Midnolin Regulates Liver Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Lentiviral Transduction of shRNAs
2.2. Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.3. Cell Proliferation Assay and Colony Formation Assay
2.4. Orthotopic Transplantation of Hepa1-6 Cells into Mice
2.5. RNA Sequencing and Analysis
2.6. Bioinformatics Analysis of Data from Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patient Cohorts
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Suppression of Midnolin Reduces Tumorigenicity of Liver Cancer Cells
3.2. Exogenous Expression of Midnolin Rescues Tumorigenicity of Liver Cancer Cells
3.3. Suppression of Midnolin Prevents Liver Tumor Formation in Mice
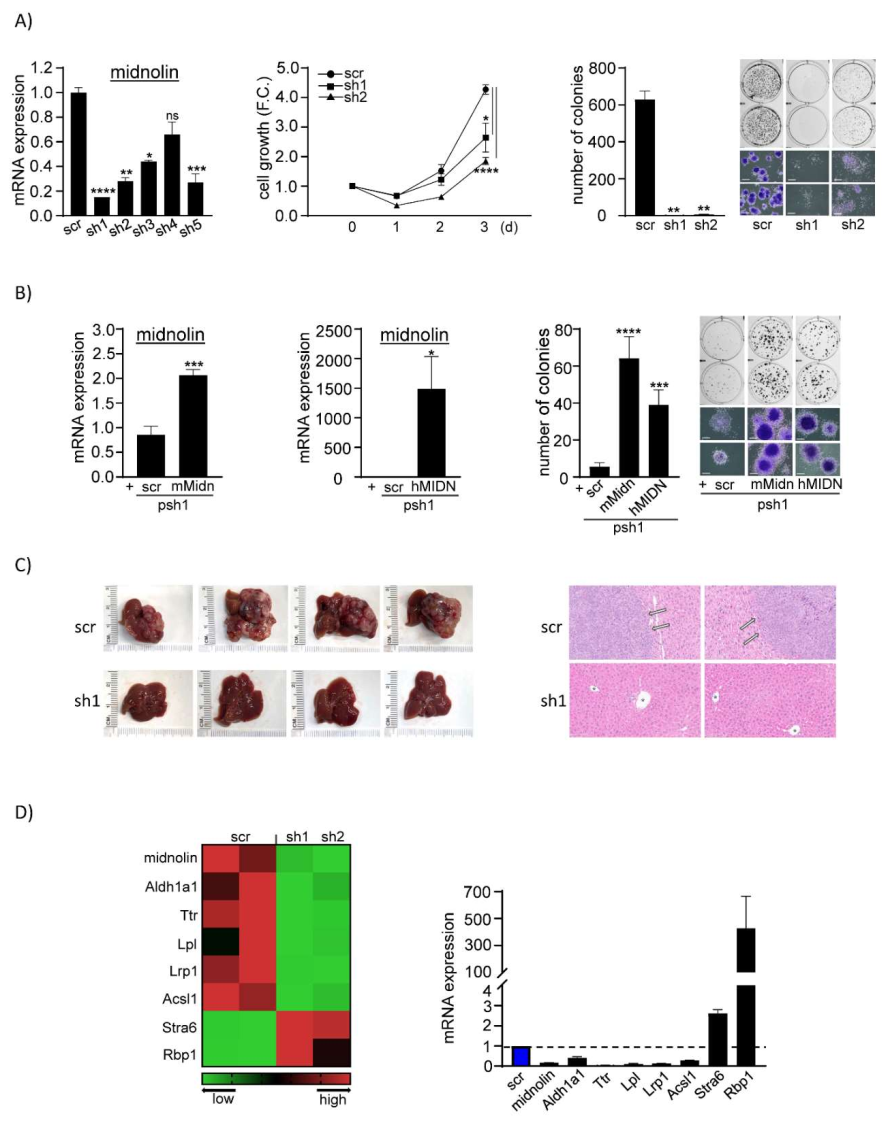
3.4. Midnolin Knockdown-Mediated Disruption of Retinoic Acid/Lipid Metabolism
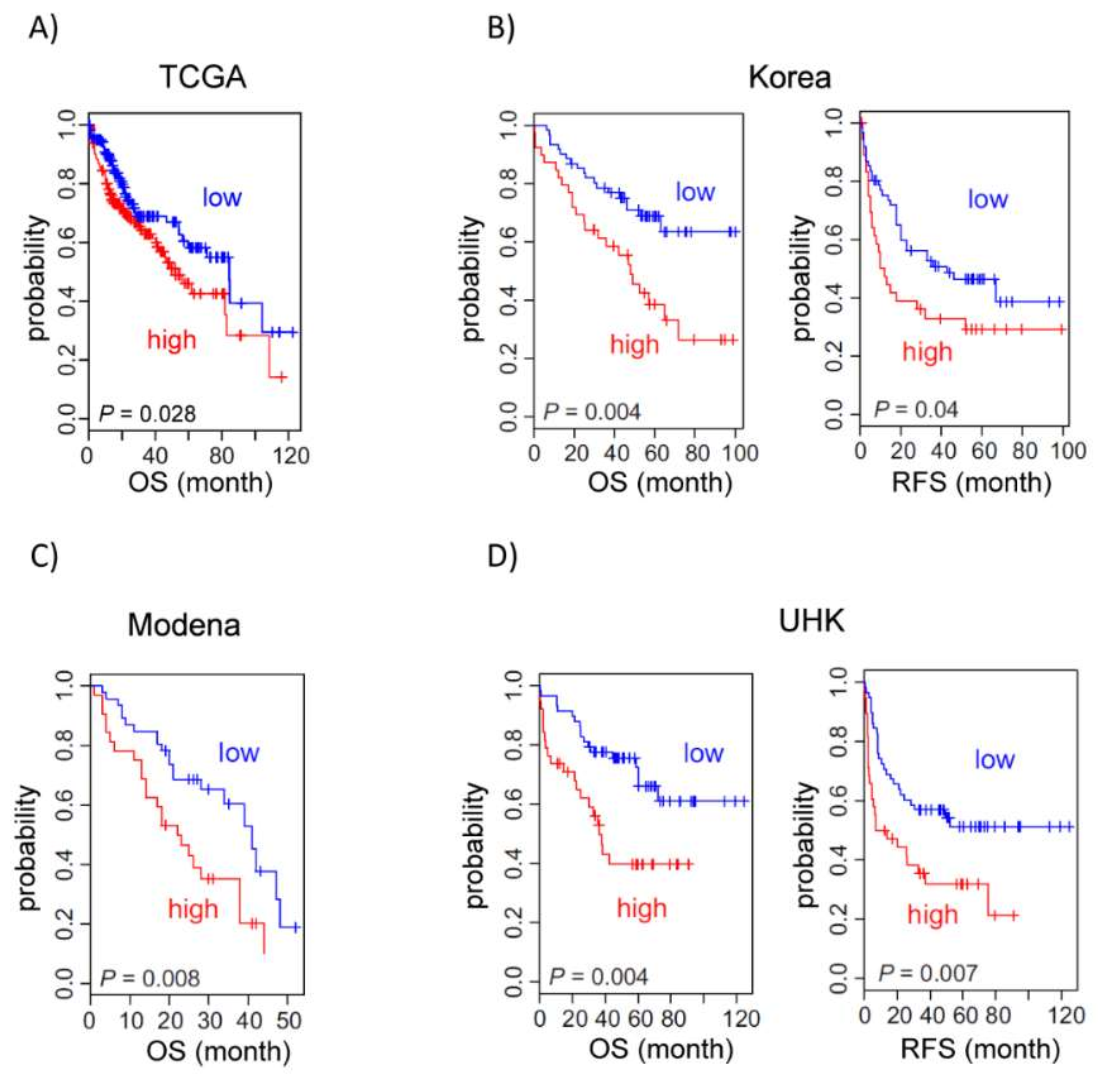
3.5. Midnolin Expression Correlates with Poor Prognosis in HCC Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGlynn, K.A.; Petrick, J.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2021, 73 (Suppl. S1), 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalesnik, M.A.; Michalopoulos, G.K. Growth factor pathways in development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Biosci. 2012, 4, 1487–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Chantar, M.L.; Avila, M.A.; Lu, S.C. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Updates in Pathogenesis, Detection and Treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Xue, R.; Jiang, R.T.; Meng, Q.H. Characterization of metabolic landscape in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 1144–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenen, D.G.; Chai, L.; Tan, J.L. Metabolic alterations and vulnerabilities in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2021, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.K.Y.; Hu, X.; Chosa, K.; Nguyen, C.; Lin, D.P.; Lai, K.K.; Kato, N.; Higuchi, Y.; Highlander, S.K.; Melendez, E.; et al. p300 Serine 89: A Critical Signaling Integrator and Its Effects on Intestinal Homeostasis and Repair. Cancers 2021, 13, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.K.Y.; (Beckman Research Institute of City of Hope, Duarte, CA, USA). Personal communication, 2021.
- Tsukahara, M.; Suemori, H.; Noguchi, S.; Ji, Z.S.; Tsunoo, H. Novel nucleolar protein, midnolin, is expressed in the mesencephalon during mouse development. Gene 2000, 254, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeister-Brix, A.; Kollmann, K.; Langer, S.; Schultz, J.; Lenzen, S.; Baltrusch, S. Identification of the ubiquitin-like domain of midnolin as a new glucokinase interaction partner. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35824–35839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Obara, Y.; Imai, T.; Sato, H.; Takeda, Y.; Kato, T.; Ishii, K. Midnolin is a novel regulator of parkin expression and is associated with Parkinson’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielak, A.E.; Canty, M.J.; Forde, N.; Coussens, P.M.; Smith, G.W.; Lonergan, P.; Ireland, J.J.; Evans, A.C. Differential expression of genes for transcription factors in theca and granulosa cells following selection of a dominant follicle in cattle. Mol. Reprod Dev. 2008, 75, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, B.H.; Shim, J.J.; Kim, S.B.; Jang, K.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, J.E.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, S.C.; et al. Inactivation of Hippo Pathway Is Significantly Associated with Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villa, E.; Critelli, R.; Lei, B.; Marzocchi, G.; Cammà, C.; Giannelli, G.; Pontisso, P.; Cabibbo, G.; Enea, M.; Colopi, S.; et al. Neoangiogenesis-related genes are hallmarks of fast-growing hepatocellular carcinomas and worst survival. Results from a prospective study. Gut 2016, 65, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burchard, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, A.M.; Poon, R.T.; Lee, N.P.; Wong, K.F.; Sham, P.C.; Lam, B.Y.; Ferguson, M.D.; Tokiwa, G.; et al. microRNA-122 as a regulator of mitochondrial metabolic gene network in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2010, 6, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koppaka, V.; Thompson, D.C.; Chen, Y.; Ellermann, M.; Nicolaou, K.C.; Juvonen, R.O.; Petersen, D.; Deitrich, R.A.; Hurley, T.D.; Vasiliou, V. Aldehyde dehydrogenase inhibitors: A comprehensive review of the pharmacology, mechanism of action, substrate specificity, and clinical application. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 520–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noy, N. Vitamin A in regulation of insulin responsiveness: Mini review. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, G.; Xu, J.N.; Liu, D.; Ding, Q.; Liu, M.N.; Chen, R.; Fan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Zou, D.J.; et al. Regulation of plasma lipid homeostasis by hepatic lipoprotein lipase in adult mice. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Actis Dato, V.; Chiabrando, G.A. The Role of Low-Density Lipoprotein Receptor-Related Protein 1 in Lipid Metabolism, Glucose Homeostasis and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Hooi, S.C.; Jiang, Y.M.; Lu, G.D. Fatty acid activation in carcinogenesis and cancer development: Essential roles of long-chain acyl-CoA synthetases. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bamodu, O.A.; Chang, H.L.; Ong, J.R.; Lee, W.H.; Yeh, C.T.; Tsai, J.T. Elevated PDK1 Expression Drives PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signaling Promotes Radiation-Resistant and Dedifferentiated Phenotype of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2020, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katare, D.P.; Malik, S.; Mani, R.J.; Ranjpour, M.; Jain, S.K. Novel mutations in transthyretin gene associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt-Gräff, A.; Ertelt, V.; Allgaier, H.P.; Koelble, K.; Olschewski, M.; Nitschke, R.; Bochaton-Piallat, M.L.; Gabbiani, G.; Blum, H.E. Cellular retinol-binding protein-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma correlates with beta-catenin, Ki-67 index, and patient survival. Hepatology 2003, 38, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Song, X.; Che, L.; Li, X.; Pilo, M.G.; Vidili, G.; Porcu, A.; Solinas, A.; Cigliano, A.; Pes, G.M.; et al. Both de novo synthetized and exogenous fatty acids support the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.Y.; Shi, G.M.; Devbhandari, R.P.; Ke, A.W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.H.; Xiao, Y.S.; Ding, Z.B.; et al. Low level of low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 predicts an unfavorable prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after curative resection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, M.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Song, T.; Cai, X.; Sun, B.; Ye, L.; Zhang, X. Long noncoding RNA HULC modulates abnormal lipid metabolism in hepatoma cells through an miR-9-mediated RXRA signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 846–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koeffler, H.P. Induction of differentiation of human acute myelogenous leukemia cells: Therapeutic implications. Blood 1983, 62, 709–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, C.R.; Schulze, A. Lipid metabolism in cancer. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 2610–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Chu, I.S.; Heo, J.; Calvisi, D.F.; Sun, Z.; Roskams, T.; Durnez, A.; Demetris, A.J.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Classification and prediction of survival in hepatocellular carcinoma by gene expression profiling. Hepatology 2004, 40, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Heo, J.; Libbrecht, L.; Chu, I.S.; Kaposi-Novak, P.; Calvisi, D.F.; Mikaelyan, A.; Roberts, L.R.; Demetris, A.J.; Sun, Z.; et al. A novel prognostic subtype of human hepatocellular carcinoma derived from hepatic progenitor cells. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obara, Y.; Sato, H.; Nakayama, T.; Kato, T.; Ishii, K. Midnolin is a confirmed genetic risk factor for Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Billingsley, K.J.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Ding, J.; Hernandez, D.; Gibbs, J.R.; Blauwendraat, C.; International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium (IPDGC). MIDN locus structural variants and Parkinson’s Disease risk. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kweon, S.-M.; Kim, G.; Jeong, Y.; Huang, W.; Lee, J.-S.; Lai, K.K.Y. Midnolin Regulates Liver Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancers 2022, 14, 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14061421
Kweon S-M, Kim G, Jeong Y, Huang W, Lee J-S, Lai KKY. Midnolin Regulates Liver Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancers. 2022; 14(6):1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14061421
Chicago/Turabian StyleKweon, Soo-Mi, Gayeoun Kim, Yunseong Jeong, Wendong Huang, Ju-Seog Lee, and Keane K. Y. Lai. 2022. "Midnolin Regulates Liver Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro and In Vivo" Cancers 14, no. 6: 1421. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14061421





