- Article
Evaluation of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste Leachates and Dairy Wastes Towards Organic-Load Reduction and Optimization of Biomethane Production
- Ioannis Kontodimos,
- Christos Evaggelou and
- Maria A. Goula
- + 3 authors
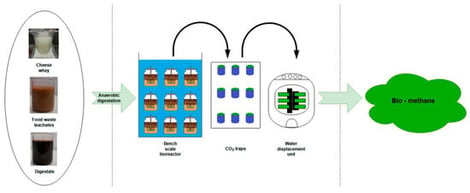
A rapidly emerging approach within the scientific community involves the utilization of waste streams for renewable energy generation, particularly through biomethane production. A key aspect of this approach lies in the co-digestion of diverse waste streams, which can enhance process efficiency and contribute to a more effective reduction in the organic load. The present study investigates the anaerobic digestion of a mixture of food waste leachates and dairy waste (cheese whey wastewater), with a dual objective: to evaluate the reduction in organic-load efficiency of the mixed substrate and to assess the production of biogas enriched in biomethane content. Three distinct mixing ratios by volume of the two waste streams (25%/75%, 50%/50% and 75%/25%) were subjected to an anaerobic digestion process under the same SIR. The performance of each mixture was assessed in terms of both reduction in organic-load efficiency and biomethane yield, followed by a comparative analysis to identify the optimal mixing ratio. The results indicate that while the organic-load reduction remains consistently effective across all mixing ratios, the biomethane production potential is notably higher for the 25%/75% waste mixture, highlighting it as the most promising configuration for both energy recovery and waste treatment efficiency.
31 January 2026