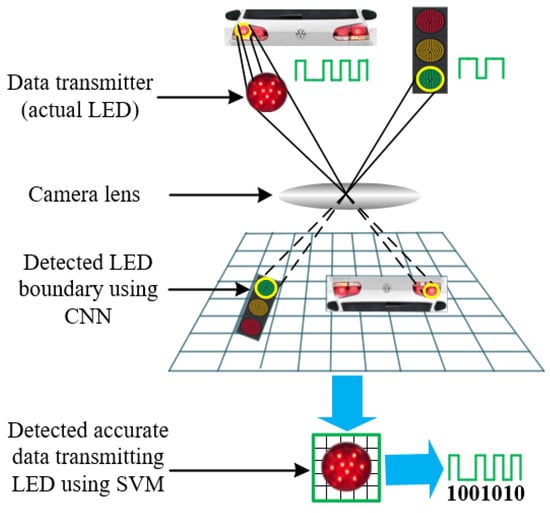
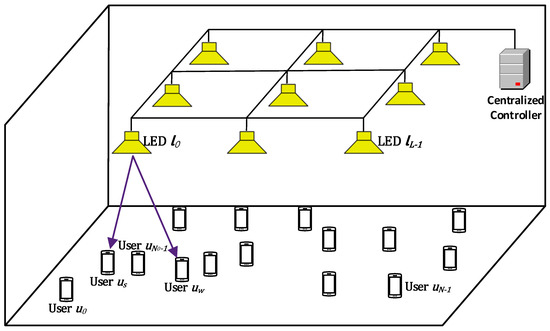
Visible Light Communication (VLC)
A topical collection in Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220). This collection belongs to the section "Communications".
Viewed by 59916
Editor
Interests: visible light communication and positioning; advanced modulation; multiple access and multiplexing
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
Visible light communication has gained enormous popularity across numerous domains, including short- and long-range communications and positioning and intelligent transport systems, amongst others. In general, it has been positioned as an emerging access network technology that has become an ever-increasing topic of interest over the last two decades.
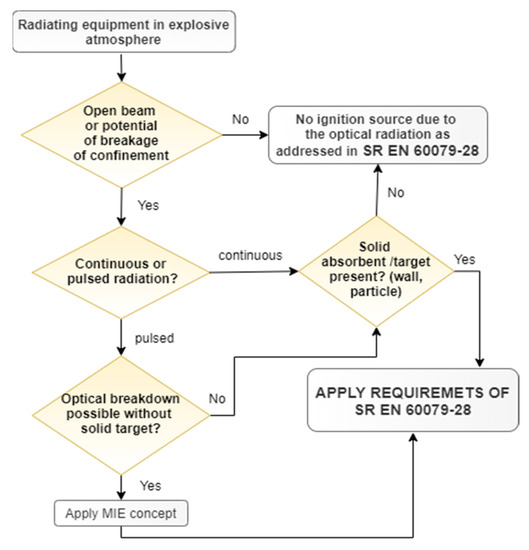
Several key research challenges have emerged within the VLC domain, including multitechnology network tenancy, high data rates, physical layer security, resource allocation, co-design of high-speed data rates and dimming capabilities, machine-to-machine, underwater links, system network topologies, front-end design, and novel material photoactive components. In terms of global development, standards have been developed that define the minimum operation of VLC networks (IEEE802.11bb, amongst others).
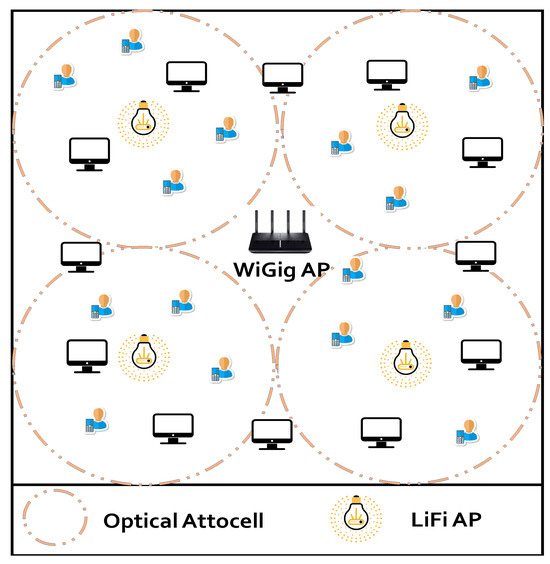
In comparison with conventional RF networks, VLC can offer several advantages, including significantly higher data rates exceeding 10 Gb/s, inherent security as light does not traverse walls and the LED beam can be dedicated to a highly defined area (attocells), license-free operation, and no interference with existing RF systems, which is valuable in airplane and hospital applications. Therefore, the field of VLC promises substantial opportunities for basic and applied research and development. The proposed Special Issue will provide an opportunity for a thorough assessment of the current state of VLC across numerous applications, helping to develop the state-of-the-art.
We welcome submissions on any topic in VLC, with particular interest in the following, nonexclusive, list of principal topics:
- Multitechnology VLC/x integration and transceiver design;
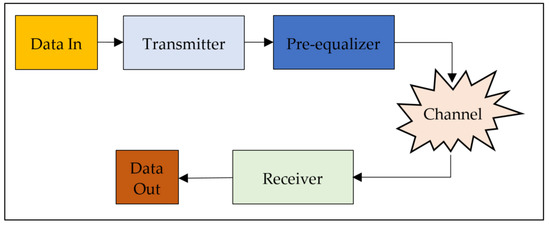
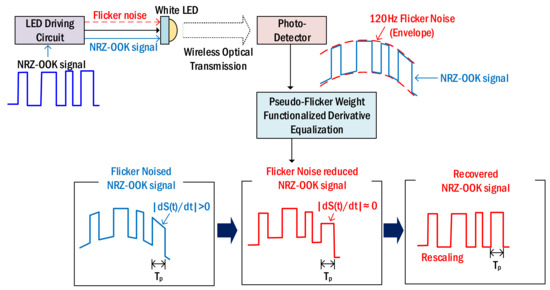
- High data rate links, channel modelling, and digital signal processing;
- Conventional and non-orthogonal modulation, coding, and multiple access;
- Optical camera communication;
- Underwater VLC;
- Intelligent transport systems;
- Mobility and integration of VLC into wider heterogeneous networks;
- Applications of neural networks and new architectures;
- VLC in healthcare sensing applications;
- Co-illumination/dimming and communication system design;
- Software-defined VLC, resource allocation, and multiuser system design.
Dr. Chen Chen
Collection Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sensors is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.