Technological Innovation and Economic Growth
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Luigi Aldieri
Prof. Dr. Luigi Aldieri
 Prof. Dr. Luigi Aldieri
Prof. Dr. Luigi Aldieri
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Department of Economic and Statistical Sciences; University of Salerno, I-84084 Fisciano (SA), Italy
Interests: innovation economics; environmental economics; labor economics; econometrics; public policy; economics of innovation; patents; knowledge diffusion process; employment; green economy; applied microeconometrics
Special Issues, Collections and Topics in MDPI journals
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
An increasing number of studies are available in the recent literature concerning a more efficient use of resources for a full achievement of economic sustainability and growth. From this perspective, the role of technological innovation is very important, but the relative empirical evidence is still weak. For this reason, this Special Issue will focus on the extent to which investments in cleaner production can stimulate economic growth in a more sustainable context.
Because innovation is one of the mechanisms through which countries deal with a changing environment, green innovation presents itself as an important tool to react to the increasing pressure and changing environment. The aim of this Special Issue is to further understand the relationship between knowledge source strategy and green innovation. This type of innovation represents a technological frontier with which economic agents are still inexperienced, and there are no accepted standards in terms of technological solutions and policy measures for evaluating environmental performance. Recent studies suggest that private firms develop insufficient innovation toward clean technologies, and that too much effort is devoted to polluting technologies. Indeed, there is path dependence: Firms that used innovative polluting technologies in the past also have higher economic incentives for using innovative polluting technologies in the future. An intervention of policymakers at the worldwide level has been important for breaking the path dependence effect by favoring cleaner technologies in terms of social optimum.
Theoretical and empirical contributions from innovation economics and environmental economics on economic growth and relative public policies are welcome in this Special Issue.
Prof. Dr. Luigi Aldieri
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sustainability is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2400 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- technological innovation
- patents
- knowledge spillovers
- green economy
- public policies
Published Papers (27 papers)
Open AccessArticle
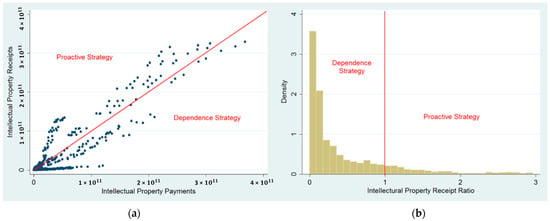
Global Financial Investment Connectedness, ICT, and Intellectual Property Strategies: A Country-Level Empirical Analysis
by
Yonghee Kim and Sungjin Yoo
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 1621
Abstract
This study investigated the direct and indirect impacts of financial investment connectedness and Information and Communication Technology (ICT) on countries’ intellectual property (IP) strategies. By utilizing the panel logit model on longitudinal country-level data, we found that countries’ positions in the global financial
[...] Read more.
This study investigated the direct and indirect impacts of financial investment connectedness and Information and Communication Technology (ICT) on countries’ intellectual property (IP) strategies. By utilizing the panel logit model on longitudinal country-level data, we found that countries’ positions in the global financial investment network significantly affect their IP strategies. Furthermore, ICT usage weakens the IP strategies’ reliance on global financial investment connectedness. This study is among the first to link financial investment connectedness and ICT to intellectual property strategy. The implications for governments managing financial investment portfolios and making intellectual property strategies are derived.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
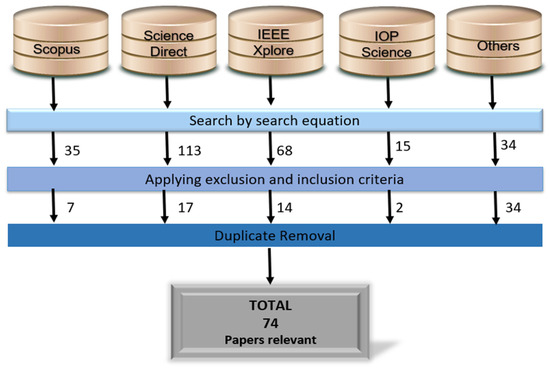
Contributions of the 5G Network with Respect to Decent Work and Economic Growth (Sustainable Development Goal 8): A Systematic Review of the Literature
by
Saul Beltozar-Clemente, Orlando Iparraguirre-Villanueva, Félix Pucuhuayla-Revatta, Fernando Sierra-Liñan, Joselyn Zapata-Paulini and Michael Cabanillas-Carbonell
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 8335
Abstract
Decent work and economic growth are fundamental elements for the sustainable development of a society, with Sustainable Development Goal 8 (SDG8) being one of the key objectives of the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda. The 5G network has great potential to contribute significantly to
[...] Read more.
Decent work and economic growth are fundamental elements for the sustainable development of a society, with Sustainable Development Goal 8 (SDG8) being one of the key objectives of the United Nations’ 2030 Agenda. The 5G network has great potential to contribute significantly to the achievement of SDG8, offering faster and more reliable connectivity, which opens up new possibilities for innovation, operational efficiency, and job creation. The present study aimed to investigate the role of 5G technologies concerning decent work and economic growth (SDG8). As part of the method, 265 articles extracted from main databases such as Scopus, IEEExplore, and ScienceDirect were analyzed using the PRISMA methodology, resulting in 74 relevant articles after applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria. As a result, a greater contribution to the use of the 5G network was identified in sectors such as manufacturing, health, and transportation, generating greater economic growth and job creation. It was also found that the technological applications with the greatest contributions are “Internet of Things” and “Artificial intelligence”. Finally, it was concluded that the results of this review are useful for future research on technologies that support 5G networks, contributing to economic growth and equitable and sustainable decent work in a wide range of sectors and rural areas.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
From Green Ideas to Green Savings: Assessing the Financial Impact of Green Innovations on Audit Fees
by
Dongxiao Wu, Xinzhong Bao and Qiulan Su
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 1905
Abstract
Green innovation is an important approach to achieving ecologically sustainable development. However, the paradox surrounding enterprises’ willingness to engage in green innovation persists in discussions. Using a sample of listed firms from 2010–2021 in the Chinese A-shares market, this study analyzed the impact
[...] Read more.
Green innovation is an important approach to achieving ecologically sustainable development. However, the paradox surrounding enterprises’ willingness to engage in green innovation persists in discussions. Using a sample of listed firms from 2010–2021 in the Chinese A-shares market, this study analyzed the impact of green innovation diversity on audit fees and the underlying mechanisms involved. Our findings reveal that (1) a higher green innovation diversity is associated with a reduction in external audit fees; (2) green innovation diversity impacts audit fees through information transparency and corporate environmental performance; and (3) the effect of green innovation diversity on audit fees is more pronounced in firms with lower scales, higher government subsidies, and lower pollution intensity. These findings provide valuable insights into promoting firms’ engagement in green innovation activities and shed light on the challenges faced by audit firms when assessing and auditing green innovation.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Determination of Importance of Key Decision Points in the Technology Commercialization Process: Attitude of the US and German Experts
by
Vaida Zemlickienė and Zenonas Turskis
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2319
Abstract
With the help of commercialization, inventions become marketable commodities that find new ways of solving problems. Turning technology into reality requires an excellent understanding of the development process from idea to market of the technology. The primary purpose of this article was to
[...] Read more.
With the help of commercialization, inventions become marketable commodities that find new ways of solving problems. Turning technology into reality requires an excellent understanding of the development process from idea to market of the technology. The primary purpose of this article was to examine the commercialization process of inventions and divide the commercialization process into stages that culminate in decision points. Opinions of different authors and representatives of R&D organizations were compared concerning the content of technology commercialization, which is understood and named differently in the scientific and practical literature. Later, with the help of two groups of experts from the US and Germany, the importance of key decision points was determined. The research results were summarized using the MCDM method: the integrated Fuzzy Delphic–Eckenrode Likert-type Scale-based Rating Technique (FDELSRT). The results of this study can be applied in practice to making strategic decisions related to the allocation of efforts, limited time, and financial resources based on the determined importance of key decision points. Research in different countries and the comparison of results will identify areas and opportunities for further mutual learning and more intensive, mutually beneficial international cooperation in technology development.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
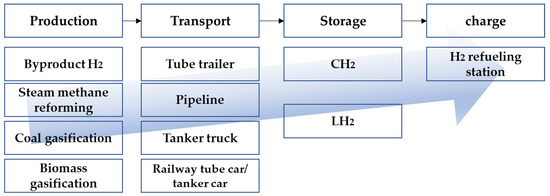
Promising Technology Analysis and Patent Roadmap Development in the Hydrogen Supply Chain
by
Jiwon Yu, Young Jae Han, Hyewon Yang, Sugil Lee, Gildong Kim and Chulung Lee
Cited by 8 | Viewed by 3366
Abstract
Hydrogen energy, one of the energy sources of the future, represents a substantial issue which affects the industries and national technologies that will develop in the future. In order to utilize hydrogen energy, a hydrogen supply chain is required so that hydrogen can
[...] Read more.
Hydrogen energy, one of the energy sources of the future, represents a substantial issue which affects the industries and national technologies that will develop in the future. In order to utilize hydrogen energy, a hydrogen supply chain is required so that hydrogen can be processed and transported to vehicles. It is helpful for technology and policy development to analyze technologies necessary to charge the hydrogen energy generated into vehicles through the supply chain to discover technologies with high potential for future development. The purpose of this paper is to identify promising technologies required in storing, transporting, and charging vehicles generated by the hydrogen fuel supply chain. Afterward, the promising technologies identified are expected to help researchers set a direction in researching technologies and developing related policies. Therefore, we provide technology information that can be used promisingly in the future so that researchers in the related field can utilize it effectively. In this paper, data analysis is performed using related patents and research papers for technical analysis. Promising technologies that will be the core of the hydrogen fuel supply chain in the future were identified using the published patents and research paper database (DB) in Korea, the United States, Europe, China, and Japan. A text mining technique was applied to preprocess data, and then a generic topographic map (GTM) analysis discovered promising technologies. Then, a technology roadmap was identified by analyzing the promising technology derived from patents and research papers in parallel. In this study, through the analysis of patents and research papers related to the hydrogen supply chain, the development status of hydrogen storage/transport/charging technology was analyzed, and promising technologies with high potential for future development were found. The technology roadmap derived from the analysis can help researchers in the field of hydrogen research establish policies and research technologies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analysis of the Technological Convergence in Smart Textiles
by
Qian Xu, Yabin Yu and Xiao Yu
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 2647
Abstract
Convergence between emerging technologies and traditional industries has become a crucial strategy for enhancing a technology’s competitiveness. Technical convergence (TC) for smart textiles aims to reveal the convergence of emerging technologies with textile technologies, including the field, structure, and critical technologies of the
[...] Read more.
Convergence between emerging technologies and traditional industries has become a crucial strategy for enhancing a technology’s competitiveness. Technical convergence (TC) for smart textiles aims to reveal the convergence of emerging technologies with textile technologies, including the field, structure, and critical technologies of the TC. For the empirical analysis, the technology life cycle (TLC) and network analysis method are utilized to observe the TC of 15,125 patent data for textiles from the Derwent Patent Database. The results indicate the following: (1) after 2021, the TC of smart textiles matured, with the number of patents reaching a peak in 2030. (2) Emerging technologies and textile technologies are inextricably linked. In addition to textile technologies, the primary technical fields involved in smart textiles are electronic engineering, tools design, chemical engineering, and mechanical engineering. Electronic engineering is the most common of these fields, accounting for 29.11%. (3) From a structural perspective, the density, breadth, and depth of the TC continues to expand. (4) Measurement, computer technology, and audio technology will be always essential to the TC, whereas electrical machinery, instrumentation, energy technology, other specialized technologies, and chemical engineering have tremendous growth potential. The findings above have substantial implications for the phenomenon of the TCs that have emerged in emerging technology and traditional industry fields. They can also aid the government in formulating policies that promote the transformation and growth of related industries.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Influence of Economic Openness on Total Factor Productivity: Evidence from China’s Belt and Road Initiative
by
Maoguo Wu and Xierui Han
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 2606
Abstract
The impact of international trade and export-oriented policies on economic growth has been an important topic. Based on an evaluation of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), this study provides new evidence of the positive causal link between increasing openness and long-term economic
[...] Read more.
The impact of international trade and export-oriented policies on economic growth has been an important topic. Based on an evaluation of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), this study provides new evidence of the positive causal link between increasing openness and long-term economic growth. Specifically, this study evaluates the BRI’s impact on 18 key provinces in China, with a focus on total factor productivity (TFP). Utilizing a panel dataset of 284 prefectural-level cities from 2007 to 2018, we examine the causal relationship between the BRI and TFP in a difference-in-differences framework. We apply the five-pronged approach to the BRI to explore the impact mechanism and examine heterogeneity in the effect in terms of geographic location and local government efficiency. We find that the BRI significantly promotes TFP in key provinces; it increases TFP through unimpeded trade, infrastructure connectivity, technical efficiency, and technological progress. The BRI promotes TFP in key coastal provinces belonging to the Maritime Silk Road while having a relatively limited impact on the other key provinces belonging to the Silk Road Economic Belt. This study has policy implications for promoting the BRI in China. It recommends that the government collaborates with firms and financial institutions in the construction of infrastructure.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
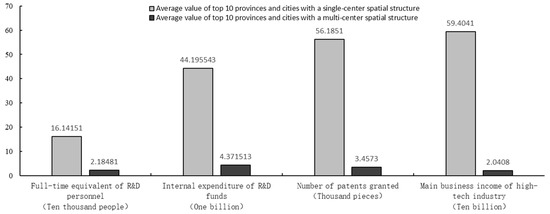
Impact of Heterogeneous Spatial Structure on Regional Innovation—From the Perspectives of Efficiency and Gap
by
Zi Ye, Chen Zou and Yongchun Huang
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 2306
Abstract
Reasonable spatial system distribution is the prerequisite for the optimization of resource and spatial allocation and the coordinated development of the regional economy. Therefore, correctly identifying the impact of different types of spatial structures on scientific and technological innovation is an important way
[...] Read more.
Reasonable spatial system distribution is the prerequisite for the optimization of resource and spatial allocation and the coordinated development of the regional economy. Therefore, correctly identifying the impact of different types of spatial structures on scientific and technological innovation is an important way to promote the rational layout of regional spatial structures and enhance the strength of regional scientific and technological innovation. Based on the theory of regional spatial structure and panel data of 26 provinces and autonomous regions in China from 2005 to 2019, this paper tested the impact of regional spatial structure on innovation efficiency and gap by constructing the regional spatial structure index, the innovation efficiency index, and the innovation gap index. The research results show that: First, the agglomeration effect produced by a single-center spatial structure is conducive to improving the efficiency of scientific and technological innovation, whereas the spillover effect generated by a multi-center spatial structure is more favorable for narrowing the gap in scientific and technological innovation. Second, the single-center spatial structure is more suitable for provinces and cities in the western region with relatively low levels of economic development, whereas the multi-center spatial structure is more beneficial to the achievement of innovative and high-quality development in the eastern region. Third, the moderating effect analysis shows that with an increase in cultural diversity and inter-city distance, the partial effects of the single-center spatial structure on innovation efficiency present an “N” shape and an “inverted-U” shape, respectively, whereas the partial effects of the multi-center spatial structure on the innovation gap exhibit “inverted-U” shapes. This research not only provides theoretical support for the impact of regional spatial structure on innovation efficiency and gap but also offers empirical evidence for future regional development path choices.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
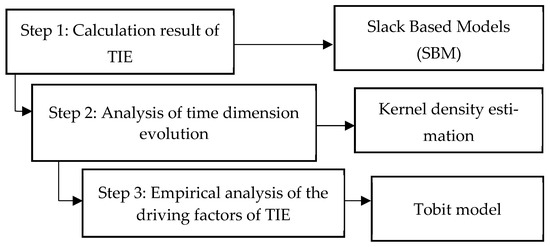
Technological Innovation Efficiency in China: Dynamic Evaluation and Driving Factors
by
Qian Wang, Yang Chen, Heshan Guan, Oleksii Lyulyov and Tetyana Pimonenko
Cited by 56 | Viewed by 5076
Abstract
Innovation is the engine and accelerator that drives high-quality economic and enterprise development. In recent years, the output of scientific and technological innovation in China has been high, but the phenomenon of low efficiency and low quality of innovation occurs frequently. In this
[...] Read more.
Innovation is the engine and accelerator that drives high-quality economic and enterprise development. In recent years, the output of scientific and technological innovation in China has been high, but the phenomenon of low efficiency and low quality of innovation occurs frequently. In this study, first, technological innovation efficiency (TIE) was measured. Then, a dynamic evaluation and analysis of spatial-temporal characteristics of efficiency were performed. Lastly, the driving factors of innovation efficiency were explored. TIE was calculated dynamically in 30 provinces of China from 2011 to 2019 based on the improved super-efficiency SBM-DEA model. Then, the kernel density estimation method was adopted to analyse the spatial-temporal differentiation characteristics and dynamic evolution process of provincial efficiency. The findings confirm that from 2011 to 2019, the top five provinces for TIE in China were Beijing (1.0), Shanghai (0.96), Hainan (0.96), Jilin (0.94) and Tianjin (0.91). The provinces with lowest average efficiency were Qinghai (0.77), Ningxia (0.73) and Inner Mongolia (0.73). The significant differences in the level of technological innovation in different regions were caused by the long-term and in-depth implementation of the government’s strategy of revitalising science and driving innovation in parts of areas. The findings of kernel function confirm that the TIE in most parts of China was gradually polarised. Furthermore, the results show that for every 1 unit of government R&D funding support, the average marginal utility of the expected TIE will reach 0.192, which is more significant in the central and western regions. On this basis, combined with environmental factors of innovation market, infrastructure, financing and enterprise innovation potential, the article also extracts the driving factors that affect the differences in provincial efficiency. The findings provide a reference for guiding provinces to carry out innovation activities independently and improve innovation quality and efficiency.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
How Does Successful Catch-Up Occur in Complex Products and Systems from the Innovation Ecosystem Perspective? A Case of China’s High-Speed Railway
by
Zhongji Yang, Liangqun Qi, Xin Li and Tianxi Wang
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 3562
Abstract
Successful catch-up is an important channel to achieve sustainable development for emerging economies; however, it is a great challenge to catch up in complex products and systems (CoPS). Studies show limited evidence on how successful catch-up occurred in CoPS for emerging economies. This
[...] Read more.
Successful catch-up is an important channel to achieve sustainable development for emerging economies; however, it is a great challenge to catch up in complex products and systems (CoPS). Studies show limited evidence on how successful catch-up occurred in CoPS for emerging economies. This study holds the view that CoPS catch-up means a narrower gap in the innovation ecosystem between latecomers and leaders. This study disentangles the CoPS innovation ecosystem and uses China’s high-speed railway (HSR) as a longitudinal case with abundant data to explore how successful catch-up in CoPS is achieved. The results show that the CoPS innovation ecosystem presents a dynamic evolution in the technology innovation subsystem, the value creation subsystem, and the habitat. Four types of forces from the innovation ecosystem mix together to drive CoPS catch-up. Finally, this study proposes a CoPS catch-up process model following the basic logic of start point, activities, and performance, and CoPS industrial standards are used to measure CoPS catch-up performance. The study on CoPS catch-up from an innovation ecosystem perspective provides new insights and useful implications for governments and entities in CoPS of emerging economies.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Can Green Innovation and New Urbanization Be Synergistic Development? Empirical Evidence from Yangtze River Delta City Group in China
by
Lindong Ma, Yuanxiao Hong, Xihui Chen and Xiaoyong Quan
Cited by 30 | Viewed by 3321
Abstract
Green innovation has become the mainstream of the era, and new urbanization is an inevitable choice in China’s urbanization development. Focusing on the topics of green innovation and new urbanization, much work has been done to analyze their influencing factors separately, while the
[...] Read more.
Green innovation has become the mainstream of the era, and new urbanization is an inevitable choice in China’s urbanization development. Focusing on the topics of green innovation and new urbanization, much work has been done to analyze their influencing factors separately, while the relationship between the two remains to be explored. This paper selects the representative indicators to study the new urbanization and green innovation of the Yangtze River Delta city group from the perspective of the whole and individual cities, in terms of spatiotemporal evolution traits, by using the SBM, entropy method, coupling model, spatial econometric and geographical detector. The results reveal the following: (1) there is a synergistic effect between green innovation and new urbanization development, and the role has been increasing; (2) green innovation and new urbanization present positive spatial autocorrelation and regional agglomeration; (3) in the detection of driving factors, economic development > social conditions > natural resources; most groups (40/66) of factor interactions present nonlinear enhancement, and the digital economy factor accounts for the largest proportion. Finally, according to the findings, we offer a suggestion and a conclusion.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
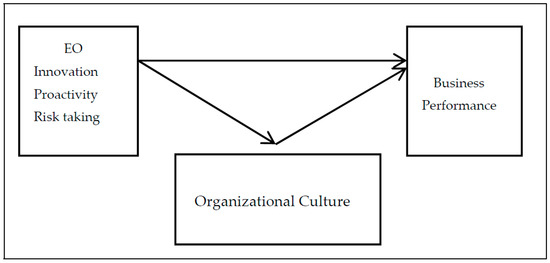
Entrepreneurial Orientation, Organizational Culture and Business Performance in SMEs: Evidence from Emerging Economy
by
Zina Arabeche, Ahlem Soudani, Mohsen Brahmi, Luigi Aldieri, Concetto Paolo Vinci and Mohammed El Amine Abdelli
Cited by 80 | Viewed by 12246
Abstract
The study objective is to empirically examine the mediating role of organizational culture on entrepreneurial orientation (EO) and business performance relationships in Algerian manufacturing SMEs. A sample of 180 Algerian Small medium enterprise (SME) owners/managers was collected for the year 2021 by using
[...] Read more.
The study objective is to empirically examine the mediating role of organizational culture on entrepreneurial orientation (EO) and business performance relationships in Algerian manufacturing SMEs. A sample of 180 Algerian Small medium enterprise (SME) owners/managers was collected for the year 2021 by using structured questionnaires. This study has contributed to the existing theory by evaluating the mediating role of Organizational Culture (OC) by using interaction effect in partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). The results have supported the hypothesized direct and mediate relationship: Entrepreneurial Orientation has the highest effect on the Organizational culture. On the other hand, Entrepreneurial Orientation has a medium influence on business performance. In addition, Organizational culture has a medium influence on business performance. Additionally, Entrepreneurial orientation and organizational culture together explain 50.2% of the variances for the business performance construct. On the other hand, 38.9% of the variances are explained by the entrepreneurial orientation for the organizational culture construct. Their relationship receives considerable scholarly attention in the literature, but few studies have been conducted among Algerian manufacturing SMEs. Hence, this investigation’s purpose is to add to the research in the newer context of Algeria. Thus, this study was an attempt to bridge this gap in the literature. This study can be used to supplement existing theories on organizational culture and small-business performance. This paper discovers an excellent link between entrepreneurial orientation and small and medium enterprise performance, with organizational culture as a partial mediating factor. This research also has significant implications for academics and practitioners to understand better entrepreneurial orientation, organizational culture perspectives, and organizational performance. The conclusions have been empirically intended to help SME authorities and future academics understand the function of entrepreneurial orientation and culture in improving the organizational performance of SMEs, particularly in North Africa.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Causality between Technological Innovation and Economic Growth: Evidence from the Economies of Developing Countries
by
Maha Mohamed Alsebai Mohamed, Pingfeng Liu and Guihua Nie
Cited by 88 | Viewed by 37325
Abstract
Economic growth is a tool for measuring the development and progress of countries, and technological innovation is one of the factors affecting economic growth and contributes to the development and modernization of production methods. Therefore, technological innovation is the main driver for economic
[...] Read more.
Economic growth is a tool for measuring the development and progress of countries, and technological innovation is one of the factors affecting economic growth and contributes to the development and modernization of production methods. Therefore, technological innovation is the main driver for economic growth and human progress. Spending on innovation, research and development as well as investment in innovation supports competition and progress. Accordingly, sustainable economic growth is achieved. This ensures the preservation of resources for future generations and the achievement of economic and social growth. Moreover, a sustainable educational level of the workforce, investment in research, creation of new products, and investor access to stock markets will be ensured through the development of the public and private sectors and the improvement of people’s living conditions. Our study aimed to measure the impact of technological innovation on economic growth in developing countries during the period 1990–2018. To this end, the error correction model (ECM) method has been applied. The results showed that the variables are unstable in the level and stable after taking the first difference. Co-integration was also tested using the ECM, and Granger’s causality test for the direction of causation. The test results showed that an increase in technological innovation indicators (such as spending on education, number of patents for residents and non-residents, R&D expenditures, number of researchers in R&D, high-tech exports, and scientific and technical research papers.) leads to an increase in economic growth in the short term and the long-run with a long-run and two-way causal relationship between technological innovation and GDP, and short-run causation spanning from technological innovation to GDP. The study also concluded that technological innovation has a direct impact on the sustainability of a country’s economic growth, which is why it is crucial to adopt strong policies that encourage international investors to allocate capital for development in developing countries and thus encourage more research and development.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
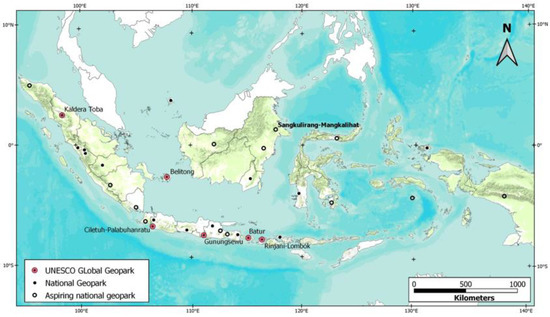
Geotourism Hazards and Carrying Capacity in Geosites of Sangkulirang-Mangkalihat Karst, Indonesia
by
Arzyana Sunkar, Anindika Putri Lakspriyanti, Eko Haryono, Mohsen Brahmi, Pindi Setiawan and Aziz Fardhani Jaya
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 5075
Abstract
The protection of resources and the safety of visitors are two essential elements in the sustainability of any tourism destination. The Sangkulirang-Mangkalihat karst has the potential to be developed as a UNESCO Global Geopark based on the diversity and unique nature of its
[...] Read more.
The protection of resources and the safety of visitors are two essential elements in the sustainability of any tourism destination. The Sangkulirang-Mangkalihat karst has the potential to be developed as a UNESCO Global Geopark based on the diversity and unique nature of its geological heritage. Proper management efforts should be carefully planned to ensure sustainability of the geosite. Intact natural conditions can be a potential hazard to visitors and, conversely, the presence of visitors can interfere with the natural preservation of the sensitive karst area. Physical, biological, and human activities that may endanger visitors should be identified and limiting the number of visitors received by each geosite should also be considered. This paper aims to identify the potential tourism hazards of physical, biological, and human activities and to calculate the tourist’s carrying capacity of three geosites (Tewet cave, Nyadeng lake, and Bloyot cave) in the Sangkulirang-Mangkalihat karst. The identification of potential hazards was conducted in each geosite and analyzed and assessed using management options referencing UNEP, NPSA, and APEC, whereas the carrying capacity was assessed with reference to the Cifuentes formulation. Meanwhile, the carrying capacity was assessed at three levels, namely physical carrying capacity (PCC), real carrying capacity (RCC), and effective carrying capacity (ECC). The highest physical and biological hazards were the ravines in the Tewet cave, as well as a moderate level of risk, such as slippery, steep terrain and the presence of crocodiles. Meanwhile, the potential hazards faced by Nyadeng lake and Bloyot cave were classified as low risk. The carrying capacity assessments indicated that Bloyot cave is able to accommodate the largest number of visitors on a daily basis. Therefore, the carrying capacity results of each geosite can serve as a reference for managers to limit the number of visitors to the site in order to ensure the sustainability of Sangkulirang-Mangkalihat geosites.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Analyzing the Role of Renewable Energy and Energy Intensity in the Ecological Footprint of the United Arab Emirates
by
Eyup Dogan and Syed Faisal Shah
Cited by 43 | Viewed by 6288
Abstract
Even though a great number of researchers have explored the determinants of environmental pollution, the majority have used carbon emissions as an indicator while only recent studies have employed the ecological footprint which is a broader and more reliable indicator for the environment.
[...] Read more.
Even though a great number of researchers have explored the determinants of environmental pollution, the majority have used carbon emissions as an indicator while only recent studies have employed the ecological footprint which is a broader and more reliable indicator for the environment. The present study contributes to the literature by exploring for the first time in the literature the role of real output, energy intensity (technology), and renewable energy in the ecological footprint under the STIRPAT framework for a Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) country—the United Arab Emirates. By applying the novel bounds testing with dynamic simulations on the data from 1992–2017, the findings of this paper reveal that energy intensity and renewable energy have a negative and significant influence on the ecological footprint but real output has a positive and significant impact on it. In other words, the empirical results indicate that a rise in the real income increases environmental pollution while increases in renewable energy and advances in technology mitigate the level of emissions. The findings also suggest that the government should establish new programs, investment opportunities, and incentives in favor of energy intensity-related technology and renewable energy for the sake of environmental sustainability. The outcomes from this research analysis are useful for policymakers, industrial partners, and project designers in the United Arab Emirates.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Effects of Patent Policy on Outputs and Commercialization of Academic Patents in China: A Spatial Difference-in-Differences Analysis
by
Jiafeng Gu
Cited by 19 | Viewed by 4537
Abstract
The development of a difference-in-differences estimator is a new move in patent policy evaluation research. However, such an estimator neglects the possibility that academic patent activities follow a spatial autoregressive process with respect to the dependent variable. The objective of this study was
[...] Read more.
The development of a difference-in-differences estimator is a new move in patent policy evaluation research. However, such an estimator neglects the possibility that academic patent activities follow a spatial autoregressive process with respect to the dependent variable. The objective of this study was to propose a spatial difference-in-differences estimator accounting for possible spatial spillover effects. In this study, an empirical analysis of a sample of 31 Chinese provinces from 2010 to 2019 indicates that an incentive patent policy has a positive impact on the output and commercialization of academic patents, with positive effects also spilling over into neighboring provinces. This study further found that incentive patent policies play a placebo role in academic patent activities. Provincial patent policies are merely a proxy for other variables that characterize the systemic differences between provinces that implement patent policies and those that do not. Therefore, the promotion of academic patent activities cannot be attributed to policy incentives.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
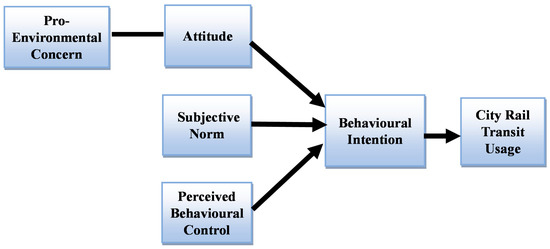
Understanding the Factors Affecting Pro-Environment Behavior for City Rail Transport Usage: Territories’ Empirical Evidence—Malaysia
by
Maryam Kalhoro, Hui Nee Au Yong and Charles Ramendran SPR
Cited by 4 | Viewed by 4344
Abstract
The emerging population has increased travel demand and improved public transport mode in cities to connect the people. (1) Background: This study used the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) to assess the usage behavior for city rail transport with the factors attitude, subjective
[...] Read more.
The emerging population has increased travel demand and improved public transport mode in cities to connect the people. (1) Background: This study used the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) to assess the usage behavior for city rail transport with the factors attitude, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control and its impact on pro-behavioral intentions to increase the actual usage of rail transports, i.e., LRT, MRT, and KTM commuter. (2) Method/Approach: To understand the antecedents of pro-environment behavioral intention, this study performed pilot testing, for which we collected the data through closed-ended questionnaires to test the instrument’s reliability, specifically from the Klang Valley in Malaysia. (3) Findings/Results: This study revealed that the public attitude due to environmental concern and subjective norms and perceived behavioral control are the strongest predictors for public transport usage through behavioral intention. The study estimated that most respondents would have agreed to choose public transport mode if quality of services increased. (4) Conclusion: In future research, the goal of this study could be extended as a strategic indicator for sustainable development through efficient mobility choice in Malaysia. The TPB model helps to present the factors involved in growing and retaining clients for rail transport. In terms of implications for policy, this study also provides policymakers with valuable information to maintain the current public transport passengers and attract new users through the perceived service quality and customer satisfaction of public transport.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
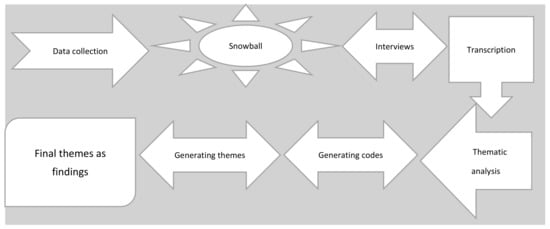
How Entrepreneurship Sustains Barriers in the Entrepreneurial Process—A Lesson from a Developing Nation
by
Muhammad Nawaz Tunio, Mushtaque Ali Jariko, Tom Børsen, Sadia Shaikh, Tania Mushtaque and Mohsen Brahmi
Cited by 40 | Viewed by 9087
Abstract
The aim of this study is to explore how entrepreneurship sustains the barriers in the entrepreneurial process in a developing country like Pakistan. To reach these findings, a qualitative approach was used in which semi-structured interviews were conducted with young entrepreneurs in the
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study is to explore how entrepreneurship sustains the barriers in the entrepreneurial process in a developing country like Pakistan. To reach these findings, a qualitative approach was used in which semi-structured interviews were conducted with young entrepreneurs in the region of Hyderabad, Pakistan. After collecting data, thematic analysis was conducted. The findings of the study in the form of final themes suggest that trust issues, family barriers, financial issues, gender issues, educational barriers, corruption, and legal barriers are among the challenges which trigger changes in the entrepreneurial process and its sustainability. This study provides implications for the regional government, academic institutes, financial institutes, entrepreneurs, and society at large when developing a support system and promoting a sustainable entrepreneurial environment by minimizing these challenges and suggestions for an entrepreneurial focus on sustainable entrepreneurship.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
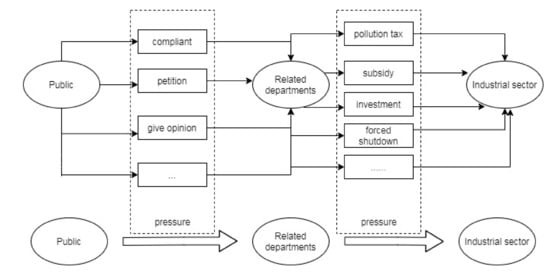
Research on the Effects of Environmental Regulations on Industrial-Technological Innovation Based on Pressure Transmission
by
Mengqi Quan, Quan Guo, Qing Xia and Min Zhou
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 3151
Abstract
This paper investigates the transmission of pressure between the public, relevant government departments, and industrial firms through the use of formal environmental regulations. The data include formal environmental regulations issued from 2005 to 2019 in 179 cities in 27 provinces in China. The
[...] Read more.
This paper investigates the transmission of pressure between the public, relevant government departments, and industrial firms through the use of formal environmental regulations. The data include formal environmental regulations issued from 2005 to 2019 in 179 cities in 27 provinces in China. The intermediary effect model and the threshold effect model are used to carry out research studies on the relationships between public-participated environmental regulations, formal environmental regulations, and industrial-technological innovations. Results indicate that: (1) Pressure is transmitted between the public, and relevant government sectors and industries. For instance, public-participated environmental regulations pressure relevant government departments to apply strong formal environmental regulations on industrial sectors. (2) Labor and capital have a positive moderating effect on the effect of formal environmental regulations on industrial-technological innovations. (3) Both public-participated and formal environmental regulations promote industrial-technological innovations. (4) There is a threshold effect in formal environmental regulations. For instance, when the intensity of public-participated environmental regulations is higher than 93, the role of formal environmental regulations in promoting industrial-technological innovation can be completely maximized.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
The Fit between Technology Management and Technological Capability and Its Impact on New Product Development Performance
by
Qian Ma, Weiwei Wu and Yexin Liu
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 3383
Abstract
In recent years, the impact of technology management and technological capability on new product development performance has aroused widespread concern. As a result, research models based on the notion of fit between technology management and technological capability seems to show promise. This paper
[...] Read more.
In recent years, the impact of technology management and technological capability on new product development performance has aroused widespread concern. As a result, research models based on the notion of fit between technology management and technological capability seems to show promise. This paper aims to whether there exists a fit between technology management and technological capability and the effect of this fit on new product development performance. Research results show that the fit between technology management and technological capability has a positive effect on new product development performance. Moreover, the fit between technology management and technological capability in firms with high new product development performance is dominated by technological capability, while that in firms with low new product development performance is dominated by technology management.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
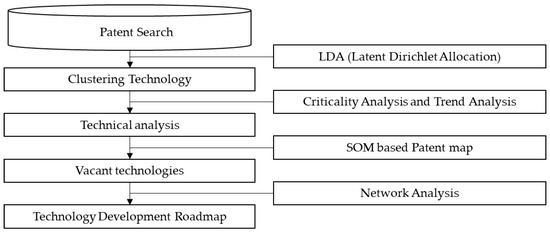
Identification of Promising Smart Farm Technologies and Development of Technology Roadmap Using Patent Map Analysis
by
Eunsuk Chun, Sungchan Jun and Chulung Lee
Cited by 15 | Viewed by 5265
Abstract
In this study, we suggest methodologies for identifying promising and vacant technologies on smart farms by analyzing patent information. Additionally, a technology roadmap for smart farms is suggested using network analysis. The database of patents related to smart farms was extracted from the
[...] Read more.
In this study, we suggest methodologies for identifying promising and vacant technologies on smart farms by analyzing patent information. Additionally, a technology roadmap for smart farms is suggested using network analysis. The database of patents related to smart farms was extracted from the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) by keyword search, and valid patents data was selected and clustered using the Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) algorithm. We also conducted the technical importance analysis and trend analysis to identify promising technology topics. By developing a patent map based on a self-organizing map (SOM), we were able to identify vacant technologies among smart farm technology groups. In order to develop vacant technologies, we presented a stepwise technology roadmap by analyzing the relationship between technology elements using network analysis. The proposed procedure and analysis method provides useful insights in establishing research and development (R&D) strategies for the development of smart farm technology roadmaps.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
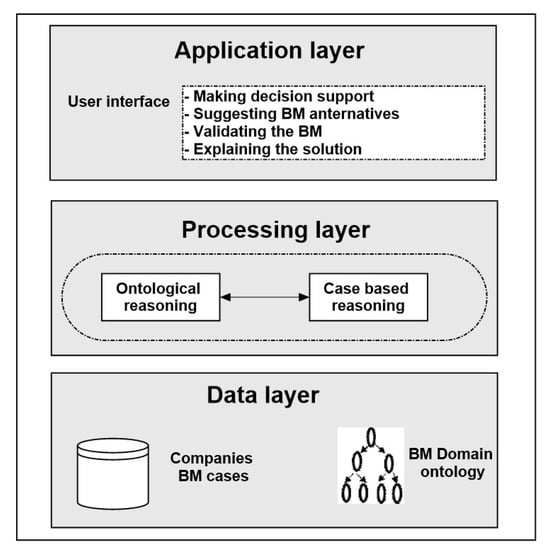
Explainable Ontology-Based Intelligent Decision Support System for Business Model Design and Sustainability
by
Basma Hamrouni, Abdelhabib Bourouis, Ahmed Korichi and Mohsen Brahmi
Cited by 38 | Viewed by 6271
Abstract
Background: Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) is a problem-solving paradigm that uses knowledge of relevant past experiences (cases) to interpret or solve new problems. CBR systems allow generating explanations easily, as they typically organize and represent knowledge in a way that makes it possible to
[...] Read more.
Background: Case-Based Reasoning (CBR) is a problem-solving paradigm that uses knowledge of relevant past experiences (cases) to interpret or solve new problems. CBR systems allow generating explanations easily, as they typically organize and represent knowledge in a way that makes it possible to reason about and thereby generate explanations. An improvement of this paradigm is ontology-based CBR, an approach that combines, in the form of formal ontologies, case-specific knowledge with domain one in order to improve the effectiveness and explanation capability of the system. Intelligent systems make daily activities more easily, efficiently, and represent a real support for sustainable economic development. On the one hand, they improve efficiency, productivity, and quality, and, on the other hand, can reduce costs and cut waste. In this way, intelligent systems facilitate sustainable development, economic growth, societal progress, and improve efficiency. Aim: In this vision, the purpose of this paper is to propose a new generation of intelligent decision support systems for Business Model having the ability to provide explanations to increase confidence in proposed solutions. Findings/result: The performance results obtained show the benefits of the proposed solution with different requirements of an explanatory decision support system. Consequently, applying this paradigm for software tools of business model development will make a great promise for supporting business model design, sustainability, and innovation.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
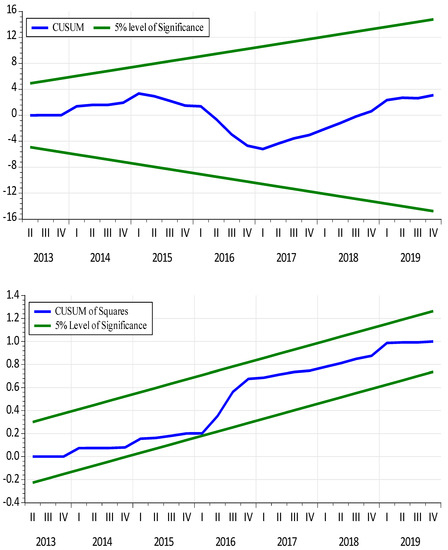
An Officious Impact of Financial Innovations and ICT on Economic Evolution in China: Revealing the Substantial Role of BRI
by
Khurram Shehzad, Umer Zaman, Ana Ercília José, Emrah Koçak and Paulo Ferreira
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 4096
Abstract
The Belt and Road Initiative removes regional barriers and brings communities closer together. In addition, ICT and financial innovation have helped transform the world into a big village and promoted economic growth. The study assessed the dynamic impact of ICT, economic globalization, and
[...] Read more.
The Belt and Road Initiative removes regional barriers and brings communities closer together. In addition, ICT and financial innovation have helped transform the world into a big village and promoted economic growth. The study assessed the dynamic impact of ICT, economic globalization, and financial innovation on China’s economic growth. The study used quarterly data from 2000 to 2019 and used the ARDL model to determine long-term and short-term consequences. The results of the study show that ICT has a positive affiliation with economic growth in China. In addition, financial innovation has also shown a direct impact on economic growth. The study shows that China’s One Belt One Road project (economic globalization) has a great positive impact on its GDP. The consequences of the causality test discovered the significant unidirectional causality running from ICT and economic globalization (ECGI) to GDP. The study recommends mandatory policies related to ICT, financial innovation, and economic globalization to achieve long-term and sustainable development in China.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
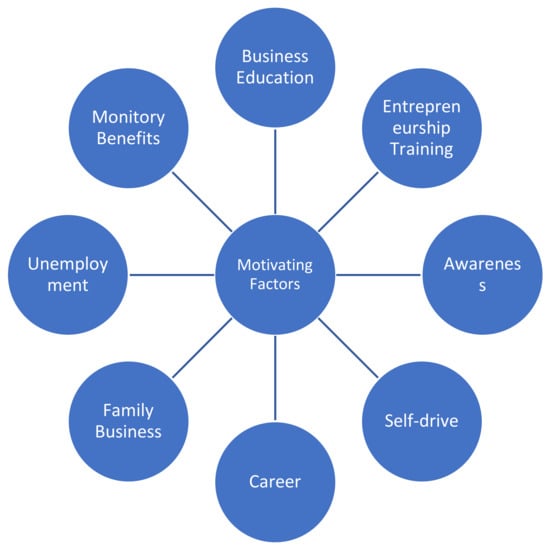
Determinants of the Sustainable Entrepreneurial Engagement of Youth in Developing Country—An Empirical Evidence from Pakistan
by
Muhammad Nawaz Tunio, Iffat Sabir Chaudhry, Sadia Shaikh, Mushtaque Ali Jariko and Mohsen Brahmi
Cited by 68 | Viewed by 8798
Abstract
The article identifies the motivating factors behind the career preferences of university graduates who chose to engage in sustainable entrepreneurship. In this research, multi-methods—theoretical investigations and qualitative interviews—have been utilized to determine the factors responsible for promoting sustainable entrepreneurship in a developing region.
[...] Read more.
The article identifies the motivating factors behind the career preferences of university graduates who chose to engage in sustainable entrepreneurship. In this research, multi-methods—theoretical investigations and qualitative interviews—have been utilized to determine the factors responsible for promoting sustainable entrepreneurship in a developing region. The sample consisted of university graduates who chose to pursue their careers in entrepreneurial activities in Hyderabad, the sixth largest city of Pakistan located in Sindh Province. While determining why young academics choose entrepreneurship as a career choice, entrepreneurial careers are explored as an ongoing process of biographical sequences in which new ways of thinking and communication, new forms of economic and occupational challenges, and necessities as well as ways of success and failure are permanently claimed or raised. Due to these challenges, the youth are confronted with complex social and economic situation to deal with. The study findings provide guidelines on how sustainable entrepreneurship can be developed, engaged, and sustained in the future in developing and under-developed regions.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
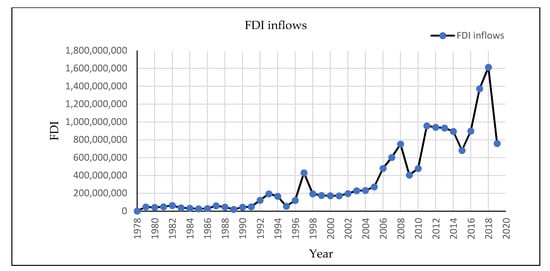
Inward Foreign Direct Investment-Induced Technological Innovation in Sri Lanka? Empirical Evidence Using ARDL Approach
by
AM.Priyangani Adikari, Haiyun Liu and MMSA. Marasinghe
Cited by 16 | Viewed by 4651
Abstract
Fostering innovation is considered one of the key policy priorities in most governments’ agendas in developing countries. Foreign direct investment (FDI) is a principal resource for financing sustainable development, corresponding to 17 sustainable development goals (SDGs). This study analyzes how inward FDI affects
[...] Read more.
Fostering innovation is considered one of the key policy priorities in most governments’ agendas in developing countries. Foreign direct investment (FDI) is a principal resource for financing sustainable development, corresponding to 17 sustainable development goals (SDGs). This study analyzes how inward FDI affects innovation in Sri Lanka using secondary data from 1990 to 2019. We used the Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL) cointegration procedure to examine the long-run relationships between variables. As per the study results, the coefficient of inward FDI is a negative sign while the coefficients of education expenditure (EDU) and research and development expenditure (RDE) show positive signs of 0.26 and 5.7, respectively, and are statistically significant in the long run. It is demonstrated that research and development expenditure is vital in explaining technological innovation, and inward FDI inflows do not contribute to widening technological innovation in Sri Lanka. More FDI inflows will not bring higher innovation. Shaping the future of FDI in Sri Lanka is essential to foster innovation capability.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
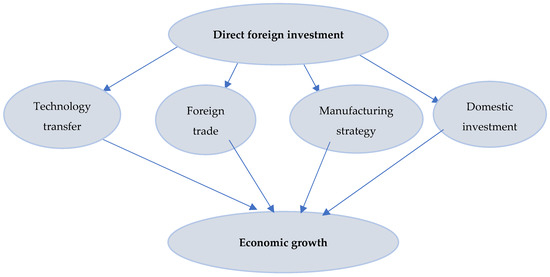
Are Technological Innovation and Foreign Direct Investment a Way to Boost Economic Growth? An Egyptian Case Study Using the Autoregressive Distributed Lag (ARDL) Model
by
Maha Mohamed Alsebai Mohamed, Pingfeng Liu and Guihua Nie
Cited by 34 | Viewed by 8537
Abstract
Both technological innovation and foreign direct investment have received widespread attention in the literature on their role in promoting economic growth. Therefore, this study aims to test the relationship between foreign direct investment, technological innovation, and economic growth of the Egyptian economy during
[...] Read more.
Both technological innovation and foreign direct investment have received widespread attention in the literature on their role in promoting economic growth. Therefore, this study aims to test the relationship between foreign direct investment, technological innovation, and economic growth of the Egyptian economy during the period between 1990–2019 using the autoregressive distributed lag model simultaneous integration test. Our findings show of the ARDL (Autoregressive Distributed Lag) model estimation a joint complementary relationship between the rate of growth of per capita gross domestic product (GDP) in US dollars and the independent variables in the model in the long and short term, which are statistically significant results. We found a positive significant relationship between the variables of incoming foreign direct investment and share of total capital formation in economic growth. Therefore, in the long term, the rate of inflation and the innovation index had a negative impact in the long term and the speed of adjustment towards equilibrium was very large, as it was estimated at 1.5 years (1/0.651). Furthermore, the study also provides valuable lessons and a strategic vision for the Egyptian government, which aspires to advance technology and attract more foreign direct investment.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
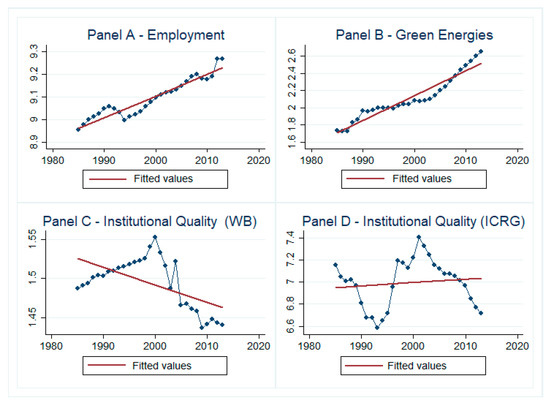
Green Energies, Employment, and Institutional Quality: Some Evidence for the OECD
by
Luigi Aldieri, Cristian Barra, Nazzareno Ruggiero and Concetto Paolo Vinci
Cited by 9 | Viewed by 2373
Abstract
Using a sample of 19 OECD countries over the 1985–2011 period, we propose the application of fixed effects regression to appraise the impact of green energies on employment and to assess how the quality of institutions shapes the relationship. The evidence reported in
[...] Read more.
Using a sample of 19 OECD countries over the 1985–2011 period, we propose the application of fixed effects regression to appraise the impact of green energies on employment and to assess how the quality of institutions shapes the relationship. The evidence reported in this paper indicates that higher supply of green energies enhances employment, though the effect is crucially mediated by the quality of institutions, depending on the measure of institutional quality employed. Further, the relationship remains stable under both Kyoto agreements and the 2007 financial crisis.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures